Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02837985 2015-06-11
A CLOSABLE EXIT OPENING IN A WIND TURBINE BLADE
DESCRIPTION
The invention relates to a rotor blade of a wind turbine, comprising a rotor
blade shell and a blade root for fixing the rotor blade on a hub of the wind
tur-
bine, wherein the rotor blade has at least one cavity, at least some portions
of
which can be accessed.
io The invention further relates to a wind turbine having a mast, a
nacelle, a hub
disposed on the nacelle, and at least one rotor blade disposed on the hub.
With the utilization of the wind energy using wind turbines, there have always
been efforts to develop the systems with the greatest possible nominal power.
is Because the nominal power of such systems is substantially determined by
the
area swept by the rotor, with ongoing development these systems became in-
creasingly large, wherein today cutting-edge systems have a rotor diameter of
well beyond 100m, which means a rotor blade length of more than 50m.
zo Rotor blades of this size can already no longer be produced from solid
materials
due to cost and weight considerations. Therefore, they are typically comprised
of an inner support structure, which is provided with an outer layer defining
the
aerodynamic properties. Whereas this outer layer in the case of smaller rotor
blades is often filled completely with a fill material, e.g. rigid foam,
larger ro-
25 tor blades have cavities.
Such a rotor blade and a wind turbine equipped therewith are described, for ex-
ample, in the document WO 2007/131937 Al. In order to allow the assembly of
the individual parts of the rotor blade, the cavity inside the rotor blade de-
30 scribed therein is designed accessible at least in portions.
Because the rotor blades for error-free function must have a closed outer enve-
2
lope, the entrance to the accessible cavities is disposed mostly in the blade
root, with
which the rotor blade is connected to the hub.
For this purpose, reference is made to the document DE 10 2006 055 091 Al
from the applicant, in which a bulkhead of a wind turbine is shown that is or
will be disposed at the blade root of a rotor blade or in the region between
the blade
root of a rotor blade and a blade hub. The bulkhead has at least two through
openings,
or respectively access openings, so that the maintenance personnel can get
into the rotor
blade.
The cavity of the rotor blade surrounded by the rotor blade shell is accessed,
for
example, by maintenance personnel in order to perform an interior inspection
of
the rotor blade, in order to be able to check, for example, connections in the
rotor
blade, for instance web connections to one or more belts of the rotor blade
shell or the bonding of rotor blade shell pieces such as the suction side to
the
pressure side of the rotor blade shell.
It is the object of the present invention to simplify the entering, or
respectively the
exiting, of the cavity of a rotor blade of a wind turbine.
Thus the object is solved by a rotor blade of a wind turbine having a rotor
blade
shell and a rotor blade root for fixing the rotor blade on a hub of the wind
tur-
bine, wherein the rotor blade has at least one cavity at least portions of
which
can be accessed, wherein the rotor blade shell has an exit opening that can be
closed.
By providing a closable exit opening, tools for example, can be conveyed
easily
into a rotor blade, or the rotor blade can be easily ventilated or exhausted.
The
rotor blade is preferably a rotor blade which is used with a wind turbine
having
CA 2837985 2018-06-11
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
1- 3 -
a horizontal axis of rotation of the rotor.
Regardless of the dimensions of generic rotor blades, the available room to ma-
neuver, particularly in the region of the entry opening is limited, which in
par-
ticular leads to the fact that a person limited in their movement due to a
work
accident or sudden illness can be rescued from the interior of the rotor blade
only with difficulty. This applies all the more so because the rescue in the
case
of rotor blades of the prior art can occur only through the narrow entry
opening
in the blade root. Here, the invention provides a remedy. Through a closable
exit opening in the rotor blade shell it is possible to convey a person to be
res-
cued directly to the outside without the path through the blade root.
