Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
=
PRIORITIZING AND PROVIDING INFORMATION
ABOUT USER CONTACTS
BACKGROUND
[0001] Personal information manager (PIM) software applications are
computer programs that allow a user to maintain and organize various types
of personal information and which provide electronic mail (email)
functionality. PIM software applications (or simply "PIM applications")
typically maintain personal information in distinct information categories.
The
information categories that are maintained usually include an email message
inbox, an email message outbox, a set of previously transmitted email
messages or "sent items", an address book containing contact information, a
scheduling calendar (or i.e. a set of appointments, notes, and a list of tasks
to be completed). PIM applications may be designed for execution by a
wireless communication device.
[0002] In certain personal information management (PIM)
applications,
news articles about a user's contacts are provided to the user via a user
dashboard user interface. It is often the case that there are many news
articles found for a user about their contacts, more than they can reasonably
consume.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0003] Example embodiments of the present disclosure will be
described below with reference to the included drawings such that like
reference numerals refer to like elements and in which:
[0004] FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a communications system that
includes a news information service, a communications network, and various
communication devices, in accordance with various example embodiments of
the present disclosure;
[0005] FIG. 2 is a block diagram of a wireless communication
system,
in accordance with various example embodiments of the present disclosure;
[0006] FIG. 3 is a flowchart of a method for presenting news
1
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
information of watched contacts, in accordance with various example
embodiments of the present disclosure;
[0007] FIG. 4 is a flowchart of a method for presenting news
information of watched contacts, in accordance with various other example
embodiments of the present disclosure;
[0008] FIGs. 5 and 6 illustrate representative examples of a user
dashboard graphical user interface, in accordance with various example
embodiments of the present disclosure; and
[0009] FIG. 7 is a block diagram of a wireless communication system
200, in accordance with various example embodiments of the present
disclosure.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0010] In accordance with the various example embodiments presented
herein, selecting what news information to display for a given user's
dashboard or daily email summary is provided. In order to properly prioritize
what is shown (i.e. displayed) to a user, it is important to look for news
articles that are widely reported on from many different sources, as an
indication of significance or news-worthiness. A method that determines a
frequency of news information occurring during a given time period that is
greater than a frequency threshold indicates a news information spike.
Variance in the number of articles written about a specific contact, whether
it
be a person or an organization, can be flagged as meaningful events.
Multiple sources will report meaningful events. In this way, contacts of
interest that are noteworthy, i.e. mentioned in blogs or news articles, can be
identified and representative news information pushed to the user.
[0011] Therefore, in accordance with an example embodiment of the
present disclosure, there is provided a method of prioritizing and presenting
news information related to contacts, including the following. For a number
of contacts, associating news information found within a time period with the
contact of the number of contacts to which the news information pertains.
For each watched contact, of a set of watched contacts of the number of
2
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
contacts, performing a news information spike analysis of news information
associated with the watched contact during the time period, and determining
from the performed news information spike analysis at least one of the
watched contacts that has experienced a frequency of news information
occurring during the time period that is greater than a frequency threshold
value and representative of a news information spike during the time period.
For at least one of the watched contacts that has experienced the news
information spike, retrieving news information associated with the watched
contact and selecting at least one news information item representative of
the news information spike associated with the watched contact during the
time period. Provide the at least one news information item representative of
the news information spike. Present in a user interface the at least one news
information item representative of the news information spike.
[0012] In
accordance with another example embodiment of the present
disclosure, there is provided a system having a processor and a contacts and
news information database coupled to the processor in which a number of
contacts and news information about the number of contacts are stored, the
processor and contacts and news information database configured as follows.
For a number of contacts, associating news information found within a time
period with the contact of the number of contacts to which the news
information pertains. For each watched contact, of a set of watched contacts
of the number of contacts, perform an news information spike analysis for
the watched contact of news information associated with the watched contact
during the time period, and determine from the performed news information
spike analysis at least one of watched contacts that has experienced a
frequency of news information occurring during the time period that is
greater than a frequency threshold value and representative of a news
information spike during the time period. For at least one of the watched
contacts that has experienced the news information spike, retrieve news
information associated with the watched contact, and select at least one news
information item representative of the news information spike associated with
the watched contact during the time period. Provide the at least one news
information item representative of the news information spike. Present in a
3
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
user interface the at least one news information item representative of the
news information spike.
