Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02808500 2013-03-08
ROAD/RAIL VEHICLE WITH TRACTIVE WEIGHT CONTROL
This invention is in the field of vehicles for used on railway tracks and
conventional
roads and highways, and in particular controlling the proportion of weight
between the
driving wheels and the rail wheels that support the vehicle on the track
rails.
BACKGROUND
It is known to adapt vehicles such as conventional highway tractors for use on
rails by
providing retractable rail wheels which are lowered to maintain the position
of the
vehicles on the railway tracks and are raised for road use of the vehicle.
For example United States Patent Number 5,103,740 to Masse discloses a vehicle
for
road and rail operation where both road and rail wheels are driven. An
adjustable
suspension can be used to vary the proportion of the vehicle weight carried by
the rear
rail wheels and rear road wheels when in the railway configuration. In wet
conditions, in
which rubber gives poor traction on steel rails, the proportion of weight
carried by the rail
wheels is increased such that a greater proportion of driving force and
braking force are
supplied through the cast iron rail wheels.
United States Patent Number 5,868,078 to Madison discloses a road/raii vehicle
that is
street legal, but also provides sufficient power to move freight cars on low
density rail
lines or at other desired locations The vehicle has a transfer case to provide
front wheel
drive by road wheels when the vehicle is in a road or highway mode and to
provide rear
wheel drive by rail wheels when in a rail mode.
United States Patent Number 5,016.544 to Woollam discloses a convertible
road/rail
power vehicle with road wheels and retractable front, middle, and rear rail
wheels for
1
CA 02808500 2013-03-08
moving rail cars. Drive is provided by a set of retractable solid rubber rail
wheels near
the longitudinal center of' gravity near the middle of the vehicle and an
adjustable air bag
suspension allows the amount of vehicle weight carried by the middle drive
wheels to
varied to vary the tractive weight exerted on the drive wheels. The rubber
rail wheels are
raised for road use.
United States Patent Number 6,976,432 to Jacob discloses a railcar moving
vehicle with
retractable rail wheels for guiding the vehicle on rails, and rubber-tired
drive wheels that
provide drive for both road and rail use. The rubber-tired drive wheels are
configured to
support the vehicle on a roadway in highway mode, and to contact the rails in
rail mode
such that the same road wheels drive the vehicle in both the rail and road
modes. A
moveable weight is disposed on a rear portion of the frame and a load-shifting
mechanism moves the moveable weight between a rearward position for rail mode
to
provide increased tractive weight on the driving road wheels contacting the
rails, and a
forward position for highway mode.
Brandt Road Rail Corporation of Regina, Canada manufactures road/rail 'vehicle
with
front and rear rubber road wheels and front and rear retractable steel rail
wheels where,
like the Jacob vehicle described above, the rubber rear wheels provide drive
for both road
and rail use. In rail mode the front rail wheels are lowered and the front
road wheels
raised above the rails. An air bag suspension controls the proportion of
vehicle weight
that is carried by the rear rail wheels and the rear drive wheels. The
tractive weight
carried by the drive wheels provides the traction between the wheels and rails
to allow
the necessary propelling force to be exerted on the rails. When starting out
under a heavy
load the maximum tractive weight is on the rubber drive wheels with therefore
reduced
weight on the rear rail wheels. As the vehicle and load starts to move, the
required
propelling force reduces, and as the speed increases the operator manipulates
a valve
CA 02808500 2013-03-08
control connected to the air bag suspension to increase the downward force on
the rear
rail wheels, reducing the tractive weight on the drive wheels.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is an object of the present invention to provide a road/rail vehicle
apparatus that
overcomes problems in the prior art.
A problem with the Brandt road/rail vehicle is that the operators do not
consistently
adjust the tractive weight as the speed increases. In addition to causing very
much
increased wear on the drive tires, operating the vehicle at higher speeds with
the
excessive tractive weight on the driving wheels creates a significant risk of
derailment.
The weight of the rear of the vehicle is carried by th.e rear rail wheels and
rear driving
wheels in varying proportions, controlled by the operator. If excessive weight
is on the
drive wheels, then reduced weight is on the rail wheels which keep the vehicle
on the
rails. As the speed of the vehicle increases, lateral forces due to uneven
tracks, curves,
and the like increase as well and there is a danger that the rear rail wheels
can slip off the
tracks if sufficient down ward force is not exerted on them to maintain
engagement with
the rails.
