Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
- 1 -
Title
IN-RACK STORAGE FIRE PROTECTION SPRINKLER SYSTEM
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0001] The following disclosure relates to a fire protection system for rack
storage, and in
particular, to an in-rack sprinkler system capable of protecting exposed,
expanded and
unexpanded, plastics.
[0002] Rack storage is a conventional storage arrangement used in various
industries and
facilities. As provided in Section 3.9.3.7 of the U.S. National Fire
Protection Association
Standard 13 (NFPA 13) (2007 Ed.), a "rack" is lalny combination of vertical,
horizontal,
and diagonal members that supports stored materials. Shelving in some racks
can be solid,
slatted, or open. Racks can also be fixed, portable, or movable. Loading
commodities can be
either manual ¨ using lift trucks, stacker cranes, or hand placement ¨ or
automatic ¨ using
machine-controlled storage and retrieval systems." Conventionally, a commodity
102 to be
protected is placed on a pallet 104 and the commodity 102 and the pallet 104
are stored
together on a shelf 106 in a rack 108, as shown in Fig. 1A.
[0003] Racks can be single row, double row, or multiple row, with or without
solid
shelving. The terms "single row", "double row", and "multiple row" refer to
the depth of
the rack configuration in terms of the number of pallets that can be stored
back to back. For
example, a double row rack 108 has a depth that can accommodate two pallets
back to back,
as shown in the end elevation view of the schematic shown in Fig. 1B. When the
palletized
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 2 -
commodities 102 are stored apart from one another in the racks 108, 108 the
spaces formed
between the palletized commodities l 02 form transverse flue spaces 112, as
shown in Figs.
lA and 1C. Also, the vertical spaces between adjoining racks 108 (i.e.,
between the backs of
rows of storage) form what are known as longitudinal flue spaces 114 (Figs. 1B
and 1C).
An isometric view of a conventional double row rack 108 showing the
relationship of
various parameters is shown in Fig. 2. As shown in Figs. 3A and 3B, double and
multiple-
row racks 108 are conventionally spaced apart from other double or multiple-
row racks 108
by an aisle width 118, which is conventionally 4 or 8 feet (1.22 to 2.44
meters). Figs. 3A
and 3B also show, respectively, a plan view and an end elevation view of two
double row
rack arrangements 108 separated by an aisle having an aisle width 118.
[0004] Fire protection sprinklers are conventionally connected to a conduit to
receive
pressurized fire-extinguishing fluid, such as water. A typical fire protection
sprinkler has a
base with a threaded portion for connection to the conduit, and an output
orifice to output
the fire-extinguishing fluid to provide fire control and/or fire suppression.
The output orifice
is sealed by a seal cap that is held in place by a release mechanism. The
release mechanism
is designed to release the seal cap under predetermined conditions, thereby
initiating the
flow of the fire-extinguishing fluid. A typical release mechanism includes a
thernially-
responsive element, e.g., a frangible bulb or fusible link, and may also
include a latching
mechanism.
[0005] Certain conventional fire protection sprinklers have a pair of arms
that extend from
the base portion and meet at a hub portion to form a frame. The hub portion is
spaced apart
from the output orifice of the base portion and is aligned with a longitudinal
axis of the base
portion. The hub portion may have a set-screw configured to apply a pre-
tension force to the
release mechanism. A deflector may be mounted on the hub, transverse to the
output orifice,
to provide dispersion of the output fire-extinguishing fluid.
[0006] Fire protection sprinklers may be mounted on a fluid conduit running
along a ceiling
and may either extend downward from the conduit, referred to as a "pendent"
configuration,
or may extend upward from the conduit, referred to as an "upright"
configuration.
Alternatively, fire protection sprinklers may be mounted on a wall, a certain
distance below
the ceiling, referred to as a "horizontal sidewall" configuration. An output
orifice of a
horizontal sidewall sprinkler is oriented so that the fire-extinguishing fluid
is output
horizontally and sprays onto an area to be protected in front of the
sprinkler.
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
-3 -
[0007] An "extended coverage storage sprinkler (specific application)," as
described in
Section 55.1 of the Standard for Automatic Sprinklers for Fire-Protection
Service, published
by Underwriters' Laboratories, 1 lth Ed., November 4, 2005 (UL199) is a
sprinkler that is
intended to be installed using the extended coverage area up to 196 square
feet (e.g., 14 ft
by 14 ft) (18.21 square meters) (e.g., 4.27 meters by 4.27 meters), and using
specific
application criteria specified in NFPA 13. These extended coverage storage
sprinklers
(specific application) incorporate a heat responsive element and release
mechanism that has
a response time equal to or less than that of a standard response sprinkler
used on sprinklers
designed for standard spacings up to 100 square feet (e.g., 10 ft by 10 ft)
(9.29 square
meters) (3.05 meters by 3.05 meters). Extended coverage sprinklers are
installed in
accordance with Section 8.8.2 of NFPA 13.
[0008] NFPA 13 defines a number of different types of storage sprinkler
configurations and
protection criteria. Fire protection systems that provide fire protection for
commodities
stored in storage racks conventionally s include sprinklers that are arranged
within the
storage racks, i.e., in-rack sprinklers, that may be disposed directly above
the commodity
stored on a shelf of the storage rack. Section 8.13 of NFPA 13 specifies
installation
requirements for in-rack sprinklers and section 8.13.2.2 of NFPA 13 requires
that in-rack
sprinklers be ordinary-temperature, standard response or quick response
sprinklers and have
a nominal K-factor of 5.6 or 8.0 gpm/(psi)I/2.
[0009] Chapter 13 of NFPA 13 describes in-rack sprinkler configurations for
various
classifications of commodities for storage heights up to 12 feet (3.66
meters). According to
section 13.3.2 of NFPA (2007 Edition), in-rack sprinklers shall have a K-
factor of 5.6
gpm/(psi)112 or greater, and shall operate at a minimum of 15 psi (1 bar).
Table 13.2.1 and
Figure 13.2.1 of NFPA 13, Chapter 13 specify the maximum ceiling height,
maximum
storage height, area of sprinkler operation, and discharge density for various
hazard classes
and storage types for in-rack sprinkler installations for storage up to 12
feet (3.66 meters) in
height. Section 16.2 of NFPA 13 provides "Protection Criteria for Rack Storage
of Class I
Through Class IV Commodities Stored Up to and Including 25 ft in Height,"
Section 16.3
provides "Protection Criteria for Rack Storage of Class I Through Class IV
Commodities
Stored Over 25 ft in Height," and Chapter 17 provides "Protection of Plastic
and Rubber
Commodities That are Stored on Racks."
