Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
TITLE OF INVENTION: SUNROOF PANEL WITH SOLAR CHARGING SYSTEM FOR
A MOTOR VEHICLE
CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATION
This application claims the benefit .of Provisional Patent
Application No. 61/538,858, filed. on 09724-2011, in the United
States Patent & Trademark Office, the disclosure of which is
incorporated herein by reference.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the Invention:
The present invention relates to a solar, collection
device, and more particularly, a. solar charging system for
motor vehicles
Many drivers choose to drive an electric or hybrid motor
vehicle in ordcr to reduce emissions of carbon dioxide however,
the current electric motor vehicle must be frequently recharged
at a charging station. Drivers often forget to charge the
battery, which can lead to a loss of power while on the road.
Many-drivers would find it convenient if they could charge the
electric motor vehicle while driving or while parked outside.
Using the sun as an energy source would be an ideal electricity
charging alternative.
The solar charging system consists of a vehicle sunroof
that utilizes a pre-installed solar panel to generate power.
The present invention can assist in producing energy in order
to power electric/hybrid motor vehicles. It can also be used
in conjunction with gas-powered motor vehicles to provide
supplemental power in order to operate an audio/video player,
a laptop computer, a. portable vacuum cleaner, a cell phone
charger, a navigation device and other electronic equipment.
Using the solar charging system to produce additional energy
eliminates the need to constantly plug in the electric motor
vehicle for. recharging.. The present invention provides
convenience and practicality to all drivers..
2
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
Description of the Prior Art:
Numerous innovations for vehicle solar panels have been
provided in the prior art that will be described. Even though
these innovations may be suitable for the specific individual
purposes to which they address, however, they differ from the
present invention.
A FIRST EXAMPLE, U.S. Patent Office Document No. 4,911,257,
Issued on 03-27-1990, to Kajimoto et al. teaches a solar battery
system for a vehicle that comprises a solar battery mounted on
a body of the vehicle, an actinometer provided on the body for
detecting the quantity of solar radiation supplied to the body,
a controller for comparing an output of the solar battery with
a detection output of the actinometer to obtain a result of
comparison and generating an alarm signal when the result of
comparison is out of a predetermined condition, and a warning
device provided in a cabin formed in the vehicle for giving a
warning in response to the alarm signal obtained from the
controller.
A SECOND EXAMPLE, U.S. Patent Office Document No. 5,089,764,
Issued on 02-18-1992, to Bobier et al, teaches an apparatus and
system for purging hot air from the cabin of vehicles when parked
under hot sun conditions. The system employs a solar panel of
relatively smaller size suited for incorporation with a sun roof
or rear window of the vehicle. A power transfer regulator is
utilized which is responsive to the peak voltage chacteristic
of the solar panel to cause the panel to substantially
continuously to perform at its peak power output capability.
As such, an equivalent power at lower voltage and enhanced
current levels is submitted to the electric drive motor of an
air purging fan within the vehicle. Switching controls are
provided which monitor the state of the vehicle's internal
3
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
combustion engine through its ignition switch and which provide
turn-on of the purging system at such time as vehicle cabin
temperatures reach predetermined levels. When the air
circulation system is disabled, the solar panel is employed for
charging the battery of the vehicle.
A THIRD EXAMPLE, U.S. Patent Office Document No. 5,288,925,
Issued on 07-20-1993, to Nath et al. teaches a photovoltaic
window assembly suitable for use in building and vehicular
applications. The window assembly includes an
optically-transmissive substrate having one or more
photovoltaic devices disposed thereon. A decorative template
having cut-outs coextensive with each of the photovoltaic
devices is disposed on the substrate such that the photovoltaic
devices extend through the cut-outs. A window opening is also
formed in the decorative template for transmission of light. An
encapsulating layer is formed on the substrate, solar cells and
decorative template to protect the solar cells and assembly from
environmental damage and deterioration.
A FOURTH EXAMPLE, U.S. Patent Office Document No. 6,406,090,
issued on 06-18-2002, to Tolinski et al. teaches a
self-powered sunroof assembly that can be mounted in the roof
of a vehicle and includes a movable panel, preferably a window,
a motor for controlling movement of the movable panel, and a
self-contained power supply unit that supplies power to the
motor. The self-contained power supply unit contains a battery
and at least one solar cell array that charges the battery. The
solar cell array is preferably attached to the movable panel but
may be located anywhere on the sunroof assembly that may be
directly or indirectly exposed to sunlight. Additionally,
placement of the solar cell array on the movable window does not
decrease visibility through the window.
