Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
A TRANSACTION SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR USE WITH A MOBILE
DEVICE
CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
[0001]
This application claims priority from U.S. Provisional Patent
Application S/N 61/494,946 filed June 6, 2011 entitled "SYSTEM AND METHOD
FOR PERFORMING A SECURE TRANSACTION"; U.S. Provisional Patent
Application S/N 61/504,754 filed July 6, 2011 entitled "SYSTEM AND METHOD
FOR PERFORMING A SECURE TRANSACTION"; U.S. Provisional Patent
Application S/N 61/529,258 filed August 31, 2011 entitled "METHOD AND
APPARATUS FOR SECURE TRANSACTIONS WITH A MOBILE DEVICE"; and
U.S. Provisional Patent Application S/N 61/566,660 filed December 4, 2011
entitled
"SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SECURE TRANSACTION PROCESS VIA
MOBILE DEVICE", the entire contents of each of which are incorporated herein
by
reference.
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0002] The
present disclosure relates generally to the field of transaction
systems and in particular to a system and method for providing transaction
relevant
information in cooperation with a mobile device and a transaction server.
BACKGROUND ART
[0003]
Payments by credit or debit cards represent a large portion of consumer
spending. Historically, credit or debit cards were encoded with a magnetic
stripe,
which allows a transaction responsive to a transaction device which is
arranged to
read information encoded on the magnetic stripe, in a secured manner. The
device
reading the magnetic stripe is typically in communication with the credit card
issuer
via a transaction network, the credit card issuer ultimately approving the
transaction.
Credit or debit cards are unfortunately susceptible to theft which may be
unrealized by
the user for a significant period of time.
[0004] Advances in technology have led to the development of
contactless
smart cards, such as those defined under ISO/IEC 7810 and ISO/IEC 14443, also
known as Near Field Communication (NFC). Similar technology is available
meeting
other standards or protocols generally under the term radio frequency
identification
(RFID), with the range of RFID typically restricted to be of the same order as
that of
1
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
NFC. The term contactless element (CE) as used throughout this document refers
to
any short range communication device operating under any of NFC, RFID or other
short range communication standard with range on the same order as that of
NFC, and
typically require that the CE be juxtaposed with a reader. The use of
optically
readable codes are specifically included herein with the definition of a CE.
Such CE
smart cards may be used for transactions, however since they may be read by
any
reader within about 4 cm, they do not provide for increased security. As such,
CE
smart cards are typically only used for low value transactions, wherein a
small value
is pre-loaded on the CE smart card, and the small value is depreciated with
each
transaction until a limit is reached.
[0005] Mobile devices (MDs) are increasingly being used for financial
transactions due to their ubiquity, available screen and input devices. An MD
as used
herein includes any electronic MD used for personal functionalities such as
multimedia playing, data communication over a network or voice communication.
One embodiment of an MD is a mobile station, also known as a mobile
communication device, mobile phone, mobile telephone, hand phone, wireless
phone,
cell phone, cellular phone, cellular telephone, mobile handset or cell
telephone.
[0006]
With the development of IEEE 802.11, and the broad establishment of
the resultant wireless networks, various MDs have been developed which
communicate over available wireless networks in addition to cellular telephone
capabilities. Furthermore, various MDs have been developed with the ability to
access the Internet both over a wireless network and/or over a cellular
network.
[0007] The
ubiquitous MD, having an associated means for user identification
and charging expenses, presents an opportunity to utilize the MD as an
electronic
wallet. There are several known methods for providing a service or a product,
and in
particular payment for products or services other than phone usage or airtime,
by
using a mobile station.
[0008] CEs
in cooperation with an MD have been developed into two main
groups, devices which are connected to a controller of the MD, such as to the
MD's
CPU, and can communicate therewith, and devices which are not connected to the
MD's CPU. In the case of CEs connected to the MD's CPU one can find various
devices, such as NFC devices on SIM cards, also known as "SIM Contactless
Element" (SCE), external cards such as SD cards with NFC devices, SIM add-on
Contactless Elements (SCCE), and NFC devices found within the MD's hardware.
2
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
The above group of devices known as "embedded CE" (ECE) devices can be used in
the same manner as CE devices which are not connected to the MD's CPU for
applications where the CE reader communicates with the CE device directly and
the
communication doesn't rely on any action of the MD's CPU. It is to be noted
that in
the event that the CE comprises an optically readable code displayed on a
display of
the MD, the MD is inherently an ECE device.
[0009] The group of CEs which are not connected to an MD CPU may
include
NFC or RFID tags, stickers, key fobs, optically readable codes which may be
affixed
to the MD, without limitation. Such a CE, when secured in relation to the MD,
may
thus be utilized to provide an identification number read by a reader within
proximity
of the CE. In one embodiment, the CE includes identification information which
may be secured or installed and protected, the information generated by a
secured
element (SE).
[00010] An SE is defined herein as a tamper proof element arranged to
embed
applications with the required level of security and features. In further
detail, an SE is
an element wherein access to data or functions stored in the SE is controlled
by
security levels such that only authorized parties may access the data or
functions.
Thus, contents of the SE can not be copied, written to, or read from, without
a
predetermined security key, access to which is controlled. The term security
key is
particularly addressed in this application to keys as known in cryptography,
and is not
meant to be a physical, or mechanical key. Typically security is provided in
cooperation with one or more keys which are controlled by the SE issuer. The
SE
may be supplied as part of the CE, as part of the MD, or as an additional
element
which is removable form the MD. There is no limitation to the number of SEs on
an
MD, and in particular a plurality of SEs may coexist on a single MD. One of
the SE's
may be implemented on a single subscriber identity module (SIM) without
limitation.
[00011] As transaction systems have become more sophisticated and in
more
widespread use, the incidence of fraudulent transactions have also increased.
In
particular, both "phishing" and "man in the middle" attacks have been shown to
defeat many CE based security systems. In a phishing attack, a user is sent a
message
indicating that connection to a specific uniform resource locator (URL) is
required,
however the URL, while appearing to be a legitimate URL, is actually that of a
fraudulent server. The user may not recognize, or notice, the slight change in
URL,
3
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
whose actual address refers to a fraudulent server. In such a manner personal
information and passwords may be obtained from an unsuspecting user.
[00012] Man in the middle attacks are particularly useful against ECE
devices,
wherein the CE may be read by a fraudulent reader, and relayed to a remote
purchasing location without the user being aware.
[00013] A CE enabled MD may be further compromised by the ability of a
CE
reader enabled malfeasant. A malfeasant, coming into close proximity of the CE
enabled MD, may read any publicly available information from the CE and
further
write inappropriate instructions into any available unprotected memory
locations of
the CE.
[00014] CE enabled posters have recently become common, with the
poster
having embedded CE devices therein. A user with an ECE juxtaposes the CE with
an
embedded CE, which acts to generate a pointer on the MD to a target URL,
perhaps
offering a discount. Unfortunately, a legitimate embedded CE may be covered by
a
fraudulent embedded CE, or may be covered by a blocking material with an
adjacent
fraudulent CE attached, causing the MD to generate a pointer to a fraudulent
URL.
[00015] An additional difficulty arises as MDs become more
sophisticated. In
particular, malicious software such as key logger software may be
surreptitiously
added to an MD, thus allowing a malfeasant to obtain any personal information
number (PIN) information. Other malicious software may in fact take over the
MD,
and allow a malfeasant to control the MD and run any payment software.
[00016] Furthermore, as the use of MD based transactions increases, it
would
be preferably to improve the security and flexibility of MD based
transactions, which
is not fully supported by the prior art.
SUMMARY OF INVENTION
[00017] In view of the discussion provided above and other
considerations, the present disclosure provides methods and apparatus to
overcome some or all of the disadvantages of prior and present methods
of performing a secure transaction. Other new and useful advantages of
4
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
the present methods and apparatus will also be described herein and can
be appreciated by those skilled in the art.
[00018] Certain embodiments enable a transaction system
comprising: a mobile device comprising a display; a transaction server;
and a communication network arranged to provide communication
between the mobile device and the transaction server, wherein the mobile
device is arranged to transmit identification information to the transaction
server via the communication network, and wherein the transaction server
is arranged to: identify the mobile device responsive to the mobile device
transmitted identification information; associate the identified mobile
device with a particular access point; transmit, via the communication
network, transaction information to the mobile device, the transmitted
transaction information responsive to the associated particular access
point, wherein the mobile device is arranged to output onto the display
information responsive to the transmitted transaction information.
[00019] In one embodiment, the transaction server is arranged to
obtain location information regarding the mobile device, the association
of the identified mobile device with the particular access point responsive
to the obtained location information. In another embodiment, the
transaction server is in communication with an electronic wallet
functionality associated with the mobile device, and wherein the
transaction information is further responsive to the electronic wallet
functionality. In one further embodiment, the mobile device is further
provided with an input device, and wherein the mobile device is arranged
to: allow for modification of the transaction information responsive to the
input device; and transmit information regarding the modification to the
server.