Thus, according to the invention, in addition to an entrance from the blade
root,
or respectively the hub of a wind turbine into the cavity of the blade root,
which
is surrounded by the rotor blade shell, an entrance, or respectively an exit,
is
also made possible by an exit opening in the rotor blade shell. Here, the
rotor
blade shell typically has a profile and comprises a suction side and a
pressure
side. An exit opening can be provided both on the suction side and on the pres-
sure side, or even on both sides of the rotor blade shell, so that possibly a
pivot-
ing of the rotor blade about a longitudinal axis, thus a pitching, need not be
per-
formed so that an injured person can be lowered by rope for example. When in
feathered position, for example, a closable exit opening is provided on the
then
lower lying suction side for example, a simple and direct rescue downward is
possible. Here, the rotor blade is then typically substantially horizontal
with the
rotor blade nose in direction of the wind.
If for closing the exit opening, a closing hatch is provided flush with the
outer
layer of the rotor blade shell, then the aerodynamic properties of the rotor
blade
are not impacted by the closed hatch.
If the hatch is designed opening with an inward directed pivot movement, then
the hatch can be easily opened and closed from inside. Here, damage to the out-
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
4 -
er layer of the rotor blade, or respectively the rotor blade shell, is
prevented in
a particularly efficient manner. Additionally, a secure fixing of the hatch in
the
rotor blade can also be provided.
If alternatively to this, the hatch is designed opening with an outward
directed
pivot movement, then the room to maneuver by the persons supporting the res-
cue is restricted as little as possible by the opened hatch. At the same time,
lit-
tle force is required for opening the hatch such that this can be handled
possibly
even by an injured or sick person.
In order to prevent an unintended opening of the hatch, and a fall hazard asso-
ciated with this, in a preferred further development of the invention, at
least one
safety device is provided against unintended opening of the hatch. This can
preferably comprise at least one locking bar.
In order to exclude a fall hazard for a person standing on the hatch, in the
case
of an outward opening hatch, the safety device is preferably further developed
so that the safety device is designed with an inside load acting against the
hatch
impeding the hatch from opening. Thereby, in the case of a load acting
outward,
an opening of the hatch e.g. by a person standing completely or partially on
the
hatch is prevented.
Preferably, the rotor blade shell is reinforced in the region of the closable
exit
opening and/or an element reinforcing the rotor blade shell is provided.
Hereby,
the weakening of the rotor blade shell created by the exit opening is on the
whole at least compensated.
Preferably the exit opening is disposed in a region of the rotor blade that
lies
between the maximum rotor blade depth and the rotor blade tip. When this fea-
ture is given, the exit opening is disposed in a region of the rotor blade in
which
the loads in the rotor blade shell are lower than in a region closer to the
rotor
blade root. The exit opening is preferably provided away from supporting ele-
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
-
ments of the rotor blade, for example, outside of a region in which a belt is
pro-
vided.
If preferably at least one, in particular closable opening, particularly an
access
5 opening, is provided in at least one web of the rotor blade, good
ventilation can
be provided, and for the case that this is an access opening, an access can
also
be provided through the web, or respectively a passage through one web or sev-
eral webs is possible. Hereby, a maintenance person can gain access to
different
regions in the rotor blade, and thus perform a very time extensive inspection.
The opening, particularly access opening, is provided preferably in the region
of neutral fibers of one or more webs, in order to not influence the stability
of
the webs as far as possible.
Preferably an edge region of the hatch is designed tapering in the closing
direc-
tion of the hatch. Due to this, falling out, or respectively an unintended
open-
ing, of the hatch can be prevented. In particular, with a hatch opening to the
inside, then at least one contact surface of the hatch is designed forming a
ramp, or respectively chamfered toward the edge region of the exit opening,
zo that is, the rotor blade shell, such that at least one contact surface
in the shape
of a ramp or chamfer comes into contact with one edge of the rotor blade
shell,
or respectively rests thereupon, and thus cannot be unintentionally opened out-
ward. The at least one ramp-shaped or chamfered contact surface is preferably
opposite from a hinge, by means of which the hatch can be pivoted open.