4
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
A FIFTH EXAMPLE, U.S. Patent Office Document No. 6,682,132,
issued on 01-27-2004, to Hahn teaches a roof module for a motor
vehicle and a process of producing a roof module which includes
at least two flat roof covers located adjacent to one another
and which are joined to one another using a tool which disperses
a peripheral foam material.
A SIXTH EXAMPLE, U.S. Patent Office Publication No.
2005/0046241, Published on 03-03-2005, to Sasaki et al. teaches
a sunroof apparatus which includes a sunroof panel mounted on
an first opening of a roof, a sun shade provided at an inner room
side of the sunroof panel, a solar cell provided to the sunroof
panel and attached at one surface which is facing the sun shade
for converting light energy incident from the one side surface
side and the other side surface side of the sunroof panel into
electric energy and a reflecting member provided to the sun shade
and attached at one surface which is facing the sunroof panel.
A SEVENTH EXAMPLE, U.S. Patent Office Publication No.
2006/0156738, Published on 07-20-2006, to Khalil teaches a
temperature regulation system, which can be used to cool the
interior temperature of an automobile/motor vehicle, when it is
parked under the sun, substantially below the external
temperature, was designed and produced. The system was powered
by solar cells, thus functioning without dissipating any energy
from the vehicle's battery. The mechanical device of the system
incorporated Peltier elements, heat sinks and fans, all
controlled by a power supply in the form of a circuit board. When
the automobile was switched on, the system could be further used
as an automobile climate control unit, for heating or cooling,
withdrawing the supplementary electricity from the battery,
another feature controlled by the circuit board.
5
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
=
AN EIGHTH EXAMPLE, U.S. Patent Office Publication No.
2007/0158978, published on 07-12-2007, to Woodhouse et al.
teaches a vehicle sunroof including a sunroof frame mounted to
a vehicle roof opening and having opposing lateral sides. The
sunroof frame has an outer edge adjacent to the outer surface
of the vehicle roof and an inner edge located within the vehicle
cabin. The vehicle sunroof also includes a number of solar panels.
Each solar panel includes a solar collection surface for
collecting sunlight for producing solar energy. The solar panels
extend between and are connected to the opposing lateral sides
of the sunroof frame.
A NINTH EXAMPLE, U.S. Patent Office Publication No.
2008/0100258, Published on 05-01-2008, to Ward teaches solar
cells that are attached to vehicle components such as a moon
roof or truck bed cover to create modular solar panels. An
adjustable mount can be attached to the solar panels to adjust
the angle of the solar cells in a direction of the sun. Sensing
for solar tracking the sun angle can be performed using solar
cells of the solar panel itself, or a separate sensor. A
telescoping moon roof mount mechanism can allow a first solar
panel to be extended above a vehicle roof to allow additional
solar panels to be telescoped out and also exposed to the sun.
An additional battery can be mounted in the truck bed cover and
connected in parallel with the hybrid battery.
A TENTH EXAMPLE, U.S. Patent Office Publication No.
2010/0026235, Published on 02-04-2010, to Harris teaches a
charging system for a vehicle that rearranges the bank of battery
cells between a series connection for delivering voltage to a
load, e.g. a motor; and a parallel connection for being charged.
The battery bank can thus be charged by a 12 volt battery charger.
The charger can be a plug in charger, or can be a solar cell.
6
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
For example, the solar cell can be moved to cover a windshield
or other surface of the vehicle whenever the vehicle is shut
down.
AN ELEVENTH EXAMPLE, U.S. Patent Office Publication No.
2010/0175819, published on 07-15-2010, to Ryu teaches a method
for manufacturing a solar cell module for a vehicle sunroof, in
which a solar cell is cut into multiple pieces so that it can
be closely adhered to a curved glasses of a sunroof which is
generally installed at an intermediate portion of a vehicle roof
so as to provide a driver with an air circulation effect in the
Interior of a vehicle and a fresh driving feeling with its open
environment. A solar cell module for a sunroof is manufactured
based on a high temperature and vacuum compression work using
a laminator as an EVA film adhering unit. So, it is possible to
easily perform a laminating work for adhering a sunroof curved
glass and a solar cell as compared to a conventional art in which
it is not easy to perform the above work.