[00020] In one embodiment, the particular access point is a web
server. In one further embodiment, the transaction system further
5
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
comprises: a user device arranged to provide at least some identification
information associated with the mobile device to the web server, wherein
the web server is arranged to transmit the user device provided
identification information to the transaction server, the transaction server
arranged to obtain an address of the mobile device responsive to the
transmitted user device provided identification information.
[00021] In another embodiment, the mobile device transmitted
identification information comprises a pseudo random number generated
responsive to a key. In one further embodiment, the mobile device is
further provided with an input device, and wherein the mobile device
transmitted identification information comprises a pseudo random
number generated responsive to a personal identification number entered
via the input device.
[00022] In one yet further embodiment, the mobile device comprises
a secure element arranged to: generate the pseudo random number
generated responsive to the key; and generate the pseudo random number
generated responsive to the personal identification number. In one yet
even further embodiment, the secure element further comprises a
quarantine functionality arranged to: read data via a communication
interface; quarantine the read data; and transmit the quarantined data to
the transaction server.
[00023] In one further embodiment, the mobile device transmitted
identification information further comprises an unencrypted readable
identifier. In another further embodiment, the transaction system further
comprises a secure device in communication with the mobile device,
wherein the pseudo random number generated responsive to the key is
generated by the secure device and transmitted to the mobile device via a
short range communication.
6
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
[00024] In
one embodiment, the transaction system further comprises
at least one of a loyalty platform and a coupons platform in
communication with the transaction server, wherein the transmitted
transaction information is further responsive to the at least one platform.
[00025] In one independent embodiment, a method of providing
transaction information is provided, the method comprising: transmitting
identification information from a mobile device to a transaction server;
identifying the mobile device responsive to the mobile device transmitted
identification information; associating the identified mobile device with a
particular access point; transmitting transaction information to the mobile
device, the transmitted transaction information responsive to the
associated particular access point; and outputting onto a display of the
mobile device information responsive to the transmitted transaction
information.
[00026] In one embodiment, the method further comprises: obtaining
location information regarding the mobile device, wherein the associating
the identified mobile device with the particular access point is responsive
to the obtained location information. In another embodiment, the
transmitted transaction information is further responsive to an electronic
wallet functionality. In one further embodiment, the method further
comprises: enabling modification of the transaction information
responsive to an input device of the mobile device; and transmitting
information regarding the modification to the transaction server.
[00027] In
one embodiment, the particular access point is a web
server. In one further embodiment, the method further comprises:
providing a user device arranged to provide at least some identification
information associated with the mobile device to the web server;
transmitting the user device provided identification information from the
web server to the transaction server; and obtaining an address of the
7
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
mobile device responsive to the transmitted user device provided
identification information.
[00028] In another embodiment, the method further comprises:
generating a first pseudo random number generated responsive to a key,
wherein the provided mobile device transmitted identification
information comprises the generated first pseudo random number. In one
further embodiment, the method further comprises: providing the mobile
device, wherein the provided mobile device is further provided with an
input device; and generating a second pseudo random number responsive
to a personal identification number entered via the input device, wherein
the mobile device transmitted identification information further
comprises the generated second pseudo random number.
[00029] In one yet further embodiment, the provided mobile device
comprises a secure element arranged to generate the first and second
pseudo random numbers. In one yet even further embodiment, the secure
element performs a method comprising: reading data via a
communication interface; quarantining the read data; and transmitting the
quarantined data to the transaction server.
[00030] In one further embodiment, the mobile device transmitted
identification information further comprises an unencrypted readable
identifier. In another further embodiment, the method further comprises
providing a secure device, wherein the first pseudo random number
generated responsive to the key is generated by the secure device, the
method further comprising transmitting the first pseudo random number
to the mobile device via a short range communication.
[00031] In one embodiment, the transmitted transaction information
is further responsive to one of a loyalty platform and a coupons platform.
[00032] Additional features and advantages of the invention will
become apparent from the following drawings and description.
8
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
[00033] For a better understanding of the invention and to show how
the same
may be carried into effect, reference will now be made, purely by way of
example, to
the accompanying drawings in which like numerals designate corresponding
elements
or sections throughout.
[00034] With specific reference now to the drawings in detail, it is
stressed that
the particulars shown are by way of example and for purposes of illustrative
discussion of the preferred embodiments of the present invention only, and are
presented in the cause of providing what is believed to be the most useful and
readily
understood description of the principles and conceptual aspects of the
invention. In
this regard, no attempt is made to show structural details of the invention in
more
detail than is necessary for a fundamental understanding of the invention, the
description taken with the drawings making apparent to those skilled in the
art how
the several forms of the invention may be embodied in practice. In the
accompanying
drawings:
[00035] FIG. lA illustrates a high level block diagram of the
advantageous
partitioning of certain embodiments;
[00036] FIG. 1B illustrates a high level architecture of an MD, in
cooperation
with a CE and in communication with a check point;
[00037] FIG. 2 illustrates a transaction flow utilizing the various
domains of
FIG. lA in cooperation with the architecture of FIG. 1B;
[00038] FIG. 3 illustrates a transaction flow utilizing the various
domains of
FIG. lA in the absence of an access point poster;
[00039] FIG. 4 illustrates a high level block diagram of an embodiment of
the
arrangement of FIG. 1A, wherein the check point is replaced by a web server;
[00040] FIG. 5 illustrates a transaction flow utilizing the various
domains of
FIG. 4;
[00041] FIG. 6A illustrates a transaction flow utilizing the various
domains of
FIG. 1A;
[00042] FIG. 6B illustrates the transaction flow of FIG. 6A, where the
customer
MD peripheral identification information transmitted to the TS does not match
information stored on the TS, or when the communication link does not allow
for
automatic detection of a customer MD;
9
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
[00043] FIG. 6C further details certain portions of the transaction
flow of FIG.
6A wherein an authorization number with auto-approval limit has been received
by
the TS;
[00044] FIG. 6D illustrates the transaction flow of FIG. 6C, when the
transaction amount is greater than an amount authorized by the issuer;
[00045] FIG. 6E illustrates the transaction flow of FIG. 6D, where TS
requests
approval from a customer MD after receiving an authorization request message
from a
check point;
[00046] FIG. 7 illustrates a high level block diagram of advantageous
partitioning of certain embodiments allowing for web out of band login (00BL);
[00047] FIG. 8 illustrates a transaction flow utilizing the various
domains of
FIG. 7;
[00048] FIG. 9 illustrates a high level block diagram of advantageous
partitioning of certain embodiments, where the financial settlement
functionality is
based on an existing financial back bone; and
[00049] FIG. 10 illustrates a transaction flow utilizing the various
domains of
FIG. 9.
DESCRIPTION OF EMBODIMENTS
[00050] Before explaining at least one embodiment in detail, it is to
be
understood that the invention is not limited in its application to the details
of
construction and the arrangement of the components set forth in the following
description or illustrated in the drawings. The invention is applicable to
other
embodiments or of being practiced or carried out in various ways. Also, it is
to be
understood that the phraseology and terminology employed herein is for the
purpose
of description and should not be regarded as limiting. In particular, the term
connected as used herein is not meant to be limited to a direct connection and
includes
communication of any sort, and allows for intermediary devices or components
without limitation.
[00051] In the following description, the term mobile device (MD)
includes
any electronic mobile device used for personal functionalities such as
multimedia
playing, data communication over a network or voice communication, including
but
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
not limited to a mobile station (MS). For clarity, the term MS refers to any
mobile
communication device, mobile phone, mobile telephone, hand phone, wireless
phone,
cell phone, cellular phone, cellular telephone, cell telephone, or other
electronic
device used for mobile voice or data communication over a network of base
stations.
Although in the following description, communication is described in certain
embodiments using an example of cellular communication, particularly, global
system
for mobile communication (GSM), it will be understood that the scope of the
invention is not limited in this respect, and that the communication method
used may
be based on any suitable communication protocol, including without limitation,
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS), IEEE 802.11x, IEEE
802.16x and CDMA. The terms "decrypted" and "decoded" are used interchangeably
and have the same meaning throughout this document.
[00052] FIG. lA illustrates a high level block diagram of an
advantageous
partitioning of certain embodiments of a transaction system arranged to
provide
improved security for transactions in cooperation with a mobile device. In
particular,
an acquirers domain 100, also known as merchants domain 100; an
interoperability
domain 110; and an issuer's domain 120, also known as customer's domain 120
are
provided. Advantageously, security information is compartmentalized to prevent
fraud.
[00053] Acquirer's domain 100 comprises an acquirer 150, comprising a
service provider database (SPDB), containing information about the service
providers
associated therewith; an access point 160; a service provider 170; and an
access point
poster or tag 180. Access point poster or tag 180 is also known as a check
point
poster. Access point 160 is also known as a check point 160. While a single
acquirer,
or a database of a single acquirer 150, access point 160, service provider 170
and
access point poster/tag 180 are illustrated this is not meant to be limiting
in any way
and a plurality of any or all of acquirers 150, or acquirer databases, access
points 160,
service providers 170 and access point posters/tags 180 may be provided
without
exceeding the scope. The SPDB of acquirer 150 is in communication with access
point 160 with a controlled communication path denoted acquirer's band 190.
