Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02857361 2014-05-29
WO 2013/078516
PCT/AU2012/001471
- 1 -
SUPPORT FOR BARRIER FENCE
FIELD OF INVENTION
The present invention relates to a support for fencing. The present invention
has particular but not exclusive application for supporting temporary plastic
barrier
fencing.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Plastic barrier fencing is generally used to temporarily cordon off areas on
constructions sites and on the roads, railways and footpaths to restrict
public access
when repair work is being carried out. The fencing material is typically made
from
polypropylene, and is usually highly coloured for good visibility. Plastic
barrier
fencing may be in the form of a woven mesh manufactured from recycled plastic
or
extruded flat plastic lattice style netting.
The plastic barrier fencing is usually supported by a number of spaced steel
posts, such as star pickets. These posts are usually inserted in the ground,
and the
fencing is attached to the erected posts using zip or cable ties, pieces of
wire or
other non-reusable securing methods.
A disadvantage of this method is that it is time consuming since at least two
or
three ties will be required to secure the plastic mesh to each post. The ties
over time
wear and break allowing the barrier fencing to move away from the post The
ties
break as a result of high winds blowing the fencing and consequently applying
breaking forces to the ties. In short, because the plastic fencing is only
connected to
the posts at a few points, the fencing can pull away from the posts or tear
fairly easily
in windy conditions.
The ties can also crease and tear the plastic fencing material. Furthermore,
it
is difficult and time consuming to remove the plastic mesh from the posts
without
damage. The method is also both uneconomical and ecologically unsound since
the
ties cannot be reused. This can lead to unnecessary material waste and
waterways
)0 pollution. When disassembling the barrier fences, the attaching ties are
usually cut
from the posts and the sharp edged plastic or wire parts are discarded on the
ground. The discarded pieces of sharp edged plastic and wire can potentially
pose a
hazard to workers, the public and to wildlife.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02857361 2014-05-29
WO 2013/078516
PCT/AU2012/001471
- 2 -
OBJECT OF THE INVENTION
It is an object of the present invention to provide temporary fence supports
that overcome at least in part one or more of the abovementioned problems.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention broadly resides in mounting means for supporting
barrier fencing having a mesh structure; said mounting means includes
an elongate mounting member;
retaining means which includes a plurality of integrally formed, spaced apart
retaining members; wherein in use the retaining members are fixed in position
along
the elongate axis of the mounting member and the retaining members are
arranged
=
to enable the mesh structure of the fencing to align and cooperate with the
retaining
members so that the fencing extends along the length of the mounting member.
Preferably there are at least two retaining members spaced apart along the
elongate mounting member.
Preferably the mesh fencing is secured to the mounting member in a
substantially vertical orientation.
Preferably the retaining means is adapted to secure the fencing flush against
the mounting member.
The mounting member is preferably a post such as a star picket or a sleeve
for positioning over a post or upright.
In one preferred form the retaining means includes a plurality of integrally
formed spaced apart retaining members and a securing rod. Preferably the
retaining
members include guides. In one embodiment the guides project through the holes
in the mesh structure of the barrier fencing and allow the positioning of the
securing
rod with the guides to secure the mesh with the guides.
In another embodiment, the guides include a plurality of loops or short tubes
wherein the securing rod can pass there through. In another embodiment the
guides
include a plurality of channeled protrusions where a securing rod can be
positioned
within the channels.
In a preferred embodiment the guides include a vertical elongate groove and
a vertical short tube adjacent the lower end of the elongate groove.
In an alternative embodiment, the retaining means is a plurality of teeth
arranged vertically in a spaced relationship along the elongate axis of the
support.
CA 02857361 2014-05-29
WO 2013/078516
PCT/AU2012/001471
- 3 -
The teeth are preferably adapted to grip lattice or woven fencing. Preferably
the
teeth have a concave profile to cooperate with the securing rod.
In another preferred form, the retaining means is a plurality of integrally
formed spaced apart retaining members wherein the retaining members are
preferably barbs or hooks which cooperate with the mesh of the barrier fencing
to
secure the fencing in position. In one embodiment there is a plurality of a
pair of
hooks, where one hook of the pair is inverted with respect to the other hook
of the .
pair.