[0013] In accordance with a further example embodiment of the
present disclosure, there is provided a non-transitory computer-readable
medium having computer-executable instructions for causing a server having
a processor and associated memory to implement the following. For a
plurality of contacts, associating news information found within a time period
with a contact of the plurality of contacts to which the news information
pertains. For each watched contact, of a set of watched contacts of the
plurality of contacts, performing a news information spike analysis of news
information associated with the watched contact during the time period, and
determining from the performed news information spike analysis at least one
of the watched contacts that has experienced a frequency of news
information occurring during the time period that is greater than a frequency
threshold value and representative of a news information spike during the
time period. For at least one of the watched contacts that has experienced
the news information spike, retrieving news information associated with the
watched contact, and selecting at least one news information item
representative of the news information spike associated with the watched
contact during the time period. Provide the at least one news information
item representative of the news information spike. Present in a user
interface the at least one news information item representative of the news
information spike.
[0014] For simplicity and clarity of illustration, reference numerals may
be repeated among the figures to indicate corresponding or analogous
elements. Numerous details are set forth to provide an understanding of the
example embodiments described herein. The example embodiments may be
practiced without these details. In other instances, well-known methods,
procedures, and components have not been described in detail to avoid
obscuring the example embodiments described. The description is not to be
considered as limited to the scope of the example embodiments described
herein.
[0015] Referring now to FIG. 1, a block diagram of a distributed
4
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
communications system 100 that includes a service 110 that may be
provided with news information about various contacts from news sources
130, a communications network 140 by which the service 110 may
communicate with a communication device 150, and third party contact
sources 160 that may provide information about contacts to the
communication device 150 and/or the service 110. Although communications
network 140 may be the World Wide Web or Internet, and in fact search
various servers 112 associated with service 110 may reside on the World
Wide Web, it is understood that the service servers and one or more
communication devices 150 may be coupled together by various types of
networks, such as local area networks (LANs), other wide area networks
(WANs) and regional networks accessed over telephone lines, such as
commercial information services. In an example embodiment, service 110
may be included in the communication device 150.
[0016] Communication device 150 is a two-way electronic
communication device having at least data and possibly also voice
communication capabilities, and the capability to communicate with other
communication devices or computer systems, for example, via the Internet.
A communication device 150 may further be a mobile or handheld electronic
device and may be wireless. Depending on the functionality provided by the
electronic communication device, in the various examples described herein,
the device may be a data communication device, a multiple-mode
communication device configured for both data and voice communication, a
smartphone, a mobile telephone or a personal digital assistant PDA (personal
digital assistant) enabled for wireless communication, or a computer system
with a wireless modem. Other examples of mobile electronic devices include
mobile, or handheld, wireless communication devices such as pagers, cellular
phones, cellular smart-phones, wireless organizers, wirelessly enabled
notebook computers, tablet computing devices, and so forth. A mobile
electronic device may also be a portable electronic device without wireless
communication capabilities, such as a handheld electronic game device,
digital photograph album, digital camera, or other device.
[0017] Service 110 may include one or more servers or processors 112,
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
a memory 114, a contacts database, a news information database, and a
news information spike analysis database (the databases are collectively
116), a contact-to-news association element 118 and a news spike analysis
element 120, as shown. The service 110 may be provided by a data center,
for example, that uses a large number of servers/processors 112 in racks.
Server 112 of service 110 may have a number of different servers, with each
server having one or more processors, databases 116, and memories 114.
The server 112 may be by way of example, and not limitation, a Network
Operations Center (NOC), such as a Blackberry Enterprise Server (BES), or
other central server arrangement that can combine many social networks and
manage them collectively. Load balancing between various servers 112 may
be employed in example configurations.
