Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02824953 2013-08-28
1
Folding Blade for a Blown Film Line as well as Blown Film
Line with such a Folding Blade
[01] The invention relates to a folding blade for a blown
film line, as well as to a blown film line with such a
folding blade.
[02] Blown film lines are used to a great extent to
manufacture a variety of film webs. In a blown film line, a
plastic melt is first extruded through a circular die using
an extruder. The inside of the resultant molten tube is
pressurized with compressed air, so that the molten tube
expands with increasing distance from the die. Reference is
there made to a tube formation zone. As the process
continues, the melt-like film bubble is cooled, and
solidifies at the so-called frost line in modern systems.
It runs through a collapsing unit until reaching take-off
pinch rolls. The take-off pinch rolls handle two functions:
They pull up the film bubble at a preset rate on the one
hand, and seal the film bubble away from the compressed air
introduced into the interior on the other.
[03] In some instances, it is desirable to feed the film
bubble to the take-off pinch rolls with folded-in sides. In
particular, it is conceivable in this case that the film
bubble be inflated to a point where the resultant
circumference would no longer have fit on the lay-flat
width of the line when simply collapsed, i.e., the freely
usable width of the rolls in the take-off or a reversing
unit unit often situated above the latter, or the other
downstream equipment of the line.
[04] Folding blades are known for folding in the sides of a
film bubble. In its simplest configuration, a folding blade
consists of a mostly at least triangular, elongated folding
surface, with the wider base being situated below, i.e.,
upstream in relation to the direction of extrusion. As the
CA 02824953 2013-08-28
2
film gets pulled up by the take-off pinch rolls, the
folding surface becomes increasingly inclined toward the
vertical axis of the film bubble, i.e., into the space that
a simply ascending film bubble would occupy. The excess
pressure inside the film bubble presses the film surface
against the folding surface. To the right and left of the
folding surface, the excess pressure makes the film bubble
try to occupy the entire original space of the ascending
film bubble. As a result, folding flanks, i.e., sections of
the film bubble extending to the rear side of the folding
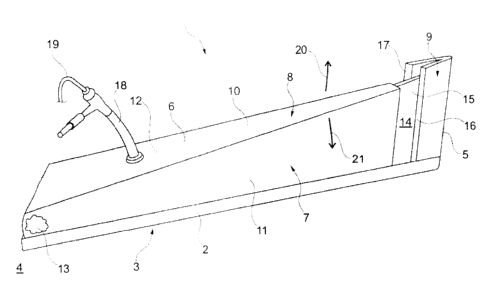
surface, form on both sides of the folding surface of the
folding blade.
[05] The more the film ascends and the more narrowly the
folding surface of the folding blade tapers, the larger the
folding flanks of the film bubble become.
[06] If the folding blade projects into the ascending film
bubble beyond a certain level perceived as critical, for
example by more than 200 mm or more than 250 mm, use is
normally made of a so-called deep folding blade. A deep
folding blade initially consists of a folding blade with
the already described folding surface. On the rear side,
i.e., on the side toward which the folding flanks extend,
the upper end of the folding blade is also provided with a
fin, which protrudes toward the back from the folding
surface. The fin ensures that the two folding flanks now
extending around the folding surface will only contact each
other to less of an extent, if at all.
[07] DE 10 2007 029 794 B4 discloses a blown film line with
two folding blades, wherein the folding blades can be
adjusted further into or out of the ascending film bubble.
[08] Italian Laid-Open Patent Specification C 2007A000023
discloses a blown film line with a deep folding blade,
wherein the deep folding blade consists of a triangular
CA 02824953 2013-08-28
3
wedge with folding surface, and wherein the rearward fin
can be made to travel along the wedge, so that the wedge
can be outwardly displaced. A large, movable part of the
fin is now downwardly displaced. An upper, fixed part of
the fin is situated above a part of the engine frame
otherwise located in the path, and as a result of the
displacement, the downwardly moved part of the fin is
situated below the part of the engine frame otherwise
located in the path.
[09] For example, other folding blades and deep folding
blades may be gleaned from DE 35 06 772 02, Patent
Specification DE 22 48 516, DE 25 10 515 03, US 2,955,318,
EP 0 457 304 Bl, US 2, 961,930, US 3,566,756, US 3,897,530
or US 3,976,418.
[10] The object of the present invention is to provide the
known prior art with a folding blade, a blown film line and
a method.
[11] In one aspect of the present invention, this object is
achieved with a folding blade for a blown film line, with a
folding surface for folding in a film bubble running
alongside, along with a fin protruding toward the back from
the folding surface for preventing folding flanks
projecting around the folding surface from coming into
contact with each other, wherein the folding blade is
characterized in that the fin exhibits a collapsible
element with an adjustment device.
