Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 PCT/EP2012/054244
Description
Method and device for controlling a lifting machine, a stor-
age medium, and a lifting machine system
The present invention relates to a method and device for con-
trolling a lifting machine, a storage medium, and a lifting
machine system and, especially, to a method and device for
controlling a lifting machine of a cage operating in a shaft,
a storage medium, and a lifting machine system including the
device.
During the loading and unloading of the lifting machine in
the mine well, the shake table receiving device needs to be
connected to the inner and outer vehicle tracks so as to
avoid an impact load from directly applying on the cage and
avoid the overlarge elongation volume of the steel wire rope
due to an overlarge load. When a heavy platform car (the ma-
ximum mass is about 39 tons) enters or exits the cage, the
elongation volume of the steel wire rope is large, and the
elongation volume is even larger for the lifting in a deep
well, in which case when the equipment enters or exits the
cage, the cage would jump up and down with instability, caus-
ing the equipment to not be able to enter or exit the cage
conveniently, reliably or stably.
Currently, commonly used supporting devices for the in-
ner/outer connection of a cage include support machines and
shake tables. The support machine requires that the cage must
have an individual movable base plate, which causes the cage
structure to be complicated and large in mass, and at the sa-
me time, the operation time is rather long, increasing the
lifting cycle time. When the shake table is receiving the ca-
go, the cage is in a hanging state, due to thc elastic defor-
mation of the lifting steel wire rope and the impact to the
cage when a mine car enters/exits the cage, the cage is cau-
sed to jump up and down and swing from side to side, and it
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 2 PCT/EP2012/054244
is quite possible that the mine car falls off the track. The
cart equipment coordinated with the shake table is generally
in an upward slope state, which requires a relatively larger
pushing force of the cart, and when passing by the up-
ward/downward slope of the shake table at the time of enter-
ing/exiting the cage, it is quite possible that the personnel
may slip and fall, which is very unsafe.
In Chinese patent application No. 200810150332.8 entitled
"Cage stabilizing/cage locking device for shaft cage", a cage
stabilizing/cage locking device for a shaft cage is dis-
closed, and a converting platform capable of receiving and
locking the cage to is also disclosed in the portion of back-
ground art, which converting platform is composed of a cage
stabilizing rocker arm, a centering device, a buffering oil
cylinder, etc., and the working principle thereof is as fol-
lows: when the cage is resting at the bottom of the well, the
cage stabilizing rocker arm is placed onto the cage, in the
cage stabilizing rocker arm there is a centering device pro-
jected into a hole preserved in the top of the cage, and the
buffering oil cylinder holds the centering device up and can
dynamically absorb the energy generated by the elastic defor-
mation of the steel wire rope.
It can be seen that the above cage stabilizing/cage locking
device for a shaft cage and the converting platform are quite
complicated in structure, and a cumbersome program is needed
to effectively control the hosting machine so as to raise and
lower the cage.
The present invention aims to provide a method for control-
ling a lifting machine in a simple and direct manner and a
corresponding device thereof, wherein after a load-
ing/unloading operation is completed at a shaft level, the
lifting machine can be controlled to release the cage locking
device in a simple manner and operate to the next shaft level
destination position.
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 PCT/EP2012/054244
3
Provided in the present invention is a method for controlling
a lifting machine, wherein said lifting machine is used for
lifting a cage operating within a shaft, said cage is pro-
vided with a plurality of stop blocks for fixing, the wall
base of said shaft is deployed with a plurality of latches,
with said latches being used for maintaining the position of
said cage by moving in the directions approaching said cage
when said cage stopped in place so as to be fixed above and
below said stop blocks for fixing, and when said cage needs
to be released, said latches are moved in the directions away
from said cage, so as to have said cage released after all of
them have been withdrawn,
releasing said cage, detecting the withdrawal status of
said latches, and sending out a latch withdrawn signal;
sending out a shaft signal for a coordinating movement if
it is indicated by said latch withdrawn signal that said lat-
ches above/below said stop blocks for fixing have been with-
drawn in one direction but not all of those in the other di-
rection have been withdrawn;
activating said lifting machine to pull said cage to car-
ry out said coordinating movement after having received said
shaft signal;
detecting the withdrawal status of said latches under
predetermined conditions after having carried out said coor-
dinating movement, and sending out a detection signal; and
pulling by said lifting machine said cage so as to run
directly to a destination position if it is indicated by said
detection signal that all of said latches have been withdrawn
under the predetermined conditions.
It can be seen that the operator of the lifting machine only
needs to operate the lifting machine once, and the lifting
machine can automatically complete the coordinating movement
as required and perform a normal movement to the destination
position thereof by releasing and applying braking for one
time, significantly enhancing the operational efficiency of
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 4 PCT/EP2012/054244
the lifting machine, having good safety monitoring for the
cage locking system so as to avoid human operation errors,
having quite high safety performance, and at the same reduc-
ing the brake wearing therein.
