Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 2870793 2017-04-26
SELF-DRAINING HOSE
SCOPE OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to hoses, and more particularly to self-draining
hoses.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The weather-proofing of water systems to prevent freeze-up and associated
damage has been the focus of many patents. However the search for reliable,
low-
cost systems still proceeds in view of the defects, drawbacks and high
installed and
operating costs of the systems presently available.
The present invention relates to the subject matter found in Canadian Patent
No. 1,122,877 Gauthier, May 1971. One of the drawbacks of the earlier Gauthier
system has been the absence of a reliable, low cost weather-proof (i.e. freeze-
insensitive or "frost-free") hose. The prior art Gauthier hose provision
comprises a
smaller diameter hose threaded through the interior of a larger outer hose.
The inner
hose has a thick wall that stretches under pumping pressure, so as to provide
elastic,
contractive energy upon the cessation of pumping, to thereby assist in the
expulsion
of water from the inner hose, as an effective portion of the dewatering
process.
Previous manufacture of the inner and outer hoses as separate entities, with
their combination into the desired frost-free format required their assembly
by
1
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
drawing the smaller hose within the larger hose. Due to the practical
difficulties
involved in this "threading" operation, the length of such a compound hose was
limited to
about approximately thirty two meters (i.e. about one hundred feet), the
threading
operation being both difficult and time consuming.
The applicant has previously disclosed in United States Patent 5,445,356 a
system for pumping liquids that are subject to solidification in the line
which uses a
compressed gas as an expulsion medium for the liquid. The compound hose
pipeline has
a variable volume gas chamber adjacent a transfer passage, extending the
length of the
pipeline. The line includes an outer hose that provides an air annulus about a
collapsible
inner hose, through which the pumped liquid can flow. Air or other gas
admitted to the
annulus operates to expel the liquid from the inner hose, either upon the loss
of
pressurization of the liquid in the inner hose, or upon the application of
adequate pressure
within the gas annulus to discharge the liquid from the inner hose.
The applicant has also previously disclosed in United States Patent 5,746,255
a pipeline compound hose having an elastomeric inner hose circumscribed by a
high
strength plastic outer hose with a sealed air cavity disposed there between.
The elastic
memory of the inner hose contributes to the de-watering capability of the
inner hose
together with the residual pressure within the sealed air cavity. The sealed
enclosure of
the pipeline includes sealed end-fittings to prevent air leakage from the
sealed air cavity.
BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present disclosure provides a hose that is self-draining to avoid freeze-
up
and water heating when between pressurized flow periods.
In one aspect, the present invention provides a self-draining hose. The hose
includes a flexible hose connected to an inlet end fitting and an outlet end
fitting and
defining a fluid passage through the flexible hose, the flexible hose
comprises an
elastomer material having a memory with a cross-sectional flat profile
defining a
collapsed position closing the fluid passage, the flexible hose being
expandable to an
expanded position opening the fluid passage; whereby, in use, upon
introduction of a
2
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
pressurized fluid at the inlet end fitting the flexible hose expands from said
collapsed
position to said expanded position to permit flow of the fluid through the
fluid passage
towards the outlet end fitting, whereby upon termination of the introduction
of the
pressurized fluid at the inlet end fitting the memory of the elastomer
material collapses
the flexible hose from said expanded position to said collapsed position
expelling the
fluid from the fluid passage.
In some embodiments, the flexible hose is made from a thermoplastic elastomer
material, such as a thermoplastic polyurethane material having a tensile
strength between
5,000 to 11,000 psi, has a Shore A durometer range between 75 and 95, and is
sufficiently stretchable to allow the fluid in the fluid passage to flow
around impediments
blocking the flow of the fluid through the fluid passage.
In some embodiments, the flexible hose is produced by extrusion through a
polished or plated dye to form the flexible hose having a cross-sectional flat
profile with
a surface smoothness selected to prevent adherence of bacteria or algae
thereon.
In some embodiments, the flexible hose and end fittings are composed of a NSF
approved material.
In some embodiments, the flexible hose has an internal diameter of at least
5/8
inches and a wall thickness of at least .045 inches.
In some embodiments, the flexible hose is transparent, and may include
phosphorescent additives or light bending additives.
In some embodiments, the flexible hose remains flexible up to -40 C.
In some embodiments, the inlet end fitting and/or the outlet end fitting are
sealing
secured to the flexible hose by a crimp-type ring clamp.
In some embodiments, the flexible hose and end fittings are fully recyclable.
