Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02844001 2015-06-16
INDUCTION DISPLACEMENT UNIT
Field of the Invention
The invention relates to an induction displacement unit,
and more particularly, to an induction displacement unit
comprising an induction plenum communicating with a first
discharge plenum and a second discharge plenum, the first
discharge plenum in communication with a heating coil and the
second discharge plenum in communication with a cooling coil.
Background of the Invention
Displacement ventilation systems are in wide spread use in
the HVAC industry. One particular application for such systems is
in educational buildings. Typically, a number of displacement air
terminal devices will be located along a perimeter wall of a
classroom space and are configured to deliver ventilation air to
the space, see Figure 1.
Displacement ventilation (DV) is an air distribution system
designed to simultaneously improve indoor air quality and reduce
energy use. Cool, rather than cold supply air is provided
directly to occupants through low, mounted diffusers. Heat
generated by the occupants and equipment in the space causes
ventilation air to be naturally drawn up by convection which
ensures fresh air is continually delivered to the breathing zone
(DE the occupants. The warm air continues to rise and contaminants
are carried away towards the ceiling exhaust, resulting in
improved indoor air quality near the occupants. Schools,
restaurants, theaters, atria, other open spaces with high
ceilings, and spaces where air quality is a concern are excellent
applications.
In addition to the displacement function, it is also known
to configure displacement devices to have induction nozzles. By
adding induction, room air from the space can be conditioned,
1
CA 02844001 2015-06-16
filtered, and returned to the space in a mixture with the
ventilation air. This type of unit is sometimes referred to as an
induction-displacement unit. In this type of system, a coil is
provided in the return air path of the induction-displacement
unit to condition the return air, as necessary. In the cooling
mode, the coil will reduce the return air temperature to a few
degrees below the space temperature. In the heating mode, the
coil may be set to raise the temperature of the return air such
that the delivered air has a higher temperature than that of the
air in the room.
In each mode a space temperature set point can be
maintained, however, in heating mode, the induction-displacement
unit can no longer function as a displacement terminal unit due
to the fact that the delivered air starts rising as soon as it
leaves the unit instead of pooling across the floor. To prevent
placing an induction-displacement unit in the heating mode, a
separate heating system can be provided in the space, such as
fin-tube radiation or radiant panels. However, as the induction-
displacement units are placed along at least one wall of the
space, such heating systems cannot be placed in the same
location. This is especially troublesome where the induction-
displacement units are located along an exterior wall of the
space because this is the location where heating is generally
most needed. As such, improvements are desired for induction-
displacement units that can simultaneously provide heating to an
exterior wall of a space and provide displacement ventilation air
to the occupied area of the space.
Representative of the art is U.S. Publication No.
2012/0270494 which discloses an induction-displacement neutral
wall air terminal unit includes a housing defining a supply
airflow path, a connected return airflow path, and a heating
airflow path separated from the supply and return airflow paths
by at least one interior wall. The unit also includes a plurality
2
CA 02844001 2015-06-16
of induction-type nozzles located within the supply airflow path,
that are deliver a ventilation air flow stream into the supply
air flow path. The nozzles induce a return air flow stream
through the return air flow path that mixes with the ventilation
air flow stream to form a supply air flow stream delivered to a
supply air outlet. A heating element is disposed within the
heating airflow oath to heat air within the heating air flow
path. A plurality of fans may be placed within the heating
airflow path to increase the overall heating capacity of the
unit.
What is needed is an induction displacement unit comprising
an induction plenum communicating with a first discharge plenum
and a second discharge plenum, the first discharge plenum in
communication with a heating coil and the second discharge plenum
in communication with a cooling coil. The present invention meets
this need.
Summary of the Invention
The primary aspect of the invention is to provide an
induction displacement unit comprising an induction plenum
communicating with a first discharge plenum and a second
discharge plenum, the first discharge plenum in communication
with a heating coil and the second discharge plenum in
communication with a cooling coil.
Other aspects of the invention will be pointed out or made
obvious by the following description of the invention and the
accompanying drawings.
In accordance with one aspect then, there is provided an
induction displacement unit comprising: an induction plenum
comprising a plurality of first nozzles communicating with a
first discharge plenum and a plurality of second nozzles
communicating with a second discharge plenum; a return air
plenum; a heating coil disposed between the return air plenum and
3
CA 02844001 2015-06-16
the first discharge plenum; a cooling coil disposed between the
return air plenum and the second discharge plenum; the induction
plenum vertically disposed between the heating coil and the
cooling coil, the heating coil disposed in an upper portion of
the unit; the first discharge plenum disposed to induce a
substantially vertical discharge; and the second discharge plenum
disposed to induce a substantially horizontal discharge, the
second discharge plenum comprising a first portion and a second
portion, the first portion receiving a return air flow from the
cooling coil and the second portion separated from the first
portion and further receiving an air flow from the induction
plenum.
