Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
1
FLOOR CONSTRUCTION FOR A VEHCLE
This invention relates to a floor construction for a vehicle particularly
but not exclusively of the type which carries passengers standing or seated,
such as
a light rail or road transit vehicle and including other vehicles used for
commercial
transportation of passengers, such as a road transit vehicle, airport and
hotel
shuttles, converted van and truck cutaways, heavy passenger rail and light
rail.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Conventionally mass transit vehicles and particularly city buses are
manufactured from a welded steel frame defining a floor frame, side wall frame
.and
roof bows which is then clad using sheet cladding material riveted, glued or
otherwise fixed to the frame. Insulation material is inserted between the
frame
members inside the exterior cladding and outside of the interior cladding.
The flooring is conventionally applied from individual simple
rectangular panels which are arranged to span across the floor frame and
fastened
to the floor frame by conventional fasteners. The panels are arranged with
butting
side edges edge to edge along the vehicle. The floor panels are often
fabricated
from plywood but however composite materials are also sometimes used including
= flooring panels manufactured from fibre reinforced plastics material. One
particular
panel is manufactured from top and bottom sheets of a fibrous mat applied on
top
and bottom surfaces of a honeycomb material manufactured from phenolic resin
impregnated paper with a thermosetting foam introduced into the honeycomb
cores.
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
2
However the panels are formed, they are conventionally rectangular
and arranged edge to edge and cut to shape and to size to complete the
necessary
flooring overlay.
It is also proposed to manufacture bus structures from fibre reinforced
composite plastics material so that the side walls, roof structure and floor
are each
formed separately from such composite materials and are attached together to
form
the complete bus structure without the necessity for an additional frame
supporting
the structure.
US Patent 6,375,249 (Stanton) issued April 23 2002 discloses a public
transit vehicle which has a vehicle body having a roof defining an interior
ceiling
surface, two side walls each extending longitudinally of the vehicle including
an
upper side wall portion connecting to the roof and a row of windows underneath
the
upper portion, a central aisle and two rows of seats each on a respective side
of the
aisle and along the side wall at the windows. The roof and floor are formed
from a
welded frame structure over which is applied a molded panel formed in single
panel
structure and bonded to the frame structure. The panel is formed by molding a
sandwich using a thermosetting resin through top and bottom fiber reinforced
sheets
and a honeycomb layer of resin impregnated paper and foam between the sheets.
The floor panel is shaped so that its thickness varies and its top and bottom
surfaces
deviate from an otherwise planar structure to incline downwardly at a door way
and
to incline upwardly to clear structural elements.
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
3
US Patent 8,006,321 (Lusk) issued November 29 2011 discloses a
structural shear panel for forming a floor panel for formed by a composite of
top and
bottom sheets and a core with a vacuum infused resin. The panel is mainly
planar
and terminates at its side edges at a portion which lies in a common plane and
portions are provided which are deformed out of the generally planar shape to
form
depending or elevated sections. The structure is formed by resin infusion into
the
sheets and core on a generally flat plate defining the planar panel portion
with
removable sections to define the depending and elevated sections. Edge pieces
are
attached to the plate to define the edges of the panel.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is one object of the present invention, therefore, to provide an
improved floor structure for a vehicle.
According to the invention there is provided a vehicle comprising:
a vehicle body having:
a roof,
a first and a second side wall each extending longitudinally of
the vehicle on respective sides of the vehicle body, each including a
plurality of
upstanding posts and a plurality of longitudinally extending members
interconnecting
the posts;
and a vehicle floor;
wherein the vehicle floor comprises:
a welded frame structure having a plurality of longitudinal rails and a
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
4
plurality of transverse rails welded thereto;
a plurality of longitudinally extending flooring planks each extending
along at least part of the length of the vehicle body;
the planks being arranged side by side so as to collectively span
between the side walls;
the planks each being molded from a composite panel having an upper
skin and a lower skin each including reinforcing fibers and an intervening
core
material layer and containing a cured resin material;
wherein an underside of the planks sits on top of the longitudinal rails
and the transverse rails of the frame structure and is attached thereto by
adhesive.
According to a second aspect of the invention there is provided a
vehicle comprising:
a vehicle body having:
a roof,
a first and a second side wall each extending longitudinally of
the vehicle on respective sides of the vehicle body, each including a
plurality of
upstanding posts and a plurality of longitudinally extending members
interconnecting
the posts;
and a vehicle floor;
wherein the vehicle floor comprises:
a welded frame structure having a plurality of longitudinal rails and a
plurality of transverse rails welded thereto;
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
a plurality of longitudinally extending flooring planks each extending
along at least part of the length of the vehicle body;
the planks being arranged side by side so as to collectively span
between the side walls;
the planks each being molded from a composite panel having an upper
skin and a- lower skin each including reinforcing fibers and an intervening
core
material layer and containing a cured resin material;
wherein an underside of the planks sits on top of the longitudinal rails
and the transverse rails of the frame structure and is attached thereto by
adhesive;
wherein there is provided a first wheel arch at said first side wall for
covering a first wheel and a second wheel arch at said second side wall for
covering
a second wheel;
and wherein the planks include a center plank of the planks which
extends between the wheel arches.