As one embodiment, if it is indicated by said latch withdrawn
signal that there are still latches that have not been suc-
cessfully withdrawn both above and below the stop blocks for
fixing, then said lifting machine is locked. If there are
still latches not withdrawn both above and below the stop
blocks for fixing, it probably means that there a failure has
occurred during the withdrawal of the latches, locking the
lifting machine at this moment will contribute towards pre-
venting accidents from happening.
As one embodiment, if it is indicated by said latch withdrawn
signal that all of the latches above and below the stop
blocks for fixing have been withdrawn, then a shaft signal
for a normal movement is sent out, and after having received
said shaft signal, said lifting machine pulls said cage so as
to run directly to the destination position. If all of the
latches above and below the stop blocks for fixing have been
withdrawn, then it indicates that there are no obstacles both
above and below the cage, and raising or lowering can be car-
ried out according to an instruction.
As one embodiment, if it is indicated by said latch withdrawn
signal that all the latches above the stop blocks for fixing
have been withdrawn but not all of those therebelow have been
withdrawn, then said shaft signal for the coordinating move-
ment is one for the cage to carry out a coordinating movement
upwards; or
if it is indicated by said latch withdrawn signal that
all the latches below the stop blocks for fixing have been
withdrawn but not all of those thereabove have been with-
drawn, then said shaft signal for the coordinating movement
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 5 PCT/EP2012/054244
is one for the cage to carry out the coordinating movement
downwards.
During the raising or lowering of the cage by the lifting ma-
chine, cooperation between the shaft operator and the lifting
machine operator is required, in the embodiments of the pre-
sent invention, if the shaft operator wants to make the cage
reach the destination position, what is needed is to only
carry out the same operation once again without sending out a
signal for the coordinating movement, that is to say, the
shaft operator can only send a normal start instruction once
to the lifting machine operator without considering which
status the latches are in. Similarly, the lifting machine op-
erator also only need to operate the lifting machine once,
i.e. control the cage to move to the destination position,
and the lifting machine can automatically complete the coor-
dinating movement as required to release and brake for one
time and to perform the normal movement to the destination
position thereof. It is unnecessary for the shaft operator to
send out an instruction twice to the lifting machine opera-
tor, and the lifting machine operator also need not operate
twice, and the lifting machine need not release and brake
twice, i.e. without carrying out movement twice. As such, the
operational efficiency of the lifting machine can be signifi-
cantly enhanced, the cage locking system has comprehensive
safety monitoring so as to avoid human operation errors, the-
re is quite high safety performance, and at the same time the
braking wearing therein is reduced, and the lifting machine
can automatically release the cage locking device after a lo-
ading/unloading is completed at a shaft level and automati-
cally operate to the next shaft level destination position.
As one embodiment, the full withdrawal of said latches under
said predetermined conditions is particularly as follows: the
distance after said cage has carried out the movement is
within a predetermined maximum distance and all of said
latches have been withdrawn, or, all of said latches have
been withdrawn within a predetermined time period after said
cage has reached said predetermined maximum distance.
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 6 PCT/EP2012/054244
When predetermining the value of the maximum distance, if the
maximum distance is too long, then it is possible that the
latches may impact the cage, while the setting of a predeter-
mined time period which needs to be awaited is mainly for
waiting for the action of the oil cylinders, i.e. waiting for
the oil cylinders to withdraw the latches in place.
As one embodiment, when said shaft signal for the coordinat-
ing movement is one for the cage to carry out the coordinat-
ing movement upwards, the maximum speed during said upward
movement is a first maximum speed, and the maximum speed dur-
ing the movement directly to the destination position after-
wards is a second maximum speed, wherein the value of said
first maximum speed is smaller than that of said second maxi-
mum speed, and
when said shaft signal for the coordinating movement is
one for the cage to carry out the coordinating movement down-
wards, the maximum speed during said downward movement is a
third maximum speed, and the maximum speed during the move-
ment directly to the destination position afterwards is a
fourth maximum speed, wherein the value of said third maximum
speed is smaller than that of said fourth maximum speed.
As one embodiment, said second maximum speed and the fourth
maximum speed are equal in value, said first maximum speed
and the third maximum speed are equal in value.
Since the distance of the coordinating movement is relatively
short, if the cage operates with a relatively low speed, then
the operational stability can be ensured, while during a nor-
mal movement, a relatively high speed can be used to operate
to a predetermined position.
As one embodiment, if not all of said latches have been with-
drawn under said predetermined conditions, then operational
braking is carried out on said lifting machine. If not all of
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 PCT/EP2012/054244
7
said latches have been withdrawn within a predetermined maxi-
mum distance after said cage has carried out the movement,
or, not all of said latches have been withdrawn within a pre-
determined time period after said cage has reached said pre-
determined maximum distance, then it means the cage locking
system fails to release and needs to carry out operational
braking so as to secure the safety.