In another aspect, there is provided a method of
conditioning a space using an induction displacement unit
comprising: inducing a return air flow into the unit by
discharging pressurized air within the unit; inducing a portion
of the return air flow through a heating coil; inducing a portion
of the return air flow through a cooling coil; discharging from
the unit the air flow from the heating coil; discharging from the
unit the air flow from the cooling coil; and discharging a third
induced air flow from the unit that solely comprises the
pressurized air.
Brief Description of the Drawings
The accompanying drawings, which are incorporated in and
form a part of the specification, illustrate preferred
embodiments of the present invention, and together with a
description, serve to explain the principles of the invention.
Figure 1 is a perspective view of a conditioned space with
two inventive units.
Figure 2 is a perspective cut-away view of an inventive
unit.
Figure 3 is a cross-sectional view of an inventive unit.
4
CA 02844001 2015-06-16
Figure 4 is a cross-sectional view of an alternate
embodiment of the inventive unit.
Figure SA is a perspective cut-away view of the inventive
unit.
Figure 5B is a detail of Figure SA.
Figure 6 is a cross-sectional view showing the cooling air
flow path.
Figure 7 is a cross-sectional view showing the heating air
flow path.
Figure 8 is a conditioned space temperature profile in
heating mode using the inventive unit.
Figure 9 is a conditioned space temperature profile in
cooling mode using the inventive unit.
Detailed Description of the Preferred Embodiment
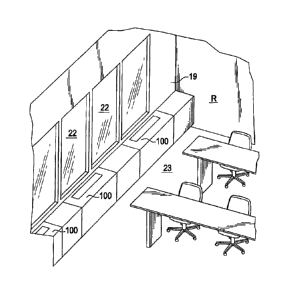
Figure 1 is a perspective view of a conditioned space such
as a classroom with two inventive units. Units 100 are typically
installed along an exterior wall. The wall displacement unit can
be utilized in building air-conditioning systems with air
handlers, chilled water circuits, and hot water boiler systems.
Figure 2 is a perspective cut-away view of an inventive
unit. Each inventive wail displacement unit 100 receives a
constant volume of pressurized prime air flow comprising
conditioned outside air at supply air temperatures, typically in
the range of approximately 50 F to 70 F, through the prime air
inlet opening 10. The prime air is pressurized as it enters the
unit.
Figure 3 is a cross-sectional view of an inventive wall
displacement unit. The unit housing comprises a top 40 to which
grille 21 is mounted. Panels 41, 42, 43, 44 typically comprise
the side of the unit adjacent the wall 19. Side panels 45, 46
complete the unit.
5
CA 02844001 2015-06-16
Wall displacement unit 100 comprises an induction plenum 11
and a coil for air heating 12 and a coil for air cooling 13.
Induction plenum 11 is vertically disposed between the heating
coil 12 and the cooling coil 13 in a stacked arrangement. Heating
coil 12 is vertically disposed in an upper portion of the unit
while the cooling coil 13 is disposed below the elevation of the
hearting coil 12. This vertical configuration takes advantage of
the buoyant (lower density) nature of warmer air when compared to
cooler air. Induction plenum 11 further comprises a plurality of
air injection nozzles 14, 15 in communication with discharge
plenum 20 and discharge plenum 18 respectively.
Air from the induction plenum 11 flows through nozzles 14,
thereby inducing a return flow of room air from the
conditioned room (R) into the return air plenum 16. A portion of
15 the returned room air flows through cooling coil 13 thereby
reconditioning the return room air prior to mixing with the
primary air jets in the lower discharge plenum 18. The return air
is then discharged at low velocity as supply air through the
lower part of the perforated front cover, 17 and 17A, in a
substantially horizontal direction when in cooling mode
operation.
In heating mode operation, the supply air discharged
through the lower part of the front cover 17, see 17A, delivers
prime ventilation air at near room temperature. The main source
for heat load neutralization of a cold outside wall or window 19
is the upper heating coil 12. The returned room air flows through
heating coil 12 to recondition the room air prior to discharge
through grille 21. The reconditioned room air is then mixed with
the primary air jets from nozzles 14 in the upper discharge
plenum 20. Nozzles 14 discharge in a generally upward direction.