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
-4-
100101 Fire protection of rack storage configurations poses a number of
challenges. Fire
sprinkler systems are usually required to be installed in warehouses and other
similar article
storage areas. Conventional sprinkler systems are generally installed in the
ceiling of the
building and the sprinklers spray water in the area of the fire to either
control and/or to
extinguish the fire. In storage areas including racks, however, a fire that
starts on a lower
rack is shielded from the spray emanating from a sprinkler positioned above
the rack, either
by shelving above the rack or by commodities stored above the rack. This
factor is
significantly aggravated as the number of shelves is increased. Moreover, in
cases in which
sprinklers are located in the ceiling above a given rack, a fire in lower
shelves of the rack
may not actuate the heating-actuated sensing elements of the sprinklers in a
sufficiently
short amount of time to provide effective control of the fire. And, as noted,
even when the
sprinklers of the fire sprinkler system are actuated, the fire on the lower
shelves is protected
from the spray by upper shelves, and thus, the fire can spread upwardly.
[0011] In particular, early suppression-fast response (ESFR) sprinklers and
control mode
special application (CMSA) sprinklers have been used as ceiling level
sprinklers in place of
in-rack sprinklers. Conventional ESFR and CMSA sprinklers must operate at a
relatively
high pressure and discharge relatively large volumes of water in order to
provide the same
level of fire protection as the in-rack sprinklers they replace. The increased
water demand
and higher operating pressure required by ESFR and CMSA sprinklers, however,
are
generally undesirable consequences. Moreover, ESFR and CMSA sprinklers are not
approved for the protection of all storage commodities and commodity storage
configurations. Furthermore, ESFR and CMSA sprinklers are limited for use
based on
building heights.
100121 Overhead or roof sprinkler systems supplemented by intermediate levels
of
sprinklers have been suggested, including, for example, sprinklers mounted
within the
storage racks, and also within aisles between racks (e.g., U.S. Patent No.
3,732,930
(D'Anneo)). This arrangement was not generally satisfactory because
consistent, timely,
and dependable detection and sprinkler actuation was not achievable.
Consequently, greater
damage to stored material, and greater risk to the stored commodity and the
building
structure, prevented widespread use of this arrangement in high storage
facilities. Moreover,
installing sprinklers within storage racks increases the cost and complexity
of the sprinkler
system, and reduces the flexibility of locating and relocating storage racks
due to the fixed
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 5 -
positions of the sprinkler plumbing. Also, because commodities may be
routinely moved in
and out of the storage racks, there is an increased risk of damage to the in-
rack sprinklers
from such handling of the commodities.
[0013] Also, fire protection systems using foam have been suggested for use in
high-rise
storage facilities. Generally, such a system has a foam generator coupled with
a suitable
sensing system that is capable of filling an entire building volume with a
light foam. Single
generators capable of producing as much as 2,000 cubic feet per minute (56.63
cubic meters
per minute) of foam are available. The time required for filling the building
varies, but
generally ranges from two to eight minutes. Such systems are not completely
satisfactory
because the foam may damage goods (i.e., commodities) stored within the
facility. Also,
when the fire occurs at a high elevation, the foam may not reach the height
where the fire is
located for some time, permitting the fire to spread to the roof or ceiling
and become out-of-
control. Further, the foam system mentioned in the D'Anneo patent is
relatively expensive,
requires great quantities of water, and requires a good deal of maintenance,
and the
generators, which are heavy and are normally mounted on the roof, may result
in structural
damage if insufficient reinforcement is provided. In addition, removal of the
foam from the
warehouse after the fire is extinguished is a problem.
SUMMARY
[0014] A fire protection system is provided that addresses the deficiencies of
conventional
in-rack and ceiling fire protection systems, and combinations of the two. In
one aspect, the
invention provides a fire protection system that uses rack-level sprinklers
for fire protection
for commodities stored in racks. A fire protection sprinkler system is
provided for the
protection of commodities including Class I-IV hazards, Group A cartoned and
exposed
plastics (expanded and unexpanded), flammable liquids, tires, roll paper, and
aerosols,
stored in a plurality of adjoining racks having a longitudinal flue space
between the racks.
The system includes a fluid supply conduit that receives a fire protection
fluid from a fire
protection fluid source, one or more solid horizontal barriers covering (i) a
rack, of the
plurality of adjoining racks, and (ii) the vertical flue space, the one or
more solid horizontal
barriers being provided at a predetermined height, and having a width that is
at least equal
to a width of the rack, of the plurality of adjoining racks, and a depth that
is at least equal to
a sum of a depth of the rack and a depth of the vertical flue space, and one
or more rack-
level fire protection sprinklers that are connected to the fluid supply
conduit, the one or
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 6 -
more rack-level sprinklers being disposed in the vertical flue space above or
below a solid
horizontal barrier, of the one or more solid horizontal barriers, and each of
the one or more
rack-level sprinklers being vertically spaced from the commodities stored on a
rack, of the
plurality of adjoining racks, that is covered by the solid horizontal barrier.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0015] Fig. lA shows a side elevation view of a double row storage rack
arrangement.
[0016] Fig. 1B shows an end elevation view of the double row storage rack
arrangement
shown in Fig. 1A.
[0017] Fig. 1C shows a plan view of the double row storage rack arrangement
shown in
Fig. 1A.
[0018] Fig. 2 shows a perspective view of another double row rack arrangement.
[0019] Fig. 3A shows a plan view of two double row rack arrangements separated
by an
aisle width.
[0020] Fig. 3B shows an end elevation view of the double row rack arrangements
shown in
Fig. 3A.
[0021] Fig. 4 shows an isometric cutaway view of an embodiment of a fire
protection
system in accordance with the invention.
[0022] Fig. 5 shows an end elevation view of the system shown in Fig. 4.
[0023] Fig. 6 is a detail view of the sprinkler system shown in Fig. 5.
[0024] Fig. 7 is an end elevation view of the system shown in Fig. 5 with the
addition of a
second level of rack storage.
[0025] Fig. 8 is an elevation view of a main array and a sprinkler system
arranged in
accordance with an example of the invention.
[0026] Fig. 9 is a plan view of the main array and sprinkler system shown in
Fig. 8 between
two side arrays separated by aisles.
[0027] Fig. 10 is a plan view of the main array and sprinkler system shown in
Fig. 8 with
the commodities and rack structure above a horizontal barrier removed for
illustration.
[0028] Fig. 11 is an elevation section view of the main array viewed along
section line 11-
11 in Fig. 9.