Also provided in the present invention is a device for con-
trolling a lifting machine, wherein said lifting machine is
used for lifting a cage operating within a shaft, said cage
is provided with a plurality of stop blocks for fixing, the
wall base of said shaft is deployed with a plurality of
latches, with said latches being used for maintaining the po-
sition of said cage by moving in the directions approaching
said cage when said cage is stopped in place so as to be fi-
xed above and below said stop blocks for fixing, and when
said cage needs to be released, said latches are moved in the
directions away from said cage, so as to have said cage re-
leased after all of them have been withdrawn, and
said device includes:
a latch state detecting unit for detecting the withdrawal
status of said latches when releasing said cage, and sending
out a latch withdrawn signal,
a coordinating movement signal unit for analyzing said
latch withdrawn signal after having received the same, and if
said latches in one direction have been withdrawn while not
all of those in the other direction have been withdrawn, for
sending out a shaft signal for the coordinating movement,
a coordinating movement control unit for activating said
lifting machine to pull said cage to carry out said coordi-
nating movement after having received said shaft signal for
the coordinating movement;
a judgment unit for detecting the withdrawal status of
said latches under predetermined conditions after having car-
ried out said coordinating movement, and sending out a detec-
tion signal; and
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 8 PCT/EP2012/054244
a normal movement control unit for sending out an in-
struction to control said lifting machine to pull said cage
so as to run directly to a destination position if it is in-
dicated by said detection signal that all of the latches have
been withdrawn.
As one embodiment, if all of the latches above said stop
blocks for fixing have been withdrawn but not all of the lat-
ches therebelow have been withdrawn, said shaft signal for
the coordinating movement sent out is one for the cage to
carry out the coordinating movement upwards, if all of the
latches below said stop blocks for fixing have been withdrawn
but not all of the latches above said stop blocks for fixing
have been withdrawn, then said shaft signal for the coordi-
nating movement sent out is one for the cage to carry out the
coordinating movement downwards.
As one embodiment, a braking unit is further included for
sending out an instruction to lock said lifting machine when
it is indicated by the latch withdrawn signal that there are
still latches that have not been successfully withdrawn both
above and below the stop blocks for fixing; and/or, for send-
ing out an instruction to carry out operational braking on
said lifting machine when it is indicated by the latch with-
drawn signal that not all of said latches have been withdrawn
under predetermined conditions.
As one embodiment, the full withdrawal of said latches under
said predetermined conditions is particularly as follows: all
of said latches have been withdrawn within a predetermined
maximum distance after said cage has carried out the coordi-
nating movement, or, all of said latches have been withdrawn
within a predetermined time period after said cage has
reached said predetermined maximum distance.
As one embodiment, when said shaft signal for the coordinat-
ing movement is one for the cage to carry out the coordinat-
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 9 PCT/EP2012/054244
ing movement upwards, the maximum speed during said upward
movement is a first maximum speed, and the maximum speed dur-
ing the movement directly to the destination position after-
wards is a second maximum speed, wherein the value of said
first maximum speed is smaller than that of the second maxi-
mum speed, and
when said shaft signal for the coordinating movement is
one for the cage to carry out the coordinating movement down-
wards, the maximum speed during said downward movement is a
third maximum speed, and the maximum speed during the move-
ment directly to the destination position afterwards is a
fourth maximum speed, wherein the value of said third maximum
speed is smaller than that of said fourth maximum speed.
As one embodiment, said second maximum speed and the fourth
maximum speed are equal in value, said first maximum speed
and the third maximum speed are equal in value.
Also provided is a lifting machine system, including a cage,
a lifting machine for lifting said cage, and further includ-
ing a device for controlling the lifting machine as described
above.
The present invention further provides a machine readable
storage medium which stores instructions for enabling a ma-
chine to carry out any of the abovementioned methods for con-
trolling the lifting machine.