The outer contour of the hatch is preferably matched to the contour of the
outer
layer of the rotor blade shell. This means in particular that also the outer
con-
tour of the hatch is matched to the curve of the outer layer of the rotor
blade
shell so that the outer profile, or respectively the contour of the outer
layer of
the rotor blade shell merge continuously into each other.
During work in the interior of a generic rotor blade, the rotor blade is
generally
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
- 6 -
located in a horizontal turning position so that maintenance personnel can
move
relatively safely. If however, the rotor begins to spin during the work, there
is
the danger for the personnel to slip in the direction toward the blade tip. In
or-
der to guarantee the safety of maintenance personnel even in this extremely un-
likely case, slinging means for fixing a personal protective equipment are
pref-
erably provided in the interior of the cavity. Here, the slinging means are
pref-
erably attached to the inside of the rotor blade shell, and in particular
preferably
to a reinforcing of the rotor blade shell. Here, the reinforcing can occur for
ex-
ample using further laminate layers. If the slinging means are disposed in par-
preferably in the region of the exit opening, the means can be used addi-
tionally to secure personnel against falling during a rescue procedure.
The pitch position of a generic rotor blade during necessary maintenance work
is generally in the feathered position, which means that the rotor blade does
not
develop any drive even with blowing wind. Otherwise, the danger of spinning
would be unnecessarily increased. With an opened exit opening, the wind can
however act in the interior of the cavity, such that torque develops acting
about
the longitudinal axis of the rotor blade and the rotor blade is thus rotated
out of
the neutral position into an active pitch position, whereby the danger of spin-
ning increases again. In order to counteract this, according to a preferred
fur-
ther development of the invention it is provided that the rotor blade shell in
ad-
dition to the exit opening has at least one further, in particular closable,
open-
ing, wherein for example a further exit opening can also be provided which al-
lows the air flow to exit from the cavity on the lee side.
In the case of very large rotor blades, transverse webs can be necessary in
the
interior of the cavity in order to absorb and dissipate forces acting during
op-
eration, or in order to control air flows in the rotor blade, for example for
de-
icing the rotor blade. In order to guarantee the shape stability of the rotor
blade,
the transverse webs can extend over the entire cross-section of the rotor
blade
and thus subdivide the cavity into a plurality of partial spaces.
Additionally,
webs disposed longitudinally axially can also lead to relatively large spatial
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
7 -
separations of the cavity, which in particular prevent efficient maintenance
work. For this case, it is preferably provided to subdivide the cavity into a
plu-
rality of partial spaces which are connected by passable access openings.
The object is further solved according to the invention by a wind turbine,
wherein the wind turbine comprises a mast, a nacelle, a hub disposed on the
nacelle, and at least one rotor blade disposed on the hub, wherein the at
least
one rotor blade is designed according to the invention as described above.
Further characteristics of the invention will become apparent from the descrip-
tion of the embodiments according to the invention together with the claims
and
the included drawings. Embodiments according to the invention can fulfill indi-
vidual characteristics or a combination of several characteristics.
The object is further solved by a rotor blade of a wind turbine having a rotor
blade shell and a blade root for fixing the rotor blade on a hub of the wind
tur-
bine, wherein the rotor blade has at least one cavity, at least some portions
of
which can be accessed, wherein the rotor blade shell has a marking in a
predefinable region that is provided as a marking of an exit opening. Here,
the
zo exit opening can be provided by separation of the rotor blade shell in
this re-
gion, or respectively at the marking. The separation in this region can be in
par-
ticular a sawing and/or cutting and/or boring, or respectively perforating.
The predefinable region is preferably disposed in the cavity, in particular in
an
accessible region of the cavity.
The predefinable region is preferably a region of the rotor blade shell, which
contributes comparatively little to the stability of the rotor blade. The
predefinable region is in particular away from a belt of the rotor blade. The
predefinable region is preferably disposed behind a web, as seen from the
rotor
blade nose, in particular behind the maximum thickness of the rotor blade or
the
corresponding profile. The predefinable region is preferably disposed between
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
8 -
the center of the rotor blade depth and the rotor blade trailing edge.