[0018] While
database 116 encompasses the functionality of a contacts
database, a news information database, and a news information spike
analysis database, it is understood that such databases may reside within
one or many databases to which the service 110 has access. A contacts
database stores contacts for which the service associates news information
available on the Internet. The contacts stored in the contacts database may
be acquired from a communication device 150 directly (for example, from a
PIM application executing on the communication device), from a third party
contact source 160, such as social network sites that have a vast amount of
contact information, or from a user of the communication device 150 electing
to provide certain of the user's contacts stored on the device for purposes of
associating available news information with the contacts. The service 110
can acquire the contacts and store them in the contacts database. As will be
discussed, the user of the communication device 150 may be presented with
an option by choosing a subset of watched contacts of the user's contacts for
which a news spike analysis may be performed to determine whether there is
an occurrence of a news spike event. The news information database
represents the news articles found by the service during a given time period
or periods, and the news information spike analysis database stores the
results of a news information spike analysis conducted by one or more
servers/processors 112 of the service.
6
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
[0019] In keeping with various examples, service 110 can acquire
contacts from a user's communication device 150 and/or various third party
contact sources 160. The service 110 associates news information with a
user's contacts. The news information may be published content on the
World Wide Web or Internet, such as might be obtained from blogs or main
stream news sources, such as local stations or a syndicated news service,
such as Reuters, etc. User contacts may be obtained directly from the
communication device 150 itself. Contact information may also be obtained
from a variety of sources on the Internet, including but not limited to GMAIL,
Google contacts, social network contacts (such as Facebook, Twitter, Linked-
In, etc.). The service 110 can associate news information for a given time
period with a contact to which the news information pertains. This contact-
to-news association is performed by contact-to-news association element 118
of the service. For a set of watched contacts, a news information spike
analysis of news information associated with at least one of the watched
contacts can be performed; news spike analysis element 120 of service 110
performs this function. From the performed news information spike analysis,
it can be determined which watched contact(s) of the set of watched contacts
has experienced a frequency of news information during a time period
greater than a frequency threshold value that is representative of a news
information spike occurring during the time period. It is noted that the
service can select the set of watched contacts or a user of the communication
device can select the set.
[0020] When it has been determined that at least one news information
spike of at least one of the watched contacts has occurred during the period
of time, the server/processor 112 of service 110 can retrieve news
information associated with the watched contact and select at least one news
information item representative of the news information spike associated with
the watched contact during the time period. The selected news information
items representative of the news information spike of a watched contact can
then be presented in a user interface. The server/processor 112 in
cooperation with the memory 114, database 116, contact-to-news
association element 118 and news spike analysis element 120 coordinates
this method.
7
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
[0021] The user can decide whether to opt-in to the service provided by
service 110 or it may be provided automatically. A PIM application that
executes on the communication device 150 may prompt the user to decide
whether to opt-in, or this may occur after the news spike analysis performed
by the service 110 has identified at least one of the watched contacts that
has experienced a news information spike and transmitted representative
news information items of the news information spike of the at least one
watched contact to the PIM application via communication network 140.
[0022] This method is further illustrated in the flows of FIGs. 3 and 4
of
the drawings, described below.
[0023] In system 200 of FIG. 2, an example of a wireless
communications network is shown. The service 110 is as shown in FIG. 1,
but the communications network 220 is shown as a mobile carrier network in
communication with one or more mobile or wireless communication devices
230, which can communicate wirelessly with carrier network 220 via one or
more base station towers. In this example, the wireless communication
devices 230 can be wireless handheld devices.
[0024] Referring now to FIGs. 3 and 4, methodology flows in
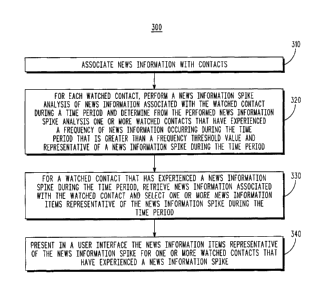
accordance with various examples given herein are provided. In flow 300 of
FIG. 3, at Block 310 the service associates news information found within a
given time period with the relevant contact to which the news information is
related. The association may be accomplished by attaching a pointer from
the news information to the contact to which the news information relates to
pair the news information with the contact. Again, the association is
performed by contact-to-news association element 118 of service 110. The
service 110 can acquire contacts from a variety of sources, as discussed
previously, whether it be from the user communication device 150 or a third
party contact source 160. A method implemented by the service can run in
the background with a list of contacts and a list of news articles, which can
be
paired up as news articles come in, by attaching a pointer to the contacts.