By way of the method, the device, the lifting machine system
as well as the storage medium provided in the present inven-
tion, the shaft operator only needs to carry out the same op-
eration once without sending out a coordinating movement sig-
nal in three different scenarios (all of the latches above
the stop blocks for fixing have been withdrawn, all of the
latches therebelow have been withdrawn, and all of the lat-
ches thereabove and therehelow have been withdrawn), i.e. it
only needs to send a normal start instruction once to the
54106-1439
lifting machine operator without considering which scenario the
cage locking device is in. Similarly, the lifting machine
operator also only needs to operate the lifting machine once,
and the lifting machine can automatically complete the coor-
5 dinating movement as required and perform the normal movement
to the destination position thereof by carrying out releasing
and braking for one time. It is unnecessary for the shaft
operator to send out an instruction twice to the lifting
machine operator, the lifting machine operator also need not
10 operate twice, and the lifting machine need not release and
brake twice, i.e. with carrying out movement twice. The
operational efficiency of the lifting machine is significantly
enhanced, the cage locking system has good safety monitoring so
as to avoid human operation errors, there is quite high safety
performance, and at the same time the braking wearing therein
is reduced, and a lifting machine can automatically release the
cage locking device after a loading/unloading is completed at a
shaft level and automatically operate to the next shaft level
destination position.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is
provided a method for controlling a lifting machine, with said
lifting machine being used for lifting a cage operating within
a shaft, and a plurality of latches being deployed on a wall
base of said shaft, comprising releasing said cage and
detecting a withdrawal status of said latches, and sending out
a latch withdrawn signal, wherein said cage is provided with a
plurality of fixing stop blocks, said latches are configured to
maintain said cage in a substantially fixed position by moving
in the directions approaching said cage so that one of the
latches is fixed immediately above each said fixing stop block
CA 2830114 2019-02-14
54106-1439
10a
and one of the latches is fixed immediately below each said
stopping block when said cage is stopped in place, and when
said cage needs to be released, said latches are moved in the
directions away from said cage, so as to have said cage
released after all of them have been withdrawn; sending a shaft
signal for a coordinating movement if it is indicated by said
latch withdrawn signal that said latches above/below said
fixing stop blocks in one direction have been withdrawn but not
all of those in the other direction have been withdrawn;
activating said lifting machine to pull said cage to carry out
said coordinating movement after having received said shaft
signal for the coordinating movement; detecting the withdrawal
status of said latches under predetermined conditions and
sending out a detection signal after having carried out said
coordinating movement; and pulling by said lifting machine
said cage so as to run directly to a destination position if it
is indicated by said detection signal that all of said latches
have been withdrawn under said predetermined conditions.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is
provided a device for controlling a lifting machine, wherein
said lifting machine is used for lifting a cage operating
within a shaft, said cage is provided with a plurality of
fixing stop blocks, a wall base of said shaft is deployed with
a plurality of latches, with said latches being used for
maintaining said cage in a substantially fixed position by
moving in the directions approaching said cage so that one of
the latches is fixed immediately above each said fixing stop
block and one of the latches is fixed immediately below each
said stopping block when said cage is stopped in place, and
when said cage needs to be released, said latches are moved in
CA 2830114 2019-02-14
'
54106-1439
10b
the directions away from said cage so as to release said cage
after all of them have been withdrawn; said device comprises: a
latch state detecting unit for detecting a withdrawal status of
said latches when said cage is released, and sending out a
latch withdrawn signal, a coordinating movement signal unit
for analyzing said latch withdrawn signal after having received
the same, and if it is indicated that said latches in one
direction have been withdrawn while not all of those in the
other direction have been withdrawn, sending out a shaft signal
for a coordinating movement, a coordinating movement control
unit for activating said lifting machine to pull said cage to
carry out said coordinating movement after having received said
shaft signal for the coordinating movement; a judgment unit for
detecting the withdrawal status of said latches under
predetermined conditions after having carried out said
coordinating movement, and sending out a detection signal; and
a normal movement control unit for sending out an instruction
to control said lifting machine to pull said cage so as to run
directly to a destination position if it is indicated by said
detection signal that all of the latches have been withdrawn.
The following accompanying drawings are only intended to
illustratively describe and explain the present invention and
not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. In
the drawings,
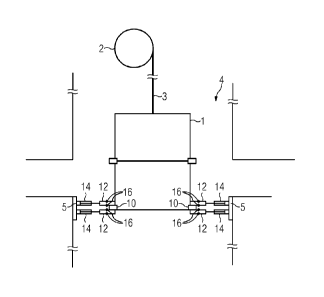
Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of a cage;
Fig. 2 is a partial flowchart of the procedure according to the
method embodiments of the present invention;
CA 2830114 2019-02-14
54106-1439
10c
Figs. 3a, 3b and 3c are partial flowcharts of the procedure
according to the method embodiments of the present
invention in different scenarios;
Fig. 4 is a partial flowchart of the procedure according to the
method embodiments of the present invention; and
Fig. 5 is a structural block diagram according to the device
embodiments of the present invention.
Description of reference signs:
1 cage
2 mine well lifting machine
CA 2830114 2019-02-14
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 PCT/EP2012/054244
11
3 head rope
4 shaft
base
stop block for fixing
5 12 latch
14 hydraulic oil cylinder
16 sensor
100 device for controlling the lifting machine
101 latch state detecting unit
10 102 coordinating movement control unit
103 judgment unit
104 normal movement control unit
105 braking unit
106 coordinating movement signal unit
For the sake of better understanding of the technical fea-
Lures, objecLs, and effecLs of the presenL invenLion, the
particular embodiments of the present invention will now be
described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
In order to solve the problem of swing and shaking when the
barney enters/exits the cage, a cage 1 is shown in Fig. 1,
and the object of stabilizing the cage is achieved by insert-
ing latches (or referred to as cage locking bolt) into the
base of the cage to lock the cage.
