Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02882845 2015-02-23
WO 2014/099785
PCT/US2013/075393
REINFORCED PLASTIC CONTAINERS
CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATION
This application claims priority to United States Application No.
13/720,569, filed December 19, 2012, which is hereby incorporated by reference
in its
entirety.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
This invention relates generally to the field of plastic containers, and
more particularly to plastic containers that require reinforcement against
deflection as
a result of internal volumetric changes or the weight of the contents of the
container.
2. Description of the Related Technology
Plastic containers such as those that are manufactured using the
extrusion blow molding process need to possess the requisite strength to limit
sidewall
and bottom deflection to stay within predetermined tolerances in response to
forces
that are applied during the filling process and during handling within the
supply chain
and by the consumer. Hot fill type plastic containers typically include vacuum
panel
areas having vacuum panels specifically designed to accommodate deflection as
a
result of the volumetric expansion and contraction that occurs during the
filling
process. However, it is desirable to minimize deflection in sidewall and
bottom
portion areas of a hot fill container other than in the vacuum panels in order
to
preserve the structural integrity of the container.
The bottom portion of a plastic container also needs to process
sufficient strength to resist deformation as a result of pressurization
changes within
the container and from the forces that are applied by the weight of the
container
contents. In hot fill type containers, it is also important for the bottom
portion to have
sufficient rigidity so that vacuum uptake is directed mainly to the vacuum
panels that
are designed for such purposes.
In certain types of plastic containers, such as those that are
manufactured using the stretch reheat blow molding process, a certain amount
of
reinforcement is inherently provided by the concave shape of the bottom
portion.
1
CA 02882845 2015-02-23
WO 2014/099785
PCT/US2013/075393
Concavity can also be designed into the bottom portion of an extrusion blow
molded
plastic container, but this sacrifices space efficiency and increases material
costs. The
extrusion blow molding process permits the fabrication of the container that
has a
substantially flat bottom. Extrusion blow molded containers that have a
substantially
rectangular profile when viewed in transverse cross-section have been
manufactured
with corrugated substantially flat bottoms for use in limiting the deflection
of the
bottom of the container as a result of the weight of solid materials within
the
container. However, to the inventor's knowledge no such bottoms have been used
when the container that is substantially round when viewed in transverse cross-
section, or in hot fill applications.
A need exists to provide a plastic container that effectively directs
vacuum uptake to the intended portions of the container, and that limits
deflection of
the bottom portion as a result of pressurization changes within the container
and the
weight of the container contents.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
Accordingly, it is an object of the invention to provide a plastic
container that effectively directs vacuum uptake to the intended portions of
the
container, and that limits deflection of the bottom portion as a result of
pressurization
changes within the container and the weight of the container contents.
In order to achieve the above and other objects of the invention, a hot
fill type plastic container according to a first aspect of the invention
includes a finish
portion defining an opening, a bottom portion and a main body portion having a
vacuum panel area with at least one vacuum panel defined therein. The vacuum
panel
is constructed and arranged to deflect in order to accommodate volumetric
expansion
and contraction during the hot fill process. The main body portion further
includes a
circumferentially extending reinforcement groove having reinforcement
structure
provided therein. The circumferentially extending reinforcement groove is
positioned
substantially adjacent to the vacuum panel area, whereby dimensional
distortion of at
least part of the main body portion that is adjacent to the vacuum panel area
is
minimized during hot fill process.
A hot fill type plastic container according to a second aspect of the
invention includes a finish portion defining an opening, a bottom portion that
is
substantially round when viewed in bottom plan and a main body portion having
a
vacuum panel area with at least one vacuum panel defined therein. The vacuum
panel
2
CA 02882845 2015-02-23
WO 2014/099785
PCT/US2013/075393
is constructed and arranged to deflect in order to accommodate volumetric
expansion
and contraction during the hot fill process. The bottom portion is constructed
and
arranged to include a substantially flat portion having a plurality of
alternating parallel
ribs and grooves defined therein. As a result, dimensional distortion of the
bottom
portion is minimized during the hot fill process and deflection as a result of
vacuum
uptake is directed toward the vacuum panel area.