[0025] Next, at Block 320, for each watched contact, the service
performs a news information spike analysis of news information associated
8
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
with the watched contact during the time period and determines from the
performed news information spike analysis at least one of the watched
contacts that has experienced a frequency of news information occurring
during the time period that is greater than a frequency threshold value and
representative of a news information spike during the time period. The
service may select the set of "watched" contacts of a user's contacts or the
user may make this selection.
[0026] A user visit to a contact's dashboard or the sending of an update
email requesting updated information, may cause the service to examine
news articles that are matched to a watched contact of interest. If the
contact or article is spiking, meaning that it is experiencing a news
information spike within a given defined period of time, it will be
prioritized.
Spiking refers to the frequency, or the number of daily articles, as an
example, that are matched to the contact. The number of articles matched
today to a particular watched entity can be counted, and compared to the
history for this particular watched contact to understand if it is important.
An
unusually high number of news articles about a given watched contact, will
indicate a news information spike for that watched contact.
[0027] Performing the news information spike analysis of news
information associated with the watched contact of Block 320 may include
calculating a periodic news information count of the news information
associated with the watched contact for a number of periods; forming a
statistical model based on the periodic news information count for the
watched contact for the periods from which the frequency of news
information occurring during the time period is determined; and comparing
the determined frequency of news information to the frequency threshold
value to determine whether a news information spike has occurred. In some
examples, from the statistical model a mean count for the watched contact
for the number of periods is determined and each period in which the period
news information count for the watched contact is greater than the means
count is identified as having a news information spike for the watched
contact. Or, a weighted average for the watched contact of news information
can be determined from the statistical model and each period in which the
9
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
periodic news information count for the watched contact is greater than the
weighted average for the watched contact is identified as having a news
information spike for the watched contact. A Gaussian distribution of news
articles may be assumed.
[0028] At Block 330, for a watched contact that has experienced a news
information spike during the time period, news information associated with
the watched contact can be retrieved and at least one news information item
representative of the news information spike for the watched contact can be
selected. These selected, representative news information items, such as a
representative news article, for at least one of the watched contacts that has
experienced new information spikes can then be presented in a user interface
at Block 340.
[0029] Presenting news information items representative of a news
information spike can include displaying on a display the news information
items representative of the news information spike for a watched contact.
This may include a personal management information (PIM) application
displaying the news information items in a user's dashboard graphical
interface of the PIM application. This may further include displaying news
information items in an email summary message or in a user's dashboard
graphical interface of a device or a browser. Moreover, an update message,
such as an update email, with at least one news information item
representative of a news information spike may be sent. The service may
transmit the update message to a communication device for display by the
communication device. A PIM application may receive and then display this
update message in a user's dashboard graphical interface of the PIM
application.
[0030] Further to just presenting news information items, a subject of a
news information spike can be identified and presented as well as the subject
of the news information spike, as discussed below. This may be
accomplished by clustering news information associated with a watched
contact to identify the subject of the news information spike and a
representative news information item, such as a representative news article,
for the news information spike. Clustering as used herein is a machine
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
learning term that may encompass K-Mean algorithm on news article titles,
for example, factor analysis, or term frequency.
[0031] Because the amount of information presented about a user's
contacts can be so vast, the at least one news information item
representative of a news information spike for a watched contact can be
prioritized over that of other news information presented about other
contacts. Thus, news information items that have been prioritized can be
presented first, more prominently, etc. over other news information
presented to a user, as discussed further below.
[0032] Referring now to flow 400 of FIG. 4, at Block 410 news
information is associated with relevant contacts, as discussed above. Block
410 may be implemented by processor 112 and/or contact-to-news
association element 118 of FIG. 1 and FIG. 2. Blocks 420-480 may be
implemented by processor 112 and/or news spike analysis element 120. At
Block 420, a set or subset of the contacts for which news information has
been associated by service 110 can be identified. The set of "watched"
contacts can be automatically determined by the service, perhaps as a
function of those contacts experiencing the most news on the Internet, or it
may be determined by a user of the user communication device 150. For
each watched contact, a news information spike analysis of news information
associated with each of the watched contacts is performed at Block 430. At
Block 440 a periodic news information count of news information associated
with each of the watched contacts for a number of periods is calculated. For
example, the period may be one day (24 hours).