In a first embodiment the present invention provides a road/rail vehicle
apparatus
comprising a vehicle with front and rear road wheels, an engine operative to
drive the
rear road wheels, and an indicator of actual vehicle speed at an operator's
station
Retractable front and rear rail wheels are mounted on the vehicle and movable
from a
raised road position where the rail wheels are above a road surface for
operation in a road
3
CA 02808500 2013-03-08
mode, to a lowered rail position where the rail wheels engage rails of a
railroad track for
operation in a rail mode. A suspension system is adjustable in the rail mode
to vary a
weight proportion of vehicle weight that is a tractive weight carried by the
rear road
wheels and a guidance weight carried by the rear rail wheels, and a suspension
control at
the operator's station is operative to adjust the suspension system to provide
a selected
weight proportion. A maximum allowable vehicle speed decreases as the tractive
weight
increases and the guidance weight decreases, and a maximum speed indicator at
the
operator's station indicates the maximum allowable vehicle speed for the
selected weight
proportion.
In a second embodiment the present invention provides a method of operating a
road/rail
vehicle. The method comprises providing a vehicle with front and rear road
wheels, an
engine operative to drive the rear road wheels, and displaying actual vehicle
speed at an
operator's station; mounting- retractable front and rear rail wheels on the
vehicle such that
the front and rear rail wheels are movable from a raised road mode position,
where the
rail wheels are above a road surface, to a lowered rail mode position; with
the rail wheels
in the road mode position, maneuvering the vehicle into alignment with rails
of a railroad
track; moving the front and rear rail wheels down to the rail mode position to
engage the
front and rear rail wheels with the rails; manipulating a suspension control
at the
operator's station to activate an adjustable suspension system to exert a
downward force
on the front and rear rail wheels and manipulating the suspension control to
achieve a
selected weight proportion of vehicle weight that is a tractive weight carried
by the rear
road wheels and a guidance weight carried by the rear rail wheels: displaying
a maximum
allowable vehicle speed for the selected weight proportion wherein the maximum
allowable vehicle speed decreases as the tractive weight increases and as the
guidance
weight decreases; and operating the vehicle at an actual vehicle speed no
greater than the
maximum allowable vehicle speed.
4
CA 02808500 2013-03-08
The present invention reduces the risk of derailment due to insufficient
guidance weight
. on the rear rail wheels, particularly at higher speeds where injury and
damage from
derailment can be severe.
DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
While the, invention is claimed in the concluding portions hereof, preferred
embodiments
are provided in the accompanying detailed description which may be best
understood in
conjunction with the accompanying diagrams where like parts in each of the
several
diagrams are labeled with like numbers, and where:
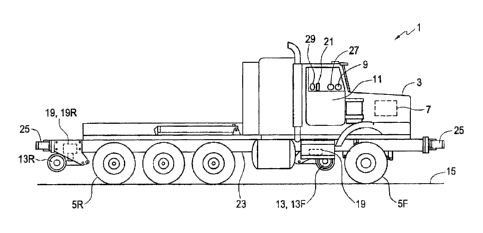
Fig. I is a side view of an embodiment of a road/rail vehicle apparatus of the
present
invention in a road mode;
Fig. 2 is a side view of the embodiment of Fig. 1 in a rail mode.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE ILLUSTRATED EMBODIMENTS
Figs. I and 2 illustrate an embodiment of a road/rail vehicle apparatus 1 of
the present
invention. The apparatus 1 comprises a vehicle 3 with front and rear road
wheels 5F, 5R
an engine 7 operative to drive the rear road wheels 5R, and an indicator 9
displaying the
actual vehicle speed to an operator at an operator's station 11. In the
illustrated apparatus
1 there are three sets of rear wheels 5R, and typically all the rear wheels 5R
will be
driving wheels to take advantage of the available weight of the vehicle 3 to
act as tractive
weight to provide as much traction as possible.
Retractable front and rear rail wheels 13F, 13R are mounted on the vehicle I
and are
movable from a raised road position where the rail wheels are above a road
surface 15 for
5
CA 02808500 2013-03-08
operation in a road mode as illustrated in Fig. 1, to a lowered rail position
where the rail
wheels engage rails 17 of a railroad track for operation in a rail mode as
illustrated in Fig.
2. The rail wheels 13 are not driven.
A suspension system, schematically illustrated in the apparatus 1 as a
plurality of air bags
19, is operative to exert a downward force on the rail wheels 13. The
suspension system
is adjustable in the rail mode to vary a weight proportion of vehicle weight
VW that is a
tractive weight TW carried by the three rear road wheels 5R and a guidance
weight GW
carried by the rear rail wheels 13R. A portion of the vehicle weight VW is of
course also
carried by the front rail wheels 13F, with typically little if any weight on
the front road
wheels, and this weight does not change significantly as the weight proportion
changes.
A suspension control 21 at the operator's station 11 is operative to adjust
the suspension
system to provide a selected weight proportion.