[12] The following are terminological explanations:
[13] The "folding surface" is meant to be the surface to be
facing the vertical axis of the film bubble, along which
the film bubble pulled by the take-off pinch rolls can thus
upwardly drift, and in so doing be folded in. In a simple
case, the folding blade is formed, for example, by a plate
CA 02824953 2013-08-28
4
made out of wood, metal and/or provided with plastic
sliding parts and shaped like a triangle, with rounded
edges and a thickness normally measuring several
centimeters, and the folding surface is simply a surface of
this plate.
[14] The "rearward" alignment in principle is only obtained
in a situation where the folding blade has been built into
a blown film line. In general, however, the folding surface
should be the side with which the folding blade is to be
aligned relative to the film web running alongside, so that
a rear side of the folding blade facing away from the
vertical axis of the film bubble comes about on the
opposing side. A fin located there is to be viewed as
rearward.
[15] The "fin" can be configured in a variety of ways. The
only requirement placed upon it is that the folding flanks
projecting around the folding surface be guided without
damage upon contact. A more or less smooth surface is
therefore recommended, in particular one without any sharp,
protruding elements.
[16] The fin is usually only provided in an upper region of
the folding blade, for example in an upper half or upper
third.
[17] According to the aspect of the invention described
above, the fin exhibits a "collapsible element". This must
be understood to mean that the fin can reduce the size of
its outer contours relative to each other. An envelope
around the fin in a non-collapsed state, i.e., in the
expanded state, thus has a larger volume than an envelope
around the collapsed fin.
[18] Within the meaning of the invention present here, the
collapsible property only exists if the fin can be re-
CA 02824953 2013-08-28
expanded. As known from US 3,566,756, for example, a fin
consists of wood. Therefore, while it can be reduced in
terms of its volume through exposure to a destructively
attacking force, it cannot be re-expanded. The inventive
5 idea present here is not intended to encompass destructive
collapsing.
[19] While the fin from the deep folding blade in
CO2007A000023 has a movable position, it remains identical
with respect to its volume, since both the fixed upper part
of the fin and the movable lower part of the fin are each
designed to be non-collapsible in terms of their volume.
[20] The introduced aspect of the invention advantageously
prevents any displacement by the fin or parts of the fin if
so desired. Rather, the fin can simply be varied in terms
of its size. As a result, it can not only be adjusted to
various fold-in depths, but, for example when suitably
configured, be laid flat so as to project toward the rear
of the folding blade only very slightly or not at all. This
gives the folding blade a wide variety of uses, and allows
it to be implemented with simple and cost-effective
technical means.
[21] The "adjustment device" can in particular include any
connecting means for applying force, air, another fluid or
electrical current.
[22] In a preferred embodiment, the collapsible element
exhibits a bellows, and the adjustment device is designed
as a volume adjustment device.
[23] A "bellows" is to be understood as any component that
exhibits a textile, soft, foldable and/or elastic sheath,
in particular with a structural reinforcement situated
therein or thereon. In particular, it must be possible to
= CA 02824953 2013-08-28
6
expand a bellows by filling it with a fluid, and collapse
it by pumping or sucking out the fluid.
[24] In a collapsible element designed in this way, the
adjustment device acts as a volume adjustment device. This
means that the adjustment device is to be set up to expand
or collapse the volume of the bellows, preferably in
several stages or even continuously.
[25] It can be provided that the bellows be outwardly
sealed fluid tight, except for the connection to the
adjustment device.
[26] Another embodiment can provide that the bellows be
semi-permeable in design, wherein the adjustment device is
connected and configured in such a way that a stream of
fluid can be supplied to the bellows so as to keep the
volume of the collapsible element constant.
[27] If an adjustment device exhibits a port for guiding
fluid, the collapsible element becomes especially easy to
collapse and re-expand: All that need be done is to secure
a line with a pump to the port. If the pump then blows a
fluid, air in the simplest case, into the collapsible
element, the collapsible element will expand. By contrast,
if air is evacuated from the collapsible element, it will
assume the collapsed state.
[28] Let it be noted that a pump does not necessarily have
to be situated outside the collapsible element. Rather,
enough installation space might also be available inside
the collapsible element to set up practically independent
adjustment devices.
[29] One example would be a hydraulic or pneumatic
cylinder, which in the collapsible element can ensure a
resizing, for example hooked up to a stabilizing framework
CA 02824953 2013-08-28
7
inside the collapsible element, which then can be sheathed
with material or film, turning it into a bellows.
[30] Independently force-applying elements can also be
provided, for example a return spring inside the
collapsible element. In such a structural design, it may be
envisaged that the return spring brings the collapsible
element into a resting volume, with the volume of the fin
only moving out of this state when an outer force is
applied. When the force is removed, the fin once again
assumes the resting volume.
[31] It is proposed that the fin exhibit a fixed element.