According to a third aspect of the invention there is provided a vehicle
comprising:
a vehicle body having:
a roof,
a first and a second side wall each extending longitudinally of
the vehicle on respective sides of the vehicle body, each including a
plurality of
upstanding posts and a plurality of longitudinally extending members
interconnecting
the posts;
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
6
and a vehicle floor;
wherein the vehicle floor comprises:
a welded frame structure having a plurality of longitudinal rails and a
plurality of transverse rails welded thereto;
a plurality of longitudinally extending flooring planks each extending
along at least part of the length of the vehicle body;
the planks being arranged side by side so as to collectively span
between the side walls;
the planks each being molded from a composite panel having an upper
skin and a lower skin each including reinforcing fibers and an intervening
core
material layer and containing a cured resin material;
wherein an underside of the planks sits on top of the longitudinal rails
and the transverse rails of the frame structure and is attached thereto by
adhesive;
wherein the floor includes a front lower deck extending from a front of
the vehicle to a transverse step and a rear upper deck extending from the
transverse
step to a rear of the vehicle with the transverse step between the decks;
and wherein the front deck is formed from a first set of said plurality of
longitudinal planks and the rear deck is formed from a second set of said
plurality of
longitudinal planks with a molded step section forming said transverse step
therebetween.
Preferably the planks are formed solely by one center plank and two
side planks. These are preferably in many cases of different lengths so that
he
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
7
center plank extends along a greater extent for example the whole length of
the floor
area and the side planks are typically shorter and are cut off at specific
locations for
example wheel arches.
The invention is therefore also directed to the kit of parts defined by
this set of planks which are pre-cut to the required lengths. This system
allows pre-
formed and pre-cut planks to be manufactured at relatively low cost and
supplied to
be assembled into the floor at the vehicle manufacturing plant. This avoids
the
necessity in the prior art to manufacture a whole floor in one piece which
requires
expensive tooling and difficult handling techniques.
The invention thus provides a new concept for structural composite
flooring for commercial vehicles. The flooring is lightweight, high strength,
and is
supplied in pultruded or vacuum-assisted resin transfer molded (VARTM) planks
in
long lengths up to for example a maximum length of 45 feet. The key benefit is
that
unlike the unitized composite flooring currently manufactured in the prior
art, the
plank flooring is easier to handle and install. That is the flooring can be
installed in
relative ease by, for example a 4' x 28' x 3/4" centre plank down the length
of the
bus (or passenger rail car) chassis, and then installing the side planks
whilst
standing on the centre plank. A further and very meaningful benefit is that
the
planks can be trimmed to any length, facilitating the manufacture of buses and
rail
cars of varying lengths without additional tooling penalties. This is not true
for the
prior art arrangements of a single panel flooring. The planks interface along
an
optional, longitudinal seat rail profile which is mechanically attached to a
longitudinal
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
8
beam which makes up part of the vehicle's chassis. The planks are bonded to
the
seat rail. In cases where the passenger seats are cantilevered off the side
wall of the
vehicle (thus requiring no seat rail in the floor), the seat rail is omitted.
The planks
are then reversed so that longitudinal flanges at the edges of the planks
overlap,
creating a leak-proof, structural joint.
Preferably the center plank has a width to form a central aisle along
which passengers can walk between the seats.
Preferably the center plank has a width spanning a distance between
two of said longitudinal rails.
Preferably the floor frame is formed by two inner rails and two outer
rails at the side edges and wherein the center plank spans the space between
the
inner rails and two side planks span the space between the inner rails and the
outer
rail where the center plank connects to the side planks at the inner rails.
This can be
at an overlap joint or may include a longitudinal support rail for supporting
a seat
frame member.
In many cases the floor also may include at least one molded section
extending across the floor at a position along the length of the floor against
which an
end of the planks abuts. The molded sections can include a front molded
section
and intermediate molded section for the floor of the vehicle which supplement
the
planks to define the full floor structure.
In the case where the floor includes a first wheel arch at one side wall
for covering a first wheel and a second wheel arch at a second side wall for
covering
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
9
a second wheel the center plank of the planks can extend between the wheel
arches
and the two side planks terminate at the wheel arches.
The planks can be formed using different processes but typically will
be arranged sò that the planks are of constant thickness along their length
and
across their width. In one process, the planks are formed by pultrusion. In
another
alternative process the planks are formed by a vacuum infused resin process on
a
mold where the planks are formed simultaneously side by side on the mold.