As shown in Fig. 1, the cage locking device is used for fix-
ing the cage 1 vertically in a predetermined loading position
and an unloading position so as to flush the cage with the
floor surface, so that the cage 1 can be fixed in a rela-
tively accurate position stably. The cage locking device is
usually fixed on the base 5 of the shaft 4, and mainly in-
cludes eight latches 12 with each of them having a position
detecting sensor 16 and being driven by a hydraulic oil cyl-
inders 14, and at four points of the bottom frame of the cage
1, the latches 12 are movable in the directions approaching
the cage 1 and are fixed above and below the stop block for
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 12 PCT/EP2012/054244
fixing (positioning block) 10 of the cage frame. When the ca-
ge 1 is unloaded under the well, due to the change in the
elongation volume of the head rope 3, the cage 1 will move
upwards after the load has been moved out of the shake table,
at this moment the latches 12 above will make contact with
the stop block for fixing 10. When the cage 1 is loaded under
the well, due to the change in the elongation volume of the
head rope, the cage 1 will move downwards after the load is
placed into the cage 1, at this moment the latches 12 below
will make contact with the stop block for fixing 10.
The cage 1 is required to stop within an error range of 20
mm under the control of a winder control system (WCS) for the
mine well lifting machine 2 so as to flush with the floor.
After the cage 1 is stopped in place, the latches 12 move in
the directions approaching the cage 1, and the positions of
all these 8 latches 12 are monitored by the sensors 16. When
all of the latches 12 have reached their positions above and
below the stop blocks for fixing 10, the shake table is low-
ered and the shaft door is opened, at this moment the loading
or unloading operation can be carried out. After the loading
or unloading operation is completed, the shaft door is closed
and the shake table is raised. Upon reaching the vertical end
position, the shake table will be locked by a locking device
on a side thereof, and when the shaft door is closed and the
shake table is raised, the hydraulic cylinders will do their
best to pull the latches out of the cage so as to release the
cage.
It can be seen after the loading or unloading, if the cage
needs to be operated to a next destination, it is required to
ensure the withdrawal of the latches from the cage, so there
is a need to control the lifting machine during this process
so as to automatically release the cage locking device after
a loading/unloading is completed at a shaft level and to
automatically operate to the next shaft level destination po-
sition.
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 13 PCT/EP2012/054244
Referring to Fig. 1, the head rope 3 of the lifting system
will elongate according to the weight loaded and the position
of the cage 1 within the shaft 4, the more weight is loaded,
or the lower position the cage 1 is in the shaft 4, the
longer the elongation of the head rope 3 would be. To this
end, after the cage 1 is unloaded, the cage 1 will move up-
wards, the stop blocks for fixing 10 on the cage 1 will press
the latches 12 thereabove, while after the cage 1 is loaded,
the cage 1 will move downwards, and the stop blocks for fix-
ing 10 on the cage 1 will press the latches 12 therebelow.
Such design of the latches 12 and the stop blocks for fixing
10 requires that when the stop blocks for fixing 10 are still
in contact with the latches 12, the latches 12 would not be
able to leave their positions, and the control system of the
lifting machine 2 needs to move the position of the cage 1 so
as to enable the latches 12 to be moved in the directions
away from the cage 1. Only the latches 12 that have not been
led (i.e. not in contact with the stop blocks for fixing 10)
can be moved in the directions away from the cage 1 without
moving the cage 1. For example, if the cage 1 is unloaded,
the cage 1 will be moved upwards. Before carrying out the
lifting cycle, the control system of the lifting machine 2
needs to move the cage 1 downwards until the latches 12 the-
reabove are disengaged. Similarly, the same process also
needs to be taken into account when carrying out the loading,
but the difference is that the cage 1 needs to be moved up-
wards so as to enable the latches 12 therebelow to be disen-
gaged.
Particularly, after the cage 1 is in place, the braking will
be carried out, then the cage 1 will be held up by 4 latches
12 above the cage 1 and 4 latches 12 below the cage 1; if a
weight is loaded into the cage 1, the cage 1 will be moved
downwards to apply forces on those 4 latches 12 therebelow as
a result of the traction of the head rope 3; before the cage
1 can be moved towards the next destination, all these 8
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 14 PCT/EP2012/054244
latches 12 need to come back to the positions away from the
shaft 4; after an operator located at the horizontal level of
the shaft 4 starts to release the cage locking system, these
8 latches 12 will be withdrawn under the drive of a hydraulic
cylinder 14 respectively, however, only those 4 latches 12
thereabove can come back to the positions away from the shaft
4, while those 4 latches 12 therebelow will still remain
pressed by the cage 1 and cannot be withdrawn, at this mo-
ment, the lifting machine 2 need to be moved upwards for a
distance until the 4 latches 12 therebelow are also with-
drawn. At this moment, all of these 8 latches 12 come back to
the positions away from the shaft 4, and now the cage 1 is no
longer blocked by the latches 12 and is movable toward the
next destination.