In such a case, the fin is composed of at least two parts,
specifically at least one fixed element and at least one
collapsible element.
[32] Let it generally be noted that, within the framework
of the present application, indeterminate articles or
numerical values are to be understood as minimum data. A
term like "one_", "two_", etc. is thus always to be
understood as at least one_", at least two_", etc.,
unless it may be gleaned from the respective context that
"precisely one_", "precisely two_", etc. is meant.
[33] As a rule, a fixed element will be more cost effective
and technically easier to construct than a collapsible
element.
[34] If a folding blade arranged on the blown film line
exhibits regions where the rearwardly protruding fin does
not hinder the variability of use, such a part can readily
be fixed in place. The collapsible element can make sense
in particular in a case where the folding blade might
otherwise collide with the engine frame when displaced or
swiveled away from the vertical axis of the film bubble,
for example with a swing bearing, a bearing ring and/or a
CA 02824953 2013-08-28
8
carrier ring, in particular of the kind that is often
encountered for an oscillation unit at roughly the height
of the take-off pinch rolls.
[35] The fin can exhibit a guide for the collapsible
element. The collapsible element can then be given a less
stable design.
[36] A guide for the collapsing element preferably is
located on a fixed element of the fin. For example, it can
be a short rail or slide bearing, or a stably designed
component of the collapsible element is guided inside the
fixed element of the fin.
[37] The collapsing element can exhibit a swiveling edge,
wherein a lower edge is preferably designed like a hinge or
otherwise pivoted. A swiveling edge allows the edge to be
swiveled on the folding blade flatly or as flatly as
possible around the pivot bearing on the lower region of
the folding blade in the collapsing process. For purposes
of re-expansion, the swiveling edge can be pivoted back
toward the rearward side from the folding blade, once again
around the hinge-like lower edge.
[38] In a second aspect of the present invention, the set
object is achieved by means of a blown film line with a
folding blade as described above, wherein the folding blade
is situated between a bubble expansion zone and take-off
pinch rolls, and the fin is aligned facing away from a
vertical axis for the running film bubble.
[39] It is proposed that a connection be used to hook up
the adjustment device to an energy source of the blown film
line, in particular to a pump.
[40] As has already been explained, the pump is set up in a
preferred embodiment of the invention in such a way that it
CA 02824953 2013-08-28
9
can pump in particular air or some other fluid into the
collapsible element or pump it out of the collapsible
element by way of a hose or pipe.
[41] For example, another embodiment provides that the
connection be a power cable, and the energy source of the
blown film line be an electrical power supply.
[42] Alternatively or cumulatively, the connection can be a
mechanical connection, for example comprised of gear
wheels, knee levers or other mechanical structures.
[43] In particular, the collapsible element is to be
situated at the height of a swing bearing or another frame
part of the blown film line, which would otherwise collide
with the fin as the folding blade or usual two folding
blades are swiveled or horizontally displaced on the line.
It is precisely there where it makes the most sense to
provide a collapsible element.
[44] The blown film line can ideally be moved into at least
two or three or four different folding operation modes by
adjusting the collapsible element, specifically:
- A deep folding operation mode, in which the folding
surface and fin are arranged so as to engage into the
ascending film bubble, and the fin protects the film
bubble folded in from the folding surface against its
folding flanks coming into contact with each other
during operation, and/or
A first folding operation mode, in which the
collapsible element is present in the collapsed state,
and the folding flanks of the film web folded in from
the folding surface still do not come into contact
with each other, and/or
CA 02824953 2013-08-28
- A second folding operation mode, in which the
collapsible element is present in the collapsed state,
and does not contact the folding flanks of the film
web folded in from the folding surface, and/or
5
- A non-folding operation mode, in which the folding
surface of the folding blade and the fin are varyingly
positioned relative to the folding operation types, so
that they do not engage into the ascending film
10 bubble, wherein the fin is preferably collapsed, so
that the folding surface generates no folding flanks
during operation, and the blown film line flattens out
the film bubble without folding in.
[45] In a third, independent aspect of the invention, the
set object is achieved by a method for retrofitting or
upgrading a blown film line, wherein a folding blade is
installed as described above, if necessary accompanied by
an expansion or modification of a folding blade or deep
folding blade or a lateral guide.
[46] In a fourth aspect of this present invention, the set
object is achieved by a method for operating a blown film
line, in which a collapsible element of a fin is brought to
a desired volume with an adjustment device in order to set
how deeply a folding blade or deep folding blade engages
into the ascending film bubble.
[47] The invention will be described in greater detail
below based on an exemplary embodiment, making reference to
the drawing. Shown on:
Fig. 1 is
a schematic, spatial view of a folding blade
with a collapsible fin, and
CA 02824953 2013-08-28
11
Fig. 2 is a highly schematic, spatial view of an
alternative folding blade with a collapsible
small fin.