A TWELFTH EXAMPLE, U.S. Patent Office Document No. RE41,597,
issued on 08-31-2010 to Kirkpatrick teaches a system for and
method for charging or maintaining a charge of a battery of a
vehicle. The system utilizes a light-transforming cell that can
transform light energy to current. The cell may be supported such
that the cell is exposed to light energy. Current produced by
the cell is communicated with the battery through electrical
connectors, which may have a switch. This invention may decrease
occasions when a vehicle operator faces a weakened or dead
battery in a vehicle because the invention serves to maintain
the charge of the vehicle's battery when the vehicle is not in
use.
7
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
A THIRTEENTH EXAMPLE, U.S. Patent Office Publication No.
2011/0089887, published on 04-21-2011 to Ward teaches a
connection system to charge a high voltage battery in an electric
vehicle with multiple low voltage solar panels (21-n). The
connection system includes sets of transmission lines to
individually connect each one of the solar panels (21-n)
to each individual one of the battery cells (341-n) making
up the battery. With the connection system the high voltage
battery can be charged by the lower voltage solar panels
(21-n) without using a lossy DC-DC converter system that
converts the DC solar panel output to AC for transforming to the
much higher voltage across the primary terminals of battery
before converting back to DC to connect to the battery.
It is apparent now that numerous innovations for vehicle
solar panels have been provided in the prior art that are
adequate for various purposes. Furthermore, even though these
innovations may be suitable for the specific individual purposes
to which they address, accordingly, they would not be suitable
for the purposes of the present invention as heretofore
described.
8
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
AN OBJECT of the present invention is to provide a solar
charging system for motor vehicles that avoids the
disadvantages of the prior art.
ANOTHER OBJECT of the present invention is to provide a
solar charging system for a motor vehicle that is simple and
inexpensive to manufacture.
STILL ANOTHER OBJECT of the present invention is to provide
a solar charging system for motor vehicles that is simple to
use.
BRIEFLY STATED, STILL YET ANOTHER OBJECT of the present
invention is to provide a solar charging system for a motor
vehicle which comprises a solar panel sunroof installed in an
opening in a roof of the motor vehicle to convert solar energy
from the sun into electrical energy and send the electrical
energy to a battery in the motor vehicle. Electronic equipment
within the motor vehicle is electrically connected to the
battery to receive supplemental power in order to be utilized
by a driver of the motor vehicle.
The novel features which are considered characteristic of
the present invention are set forth in the appended claims. The
invention itself, however, both as to its construction and its
method of operation, together with additional objects and
advantages thereof, will be best understood from the following
description of the specific embodiments when read and understood
in connection with the accompanying drawing.
9
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
The figures of the drawings are briefly described as follows:
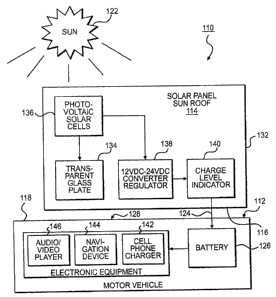
Figure 1 is a block diagram showing the various components of
the present invention;
Figure 2 is a perspective view of a motor vehicle showing the
solar panel sunroof installed in an opening in a roof of the motor
vehicle; and
Figure 3 is a perspective view of the interior of the motor
vehicle showing electronic equipment being powered by the solar
panel sunroof.
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
REFERENCE NUMERALS UTILIZED IN THE DRAWING
110 solar charging system
112 motor vehicle
114 solar panel sunroof of system 110
116 opening in roof 118
118 roof of motor vehicle 112
120 solar energy from sun 122
122 sun
124 electrical energy from solar panel sunroof 114
126 battery in motor vehicle 112
128 electronic equipment in motor vehicle 112
130 driver of motor vehicle 112
132 frame of solar panel sunroof 114
134 transparent glass plate of solar panel sunroof 114
136 photovoltaic solar cells of solar panel sunroof 114
138 12VDC-24VDC converter/regulator of solar panel sunroof 114
140 charge level indicator of solar panel sunroof 114
142 cell phone charger for electronic equipment 128
144 navigation device for electronic equipment 128
146 audio/video player for electronic equipment 128
11
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
As shown in Figure 1, the present invention is a solar
charging system 110 for motor vehicles 112 which comprises a
solar panel sunroof 114 installed in an opening 116 in a roof
118 of the motor vehicle 112 to convert solar energy 120 from
the sun 122 into electrical energy 124 and send the electrical
energy 124 to a battery 126 in the motor vehicle 112. Electronic
equipment 128 within the motor vehicle 112 is electrically
connected to the battery 126 to receive supplemental power in
order to be utilized by a driver 130 of the motor vehicle 112.