[0029] Fig. 12 is a plan view of the main array and sprinkler system shown in
Fig. 8, and
shows an array of ceiling-level sprinklers arranged in accordance with an
example of the
invention.
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
-7-
100301 Fig. 13 includes tables listing maximum temperatures and activation
times from
testing of the sprinklers shown in Fig. 12.
[0031] Figs. 14 and 15 are side elevation views of the main array shown in
Fig. 8 showing
damage that occurred as a result of the test conducted.
[0032] Fig. 16 is a side elevation view of the north side of a main array
showing damage
that occurred as a result of a test conducted on a system constructed in
accordance with an
example of the invention.
[0033] Fig. 17 is a side elevation view of the south side of the main array
shown in Fig. 16.
[0034] Fig. 18 is a side elevation view of the north side of a main array
showing damage
that occurred as a result of a test conducted on a system constructed in
accordance with an
example of the invention.
[0035] Fig. 19 is a side elevation view of the south side of the main array
shown in Fig. 18.
[0036] Reference numerals that are the same, but that appear in different
figures, represent
the same elements, even if those elements are not described with respect to
each figure.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0037] As used in this detailed description, the term "rack-level" denotes a
position within
the longitudinal flue space between rows of adjoining racks between a floor
and a top of the
racks, but not disposed in a rack. Moreover, as used in this detailed
description, the term
"ceiling-level" denotes a position between the top of the racks and a ceiling
of a building.
[0038] A fire protection system for single, double, and multiple row rack
storage and racks
for automatic rack systems is provided that includes at least one rack-level
sprinkler fluidly
coupled to a fluid supply conduit. In one embodiment, the rack-level sprinkler
is constructed
as an extended coverage storage sprinkler. For example, the extended coverage
storage
sprinkler used as the rack-level sprinkler is a model N252 EC fire sprinkler,
manufactured
by The Reliable Automatic Sprinkler Company, Inc. (Liberty, South Carolina).
The N252
EC fire sprinkler has a relatively wide water distribution pattern of up to
196 square feet,
and produces a large droplet size. The N252 EC fire sprinkler is capable of
pre-wetting
areas (surrounding a fire) that have not yet combusted, so as to contain the
spread of the fire
to adjacent areas. In at least one embodiment in which extended coverage
storage sprinklers
are employed as rack-level sprinklers, it is possible to eliminate using fire
sprinklers in the
transverse flue space and to reduce the overall number of rack-level
sprinklers.
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
-8-
100391 As shown in Fig. 4, two racks 108 are arranged, one on top of the
other, in two
levels, to form a storage array 140. A solid horizontal barrier 142 is
provided above the
uppermost rack 108. The solid horizontal barrier 142 can be constructed of a
solid material,
such as wood, metal, or a non-combustible material, as defined in NFPA 13. A
horizontal
barrier 143 that is a slatted or a wire grate is provided between the racks
108. Rack-level
sprinklers 144 are positioned below the solid horizontal barrier 142. The
solid horizontal
barrier 142 may be positioned at a maximum predetermined height based on the
commodities 102 stored in the racks 108 and the construction of the rack-level
sprinklers
144. In the embodiment shown in Fig. 5, each rack 108 has a respective height
of about 10
feet (3.05 meters), and the racks 108 are stacked one on top of the other in
two levels
forming a multi-row rack having a total height of 20 feet (6.096 meters). It
should be noted
that, although two racks 108 are shown stacked in the example arrangement
shown in Fig.
5, the arrangement may include any number of racks 108 in combination stacked
below the
solid horizontal barrier 142 up to the predetermined height, which is 20 feet
(6.096 meters)
in this embodiment.
100401 Palletized commodities 102 are stacked in each level of the racks 108.
The
commodities 102 storcd in the racks 108 may include one or more of Class I-Iv
hazards,
Group A cartoned and exposed plastics (expanded and unexpanded), flammable
liquids,
tires, roll paper, and aerosols, as defined in NFPA 13. In the example shown
in Fig. 5, in
each 10-foot (3.05 meter) high level of the racks, two palletized commodities
102 are
stacked on top of one another at a height that is between 8 and 9 feet (2.44
and 2.74 meters)
from the floor. Thus, in the embodiment shown in Fig. 5, the solid horizontal
barrier 142 is
spaced from the commodity 102 directly below the solid horizontal barrier 142
by 1 to 2
feet (0.30 to 0.61 meter), and the dimension from the floor to the top of the
upper
commodity 102 in the upper level of the racks 108 is between 18 and 19 feet
(5.49 and 5.79
meters). The length of each rack 108 is about 8 feet (2.44 meters). The rack-
level sprinklers
144 are disposed in the vertical flue space 114 at a height of about 20 feet
(6.096 meters)
from the floor, and are centered with the length of the racks 108 (i.e., at
about 4 feet (1.22
meters) from the ends of the racks). The sprinklers 144 are horizontally
spaced about every
8 feet (2.44 meters) in the vertical flue space 114, as shown in Fig. 4. In
other arrangements,
however, the rack-level sprinklers 144 may be spaced on a branch line 116 at a
spacing of
between about 8 and 18 feet (2.44 and 5.49 meters).
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 9 -
[0041] The solid horizontal barrier 142 may extend horizontally across the
racks 108 and
may extend fully or partially into the vertical flue space 114 above the rack-
level sprinklers
144 in between the rear faces 150 of both racks 108, as shown in Figs. 5 and
7. The solid
horizontal barrier 142 can collect heat that rises as a result of combustion
occurring between
the floor and the solid horizontal barrier 142, and can also direct such heat
toward the
thermally responsive element that activates the rack-level sprinkler 144.
Since the
commodities 102 themselves, when stored in the racks 108, cover a substantial
horizontal
area of the rack 108, however, the undersides of the commodities 102 may
partially
substitute for dedicated solid horizontal barriers 142 by collecting heat from
below the
commodities 102. For example, in one embodiment, the solid horizontal barriers
142 shown
in Figs. 5 and 7 may be substitutcd with one or more partial horizontal
barriers to cover
horizontal areas in the racks 108 that are not suitably covered by the stored
commodities
102. For example, a relatively shorter horizontal barrier (not shown) may
extend from the
rear face 152 of the commodity 102 and extend toward the longitudinal flue
space 114.
Such a shorter horizontal barrier may extend into the vertical flue space 114
and may extend
over the rack-level sprinklers 144.
[0042] As a substitute for solid horizontal barriers 142, either in the racks
108 and/or in the
vertical flue spaces 114, horizontal barriers having one or more openings may
be employed.