The marking is preferably disposed on the inside of the rotor blade shell
and/or
the outside of the rotor blade shell. The marking can be provided by a
coloring.
The invention is described below, without restricting the general intent of
the
invention, based on exemplary embodiments in reference to the drawings,
whereby we expressly refer to the drawings with regard to the disclosure of
all
details according to the invention that are not explained in greater detail in
the
text. The figures show:
Fig. 1 a wind turbine in a schematic front view,
Fig. 2 a schematic three-dimensional representation of a part of a
rotor
blade according to the invention,
Fig. 3 a schematic partial sectional view of a rotor blade according to
the
invention,
Fig. 4 a schematic representation of a hatch with a safety device,
Fig. 5 a schematic representation of a further hatch, and
Fig. 6 a schematic representation of a cross-section through a rotor
blade
according to the invention.
In the following figures, the same or similar types of elements or
corresponding
parts are provided with the same reference numbers so that a corresponding re-
introduction can be omitted.
Fig. 1 shows a wind turbine 1 having a tower 2 and a nacelle 3. A hub 4, on
which three rotor blades 5 are disposed, is located on the side of the nacelle
3
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
9
facing the wind.
Such wind turbines are now being offered with high nominal power, and there-
fore, have very large dimensions. For example the M6 model from the applicant
attains a nominal power of more than 6 MW and has a rotor diameter of 126 m,
which corresponds to a rotor blade length of 63 m.
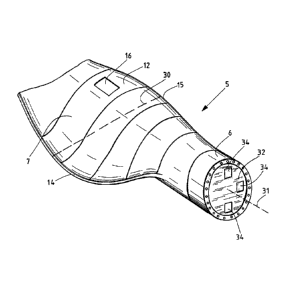
Fig. 2 shows an individual rotor blade 5 of the wind turbine 1. The rotor
blade
has a blade root 6 for fixing on the hub 4 and a rotor blade shell 7, around
which the wind flows during operation, and due to the special aerodynamic
shape thereof delivers the drive for the rotor formed from the rotor blades 5.
The rotor blade 5 represented schematically in Fig. 2 is, as can be seen, only
partially represented, that is, the region toward the tip of the rotor blade
is
missing. A nose 15 and a trailing edge 14 are also shown. The rotor plate 5 it-
self can be entered via the rotor blade root 6 and there through access
openings
34 of the bulkhead 32. Accordingly, a plurality of access openings 34 are pro-
vided in order to conveniently access the rotor blade 5, or respectively the
cavi-
ty in the rotor blade 5, in different rotational positions, or respectively at
differ-
ent pitch angles, that is, angular positions of the rotor blade 5 relative to
the
axis of rotation 31. In the position of Fig. 2, the rotor blade 5 can be
easily ac-
cessed, for example, through the lower disposed access opening 34. In this rep-
resentation, a hatch 16 is shown in the rotor blade shell 6, or respectively
the
outer layer of the rotor blade 5, that when it is opened, would represent an
exit
opening 13. Logically then, the rotor blade 5 rotates by 1800 so that the
hatch
16 is no longer disposed in the upper region of the rotor blade 5, but rather
lies
underneath so that an injured person can be lowered by rope, for example.
Preferably, a further hatch 16, and thus a further exit opening, is also
provided
namely on the side of the rotor blade 5, covered in Fig. 2, for example lying
opposite the hatch 16. If the hatch 16 is disposed for example on the suction
side of the rotor blade 5, a further hatch 16 could be disposed on the
pressure
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
-
side.
Preferably, the exit opening is or the exit openings 13 are disposed between
the
rotor blade tip 45 and a region in which there is the largest rotor blade
depth 30.
5 The rotor blade depth 30 is a chord from the blade tip 15 to the blade
trailing
edge 14. The largest forces in the rotor blade are predominantly in the region
from the rotor blade root to a maximum rotor blade depth. Thus, the exit open-
ings would be introduced in a region in which less force predominates, so that
an opening in the outer layer 12, or respectively the rotor blade shell 7, is
less
io problematic.
