Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02844719 2014-03-04
- 1 -
High Power LED Bulb
Field of the Invention
[0001] The invention relates generally to the field of LED lighting
technology, in particular
to a high power LED bulb.
Description of the Related Art
[0002] In recent years, LED lighting technology has developed rapidly, and
various high
power LED bulbs have been available in the market successively and widely
applied. An LED
bulb has comparatively similar appearance and structure to general lighting
bulbs such as
incandescent lamps and energy-saving lamps, and is composed of a holder, a
lamp housing and
a lamp shade. The holder is generally of screw structure and can be directly
connected to
alternating current. The holder is internally provided with a power module for
converting AC
voltage into LED operating voltage. The lamp housing is internally provided
with a substrate
and radiators, and LEDs of different quantities are installed on the substrate
based on different
powers and LED power capacities. In order to protect LED chips and avoid
stimulation from
strong light, the LEDs are sealed in the lamp shade, and each LED is connected
with the power
module through a circuit on the substrate. However, as high power LEDs have
large calorific
capacity in operation, LED chips will suffer from irreversible damage if heat
is untimely
exchanged with the atmosphere, accelerating light failure of LEDs. Existing
high power LED
bulbs have inappropriate heat dissipation in structural design, resulting in
abnormal light failure
of LED and shortened service life of LED drive power. In practical
application, these LED
bulbs have low heat dissipation efficiency, resulting in heat accumulation and
accelerating light
failure of LEDs. Meanwhile, heated air rises, and temperature at holder part
rises, aggravating
heat accumulation of the power modules encapsulated in the holders, thus
greatly shortening
the service life of power module components, and becoming bottleneck of the
service life of
high power LED bulbs.
Summary of the Invention
[0003] For the structural disadvantage of poor heat dissipation of high power
LED bulbs in
the prior art, a technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide
a high power LED
bulb to improve heat dissipation effect by improving heat dissipation channels
of an LED bulb.
CA 02844719 2014-03-04
- 2 -
[0004] A technical solution to solving the technical problem is a high power
LED bulb
comprising a holder, a lamp housing and a lamp shade, the holder is internally
provided with a
power module, the lamp housing is internally provided with a substrate and
radiators, and
LEDs are installed on the substrate, sealed in the lamp shade and connected
with the power
module, and the high power LED bulb is characterized in that the substrate is
provided with a
through hole, the holder is of tubular shape and has a sealed end and an open
end extending
into the lamp housing and communicated with the outside through the through
hole, a vent hole
is arranged on the holder exposing the lamp housing, and the lamp housing is
provided with
heat dissipation holes communicated with the outside through the through hole.
[0005] The technical solution is as follows: heat generated by the power
module in the
tubular holder can be dissipated by convection through the open end and the
vent hole on the
holder, and heat generated by the radiators installed on the substrate can be
dissipated by
convection through the through hole on the substrate and the heat dissipation
holes on the lamp
housing. The two heat dissipation channels are independent, thus greatly
improving heat
dissipation effect on the premise of ensuring seal integrity of LEDs.
[0006] Preferably, the open end of the holder is of conical shape and passes
through the
through hole.
[0007] The open end of the holder is of conical shape and passes through the
through hole,
and can isolate the two heat dissipation channels in a better manner.
Increased length of the
tubular holder is favorable for improving heat dissipation of the power module
in the holder.
The conical structure of the open end of the holder can increase air
circulation and improve
heat dissipation effect of radiators in the lamp housing.
[0008] Further, the LEDs are uniformly distributed around the through hole.
[0009] Uniform distribution of the LEDs can improve luminance uniformity of
the bulb, and
improve lighting effects.
[0010] The recommended installation positions of the LEDs are corresponding to
installation
positions of the radiators.
CA 02844719 2014-03-04
- 3 -
[0011] In the solution, the radiators and the LEDs are respectively installed
at both sides of
the substrate, and the installation positions of the radiators are
corresponding to the installation
positions of the and the LEDs, which is favorable for improving heat
dissipation effect of the
LEDs and reducing light failure.
[0012] Specifically, the heat dissipation holes are arranged on the side
wall and/or at the top
of the lamp housing.
[0013] The heat dissipation holes are arranged on the side wall or at the top
of the lamp
housing, and can be selected based on detailed design. Dustproof effect is
good when the heat
dissipation holes are arranged on the side wall of the lamp housing, and air
mobility is good
when the heat dissipation holes are arranged at the top of the lamp housing,
either of them has
its own advantage.
[0014] Specifically, the substrate is an aluminum substrate.
[0015] Aluminum substrate is a widely used LED lighting substrate, and
characterized by
low cost and high thermal conductivity.
[0016] Specifically, the radiators are graphite radiators.
[0017] Graphite radiators are characterized by convenient processing and good
formability,
and very suitable for heat dissipation of LED lighting devices.
[0018] The high power LED bulb has the following benefits: the power module
and heat
dissipation channels of the LED radiators are reasonably designed based on
structural features
of the bulb, thus greatly improving heat dissipation efficiency and extending
the service life of
the bulb. The high power LED bulb is also characterized by compact structure
and attractive
appearance.