For example, the horizontal barriers may be constructed as sheets with one or
more
apertures.
[0043] Also, in at least one embodiment, a separate horizontal barrier (not
shown) may be
positioned over each rack-level sprinkler 144 in the vertical flue space 114
to collect heat
around a thermally responsive element that activates each rack-level sprinkler
144. The
separate horizontal barrier can be constructed of a solid material, such as
one or more pieces
of metal, wood, or non-combustible materials, as defined in NFPA 13. The
separate
horizontal barrier may be a continuous piece that extends to cover a plurality
of rack-level
sprinklers 144 that are connected along the length of the supply conduit 116.
The separate
horizontal barrier may be constructed with or without openings between the
horizontally
adjacent rack-level sprinklers 144. Alternatively, each rack-level sprinkler
144 may be
covered separately by a corresponding horizontal barrier (not shown) that
covers a single
rack-level sprinkler 144. Such a single-sprinkler horizontal barrier may be
smaller to cover
individual rack-level sprinklers 144 so that there are horizontal spaces
between adjacent
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 10 -
horizontal barriers. For structural support and positioning, the horizontal
barriers may be
attached to the rack-level sprinklers 144, to supporting supply conduit piping
116, or to the
racks 108.
[0044] Vertical barriers may also be used to control the spread of heat and
fire horizontally
within and between the racks 108, and to facilitate the transmission of heat
vertically toward
the rack-level sprinklers 144. Such vertical barriers can compartmentalize the
storage areas
occupied by the commodities 102 into fire zones that are protected by rack-
level sprinklers
144 associated with that fire zone. The vertical barriers may be formed of
solid materials,
such as metal and wood, or non-combustible materials as defined in NFPA 13.
The vertical
barriers may be used with or without solid horizontal barriers 142.
[0045] In one embodiment, horizontal and vertical barriers are not employed.
When such
barriers are not employed, the rack-level sprinklers 144 used are selected to
have a
sufficient thermal sensitivity and release timing so that the rack-level
sprinklers 144 are
activated.
[0046] As shown in Fig. 5, two sets of multiple-row racks 108 are arranged
back-to-back
with their rear faces 150 defining the vertical flue space 114 between the
racks 108. In the
example shown in Fig. 5, the combined rack depth (H, Fig. 2) is between 7 and
8 feet (2.13
and 2.44 meters), with the depth between a front and rear face of each rack
being between 3
and 4 feet (0.91 and 1.22 meters), and with the distance between opposing rear
faces (L,
Fig. 2) being about 6 to 12 inches (15.24 to 30.48 centimeters). In general,
the rack-level
sprinklers 144 are disposed centrally in the vertical flue space 114. As shown
in greater
detail in Fig. 6, the rack-level sprinklers 144 are approximately centered
between the two
sets of racks 108. For example, when the racks 108 are spaced apart by 9
inches (22.86
centimeters), the rack-level sprinkler 144 is located 4.5 inchcs (11.43
centimeters) from the
rear face 150 of each rack 108. Also, as shown in Fig. 6, a deflector 148 of
the rack-level
sprinkler 144 is spaced from the top of the commodity 102 by about 7.5 inches
(19.05
centimeters). It should be noted, however, that in other embodiments, the
deflector 148 may
be spaced about 1 to 12 inches (2.54 to 30.48 centimeters) or more above the
commodity
102.
[0047] In Figs. 4 and 5, a solid horizontal barrier 142 is located above the
uppermost level
of the rack 108, so that commodities 102 stored in the rack 108 up to a
predetermined height
are disposed between the solid horizontal barrier 142 and the floor 145. A
plurality of
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 11 -
ceiling-level sprinklers 146 are located at the ceiling 147 above the solid
horizontal barrier
142 and above all of the racks 108. The ceiling-level sprinklers 146 provide
fire protection
for commodities 102 stored above the uppermost solid horizontal barrier 142,
which are not
protected by the rack-level sprinklers 144. As discussed herein, each solid
horizontal barrier
142 collects the heat between the solid horizontal barrier 142 and a lower
solid horizontal
barrier 142 (or floor, for the lowermost solid horizontal barrier 142) below
the solid
horizontal barrier 142, in order to prevent or to reduce the number of the
ceiling-level
sprinklers 146 from operating in the event of a fire below the solid
horizontal barrier 142. In
the embodiment described herein, the predetermined spacing between two solid
horizontal
barriers 142 is up to 20 feet (6.10 meters). It will be appreciated that the
floor 145 is
considered to be a solid horizontal barrier. Such spacing between the solid
horizontal
barriers 142 may depend on the commodity 102 stored, the rack-level sprinklers
144 used,
and the hazard classification, so that, in other embodiments, the spacing
between solid
horizontal barriers 142 may be between about 10 to 30 feet (3.05 to 9.14
meters). It should
also be appreciated that, in embodiments in which solid horizontal barriers
142 are not used,
the spacing between vertically adjacent rack-level sprinklers 144 may also
depend on the
same factors as those in which solid horizontal barriers 142 are used, i.e.,
the spacing may
depend on the commodity 102 stored, the rack-level sprinklers 144 used, and
the hazard
classification. Other factors may include the width of the aisle 118 between
racks 108 and
the water pressure. For example, if the hazard to be protected is less severe,
a spacing
between solid horizontal barriers 142 greater than 20 feet (6.10 meters) may
be used,
whereas in another example, if the hazard is more severe, a spacing between
solid
horizontal barriers 142 less than 20 feet (6.10 meters) may be used.
[0048] The arrangement of rack-level sprinklers 144 used concurrently with
ceiling-level
sprinklers 146, in accordance with the invention described herein, permits
such an
arrangement to be used to protect Class I-Iv hazards, Group A cartoned and
exposed
plastics (expanded and unexpanded), flammable liquids, tires, roll paper, and
aerosols stored
in racks in occupancies having ceilings 147 of any height, including those
having ceiling
heights above 45 feet (13.72 meters).