In some embodiments, the flexible hose defines a plurality of apertures
extending
between the fluid passage and an exterior of the flexible hose. The apertures
may be
3
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
aligned linearly along a length of the flexible hose, and the outlet end
fitting may act as
end cap of the flexible hose.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a self-draining hose. The
hose
includes a flexible inner hose connected to an inlet end fitting and an outlet
end fitting
and defining a fluid passage through the inner hose, the inner hose comprising
an
elastomer material and having a collapsed position closing the fluid passage
and an
expanded position opening the fluid passage; a flexible outer hose disposed
about the
inner hose and being connected to the inlet end fitting and the outlet end
fitting, and
defining a sealed space disposed between the inner hose and the outer hose,
the space
having a predetermined initial pressure; whereby, in use, upon introduction of
a
pressurized fluid at the inlet end fitting at a pressure exceeding the
predetermined initial
pressure, the inner hose expands from said collapsed position to said expanded
position to
permit flow of the fluid through the fluid passage towards the outlet end
fitting, said
expanded position increasing the pressure in the space from said predetermined
initial
pressure, whereby upon termination of the introduction of the pressurized
fluid at the
inlet end fitting the increased pressure in said space collapses the inner
hose to said
collapsed position expelling the fluid from the fluid passage.
In some embodiments, the inner hose elastomer material has a memory with a
cross-sectional flat profile, whereby upon termination of the introduction of
the
pressurized fluid at the inlet end fitting the memory of the elastomer
material together
with the increased pressure in said space collapses the inner hose to said
collapsed
position expelling the fluid from the fluid passage.
In some embodiments, the inner hose is made from a thermoplastic elastomer
material, such as a thermoplastic polyurethane material having a tensile
strength between
5,000 to 11,000 psi and is sufficiently stretchable to allow fluid in the
fluid passage to
flow around impediments blocking the flow through the fluid passage, and the
outer hose
is made from a polyethylene elastomer material having a tensile strength
between 1,000
to 4,000 psi.
In some embodiments, the inner hose is produced by extrusion through a
polished
4
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
or plated dye to form the inner hose with the cross-section flat profile with
a surface
smoothness selected to prevent adherence of bacteria or algae thereon.
In some embodiments, the inner hose is composed of a NSF 61 approved
material.
In some embodiments, the inner hose has a wall thickness between .010 to .045
inches and the outer hose has a wall thickness between .020 inches to .075
inches.
In some embodiments, the inner hose and the outer hose are transparent, and
the
outer hose may include phosphorescent additives and/or light bending
additives.
In some embodiments, in the collapsed position the outer hose has a visually
soft
substantially oval cross-sectional profile, and in the expanded position the
outer hose has
a visually hard substantially round cross-sectional profile.
In some embodiments, the outer hose is made from a woven fire hose material
with an elastomeric interior coating, an elastomeric material, or a corrugated
hose
material.
In some embodiments, the outer hose is an extruded or molded elastomer
material
having memory with a cross-sectional flat profile.
In some embodiments, the outer hose is made from a polyolefin elastomer
material.
In some embodiments, the sealed space extends between the inlet end fitting
and
an outlet end fitting.
In some embodiments, the predetermined initial pressure of the space is at
least 5
psi.
In some embodiments, the self-draining hose includes an air valve in
communication with said space. The air valve may be provided in the inlet end
fitting
and/or the outlet end fitting, and may be a ball and spring assembly or an
elastomer
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
orifice to be used with a needle.
In some embodiments, the self-draining hose includes a plastic or metal wire
of
sufficient rigidity arranged in at least one of the outer hose and the space,
and the metal
wire may be used as a signal conductor.
In some embodiments, the self-draining hose remains flexible up to -40 C.
In some embodiments, the inlet end fitting and/or the outlet end fitting are
barbed
end fittings.
In some embodiments, the self-draining hose includes a bushing disposed about
the inner hose to secure the inner hose against an outer surface of the inlet
end fitting
and/or the outlet end fitting; and a circular clamp is applied about the
bushing to sealingly
secure the inner hose to the inlet end fitting and/or the outlet end fitting.
The self-
draining hose may also include a second circular clamp disposed about the
outer hose to
sealingly secure the outer hose against the outer surface of the inlet end
fitting and/or the
outlet end fitting.
In some embodiments, the self-draining hose includes a bushing disposed about
the inner hose to secure the inner hose against an outer surface of the inlet
end fitting
and/or the outlet end fitting; and a circular clamp is applied about the outer
hose over an
area of the bushing to sealingly secure the outer hose and the inner hose to
the inlet end
fitting and/or the outlet end fitting.
