Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02864463 2014-08-11
Computing method for continuous power flow based on wind
power fluctuation rules
Technical field
The present invention relates to the field of grid connection techniques of
wind
photoelectricity, specifically relates to a computing method for continuous
power flow
based on wind power fluctuation rules.
BackEround
Along the adjustment of the energy structure in our country, green energy has
attached importance increasingly in recent years. Wind photoelectricity is the
renewable
green energy; meanwhile, the randomness and intermittent of the wind
photoelectricity
cannot be adjusted, so new requirements are put forwards to the power flow
computation
containing wind power generators.
The common computing method for power flow containing wind power generators
comprises:
(1) The fan access point is regarded as PQ node (the active power P and
reactive
power Q of PQ node are given; and node voltage V and phase 6 are the
quantities to be
obtained); the active power and reactive power of the wind power generator are
computed according to the given wind speed and power factor; however, the
method
does not consider the reactive real-time variation of the fan.
(2) The wind power plant adopts PX model which is more improved than other
models fully considering the characteristics of output power of the wind power
generator. The iterative process in of the PX model is divided into two steps:
iterative
computation for normal power flow and slip frequency iterative computation for
asynchronous wind power generator; and it has more total iterations and slower
convergence rate.
Therefore, it is important to select the power flow computing method
considering
the fluctuation characteristic of the wind power and the computing speed.
During the process for realizing the invention, the inventor discovered the
current
technology without considering the fluctuation characteristic of the wind
power and the
slower computing speed.
Summary of the invention
For solving the above problems, the invention aims at providing a computing
1
CA 02864463 2014-08-11
method for continuous power flow based on wind power fluctuation rules which
has the
fluctuation characteristic of the wind power and the faster computing speed.
In order to realize the above purpose, the technical solution adopted in the
invention is a computing method for continuous power flow based on wind power
fluctuation rules which comprises:
a. analyzing the fluctuation characteristics of active power in a wind power
plant by
the analytical method of Poisson process and setting up a probability model;
b. confirming the time interval of wind power output fluctuation and the
output
variation situation of the wind power plant power according to the statistical
result of
the probability model obtained in step a and the wind power variation so as to
obtain the
fluctuation rules of the wind power output;
c. computing the continuous power flow in the same time interval according to
the
fluctuation rules obtained in step b so as to obtain the state variable value;
and
d. analyzing the state variable value obtained in step c and the influence of
large-scale wind photoelectricity access on the power flow so as to obtain the
influence
of the wind power on the power flow.
Further, in step b, the time interval of the wind power output fluctuation is
obtained
by the analytical method of Poisson process; and the output variation
situation of the
power in the wind power plant complies with the normal distribution.
Further, in step b, the operation for confirming the time interval of the wind
power
output fluctuation comprises confirming the time interval of the power flow
computation
and the wind power output situation of the power flow computation according to
the
probability statistics analysis.
Further, in step a, the operation for analyzing the fluctuation
characteristics of
active power in a wind power plant by adopting the analytical method of
Poisson
process comprises the steps of:
al. Obtaining the fluctuation characteristics of wind power based on the time
interval of the power fluctuation in the wind power plant, namely:
Observing the occurrence times of power fluctuation PB at the moment t in a
probability space [m1 ,m2], selecting a counting process (s) , if S 0, it
meets
N(0) = 0
The above process is called as the Poisson process and defined as:
2
CA 02864463 2014-08-11
(1)N(õ) =0
(2) The increment in the non-intersect area is independent;
(3)s,t 0; when P13 = )9(1+') P(l) given the monthly installed capacity of the
whole
wind power is PR,P = (P B I N)x 100%; it meets P1N(s +t)¨N(t) = 1c)=
(.1,$)k 1k!