The solar panel sunroof 114 comprises a frame 132. A
transparent glass plate 134 is mounted in the frame 132. A
plurality of photovoltaic solar cells 136 are positioned in
series on the transparent glass plate 134. The solar panel
sunroof 114 further comprises a 12VDC-24VDC converter/regulator
138 and a charge level indicator 140tvoltagemayvarywitheachmodels]
Figure 2 shows the solar panel sunroof 114 in the opening
116 in the roof 118 of the motor vehicle 112. Figure 3 shows
the interior of the motor vehicle 112 with the electronic
equipment 128 consisting of a cell phone charger 142, a
navigation device 144 and an audio/video player 146.
The solar panel sunroof 114 may be manually operated or
motor driven, and is available in many shapes, sizes and styles.
The solar panel sunroof 114 actually includes a transparent
glass plate 114 has inlaid photovoltaic solar cells 136 making
the transparent glass plate 134 totally opaque. While the solar
panel sunroof 114 operates identically to conventional
factory-fitted glass moonroofs (tilting and retracting), the
solar panel sunroof 114 can provide electricity to power
interior ventilation fans, tor cooling the motor vehicle.
interior on hot days when the motor vehicle 112 is standing
12
=
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
outside in the sunlight. The present invention's main function
is to supply electricity via the battery 126 to the electronic
equipment 128. The solar panel sunroof 114 can be available as
a factory option on the 2010 Prius, recent Audi cars, Renault
Zoe, and also on some versions of the Mazda Millennia.
In review, the solar charging system 110 enables a driver
130 to charge a battery 126 of a motor vehicle 112 using a solar
panel sunroof 114. The present invention is comprised of the
solar panel sunroof 114 that is similar in appearance to
conventional motor vehicle sunroofs. The solar panel sunroof
114 is installed into an opening 116 in a roof 118 of the motor
vehicle 112 in a similar manner as other sunroofs and may
function in much the same way. The unique feature of the solar
panel sunroof 114 is that it includes a frame 132, a plurality
of photovoltaic solar cells 136 in series on a transparent glass
plate 134, a 12 VDC-24 VDC converter/regulator 138, and charge
level indicator 140 to harness the solar energy 120 from the
sun 122. The solar panel sunroof 114 may be made to be both
retractable and non-retractable configurations. When closed,
the solar panel sunroof 114 traps energy from the sun 122 and
converts it to electrical energy 124. This power is then sent
via wiring to the battery 126 and to electronic equipment 128
in the motor vehicle 112. The electronic equipment 128 can be
a cell phone charger 142, a navigation device 144 and an
audio/video player 146. The battery 126 can be charged while
13
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
The motor vehicle 122 is driven or parked. The solar panel
sunroof 114 may be available in a variety of shapes and sizes
depending on the motor vehicle 112. Some solar panel sunroofs
114 may contain other materials or a combination of materials
such as glass to give it an attractive look and style. The exact
specifications may vary.
It will be understood that each of the elements described
above, or two or more together, may also find a useful
application in other types of constructions differing from the
types described above.
While the invention has been illustrated and described as
embodiments of a solar charging system for a motor vehicle,
accordingly it is not limited to the details shown, since it will
be understood that various omissions, modifications,
substitutions and changes in the forms and details of the device
illustrated and its operation can be made by those skilled in
the art without departing in any way from the spirit of the
present invention.
Without further analysis, the foregoing will so fully
reveal the gist of the present invention that others can, by
applying current knowledge, readily adapt it for various
applications without omitting features that, from the
standpoint of prior art, fairly constitute characteristics of
the generic or specific aspects of this invention.
14
CA 02803592 2013-01-22
10 The foregoing exemplary descriptions and the illustrative
prefered embodiments of the present invention have been
explained in the drawings and described in detail, with
varying modifications and alternative embodiments being
taught. it is also worth noting design, materials, size,
voltage, sensor and etc. may vary with each model and as
technology advances these and the likes may De modified
to further update and upkeep the solar panel sunroof.
while the invention has so shown, described and
illustrated, it should be understood by those skilled in the
art that equivalent changes in form and detail may be
made therein without departing from the true spirit and
scope of the invention, and that the scope of the present
invention is to be limited only to the claims except as
precluded by the prior art. Moreover, the invention as
disclosed herein may be suitably practiced in the absence
of the specific elements which are disclosed herein.
=
11-ta