Similarly, when a weight is moved out of the cage 1, the cage
1 will be moved upwards to apply forces to those 4 latches 12
thereabove as a result of the tensioning of the head rope 3;
before the cage 1 can be moved toward the next destination,
all these 8 latches 12 need to come back to the positions
away from the shaft 4; after an operator located at the hori-
zontal level of the shaft 4 starts to release the cage lock-
ing system, these 8 latches 12 will be withdrawn under the
drive by the hydraulic cylinder 14 respectively, however,
only those 4 latches 12 therebelow can come back to the posi-
tions away from the shaft 4, while those 4 latches 12 there-
above will still remain stuck by the cage 1 under the ten-
sioning of the head rope 3 and cannot be withdrawn, at this
moment, the lifting machine 2 need to be moved downwards for
a distance until the 4 latches 12 thereabove are also with-
drawn. At this moment, all of these 8 latches 12 come back to
the positions away from the shaft 4, and now the cage 1 is no
longer blocked by the latches and is movable toward the next
destination.
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397
PCT/EP2012/054244
Now the embodiments of the present invention will be de-
scribed in detail in conjunction with the flowcharts shown in
Figs. 2, 3a, 3b, 3c and 4.
5 As shown in Fig. 2:
Si: initial state - the cage is in place, braking is ap-
plied, and the cage is locked by the cage locking device;
S2: loading or unloading is carried out on the cage, if a
load is loaded into the cage, the elongation volume of the
10 head rope becomes large, the cage would be moved downwards to
apply forces to the 4 latches therebelow, while in case of
moving the load out from the cage, the elongation volume of
the head rope becomes small and forces are applied to the 4
latches thereabove;
15 S3: after the operation in S2 is completed, the operator
located at the horizontal level of the shaft 4 starts the re-
leasing operation of the cage locking system, at this moment
these 8 latches will try to be withdrawn under the drive by
the respective hydraulic cylinder thereof. In the case of a
loading operation being carried out in S2, it is possible
that only those 4 latches thereabove will come back to the
withdrawn positions away from the cage, while possibly not
all of those 4 latches therebelow may be able to be withdrawn
as a result of being stuck by the cage; in the case of an un-
loading operation being carried out in S2, it is possible
that only those 4 latches therebelow will come back to the
withdrawn positions away from the cage, while possibly not
all of those 4 latches thereabove may be able to be withdrawn
as a result of being stuck by the cage; and if the shaft le-
vel where the cage is located is relatively high, it is pos-
sible that all of the 8 latches may come back to the with-
drawn positions after the completion of the loading operation
as a result of a shorter head rope above the cage or a
smaller change in the load.
S4: judging whether all of the 4 latches thereabove have
been withdrawn or if all of the 4 latches therebelow have
been withdrawn;
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 16 PCT/EP2012/054244
S5: if the judgment result in S4 is no, i.e. there are
latches that have not been successfully withdrawn both there-
above and therebelow, then the lifting machine is locked up
and prohibited from releasing the braking for operation, and
at the same time, sends out the fault information that the
releasing of the cage locking system is failed;
S6: if the judgment result in S4 is yes, then the shaft
operator can send a normal movement instruction to the opera-
tor of the lifting machine;
S7: after having received the instruction, the operator
of the lifting machine starts the lifting machine;
now the operation of the lifting machine will be de-
scribed according to different operation scenarios:
Scenario I, as shown in Fig. 3a:
S8a: in this scenario, only those latches thereabove have
been completely withdrawn (the operation in S2 is a loading
operation);
S9a: the lifting machine releases the braking automati-
cally;
SlOa: a coordinating movement is started, i.e. the lift-
ing machine starts to move upwards automatically with a rela-
tively low maximum speed of about 0.1 m/s during the move-
ment, which is mainly because that the operational stability
can he ensured with a relatively low speed in a rnmparatively
short distance of the upward movement;
Slla: this scenario is that: during the coordinating mo-
vement in SlOa, if all of the latches have been withdrawn,
then S13 should be carried out;
Sl2a: during the coordinating movement in SlOa, if the
movement distance of the cage reaches a predetermined maximum
distance, then, at this moment, the cage stops moving, and
after having waited for a predetermined time period (for ex-
ample 2 s), if there are still any latches not withdrawn at
this moment, i.e. not all of the latches have been withdrawn
within said predetermined maximum distance and not all of
said latches have been withdrawn within said predetermined
time period, then S13a should be carried out; when predeter-
mining the value of the maximum distance, if the maximum dis-
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 17 PCT/EP2012/054244
tance is too long, then it is possible that the latches may
impact the cage, while the setting of a predetermined time
period which needs to be awaited is mainly for waiting for
the action of the oil cylinders, i.e. waiting for the oil cy-
linders to withdraw the latches in place.