[0049] The ceiling-level sprinklers 146 may be any storage sprinkler having a
K-factor of
about 11.2 gpm/(psi)"2 or greater. The ceiling-level sprinklers 146 may also
be an extended
coverage control mode special application (EC CMSA), a special application, an
extended
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 12 -
coverage (EC), a storage, an extended coverage storage, or an early
suppression fast
response (ESFR) sprinkler. Also, in at least one embodiment, the ceiling-level
sprinklers
146 can be the same type of sprinkler as the rack-level sprinklers 144. For
example, in one
embodiment of a sprinkler system, the ceiling-level sprinklers 146 and the
rack-level
sprinklers 144 are all model N252 EC sprinklers, manufactured by The Reliable
Automatic
Sprinkler Co., Inc. of Liberty, South Carolina. The ceiling-level sprinklers
146 are spaced
from each other on a ceiling-level branch line conduit 154 at a spacing of
about 8 to 20 feet
(2.44 to 6.10 meters). The clearance between the ceiling-level sprinklers 146
and the racks
108, and the clearance between the ceiling-level sprinklers 146 and the
commodities 102
stored in the racks 106 below the ceiling-level sprinklers 146, are determined
based on the
relevant agency approval listing for those ceiling-level sprinklers 146. Since
rack-level
sprinklers 144 below the solid horizontal barriers 142 (or the rack-level
sprinklers 144 in
cases when solid horizontal barriers are not used) are expected to operate in
the event of a
fire condition occurring below the solid horizontal barriers 142 (or rack-
level sprinklers
144), the total hydraulic demands of the system may be reduced.
[0050] The rack-level sprinklers 144 have a K-factor that is between about
11.2 and 30
gpm/(psi)112. In one embodiment, all of the rack-level sprinklers 144 have the
same K-
factor. In another embodiment, however, not all of the rack-level sprinklers
144 have the
same K-factor. For example, in one embodiment, the K-factor of the rack-level
sprinklers
144 may depend on the vertical position of the rack-level sprinkler 144 in the
racks 108,
such that rack-level sprinklers 144 located at higher positions in the racks
108 have a greater
K-factor than rack-level sprinklers 144 located at lower positions in the
racks 108, or vice
versa. Alternatively, rack-level sprinklers 144 having a higher K-factor may
be positioned
in the rack 108 closer to fire zones in which more severe hazards are stored.
In the case of a
rack-level sprinkler 144 constructed as an N252 EC sprinkler, the rack-level
sprinklers 144
operate at a minimum pressure of about 7 psig (48.26 kPa) and discharge water
at a rate of
at least about 67 gpm (253.62 liters per minute). For rack-level sprinklers
144 having a
lesser or greater K-factor, the sprinklers 144 will operate at a pressure of
at least 7 psig
(48.26 kPa). The minimum pressure is based on the commodity 102 being
protected and the
vertical spacing between the solid horizontal barriers 142, or, in a case in
which the solid
horizontal barriers 142 are not used, the minimum pressure may be based on the
vertical
spacing between vertically adjacent rack-level sprinklers 144.
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 13 -
[0051] As shown in Figs. 5 and 7, one rack-level sprinkler line 116 extends
through the
vertical flue space 114 between each level of the solid horizontal barriers
142. Each rack-
level sprinkler line 116 extends between about 5 and 40 feet (1.52 to 12.19
meters). The
rack-level sprinkler lines 116 connected to the rack-level sprinklers 144 are
separate from
the ceiling-level branch line conduit 154 connected to the ceiling-level
sprinklers 146, so as
to create multiple, separate fire areas. The hydraulic demand caused by the in-
rack
sprinklers 144 may or may not be added to the hydraulic demand caused by the
ceiling-level
sprinklers 146.
[0052] The rack-level sprinklers 144 can be of the pendent, upright,
horizontal sidewall,
vertical sidewall, and conventional types (can be oriented in either a pendent
or upright
position). In addition, the rack-level sprinklers 144 can be constructed
having ordinary,
intermediate, or high thermal sensitivity (i.e., response time index, or RTI).
The rack-level
sprinklers 144 may be arranged with a water shield, constructed like the water
shields used
with model Fl and F1 FR intermediate level sprinklers manufactured by The
Reliable
Automatic Sprinkler Company, Inc. of Liberty, South Carolina. Also, the rack-
level
sprinklers 144 may be arranged with a guard, such as sprinkler guards for
Model C
sprinklers manufactured by The Reliable Automatic Sprinkler Company, Inc. of
Liberty,
South Carolina. The rack-level sprinklers 144 may also be constructed with a
thermal
release element (i.e., a thermally responsive element) that is a bulb or a
solder element. In at
least one alternate arrangement, the rack-level sprinklers 144 are not
arranged in an upright
orientation and/or are not constructed as upright sprinklers.
[0053] Fig. 7 shows a sprinkler system in which an upper set of racks 109 is
installed above
the solid horizontal barrier 142 shown in Fig. 5, below which a first level of
rack-level
sprinklers 144 is connected to a rack-level fluid supply conduit 116. The
upper set of racks
109 and palletized commodities 102 are arranged in the same manner as are the
lower racks
108 and palletized commodities 102. Likewise, a second rack-level conduit 117
extends in
the flue space 114 below a second solid horizontal barrier 149 at the top of
the upper set of
racks 109. A second level of rack-level sprinklers 144 is fluidly coupled to
the second rack-
level conduit 117. The second level of rack sprinklers 144 are aligned
vertically and
horizontally with the first level of rack-level sprinklers 144 described above
with respect to
Fig. 5. In the embodiment shown in Fig. 7, the vertical spacing between the
two levels of
rack-level sprinklers 144 and the solid horizontal barriers 142 and 149 is up
to about 20 feet
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 14 -
(6.10 meters). In other embodiments, however, the vertical spacing between the
two levels
of rack-level sprinklers 144 and the solid horizontal barriers 142 and 149 may
be between
about 10 to 30 feet (3.05 to 9.14 meters). Though not shown in Fig. 7,
additional racks may
be stacked in the same way as those racks 109 of the second level and are
protected by
providing additional rack-level sprinklers and solid horizontal barriers
spaced vertically up
to the predetermined limit, such as every 10 to 30 feet (3.05 to 9.14 meters).
[0054] The volume between the solid horizontal barriers (floor 145, 142 and
149), or
between vertically adjacent rack-level sprinklers 144 in arrangements without
the solid
horizontal barriers, can be considered compartments. Such compartments may be
further
subdivided into a plurality of fire areas associated with each rack-level
sprinkler 144. The
hydraulic demand for the racks 108 and 109 is determined by the most demanding
fire area
or the most demanding ceiling-level sprinkler 146. Thus, as a result of the
arrangement of
fire areas within the racks 108 and 109 and separate ceiling-level sprinkler
146
arrangement, the hydraulic demand of the rack-level sprinklers 144 may or may
not be
added to the hydraulic demand of the ceiling-level sprinklers 146.