[48] From a structural standpoint, the folding blade 1 on
the figure initially consists of a triangular base plate 2.
The base plate 2 is made out of a wood-based material, and
has rounded edges.
[49] While facing the vertical axis of a film bubble, a
front side 3 (covered on the figure) is provided for
purposes of immersion at an angle into the film bubble
pulled up by the take-off pinch rolls on a blown film line.
[50] The rear side of the folding blade 1 carries a fin 7.
The fin 7 essentially consists of a collapsible bellows 8
and fixed angle section 9.
[51] The bellows 8 is composed of a rigid plate 10 and soft
cloth or film on a first flank 11 and on a second flank 12
(covered), wherein the flanks 11, 12 join the rigid plate
10 with the base plate 2. The rigid plate 10 is also joined
with the base plate 2 inside the bellows by an articulated
mechanism 13 (not shown in detail).
[52] In an upper region 14 of the bellows 8, the two flanks
11, 12 converge and the rigid plate 10 tapers.
[53] Two recesses 15 on the rigid plate 10 that otherwise
runs with three straight edges at a certain distance leave
space for two edges 16, 17 of the angle section 9.
[54] The rigid plate 10 is interrupted by an opening, to
which a hose 19 is connected by way of a fitting 18, so
that the hose 19 can communicate with the internal space of
the bellows 8.
CA 02824953 2013-08-28
12
[55] A pointed extension (covered by the leg of the angle
section 9) of the rigid plate 10 projects as far as into
the angle section 9.
[56] If air is pumped into the bellows 8 through the hose
19 during operation, the excess pressure inside the bellows
8 causes the rigid plate 10 to lift from the base plate 2
in a direction of expansion 20, specifically to pivot
around the articulated mechanism 13. The movement continues
until the two flanks 11, 12 are tensioned. The rigid plate
10 then runs in alignment with the rearwardly averted edges
of the angle section 9.
[57] By contrast, if air is sucked out of the bellows 8
through the hose 19, the bellows 8 collapses, and the rigid
plate 10 comes to lie flat on the base plate 2 along a
collapsing direction 21 around the articulated mechanism
13.
[58] In both the collapsing and expanding process, the tip
of the rigid plate 10 is guided in the angle section 9.
[59] A sealed hollow space can be provided inside the
bellows 8 for the air that was forced in and sucked out.
The two flanks 11, 12 should then form an essentially or
hermetically tight seal with the rigid plate 10 and base
plate 2.
[60] For example, it is simpler to provide a hydraulic
cylinder between the rigid plate 10 and base plate 2, which
ensures the movement.
[61] The labile flanks 11, 12 follow the movement of the
rigid plate 10. If the entire internal space of the bellows
8 is exposed to a vacuum in the collapsing process, the two
flanks 11, 12 are automatically retracted into the interior
during the collapsing movement, and hence do not endanger
* CA 02824953 2013-08-28
13
the film bubble. By contrast, if the internal space of the
bellows 8 is not subjected to a vacuum in the collapsing
process, it is advisable that bands, e.g., rubber bands, be
provided between the two flanks 11, 12, so as to reliably
fold the latter into the internal space.
[62] The alternative deep folding blade 22 on Fig. 2 has a
fin 23 with a technically very similar structural design.
Therefore, no detailed description will be provided at this
juncture.
[63] From at technical standpoint, the fin 23 initially
differs from the one from the embodiment described on Fig.
1 in that there is no fitting 18 for compressed air.
Provided instead is an electrical power line (not shown),
which drives an adjustment system located inside the
bellows.
[64] However, a separate guide with a fixed part was
omitted on an upper edge 24 of the fin 23. As a
consequence, the collapsible element embodied by the fin 23
extends up until the upper edge 24 of the alternative deep
folding blade 22.
[65] In terms of proportions, the fin 23 is only situated
in an upper region 25 of the alternative deep folding blade
22. For this reason, an articulated mechanism 26 is not
located on a lower side of the deep folding blade, but
rather further up, preferably above the center of the
alternative deep folding blade 22. As a consequence, a base
plate 27 extends with a free part 28 under the fin 23 up to
a lower edge 29 of the alternative deep folding blade 22.
' CA 02824953 2013-08-28
. .
14
Reference List
1 Folding blade
2 Base plate
3 Front side
4 Lower side
5 Upper edge
6 Rear side
7 Fin
8 Bellows
9 Angle section
10 Plate
11 First flank
12 Second flank
13 Articulated mechanism
14 Upper region
15 Recesses
16 Edge of angle section 9
17 Edge of angle section 9
18 Fitting
19 Hose
20 Direction of expansion
21 Collapsing direction
22 Alternative deep folding blade
23 Fin
24 Upper edge
25 Upper region
26 Articulated mechanism
27 Base plate
28 Free part
29 Lower edge