In some embodiments, the inner hose has a Shore A durometer range between 35
and 95 and the outer hose has a Shore A durometer range between 60 and 95.
In other embodiments of the invention, any of the aspects above can include
one
or more of the above features. One embodiment of the invention can provide all
of the
above features and advantages. These and other features will be more fully
understood by
reference to the following description and drawings, which are illustrative of
exemplary
embodiments of this invention.
6
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE SEVERAL VIEWS OF THE DRAWING
Reference may now be had to the following detailed description taken together
with the accompanying drawings in which:
Fig. 1 is a diagrammatic cross section view of a self draining hose in
accordance
with a first embodiment of the invention.
Fig. 2 is a diagrammatic cross section view of two self draining hoses in
accordance with Figure 1, showing the inner hose in an expanded and collapsed
position.
respectively.
Fig. 3 is a diagrammatic cross section view of a self draining hose in
accordance
with a second embodiment of the invention.
Fig. 4 is a diagrammatic illustration of an open end fitting for the self
draining
hoses shown in Figures 1 and 3.
Fig. 5 is a diagrammatic cross section view of a self draining hose in
accordance
with a third embodiment of the invention, showing the hose separately in empty
and full
states, respectively, and showing how the hose stretches to accommodate
residual ice in the
hose.
Fig. 6 is a diagrammatic illustration of a method for assembling a self
draining-
hose in accordance with the present invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
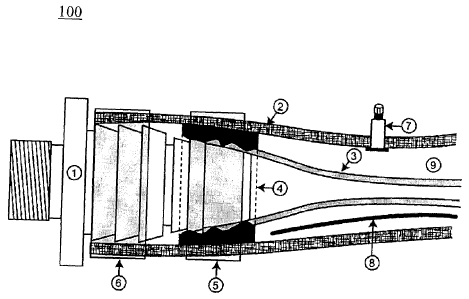
Reference may now be made to Figure 1 which illustrates a preferred embodiment
of a self-draining hose 100 in accordance with a first embodiment of the
present
invention.
The self-draining hose 100 includes a flexible inner hose 3, a flexible outer
hose
7
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
2, an inlet end fitting 1 and an outlet end fitting (not shown).
The inner hose 3 is connected to the inlet end fitting 1 and the outlet end
fitting
and defines a fluid passage through the inner hose 3. The inner hose 3 is made
from an
elastomer material, preferably a thermoplastic elastomer material molded or
extruded to
have a memory with a cross-sectional flat profile defining a collapsed
position (empty)
closing the fluid passage, and is expandable into an expanded position (full)
opening the
fluid passage as shown in Figure 2.
Most preferably the inner hose 3 is made from a thermoplastic polyurethane
material having a tensile strength between 5,000 to 11,000 psi and is produced
by
extrusion through a polished or plated dye to form the inner hose having a
flat profile
with a surface smoothness selected to prevent adherence of bacteria or algae
thereon.
The outer hose 2 is disposed about the inner hose 3 and is also connected to
the
inlet end fitting 1 and the outlet end fitting.
A substantially sealed space or air chamber 9 having a predetermined initial
pressure is disposed between the inner hose portion 3 and the outer hose
portion 2. The
space 9 preferably extends between the inlet end fitting 1 and an outlet end
fitting.
In use, upon introduction of a pressurized fluid at the inlet end fitting 1 at
a
pressure exceeding the predetermined initial pressure, the inner hose 3
expands from the
collapsed position to the expanded position to permit flow of the fluid
through the fluid
passage towards the outlet end fitting. This flow increases the pressure in
the space 9
from the predetermined initial pressure, and upon termination of the
introduction of the
pressurized fluid to the inlet end fitting 1 the memory of the elastomer
material of the
inner hose 3 together with the increased pressure in space 9 collapses the
inner hose 3 to
the collapsed position expelling the fluid from the fluid passage.
The self-draining hose 100 in accordance with this embodiment provides a hose-
within-a-hose system and may include a double-barbed end fitting that
maintains the air
seal in the space 9. Preferably the space holds a pressure of at least 5 psi
between the two
hoses. When pressurized fluid enters the inner hose 3, the inner hose 3
expands and
8
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
when there is no pumping or fluid pressure, the air pressure within the space
9 assists to
expels the fluid forcing it out the discharge end of the hose.