Access
point 160 may be a cash register, check out location, controlled point or
entry, without
exceeding the scope. Access point 160 may be further implemented as a web
server
as will be described further below, without exceeding the scope.
11
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
[00054]
Interoperability domain 110 comprises: a transaction server (TS) 210;
a financial settlement functionality 220; and a plurality of databases/
functionality
servers, wherein particularly illustrated are a customer wallet functionality
231,
customer credential 232, location based services 233, loyalty platform 234,
coupons
platform 235 and other databases 236. Financial settlement functionality 220,
represented by a cloud, may comprise any, or all of, a brand's functionality,
a hub
functionality and an automated clearinghouse functionality, without exceeding
the
scope. TS 210 is in communication with each of financial settlement
functionality
220, customer wallet functionality 231, customer credential 232, location
based
services 233, loyalty platform 234, coupons platform 235 and other databases
236.
TS 210 is further in communication with the SPDB of acquirer 150. Customer
wallet
functionality may be implemented within TS 210 without exceeding the scope,
and
may particularly implement an electronic wallet as known to those skilled in
the art.
Advantageously, as will be described below, the electronic wallet is provided
herein
with added functionality.
[00055]
Issuer's domain 120 comprises customer's payment resources 250, i.e.
issuers of payment options and devices, and a MD 260 comprising a CE 270 and
running an application 265 on a processor thereof, application 265 stored on a
memory associated with MD 260. MD 260 comprises a display device 267 for
displaying information to a user, and an input device 268 for receiving input
from a
user. Customer's payment resources 250 represents various card issuers, both
debit
and credit, as well as prepaid cards and e-wallets, without limitation.
Customer's
payment resources 250 are in communication with MD 260 via an issuer's
controlled
communication band 280. MD 260, particularly CE 270, is in NFC or RFID
communication with access point 160, which in one embodiment represents a
provider access device (PAD). Customer's payment resources are further in
communication with TS 210. MD 260 is further in communication with TS 210,
over
a network, denoted pre-band 295, which in embodiment is implemented via a
cellular
network, without limitation. Optionally, as will be described below, an
additional
secure device 275 is provided, having an input device 278, such as a keypad,
thereon.
[00056] FIG.
1B illustrates a high level architecture of MD 260, having
embedded thereon CE 270, wherein CE 270 is in communication with access point
160. In particular, MD 260 comprises an MD application processor 300; an MD
input
device 268 and CE 270. MD application processor 300 comprises a PRN generator
12
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
305 and is in communication with CE 270 as will be described in further detail
below.
Access point 160 comprises an NFC communication interface 360.
[00057] CE
270 comprises a secured element (SE) 315; a control circuitry 372;
a secured key pad 379; and an NFC communication interface 360. SE 315
comprises:
a secured ID1 storage functionality 320; a secured ID2 PRN generator
functionally
330; a secured ID3 PRN generator functionality 340; one or more secured IDn
storage
functionalities 351; and a secured keys storage 350. Secured ID2 PRN generator
functionality 330 comprises an NFC associated ID2 PRN generator functionality
332
and an MD associated ID2 PRN generator functionality 336, which may be
implemented as two functions of a single PRN generator functionality. Secured
ID3
storage functionality 340 comprises an NFC associated ID3 PRN generator
functionality 342 and an MD associated ID3 PRN generator functionality 346
which
may be implemented as two functions of a single PRN generator functionality.
Each
of NFC associated ID2 PRN generator functionality 332, MD associated ID2 PRN
generator functionality 336, NFC associated ID3 PRN generator functionality
342 and
MD associated ID3 PRN generator functionality 346 is arranged to generate a
pseudo-
random number responsive to one or more keys securely stored on secured keys
storage 350. NFC communication interface 360 of MD 260 is in communication
with
MD processor 300 and is further arranged to be in near field communication
with an
external NFC communication interface 360, which in one embodiment is embedded
within access point 160. Each secured IDn storage functionality 351 is
arranged to
transmit a respective ID to NFC communication interface 360 of MD 260
responsive
to a request received by the respective IDn storage functionality 351 from MD
application processor 300. Advantageously, the respective IDn is not
transmitted to
MD application processor 300. Secured key pad 379 is in communication with
control circuitry 372, with ID3 PRN generator functionality 342 and with MD
associated ID3 PRN generator functionality 346. Control circuitry 372 is in
communication with SE 315 and NFC communication interface 360.
[00058] NFC
communication interface 360 of access point 160 communicates
with NFC communication interface 360 of access point 160 when the various NFC
communication interfaces 360 are juxtaposed with each other within a pre-
determined
range. In one embodiment the pre-determined range is about 4 cm.
[00059] In
operation, and as will be described further below, secured ID1
storage functionality 320 is arranged to respond to identification requests
from either
13
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
MD application processor 300 or from access point 160 received via NFC
communication interface 360 of MD 260, with identification information,
denoted
herein as ID1. Such identification information preferably comprises an address
of
MD 260, such as an MSISDN, or other identifier which is translatable by a
transaction
server, such as TS 210 to an address, i.e. MD 260 is addressable by TS 210
over
network 295 responsive to ID1. Secured ID1 storage functionality 320 may be
read
by MD application processor 300.
[00060] NFC associated ID2 PRN generator functionality 332 is arranged
to be
in communication with NFC communication interface 360, and is responsive to a
request for a machine generated PRN, denoted MPRN1, to generate a PRN
responsive
to one or more keys stored on keys storage 350 and respond with a generated
MPRN1. Advantageously, and as described above, the keys stored on keys storage
350 are preregistered with TS 210, and are decipherable by TS 210 to verify
the
authenticity of MPRN1. It is to be noted that MD application processor 300 is
preferably unable to obtain MPRN1 from NFC associated ID2 PRN generator
functionality 332. Optionally, NFC associated ID2 PRN generator functionality
332
may be disabled responsive to MD application processor 300 so as to prevent
release
of MPRN1 without authorization.
[00061] MD associated ID2 PRN generator functionality 336 is arranged
to be
in communication with MD application processor 300, and is responsive to a
request
for a machine generated PRN, denoted MPRN2, to generate a PRN responsive to
one
or more keys stored on keys storage 350 and respond with a generated MPRN2.
Advantageously, and as described above, the keys stored on keys storage 350
are
preregistered with TS 210, and are decipherable by TS 210 to verify the
authenticity
of MPRN2. Preferably MPRN2 is distinguished from MPRN1 and may be encoded
with different keys stored on keys storage 350 without exceeding the scope.
[00062] NFC associated ID3 PRN generator functionality 342 is arranged
to be
in communication with NFC communication interface 360, and is responsive to a
personal information number (PIN) provided from MD application processor 300
to
generate a PRN responsive to one or more keys stored on keys storage 350, and
to
respond with a generated PIN supported PRN, denoted PPRN1. In one embodiment,
the PIN is first verified by SE 315, in one embodiment by utilizing a PIN
verification
value (PVV) calculated by control circuitry 372. Advantageously, and as
described
above, the keys stored on keys storage 350 are preregistered with TS 210, and
are
14
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
decipherable by TS 210 to verify the authenticity of PPRN1. It is to be noted
that MD
application processor 300 is preferably unable to obtain PPRN1 from NFC
associated
ID3 PRN generator functionality 342. It is to be noted that in the absence of
a PIN
provided from MD application processor 300, NFC associated ID3 PRN generator
functionality 342 does not generate PPRN1. Alternatively, an ID2 is provided
to
access point 160 which has at least field indicative that no PIN was supplied
for
generation of the 13.
[00063] The term PIN as used herein is not meant to be limited to a
number or
string of number, and an alphanumeric string may be utilized without
limitation,
including non-alphabetic characters and spaces, without exceeding the scope.
[00064] MD associated ID3 PRN generator functionality 346 is arranged
to be
in communication with MD application processor 300, and is responsive to a
request
for a PIN supported PRN, denoted PPRN2, to generate a PRN responsive to one or
more keys stored on keys storage 350, and to a PIN received from MD
application
processor 300 to respond with a generated PPRN2. Advantageously, and as
described
above, the keys stored on keys storage 350 are preregistered with TS 210, and
are
decipherable by TS 210 to verify the authenticity of PPRN2. Preferably PPRN2
is
distinguished from PPRN1 and may be encoded with different keys stored on keys
storage 350 without exceeding the scope. There is no requirement that each of
PPRN1, PPRN2, MMPRN1 and MMRPN2 be supported in each embodiment, and in
particular in certain embodiment PPRN2 and MMPRN2, and the associated
generating functionalities are not supplied.
[00065] MD application processor 300 is optionally further provided
with an
internal PRN (IPRN) generator 305, which is preferably utilized in the absence
of CE
270 or in the event that the various PRN generator functionalities 332, 336,
342 and
346 are not able to be loaded onto SE 315 as will be described further below.
The
generated PRN of internal PRN generator 305 is denoted herein as IPRN.
[00066] Secured keypad 379 prevents key logging theft by malicious
software
loaded onto MD application processor 300 since it is not involved in other
data entry
operations, and thus is preferably immune to key logging software. In one
embodiment, secured keypad 379 is internally hardware encoded to output a
resultant
PIN to secured ID3 storage functionality 340 without utilizing software
susceptible to
key logging.