For illustration purposes air bags 19 are schematically illustrated as
exerting forces on the
front and rear rail wheels 13F, 13R, however typically the vehicle frame 23 is
suspended
on the road wheels 5 with air bags as well, and air pressure in all the air
bags is increased
or decreased to achieve the desired selected weight proportion, as is known in
the art. In
the illustrated apparatus 1 increasing the pressure in the rear air bag 19R
will shift the
weight proportion by increasing the guidance weight GW carried by the rear
rail wheels
13R and decreasing the tractive weight TW carried by the driving rear road
wheels 5R.
For safety the suspension control 21 is typically operative to adjust the
suspension system
to provide a guidance weight GW only in a range between a minimum guidance
weight,
determined to provide sufficient guidance weight to ensure the apparatus 1
stays on the
rails and a maximum guidance weight, which will provide a corresponding
tractive
weight TW that is still sufficient to drive the apparatus along the rails 17.
Because the
6
CA 02808500 2013-03-08
adjustment is proportional between the guidance and tractive weights,
corresponding
maximum and minimum tractive weights TW will be provided as well.
The apparatus 1 has rail car hitches 25 at front and rear ends thereof and is
used for
moving rail cars connected to a hitch 25. For start-up under load it will
generally be
desired to have as much traction as possible, at least where a heavy load is
being moved.
The operator will thus typically manipulate the suspension control to adjust
the air bags
19 to provide the minimum guidance weight and maximum tractive weight. As the
apparatus I starts to move and pick up speed, lateral forces due to uneven
rails, curves,
and the like will increase as the speed increases. In order to reduce the risk
of derailment,
the guidance weight OW must be increased as the speed increases to provide
sufficient
downward guidance force to ensure engagement of the rear rail wheels 13R with
the rails
17.
Put another way, the maximum allowable vehicle speed decreases as the tractive
weight
increases and the guidance weight decreases, and for a given apparatus 1 a
maximum
speed can be determined for any particular weight ratio and displayed on a
maximum
speed indicator 27 at the operator's station 11. The operator can then compare
the actual
speed indicated on the speed indicator 9 and compare same with the maximum
allowable
vehicle speed for the weight proportion that is selected at that time, and
adjust
accordingly.
To avoid operator error, the apparatus 1 can also include a speed limiting
control 29
operative to prevent the vehicle speed from exceeding the maximum allowable
vehicle
speed. Alternatively to achieve a similar result, the suspension control 21
can also be
operative to receive speed signals indicating the actual vehicle speed and
adjust the air
bags 19 to provide a weight proportion where the corresponding maximum
allowable
vehicle speed is at least equal to the actual vehicle speed.
7
CA 02808500 2013-03-08
The present invention also provides a method of operating a road/rail vehicle
comprising -
providing a vehicle 3 with front and rear road wheels 5, an engine 7 operative
to drive the
rear road wheels 5R, and displaying actual vehicle speed on the indicator 9 at
the
operator's station 11, and mounting retractable front and rear rail wheels 13
on the vehicle
such that the front and rear rail wheels are movable from a raised road mode
position as
illustrated in Fig. 1, where the rail wheels 13 are above the road surface 15
to a lowered
rail mode position as illustrated in Fig. 2; with the rail wheels 13 in the
road mode
position, maneuvering the vehicle 3 into alignment with rails 17 of a railroad
track;
moving the front and rear rail wheels 13 down to the rail mode position to
engage the
front and rear rail wheels 13 with the rails 17; manipulating the. suspension
control 21 at
the operator's station 11 to activate an adjustable suspension system,
provided in the
illustrated apparatus by air bags 19, to exert a downward force on the front
and rear rail
wheels 13 and manipulating the suspension control 21 to achieve a selected
weight
proportion of vehicle weight VW that is a tractive weight TW carried by the
rear road
wheels 5R and a guidance weight OW carried by the rear rail wheels 13R;
displaying a
maximum allowable vehicle speed for the selected weight proportion wherein the
maximum allowable vehicle speed decreases as the tractive weight increases and
as the
guidance weight decreases; and operating the vehicle 3 at an actual vehicle
speed no
greater than the maximum allowable vehicle speed.
The method may be automated by automatically limiting the vehicle speed to
the.
maximum for the selected weight proportion, or by automatically adjusting the
weight
proportion to provide a maximum speed at least as high as the actual vehicle
speed.
The present invention thus provides increased safety as the risk of derailment
due to
insufficient guidance weight GW is reduced.
8
CA 02808500 2013-03-08
The foregoing is considered as illustrative only of the principles of the
invention.
Further, since numerous changes and modifications will readily occur to those
skilled in
the art, it is not desired to limit the invention to the exact construction
and operation
shown and described, and accordingly, all such suitable changes or
modifications in
structure or operation which may be resorted to are intended to fall within
the scope of
the claimed invention.
9