A polypropylene container according to a third aspect of the invention
includes a finish portion defining an opening, a main body portion having a
vacuum
panel area defined therein and a bottom portion that is fabricated from
polypropylene
and that is substantially round when viewed in bottom plan. The bottom portion
is
constructed and arranged to include a substantially flat portion having a
plurality of
alternating parallel ribs and grooves defined therein. As a result,
dimensional
distortion of the bottom portion is minimized.
These and various other advantages and features of novelty that
characterize the invention are pointed out with particularity in the claims
annexed
hereto and forming a part hereof. However, for a better understanding of the
invention, its advantages, and the objects obtained by its use, reference
should be
made to the drawings which form a further part hereof, and to the accompanying
descriptive matter, in which there is illustrated and described a preferred
embodiment
of the invention.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
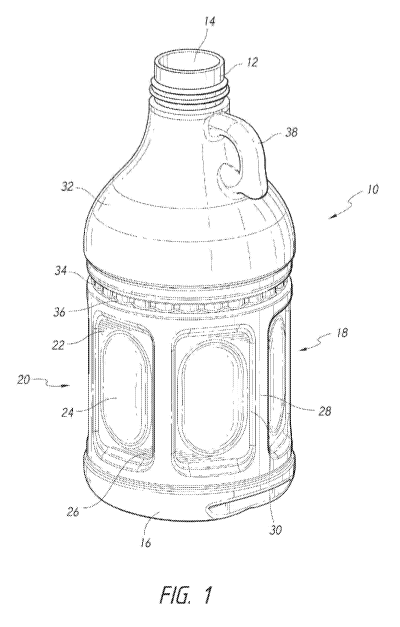
FIGURE 1 is a first perspective view of a plastic container that is
constructed according to a preferred embodiment of the invention;
FIGURE 2 is a side elevational view of the plastic container that is
shown in FIGURE 1;
FIGURE 3 is a longitudinal cross-sectional view taken along lines 3-3
in FIGURE 1;
FIGURE 4 is a transverse cross-sectional view taken along lines 4-4 in
FIGURE 2;
FIGURE 5 is a transverse cross-sectional view taken along lines 5-5 in
FIGURE 2;
FIGURE 6 is a second side elevational view of the plastic container
that is shown in FIGURE 1;
3
CA 02882845 2015-02-23
WO 2014/099785
PCT/US2013/075393
FIGURE 7 is a fragmentary cross-sectional view taken along lines 7-7
in FIGURE 6;
FIGURE 8 is a rear elevational view of the container that is depicted in
FIGURE 1;
FIGURE 9 is a front elevational view of the container that is depicted
in FIGURE I;
FIGURE 10 is a top plan view of the container that is depicted in
FIGURE 1;
FIGURE 11 is a bottom plan view of the container that is depicted in
FIGURE 1;
FIGURE 12 is a cross-sectional view taken along lines 12-12 and
FIGURE 11;
FIGURE 13 is a bottom perspective view of the container that is
depicted in FIGURE I;
FIGURE 14 is a finite element analysis image comparison illustrating
the top load performance benefits of the container that is constructed
according to the
preferred embodiment of the invention;
FIGURE 15 is a graph depicting the improvement in top load
performance that is exhibited by a container that is constructed according to
the
preferred embodiment of the invention; and
FIGURE 16 is a table comparison demonstrating the improvement in
bottom deflection performance in a container that is constructed according to
the
preferred embodiment of the invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT(S)
Referring now to the drawings, wherein like reference numerals
designate corresponding structure throughout the views, and referring in
particular to
FIGURE 1, a plastic container 10 that is constructed according to a preferred
embodiment of the invention is preferably fabricated from polypropylene using
a
conventional extrusion blow molding process. Plastic container 10 in the
preferred
embodiment is designed for use with a conventional hot fill process. Plastic
container
10 includes a finish portion 12 that defines an opening 14 that is in
communication
with the interior of the container 10. Plastic container 10 further includes a
bottom
portion 16, which will be described in greater detail below.