Preferably the retaining means secures the top and bottom sections of the
fencing to the mounting member. Preferably the retaining means are located in
spaced relationship across substantially the full width of the fencing.
In one embodiment the mounting member is integrally formed with the
mounting means.
In an alternative embodiment the mounting member is operationally
attachable to the mounting means. When the mounting member is operationally
attachable to the mounting means, the mounting member is preferably in the
form of
a sleeve which is of suitable dimensions and is adapted to fit over an erected
post,
such as a star picket or other type of temporary post.
Preferably when in position on the post or picket, the lower end of the sleeve
rests on the ground. Preferably the mounting means is slightly taller than the
vertical
height of the barrier fencing.
Preferably the upper and lower guides on the sleeve are angled to enable
them to hold the barrier fencing in position before it is secured to the
mounting
member.
When the retaining means includes a securing rod, preferably an end of the
securing rod is adapted so the upper end of the rod may be secured in place by
inserting it into the top of the mounting means for safety. Preferably the end
of the
securing rod is adapted to cooperate with the upper end of a star picket or
other type
of post to prevent the mounting member from rotating about the post.
Preferably the
upper end of the securing rod is bent to form a hook or U-shape. In another
form the
upper end of the securing rod is adapted to clamp the upper edge of the
fencing to
the upper end of the mounting member.
In another preferred embodiment the securing rod includes one or more
fasteners along its length. The one or more fasteners cooperate with the
mounting
'
I
=
CA 02857361 2014-05-29
WO 2013/078516
PCT/AU2012/001471
- 4 -
means to secure the barrier fencing to the mounting means. In a preferred
form,
each of the one or more fasteners is a rigid tube section engagable within the
vertical
elongate groove. The rigid tube section is adapted to clamp the barrier
fencing to
the mounting means when the rigid tube section engages the vertical elongate
groove.
In a further embodiment, the retaining means include a plurality of paired
vertically orientated opposing hooks located in spaced relationship along the
height
of the mounting member. Preferably each pair of hooks includes an upward
pointing
supporting hook and a downward pointing locking hook, the two hooks being
located
in horizontal alignment on the mounting member. Preferably each upwardly
pointing
supporting hook is longer than the corresponding downwardly pointing locking
hook.
This embodiment may be used with lattice barrier fencing. preferably the
paired hooks are arranged along the elongate axis of the mounting means with
spacing to correspond with the aperture=spacing in the lattice barrier
fencing.
When the mounting member is a sleeve intended for use with a star picket or
other form of steel post, preferably the mounting member is made from a softer
material than steel to reduce the likelihood of injury to members of the
public if they
come in contact with the mounting means.
In one embodiment the mounting means is adapted to be driven into the
ground. In this embodiment preferably the mounting means is constructed of
steel or
a similar suitably strong material and may be driven into the ground. In one
aspect
the mounting means may be in the form of a U-shaped steel rod. One leg of the
U
shape is longer and is adapted to be driven into the ground. The second leg is
adapted to cooperate with barrier fencing. Preferably the second leg includes
a
plurality of spaced teeth, books or barbs to cooperate with and secure barrier
fencing
to the mounting means. The mounting means may include a pointed lower end to
allow it to be driven into the ground. Side plates may be attached towards the
lower
end of the mounting means to enable it to be pushed into the ground by the
installers
own body weight.
In a further embodiment, the mounting means may include a free-standing
support. A free-standing support may be useful in situations where it is
difficult or
undesirable to create holes in a surface to erect a steel post or star picket.
Free-
standing mounting means may be constructed by affixing a plate, platform or
conical
support to the lower end of mounting means as defined above.
CA 02857361 2014-05-29
WO 2013/078516
PCT/AU2012/001471
- 5 -
Preferably the mounting means of the present invention are manufactured or
painted in a high visibility colour or fluorescent material for safety.
Preferably the
mounting means are fitted with reflective tape or other reflective devices to
improve
night time visibility.
Preferably the mounting means are fitted with protective caps. Where a
securing rod is used, preferably the protective cap is adapted to fit over the
end of
the securing rod. Alternatively a protective cap may be adapted to cooperate
with
the top end of the securing rod to secure it in position. Preferably a
protective cap is
adapted to friction fit with the top of the mounting means. Preferably a
protective cap
may be adapted to friction fit with the inside of the mounting means.