Fig. 3 shows a schematic partial section from the rotor blade 5 according to
the
invention. The rotor blade 5 has a cavity 8. Regular inspections of the rotor
blade 5 are required.
If a maintenance worker, during the stay in the rotor blade 5 suddenly becomes
seriously ill, or is injured during a work accident, the worker can be rescued
only with difficulty, or not at all, through the access opening 34 of the
bulkhead
32. In order to allow a rescue nevertheless, a closable access opening 13 is
pro-
m vided in the outer layer 12, or respectively the rotor blade shell 7, of
the rotor
blade 5 through which an affected person can be evacuated from the cavity 8
and can be lowered by rope to the ground, or respectively the surface of the
wa-
ter. The rescue of a person is most simple if the exit direction is directly
down-
ward. Because the rotor blades 5 of the wind turbine 1 are typically brought
into a feathered position during maintenance work, the exit direction, or
respec-
tively the exit opening 13, in this example embodiment lies on the suction
side
of the rotor blade 5.
The exit opening 13 shown in Fig. 3 is provided with a hatch 16', which is rep-
30 resented in dashed form pivoted away from the exit opening 13, and is
shown
with solid lines lying in the exit opening 13. The hatch 16' is represented
here
mounted with a hinge.
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
- 11 -
In order to also reach through a web 37, an access opening 38 can also be pro-
vided. For maintenance work then, the connections of webs to corresponding
belts, or respectively to the rotor blade shell 7, between two webs or other
cavi-
ties can also be accessed.
So that the aerodynamic properties of the rotor blade 5 are not impacted by
the
exit opening 13, the opening can be closed during operation of the wind
turbine
1 by a hatch 16, 16', 16", which can be opened inward or outward, and closing
flush with the outer layer 12 of the rotor blade shell 7.
Figure 3 schematically shows a variant of a rotor blade 5 according to the in-
vention in an enlarged partial section. In this variant, an inward opening
hatch
16' is provided that is represented once closed, and once opened using dotted
lines. Slinging means 17 are provided in the interior of the cavity 8 near the
exit opening 13, for fixing personal safety equipment 18 with which the
maintenance worker 11 is secured against falling. The slinging means are dis-
posed as lifting eyes in the region of the exit opening 13 so that a line for
low-
ering a person to be rescued can also be attached thereto.
When the hatch 16 is opened, wind can act in the exit opening 13 and exert
torque altering the pitch of the rotor blade 5. As a result, the theoretical
danger
exists that the pitch is altered and the rotor begins to spin. In order to
prevent
this, further in particular closable openings 19 are provided in the web 37.
The-
se openings can be further used for the purpose to provide sufficient
ventilation
during work in the interior of the cavity 8.
Further exit openings 13 can also be provided for the purpose of discharging
wind pressure arriving in an exit opening 13 outward again.
The hatch 16, 16', 16" in both embodiment variants is opened outwards from the
inside of the cavity 8, for which purpose a customary hand lever with handle,
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
12 -
not shown, can be provided. In order to prevent an unintended opening of the
hatch 16, 16', 16", and a fall hazard associated with this for people or
objects
standing on the hatch 16, 16', 16", an additional safety device is provided. A
possible embodiment of such a safety device is shown schematically in Figure
4. The hatch 16, which for clarity is shown without hand levers, comprises a
hatch body 22 in which a plurality of locking bars 23 run in channels. The
lock-
ing bars represented in the unlocked position are connected via articulated
lev-
ers 24 to a step plate 25, which in the example covers the entire top side of
the
hatch body 22. If the step plate 25 is now loaded by people or objects
standing
io thereupon, then the articulated levers 24 are pressed downward and to
the side,
and in doing so push the locking bars 23 into recesses 26 in the outer layer
12
of the rotor blade 5. An opening of the hatch 16 is thereby reliably
prevented,
until the loading of the step plate is eliminated.