[0033] At Block 450, a statistical model based on the periodic news
information count for each of the watched contacts for the number of periods
from which the frequency of news information occurring during the time
period is determined. The determined frequency of news information is
compared to a frequency threshold value to determine whether a news
information spike has occurred for a watched contact at Block 460.
[0034] In some examples, from the statistical model a mean count for
the watched contact for the number of periods is determined and each period
11
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
in which the period news information count for the watched contact is greater
than the means count is identified as a news information spike for the
watched contact. Or, a weighted average for the watched contact of news
information can be determined from the statistical model and each period in
which the periodic news information count for the watched contact is greater
than the weighted average for the watched contact is identified as a news
information spike for the watched contact
[0035] For each of the periods in which a news information spike of a
watched contact has occurred, information associated with the watched
contacts is retrieved from the database 116 and at least one news
information item representative of the information spike is selected at Block
470. The selected new information items representative of a news
information spike are provided at Block 480. This selected new information
may be transmitted from service 110 to communication device 150 of FIG. 1
or to one of the communication devices 230 of FIG. 2. The selected news
information items representative of a news information spike is presented in
a user interface at Block 490. Block 490 may be implemented by
communications device 150 of FIG. 1 or one of the communication devices
230 of FIG. 2.
[0036] While the blocks including the methods are shown as occurring
in a particular order, it will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that
many of the blocks are interchangeable and can occur in different orders than
that shown without materially affecting the end results of the methods.
[0037] Referring now to FIGs. 5 and 6, examples of a user's dashboard
graphical user interface are provided. The user's dashboard graphical user
interface may be implemented in a display of communications device 150 of
FIG. 1 or one of the communication devices 230 of FIG. 2. In the dashboard
graphical user interface 500 of FIG. 5, dashboard view 510 shows
presentation of information about a contact that has experienced a news
spike. The source of contacts is provided by icon 520, which may include the
user's contacts database, Facebook, etc. Field 530 of the dashboard
indicates that the periods analyzed is every 24 hours and that a database of
30 days have been saved in the service's analysis database 116. The contact
12
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
of interest is shown in field 540 and the importance of the information is
indicated in field 550. The contacts are sorted in accordance with pull-down
field 560; in this example, the most recent contact item is displayed first
and
so contact Michael Anissimov is listed first, followed by Patri Friedman, and
then Ben Gertzel. In field 570, the most recent news item is associated with
Michael Anissimov and is entitled, "Extreme Futurist Festival in L.A." Below
that, in field 580, representative news items of Patri Friedman over several
days are listed. In this example, contact Patri Friedman has experienced a
news spike and the news articles listed are news information items
representative of the news spike. It can be seen that Patri Friedman has 16
associated news articles over the last 30 days from different news sources.
The subject of the news spike is pirating. A representative, recent news
article entitled "South Bend Seven: Occupationism vs Seasteading" dated 11-
15-2011 is shown. It can be seen that the number of news articles of this
watched contact have been prioritized and at least one news information
items presented in accordance with that prioritization in a user interface of
a
dashboard. Determination of this contact as having a news spike may occur,
for example, if the number of 16 news articles exceeds a mean, weighted
average, etc. determined for the contact, as noted above.
[0038] Referring to dashboard graphical user interface 600 of FIG. 6, a
screen cap of dashboard view 610 shows a mechanism that allows the user to
select which contacts appear on the dashboard and are included in news
spike analysis. This screen cap of the dashboard view is for Patri Friedman in
field 620 and field 630 indicates that this contact is to be found in various
social network contact databases. Selection of tab 640 in the dashboard
allows details of the selected contact to be shown, while selection of edit
tab
650 allows a user to edit the contact, as shown here. Field 660 indicates that
"news for this person is currently being monitored on your Dashboard." For
news setting tab 670, there are three options presented to the user: Always
search, Never search, Let service decide. This feature of the dashboard
graphical user interface allows the user to opt-in or opt-out of deciding
whether to select contacts to be part of the "watched" set of contacts.
