Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
ROTARY DISK HEADER WITH A ROLLER FOR TRANSFERRING THE CROP
SUPPORTED BY A CENTER BEARING
This invention relates to a crop harvesting header which has a cutter
bar across the width of the header which carries and drives a plurality of
transversely
spaced rotary disks and particularly to an improved arrangement of a transfer
roller
supported by a center bearing for transferring the cut crop from the disks to
a
discharge opening.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Crop harvesting headers which use rotary cutters in replacement for
the more conventional sickle knife systems have been available for many years.
It is
well known that such rotary cutters include a cutter bar or gear train which
provides
the main structural and drive communication components of the cutter. The
cutter
bar provides a series of longitudinally spaced vertical drive members each of
which
drives a respective one of a plurality of cutting disks at spaced positions
along the
cutter bar. The disks are mounted for rotation about a vertical axis standing
upwardly from the cutter bar. The disks carry at a point on their outer edge a
plurality, generally two, of flail type blades which rotate with the disk
around the
vertical axis in a cutting action.
One example of an arrangement of this type is shown US patent
8.069,640 (Barnett) issued 6 December 2011 to the present Assignees. This
shows
in Figures 8 and 10 a transfer roller for carrying the crop from the rear of
the cutting
disks at the cutter bar to a conditioning system where the transfer roller is
longer
than the conditioning system and because of the length, diameter and speed of
this
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
2
element a center support member with a bearing attached is needed to support
this
element relative to the cutter bar to reduce flex.
The support member must be attached to the cutter bar which is also
flexible with the result that the connection in the middle moves relative to
the ends
so that the design must accommodate this flexibility.
The arrangement shown in the above patent has a long rigid shaft
which couples the two parts together with eth-the bearing in the center. This
shaft
needs to flex as the center of the roller moves relative to the ends. If the
roller is
assembled with too much misalignment, or a deflection in the center occurs
that
causes bending of the shaft beyond its yield point so that it takes on a
permanent
bend, then the shaft will in too short a time fails from fatigue.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is one object of the invention to provide a crop harvesting header of
the type having a series of rotary cutting disks on a cutter bar where the
transfer
roller is supported one or more intermediate support members.
1. According to a first aspect of the invention there is
provided a
crop harvesting header comprising:
a header frame arranged to be transported across ground on which
there is a standing crop for harvesting;
a cutter bar mounted on the header frame across a width of the header
for movement across the ground for harvesting the standing crop;
a plurality of generally horizontal cutter disks mounted on the cutter bar
at positions spaced transversely of the header with the disks being mounted on
the
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
3
cutter bar for driven rotation about respective generally upright axes spaced
along
the cutter bar;
each disk having mounted thereon at a position spaced outwardly from
the respective axis thereof at least one cutter blade such that rotation of
the disk
about an axis of the disk causes a standing crop to be cut by the blade as the
blade
rotates around the axis on the disk;
the header frame defining a discharge opening behind the cutter bar
into which the cut crop enters so that the crop is discharged behind the
discharge
opening for forming a swath behind the header;
the discharge opening having ends which are spaced inwardly from
ends of the cutter bar so that the discharge opening is narrower than the
cutter bar;
the cutter bar having at each end of the cutter bar at least one outer
cutter disk of the plurality of cutter disks, at least part of which is
located outwardly of
a respective end of the discharge opening;
a common rotary member extending across the discharge opening and
arranged to rotate about a longitudinal axis of the common rotary member in a
direction with a front face of the common rotary member turning upwardly and
rearwardly;
the common rotary member having, at a position located part way
along the common rotary member, a support coupling member connected between
the common rotary member and the cutter bar and including a bearing for
allowing
rotation of the common rotary member relative to the cutter bar;
the common rotary member comprising a first portion and a second
!
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
4
portion coaxial with the first portion and connected at the support coupling
member
for common rotation;
the support coupling member comprising:
a mounting member attached to the cutter bar;.
a bearing connected between the mounting member and an end
of the first portion, the bearing having an outer bearing element fixed to the
mounting
member and an inner bearing element fixed to said end of the first portion;
such that loads from said end of the first portion are supported
by the cutter bar directly through the bearing and the mounting member;
and;
a universal joint connected between the end of the first portion
and an adjacent end of the second portion;
such that loads from the adjacent end of the second portion are
supported relative to the cutter bar through the universal joint, the bearing
and the
mounting member.