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
[00067] The above has been described in an embodiment wherein various
PRN
generators are provided within SE 315. In an alternative optional embodiment,
as
shown in FIG. 1A, a separate secure device 275 is provided, with an input
device 278,
such as a keypad. Secure device 275 comprises an NFC communication interface
360
(not shown) arranged to communication with NFC communication interface 360 of
MD 260 when juxtaposed therewith. Secure device 275 is juxtaposed with NFC
communication interface 360 of MD 260, a PIN is entered onto entry device 278,
and
responsive thereto PPRN1 is generated and transmitted to MD 260 via the
embedded
NFC communication interface 360 and NFC communication interface 360 of MD
260. MD 260 is arranged to receive the generated PPRN1 and forward PPRN1 as if
it
was internally generated. Such a separate key system adds additional security,
since
PPRN1 is not physically generated within MD 260. Alternatively, a PIN entered
on
secure device 275 activates PRN generator functionality 342 of SE 315. In such
an
embodiment PPRN1 is generated and transmitted to access point 160 when CE 270
is
juxtaposed with access point 160.
[00068]
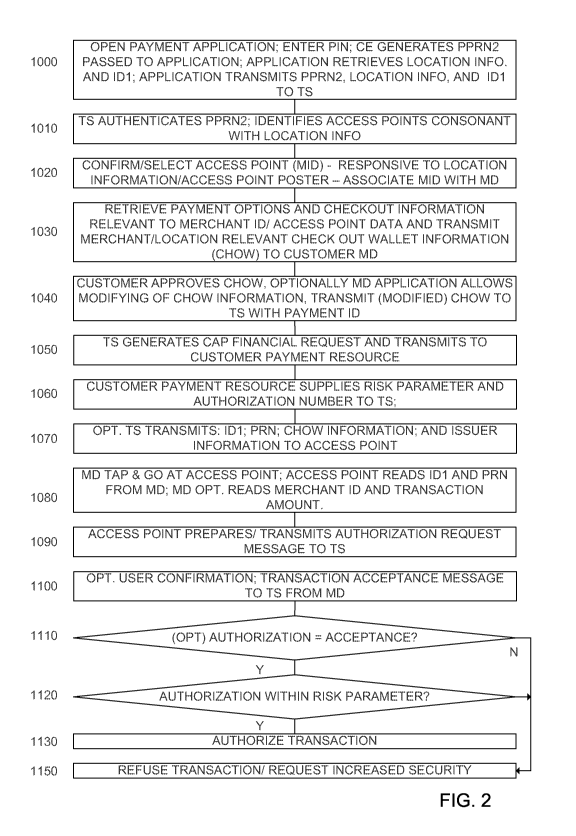
FIG. 2 illustrates a transaction flow utilizing the various domains of
FIG. lA in cooperation with the architecture of FIG. 1B, FIGs. 1A, 1B and 2
being
described herein together for ease of understanding. Advantageously, TS 210 is
arranged to provide MD 260 with relevant checkout information, while
maintaining
security and fraud control.
[00069] In
stage 1000, a user opens payment application 265 running on a
processor of MD 260 and enters a PIN which has been preregistered with TS 210.
Payment application 265, in cooperation with SE 315, and in particular in
cooperation
with MD associated ID3 PRN generator functionality 346, responds to a request
from
MD application processor 300 responsive to payment application 265 with PPRN2
responsive to a PRN key which was initially loaded at registration, and
preferably
stored in secured keys location 350. MD 260 further retrieves from secured ID1
storage functionality 320 ID1. Application 265 further retrieves location
information,
as will be described below, and transmits to TS 210 the generated PPRN2,
location
information and ID1. As described above, ID1 preferably represents a readable
ID of
CE 270. Location information may be generated by one or both of on board GPS
electronics, or responsive to base station transmission calculations. The
readable ID
of CE 270 received from secured ID1 storage functionality 320 may be directly
transferred, or an encoded identifier may be utilized without exceeding the
scope.
16
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
The readable ID of CE 270 is denoted ID1, for ease of identification, and in
one
embodiment is a readable identifier of MD 260.
[00070] In stage 1010, responsive to the received transmission of
stage 1000,
TS 210 authenticates the received PPRN2 responsive to keys stored thereon. In
the
event that TS 210 fails to authenticate the received message, no further
action is taken
(not shown), or alternately a fail message is returned to application 265. TS
210
further identifies the access points 160 in geographic proximity to MD 260
responsive
to the received location information, i.e. TS 210 determines the registered
access
points 160 whose locations are consonant with the location of MD 260. The term
consonant with, as used in the context of location information, and as used
herein,
does not require an exact location match, but instead is indicative of a
location match
within a pre-determined range, which preferably takes into account location
determining errors, the amount of which errors may be further location
dependent.
[00071] In stage 1020 a merchant ID (MID) is identified and associated
with
MD 260. In the event that only a single access point 160 registered with TS
210
exhibits a location consonant with the received location information, TS 210
transmits
the name of the identified access point 160 to MD 260 for confirmation. In the
event
that a plurality of access points 160 are consonant with the received location
information, for example in a mall, a list of registered access points 160
with
consonant location information is transmitted to MD 260, and the appropriate
merchant, i.e. the appropriate access point 160, wherein MD 260 is currently
located
and for which the user of MD 260 wishes to consummate a transaction is
selected
responsive to a user gesture on input device 268 of MD 260 and the selection
is
transmitted to TS 210 as the merchant ID.
[00072] Alternatively, an access point poster 180, arranged to transmit a
merchant ID is provided, and MD 260 reads the merchant ID from access point
poster
180 by juxtaposing MD 260 with access point poster 180. Advantageously, in
place
of a pointer of the prior art, MD 260 is arranged to transmit the read MID
from access
point poster 180 to TS 210 thus providing location information for MD 260 and
other
useful information regarding the merchant specific ID to TS 210.
[00073] Alternatively, access point poster 180 may be arranged to read
ID1 of
CE 270 via the respective NFC communication interfaces 360. In such an
embodiment, access point poster 180 transmits read identifier ID1 of CE 270 to
TS
210 along with self identifying information, thus providing TS 210 with
location
17
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
based information regarding MD 260 since the location of access point poster
180 is
pre-registered with TS 210. In summary, an MID is obtained responsive to the
juxtaposition of MD 260 with a particular area on access point poster 180, or
responsive to location information of stage 1000, or responsive to a user
input from a
provided list of merchants, which are selected responsive to location
information.
Advantageously, the MID obtained represents an intended transaction location/
merchant for the user of MD 260, and is now associated with MD 260 until a
transaction is completed, a different merchant ID is obtained, or a
predetermined time
period has expired.
[00074] In stage 1030, the obtained MID of stage 1020 associated with MD
260 is transmitted to the various databases 231 ¨ 236, to determine if any
promotions,
loyalty benefits, pre-purchase coupons, or gift certificates, without
limitation, for the
associated obtained MID of stage 1020 are relevant to MD 260. Similarly,
information regarding payment options for the identified access point 160 is
determined, and the relevance to the customer's wallet is retrieved from
customer
wallet functionality 231. For example, only certain payment options may be
accepted
by identified access point 160, and a nexus of accepted payment options and
available
payment options from customer wallet functionality 231 is determined. Any
relevant
coupons retrieved from customer wallet functionality 231 and/or coupons
platform
235 may be optionally validated by the issuer, if required. Check Out Wallet
(CHOW) information is generated by TS 210 and transmitted to MD 260, the CHOW
information being advantageously defined in relation to the obtained MID and
is thus
location relevant, exhibiting only offers, discounts or payment options
relevant to the
merchant which has been associated with MD 260 as described in stage 1020.
[00075] In optional stage 1040, MD 260 may modify the received CHOW
information, responsive to a user gesture in relation to input device 268 of
MD 260,
particularly selecting from among various payment options and/or agreeing to
utilize
one or more benefits offered. Any CHOW based selections, as modified, are
transmitted to TS 210, or alternatively only modifications are transmitted to
TS 210.
It is to be noted that all of the above mentioned communication between MD 260
and
TS 210 has preferably been accomplished exclusively along pre-band 295 which
is
secured, in one embodiment by a secure sockets layer (SSL). The CHOW
information preferably includes an identifier of the desired payment method of
the
user of MD 260, shown as a payment ID.
18
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
[00076] In
stage 1050, TS 210, responsive to the received CHOW based
selections, or simple CHOW approval, of stage 1040, generates a cap financial
transaction request from an issuer within customer's payment resources 250.
The cap
financial request preferably comprises the initially generated PPRN2, the
selected
payment ID and an identifier of access point 160, and ID1. Alternatively, a
newly
generated authenticated PRN is utilized in place of PPRN2.
[00077] In
stage 1060, the issuer, or other payment resource, calculates a risk
parameter, and generates an authorization number. The risk parameter typically
comprises a financial transaction limit, below which no further authorization
is
required. In one embodiment, the risk information is generated responsive to
the
received PRN or PPRN2. This communication is preferably performed solely
between TS 210 and customer payment resources 250.