Brief Description of the Drawings
[0019] Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of example 1;
[0020] Figure 2 is a top view of Figure 1;
[0021] Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of distribution of LEDs on a substrate
of example 1;
CA 02844719 2014-03-04
- 4 -
[0022] Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of distribution of radiators on the
substrate of
example 1;
[0023] Figure 5 is a schematic diagram of example 2;
[0024] Figure 6 is a top view of Figure 5;
[0025] Figure 7 is a schematic diagram of distribution of LEDs on the
substrate of example
2; and
[0026] Figure 8 is a schematic diagram of distribution of radiators on the
substrate of
example 2.
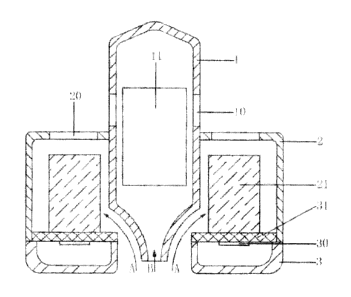
[0027] In the figures, 1 represents a holder, 10 represents a vent hole, 11
represents a power
module, 2 represents a lamp housing, 20 represents heat dissipation holes, 21
represents
radiators, 3 represents a lamp shade; 30 represents LEDs, 31 represents a
substrate, 32
represents a through hole, and arrows A and B represent air flow directions.
Description of the Preferred Embodiments
[0028] The technical solution will be described in detail in combination with
drawings and
examples.
[0029] For the high power LED bulb, different heat dissipation channels are
designed for the
power module and LED radiators so as to completely avoid heat accumulation and
superposition, and greatly improve heat dissipation conditions of the bulb.
Heat generated by
the power module in the tubular holder can be dissipated by convection through
the open end
and the vent hole on the holder, and heat generated by the radiators installed
on the substrate
can be dissipated by convection through the through hole on the substrate and
the heat
dissipation holes on the lamp housing. The two heat dissipation channels are
independent, thus
greatly improving heat dissipation effect on the premise of ensuring seal
integrity of LEDs.
[0030] Example 1
[0031] Referring to Figures 1 to 4, the high power LED bulb in the example
comprises a
holder 1, a lamp housing 2 and a lamp shade 3. The holder 1 is internally
provided with a
power module 11, the lamp housing 2 is internally provided with an aluminum
substrate 31 and
graphite radiators 21, and six LEDs 30 are installed on the back of the
aluminum substrate 31,
CA 02844719 2014-03-04
- 5 -
uniformly distributed around a through hole 32 on the aluminum substrate 31,
and sealed in the
lamp shade 3. Radiators 21 of the same number are installed at positions
corresponding to the
LEDs 30 on the front of the aluminum substrate 31 for improving heat
dissipation effect. If
power of each LED is low and installation density is low, the quantity of
radiators 21 can be
properly reduced to reduce the bulb weight and cost. The lamp shade 3 is
generally made of a
transparent material such as glass, the lamp housing 2 can be made of plastic
or metal, and the
holder 1 has metal thread for connecting to alternating current. The aluminum
substrate 31 is
provided with circuits, and the LEDs 30 are connected with the power module 11
through
leads. It can be seen from Figure 1 that the holder 1 in the example is of
tubular shape and has a
sealed end and an open end, the open end is of conical shape, extends into the
lamp housing 2
and is communicated with the outside through the through hole 32 on the
aluminum substrate
31. A vent hole 10 is arranged on the holder 1 exposing the lamp housing 2 and
communicated
with the open end of the holder 1, and air enters the holder 1 in the
direction of arrow B and
carries away heat generated by the power module 11 through the through hole
10. Heat
dissipation holes 20 arranged on the lamp housing 2 are communicated with the
outside
through the through hole 32, and air enters the lamp housing 2 in the
direction of arrow A,
exchanges heat with the radiators 21 and carries away heat through the heat
dissipation holes
20. The conical structure of the open end of the holder 1 can increase air
flow in the direction
of arrow A and improve heat dissipation effect of the radiators 21 in the lamp
housing 2. It can
be seen from Figures 1 and 2 that the heat dissipation holes 20 in the example
are arranged at
the top of the lamp housing 2, and uniformly distributed around the holder 1.
Such heat
dissipation holes can be made into heat dissipation holes of shutter type to
improve dustproof
effect. The LED bulb in the example has a cylindrical shape and a symmetrical
structure, thus
the LED bulb is beautiful and practical, and easy in processing and
manufacture.
[0032] Example 2
[0033] The LED bulb in the example has a structure as showed in Figures 5 to
8, the holder
1 is of cylindrical shape, the lamp housing 2 is of right quadrangular prism
shape, and the
corresponding aluminum substrate 31 is of square shape, as shown in Figures 7
and 8. As
shown in Figure 5, the heat dissipation holes 20 in the example are arranged
on the side wall of
CA 02844719 2014-03-04
- 6 -
the lamp housing 2 for dust prevention and heat dissipation. Refer to
description of example 1
for other structures in the example.
[0034] Various embodiments of the invention have now been described in detail.
Those
skilled in the art will appreciate that numerous modifications, adaptations
and variations may
be made to the embodiments without departing from the scope of the invention,
which is
defined by the appended claims. The scope of the claims should be given the
broadest
interpretation consistent with the description as a whole and not to be
limited to these
embodiments set forth in the examples or detailed description thereof.