Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02890531 2016-12-20
Sealed Lathe Conveyor Pulley Cleaner
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0001] Conveyor Pulley Cleaners
BACKGROUND
[0002] Belt conveyors are used in numerous industries to transport
material. Belt conveyors
are essentially comprised of conveyor belting, belt support idlers and
pulleys. Pulleys are drum like
devices that are utilized to provide changes in direction for the belting as
needed for power
transmission, tension control and travel path. For applications where earth
materials are conveyed,
some of the material can be transferred to the underside of the belt and
subsequently transferred onto
the pulleys. Depending on the nature of the material, the material may build
up and compact on the
pulley face. Buildup of materials onto a pulley is undesirable for conveyor
operation and performance.
Uneven material build up creates belt tracking issues, which if left unaltered
can be destructive to the
belt, conveyor drive equipment and the conveyor structure. In addition to
tracking issues the buildup
can overload the conveyor belt in the regime of the material buildup causing
belt ruptures and eventual
shutdown of the conveyor. Continual removal of material from the pulleys is
required to avoid these
problems.
[0003] There are pulley cleaners currently available in the market that
employ a chain drive and
multiple knives to remove build up. The knives are attached to a chain and as
the chain travels between
the drive and idler sprocket the knives are dragged across the pulley surface
to clean it. These pulley
cleaners are prone to clogging as the freed material builds up in the drive
chain. As a result the motor
that drives the chain is overloaded and the cleaner fails requiring removal of
the entire assembly for
cleaning and maintenance. Removal of the cleaner requires the conveyor to be
shut down and locked
out for personnel protection.
[0004] Reciprocating Conveyor Pulley Cleaner patent number CA02853395 is a
related patent
that utilizes a plurality of reciprocating cutters to cover the width of the
pulley. This cleaner relies on the
multiple sets of fixed length cutters traveling a relatively short distance as
to cover the entire pulley
face. If the distance between the multiple cutters becomes too large the
reciprocating bar would
become impractical to use as the width of the cutter sets would protrude
further past the existing
structure and interfere with walkways. Inherent in the design is the relative
motion of the cutters that
reciprocate past the outside of the conveyor belt. The extending of
reciprocating cutters outside is a
1
CA 02890531 2016-12-20
potential safety concern if a personal catwalk is near (which is typical in
most cases). The design
accounts for impact loading from material build on the pulley with a pivot on
the cutter tooth sets. If the
existing pulley support structures are ignored the cleaner can be rotated 180
degrees and the spare
teeth on the back side can be used when the front teeth wear out or get
damaged. The conveyor would
need to be shut down to perform this operation as the bar holding the teeth
would be in contact with
the rotating pulley as it was removed. In addition to this, material build up
left behind on the pulley
from the worn teeth would need to be removed manually off the pulley to allow
insertion of the new
teeth. The design does not address the complete sealing of the mechanism, the
bottom is open to the
environment. The multiple teeth are also a potential maintenance concern as if
a single tooth gets
damaged it would require the full tooth set to be removed and replaced. If the
tooth set was left in
place for example with 4 good teeth and 1 bad tooth there would be a localized
spot on the pulley face
they would not get cleaned and thus back to the original problem of localized
material build up.
SUMMARY
[0005] In an embodiment, there is provided a pulley cleaner, comprising a
main frame having a
base for fixing the main frame to a pulley frame and spacing the main frame
from a conveyor pulley; a
linear actuator attached to the main frame and extending along the length of
the main frame; a tooth
block attached to the linear actuator for translation along the linear
actuator within the main frame; and
a cutter tooth extending from the tooth block for preventing build-up of
material on the conveyor
pulley, the length of the tooth being adjustable.