and k = I n ;
a2. The arrival time interval of the Poisson process is the independently
distributed
random variable, the obtained counting process is called as the updating
process,
namely,
T }Assuming n is a row of independent random variable with same distributed F
and n = 1'2. = = n ;
F(0) = P {Tn = 0} < 1 ; ,u = ET TdF(T)
Assuming commanding 1' , it
can be know
that < from Tn 0, F(0) <1;
0
And assuming = So , Sn _
¨ i=1 , the counting process is updated as
N(t) = sup{n, St, t} and t
Further, in step a, the operation for analyzing the fluctuation
characteristics of
active power in a wind power plant by adopting the analytical method of
Poisson
process further comprises the steps of:
a3. Obtaining the output variable situation of wind power plant, namely:
The relative variation of the action power of the wind power is in normal
= e
distribution, assumingT [0,GO,t Tthe relative variation p(t) of the power is
the
normal random process;
If random time frame t and t1 t. E T , At,,)
is n-dimensional normal
vector; the density function of n-dimensional normal distribution 19(a 'B) is
F(x)= ____________ exp[¨ ¨1(x¨ a)B-1 (x ¨ a)11
(2700 21B1. - 2
Wherein B is the positive definite covariance matrix, the relative change rate
of the
(Põ I Põ)x100% =1(P(,,,)¨ P(0)1 Põ Ix 100%
power in any time frame is z
3
CA 02864463 2014-08-11
If [m19m21 N(rn) 1
, if not,
N(sn) = 0 , the rate at this time is
Q = N On) /IN (s") ; in the above formula, PH is the wind power output
fluctuation
value in any time; PR is monthly installed capacity; An is fluctuation rate;
kni'md
is probability interval; and N (sn) is the counting process.
The computing method for continuous power flow based on wind power fluctuation
rules in each embodiment of the invention comprises steps of analyzing the
fluctuation
characteristics of active power in a wind power plant by adopting the
analytical method
of Poisson process so as to set up a probability model, confirming the time
interval of
wind power output fluctuation and the output variation situation of the wind
power plant
power according to the statistical result of the obtained probability model
and the wind
power variation so as to obtain the fluctuation rules of the wind power
output;
computing the continuous power flow in the same time interval according to the
fluctuation rules so as to obtain the state variable value; analyzing the
obtained state
variable value and the influence of large-scale wind photoelectricity access
on the power
flow so as to obtain the influence of the wind power on the power flow;
obtaining the
detail data of the grid power flow influence of wind power with different
capacities
according to the probability accessing network by analyzing the fluctuation
characteristic and power characteristic of the active power of the wind power,
which is
of great importance to reduce the voltage fluctuation of the system caused by
the wind
power online, improve the system stability margin and voltage level of wind
power
integration point, reduce transmission losses, etc, thereby the defect of not
considering
the wind power fluctuation and the slow computing speed in the prior art can
be
overcame; and the advantages of considering the wind power fluctuation and the
fast
computing speed are realized.
Other characteristics and advantages of the invention shall be stated in the
follow
specification; partial characteristics and advantages are obvious from the
specification
or known by implementing the invention. The purposes and other advantages of
the
invention can be realized and obtained by the specification, claims and
structure special
pointed in the attached drawings.
The technical solution of the invention is further described in details by the
attached drawings and embodiments.
Brief description of the drawings
4
CA 02864463 2014-08-11
The attached drawings are used for understanding the invention further or
forming
a part of the specification; the attached drawings and the embodiments are
used for
explaining the invention and do not limit the invention. In the attached
drawings:
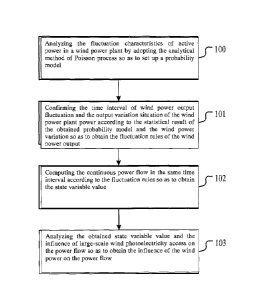
FIG.1 is the flow diagram of the computing method for continuous power flow
based on wind power fluctuation rules;
FIG.2 is the schematic diagram of probability statistics of the wind power
fluctuation rules in some area (probability distribution of power change rate
of wind
power in a certain domestic wind power plant within 5min).
Specific embodiments
The optimized embodiment of the invention is explained by combining the
attached
drawings; it is understood that the optimized embodiment described here is
only used
for explaining and stating the invention rather than limiting the invention.