Preferably a single support coupling member is located at the center of
the common rotary member but in some cases more than one such member may be
provided at axially spaced locations.
Preferably the bearing includes a spherical surface which allows
twisting of an axis of the end of the first portion relative to the mounting
member and
therefore relative to the cutter bar.
Preferably the common rotary member includes a cylindrical wall,
defining a tube of the member on which auger flight elements can be carried at
least
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
adjacent the ends. That is the first portion of the common rotary member
includes a
first part of the cylindrical wall and the second portion of the common rotary
member
includes a second part of the cylindrical wall at a common diameter with the
first
part. Preferably the first portion defines a first shaft coaxial with the
first part of the
cylindrical wall where the shaft is carried by the bearing.
Preferably the bearing has an inner bearing element which is carried
on the shaft and includes a spherical surface between the inner bearing
element of
the bearing and the mounting member which allows twisting of an axis of the
end of
the first portion of the common rotary member relative to the mounting member.
Preferably the first part of the cylindrical wall has an end edge at the
bearing so as to provide a cover for the bearing.
Preferably the universal joint has a first member attached to the shaft
of the first portion of the common rotary member and a second member attached
to
the adjacent end of the second portion of the common rotary member with a
universal coupling between the first member and the second member. It will be
appreciated that the universal joint can be arranged in either orientation
with a shaft
coupling attached either to the driven or non-driven portion of the common
rotary
member and a disk coupling to the other of the portions. Different
arrangements of
universal joint can also be used where the parts of the joint connect to the
associated portions in different ways.
Preferably the second shaft at the end of the second portion of the
common rotary member is fixed relative to the second part of the cylindrical
wall of
the second portion of the common rotary member.
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
6
Preferably the second part of the cylindrical wall of the second portion
is spaced axially from the first part of the cylindrical wall of the first
portion and there
is provided a cylindrical cover member attached to the second part of the
cylindrical
wall of the second portion to surround the universal joint.
Preferably the mounting member comprises a disk which surrounds
the bearing and lies in a radial plane of the axis of the bearing with an
outer edge of
the disk attached to the cutter bar.
The common rotary member is typically driven from one end only and
this may be the portion with the shaft coupling to the universal joint or may
be the
other portion.
This arrangement of the common rotary member is typically used in a
system in which the common rotary member at each end of the cutter bar carries
a
respective crop converging auger arranged to receive crop cut by the cutter
disks at
the respective end of the cutter bar and arranged to move the crop inwardly
toward
the discharge opening. Preferably each auger element is arranged generally
longitudinal of the cutter bar with an outer end thereof spaced outwardly of
the
respective end of the discharge opening so as to carry the cut crop
longitudinally of
the cutter bar behind the cutter disks to the discharge opening.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure 1 is an isometric view from the top of a header of a type with
which the present invention is concerned the present invention and taken from
Figure 8 of US Patent 8.069,640 above, the disclosure of which may be
referenced
to show details of the present invention otherwise not described.
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
7
Figure 2 is a cross sectional view along the lines 2-2 of Figure 1 which
is taken from Figure 10 of the above patent.
Figure 3 is a first isometric view of the center support for the transfer
roller in an embodiment according to the present invention.
Figure 4 is a second isometric view of the center support for the
transfer roller in an embodiment according to the present invention.
In the drawings like characters of reference indicate corresponding
parts in the different figures.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
In Figure 1 is shown schematically a header for attachment to
conventional swather tractor of the well known type having driven ground
wheels
and rear castor wheels.
An alternative arrangement can be of the pull-type for towing behind a
tractor and the construction of the hitch and support wheels of such a device
is well
known to a person skilled in this art.
A front support assembly of the tractor carries the header 14 including
left and right lift arms which carry the header in a floating action across
the ground
along skid plates (not shown) of the header. The header includes side walls 15
and
16 forming part of a frame 17 attached to the conventional transport system of
the
tractor. The frame carries top covers (not shown) which support a front skirt
in front
of the cutter bar.
The frame 17 includes a main transverse beam which is attached to
the tractor. The main beam carries the side walls 15 and 16 so as to confine
crop
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
8
material to the interior of the header between the side walls for cutting
action
effected by a cutter bar 24 carried at ends on the frame 17.