In both processes the planks can be formed either by pultrusion or on
the mold with side edges of part of reduced thickness to allow the formation
of an
overlap joint during assembly. Preferably in the molding process the planks
are
formed as a common structure with the upper and lower sheets joined together
at
side edges to allow cutting through the sheets at right angles at the side
edges to
separate the planks to define the three (or more) separate planks for separate
transport and installation for subsequent assembly in place.
In some cases a part of the core can be formed of a material of higher
density than other parts which can be used for mounting of components to be
connected to the floor such as stanchions where the base of the stanchion is
connected to the floor by self-tapping screws threaded directly into the high
density
material or through the higher density core portion to a tapping plate bonded
underneath the floor plank.
Preferably an outer edge part of each of the side planks is formed of a
material of higher density than other parts to allow cutting of the plank
around side
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
posts of the frame. This allows the plank to be cut thus penetrating the upper
and
lower sheets to the core whilst preventing the capillary intrusion of water
into the
core due to the use of the higher density non-absorbent core portion.
In a particularly important arrangement for low floor transit vehicles, the
floor includes a front lower deck extending from a position adjacent a front
wall to a
transverse step and a rear upper deck extending from the transverse step to a
rear
wall with the transverse step between the decks, the front deck being formed
from a
first set of planks and the rear deck being formed from a second set of planks
with a
molded step section forming said transverse step therebetween. In this case
the
front lower deck may include a downwardly inclined molded portion at a forward
end
thereof against which a front end of the planks abuts.
Preferably the bottom frame includes two longitudinal side rails and a
plurality of transverse rails and the underside of the planks is attached to
the rails of
the bottom frame by adhesive.
The invention also provides a method of manufacturing a floor for a
vehicle where the planks as defined above are pultruded, cut to length and
installed
side by side in the vehicle.
The invention also provides a method of manufacturing a floor for a
vehicle where the planks as defined above are molded side by side by a resin
infusion system on a mold and are cut to length and installed side by side in
the
vehicle.
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
11
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
One embodiment of the invention will now be described in conjunction
with the accompanying drawings in which:
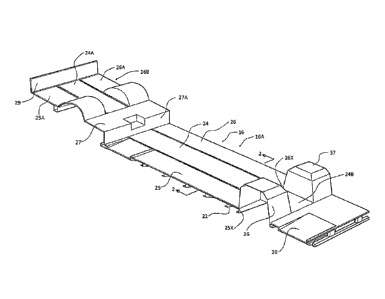
Figure 1 is an isometric view of a floor of a transit vehicle with the
remaining structure of the vehicle omitted for convenience of illustration,
the floor
planks being designed for connection side by side at a coupling which supports
a
seat rail.
Figure 2 is a cross-sectional view along the lines 2-2 but also showing
the walls, roof and interior seating of the vehicle of Figure 1.
Figure 3 is an isometric view of part of the floor and part of one wall of
the vehicle of Figure 1.
Figure 4 is a cross-sectional view of a mold for forming the floor planks
for a vehicle of the general type shown in Figure 1.
Figure 5 is a cross-sectional view of the floor planks when removed
from the mold of Figure 4.
Figure 6 is a cross-sectional view of the floor planks when removed
from the mold of Figure 4 and assembled without the seat rail coupling into
the
vehicle of the type shown in Figure 1.
Figure 7 is a cross-sectional view along the lines 7-7 of Figure 3.
Figure 8 is a cross-sectional view along the lines 8-8 of Figure 3.
In the drawings like characters of reference indicate corresponding
parts in the different figures.
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
12
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The vehicle of the present invention can be of various different
configurations and structures but generally includes a vehicle body 10 having
a roof
11 two side walls 12, 13 typically including windows each extending
longitudinally of
the vehicle, seating rows 14 and 15 and a vehicle floor 16.
The vehicle side walls and roof typically are formed from a frame
including posts 17 and longitudinal rails 17A clad by suitable materials,
often
aluminum panels.
The floor 16 has a bottom frame including a plurality of rails 18, 19, 20
and 21 with welded cross members 22 supporting a planar floor structure 23.
The vehicle floor structure on top of the frame comprises three
longitudinally extending flooring planks 24, 25 and 26 each extending along at
least
part of the length of the vehicle body. The planks are arranged side by side
so as to
collectively span between the side walls 12 and 13. In the example shown, the
floor
includes only the three planks defined by a center plank 24 and two side
planks 25
and 26 of different lengths relative to the center plank 24.
In the example of the low floor transit bus shown, the floor includes a
front lower deck 16A extending from a position adjacent a front wall to a
transverse
step 27 and a rear upper deck 16B extending from the transverse step 27 to a
rear
wall 29 with the transverse step 27 between the decks. In this arrangement the
front
deck 16A formed from a first set of planks 24, 25 and 26 and the rear deck 16B
is
elevated over the transmission and rear axle and is formed from a second set
of
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
13
planks 24A, 25A and 26A with the molded step section 27A forming the
transverse
floor section 27 therebetween. The planks of the lower deck are cut from the
same
profile as the planks of the upper deck allowing the flooring system to be
manufactured easily with constant tooling.