CA 02882845 2015-02-23
WO 2014/099785
PCT/US2013/075393
Plastic container 10 also includes a main body portion 18 having a
vacuum panel area 20, each of which includes a vacuum panel 22 having inner
portion 24 and an outer portion 26. The vacuum panel area 20 is preferably
recessed
with respect to an outer sidewall 28 of the main body portion 18. As FIGURE 5
shows, the outer portions 26 of the vacuum panels 22 are substantially flat
and
substantially perpendicular to a radius extending from a longitudinal axis 25
of the
container 10. The inner portions 24 of the vacuum panels 22 are constructed so
as to
be slightly convex and are designed to flex inwardly when an under pressure
exists
within the container 10 during the hot fill process.
The vacuum panel area 20 further includes transition portions 30 that
connect the outer portions 26 of the vacuum panels 22 to the outer sidewall 28
of the
main body portion 18.
Plastic container 10 further includes a dome or shoulder portion 32 that
connects the finish portion 12 to the main body portion 18. In the preferred
embodiment, the dome portion 32 is provided with a handle 38 that is
constructed and
arranged to facilitate a single finger grip.
Container 10 is preferably a round container, meaning that its
outermost surfaces as viewed in transverse cross-section are substantially
circular.
This may best be seen in FIGURES 4 and 5.
The main body portion 18 further preferably includes a
circumferentially extending reinforcement groove 34 that has reinforcement
structure
36 provided therein. The reinforcement groove 34 imparts additional top load
strength
of the container 10, as well as hoop strength, meaning that it stabilizes
adjacent
portions of the sidewall of the container 10 against radial displacement as a
result of
internal pressurization changes and squeezing forces that may be applied to
the
container 10 during handling or by a consumer.
The circumferentially extending reinforcement groove 34 is preferably
shaped and proportioned the same as those that are disclosed in U.S. Patent
Application 13/348,249, filed May 30, 2012, the entire disclosure of which is
hereby
incorporated by reference as if set forth fully herein.
The reinforcement groove 34 is preferably positioned substantially
adjacent to the vacuum panel area 20 in order to minimize dimensional
distortion of
the sidewall of the main body portion 18 adjacent to the vacuum panel area 20
during
the hot fill process. Preferably, the reinforcement groove 34 is positioned
within a
5
CA 02882845 2015-02-23
WO 2014/099785
PCT/US2013/075393
distance Ll of the vacuum panel area 20 that is substantially no greater than
about 34
millimeters, more preferably substantially no greater than about 22
millimeters and
most preferably substantially no greater than about 14 millimeters.
In the preferred embodiment, the reinforcement groove 34 includes a
plurality of flutes 40 that are situated within the groove 34. Each of the
flutes 40
preferably has a vertical component, and more preferably is oriented so as to
be
substantially vertical. The reinforcement groove 34 preferably extends about
an entire
circumference of the main body portion 18.
As FIGURE 4 shows, the flutes 40 are preferably defined by
alternating convex outer surfaces 43 and concave surfaces 42. The main body
portion
18 has a maximum lateral dimension WmAx, as is also shown in FIGURE 4. The
reinforcement groove 34 has a minimum depth DMIN and a maximum depth DmAx as
measured from the outer sidewall 28, with a minimum depth DmiN being defined
at
the peaks of the convex surfaces 43 and the maximum depth DmAx being defined
at
the radially innermost points of the concave troughs that are formed by the
concave
surfaces 42.
Preferably, a ratio DmiN/DmAx of the minimum depth of the maximum
depth is substantially within a range of about 0.1 to about 0.9, more
preferably
substantially within a range of about 0.2 to about 0.8 and most preferably
substantially within a range of about 0.35 to about 0.65.
As FIGURE 7 shows, the circumferentially extending reinforcement
groove 34 as viewed in side profile or longitudinal cross-section has a first
upper
groove sidewall 47 that is angled with respect to a groove bottom 48 at a
first angle
and a second lower groove sidewall 49 that is angled with respect to the
groove
bottom 48 that a second angle. In the preferred embodiment, the first and
second
angles are preferably substantially the same. In addition, the first upper
groove
sidewall 47 defines a wedge angle Al with respect to the second lower groove
sidewall 49 that is preferably substantially within a range of about 15 to
about 45
and more preferably substantially within a range of about 20 to about 40 .