Alternatively a
protective cap may be adapted to friction fit over the top end of the mounting
means.
Preferably, there is a plurality of mounting means spaced apart from each
other enabling a length of barrier fencing to be fixed in position.
In another aspect the invention broadly resides in a system for fixing barrier
fencing wherein a plurality of mounting means as described above are spaced
apart
and serve to position and secure the barrier fencing.
The barrier fencing can be made of a plastic mesh, plastic lattice, hessian or
wire mesh such as chicken wire.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
In order that the present invention can be more readily understood and put
into practical effect, reference will now be made to the accompanying drawings
wherein:
Figure 1 shows diagrammatic views of a first preferred embodiment of the
fence support including guides mounted on a star picket and secured in place
by a
securing rod;
Figure 2 is a diagrammatic representation showing construction of temporary
fencing using the fence support of Figure 1 and plastic lattice barrier
fencing;
Figure 3 is a diagrammatic view of a second preferred embodiment of the
fence support where the retaining means include teeth and guides;
Figures 4 to 7 illustrate the securing of plastic mesh fencing to the fence
= support of the second preferred embodiment of Figure 3;
Figure 8 is a diagrammatic view of a third preferred embodiment of the fence
support including hook attachments and shown mounted on a star picket;
CA 02857361 2014-05-29
WO 2013/078516
PCT/AU2012/001471
- 6 -
Figures 9 toll illustrate the securing of plastic lattice fencing to the fence
support of the third preferred embodiment of Figure 8;
Figure 12 is a diagrammatic view of a fourth preferred embodiment of the
fence support including teeth and a lower guide mounted on a star picket;
Figures 13 to 15 illustrate the securing of plastic mesh fencing to the fence
support of the fourth preferred embodiment of Figure 12;
Figure 16 is a diagrammatic view of a fifth preferred embodiment of the fence
support including an elongate channel and a lower guide mounted on a star
picket;
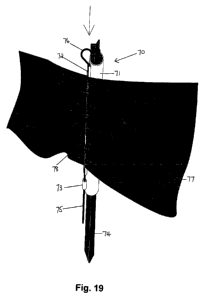
Figures 17 to 19 illustrate the securing of plastic mesh fencing to the fence
Figures 20 and 21 are cross sectional views of the fence support of the fifth
embodiment illustrating the mechanism of securing the mesh fencing to the
fence
support.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
With reference to Figure 1 there is shown a fence support 10 for use with
plastic lattice barrier fencing according to a first preferred embodiment. The
fence
support 10 includes a tubular sleeve 11 and is of suitable internal dimensions
to
allow it to be mounted on a star picket 14 or other suitable post. The tubular
sleeve
11 has a plurality of vertical cylindrical guides 12 attached in a spaced
arrangement
along the outside surface of the sleeve 11. The guides 12 are adapted to
accommodate a vertical securing rod 15. The securing rod 15 is bent at one end
to
form a U-shaped hook 17 which, when in position in the fence support, can
cooperate with the upper end of the star picket 14 to prevent the sleeve 11
from
rotating on the star picket. The main leg 16 of the securing rod 15 is of
slightly
smaller diameter than the internal diameter 13 of the guide 12.
With reference to Figure 2 there is illustrated fence construction using
plastic
lattice barrier fencing 18 and fence supports 10 mounted on a star picket 14.
The
top edge of the lattice fencing is placed below the uppermost vertical guide
12 with
the second guide 12 placed in the uppermost aperture 19 of the fencing 18. The
position of each vertical guide 12 corresponds with the spacing of the
apertures 19 of
the lattice fencing 18 such that each guide 12 fits through an aperture 19 to
support
the fencing 18. The fencing 18 is secured in place on the fence support 10 by
CA 02857361 2014-05-29
WO 2013/078516
PCT/AU2012/001471
- 7 -
threading the main leg 16 of the securing rod 15 vertically downwards through
the
guides 12 to clamp the lattice fencing 18 against the support 10.
The upper and lower surfaces of the guides 12 may be angled to allow them
to hold the plastic fencing 18 before it is secured to the fence support 10.
For safety, the upper end of the securing rod 15 is bent into a U-shape to
enable the upper end 17 to be placed in the upper open end 20 of the fence
support
10. The securing rod end 17 may also cooperate with the upper end of the star
picket 21 to prevent the fence support 10 rotating about the star picket 14 on
which it
is mounted.