Nozzles 15 discharge in a generally downward direction. Discharge
plenum 20 is in an upper portion of the unit so as to facilitate
an upward or substantially vertical air flow.
6
CA 02844001 2015-06-16
Heating coil 12, disposed in an uppermost portion of the
unit, heats the air and when mixed with the air flow from nozzles
14 elevates the temperature of the return air entering the coil
from the return plenum 16, thereby causing forced convection.
Heated air is discharged upward through the grill 21 on top of
the unit. Upon exiting grille 21 the heated air rises along the
perimeter wall 19 and window 22 to create a building heating load
neutralizing warm air curtain.
Each unit can be sized to fit under a sill adjacent to the
perimeter wall 19 mounted to the floor 23 or wall 19. The unit
provides spacing for connecting hardware 24 on both sides of the
unit inside the housing. Although the unit is designed for use in
new buildings, it can also be used for refurbishing existing
high-pressure induction systems.
Figure 4 is a cross-sectional view of an alternate
embodiment of the inventive unit. In this alternate embodiment
induction plenum 11 of unit 200 receives a constant volume of
pressurized prime air flow of conditioned outside air at supply
air temperatures, typically approximately 50 F to 70 F, through
the prime air inlet opening 10. Unit 200 comprises an induction
plenum 11 and separate coils 13 for cooling. The cooling supply
air stream is separated into two distinctive plenum sections, a
main lower discharge plenum 110 and a secondary lower discharge
plenum 111. Plenums 110 and 111 are separated by wall member 112.
Plenum section 110 provides a high induced flow and plenum
section 111 adds required ventilation air to the induced flow.
Both flows exit the unit in a substantially horizontal direction.
Figure 5A is a perspective cut-away view of the inventive
unit. Unit 100 receives a constant volume of pressurized prime
air flow of conditioned ventilation air at prime air
temperatures, typically in the range of approximately 50 F to
70 F, through the prime air inlet opening 10. Unit 100 is
equipped with air damper 25 to control the ventilation air
7
CA 02844001 2015-06-16
volume. In Figure 5B, damper 25 is connected to inlet opening 10.
Damper 25 operates with the building control system (not shown)
and reduces or shuts off the primary air flow to the induction
plenum 11 when demand is low, for example, when the building is
unoccupied. When demand is reduced it is also possible to operate
just one or two units when a partial load is required thereby
shutting off other units in the system.
Unit 100 further comprises water control valves 26, 27.
Valve 26 controls hot water flow from a boiler (not shown) to the
heating coil 12. Valve 27 controls cold water flow from a chiller
(not shown) to the cooling coil 13. A thermostat (not shown) in
the conditioned space controls the room temperature by
controlling operation of the water circuits entering the coils
through the water control valves 26, 27. The heating and cooling
coils may be controlled by either a two-way water valves 26, 27
or alternatively with three-way water valves.
Figure 6 is a cross-sectional view showing the cooling air
flow path. Room return air 28 enters the upper part of the
housing, thereby entering the return air plenum 16. In this
example heating coil 12 is shutoff because it does not operate
during a cooling season. Induction nozzles 14, 15 located on the
induction plenum 11 are pressurized by prime air at approximately
0.25" to 1.0" w.g. and a temperature in the range of
approximately 55 F to 58 F. Discharge of the positive pressure
air through the nozzles 15 induces a flow of return air 28B
through cooling coil 13. Conditioned return air leaving cooling
coil 13 at approximately 68 F mixes with the prime air at
approximately 55 F in the discharge plenum 18. The prime air
entering the induction plenum 11 is conditioned by an outdoor air
handler known in the art (not shown). Mixed air (65 F) 29 is
discharged through the lower discharge plenum 18 into the room in
a substantially horizontal direction 29.
8
CA 02844001 2015-06-16
In this embodiment the inlet air flow is received into the
unit through the front of the unit 17. A portion of the inlet
flow is diverted through the heating coil 12 and a portion
through the cooling coil 13. In particular, since heating coil 12
and cooling coil 13 are immediately adjacent the induction plenum
the primary air discharged from the induction plenum 11 through
nozzles 14, 15 is efficiently used to induce an air flow for both
heating 31 through heating coil 12 and for cooling 29 through
cooling coil 13. This configuration does not require fans to move
the air through the unit.