The outer hose 2 uses a material that allows for expansion unlike a rigid, or
semi-
rigid plastic pipe or rubber hose. The outer hose 2 may be made from a woven
fire hose
material with an elastomeric interior coating, an elastomeric material or a
corrugated hose
material.
Preferably the outer hose comprises a polyethylene elastomer material having a
tensile strength between 1,000 to 4,000 psi. This material remains flexible to
-40 C/F.
While the inner hose 3 and outer hose 2 material selection is dependent on the
intended
use of the hose and the required water pressure rating for example,
preferably, the inner
hose 2 has a wall thickness between .010 to .045 inches and the outer hose 2
has a wall
thickness between .020 inches to .075 inches.
The fire hose version provides a woven flat expandable outer hose 2, more
easily
allowing for visual inspection of the pre-charged air pressure in the space 9.
Unpressurized the hose 100 would appear flat. Partially pressurized the hose
100 would
appear semi-flat like an under inflated tire, and when pressurized to the
recommended 5
psi the hose 100 appears almost round and is soft to the touch. During
operation, with the
introduction of fluid pressure the outer hose 2 of the hose 100 becomes fully
round and
hard to the touch. The woven hose 2 allows for an increase of pre-charged air
pressure
above the normal 5 psi used in the prior rigid outer pipe or hose. Increased
air pressure
improves both the speed (i.e. time taken to discharge the fluid to prevent
freezing) as
well as delivering improved lift (every 1 psi of pressure = 2.31 feet of
lift).
The flat woven fire hose jacket has the ability to expand without the need for
an
expansion tank to prevent chatter or vibration at the discharge end which can
result in
damage and failure of the inner hose. An alternative to the air expansion tank
for longer
lengths of hose is the implementation of an air expansion sleeve about the
outer hose 2.
A smooth surface such as the coated fire hose or other thermoplastic
elastomers such as
polyolefin can be fitted with a larger thin-walled elastomer sleeve covering
an air access
hole located near the discharge end of the hose 100, and then secured and
clamped
9
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
thereto. The sleeve is further reinforced with a protective larger, rigid
sleeve which
controls the extent of inflation of the elastomer sleeve.
The self-draining hose 100 may be provided with an air valve 7 through the
outer
hose 2, which allows it to move when it is in contact with any obstacle making
it less
likely to be caught and damaged as compared to an air valve on a rigid pipe or
hose. For
example, the flat woven fire hose version (minus the air) is much more compact
and
lighter than rigid hose for installation as well as handling, shipping,
merchandising and
storing.
The woven fire hose version of the outer hose 2 will also take much higher
working pressures than the rigid, semi-rigid plastic pipe or rubber hose known
in the art.
This is particularly beneficial where large diameter hoses (4" and up) are
required. These
higher working pressures also help prevent kinking of the outer woven hose.
The hose 100 may also include a plastic or metal wire of sufficient rigidity
woven
into the fabric of an outer woven hose 2, and may include a plastic or metal
wire 8 of
sufficient structural rigidity placed between the inner hose portion 3 and the
outer hose
portion 2. The plastic or metal wire 8 placed loosely between the inner flat
hose 3 and
the outer woven hose 2, and/or woven into the fabric of the outer woven hose
prevents or
reduces kinking, or may be used to transmit electrical signals through the
hose, as for
example to connect to a hydraulic pump.
The inner hose 3 leaves a space 9 between the inner and outer hose 2. In order
to
fill this space and cushion the thin-walled inner hose 3 from damage by the
clamp force
that secures the inner hose 3 to the end fitting 1, a tight rubber-like
bushing 4 is placed
over the inner hose 3. Then a clamp 5 is applied directly over the bushing 4
to secure the
inner hose 3 to the end fitting 1. A second clamp 6 is applied to secure the
outer hose 2
on the end fitting 1.
Alternately, both clamps 5, 6 can be applied on the exterior of the outer hose
2,
one over the area where bushing 4 fills and cushions the space 9 between the
inner 3 and
outer hoses 2, and the second against the shoulder of the fitting 1
reinforcing the air seal
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
between the inner 3 and outer hoses 2, respectively. Applying two clamps to
the exterior
of the outer hose 2 better secures against air loss at a single potential
pivot point.