A temporary fence is constructed by stretching the length of plastic fencing
18
to other fence supports 10 and repeating the clamping process to secure the
plastic
fencing to each sequential support.
When it is necessary to dismantle the temporary fence, the lattice fencing 18
is simply released from the fence support 10 by removing the securing rod 15
from
the guides 12.
The shape of the sleeve 11 is of circular cross section, but other shapes such
as square, rectangular or triangular may be used.
The guides 12 may be cast or extruded with the sleeve 11.
With reference to Figure 3 there is shown a fence support for plastic barrier
fencing in accordance with a second preferred embodiment of the present
invention.
The fence support 30 includes a tubular sleeve 31 adapted for use with plastic
lattice
barrier fencing or plastic mesh fencing. The fence support 30 is of suitable
internal
dimensions to allow it to be mounted on a star picket 35. The tubular sleeve
31 has
a line of teeth 32 attached in a vertically spaced arrangement along the
outside
surface of the sleeve 31. The teeth 32 are shaped to enable them to grip the
plastic
barrier fencing. Additionally the teeth 32 are concave in profile in a
vertical direction
to allow them to accommodate a securing rod. There are guides 33 and 34 at the
upper and lower ends of the line of teeth 32 to accommodate a securing rod.
The
guides 33 and 34 and teeth 32 may be manufactured by casting or extruding a
line of
guides along the length of the sleeve 31. The line of guides is then modified
by
cutting a plurality of teeth 32 from all but the two end guides 33 and 34.
Guides 33
and 34 remain at the upper and lower ends of the sleeve 3.1.
With reference to Figures 4 and 5 there is shown the fence support 30 of
Figure 3 mounted on a star picket 35. The cooperation between the fence
support
CA 02857361 2014-05-29
WO 2013/078516
PCT/AU2012/001471
-8-
30 and a securing rod 37 is illustrated. The securing rod 37 is of slightly
smaller
diameter than the guides 33 and 34. In use the securing rod 37 is threaded
vertically
through the upper guide 34 and the lower guide 33, allowing it to lie along
the line of
concave vertically orientated depressions in the teeth 32.
The securing rod 37 is bent at one end to form a U-shaped hook 39 which can
cooperate with the upper end of the star picket 35 to prevent the sleeve 31
from
rotating. The main leg 38 of the securing rod 37 is of slightly smaller
diameter than
the internal diameter of the guides 33 and 34.
With reference to Figures 6 and 7 there is illustrated the construction of a
temporary barrier using the fence support 30 of Figures 3, 4 and 5 and plastic
mesh
barrier fencing 40. The plastic mesh fencing 40 is secured on the fence
support 30
mounted on a star picket 35. The plastic mesh fencing 40 is secured in place
on the
fence support 30 by threading the main leg 38 of the securing rod 37
vertically
downwards through the upper guide 34. The plastic fencing 40 is inserted in
the
vertical space between the upper guide 34 and lower guide 33, and the rod leg
38 is
then inserted through lower guide 33 to clamp the plastic fencing 40 against
the
teeth 32 to secure the fencing 40 in place.
A temporary fence is constructed by stretching the length of plastic fencing
to
other supports and repeating the clamping process to secure the plastic
fencing to
each sequential support. For safety the upper end of the securing rod 37 is
bent to
enable the upper end 39 to be placed in the upper open end 36 of the fence
support
30. The securing rod end 39 may also cooperate with the upper end of the star
picket 35 to prevent the fence support 30 rotating about the star picket 35 on
which it
is mounted.
When it is necessary to dismantle the temporary fence, the plastic mesh
fencing 40 is simply released from the fence support 30 by removing the
securing
rod 37 vertically upwards from guides 33 and 34, and easing the mesh 40 free
from
the teeth 32.