[0055] The arrangement of rack-level sprinklers 144 and ceiling-level
sprinklers 146, as
described herein, provides a number of advantages over approaches to
protection for rack
storage described in the prior art. For example, the plurality of fire areas
protected by rack-
level sprinklers 144 eliminates the conventional requirements for ceiling-
level sprinklers
146 to penetrate a deeply-rooted, floor-level fire. Instead, as described in
accordance with
an aspect of the invention, fire protection rack-level sprinklers 144 and
ceiling-level
sprinklers 146 are positioned closer to the origin of a fire to contain the
spread of fire.
Moreover, sprinklers are not required to be placed in transverse flue spaces
112 or at the
faces 150 of racks 108 and 109, thereby improving access to the storage
locations and
reducing the chance of damaging the sprinklers during movement of commodities
in and out
of the racks. Instead, as described in accordance with an aspect of the
invention, sprinklers
that have a relatively large K-factor and are capable of producing large
droplet sizes, can be
positioned in the vertical flue space 114 closer to the potential fire
locations, which can
reduce the number of sprinkler heads opened during a fire and, therefore,
reduce the amount
of water typically required as compared with the ceiling-based sprinkler
systems.
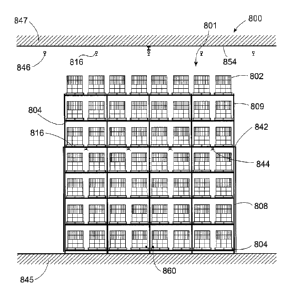
100561 Fire testing has been conducted for a fire protection system 800
arranged in
accordance with an aspect of the invention. Fig. 8 shows a side elevation view
of the tested
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 15 -
system 800 that has a solid horizontal barrier 842 at a height of 20 feet
above four levels of
double row rack storage. The width of the racks 808 is about 33 feet (10.06
meters). Above
the solid horizontal barrier 842, another three levels of rack storage 809 are
provided, such
that the height from the top of uppermost commodity 802 to the floor 845 is
about 35 feet
(10.67 meters), and the height of the ceiling 847 above the racks is about 40
feet (12.19
meters) from the floor. Just below the horizontal barrier 842, a set of rack-
level sprinklers
844 is connected to a fluid conduit 816, and is horizontally spaced from each
other by about
8 feet (2.44 meters). The horizontal barrier 842 is a solid barrier formed of
3/8 inch (9.53
millimeters) thick plywood.
10057] The racks 808 and 809 are double-row racks in which exposed, expanded
Group A
plastic placed on 2-way entry, hardwood stringer pallets 804 are stored. Fig.
9 shows a plan
view of the test configuration of the double-row racks 808 and 809. The racks
808 and 809
of the main array 801 are spaced from other racks 808 and 809 by aisles 818
that are about 8
feet (2.44 meters) wide. It should be noted that the width of each aisle 818
may be about 2
feet (0.61 meter) or greater in other arrangements. As shown in Figs. 8 and 9,
an ignition
source 860 is located at the base of the main array 801 approximately at the
midpoint of the
width of main array 801 and between two ceiling-level sprinklers 846 and two
rack-level
sprinklers 844.
100581 The ceiling-level sprinklers 846 are fluidly connected to a conduit
854, so that the
deflectors of the ceiling-level sprinklers 846 are spaced about 14 inches
(355.6 millimeters)
from the ceiling 847. The horizontal spacing between the ceiling-level
sprinklers 846 is
about 10 feet (3.05 meters) along the width of the main array 801. The ceiling-
level
sprinklers 846 are spaced about 10 feet (3.05 meters) on either side of the
midpoint of the
width of the main array 801, as shown in Fig. 8. In the example test
arrangement, the
ceiling-level sprinklers 846 are ESFR pendent sprinklers having a K-factor of
16.8
gpm/(psi)1/2. The temperature rating of the ceiling-level sprinklers 846 is
212 degrees
Fahrenheit. The response type of the ceiling-level sprinklers 846 is a quick
response (QR),
and the thermal release element is a fusible solder link type. The nominal
discharge density
of the ceiling sprinklers 846 is 1.19 gpm/square foot (48.49 lpm/square meter)
and the
nominal discharge pressure is 50 psig (344.74 kPa).
[0059] The rack-level sprinklers 844 are fluidly coupled to a 3-inch (76.2
millimeters),
schedule 40 branch line conduit 816 that is hydraulically separate from the
conduit 854
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 16 -
serving the ceiling-level sprinklers 846. The rack-level sprinklers 844 are
extended
coverage (EC) type sprinklers oriented in a pendent configuration and having a
K-factor of
25.2 gpm/(ps01/2. The deflectors of the rack-level sprinklers 844 are spaced
about 9.5 inches
(241.3 millimeters) from the top of the commodity 802 directly below the rack-
level
sprinklers 844. The response type of the rack-level sprinklers 844 is a quick
response (QR)
and the thermal release element is a fusible solder link type. The nominal
discharge pressure
is 30 psig (206.84 kPa) and the nominal discharge flow rate is 138 gpm (522.39
liters per
minute).
[0060] Fig. 10 shows details of the arrangement of the solid horizontal
barrier 842 of the
main array 801 at the 20 foot (6.10 meters) elevation in Fig. 8, as well as
solid horizontal
barriers 804 and 805, respectively, in arrays 802 and 803. Fig. 11 shows a
section view of
the main array 801 viewed from section line 1 1-1 1 in Fig. 9. Rear faces 850
of rack supports
851 are spaced about 15 inches (381 millimeters) apart, while the rear faces
852 of the
commodities in the racks 808 and 809 are spaced about 6 inches (152.4
millimeters) apart.
The deflector 848 of each of the rack-level sprinklers 844 is approximately
centered in the
flue space 814 between the racks 808 and 809, and the deflector 848 is spaced
about 8
inches (203.2 millimeters) from the uppermost side of the commodity 802. The
solid
horizontal plywood barrier 842 extends fully across the racks 808 and 809 and
the vertical
flue space 814. The conduit 816 is not disposed below the horizontal rack
supports 880 of
the rack frame of the racks 808 and 809. The deflector 848 of the rack-level
sprinkler 844
and/or a portion of a frame of the rack-level sprinkler 844 may protrude below
the rack
supports 880 adjacent to the conduit 816.
[0061] Fig. 12 shows a test map of locations of an array of ceiling-level
sprinklers 846
disposed above the arrays 801, 802, and 803 where temperature measurements
were taken
during the testing. The test parameters and results are summarized in Table 1,
below.