Figure 3 shows an alternative embodiment of a self-draining hose 200 in
accordance with the invention. As shown in Figure 3, the end fitting 10 may
incorporate
a point of air access 15 through the fitting 10. Preferably the fitting 10 is
constructed
from a thermoplastic material such as Acetal, or a NSF approved material like
nylon. In
order to pre-charge the space 18, the fitting 10 incorporates an air valve 16,
as for
example either a ball and spring assembly in the passageway or an elastomer
orifice to be
used with a needle (as in an inflatable soccer ball). Preferably, in this
arrangement the
clamping 13 of the inner hose 3 is done internally as shown in Figure 3 and a
second
clamp 14 is used to secure the outer hose 11 to the fitting 10.
An alternative to the woven outer hose version uses a corrugated hose
material,
such as 1-1/4" or 1-1/2" sump pump hose, providing a lower cost, non-kinking
operation
achieved without any pre-charged air aspect requiring an air valve, for uses
that require
little lift but need the hose to self-empty to minimize freezing. The inner
hose 12 may
also be made from an elastomer with a lower durometer and therefore more
easily opened
by low pressure. (e.g. 35 durometer is more elastic than 75 durometer). The
inner hose 12
can be made of a material with a durometer that matches the requirements of
the specific
low pressure application. The inner hose 12 may be installed and air-sealed,
using a
double-barbed end fittings 10, into a 1-1/4" or 1-1/2" corrugated style hose,
such as sump
pump hose. The corrugated outer jacket limits and supports the expansion of
the inner hose
12.
Low pressure pumps, such as sump pumps, deliver adequate pressure for easy
expansion of the inner hose during flow periods. As the water pressure expands
the
inner flat hose 12, from about 10 to 12 psi is developed in the air chamber 18
between
the inner hose 12 and the corrogated outer hose 11 which is more than ample to
discharge any water remaining in the inner hose 12 at the conclusion of
pumping.
The inner hose 12 can be extruded or molded using a thin-walled flat profile
that
promotes a more complete collapse of the inner hose when there is no fluid
pressure
11
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
expanding it. The inner hose 12 can be made of polyurethane or a similar high
tensile
strength (5,000 to 7,000 PSI) hose material with elastic qualities such as a
polyolefin
elastomer. The flat profile as shown for example in Figure 2 includes a half-
moon cross-
sectional profile having a concave surface folded in mating relationship on
top of the
opposing matching concave surface. This concavity relationship provides
additional
strength to the hose 12.
The inner hose 12 may be formed from a polyurethane or elastomeric material
and can be further strengthened through an orienting process that increases
its tensile
strength 3-fold, increasing the pressure rating for the hose.
The inner hose 12 and outer hose 11 may be made of a transparent material,
which allows for visual inspection of the conditions within the hoses and
allows sunlight
exposure along with dewatering to control bacteria growth and can be made with
a
material, such as polyurethane, that is NSF approved for potable drinking
water use. The
hoses 12, 11 may also include phosphorescent additives or light bending
additives to
increase the visibility of the inner hose 12 and outer hose 11.
Figure 4 illustrates and open end fitting 40 for the self-draining hose in
accordance with the present invention. To form the open end fitting 40, the
inner hose 12
is pulled through and back over a circular donut 42 and sandwiched between the
outer
circumference of the donut 42 and the outer hose 11. A clamp 44 is positioned
about the
outer hose 11 over the donut and a clamping force is applied to secure the
inner hose 12
between the donut 42 and the outer hose 11.
Figure 5 illustrates a further embodiment of a self-draining hose 300 in
accordance with the present invention. The self-draining hose 300 includes a
flexible
hose 22 connected to an inlet end fitting 30 and an outlet end fitting 20 and
defines a fluid
passage through the flexible hose 22. The flexible hose 22 is made from an
elastomer
material having a memory with a cross-sectional flat profile defining a
collapsed position
closing the fluid passage, and is expandable to an expanded position opening
the fluid
passage.
12
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
In use, upon introduction of a pressurized fluid at the inlet end fitting 30
the
flexible hose 22 expands (24) from the collapsed position to the expanded
position to
permit flow of the fluid through the fluid passage towards the outlet end
fitting 20. Upon
termination of the introduction of the pressurized fluid at the inlet end
fitting 30 the
memory of the elastomer material collapses the flexible hose 22 from the
expanded
position (24) to the collapsed position expelling the fluid from the fluid
passage.