[00078] In stage 1070, responsive to the received authorization
number, TS 210
optionally generates a message for transmission to access point 160 associated
with
MD 260 of stage 1020 comprising: ID1, the modified CHOW information and an
identifier of the issuer.
[00079] In
stage 1080, after the user associated with MD 260 has determined
the ultimate desired transaction, and preferably a PIN has been entered via
input
device 268 of MD 260, CE 270 is juxtaposed with access point 160, in a process
known as Tap and Go, which limits the juxtaposed time to a predetermined
minimum.
Access point 160 reads ID1 and PPRN1 from CE 270 and MD 260 optionally reads
the MID of access point 160 and the transaction amount. In particular, access
point
160 optionally calculates the amount left to be paid of the transaction after
deducting
any CHOW based credits. PPRN1 is read responsive to the input PIN. In another
embodiment MPRN1 is read and thus a PIN is not required to be entered via
input
device 268 into MD 260.
[00080] In
stage 1090, responsive to the read ID1, access point 160 prepares an
authorization request message to conclude the transaction, the authorization
request
message being transmitted to TS 210. The authorization request message is
generated
preferably comprising: ID1 read during the Tap and Go procedure of stage 1080;
PPRN1 read during the tap and go procedure of stage 1080; the MID for access
point
160; any loyalty, coupons, gift card or other CHOW based discounts; the
amount; and
a transaction identifier. As described above, the authorization request
message
generated by access point 160 is transmitted by access point 160 via
provider's band
19
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
190 to acquirer 150, and acquirer 150 transmits an authorization request
message to
TS 210. In one embodiment, the loyalty and coupon information is transmitted
directly to TS 210 from access point 160.
[00081] In optional stage 1100, MD 260, particularly application 265,
presents
a confirmation message for acceptance by a user, preferably requiring input of
a code,
such as PIN for authorization. Responsive to an acceptance gesture, and/or
code
input, via input device 268, MD 260 transmits a transaction acceptance message
to TS
210 comprising ID1, PPRN2, read access point 160 identifier, and the amount.
Optionally, a payment identifier is further transmitted to MD 260 in the Tap
and Go
procedure of stage 1080 and provided as part of the transaction acceptance
message.
In one embodiment, a subset of the above information is transmitted so as not
to
exceed the time limit of the Tap and Go.
[00082] TS 210 thus receives an authorization request message
generated by
access point 160 in stage 1090 and optionally a transaction acceptance message
generated by MD 260 in stage 1100. In optional stage 1110, the elements of the
received authorization request message of stage 1090 are compared with the
transaction acceptance message match of stage 1100, and in the event that they
match,
i.e. the messages ID1, access point 160 identifier, payment ID and amount
match, and
PPRN1 points to the same device address as PPRN2, in stage 1120 TS 210
compares
the transaction amount of the authorization request message of state 1090 with
the
received risk parameter of stage 1060.
[00083] As described above, PPRN1 and PPRN2 are generated as part of
SE
315 from a set of keys stored on secured keys storage 350. Deciphering of
PPRN1
and PPRN2 is advantageously accomplished by TS 210 responsive to key
information, and reveals a singular identifier, or a pair of identifiers which
are stored
as being equivalent on a database accessible by TS 210. In the event that in
stage
1110 the messages do not match, an error condition is flagged and the
transaction is
not completed as shown in stage 1150.
[00084] In the event that in stage 1120 the transaction amount is less
than that
approved by the received risk information, in stage 1130 the transaction is
authorized
by TS 210. The authorization number received from the issuer by TS 210 in
stage
1060 is transmitted to access point 160 via acquirer 150 through acquirer band
190. A
transaction confirmation message is similarly transmitted by TS 210 to
customer
payment resources 250, e.g. to an issuer, comprising: ID1; the PRN agreed
between
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
TS 210 and the issuer; and the amount for settlement. Optionally, one of PPRN1
and
PPRN2 is further transmitted to the issuer confirming that a PIN has been
received as
part of the transaction. Any gift, coupon or loyalty information is similarly
transmitted to the respective database/ server. A transaction approval message
is
transmitted to MD 260 by TS 210, optionally the transaction approval message
includes further local relevant information, such as promotions by adjacent
vendors.
[00085] In one embodiment however, as shown, in the event that in
stage 1120
the transaction amount is greater than that approved by the received risk
information,
or in the event that in optional stage 1110 elements of the received
authorization
request message of stage 1090 do not math the transaction acceptance message
match
of stage 1100 in stage 1150 the transaction is refused or increased security
is required
as will be described further below in relation to FIG. 3.
[00086]
Thus, by the utilization of the server based architecture described
herein, location based promotions and transaction completion may be
advantageously
accomplished, providing relevant check out information. In particular, the
check out
information is relevant to the actual merchant associated with MD 260 and for
which
a transaction is to be pending.
[00087]
FIG. 3 illustrates a transaction flow utilizing the various domains of
FIG. lA in the absence of access point poster 180, and further requiring an
additional
authorization in the event that the amount exceeds the cap amount determined
by the
received risk information. Thus, the transaction flow is in all respects
similar to that
of FIG. 2, described above, except as detailed herein.
[00088]
Stage 2000 ¨ 2020 are thus in all respects identical with stages 1000 ¨
1020 described above, respectively, however in the absence of access point
poster
180, location information is in one embodiment supplied responsive to one or
both of
MD 260 GPS electronics or responsive to base station transmission
calculations.
Thus, TS 210 obtains location information either from the cellular network
handling
MD 260 or from MD 260, without limitation. In yet another embodiment, where
GPS
functionality is not available in MD 260, application 265 obtains location
information
from the network and transmits the obtained location information to TS 210.
Thus, in
stage 2010 - 2020, in the event that a singular access point 160 cannot be
determined,
a list of possible registered suppliers, i.e. access points 160 whose location
are
consonant with the obtained location of MD 260 are transmitted to MD 260 by TS
21
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
210, and a selected supplier is returned to TS 210 by MD 260 and the MID of
the
selected access point 160 is associated with MD 260.
[00089] Stage 2030 represents stages 1030 ¨ 1100 of FIG. 2, and the
interest of
brevity will not be further described.
[00090] Stage 2040 is in all respects identical to stage 1110 of FIG. 2. In
the
event that in stage 2040 the messages do not match, an error condition is
flagged and
the transaction is not completed as shown in stage 2070. In the event that in
stage
2040 the messages do match, in stage 2050 TS 210 compares the transaction
amount
of the authorization request message of state 1090 with the received risk
parameter of
stage 1060. In the event that the transaction amount is less than that
approved by the
received risk information, in stage 2060 the transaction is authorized by TS
210.
[00091] In the event that in stage 2040 the transaction amount is
greater than
that approved by the received risk information, in on embodiment (not shown)
TS 210
requests authorization from the issuer. In another embodiment, as illustrated
by stage
2110, a message is transmitted from TS 210 to MD 260, requesting that the user
of
MD 260 log into the issuer/user domain. In stage 2120 MD 260 logs into the
directed
issuer web page and transmits ID1, PPRN2, the payment ID and the transaction
amount. In stage 2130 the issuer web page may authorize the transaction, but
typically will require some identification, such as a PIN related to the
specific chosen
payment ID or other restricted information to reduce the risk. Upon receipt of
the
additional information, and in the event that the issuer agrees to authorize
the
transaction, an authorization message, including: an authorization number;
ID1; the
PRN agreed between TS 210 and the issuer; the payment ID; and the transaction
amount, is transmitted directly to TS 210. Transaction approval is finalized
as
described above in relation to FIG. 2.
[00092] FIG. 4 illustrates a high level block diagram of an embodiment
of the
arrangement of FIG. 1A, wherein access point 160 is replaced by a web server
410.
An additional customer device 425, such as a computer is further provided,
customer
device 425 in communication with web server 410 over a network 450 such as the
Internet, network 450 also denoted cookie/ UID band 450. MD 260 is in
communication with TS 210 via a network, such as a cellular network, denoted
password band 460. All other elements in FIG. 4 are substantially identical
with those
of FIG. 1A, and thus in the interest of brevity will not be further detailed.
FIG. 5
22
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
illustrates a transaction flow utilizing the various domains of FIG. 4, FIGs.
4 and 5
being described herein together for ease of understanding.
[00093] In
stage 3000, customer device 425 is desirous of purchasing a product
or service from web based service provider 170 and initiates a checkout
request. In
stage 3010, web based service provider 170 provides customer device 425 with a
checkout page and preferably further requests that the customer open payment
application 265 on MD 260. In stage 3020 customer device 425 selects checkout
in
cooperation with TS 210 from among the various options, and web based service
provider 170 transmits a transaction ID, amount and merchant ID to web server
410.
Customer device 425 preferably provides a user ID stored on a cookie to web
server
410. In one embodiment, the user ID is ID1 of MD 260, which has been sent to
customer device 425 when registered with TS 210. In one embodiment, the user
ID is
the MSISDN of MD 260 and is thus easily entered via an input device of user
device
425.
[00094] In stage 3030, web server 410 transmits a message to TS 210, via
acquirer 150, including the obtained user ID, web server or MID, a transaction
ID
generated by web server 410 and the transaction amount.