With reference to Figure 8 there is shown a fence support 50 according to a
third preferred embodiment. The fence support 50 includes a tubular sleeve 51
and
is adapted for use with plastic lattice barrier fencing. The sleeve 51 is
slightly taller
than the height of the plastic fencing, and of suitable internal dimensions to
allow it to
be mounted on a star picket 54. The tubular sleeve 51 has a plurality of
paired
hooks 52 and 53 attached in a vertically spaced arrangement along the outside
CA 02857361 2014-05-29
WO 2013/078516
PCT/AU2012/001471
-9..
surface of the sleeve 51 for cooperating with the lattice fencing. The pairs
of hooks
52 and 53 are spaced to correspond with the apertures of plastic lattice
fencing. The
paired hooks 52 and 53 are located side by side along the length of the
sleeve. The
pairs of hooks are vertically orientated and directionally opposed. Hook 52
points
upwards and is slightly longer than downwardly pointing hook 53.
Figures 9 to 11 illustrate the construction of a temporary barrier using the
fence support 50 of Figure 8 and plastic lattice barrier fencing 55. The
lattice fencing
55 is secured on the fence support 50 mounted on a star picket 54. The lattice
fencing 55 is secured by attaching the upper edge 56 of the lattice fencing 55
over
the uppermost upwardly facing hook 52a to support the fencing 55. The
horizontal
= fencing edge 56 is then looped under the corresponding downwardly facing
shorter
hook 53a to lock the fencing 55 into position to prevent it from being removed
from
the hook 52a if buffeted by the wind. The paired hooks 52 and 53 are spaced at
intervals along the length of the sleeve 51 to correspond with the spacing of
the
apertures 57 of the plastic lattice fencing 55. The attachment operation is
repeated
with each pair of hooks 52, 53 along the fence support 50 until the fencing is
secured
all the way along. The smaller the horizontal distance of the hooks from the
sleeve
51, the more tightly the fencing is held against the fence support 50.
Figures 12 to 15 illustrate a yet further embodiment of a fence support in
accordance with the present invention. The fence support 60 is suitable for
use with
plastic mesh barrier fencing, and is similar to the fence support 30 of
Figures 3 to 7,
except that the fence support 60 does not have a vertical upper guide. The
fence
support 60 includes a tubular sleeve 61 adapted for use with plastic mesh
barrier
fencing. The fence support 60 is of suitable internal dimensions to allow it
to be
mounted on a star picket 64. The sleeve 61 has a line of teeth 62 attached in
a
vertically spaced arrangement along the outside surface of the sleeve 61. The
teeth
62 are adapted to enable them to grasp the plastic barrier fencing.
Additionally the
teeth 62 are concave in a vertical direction to allow them to accommodate a
vertical
securing rod 65. There is a vertical cylindrical guide 63 at the lower end of
the line of
teeth 62 to accommodate a securing rod 65. The fence support 60 is mounted on
an
erected star picket 64. The securing rod 65 is of slightly smaller diameter
than the
guide 63. In use the securing rod 65 is threaded through guide 63. The plastic
mesh fencing 67 is placed above the guide 63 and against the sleeve 61 to
allow it to
be gripped by the teeth 62. The securing rod 65 is then clamped against the
sleeve
CA 02857361 2014-05-29
WO 2013/078516
PCT/AU2012/001471
- 10 -
61, allowing it to lie along the line of concave depressions in the teeth 62
to secure
the fencing 67 to the fence support 60.
The securing rod 65 is bent at one end to form a hook 66 which is adapted to
clip onto the top of the sleeve 61 to allow the top end of the rod 65 to
maintain close
contact with the fencing 67 and the sleeve 61 to clamp the upper edge of the
fencing
67 to the top of the support 61 and thus provide a secure grip.
Figures 16 to 21 illustrate further embodiment of a fence support in
accordance with the present invention. The fence support 70 is suitable for
use with
a variety of types of barrier fencing materials including plastic mesh,
plastic lattice
and hessian.
The fence support 70, as shown in Figure 16, includes a tubular sleeve 71 of
suitable internal dimensions for mounting on a star picket 74. When mounted on
an
erected star picket 74, the lower end of the sleeve 71 rests on the ground.
There is
an elongate vertical groove 72 on the outside surface of the sleeve 71. The
groove
72 has a "C" shaped cross section. There is a vertical cylindrical guide 73 at
the
lower end of the groove 72 to accommodate a securing rod 75.