FIRE TEST NUMBER Test 1
Test Date August 8, 2012
Test Parameters
Storage Type Double Row Rack
Commodity Type Exposed Expanded Group A Plastic
Pallet Type 2 way entry, stringer, hardwood
Nominal Storage Height, ft. (m) 35 (10.69)
Ceiling Height, ft. (m) 40 (12.19)
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 17 -
Nominal Clearance, ft. (m) 5 (1.52)
Aisle Width, ft. (m) 8 (2.44)
Between 2 Ceiling-Level and Rack-Level
Ignition Location
Sprinklers (Face Fire in Aisle Space)
Ceiling Sprinkler System
Sprinkler Type K = 16.8 ESFR Pendent
Deflector to Ceiling, in. (mm) 14 (355.6)
Ceiling-Level Sprinkler Spacing, sprinkler
by 10 (3.05 by 3.05)
by branchline ft. by ft. (m by m)
Temperature Rating, F 212
Sprinkler Response Type QR (link)
Nominal Sprinkler Discharge Coefficient K,
16.8
gpm/(psi)1/2
Nominal Discharge Dcnsity, gpm/ft2
1.19 (48.49)
(1pm/m2)
Nominal Discharge Pressure, psig (kPa) 50 (344.74)
Rack-Level Sprinkler System
Sprinkler Type K= 25.2 Extended Coverage Pendent
Deflector to Commodity, in. (mm) 9.5 (241.3)
Sprinkler Spacing, ft. (m) 8.25 (2.51) (centered on the rack bays)
Temperature Rating, F 212
Sprinkler Response Type QR (link)
Nominal Sprinkler Discharge Coefficient K,
25.2
gpm/(pStf2
Nominal Discharge Pressure, psig (kPa) 30 (206.84)
Nominal Discharge Flowrate, gpm (lpm) 138 (522.39)
Test Results
Length of Test, minutes 31
Peak Gas Temperature at Ceiling Above
410
Ignition, F
Maximum 1 minute Average Gas
218
Temperature at Ceiling Above Ignition, F
Peak Steel Temperature at Ceiling Above
102
Ignition, F
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 18 -
Maximum 1 minute Average Steel
102
Temperature at Ceiling Above Ignition, F
Fire Travel to Extremities of Test Array No
Ceiling Sprinkler System
First Sprinkler Operation Time, min:sec 1:02
Last Sprinkler Operation Time, min:sec 1:02
Number of Operated Sprinklers 1
Rack-Level Sprinkler System
First Sprinkler Operation Time, min:sec 0:49 (East Central Sprinkler)
Last Sprinkler Operation Time, min:sec 0:52 (West Central Sprinkler
Number of Operated Sprinklers 2 (out of 4 active in main array)
TABLE 1
[0062] Fig. 13 shows maximum temperatures that were recorded during the test
at the
locations shown in Fig. 12, and also shows activation time of the ceiling-
level sprinklers
846. The testing showed that, during a fire condition, only two rack-level
sprinklers 844 out
of four rack-level sprinklers 844 operated during the fire, and only one
ceiling-level
sprinkler 846 operated. Fig. 14 shows a view of the pattern of damage to the
main array 801
from one side, and Fig. 15 shows a view of damage to the main array 801 from a
side
opposite to the side shown in Fig. 14.
[0063] Conventional in-rack sprinkler systems are designed such that, in the
event of a fire,
up to eight sprinkler heads may operate. The sprinkler system described in
accordance with
the invention is constructed to reduce the number of opened sprinlder heads to
five or fewer,
which reduces the hydraulic demand on the system in the event of a fire. While
the system
described herein can be constructed for a new rack storage installation, it
will be appreciated
by those of ordinary skill in the art that the system can be implemented to
retrofit existing
sprinkler systems for rack storage by incorporating rack-level sprinklers into
an existing
rack storage sprinkler system.
[0064] Fire testing has been conducted for a fire protection system 900
arranged in
accordance with an aspect of the invention. The details of the testing and the
arrangement of
the system are summarized in Table 2, below.
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 19 -
Test Parameters
Storage Type Double Row Rack
Commodity Type Cartoned
Unexpanded Group A Plastic
Pallet Type 2 Way Entry, Stringer, Hardwood
Nominal Storage Height, ft. (m) 43 (13.11)
Ceiling Height, ft. (m) 48 (14.63)
Nominal Clearance, ft. (m) 5 (1.52)
Aisle Width, ft. (m) 8 (2.44)
Between 2 Ceiling-Level and Rack-Level
Ignition Location Sprinklers
(Face of Commodity in Aisle
Space)
Ceiling Sprinkler System
Sprinkler Type K = 25.2
Extended Coverage Pendent
Deflector to Ceiling, in. (mm) 14 (355.6)
Ceiling-Level Sprinkler Spacing, sprinkler
14 by 14 (4.27 by 4.27)
by branchline ft. by ft. (m by m)
Temperature Rating, F 212
Sprinkler Response Type QR (link)
Nominal Sprinkler Discharge Coefficient K,
25.2
gpm"so 1 /2
Nominal Discharge Density, gpm/112
0.7 (28.52)
(lpm/m2)
Nominal Discharge Pressure, psig (kPa) 30 (206.84)
Rack-Level Sprinkler System
Sprinkler Type K= 25.2
Extended Coverage Pendent
Deflector to Bottom of Solid Horizontal
7.5 (190.5)
Barrier, in. (mm)
Sprinkler Spacing, ft. (m) 8.25 (2.51) (centered on the rack bays)
Temperature Rating, F 212
Sprinkler Response Type QR (link)
Nominal Sprinkler Discharge Coefficient K,
25.2
gpm/(psi)1/2
Nominal Discharge Pressure, psig (kPa) 30 (206.84)
Test Results
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 20 -
Length of Test, minutes 34
Peak Gas Temperature at Ceiling Above
722
Ignition, F
Maximum 1 minute Average Gas
353
Temperature at Ceiling Above Ignition, F
Peak Steel Temperature at Ceiling Above
152
Ignition, F
Maximum 1 minute Average Steel
150
Temperature at Ceiling Above Ignition, F
Fire Travel to Extremities of Test Array No
Ignition of Target Commodity No
Ceiling Sprinkler System
First Sprinkler Operation Time, min:sec 3:01
Last Sprinkler Operation Time, min:sec 3:01
Number of Operated Sprinklers 1
Rack-Level Sprinkler System
First Sprinkler Operation Time, min:sec 2:53 (West Central Sprinkler)
Last Sprinkler Operation Time, min:sec 2:59 (East Central Sprinkler)
Number of Operated Sprinklers 2 (out of 4 active in main array)
TABLE 2
[0065] As distinguished from system 800, system 900 employs extended coverage
fire
sprinklers for the ceiling-level sprinklers. The ceiling-level sprinklers used
in the system
900 have a nominal K-factor of 25.2 and are constructed as Model N252 EC
sprinklers
manufactured by The Reliable Automatic Sprinkler Co., Inc., of Liberty, South
Carolina.