[00095] In stage 3040, responsive to the opening of application 265 of
stage
3010, MD 260 initiates a payment transaction function of application 265, and
selects
web based transactions. A PIN or other code preregistered with TS 210 is
entered
into MD 260 to enable the generation of PPRN2 as described below.
[00096] In stage 3050, MD 260 creates and transmits a message to TS
210
comprising ID1, i.e. a readable identifier of CE 270; PPRN2; and location
information. In one embodiment, location information is generated responsive
to one
or both of on board GPS electronics and base station transmission
calculations. In
one embodiment, location information is optional.
[00097] In
stage 3060, TS 210 matches the received message from MD 260 of
stage 3050 with the received transaction message from web server 410 of stage
3030
responsive to consonance of ID1 with the user ID. In one embodiment, as
described
above, the provided user ID is the same as ID1 and in another embodiment the
provided user ID is uniquely cross referenced with ID1, i.e. with the readable
identifier of CE 270 in a database accessible by TS 270 such as customer
credentials
DB 232. MD 260 is therefore associated with web server 410 for the purposes of
a
transaction.
23
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
[00098] In stage 3070 TS 210 retrieves data from the various databases
231 ¨
236 to determine if any promotions, loyalty benefits, pre-purchase coupons, or
gift
certificates, without limitation, are relevant to the customer in relation to
web server
410.
[00099] Similarly, information regarding payment options for the web server
410 is determined, and the relevance to the customer's wallet is retrieved
from
customer wallet functionality 231. Any relevant coupons retrieved from coupons
platform 235 may be optionally validated by the issuer. CHOW information is
generated by TS 210 and transmitted to MD 260, and information responsive
thereto
is displayed on display device 267. Advantageously, the CHOW information is
relevant to web server 410, exhibiting only offers, discounts or payment
options
relevant to MD 260 in relation to web server 410 and/or web service provider
170 and
any associated links. In one embodiment, a subset of the CHOW information is
transmitted to, and displayed on, customer device 425.
[000100] In optional stage 3080, a user of MD 260 may modify the received
CHOW, particularly selecting from among various payment options and/or
agreeing
to utilize one or more benefits offered, via a user gesture in relation to
input device
268 of MD 260. The CHOW further comprises the payment amount information as
initially received from web server 410. Information regarding any CHOW based
selections are transmitted to TS 210 in cooperation with a payment ID.
[000101] In stage 3090, TS 210 prepares and transmits a CHOW responsive
message to web server 410 comprising the payment ID received from MD 260,
PPRN2 generated by MD 260, ID1 of MD 260, or a code translatable thereto, and
any
discount information such as loyalty, coupons and gift card information.
[000102] In stage 3100, web server 410, responsive to the received message
from TS 210 of stage 3090 determines a payment balance for web based service
provider 170, and obtains acknowledgement/ approval therefrom. In stage 3110,
web
server 410, responsive to the received acknowledgement/approval transmits an
authorization request with a net amount to TS 210.
[000103] In stage 3120 TS 210 generates a financial transaction request
from an
issuer within customer's payment resources 1350, responsive to the payment ID.
The
financial transaction request preferably comprises the above mentioned ID1,
the
initially generated PPRN2, the selected means of payment ID, the MID and the
amount.
24
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
[000104] In
stage 3130 the issuer, or other payment resource, calculates a risk
parameter, and if the transaction amount is less than a predetermined risk
value
generates an authorization number in stage 3140.
[000105] In
the event that the transaction amount is in excess of the
predetermined risk value, in stage 3150 TS 210 communicates with MD 260 to
direct
a user of MD 260 to log onto the issuer/customer domain so as to obtain
authorization. MD 260 logs into the directed issuer web page and transmits
ID1, the
PPRN2, the means of payment ID and the transaction amount. In stage 3160 the
issuer web page may authorize the transaction, but typically will require some
identification, such as a PIN or other restricted information to reduce the
risk. Upon
receipt of the additional information, and in the event that the issuer agrees
to
authorize the transaction, an authorization message including an authorization
number, ID1, PPRN2, the payment ID and the transaction amount is transmitted
directly to TS 210.
[000106] In stage 3170, the authorization number received by TS 210 is
transmitted to web server 410 via acquirer 150 through acquirers band 190. Any
gift,
coupon or loyalty information is similarly transmitted to the respective
database/
server. A transaction approval message is transmitted to MD 260 by TS 210,
optionally including further local relevant information, such as promotions by
adjacent vendors responsive to the initial location information, or other
related web
servers 410.
[000107] In
the event that in stage 3140 the issuer has generated an authorization
number, stage 3170 is similarly performed.
[000108]
FIG. 6A illustrates a transaction flow utilizing the various domains of
FIG. 1A, wherein TS 310 acts as a remote firewall for MD 260 in relation to
access
point poster 180.
[000109] In
stage 4000 a user opens payment application 265 on MD 260 and
MD 260 communicates with TS 210. In one embodiment, MD 260 communicates
with TS 210 via a wireless network utilizing General Packet Radio Service
(GPRS)
and in another embodiment via a wireless network utilizing an IEEE 802.11
standard,
such as WiFi via pre-band 295 or password band 460 of FIGs. 1A, 4,
respectively.
MD 260 transmits to TS 210 information, including: ID1, or a code translatable
thereto; MD peripherals identification information stored on a cookie, such as
the
International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) of MD 260, the International
Mobile
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
Equipment Identity (IMEI) of MD 260 and/or the Bluetooth ID of MD 260;
location
information which may be generated by one or both of on board GPS electronics,
or
responsive to base station transmission calculations; and optionally an IP
header
tagging message, in the event the communication between MD 260 and TS 210 is
via
GPRS.
[000110] In
stage 4010, in the event ID1 and the MD peripherals identification
information matches information stored on TS 210, TS 210 optionally transmits
a
personalized confirmation message (PCM) which has been pre-registered with TS
210
and a request for a PIN to MD 260. The customer enters a PIN and preferably,
for
each section of the PIN entered, a portion of the PCM is displayed on MD 260,
thus
aiding as anti-phishing detection. In the event the user of MD 260 does not
recognize
the portion of the PCM being displayed, the user is thus made aware that a
phishing
attack is taking place and can stop entering the PIN. After completion of
entering the
PIN, the PIN is transmitted to TS 210.
[000111] In stage
4020, TS 210 transmits to MD 260 a request to select an
access point 160 from a list, or to juxtapose MD 260 with access point poster
180 so
that NFC communication interface 360 of MD 260 is enabled to read an
identifier of
access point 160 from access point poster 180.
[000112] In
stage 4030, in the event that MD 260 is juxtaposed with access point
poster 180, also known as "tapping", merchant information such as identifier
of
access point 160 is received by MD 260 via near field communication. Since
access
point poster 180 is easy, simple and widely open to malicious attacks, in
stage 4040
the received merchant information is quarantined by MD application 265, i.e.
not read
but only transferred as is, and transmitted to TS 210 which acts as a remote
fire wall
for MD 260.
[000113] In
stage 4050 TS 210 opens the quarantined read information and
checks for malicious content. If no malicious content is present, in stage
4060 TS 210
retrieves the relevant merchant information of access point 160 and associates
MD
260 with the MID responsive to the merchant information. In the event
malicious
content is found, TS 210 acts to block any transaction or infection.
[000114] In stage 4060, TS 210 retrieves from customer wallet
functionality 231
information relevant to the merchant of access point 160 in relation to MD 260
such
as payment means available to MD 260 which are accepted by access point 160.
TS
210 transmits the merchant information to the various databases 232 ¨ 236 to
26
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
determine if any promotions, loyalty benefits, pre-purchase coupons, or gift
certificates, without limitation, are relevant to the current MD 260
condition, i.e.
preparation to engage in commerce with access point 160, and validate current
information stored in the customer wallet. Any relevant coupons retrieved from
customer wallet functionality 231 and/or coupons platform 235 may be
optionally
validated by the issuer. CHOW information is generated by TS 210 and
transmitted
to MD 260, the CHOW information being advantageously defined in relation to
the
defined access point 160 of stage 4030 and is thus relevant, exhibiting only
offers,
discounts or payment options relevant to the current merchant MD 260 is
associated
with. Additionally, a One Time Transaction Number (OTTN) is transmitted to MD
260, the OTTN generated uniquely for the present transaction.
[000115] In
stage 4070, responsive to an input gesture in relation to input device
268 of MD 260, an issuer is selected from the CHOW selection of stage 4060. In
one
embodiment, the customer can modify the received CHOW information. In stage
4080 MD 260 transmits the issuer ID, the OTTN and the modified CHOW
information to TS 210. Alternately, only information regarding selections made
is
transmitted. In stage 4090, TS 210 transmits to the selected issuer the ID1 of
stage
4000, the OTTN, the MID and payment ID, such as a transaction number. In stage
4100 the issuer calculates a risk parameter for the customer and optionally an
authorization number and transmits them to TS 210. Various failure modes, such
as
the transaction amount exceeding the risk exist, however these may be handled
as
described above without exceeding the scope.
