Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent Application: | (11) CA 2858875 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | COIN BLANK |
| (54) French Title: | FLAN MONETAIRE |
| Status: | Deemed Abandoned and Beyond the Period of Reinstatement - Pending Response to Notice of Disregarded Communication |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | BROUILLETTE LEGAL INC. |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | |
| (86) PCT Filing Date: | 2012-07-31 |
| (87) Open to Public Inspection: | 2013-06-27 |
| Examination requested: | 2014-06-10 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | Yes |
|---|---|
| (86) PCT Filing Number: | PCT/EP2012/003261 |
| (87) International Publication Number: | EP2012003261 |
| (85) National Entry: | 2014-06-10 |
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
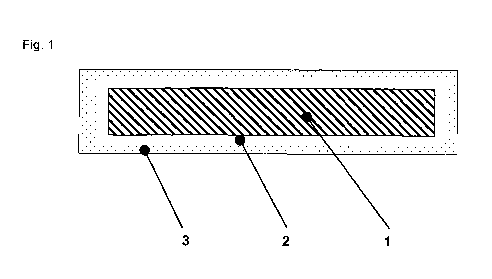
Coins which consist of a steel core having an electrolytic covering layer composed of copper are internationally routine, e.g. the 1, 2 and 5 eurocent coins. Copper has the disadvantage that a matt patina is formed during use of the circulating coin, as a result of which gloss and the original colour are lost. It is an object of the invention to provide a coin blank which contains a steel core (1) having a covering layer (2) which is composed of copper/copper alloy and retains brightness and colour shade in long-term use of the coin minted therefrom. The covering layer (2) of the coin blank is, according to the invention doped with nickel (3), as a result of which copper-coloured brightness and constancy of colour of the minted circulating coins are ensured.
L'invention concerne un flan monétaire. Les pièces de monnaie, constituées d'un noyau d'acier galvaniquement recouvert d'une couche de cuivre, sont utilisées dans le monde entier, comme c'est par exemple le cas pour les pièces de 1, 2 ou 5 centimes d'Euro. Le cuivre a pour inconvénient que plus les pièces circulent, plus une patine matte se forme, les pièces perdant alors leur éclat et leur couleur initiale. L'invention vise à fournir un flan monétaire contenant un noyau d'acier (1) recouvert d'une couche (2) de cuivre/d'un alliage de cuivre, permettant aux pièces de monnaie frappées à partir dudit flan de conserver leur éclat et leur teinte, y compris lorsqu'elles sont utilisées très longtemps. La couche de recouvrement (2) du flan monétaire est, selon l'invention, dopée avec du nickel (3), ce qui permet de garantir que les pièces frappées et en circulation conservent l'éclat de leur couleur cuivrée.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Inactive: Dead - No reply to s.30(2) Rules requisition | 2017-05-24 |
| Application Not Reinstated by Deadline | 2017-05-24 |
| Deemed Abandoned - Failure to Respond to Maintenance Fee Notice | 2016-08-01 |
| Inactive: Abandoned - No reply to s.30(2) Rules requisition | 2016-05-24 |
| Inactive: S.30(2) Rules - Examiner requisition | 2015-11-23 |
| Inactive: Report - QC passed | 2015-11-17 |
| Inactive: Cover page published | 2014-09-05 |
| Inactive: Acknowledgment of national entry - RFE | 2014-08-15 |
| Letter Sent | 2014-08-15 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2014-08-12 |
| Application Received - PCT | 2014-08-12 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2014-08-12 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2014-08-12 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2014-08-12 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2014-08-12 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2014-08-12 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2014-08-12 |
| Request for Examination Requirements Determined Compliant | 2014-06-10 |
| Amendment Received - Voluntary Amendment | 2014-06-10 |
| All Requirements for Examination Determined Compliant | 2014-06-10 |
| National Entry Requirements Determined Compliant | 2014-06-10 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 2013-06-27 |
| Abandonment Date | Reason | Reinstatement Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2016-08-01 |
The last payment was received on 2015-06-18
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Patent fees are adjusted on the 1st of January every year. The amounts above are the current amounts if received by December 31 of the current year.
Please refer to the CIPO
Patent Fees
web page to see all current fee amounts.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic national fee - standard | 2014-06-10 | ||
| Request for examination - standard | 2014-06-10 | ||
| MF (application, 2nd anniv.) - standard | 02 | 2014-07-31 | 2014-06-10 |
| MF (application, 3rd anniv.) - standard | 03 | 2015-07-31 | 2015-06-18 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| SAXONIA EUROCOIN GMBH |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| STEPHAN SIEGEL |
| THOMAS BILAS |