The rack-level sprinklers used in the system 900 are the same as the ceiling-
level sprinklers.
The results of the test of the system 900 are noted in Table 2.
[0066] Fig. 16 shows a photograph of the north side of the main test array
protected by the
system 900 and the damage caused by the fire testing of the system 900. Fig.
17 shows a
photograph of the south side of the main test array protected by the system
900 and the
damage caused by the fire testing of the system 900. At the aisle spacing of
eight feet (2.44
meters), no damage was observed to the commodities in either of the two racks
spaced from
the main array in testing the system 900. Testing of the system 900 confirmed
that the
growth of the fire was substantially vertical.
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 21 -
[0067] Fire testing has been conducted for a fire protection system 1000
arranged in
accordance with an aspect of the invention. The details of the testing and the
arrangement of
the system are summarized in Table 3, below.
Test Parameters
Storage Type Double Row Rack
Cartoned Unexpanded Group A Plastic
Commodity Type (Polystyrene Cups in Corrugated
Containers)
Pallet Type 2 way entry, stringer, hardwood
3/8 inch (9.53 mm) Plywood at 20 ft. (6.10
Horizontal Barrier Within Rach
m) and 40 ft. (12.19 m) Elevation
Nominal Storage Height, ft. (m) 43 (13.11)
Ceiling Height, ft. (m) 48 (14.63)
Nominal Clearance, ft. (m) 5 (1.52)
Aisle Width, ft. (m) 4 (1.22)
Between 2 Sprinklers (offset in transverse
Ignition Location
flue space)
Ceiling Sprinkler System (Initially Dry ¨ Activated after significant fire
load at the
ceiling)
Sprinkler Type K = 25.2 Extended Coverage Pendent
Deflector to Ceiling, in. (mm) 14 (355.6)
Ceiling-Level Sprinlder Spacing, sprinkler
14 by 14 (4.27 by 4.27)
by branchline ft. by ft. (m by m)
Temperature Rating, F 212
Sprinkler Response Type QR (link)
Nominal Sprinkler Discharge Coefficient K,
25.2
gpm/(psoti2
Nominal Discharge Density, gpm/ft2
0.7 (28.52)
(lpm/m2)
Nominal Discharge Pressure, psig (kPa) 30 (206.84)
Rack-Level Sprinkler System (at nominal 20 ft. (6.10 m) and 40 ft. (12.19 m)
levels)
Sprinkler Type K= 25.2 Extended Coverage Pendent
Deflector to Commodity, in. (mm) 8 (203.2) (nominal)
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 22
8.25 (2.51) (centered on the rack bays) (4
Sprinkler Spacing, ft. (m) sprinklers, centered on the bay of
commodity)
Temperature Rating, F 165
Sprinkler Response Type QR (link)
Nominal Sprinkler Discharge Coefficient K,
25.2
gpm/(ps01/2
30 (206.84) (at 40 ft. (12.19 m) elevation)
Nominal Discharge Pressure, psig (kPa)
39 (at 20 ft. (6.10 m) elevation)
138 (522.39) (at 40 ft. (12.19 m) elevation)
Nominal Discharge Flowrate, gpm (1pm)
157 (594.31 ) (at 20 ft. (6.10 m) elevation)
Test Results
Length of Test, minutes 60
Peak Gas Temperature at Ceiling Above
1583
Ignition, F
Maximum 1 minute Average Gas
1093
Temperature at Ceiling Above Ignition, F
Peak Steel Temperature at Ceiling Above
450
Ignition, F
Maximum 1 minute Average Steel
445
Temperature at Ceiling Above Ignition, F
Fire Travel to Extremities of Test Array No
Ignition of Target Commodity No
Ceiling Sprinkler System (Initial Operating Time without Water) ¨ Water Began
Discharging 21 minutes 15 seconds after Ignition
First Sprinkler Operation Time, min:sec 20:40
Last Sprinkler Operation Time, min:sec 21:15
Number of Operated Sprinklers 3
Rack-Level Sprinkler System
1:13 (East Central Sprinkler 20 ft. (6.10 m)
First Sprinkler Operation Time, min:sec
Elevation)
13:40 (East Central Sprinkler ¨ 40 ft. (12.19
Last Sprinkler Operation Time, min:sec
m) Elevation)
(out of 8 active in main array)
Number of Operated Sprinklers
No operation of Target Rack-Level
CA 2863034 2017-12-22
- 23 -
Sprinklers
TABLE 3
[0068] As distinguished from the testing of the system 800 and the system 900,
the system
1000 was tested in a main array and two other arrays having two solid
horizontal barriers, a
lower barrier at a 20 foot (6.10 meter) elevation, and an upper barrier at a
40 foot (12.19
meter) elevation. Also, distinguished from testing of the system 800 and the
system 900, in
the test arrangement of the system 1000, the aisle width between the main
array and the
other two arrays was four feet (1.22 meters) instead of eight feet (2.44
meters), as in the test
arrangement of the systems 800 and 900. The test arrangement used to test the
system 1000
employs extended coverage fire sprinklers for the ceiling-level and rack-level
sprinklers.
The ceiling-level and rack-level sprinklers used in the system 1000 have a
nominal K-factor
of 25.2 gpm/(psi)1/2 and are constructed as Model N252 EC sprinklers
manufactured by The
Reliable Automatic Sprinkler Co., Inc., of Liberty, South Carolina. The
results of the test of
system the 1000 are noted in Table 3.
[0069] Fig. 18 shows a photograph of the north side of the main test array
protected by the
system 1000 and the damage caused by the fire testing of the system 1000. Fig.
19 shows a
photograph of the south side of the main test array protected by the system
1000 and the
damage caused by the fire testing of the system 1000. At the aisle spacing of
four feet (1.22
meters), no damage was observed to the commodities in either of the two racks
spaced from
the main array in testing the system 1000. Testing of the system 1000
confirmed that the
growth of the fire was substantially vertical.
[0070] While the present disclosure has been described with respect to what
are, at present,
considered to be the preferred embodiments, it is to be understood that the
invention is not
limited to the disclosed embodiments. To the contrary, the invention is
intended to cover
various modifications and equivalent arrangements included within the spirit
and scope of
the appended claims.
CA 2863034 2017-12-22