[0039] To illustrate example system architecture, FIG. 7 shows a block
13
CA 02764990 2014-05-30
diagram of a wireless communication system 700 which includes an electronic
communication device 710, such as a wireless or mobile communication
device, which communicates through a wireless communication network 750,
to a server 795. An example wireless implementation of electronic
communication device 710 and a wireless communication network 750 with
which it communicates will now be discussed. Communication device 710
has a visual display 712, a keyboard 714, and perhaps one or more auxiliary
user interfaces (UI) 716, each of which are coupled to a controller 718.
Controller 718 is also coupled to radio frequency (RF) transceiver circuitry
720 and an antenna 721. Controller 718 may be embodied as a central
processing unit (CPU) which runs operating system software in a memory
component (not shown). Controller 718 will normally control overall operation
of electronic communication device 710, whereas signal processing
operations associated with communication functions may be performed in RF
transceiver circuitry 720. Controller 718 interfaces with device display 712
to
display received information, stored information, user inputs, and the like.
Keyboard 714, which may be a telephone type keypad or full alphanumeric
keyboard, is normally provided for entering data for storage in electronic
communication device 710, information for transmission to network 750, a
telephone number to place a telephone call, commands to be executed on
electronic communication device 710, and possibly other or different user
inputs.
[0040] Electronic communication device 710 sends communication
signals to and receives communication signals from network 750 over a
wireless link via antenna 721. RF transceiver circuitry 720 performs functions
similar to those of a tower station 770 and a base station controller (BSC)
760, including for example modulation/demodulation and possibly
encoding/decoding and encryption/decryption. It is also contemplated that RF
transceiver circuitry 720 may perform certain functions in addition to those
performed by BSC 760. It will be apparent to those skilled in art that RF
transceiver circuitry 720 will be adapted to particular wireless network or
networks in which electronic communication device 710 is intended to
operate. When electronic communication device 710 is fully operational, an
RF transmitter of RF transceiver circuitry 720 is typically keyed or turned on
14
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
only when it is sending to network, and is otherwise turned off to conserve
resources. Similarly, an RF receiver of RF transceiver circuitry 720 is
typically
periodically turned off to conserve power until it is needed to receive
signals
or information (if at all) during designated time periods.
[0041] Electronic communication device 710 includes a battery interface
726 for receiving one or more rechargeable batteries 740. Battery 740
electrical power to electrical circuitry in electronic communication device
710,
and battery interface 726 provides for a mechanical and electrical connection
for battery 740. Battery interface 726 is coupled to a regulator 728 which
regulates power to the device. Electronic communication device 710 may be
a handheld portable communication device, which includes a housing (e.g. a
plastic housing) which carries and contains the electrical components of
electronic communication device 710 including battery 740. Electronic
communication device 710 operates using a Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)
730 which is connected to or inserted in electronic communication device 710
at a SIM interface 724. SIM 730 is one type of a conventional "smart card"
used to identify an end user (or subscriber) of electronic communication
device 710 and to personalize the device, among other things. Without SIM
730, the communication device terminal is not fully operational for
communication through wireless network 750. By inserting SIM 730 into
electronic communication device 710, an end user can have access to any
and all of his/her subscribed services. SIM 730 generally includes a processor
and memory for storing information. Since SIM 730 is coupled to SIM
interface 724, it is coupled to controller 718 through communication lines
722. In order to identify the subscriber, SIM 730 contains some user
parameters such as an International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI). An
advantage of using SIM 730 is that end users are not necessarily bound by
any single physical mobile communication device. SIM 730 may store
additional user information for the communication device 710 as well,
including datebook (or calendar) information and recent call information.
[0042] Electronic communication device 710 may consist of a single
unit, such as a data communication device, a cellular telephone, a multiple-
function communication device with data and voice communication
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
capabilities, a personal digital assistant (PDA) enabled for wireless
communication, or a computer incorporating an internal modem. Electronic
communication device 710 may be a handheld portable communication
device which includes a housing (e.g. a plastic housing) which carries and
contains the electrical components of electronic communication device 710.