The embodiment of the invention provides a computing method for continuous
power flow based on wind power fluctuation rules. As shown in figure 1, the
embodiment comprises:
Step 100: analyzing the fluctuation characteristics of active power in a wind
power
plant by adopting the analytical method of Poisson process so as to set up a
probability
model;
In the step 100, the operation for analyzing the fluctuation characteristics
of active
power in a wind power plant by adopting the analytical method of Poisson
process
comprises the steps of:
(1). obtaining the fluctuation characteristics of wind power based on the time
interval of the power fluctuation in the wind power plant, namely:
Observing the occurrence times of power fluctuation PB at the moment t in a
probability space [m, m2], selecting a counting process N ( > 0 i0, if s ¨
, t meets N( ) = 0 =
The above process is called as the Poisson process and defined as:
(1)N(0) =0
(2) The increment in the non-intersect area is independent;
(3)s,t P =
when B ("-') (`) given the monthly installed
capacity of the whole
wind power is P R P it meets
= (pB 1 põ)x100% pIN (s
+ t) ¨ N (t)= k} = CA' (As)k 1k!
and k = 1 ¨ n ;
(II). the arrival time interval of the Poisson process is the independently
distributed
5
CA 02864463 2014-08-11
random variable; the obtained counting process is called as the updating
process,
namely:
IT i
Assuming n s a row of independent random variable with same distributed F,
n = 1,2== = n
Assuming F(0)= P{Tn = 0} <1 p = ET
, commanding n=
TdF (T)
, it can be know
that 0 </1 Go from Tn 0, F(0) <1 .
And assuming so = o Sn = t=1 , the
counting process is updated as
N(t) = sup{n, Sn t} and t O.
(III). obtaining the output variable situation of wind power plant, namely:
The relative variation of the action power of the wind power is in normal
distribution, assuming T = [0 , co) , t e T the relative variation p(t) of the
power is the
normal random process;
If random time frame t and ti tn T p(t1) no( )
= is n-dimensional normal
vector; the density function of n-dimensional normal distribution p(a,B) is
1
F (x) =-
112 exp[- ¨1(x¨ a)B1 (x ¨ a)11
(27r)n/21B1 2
Wherein B is the positive definite covariance matrix; the relative change rate
of the
2õ = (P, I Põ) x 100% =[(P(,õ) ¨ P(0)1 Põ ix 100%
power in any time frame is
A E [rn M 1N =1
If it 1, 2 ( vti) , if
not N (sn) = 0 , the rate at this time is
Q = N0,01EN("0 ; in the above formula, pB is the wind power output fluctuation
value in any time; PR is monthly installed capacity; /1 ' is fluctuation rate;
[m1 ,m2]
is probability interval; and N (sn) is the counting process.
Step 101: confirming the time interval of wind power output fluctuation and
the
output variation situation of the wind power plant power according to the
statistical
result of the probability model obtained in step 100 and the wind power
variation so as
to obtain the fluctuation rules of the wind power output;
In step 101, the time interval of the wind power output fluctuation is
obtained by
6
CA 02864463 2014-08-11
the analytical method of Poisson process; and the output variation situation
of the power
in the wind power plant complies with the normal distribution;
In step 101, the operation for confirming the time interval of the wind power
output
fluctuation comprises confirming the interval time of the power flow
computation and
the wind power output situation of the power flow computation according to the
probability statistics analysis;
Step 102, computing the continuous power flow in the same time interval
according
to the fluctuation rules obtained in step 101 so as to obtain the state
variable value;
Step 103: analyzing the state variable value obtained in step 102 and the
influence
of large-scale wind photoelectricity access on the power flow so as to obtain
the
influence of the wind power on the power flow.