S13a: applying working braking, and sending out the fault
information that the releasing of the cage locking system has
failed;
Scenario II, as shown in Fig. 3b:
S8b: in this scenario, only those latches therebelow have
been completely withdrawn (the operation in S2 is an unload-
ing operation);
S9b: the lifting machine releases the braking automati-
cally;
SlOb: a coordinating movement is started, i.e. the lift-
ing machine starts to move downwards automatically with a
relatively low maximum speed (for --------------------------------------
example, it can be the same
as that in SlOa) of about 0.1 m/s during the movement, which
is mainly because that the operational stability can be en-
sured with a relatively low speed in a comparatively short
distance of the downward movement;
Sllb: this scenario is that during the coordinating move-
ment in SlOb, in the case of all of the latches having been
withdrawn, then S13 should he carried out;
S12b: in this scenario, during the coordinating movement
in SlOb, if the movement distance of the cage reaches a pre-
determined maximum distance, then, at this moment, the cage
stops moving, and after having waited for a predetermined
time period (for example 2 s), if there are still any latches
not withdrawn at this moment, then S13b should be carried
out; for the same reason, when predetermining the value of
the maximum distance, if the maximum distance is too long,
then it is possible that the latches may impact the cage,
while the setting of a predetermined time period which needs
to be awaited is mainly for waiting for the action of the oil
cylinders, i.e. waiting for the oil cylinders to withdraw the
latches in place.
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 18 PCT/EP2012/054244
S13b: apply working braking, and send out the fault in-
formation that the releasing of the cage locking system has
failed;
Scenario III, as shown in Fig. 3c:
S8c: in this scenario, all of those latches thereabove
and therebelow have been withdrawn (the head rope above the
cage is relatively short or the change in the load is rela-
tively small);
S9c: the lifting machine releases the braking automati-
cally;
following each of the above three scenarios, as shown in
Fig. 4, continue to carry out the following steps:
S13: following the above scenario Slla or Sllb or S9c,
the lifting machine starts to carry out a normal movement to-
wards the destination position thereof, and the value of the
maximum speed in the normal movement can be larger than that
of the maximum speed in SlOa and/or SlOb;
S14: when the lifting machine has reached the destination
position by the normal movement, working braking is applied;
S15: the shaft operator starts a cage locking operation
of the cage locking system; and
S16: S16 is in the end state, similar to the initial sta-
te Sl, the cage is in place, braking is applied, and the cage
is locked by the cage locking device, then a lifting cycle is
completed.
As shown in Fig. 5, also provided in the present invention is
a device 100 for controlling a lifting machine, wherein said
lifting machine is used for lifting a cage operating within a
shaft, the bottom of said cage is provided with a plurality
of stop blocks for fixing, the wall base of said shaft is de-
ployed with a plurality of latches, with said latches being
used for maintaining the position of said cage by moving in
the directions approaching said cage when said cage is
stopped in place so as to be fixed above and below said stop
blocks for fixing, and when said cage needs to be released,
said latches are moved in the directions away from said cage,
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 PCT/EP2012/054244
19
so as to have said cage released after all of them have been
withdrawn, and said device includes:
a latch state detecting unit 101 for detecting the with-
drawal status of said latches when releasing said cage, and
sending out a latch withdrawn signal,
a coordinating movement signal unit 106 for analyzing
said latch withdrawn signal after having received the same,
if said latches in one direction have been withdrawn while
not all of those in the other direction have been withdrawn,
sending out a shaft signal for a coordinating movement,
a coordinating movement control unit 102 for activating
said lifting machine to pull said cage to carry out said co-
ordinating movement after having received said shaft signal
for the coordinating movement;
a judgment unit 103 for detecting the withdrawal status
of said latches under predetermined conditions after having
carried ouL said coordinaLing movemenL, and sending ouL a de-
tection signal; and
a normal movement control unit 104 for sending out an in-
struction to control said lifting machine to pull said cage
so as to run directly to a destination position if it is in-
dicated by said detection signal that all of the latches have
been withdrawn.
As one embodiment, if all of the latches above said stop
blocks for fixing have been withdrawn but not all of the lat-
ches therebelow have been withdrawn, then said shaft signal
for the coordinating movement sent out is one for the cage to
carry out the coordinating movement upwards, if all of the
latches below said stop blocks for fixing have been withdrawn
but not all of the latches above said stop blocks for fixing
have been withdrawn, then said shaft signal for the coordi-
nating movement sent out is one for the cage to carry out the
coordinating movement downwards.
As one embodiment, a braking unit 105 is further included for
sending out an instruction to lock said lifting machine when
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 20 PCT/EP2012/054244
it is indicated by the latch withdrawn signal that there are
latches not been successfully withdrawn both above and below
the stop blocks for fixing; and/or, for sending out an in-
struction to carry out operational braking on said lifting
machine when it is indicated by the latch withdrawn signal
that not all of said latches have been withdrawn under prede-
termined conditions.
As one embodiment, the full withdrawal of said latches under
said predetermined conditions is as follows: all of said
latches have been withdrawn within a predetermined maximum
distance after said cage has carried out the coordinating
movement, or, all of said latches have been withdrawn within
a predetermined time period after said cage has reached said
predetermined maximum distance.