Within the cutter bar 24 is provided a gear train (not shown) of meshing
gears carried on suitable bearings so as to provide communication of drive of
a
number of vertical shafts carried on the cutter bar each for rotating a
generally
horizontal disk 26 about a vertical axis of the shaft. The disks are
substantially
identical. The disks are generally elliptical in shape so that a length
between two
ends is significantly greater than a distance between the side edges in a
direction at
right angles to the length. At each of the ends 26A and 26B is mounted a
respective
one of a pair of flails 27 each for pivotal movement about a flail mounting
pin 27A.
The mounting pins are arranged at the ends and thus at the maximum extent of
the
disk so that the flails project outwardly beyond the edges of the disk for
rotation in a
common horizontal cutting plane generally parallel to the plane of the cutter
bar in a
cutting action.
The disks are intermeshed so as to driven synchronously and they are
arranged at 900 phase difference so that adjacent pairs of the disks are at 90
offset
as they rotate to avoid interference between the disks and the blades 27
carried
thereby.
The cutter bar of this general construction is of a conventional nature
and many examples of a commercial arrangement of this type are available in
the
market place. Thus the details of the cutter bar and its mounting are well
known to
one skilled in the art and further details can be obtained from such
commercial
devices.
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
9
The cutter bar 24 is wider than a discharge opening 30 with an
entrance mouth having ends 30A and 30B defined in a back sheet (not shown)
forming a vertical rear panel of the header behind the cutter bar. A
conditioning
system 31 is mounted in the discharge opening 30. Thus the crop material
passes
over and between the disks when cut and also must be converged from the full
cut
width into the entrance mouth of the discharge opening 30.
The discharge opening 30 has side walls (not shown) which are
vertical and parallel and extend rearwardly from the mouth and which confine
the
crop material to pass through the discharge opening over a width less than the
width
of the header so that the side walls are spaced inwardly from the respective
end
walls 15 and 16 of the header.
The crop conditioning system 31 is arranged to span the width of the
crop discharge opening so that the width of the conditioning system is equal
to the
width of the discharge opening. The conditioning system comprises a top roller
34
and a bottom roller 35 which have flutes 36 arranged in a meshing arrangement
so
that the crop material passing through the discharge opening passes through a
nip
37 between the conditioning rolls and is discharged from the rear of the
conditioning
system as a swath of material to be discharged onto the ground or to be
collected as
required.
The disks 26 mounted on the cutter bar 24 include a series of disks
which are located in front of the discharge opening 30. Outward of these disks
and
either side is provided a pair of outer disks indicated at 261 and 262 with
the disk
262 outermost. These disks are arranged to rotate inwardly as indicated by
arrows
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
D so that the front extremity and the blade carried thereby rotates in the
direction
indicated at the arrows D1, D2 to carry the crop material which is cut by
those disks
between the disks.
The disk 262 carries an impeller 40 mounted on the disk so as to be
5 carried thereby and driven thereby and so as to be directly co-axial with
the disk
262. A hanging impeller (not shown) can be used to replace this impeller also
co-
axially arranged with the corresponding disk 262 or the axis of the impeller
may be
offset from the axis of the disk. It will be appreciated that the disk and the
impeller
co-operate to assist in carrying the crop material inwardly toward the
discharge
10 opening and to resist the crop material from moving rearwardly over the
disks 262 to
the rear bulkhead panel which could cause collection of the crop material and
eventual blockage of the system.
The top conditioning roller 34 is located above the bottom conditioning
roller 35. These define between them the nip 37 through which the crop
material is
controlled to pass. The top conditioning roll 34 and the bottom conditioning
roll 35
are parallel and arranged such that the crop passes through the nip 37 between
the
top and bottom conditioning rolls. The top and bottom conditioning rolls are
arranged such that the nip 37 is raised above the common cutting plane P and
is
located behind the disks 26. The top and bottom conditioning rolls 34, 35 each
comprising a cylindrical body 77, mounted for rotation about an axis 78, 79
thereof.
In one example, on the cylindrical body 77 is mounted a series of
longitudinally
extending, angularly spaced flutes 36 arranged such that the flutes 36 of the
top roll
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
11
34 mesh with the flutes of the bottom roll 35 in the conditioning action, as
is well
known.