[0006] In various embodiments, there may be included any one or more of
the following
features: the tooth is removably connected to the tooth block; the main frame
is longer than the width
of the conveyor pulley; the tooth block is connected to a deflector plate, the
deflector plate shaped to fit
around the tooth; the pulley cleaner further comprises cover plates attached
to the main frame,
wherein a slot is formed by the cover plates facing the conveyor pully sized
to provide passage for the
cutter tooth; the pulley cleaner further comprises a seal belt supported by
pulleys connected to the
main frame and the seal belt secured to the tooth block adjacent to the slot
to block debris from passing
through the slot; the width of the seal belt is greater than the width of the
slot; the seal belt is guided
within grooves formed between the cover plates and seal plates fixed to the
cover plates to maintain
the seal belt adjacent to the slot; the pulley cleaner further comprises at
least one scraper element fixed
to the cover plates and aligned with the seal belt to remove debris from the
seal belt; heating elements
2
CA 02890531 2016-12-20
are attached to the seal plates adjacent to the grooves to prevent the seal
belt from freezing; the main
frame is fabricated from a common wide flange beam or welded plates; the tooth
has a cutting portion
and a base portion, and the cutting portion is connected by a threaded
connection to the base portion;
the tooth is spaced from the conveyor pulley; the linear actuator is any one
of a nut and shaft, ball
screw, wire rope lines on a winch, rack and pinion, hydraulic rams, scissor
mechanisms, telescoping rod
or magnetic driven plates; the pulley cleaner further comprises a dribble belt
supported by the main
frame to catch and remove debris which have been dislodged from the conveyor
pulley; the pulley
cleaner further comprises a "go/no-go" gauge connected to the base to prevent
the tooth from
becoming overextended towards the conveyor pulley; the main frame has an end
portion which extends
away from the conveyor pulley beyond the pulley frame; the main frame has
tooth maintenance access
plugs positioned on the end portion of the main frame; the cover plates have
at least one removable
cover plate and the removable cover plate is removably attached to the end
portion of the main frame
to allow access to the interior of the pulley cleaner while the conveyor
pulley is in operation.
[0007] In an embodiment, there is provided a method of cleaning a conveyor
pulley cleaner,
comprising the steps of providing a pulley cleaner in accordance with claim 1;
mounting the pulley
cleaner adjacent a conveyor pulley; translating the tooth block along the
conveyor pulley; and halting
the tooth block when the tooth block is translated beyond the edge of the
conveyor pulley.
[0008] In various embodiments, there may be included any one or more of
the following steps:
removing the tooth from the tooth block; adjusting the length of the tooth;
inserting the tooth into the
tooth block; rotating the tooth 180 degrees before inserting the tooth into
the tooth block; reversing the
direction of translation of the tooth block when the tooth reaches an edge of
the pulley.
[0009] These and other aspects of the device are set out in the claims.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
[0010] Embodiments will now be described with reference to the figures, in
which like
reference characters denote like elements, by way of example, and in which:
[0011] Fig. 1 is an isometric view of an embodiment of a pulley cleaner;
[0012] Fig. 2 is an isometric view of an embodiment of a pulley cleaner
with cover plates
removed to show internal mechanisms;
[0013] Fig. 3 is a side view of an embodiment of a pulley cleaner;
[0014] Fig. 4 is a side view of an embodiment of a pulley cleaner with
mount plate hidden;
3
CA 02890531 2016-12-20
[0015] Fig. 5 is a cross-section view of an embodiment of a pulley
cleaner;
[0016] Fig. 6 is bottom view of an embodiment of a pulley cleaner
installed on a pulley frame;
[0017] Fig. 7 is a side view of an embodiment of an embodiment of a pulley
cleaner installed on
a pulley frame;
[0018] Fig. 8 is a perspective view of an embodiment of a pulley cleaner
installed on a pulley
frame;
[0019] Fig. 9 is an exploded view of an embodiment of a pulley cleaner;
and
[0020] Fig. 10 is a flow chart of a method of cleaning a conveyor pulley,
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0021] The lathe style pulley cleaner invention (the Cleaner) is designed
to overcome the
clogging and maintenance problems outlined above that are associated with
traditional pulley cleaners.
A cutter tooth will translate horizontally the full width of the pulley with
componentry similar to that of
a conventional lathe. The cutter tooth's length can be adjusted to maintain
the target of 1/4" material
build up on the pulley face. The cutter tooth has an adjustable length which
allows the cutter tooth to
be progressed forward as its length is reduced due to wear from operation. The
cutter tooth has
approximate 2" of length adjustment, and once the cutter tooth has worn out it
can be easily replaced
while the conveyor stays in operation. Cutter tooth length adjustment can also
be performed while
conveyor is in operation.