Alternatively, electronic communication device 710 may be a multiple-module
unit including a plurality of separate components, including but in no way
limited to a computer or other device connected to a wireless modem. In
particular, for example, RF transceiver circuitry 720 and antenna 721 may be
implemented as a radio modem unit that may be inserted into a port on a
laptop computer. In this case, the laptop computer would include display
712, keyboard 714, one or more auxiliary UIs 716, and controller 718
embodied as the computer's CPU. It is also contemplated that a computer or
other equipment not normally capable of wireless communication may be
adapted to connect to and effectively assume control of RF transceiver
circuitry 720 and antenna 721 of a single-unit device such as one of those
described above.
[0043] Electronic communication device 710 communicates in and
through wireless communication network 750. Wireless communication
network 750 may be a cellular telecommunications network. In an example
embodiment, wireless network 750 is configured in accordance with General
Packet Radio Service (GPRS) and a Global Systems for Mobile (GSM)
technologies. Today, such a mobile communication device may further
operate in accordance with Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE) or
Enhanced GPRS (EGPRS), as described in the Background section. In such
environment, wireless network 750 includes a base station controller (BSC)
760 with an associated tower station 770, a Mobile Switching Center (MSC)
752, a Home Location Register (HLR) 754, a Serving General Packet Radio
Service (GPRS) Support Node (SGSN) 758, and a Gateway GPRS Support
Node (GGSN) 756. MSC 752 is coupled to BSC 760 and to a landline network,
such as a Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) 780. SGSN 758 is
coupled to BSC 760 and to GGSN 756, which is in turn coupled to a public or
private data network 790 (such as the Internet). HLR 754 is coupled to MSC
752, SGSN 758, and GGSN 756.
16
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
[0044] Station 770 is a fixed transceiver station, and station 770 and
BSC 760 may be referred to as transceiver equipment. The transceiver
equipment provides wireless network coverage for a particular coverage area
commonly referred to as a "cell". The transceiver equipment transmits
communication signals to and receives communication signals from mobile
communication devices within its cell via station 770. The transceiver
equipment normally performs such functions as modulation and possibly
encoding and encryption of signals to be transmitted to the mobile
communication device in accordance with particular, usually predetermined,
communication protocols and parameters, under control of its controller. The
transceiver equipment similarly demodulates and possibly decodes and
decrypts, if necessary, any communication signals received from electronic
communication device 710 within its cell. Communication protocols and
parameters may vary between different networks. For example, one network
may employ a different modulation scheme and operate at different
frequencies than other networks.
[0045] The wireless link shown in communication system 700 of FIG. 7
represents one or more different channels, typically different radio frequency
(RF) channels, and associated protocols used between wireless network 750
and electronic communication device 710. An RF channel is a limited resource
to be conserved, due to limits in overall bandwidth and a limited battery
power of electronic communication device 710. Those skilled in art will
appreciate that a wireless network in actual practice may include hundreds of
cells, each served by a station 770 (i.e. or station sector), depending upon
desired overall expanse of network coverage. All pertinent components may
be connected by multiple switches and routers (not shown), controlled by
multiple network controllers.
[0046] For all electronic communication devices 710 registered with a
network operator, permanent data (such as electronic communication device
710 user's profile) as well as temporary data (such as electronic
communication device's 710 current location) are stored in HLR 754. In case
of a voice call to electronic communication device 710, HLR 754 is queried to
determine the current location of electronic communication device 710. A
17
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
Visitor Location Register (VLR) of MSC 752 is responsible for a group of
location areas and stores the data of those mobile electronic communication
devices that are currently in its area of responsibility. This includes parts
of
the permanent communication device data that have been transmitted from
HLR 754 to the VLR for faster access. However, the VLR of MSC 752 may also
assign and store local data, such as temporary identifications. Optionally,
the
VLR of MSC 752 can be enhanced for more efficient co-ordination of GPRS
and non-GPRS services and functionality (e.g. paging for circuit-switched
calls which can be performed more efficiently via SGSN 758, and combined
GPRS and non-GPRS location updates).