The hose 22 provides similar discharge capabilities as the inner hoses 3 and
12 of
the hoses 100 and 200 described above when there is no fluid pressure
expanding the
hose 22. The discharge may be enhanced with the use of a vacuum breaker
installed at
the fluid source. The hose 22 is flexible to -40 C/F but is subject to climate
conditions
such as wind-chill and snow cover which influence minimum temperature at which
it will
operate. For example, -10 C/14 F is the recommended lowest temperature for
effective
operating with high wind-chill, however, with no wind or insulating snow
cover,
operating temperatures will be considerably lower.
Preferably, the flexible hose 22 is made from a thermoplastic elastomer
material,
such as a thermoplastic polyurethane material and has a tensile strength
between 5,000 to
11,000 psi with elastic qualities, such as a polyolefin elastomer, as for
example having a
Shore A durometer range between 75 and 95. It is to be understood that the
selection of
the elastomer material and wall thickness of the flexible hose 22 is such that
it is to be
sufficiently stretchable to allow the fluid in the fluid passage to flow
around impediments
blocking the flow of the fluid through the fluid passage. For a flexible hose
22 having an
internal diameter of 5/8 inches, the wall thickness of the flexible hose is
preferably at
least .045 inches.
The hose 22 uses its elastic qualities to stretch when fluid pressure
encounters
impediments 23, as for example ice formed in the fluid passage. Fluid pressure
expands
the hose 22(24) to allow flow around residual ice 23 in the fluid passage of
the hose
22(24), and the flow of fresh, comparatively warmer fluid will melt the
residual ice in the
hose 22(24).
In a preferred aspect, the flexible hose 22 may include an outlet end fitting
which
13
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
caps the end of the hose 22 and a plurality of apertures which extend between
the fluid
passage and an exterior of the flexible hose. The apertures may be aligned
linearly along
a length of the flexible hose 22 so that the hose 22 may be used fro example
as a sprinkler
garden hose. Preferably, the self-draining hose 300 is fully recyclable.
The flexible hose 22 most preferably is produced by extrusion using a thin-
walled
flat profile that promotes a more complete collapse of the hose 22 when there
is no fluid
pressure expanding it. Preferably the flexible hose 22 is extruded through a
polished or
plated dye to form the flexible hose 22 having the cross-sectional flat
profile with a
surface smoothness selected to prevent adherence of bacteria or algae thereon.
The
flexible hose and the inlet end fitting and the outlet end fitting may be
composed of a
NSF approved material so that the hose can be used to transport drinking water
without
adding toxins to the water.
The flexible hose 22 may be transparent and include phosphorescent additives
and/or light bending additives which enhance the visibility of the flexible
hose 22.
The inlet end fitting 30 and the outlet end fitting 20 may be sealing secured
to the
flexible hose by a crimp-type ring clamp in accordance with the steps
illustrated in Figure
as follows:
(a) Measure and cut required length of hose
(b) Fold hose to minimize width and slip a PEX ring over the end of the hose
(c) Hose may need to be stretched to accept fitting. Either immerse hose end
in hot water
or use stretcher tool as shown.
(d) Insert fitting, wiggling the hose from side to side, until hose end is
half the width of
the PEX ring from the fittings shoulder.
(e) Slide PEX ring over fitting as shown. If needed use closed crimping tool
to push
ring. Then position crimping tool over the ring at a 90 angle to the hose and
compress
securely.
14
CA 02870793 2019-10-17
WO 2013/155596
PCT/CA2013/000353
Repeat steps 2, 3, 4 and 5 for the other end of the hose.
To the extent that a patentee may act as its own lexicographer under
applicable
law, it is hereby further directed that all words appearing in the claims
section, except for
the above defined words, shall take on their ordinary, plain and accustomed
meanings (as
generally evidenced, inter alia, by dictionaries and/or technical lexicons),
and shall not be
considered to be specially defined in this specification. Notwithstanding this
limitation on
the inference of "special definitions," the specification may be used to
evidence the
appropriate, ordinary, plain and accustomed meanings (as generally evidenced,
inter alia,
by dictionaries and/or technical lexicons), in the situation where a word or
term used in
the claims has more than one pre-established meaning and the specification is
helpful in
choosing between the alternatives.
It will be understood that, although various features of the invention have
been
described with respect to one or another of the embodiments of the invention,
the various
features and embodiments of the invention may be combined or used in
conjunction with
other features and embodiments of the invention as described and illustrated
herein.
Although this disclosure has described and illustrated certain preferred
embodiments of the invention, it is to be understood that the invention is not
restricted
to these particular embodiments. Rather, the invention includes all
embodiments, which
are functional, electrical or mechanical equivalents of the specific
embodiments and
features that have been described and illustrated herein