As one embodiment, when said shaft signal for the coordinat-
ing movement is one for the cage to carry out the coordinat-
ing movement upwards, the maximum speed during said upward
movement is a first maximum speed, and the maximum speed dur-
ing the movement directly to the destination position after-
wards is a second maximum speed, wherein the value of said
first maximum speed is smaller than that of said second maxi-
mum speed, and
when said shaft signal for the coordinating movement is
one for the cage to carry out the coordinating movement down-
wards, the maximum speed during said downward movement is a
third maximum speed, and the maximum speed during the move-
ment directly to the destination position afterwards is a
fourth maximum speed, wherein the value of said third maximum
speed is smaller than that of said fourth maximum speed.
As one embodiment, said second maximum speed and the fourth
maximum speed are equal in value, and said first maximum
speed and the third maximum speed are equal in value.
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 21 PCT/EP2012/054244
Furthermore, also provided is such a lifting machine system,
which includes a cage, a lifting machine for lifting said
cage, further includes a device for controlling the lifting
machine as described above.
The present invention further provides a machine readable
storage medium which stores instructions for enabling a ma-
chine to carry out the method for controlling the lifting ma-
chine according to the description of the present document.
In particular, it is possible to provide a system or device
provided with the storage medium on which the software pro-
gram codes performing the functions of any one of the above-
mentioned embodiments are stored, and to enable the computer
(or CPU or MPU) of the system or device to read out and exe-
cute the program codes stored in the storage medium.
In this case, the program codes read from the storage medium
per se are capable of performing the functions of any one of
the abovementioned embodiments, thus the program codes and
the storage medium storing the program codes constitute a
part of the present invention.
The storage medium embodiments for providing the program
codes include floppy disks, hard disks, magneto optical
disks, compact disc (such as CD-ROM, CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-ROM,
DVD-RAM, DVD-RW, DVD+RW), magnetic tape, nonvolatile storage
card and ROM. Optionally, the program codes can be downloaded
from a server computer via communication networks.
In addition, it should be clear that the functions of any one
of the abovementioned embodiments can be performed not only
by executing the program codes read by the computer but also
by enabling the operation system operated on the computer,
etc. to perform a part of or all of the actual operations
based on the instructions of the program codes.
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 22 PCT/EP2012/054244
In addition, it should be understood that the program codes
read from the storage medium are written into the memory pro-
vided in an extension board within the computer or written
into the memory provided in an extension unit connected to
the computer, afterwards a part of or all of the actual op-
erations will be performed by the CPU, etc. mounted in the
extension board or the extension unit based on the instruc-
tions of the program codes so as to perform the functions of
any one of the abovementioned embodiments.
Provided in the present invention is a method and device for
controlling a lifting machine, wherein when releasing a cage,
the lifting machine is a controller, according to the with-
drawal status of the latches above or below the stop blocks
for fixing, for automatically completing the coordinating
movement upwards or downwards and performing a normal move-
ment to the destination position thereof. The method and de-
vice of the present invention can significantly enhance the
operational efficiency of the lifting machine, have good sa-
fety monitoring of the cage locking system so as to avoid hu-
man operation errors, have quite high safety performance, and
at the same time reduce the braking wearing therein.
By way of the method and device for controlling a lifting ma-
chine as well as a lifting machine system provided in the
present invention, the shaft operator only needs to carry out
the same operation once without sending out a coordinating
movement signal in three different scenarios (all of the lat-
ches above the stop blocks for fixing have been withdrawn,
all of the latches therebelow have been withdrawn, and all of
the latches thereabove and therebelow have been withdrawn),
i.e. it only needs to send a normal start instruction once to
the lifting machine operator without taking the scenario
which the cage locking device is in into account. Similarly,
the lifting machine operator also only needs to operate the
lifting machine once, and the lifting machine can automati-
cally complete the coordinating movement as required and per-
CA 02830114 2013-09-13
WO 2012/123397 PCT/EP2012/054244
23
form the normal movement to the destination position thereof
by releasing and applying the braking for one time. It is un-
necessary for the shaft operator to send out an instruction
twice to the lifting machine operator, the lifting machine
operator also need not operate twice, and the lifting machine
need not release and apply braking twice, i.e. without carry-
ing out movement twice. The operational efficiency of the
lifting machine is significantly enhanced, there is good sa-
fety monitoring of the cage locking system so as to avoid hu-
man operation errors, there is quite high safety performance,
and at the same time the braking wearing therein is reduced,
and a lifting machine can automatically release the cage lo-
cking device after a loading/unloading is completed at a
shaft level and to automatically operate to the next shaft
level destination position.
What is described above is merely illustrative of particular
embodiments of the present invention and not intended to
limit the scope of the present invention. Any equivalent
variation, modification, and combination made by those skil-
led in the art without departing from the concept and princi-
ples of the present invention shall belong to the scope of
protection of the present invention.