The presence of the circumferentially extending reinforcement groove
34 materially improves both the top load and pressure resistance performance
of the
container in comparison to a similar container that does not include such a
reinforcement groove 34. FIGURE 14 is a finite element analysis comparison
depicting the relative deflections under a top load force between a container,
shown
6
CA 02882845 2015-02-23
WO 2014/099785
PCT/US2013/075393
on the left, which does not include a reinforcement groove 34 and the
container that is
constructed according to the preferred embodiment, which is shown on the
right. The
darker coloration of the container that is shown on the right is
representative of a
lessened amount of deflection relative to the container on the left.
FIGURE 15 is a graphical depiction of the relative top load
performance of the containers shown on the left and right, respectively, in
FIGURE
14. The horizontal axis in FIGURE 15 represents displacement, while the
vertical axis
represents a top load force that is applied to the container. The container
that is shown
on the left in FIGURE 14, which does not include a profiled reinforcement
groove 34,
as indicated as the "original structure" in FIGURE 15. The container that is
shown on
the right in FIGURE 14 is constructed according to the preferred embodiment of
the
invention and does include a reinforcement groove 34, is indicated as the
"final
structure" in FIGURE 15. As FIGURE 15 shows, a significant improvement in top
load performance is achieved by the inclusion of the profiled reinforcement
groove
34.
Referring now to FIGURES 11 and 13, it will be seen that the bottom
portion 16 is constructed and arranged to include a substantially flat portion
52 that
has a plurality of alternating ribs 56 and grooves 58 defined therein. The
presence of
the alternating ribs and grooves 56, 58 minimize dimensional distortion of the
bottom
portion 16 during the hot fill process and direct deflection as a result of
vacuum
uptake to portions of the container 10 that are designed to accommodate such
uptake,
namely the vacuum panel area 20.
Bottom portion 16 further includes a standing ring 50 that in the
preferred embodiment extends continuously about an outer periphery of the
bottom
portion 16 as viewed in bottom plan. The substantially flat portion 52 is
preferably
positioned within the standing ring 50 and is substantially centered with
respect to the
standing ring 50. The substantially flat portion 52 moreover preferably
occupies at
least 75% of the space that is defined within the standing ring 50. A
transitional
surface 54 is preferably defined between the substantially flat portion 52 and
the
standing ring 50. The transitional surface 54 is also preferably shaped so as
to be
substantially symmetrical about the longitudinal axis 25 of the container 10.
As FIGURE 11 shows, the alternating parallel ribs and grooves 56, 58
intersect the transitional surface 54 to form a complex shape that stiffens
the bottom
portion against deformation. The complex shape is particularly effective in
stiffening
7
CA 02882845 2015-02-23
WO 2014/099785
PCT/US2013/075393
the bottom portion when the bottom portion 16 is fabricated from
polypropylene, as a
result of the characteristic material properties of polypropylene.
FIGURE 16 is a table comparison showing the improved performance
of the bottom portion 16 of the container 10 that is constructed according to
the
preferred embodiment of the invention relative to a similar predecessor
container that
does not have the alternating parallel ribs and grooves 56, 58. The table on
the left in
FIGURE 16 depicts the base deflection at various points on the container
bottom on
the predecessor container. The table on the right in FIGURE 16 depicts the
base
deflection at analogous points in a container 10 that is constructed according
to the
preferred embodiment of the invention. The diminution in deflection and
resulting
enhanced dimensional stability of the bottom portion and a container that is
constructed according to a preferred embodiment of the invention is evident
from the
data that is provided in FIGURE 16.
It is to be understood, however, that even though numerous
characteristics and advantages of the present invention have been set forth in
the
foregoing description, together with details of the structure and function of
the
invention, the disclosure is illustrative only, and changes may be made in
detail,
especially in matters of shape, size and arrangement of parts within the
principles of
the invention to the full extent indicated by the broad general meaning of the
temis in
which the appended claims are expressed.
8