However the present invention is also applicable to conditioning rolls of
the type which have no flutes or ribs so that the conditioning action is
effected by a
high crushing force between two plain rollers. The rollers can be smooth or
may
include grooves or indentations which are not intended to mesh in the crushing
action. Crushing conditioner rolls of this type are well known to persons
skilled in
this art and different designs may be selected and used as will be known to
such
persons.
In addition the present invention can be used in an arrangement in
which the conditioning rollers are omitted so that no conditioning occurs in
the
discharge opening.
In a ten or twelve disk mower, in front of the discharge opening there
are located eight of the cutter disks arranged in four pairs of disks with
each pair
arranged to rotate in opposite directions such that the crop tends to pass
between
the pair of disks.
Narrower machines of the type typically used in Europe or other
countries where smaller machines are more suitable may have only three pairs
of
disks in front of the discharge opening.
The pairs of the cutter disks in front of the discharge opening include a
first end disk 261 located in line with the first end wall 32 of the discharge
opening
and a second end disk (at the opposite end not illustrated) located in line
with the
second end of the discharge opening. That is an imaginary line extending
forwardly
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
12
from the end 30B intersects the disk 261. This is typically located at a
position
thereon spaced inwardly from its axis but can be outside the axis of the disk
261.
The axis and main body of the end disks 261 are mounted outboard of the
imaginary
line of the opening so that the next adjacent disks define a cutting circle
which is
closely adjacent or at the line. Thus the majority of the end disks 261 are
outboard
of the respective line.
The end disk is arranged to rotate so that a front of the first disk 261
moves outwardly of the respective end of the discharge opening as marked at
direction arrow Dl. A first outer disk 262, which is mounted outwardly of the
end line
of the discharge opening and outwardly of the end disk rotates in the opposite
direction to the disk 261 as indicated at D2. A third disk 263 inward of the
disk 261
rotates in a direction opposite to the disk 261 so as to form a pair with the
disk 261
such that at least some of the crop tends to be swept into a first zone
between the
first pair of disks 261, 262 and to pass through that zone.
A crop converging structure 59 is located behind the disks 261 and 262
and tends to move the crop inwardly toward the discharge opening 30. The crop
converging structure 59 comprises an auger element 60.
The end disk 262 is located immediately adjacent the end wall 16, 17
of the header. The end wall is connected to a connecting wall which is curved
around the path of the cutting blade 27 of the end disk 262 so as to extend
inwardly
and rearwardly from the end wall 16 to a recessed end wall spaced inwardly
from
the end wall 16. Thus the wall is located at a position spaced inwardly from
the end
of the header. Behind the end wall is provided the rear bulkhead which extends
1
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
13
inwardly at right angles to the end wall up to the entrance mouth of the
discharge
opening 30. The rear wall is spaced rearwardly from the rear edges of the path
of
travel of the cutting blades by a distance equal to the length of the recessed
end wall
62. This provides a region for the auger element 60 which acts as a converging
member for converging the crop behind the end cutters 261 and 262.
The auger element 60 comprises an auger tube 63 and an auger flight
64 carried on the tube. In the embodiment of Figures 2, 3 and 4, the auger
flight 64
is a single auger flight shaped such that rotation of the auger tube in the
direction D4
acts to lift the crop upwardly and over the auger element as an overshot auger
while
at the same time the helical angle of the flight 64 acts to carry the crop on
top of the
auger tube inwardly toward the discharge opening 30.
The rear wall behind the auger element includes an upper part which
curves upwardly and forwardly to connect to a top wall of the header
construction
which extends over the cutting area and over the cutter bar 24. Also the rear
wall
underneath the auger 60 curves forwardly in a part cylindrical shape as
indicated at
so as to wrap around the outer edge of the periphery of the flight 64. This
portion
thus forms a pan underneath the auger and extending to a forward edge which is
located just behind the rear tip of the blade 27. Thus the upper part of the
auger and
the front of the auger are exposed to the crop and the pan extends only to the
rear
and underneath.
The auger flight 64 has smooth outer edges so that it provides no
cutting or grasping action on the crop allowing the auger flight to merely act
as a
transfer member carrying the crop inwardly as the helical flight rotates.
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
14
Typically the diameter of the tube 63 can lie in the range 100 to 200
mm. The height of the auger flight lies in the range 25 to 50 mm. In a typical
example therefore the tube is of 150 mm diameter and the flight is of 40 mm
height.
The tangent at the bottom of the flight as indicated at T1 is located at a
height
slightly below the cutting plane P that is the bottom edge of the blade.