Figure 7 is a cross-sectional view showing the heating air
flow path. Room air 30 at approximately 70 F to 72 F enters the
upper part of the housing, thereby entering return air plenum 16.
Cooling coil 13 is typically shutoff and does not operate during
a heating season. Induction nozzles 14, 15 located on the
induction plenum 11 are pressurized by prime air at approximately
0.25" to 1,0" w.g. Discharge of the positive pressure prime air
through nozzles 14 induces a flow of return air through heating
coil 12 which is at a temperature of approximately 120 F to
180 F. The conditioned air leaves the heating coil at a
temperature in the range of approximately 90 F to 105 F and
thereafter mixes with the conditioned prime air at approximately
65 F. Heating coil 12 may comprise a nydronic or water heating
element, a steam heating element, or an electric heating element.
The mixed air at a temperature of approximately 85 F to 90 F is
discharged through the upper discharge plenum 20 through grill 21
into the conditioned room in a substantially vertical direction
31.
The mass flow of the discharged heating supply air can be
adjusted by the quantity of nozzles 14 dedicated to heating. The
air curtain created by discharge 31 in front of a window or cold
wall is configured to roll the air within the adjacent area of
the perimeter wall, and not to disturb the stratification created
9
CA 02844001 2015-06-16
by the displacement ventilation. The mass flow, and therefore the
quantity of nozzles 14 dedicated to heating, can be customized to
accommodate 120 F, 140 F and 180 F water entering from a boiler
(not shown).
Cooling coil 13 is not operating during the heating season,
but prime air pressurizing at approximately 0.25" to 1.0" w.g.
induction nozzles 15 causes the return air 3013 to be drawn
through the cooling coil 13. Return air leaving the cooling coil,
at approximately 72 F, will mix with the conditioned prime air at
approximately 65 F. The mixed air 32 at approximately 68 F is
discharged through the lower discharge plenum 18 in a
substantially horizontal direction.
The unit provides at least 8,000 btuh of heating through
the heating airflow path when the heating coil 12 is served by
hot water having a temperature of approximately 180 F. The unit
can be configured to operate in a heating mode wherein the
heating coil 12 provides heated air through the heating airflow
path; and a ventilation mode wherein the unit provides a supply
airflow stream having a temperature of about 53 F. The heating
mode can be simultaneously activated with a ventilation mode.
The number and diameter of nozzles 14 can be selected based
upon the temperature of the water entering the heating coil 12.
The numeric values included in this description are not intended
to limit the scope of the invention and are provided as examples
only.
Assuming a total of 42 nozzles (14), the diameters are:
Entering Water Nozzle diameter
Temperature [ F] [inches]
120 0.140
. 140 0.188
180 0.250
CA 02844001 2015-06-16
Assuming a nozzle diameter of 0.188 inches the nozzle
quantities are:
Entering Water F-Nozzle quantity
Temperature [ F]
120 32
140 42
180 56
In operation, the inventive unit creates a simultaneous
mixing heating curtain neutralizing cold perimeter loads while
utilizing displacement ventilation for the inner occupied space.
The inventive induction displacement wall unit also meets the
noise requirements of ANSI Standard S12.60, which is advantageous
in applications where reduced noise is desirable, such as in
school classrooms.
In operation the unit provides a method of conditioning a
space using an induction displacement unit. The unit induces a
return air flow into the unit by discharging pressurized air
within the unit. The return air flow stream comprises a single
stream of air entering the unit through the front of the unit.
The unit induces a portion of the return air flow stream 28 to
flow through a heating coil and induces a portion of the return
air flow stream 288 to flow through a cooling coil. The unit
discharges the ai.r flow from the heating coil in a substantially
vertical direction. The unit discharges the air flow from the
cooling coil in a substantially horizontal direction.
Figure 8 is a conditioned space temperature profile in
heating mode using the inventive unit. The unit provides uniform
distribution of conditioned air to the space. The heated air is
evenly distributed through the space while cool air is drawn to
the unit along the floor.
Figure 9 is a conditioned space temperature profile in
cooling mode using the inventive unit. The unit provides uniform
11
CA 02844001 2015-06-16
distribution of conditioned air to the space. The chilled air is
evenly distributed through the space while hot air is drawn to
the unit along the ceiling.
Although a form of the invention has been described herein,
it will be obvious to those skilled in the art that variations
may be made in the construction and relation of parts without
departing from the scope of the invention described herein and as
defined in the attached claims.
12