The computing method for continuous power flow based on wind power fluctuation
rules in the above embodiment simulates the influence of the wind power with
different
capacities on the grid power flow according to the probability access network
by
analyzing the fluctuation characteristics and power characteristics of the
active power of
wind power. The method is the interval power flow computation by the
probability
statistics of wind power fluctuation under the preconditions of not changing
the access
model of the fan and ensuring the probability; provides more detail data to
analyze the
fluctuation of the wind power; fully analyzes the voltage and branch power of
each node
of the wind power plant integration system to provide reference to the
integration
scheme of the wind power plant.
The computing method for continuous power flow based on wind power fluctuation
rules in the above embodiment computes the continuous power flow based on the
statistic analysis of the wind power fluctuation rules. Compared with the
normal power
flow, the computing method considers the fluctuation characteristics of the
wind power
and the power flow computing speed; meanwhile, the method has the advantages
of
simple computation, easy realization, convenience for interfacing with general
power
flow program and a certain practicability; and the computing method is
beneficial to
increasing the accuracy and practicability of the grid power flow computation
comprising large-scale wind photoelectricity.
For example, the probability distribution of power change rate of wind power
in a
certain domestic wind power plant within 5min is shown in FIG.2; the power
flow is
computed by taking 5min as the time interval and progressive manner of 1% of
the wind
power fluctuation capacity; and the results are as shown below:
7
CA 02864463 2014-08-11
Time Output level of wind power Voltage of access point of
plant group wind power plant group
0 61% 760.507kV
5min 62% 740.99kV
10min 63% 727.168kV
It can be seen that the wind power fluctuation has great influence on the
voltage of
the access point; it is considered that the voltage of the access point is a
fixed value at
this time in the traditional power flow computation, so the method reflects
the influence
of the wind power fluctuation on the grid accurately and helps the safe and
steady
operation of the grid.
The actual grid data of some province can be shown in figure 2; the example is
counted by the wind power fluctuation probability obtained by the method of
the above
embodiment; the power flow is computed according to the statistical result and
the same
time interval so as to obtain the detail influence of the wind power
fluctuation on the
grid.
It can be known from the instance analysis shown in figure 2 that the
computing
method for continuous power flow based on wind power fluctuation rules in the
above
embodiment can overcome the defects of not considering the reactive real-time
variation
of fan, more algorithm iterations and slow convergence rate in the traditional
method,
obtain the influence of the wind power output fluctuation on the access point
of the wind
power plant group and the regional grid voltage; it is of great importance to
reduce the
voltage fluctuation of the system caused by the wind power online, improve the
system
stability margin and voltage level of wind power integration point, reduce
transmission
losses, etc; and it has reference value to guide the generation schedule of
large-scale
wind power network operation.
In conclusion, the computing method for continuous power flow based on wind
power fluctuation rules in the each embodiment of the invention relates to the
field of
the wind photoelectricity grid connection techniques; and the method comprises
the
steps of analyzing the fluctuation characteristics of the wind power plant by
adopting the
8
CA 02864463 2014-08-11
analytical method of Poisson process so as to set up a probability model,
confirming the
time interval of wind power output fluctuation and the output variation
situation of the
wind power plant power according to the model and the statistical result so as
to obtain
the fluctuation rules of the wind power output; computing the continuous power
flow
according to the fluctuation rules so as to obtain the state variable value;
analyzing the
obtained state variable value and the influence of large-scale wind
photoelectricity
access on the power flow; the detail data of the grid power flow influence of
wind power
with different capacities according to the probability accessing network can
be obtained
by analyzing the fluctuation characteristic and power characteristic of the
active power
of the wind power; it is of great importance to reduce the voltage fluctuation
of the
system caused by the wind power online, improve the system stability margin
and
voltage level of wind power integration point, reduce transmission losses,
etc.
What to be explained finally is that the above embodiment is the optimized
embodiment of the invention rather than limiting the invention. The invention
is
explained in details by referring to the above embodiment; the technician in
the field can
modify the technical solution recorded in the above embodiment or replace
partial
technical characteristics equally. Any modification, equal replacement,
improvement
and the like in the spirit and principle of the invention should be contained
in the
protection scope of the invention.
9