[000116] FIG.
6B illustrates the transaction flow similar to that of FIG. 6A,
where the MD 260 peripheral identification information transmitted to TS 210
by MD
260 does not match information stored on TS 210; or when communication between
MD 260 and TS 210 does not allow automatic detection of MD 260 and the
customer
MD peripheral identification information was not transmitted on a cookie. Such
a
communication liffl( is exemplified by WiFi, however this is not meant to be
limiting
in any way.
[000117] In stage 4500 responsive to a user gesture in relation to input
device
268 payment application 265 is initiated on MD 260 and responsive thereto MD
260
communicates with TS 210. As indicated above, complete information is however
not successfully transferred.
27
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
[000118] In stage 4510, a message is transmitted from TS 210 to MD 260,
preferably by SMS, in one embodiment requesting a background authorization
from
MD 260, i.e. an automatic authorization without user input. In one embodiment,
the
message comprises an ID number. In another embodiment, where the communication
between MD 260 and TS 210 is by GPRS, the MD ID number is transmitted via an
IP
header tagging message.
[000119] In stage 4520, a response is received from MD 260, including
the
missing information. Stage 4510 ¨ 4520 may also be used to improve the
security
level even in the event that full information is initially transferred.
[000120] In stage 4530, stages 4010 ¨ 4100 as described above are
performed.
[000121] FIG. 6C illustrates a transaction flow for the embodiments of
FIGs. 6A
¨6B, further detailing the transaction flow of stage 4100, wherein an
authorization
number with auto-approval limit has been received by TS 210.
[000122] In stage 5000, TS 210 optionally transmits to access point 160
ID1 of
MD 260, the issuer ID and the optionally modified CHOW information. In stage
5010, MD 260 is juxtaposed with access point 160, to initiate a Tap and Go
procedure, i.e. reading by each of the respective NFC interfaces 360. ID1 and
optionally the OTTN are transmitted to access point 160 by MD 260 via the
respective NFC interfaces 360. Access point 160 optionally transmits to MD 260
the
MID of access point 160 and the transaction amount, if applicable. Optionally,
MD
application 265 generates and outputs on display device 267 of MD 260 a
message
including the MID and the transaction amount and requests authorization.
Further
optionally, responsive to a customer's acknowledgement via a user gesture in
cooperation with input device 268 of MD 260, MD 260 transmits to TS 210 ID1,
the
OTTN, the MID, the payment ID and the transaction amount variously as read in
stage 5010.
[000123] In stage 5020, in the event that TS 210 has not transmitted
ID1 of MD
260 to access point 160, as well as the issuer ID and the optionally modified
CHOW
information, access point 160 transmits to TS 210 an information request
message and
TS 210 responds with the ID1 of MD 260, the generated OTTN, the optionally
modified CHOW information and the issuer ID. In stage 5030, responsive to the
received information, access point 160 transmits an authorization request
message to
TS 210. In one embodiment, the authorization request message is accompanied
with:
28
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
ID1; the OTTN; updated loyalty, coupons and gift information relevant to MD
260;
the payment ID; and the transaction amount due.
[000124] In stage 5040, TS 210 compares the received data from access
point
160 to the optionally received data from MD 260. In the event that the
received data
from both of access point 160 and MD 260 match, in stage 5050 TS 210 compares
the
amount due to the risk information received from the issuer. In the event that
in stage
5050 the amount due is within a cap amount determined by the risk information,
in
stage 5060 TS 210 transmits the authorization received from the issuer to
access point
160. Additionally, TS 210 transmits to the issuer ID1, the OTTN and the
transaction
amount due. In addition, TS 210 transmits to the various databases 231 ¨ 236
the
updated loyalty, gift and coupon information. Preferably, the customer wallet
stored
on customer wallet functionality 231 is then updated by TS 210. In stage 5070,
TS
210 transmits to MD 260 a transaction approval message and preferably useful
local
information, such as the location of other merchants.
[000125] In the event that in stage 5040 the received data from both of
access
point 160 and MD 260 does not match, or in the event that in stage 5050 the
amount
due exceeds the cap amount determined by the risk information, in stage 5070
the
transaction fails.
[000126] FIG. 6D illustrates the transaction flow of FIG. 6C, in the
event that
the transaction amount is greater than the amount authorized by the issuer,
however
without immediately implementing stage 5070. In stage 5100, in the event that
in
stage 5050 the amount due exceeds the cap amount determined by the risk
information, TS 210 transmits to MD 260 a message stating that issuer
authorization
is necessary.
[000127] In stage 5110, MD 260 connects to the issuer via customer band 280
and transmits the relevant information, i.e. ID1, the OTTN, the payment ID and
the
transaction amount. In stage 5120, the issuer requests from MD 260 to enter a
PIN or
other secure ID information. In stage 5130, responsive to entered relevant
information, the issuer transmits to TS 210 an authorization number.
[000128] FIG. 6E illustrates the transaction flow of FIG. 6D, in the event
that
TS 210 requests approval from MD 260 after receiving an authorization request
message from access point 160. In stage 5500, TS 210 transmits to MD 260 the
OTTN, the merchant ID, the payment ID and the transaction amount. In stage
5510,
MD 260 replies with the received information approval, responsive to a user
input. In
29
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
stage 5520, the transaction amount is compared to an amount automatically
approved
by the issuer, as described above in relation to the transaction flows of
FIGs. 6C and
6D, and in the interest of brevity not further described.
[000129] FIG. 7 illustrates a high level block diagram of advantageous
partitioning of certain embodiments allowing for web out of band login (00BL).
In
particular, a service provider domain 500; an interoperability domain 510; and
a
customer domain 520 are provided. Advantageously, security information is
compartmentalized to prevent fraud.
[000130]
Service provider domain 500 comprises a service provider web server
530, which as will be understood is a particular embodiment of access point
160 as
described above. Interoperability domain 510 comprises a TS 210 and a customer
credential database 532, in communication with each other. Customer domain 520
comprises: a customer device 540, illustrated without limitation as a portable
computer; and an MD 260, comprising a CE 270. MD 260 has loaded thereon an
application 265 run on a processor of MD 260, and optionally stored on a
memory
portion of MD 260. Customer device 540 is in communication with service
provider
web server 530 over a wireless network, such as the Internet, which is denoted
cookie/
username band 550. MD 260 is in communication with TS 210 over a wireless
network, such as a cellular network, which is denoted customer band 580. MD
260 is
in communication with service provider web server 530 over a wireless network,
such
as the Internet, which is denoted password band 590. TS 210 is in
communication
with service provider web server 530 over a wireless network, such as the
Internet,
which is denoted service provider band 530.
[000131]
FIG. 8 illustrates a transaction flow utilizing the various domains of
FIG. 7, the operation of the figures being described together. In stage 6000,
a
customer using customer device 540 communicates with service provider web
server
530 by entering a web site. In stage 6010, service provider web server 530,
opens a
security login page. In one embodiment the security login page is opened
responsive
to a lack of cookie information of customer device 540. In one embodiment, the
security login page exhibits a quick 00BL logo 545, i.e. notifies the user of
customer
device 540 via a display device of customer device 540 that login is to be
completed
through MD 260. In stage 6020, a username is entered in the displayed login
page via
an input device of the customer device 540. After validating the entered
username,
service provider web server 530 requests from TS 210 to arrange an 00BL for
the
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
customer including customer ID and service provider information. Service
provider
web server 530 further outputs a display on the display device of customer
device 540
to proceed with login via MD 260.
[000132] In stage 6030, responsive to the instructions displayed on
customer
device 540, application 265 on MD 260 is opened, and responsive to a user
gesture to
input device 268 of MD 260, including the entering of a PIN, application 265
requests
ID1 from secured ID1 storage functionality of CE 270 and PPRN2 from CE 270 as
described above in relation to FIG. 1B. Application 265 further communicates
with
TS 210 over customer band 580 and transmits ID1 and PPRN2 retrieved from CE
270
to TS 210.
[000133] In stage 6040 TS 210 authenticates the received PPRN2
responsive to
information stored on customer credentials database 532 and then requests
login
information from MD 260, such as a password, by supplying to application 265
of
MD 260 the URL of service provider web server 530. TS 210 additionally
transmits
the received ID1 and PPRN2 to service provider web server 530. MD 260 is thus
associated with service provider web server 530, at least for a login process
transaction.
[000134] In stage 6050, application 265, responsive to a user input
gesture
authorizing connection with the URL of stage 6040, communicates with service
provider web server 530, utilizing the received URL, and supplies login
information
to provider web server 530. In particular, the login information includes ID1,
PPRN2,
a password and location information. Other information can be included as
requested
by the service provider. In stage 6060 service provider web server 530
validates the
password, ID1 and PPRN2 responsive to the received information transmitted in
stage
6040. In stage 6070, upon validation, service provider web server 530 opens a
secured web page on customer device 540 via cookie/username band 550,
transmits a
login approval message to TS 210 via service provider band 560 and optionally
transmits a login approval message to MD 260 via password band 590.
[000135] The above described login procedure thus provides increased
security
when customer device 540 is located in an unsecured location, such as an
Internet
cafe.