However this
position may be slightly raised so that it is located directly at the cutting
plane
defined by the sharpened edge or it may be even slightly above that cutting
plane.
The bottom tangent T2 of the tube is above the cutting plane. The forwardmost
tangent T3 of the flight is located substantially at the rear edge of the
blade 27.
The tube 63 extends along the header from a first end at the end wall
16 to a second end at the end wall 17 Bearings (not shown) for the auger tube
63
are arranged at the ends.
The auger flight 64 is arranged so that it causes movement of the crop
engaging the tube 63 in the direction of the arrow D4. The flight section 74
in a
central area aligned with the opening 30 is arranged at a very shallow helical
angle
so as to provide little or no transverse movement in this area so that it can
act as a
feeding flange acting to engage the crop and tending to assist the movement of
the
crop into the discharge opening and into the nip 37 between the conditioning
rollers.
The flight section 74 can be replaced by axial bars having no helical effect.
The location of the end of the auger element or transfer roller at a
position spaced inwardly from the end wall 16 allows the positioning of the
drive
elements and bearings well within the extent of the frame as defined by the
end wall
16. This area therefore provides space for the drive elements without the
necessity
i
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
for these elements projecting beyond the end wall 16. The transfer of the crop
material to the discharge opening 30 is effected by a co-operation between the
rotation directions of the cutting disks 261 and 262 together with the
operating action
of the impeller 40 and also the transfer action of the auger element itself.
The auger
5 element is located in front of the conditioning rollers so that the auger
element can
extend to a position where the flight 64 is located directly in front of the
conditioning
rollers allowing the crop material to turn at an angle significantly less than
90 to
enter the nip 37 between the conditioning rollers. Thus there are no sharp
turns
involved in the movement of the crop as it is transferred from the area behind
the
10 disks 261 and 262 into the area of the nip 37.
A stripper member is mounted on the rear wall at positions outwardly
of the entrance mouth and projects forwardly from the rear wall so as to
provide a
forwardmost edge in contact with or immediately adjacent the outer periphery
of the
flight as the flight rotates. The stripper member thus provides a surface
which
15 prevents crop from entering the area between the auger flight and the pan.
This
arrangement therefore helps in preventing any wrapping of the crop around the
auger elements and particularly the auger tube. The auger flight 64 terminates
at
the end which is located just inside the mouth 30A. However the auger flight
64 can
extend to a position closely adjacent the middle of the header that is midway
across
the conditioning rollers. In this area the auger flight acts to assist in
spreading the
material from the area outside the discharge opening, across the discharge
opening
so as to tend to even out the crop material across the width of the discharge
opening.
,
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
16
In Figure 1 is shown a rotation pattern of a 10 disk machine arranged
in pairs with each pair rotating toward one another so as to form streams
where
each stream includes the material from two disks. This again balances the
material
cross the conditioner 31.
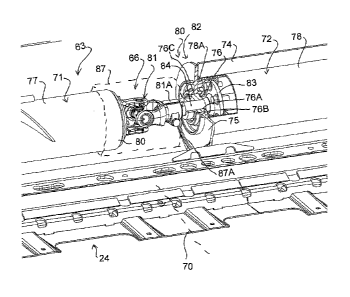
The roller 63 of the common rotary member is divided at or adjacent a
center line 70 into two separate roller portions 71 and 72 on respective sides
of the
center line which are coaxial and mounted and connected for common rotary
movement about the common longitudinal axis. The portions 71 and 72 each have
a
coaxial cylindrical wall 77 and 78 for carrying the bars and/or flights 74 of
the
common rotary member.
This allows a bearing assembly 66 to be provided at the center line 70
which acts to provide support for the center of the rotary member 63 from the
cutter
bar. The bearing assembly 66 forms the subject of the present invention and is
shown in more detail in Figure 3. Thus load from the center of the common
auger
member 66 is transferred to the cutter bar 24 and is carried thereby to reduce
flexing
of the roller 63.
The bearing 66 includes a center support member in the form of a
plate or disk 75 attached at the bottom to the cutter bar 24 and a bearing 76.
Suitable mounting brackets can be provided depending on the construction and
shape of the cutter bar 24.