Figures 17 to 19 show the fence support 70 mounted on an erected star
picket 74. The securing rod 75 is of slightly smaller diameter than the
internal
dimensions of the guide 73. The securing rod 75 may be used with or without a
locking tube 78. Higher clamping forces are obtained when a locking tube 78 is
used
and this is beneficial in high winds or when the barrier fencing is erected
and is to be
used and not disturbed for a long period. The securing rod 75 has a hook 76 at
one
end and has a cylindrical locking tube 78 that surrounds the securing rod 75.
The
locking tube 78 has a similar radius to the internal radius of the groove 72.
The hook
76 forms a clamping section with the free end returning back on the rod 75.
The
locking tube 78 can be fixed or moveable along the length of the securing rod
75 or
removed from the securing rod 75.
In use, the securing rod 75 is engaged with the guide 73 and the barrier
fencing 77 is held against the sleeve 71. The hook 76 is clamped over the top
edge
of the sleeve 71 and the locking tube 78 is pressed firmly into the groove 72
to
engage with the groove 72 and hold the fencing 77 tightly against the sleeve
72.
The locking tube 78 is made of a hard non-deformable material, such as a
hard plastic, so that it snaps into the vertical groove 72 on the sleeve 71.
CA 02857361 2014-05-29
WO 2013/078516
PCT/AU2012/001471
- 11 -
Fence support 60 or fence support 70 can be used to support electric fence
tape providing that the securing rod 65 (or 75) does not contact the ground to
cause
the live electric fence to earth.
For increased safety, a fence support in accordance with the present
invention may be manufactured in, or painted with, a high visibility colour.
It may
also have reflective tape or other reflective devices attached to improve
night time
visibility. A fence support can be manufactured from fluorescent plastic
material to
improve visibility in poor light conditions such as at night. The fence
supports can be
manufactured from UV stabilized material to avoid degradation in sunlight.
A fence support may be made from a softer material to protect the members
of the public against injury they may sustain should they come into contact
with a
star picket steel post. Protective caps may be used to fit the fence supports.
These
protective caps may be adapted to fit over the top of the fence supports, and
may
include a hole to accept securing rods where they are used. Alternatively the
protective caps may be adapted to fit over both a fence support and a securing
rod.
The protective caps may be friction fitted with the inner or outer surface of
the fence
support. Where the protective caps fits over the fence support, guides may be
provided in the cap to allow it to fit around any of the retaining means.
The fence support may include a suitable pointed shape to allow it to be
driven into the earth in a similar manner to that of a star picket or other
regular steel
post. It may be hammered into the earth or side plates may be attached close
to the
base so that fence support can be pushed into the earth using the installer's
own
body weight. A flat fixed or removable plate may be attached to the bottom of
the
fence support to enable it to remain vertical without additional support. The
fence
support may have a fixed or removable weighted base.
The fence support of the present invention may be used to support a variety
of mesh fencing materials including plastic mesh fencing (woven material,
lattice
netting), hessian and chicken wire.
ADVANTAGES
An advantage of the preferred embodiment of the barrier fencing support is
that the retaining means provide multiple attachment points and support for
the
barrier fencing and reduce the stress on the fencing material to prevent
damage. It
=
CA 02857361 2014-05-29
WO 2013/078516
PCT/AU2012/001471
- 12 -
allows quick and easy means of attaching the fencing to the support, together
with
quick dismantling and less waste.
Fencing can be assembled or' dismantled quickly using the fencing supports
of the present invention. The fence supports are reusable and there is no
waste
generated from discarded zip ties or wire.
The fencing supports can accommodate both lattice and mesh type fencing,
such as plastic barrier fencing and plastic mesh fencing, in addition to
hessian,
chicken wire and electric fence tape. Additional securing means are not
required.
When the fencing support is in the form of a sleeve to be used in conjunction
with a steel post, such as a star picket, the sleeve may be made in a softer
material
than steel to reduce the chance of injury if a pedestrian were to collide with
the
fencing. The fencing supports may also be brightly coloured, be made of
fluorescent
plastic material, or have reflective material applied, to increase visibility.
=
VARIATIONS
It will of course be realised that while the foregoing has been given by way
of
illustrative example of this invention, all such and other modifications and
variations
= thereto as would be apparent to persons skilled in the art are deemed to
fall within
the broad scope and ambit of this invention as is herein set forth.
Throughout the description and claims this specification the word "comprise"
and variations of that word such as "comprises" and "comprising", are not
intended to
exclude other additives, components, integers or steps.