[000136] FIG. 9 illustrates a high level block diagram of advantageous
partitioning of certain embodiments is in all respects similar to the
partitioning of
FIG. 1A, with the exception that: acquirers SPDB 150 is in communication with
31
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
customer's payment resources 250 via financial settlement functionality 220;
and
access point 160 is in communication with TS 210 over a network 195, denoted
CHOW band.
[000137] FIG. 10 illustrates a transaction flow utilizing the various
domains of
FIG. 9, the operation of the figures being described together. In stage 6500,
application 265 on MD 260 is initiated, and a PIN which has been preregistered
with
TS 210 is entered responsive to a user gesture towards input device 268 of MD
260.
Application 265 requests ID1 from secured ID1 storage functionality of CE 270
and
PPRN2 from CE 270 as described above in relation to FIG. 1B. As described
above,
PPRN2 is generated responsive to the received PIN and further responsive to a
PRN
key which was initially loaded at registration, and preferably stored in
secured keys
location 350 of FIG. 1B. There is no requirement that both ID1 and PPRN2 be
retrieved, and in another embodiment only PPRN2 is retrieved from CE 270.
Application 265 further transmits to TS 210 the optionally retrieved ID1 and
the
retrieved generated PPRN2 and location information. Location information may
be
generated by one or both of on board GPS electronics, or responsive to base
station
transmission calculations. ID1 may be directly transferred, or an encoded
identifier
may be utilized without exceeding the scope.
[000138] In stage 6510 TS 210 authenticates the received PPRN2
responsive to
keys stored thereon, such as on customer credentials DB 232, and further
identifies all
access points 160 registered with TS 210 in geographic proximity to MD 260
responsive to the transmitted location information of stage 6510. In
particular, in the
event that only a single access point 160 registered with TS 210 exhibits a
location
consonant with the received location information transmitted in stage 6500, TS
210
transmits the name of the identified access point 160 to MD 260 for
confirmation. In
the event that a plurality of access points 160 are consonant with the
received location
information, for example in a mall, a list of registered access points 160
with
consonant location information is transmitted to MD 260, and the appropriate
access
point 160 with which MD 260 is to be associated for a transaction is selected
responsive in stage 6520 to a user gesture in cooperation with input device
268 of MD
260. The selected access point 160 is defined by an MID.
[000139] Alternatively, as illustrated in FIG. 9, an access point
poster or tag 180,
which transmits an MID is provided, and MD 260 reads the MID by juxtaposing MD
260 with access point poster or tag 180. Preferably, MD 260 transmits the read
32
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
merchant ID to TS 210 thus providing location information for MD 260, and
particularly information regarding the particular access point 160 with which
MD 260
is to be associated for a transaction. Other information may be transferred as
well. In
one particular embodiment, location information for the particular access
point 160 is
compared with the received location information for MD 260, and if not
consonant,
i.e. not geographically feasible, any transaction is blocked.
[000140] In
stage 6530, the MID with which MD 260 is to be associated for a
transaction is transmitted to the various databases 231 ¨ 236, to determine if
any
promotions, loyalty benefits, pre-purchase coupons, or gift certificates,
without
limitation, are relevant to the particular MID for the particular MD 260.
Similarly,
information regarding payment options for the particular MID is determined,
and the
relevance to the customer's wallet is retrieved from customer wallet
functionality 231.
Any relevant coupons retrieved from customer wallet functionality 231 and/or
coupons platform 235 may be optionally validated by the issuer. CHOW
information
is generated by TS 210 and transmitted to MD 260, the CHOW information being
advantageously defined in relation to the particular access point 160 and is
thus
location relevant, exhibiting only offers, discounts or payment options
relevant to the
particular access point 160 with which MD 260 has indicated is to be
associated for a
transaction.
[000141] In optional stage 6540, a user of MD 260 may modify the received
CHOW, particularly selecting from among various payment options and/or
agreeing
to utilize one or more benefits offered responsive to a user gesture in
cooperation with
input device 268 of MD 260. Any CHOW based selections are transmitted to TS
210,
as a modified CHOW or as information regarding selections made. It is to be
noted
that all of the above mentioned communication has been accomplished between TS
210 and MD 260 exclusively along pre-band 295 which is secured, in one
embodiment by a secure sockets layer (SSL). The CHOW information preferably
includes an identifier of the desired payment method of the user of MD 260,
denoted
as payment ID.
[000142] In stage 6560, TS 210, responsive to the received CHOW based
selections, or simple CHOW approval, of stage 6550, generates a cap financial
transaction request from an issuer within customer's payment resources 250.
The cap
financial request preferably comprises the above mentioned ID1, the initially
generated PPRN2, the selected payment ID and an identifier of the particular
selected
33
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
access point 160, i.e. the merchant ID. Alternatively, a newly generated
authenticated
PRN is utilized in place of PPRN2.
[000143] In stage 6560, the issuer, or other payment resource,
calculates a risk
parameter, generates an authorization number. The risk parameter typically
comprises a financial transaction limit, below which no further authorization
is
required. In one embodiment, the risk information is generated responsive to
the
received PRN. Optionally, the risk information is transmitted to TS 210.
[000144] In stage 6570, once the user associated with MD 260 has
determined
the precise desired transaction, CE 270 of MD 260 is juxtaposed with access
point
160, i.e. in a Tap and Go process. Access point 160 reads an ID of MD 260. In
one
embodiment the read ID is a Track 2 ID registered with an issuer, as know in
the prior
art. In another embodiment the read ID is an ID preregistered with financial
settlement functionality 220. In yet another embodiment, the ID comprises the
MSISDN of MD 260. Optionally, the read ID is ID1 as described above.
[000145] In stage 6580, responsive to the read ID of stage 6580, access
point
160 prepares a CHOW request message comprising the read ID of stage 6580 and
the
merchant ID and transmits to TS 210 the CHOW request message. In optional
stage
6590, responsive to the request of stage 6580, TS 210 transmits to access
point 160
the generated CHOW information and the received ID.
[000146] In stage 6600, responsive to the received ID and CHOW information,
access point 160 prepares an authorization request message to conclude the
transaction for transmission to the issuer. In the embodiment where the ID is
an
issuer registered Track 2 ID, the authorization request message is transmitted
to the
issuer via acquirers SPDB 150 and financial settlement functionality 220. The
authorization request message is generated comprising: the ID read during the
Tap
and Go procedure; the merchant ID for access point 160 and a transaction
identifier.
[000147] In stage 6610, the issuer compares the amount included in the
transaction identifier with the risk parameter generated above, and if the
amount is
less than the risk parameter, in stage 6620 the above generated authorization
number
is transmitted to access point 160 via financial settlement functionality 220
and
acquirers SPDB 150 to complete the transaction. Additionally, the
authorization
number is transmitted TS 210.
[000148] In stage 6630, any gift, coupon or loyalty information is
transmitted to
the respective database/ server by TS 210. A transaction approval message is
34
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940
PCT/1L2012/050199
transmitted to MD 260 by TS 210, optionally including further local relevant
information, such as promotions by adjacent vendors.
[000149] In the event that in stage 6610 the transaction amount is
greater than
the generated risk parameter, in stage 6640 the issuer notifies TS 210, and TS
210
transmits to MD 260 an issuer authorization request message. Specifically, a
message
is transmitted from TS 210 to MD 260 requesting that MD 260 log into the
issuer/user
domain.
[000150] In stage 6650 MD 260 logs into the directed issuer web page.
The
issuer web page may authorize the transaction, but typically will require some
identification, such as a PIN or electronic signature. In one embodiment, the
required
identification is responsive to the particular payment ID. Upon receipt of the
identification, and in the event that the issuer agrees to authorize the
transaction, as
described above in relation to stage 6620 - 6640.
[000151] It is appreciated that certain features of the invention,
which are, for
clarity, described in the context of separate embodiments, may also be
provided in
combination in a single embodiment. Conversely, various features of the
invention
which are, for brevity, described in the context of a single embodiment, may
also be
provided separately or in any suitable sub-combination.
[000152] Unless otherwise defined, all technical and scientific terms
used herein
have the same meanings as are commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in
the
art to which this invention belongs. Although methods similar or equivalent to
those
described herein can be used in the practice or testing of the present
invention,
suitable methods are described herein.
[000153] All publications, patent applications, patents, and other
references
mentioned herein are incorporated by reference in their entirety. In case of
conflict,
the patent specification, including definitions, will prevail. In addition,
the materials,
methods, and examples are illustrative only and not intended to be limiting.
[000154] The terms "include", "comprise" and "have" and their
conjugates as
used herein mean "including but not necessarily limited to". The term
"connected" is
not limited to a direct connection, and connection via intermediary devices is
specifically included.
[000155] It will be appreciated by persons skilled in the art that the
present
invention is not limited to what has been particularly shown and described
hereinabove. Rather the scope of the present invention is defined by the
appended
CA 02875445 2014-12-02
WO 2012/168940 PCT/1L2012/050199
claims and includes both combinations and sub-combinations of the various
features
described hereinabove as well as variations and modifications thereof, which
would
occur to persons skilled in the art upon reading the foregoing description.
36