As the crop passes over the roller 63 in the central area at the center
line 70, the presence of the support plate 75 and the bearing 76 does not
significantly interfere with the passage of the crop. The bearing 76 is
desirable in
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
17
some cases where the common auger member is greater than a certain length
where unacceptable flexing will occur. If required, more than one bearing can
be
used at spaced positions along the member 63 so that the load is transferred
to the
cutter bar structure 24 at locations other than the center.
The common rotary member has therefore the support coupling
member 66 including the bearing 76 for allowing rotation of the common rotary
member 63 relative to the cutter bar. The support coupling member includes the
mounting member attached to the cutter bar in the form of the disk 75 lying in
a
radial plane of the axis of the roller. The bearing 76 is connected between
the
mounting member or disk 75 and an adjacent end 80 of the first portion 72 of
the
roller. This acts to support the end 80 relative to the disk 75 and to the
cutter bar so
that the portion 72 is carried at its outer end on an outer bearing (not
shown) and at
its inner end on the bearing 76. The length of the portion 72 is such that
only
acceptable flexing can occur between these bearings.
A universal joint 81 is connected between the end 80 of the first portion
72 and an adjacent end 82 of the second portion 71. In this way loads from the
adjacent end 82 of the second portion 71 are supported relative to the cutter
bar
through the universal joint 81, the bearing 76 and the mounting member 75.
There
is no bearing for the end 82 and no support for the end 82 apart from the
above
connection. In this way both portions are supported on the same support disk
and
only one bearing is provided. Flexing movement will occur between the end 82
and
the end 80 and is taken up by movement within the universal joint 81.
The first portion 72 defines a first stub shaft 84 coaxial with the first
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
18
part 78 of the cylindrical wall and attached thereto by a support bracket 83.
Thus the
stub shaft 84 is carried by the bearing 76. The bearing 76 includes an inner
bearing
element 76A which is carried on the shaft 84 and an outer bearing element 76B
with
ball or roller bearing between the two elements. A spherical coupling or
surface 76C
is provided between the bearing element 76B of the bearing 76 and the mounting
disk 75 which allows twisting of an axis of the end 80 of the first portion of
the
common rotary member relative to the mounting disk 75. In this way flexing of
the
cutter bar which causes up and down movement of the disk 75 is taken up
relative to
the end 80 of the portion 72 in the spherical bearing surface 76C without
ending of
the shaft or other element.
The first part 78 of the cylindrical wall has an end edge 78A at the
bearing and closely adjacent the side of the disk 75 so as to provide a cover
for one
side of the bearing. The second part 77 of the cylindrical wall of the second
portion
71 is spaced axially from the first part 78 of the cylindrical wall of the
first portion and
there is provided a cylindrical cover member 87 attached to the second part of
the
cylindrical wall of the second portion to surround the universal joint with an
outer
edge 87A of the cover 87 immediately adjacent the disk 5..
The universal joint 81 is of a conventional commercially available
construction with a first member 81A attached to the first portion 72 and a
second
member 81B attached to the second portion 71 with a universal coupling 81C
between the first member and the second member.
Typically such universal joints include an arrangement in which the
member 81A attaches to a shaft and the second member attaches to an end disk.
CA 02810861 2014-11-18
19
Thus in this case the member 81A attaches to the shaft 84 at the end of the
portion
72 and the member 81B attaches to an end disk 85 (Figure 4) of the portion 72.
However this arrangement may be reversed and the portion 17 may be provided
with a mounting shaft. In addition other arrangements of universal coupling
may be
provided where the mounting of the members may be different.
The disk 85 at the end of the second portion 71 is fixed relative to the
second part of the cylindrical wall of the second portion and has no flexible
connection therebetween as all the necessary flexing action at the end of the
portion
71 is provided at the universal joint which is designed to accommodate this.
The design provides an arrangement which allows for more flexibility at
the joint by providing the universal joint which is placed at the center of
the auger
roller so that the center of the auger roller can pivot.
The side of the auger roller connected to a single input drive
arrangement is the portion 72 at the outer end of the portion 72. The portion
72
thus has the male stub shaft 84 thereon at the inner end and is supported by
two
bearings including one (not shown) at the driven outer end and the bearing 76
at the
center. The flexible joint 81 couples between the male stub shaft 84 at the
center of
the first portion 72 of the auger roller and the second part 71 of the auger
roller. The
universal joint 81 is covered by the cylindrical cover shield 87 which is
formed of two
parts each half cylindrical and connected around the end of the portion 71.