is A further safety device, or respectively a variant, in which the hatch
with the
reference number 16' is protected against unintended opening, is shown sche-
matically in Fig. 5. Here, a rotor blade shell 7 is shown in which a hatch 16'
is
introduced. This is mounted at a hinge 43 and can be pivoted into the cavity
of
the rotor blade 5. In order to now allow a reliable closure and a safety
against
20 falling out in the direction of closing 42, the hatch is designed
tapering in the
direction of closing 42 in an edge region 41, 41'. This results in a ramp-
like, or
respectively chamfered embodiment, which is complementary in shape to the
opening edge of the rotor blade shell 7. During closure of the hatch 16', the
contact surfaces of the rotor blade shell 7 come into contact with the hatch
16'
25 and prevent a further movement of the hatch 16' in the direction of
closing 42.
Fig. 6 shows a schematic sectional representation through a rotor blade 5 ac-
cording to the invention. The rotor blade 5 has a rotor blade shell 7 in which
four belts 40 are installed. The belts 40, and specifically every two belts,
are
30 connected in each case to a web 37. The two webs 37 form three cavities,
or
respectively partial cavities 8, 8', 8". Access openings can be provided in
the
webs 37, which are not shown. In this example embodiment, two hatches 16'
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
- 13 -
and 16" are provided on the suction side 35, and one hatch 16 is provided on
the
pressure side, for allowing a respective exit opening. The hatch 16" is
provided
near the nose region of the rotor blade 5 and the hatches 16' and 16 are
provided
further in the region toward the trailing edge 14 of the rotor blade. As an
exam-
ple embodiment, a reinforcing frame 39 is schematically represented around the
hatch 16' at the edge region to the arising exit opening 13 of the rotor blade
shell 7, and is provided for the purpose to again negate a weakening of the
rotor
blade shell 7 resulting due to the hatch, or respectively due to the arising
exit
opening.
The invention is solved by an embodiment of the blade structure with which one
or more manholes, or respectively exit openings are made possible in an acces-
sible region of the rotor blade. Openings can be provided in the pressure side
and the suction side in order to avoid a rotation of the rotor blade in the
case of
an emergency. A closure of the openings, or respectively exit openings, are
preferably with quick-release fasteners, or the like, for example with covers
or
hatches which nestle into the profile contour of the rotor blade, or
respectively
rotor blade shell.
Additionally, slinging points for descent devices and safety mechanisms, such
as personal protective equipment for rescuers and injured persons are provided
in the region of the access openings. The hatch, or respectively flap, is
prefera-
bly opened inwards. The outer laminate of the rotor blade shell can be rein-
forced such that the flap can lie thereupon and can be locked on the inside.
As a
result of this, the escape route in the case of workers in the rotor blade and
pos-
sibly also in the hub, is facilitated, or respectively first made possible.
For im-
proved supply of oxygen. the flaps, or respectively hatches, can also be appro-
priately opened. The hatch, or respectively flap, nestles, preferably exactly,
in
the profile contour of the rotor blade so that no disruption of the
aerodynamics
of the rotor blades is anticipated.
All named characteristics, including those taken from the drawings alone, and
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
14 -
individual characteristics, which are disclosed in combination with other char-
acteristics, are considered individually and in combination as essential to
the
invention. Embodiments according to the invention can be fulfilled through in-
dividual characteristics or a combination of several characteristics.
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
15 -
Reference list
1 wind turbine
2 tower
3 nacelle
4 hub
5 rotor blade
6 rotor blade root
7 rotor blade shell
8 cavity
8, 8" cavity
11 maintenance worker
12, 12 external layer
13 exit opening
14 trailing edge
15 nose
16, 16', 16" hatch
17, 17' slinging means
18 personal protective equipment
19 opening
22 hatch body
23 locking bar
24 articulated lever
step plate
25 30 rotor blade depth
31 axis of rotation
32 bulkhead
34, 34' access opening
suction side
30 36 pressure side
37 web
38 access opening
CA 02837985 2013-12-03
-16-
39 reinforcement frame
40 belt
41 edge region
42 direction of closing
43 hinge
45 rotor blade tip