At the front of the lower deck is provided an inclined molded portion 30
defining the entrance area. The vehicle includes a first wheel arch 36 at one
side
wall for covering a first wheel and a second wheel arch 37 at a second side
wall for
covering a second wheel and the center plank 24 extends between the wheel
arches
at a portion 24B while the two side planks 25 and 26 terminate at end edges
25X,
26X the wheel arches.
The floor frame is formed by two inner rails 19 and 20 and two outer
rails 18 and 21 at the side edges. The center plank 24 spans the space between
the
inner rails 19 and 20 and the side plank 26 spans the space between the inner
rail
19 and the outer rail 18 and symmetrically the plank 25 spans the space
between
the inner rail 20 and the outer rail 21. Thus the center plank 24 has a width
to form a
central aisle along which passengers can walk between the seats and has a
width
spanning a distance between two of the longitudinal rails 19 and 20. The
center
plank 24 connects to the side planks 25 and 26 at overlapping joints 31, 32
overlying
the inner rails as best shown in Figure 6.
As shown in the alternative arrangement of Figures 2, 3 and 8, the
center plank 24 connects to the respective side planks at a joint which
includes a
longitudinal support rail 33 for supporting a seat frame member 34 of the row
of
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
14
seats 14, 15.1n this arrangement the planks include portions 35 which overlie
side
parts of the rail 33. The planks-are attached to the top surface of the
underlying rails
by adhesive A which also connects the planks at the rail joints.
The planks are molded as shown in Figure 6 from a composite material
having an upper skin 40 and a lower skin 41 of material each including
reinforcing
fibers and an intervening core material layer 42 all containing a cured resin
material.
Materials of this type are well known and can be manufactured using different
processes. In Figure 6, the planks including the upper and lower sheets and
the
core are formed by pultrusion using well known techniques of core and fiber
feeding.
In Figures 4 and 5, the planks 24, 25 and 26 including the upper and
lower sheets and the core are formed by a vacuum infused resin (VARTM) process
on a mold 45. Using well known molding techniques, the planks 24, 25 and 26
are
formed simultaneously side by side on the mold 45 with side edges 35 of part
thickness to allow overlap during the assembly. The molding technique uses
movable cores that form the "side edges". These are molded silicone trapezoids
with
a steel core. They are bolted to the core mold and can be moved laterally to
make
wider or narrower planks to fit the particular configuration of the vehicle.
So for
example the spacing between the longitudinal frame members on a hotel shuttle
(such as a Mercedes Sprinter) may be more narrowly spaced than a full-width
low
floor transit bus. The width of the centre panel can be adjusted to the
narrower width
by moving the silicone inserts. Silicone is used rather than standard, rigid
tooling
materials so that a seal can be maintained between the core mold surface and
the
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
insert, preventing resin from flowing between the insert and the core mold
surface,
locking the part in the mold.
Figure 4 shows the VARTM method of forming the planks, which may
be used in the exact same manner as the pultruded planks.
The configuration shown in Fig. 6 can be either the VARTM planks or
the pultruded plank. As shown at 46 in Figure 5 the planks are formed with
joined
upper and lower sheets at side edges 35 to allow cutting at the side edges to
separate the planks for subsequent assembly in place.
Thus as shown best in Figures 5, 6 and 8, the planks are formed with
flanges 53 and 54 defined by the joined upper and lower skins 40, 41 with no
intervening core. The core is shaped with a reduced thickness portion along
the
edge of the plank at 56 so that the skin 41 is recessed by the thickness of
the flange
53, 54 allowing a symmetrical overlap joint where the flanges 53 and 54 sit in
the
recesses defined by the portion 56. The joining edge portion 55 is inclined at
an
angle of the order of 45 degrees so as to communicate loading between the
planks
at the overlap joint. As shown in Figure 8 the same edge shapes including the
flanges 53 and 54 are used with the rail 33 which has side flanges 56 and 57
to sit in
the recessed portions 55 and has shoulders 58 and 59 to receive the flanges
53, 54.
Thus the planks of the same configuration can be used with the joint including
the
rail or with the overlap joint. The width of the planks may be modified to
accommodate the intervention of the rail in Figure 8.
As shown at 50 a part of the core is formed of a material of higher
CA 02887720 2016-11-25
16
density than other parts. Thus for example an outer edge part 51 of each of
the side
planks is formed of a material of higher density than other parts to allow
cutting of
the side planks at cut-outs 52 around the side posts 17 of the frame as shown
in
Figure 3 whilst preventing the capillary intrusion of water.