[0047] Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) 758 is at the same
hierarchical level as MSC 752 and keeps track of the individual locations of
communication devices. SGSN 758 also performs security functions and
access control. Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) 756 provides
interworking with external packet-switched networks and is connected with
SGSNs (such as SGSN 758) via an IP-based GPRS backbone network. SGSN
758 performs authentication and cipher setting procedures based on
algorithms, keys, and criteria (e.g. as in existing GSM). In conventional
operation, cell selection may be performed autonomously by electronic
communication device 710 or by the transceiver equipment instructing
electronic communication device 710 to select a particular cell. Electronic
communication device 710 informs wireless network 750 when it reselects
another cell or group of cells, known as a routing area.
[0048] In order to access GPRS services, electronic communication
device 710 first makes its presence known to wireless network 750 by
performing what is known as a GPRS "attach". This operation establishes a
logical link between electronic communication device 710 and SGSN 758 and
makes electronic communication device 710 available to receive, for
example, pages via SGSN, notifications of incoming GPRS data, or SMS
messages over GPRS. In order to send and receive GPRS data, electronic
communication device 710 assists in activating the packet data address that
it wants to use. This operation makes electronic communication device 710
known to GGSN 756; interworking with external data networks can thereafter
18
CA 02764990 2012-01-20
commence. User data may be transferred transparently between electronic
communication device 710 and the external data networks using, for
example, encapsulation and tunneling. Data packets are equipped with GPRS-
specific protocol information and transferred between electronic
communication device 710 and GGSN 756.
[0049] From the above description, it can be seen that a service,
coupled to a communications network, can prioritize and present news
information related to watched contacts. A contacts and news information
database, coupled together and in cooperative arrangement, are configured
to implement the following. For a number of contacts, associating news
information found within a time period with a contact to which the news
information pertains. For each watched contact of a set of watched contacts
of the number of contacts, perform an news information spike analysis of
news information associated with the watched contact and determine from
the performed news information spike analysis at least one of the watched
contacts that has experienced a frequency of news information occurring
during the time period that is greater than a frequency threshold value and
representative of a news information spike during the time period. For at
least one of the watched contacts that has experienced the news information
spike during the time period, retrieve news information associated with the
watched contact and select at least one news information item representative
of the news information spike associated with the watched contact during the
time period. Provide the at least one news information item representative of
the news information spike. Present in a user interface the at least one news
information item representative of the news information spike.
[0050] The implementations of the present disclosure described above
are intended to be examples only. Those of skill in the art can effect
alterations, modifications and variations to the particular example
embodiments herein without departing from the intended scope of the
present disclosure. Moreover, selected features from one or more of the
above-described example embodiments can be combined to create
alternative example embodiments not explicitly described herein.
19
CA 02764990 2014-05-30
,
[0051] It will be appreciated that any module or component
disclosed
herein that executes instructions may include or otherwise have access to
non-transient and tangible computer readable media such as storage media,
computer storage media, or data storage devices (removable or non-
removable) such as, for example, magnetic disks, optical disks, or tape data
storage. Computer storage media may include volatile and non-volatile,
removable and non-removable media implemented in any method or
technology for storage of information, such as computer readable
instructions, data structures, program modules, or other data. Examples of
computer storage media include RAM, ROM, EEPROM, flash memory or other
memory technology, CD-ROM, digital versatile disks (DVD) or other optical
storage, magnetic cassettes, magnetic tape, magnetic disk storage or other
magnetic storage devices, or any other medium which can be used to store
the desired information and which can be accessed by an application,
module, or both. Any such computer storage media may be part of the
server, any component of or related to the network, backend, etc., or
accessible or connectable thereto. Any application or module herein
described may be implemented using computer readable/executable
instructions that may be stored or otherwise held by such computer readable
media.
[0052] The present disclosure may be embodied in other specific
forms
without departing from its essential characteristics. The described example
embodiments are to be considered in all respects only as illustrative and not
restrictive. The scope of the disclosure is, therefore, indicated by the
appended claims rather than by the foregoing description. All changes that
come within the meaning and range of equivalency of the claims are to be
embraced within their scope.