[0022] To prevent contamination and debris build up on the Cleaner
components, a deflector
plate travels with the cutting tooth to prevent the majority of freed
materials from making contact with
the rest of the Cleaner. Further, a linear sealing system will prevent the
remaining freed materials from
contaminating the Cleaner internal mechanisms. The Cleaner will have seal
scrapers to remove exterior
buildup of materials on the Cleaner seal.
[0023] The Cleaner will employ a structural frame that is left in place
for routine maintenance
activities and changing the cleaner tooth orientation. Maintenance access
panels are positioned in
locations so that maintenance personnel can safely perform routine maintenance
activities while the
conveyor remains in operation. Activities include tooth adjustment, tooth
replacement, seal
replacement, lubrication, drive mechanism service and replacement.
[0024] The Cleaner components are robust and designed to withstand shock
loading from
compacted material adhered to the pulley face.
4
CA 02890531 2016-12-20
[0025] The Cleaner frame is symmetric and can be readily configured with
either a left hand or
right hand drive. A right hand drive is shown in the drawings "Figures 1 to
9". The Cleaner may also be
used in a top cut or a bottom cut by changing the orientation of the cutting
tooth.
[0026] The Cleaner has heater lines in the assembly face near the linear
sealing belt. The lines
can be used to input heat to the Cleaner to prevent accumulated materials from
freezing the sealing belt
in place.
[0027] Based on the clogging issues, practicality, maintainability and
shortcomings of the
existing chain and reciprocating multiple cutter cleaner designs, a fully
sealed/contained, online
maintainable, variable length and cut orientation Cleaner was developed.
[0028] The lathe style pulley Cleaner invention provides the online
maintenance features,
impact shock loading resistance, sealing against debris, multiple cleaning
orientations and quick online
tooth length adjustment and/or replacement.
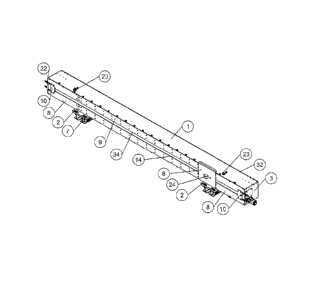
[0029] FIGURE 1 is an isometric view of the fully assembled unit with all
cover plates and
hardware in place. The Cleaner has removable cover plates outside the conveyor
operating area which
allow access for maintenance with the conveyor in operation. The cleaner may
be completely sealed
from the environment by a linear sealing system, including seal belt 14. In
this view it can be seen how
the seal belt 14 travels the majority of the width of the Cleaner front face
ending on each side with the
belt scraper 10. The surface of the seal belt may be automatically cleaned by
the belt scrapers, which
may have replaceable scraper blades. The sealing belt may have external
adjustment for tension. During
operation the cutter tooth 24 moves with the deflector plate 6 providing
protection to the seal belt from
the majority of the material that is removed from the pulley. The removable
cover plates 3, 5, and 8
extend past the existing conveyor structure and can safely be removed when the
conveyor is in
operation when Cleaner maintenance or tooth adjustments are required. The
front cover plates 9 house
the seal belt heating lines 22, minimize the opening for debris and provide a
lip/edge for the front face
of the seal 14. The front cover plates 9 form a slot 34. The seal belt 14 may
be held or guided inside a
low friction coated groove 35 (shown in Fig. 5) that runs along the front of
the cleaner and terminates at
the scraper blades. The seal belt 14 may be heated by heating elements 22,
such as heating lines, that
run along the groove 35 to prevent the surface of the seal belt 14 from
freezing during sub-zero
operations. An end portion 32 of the main frame extends beyond the existing
conveyor pulley.
[0030] The cutter tooth 24 may be held in a tooth block 11 that translates
horizontally across
the full width of the pulley face in one continuous motion. The deflector
plate 6 may be attached to the
CA 02890531 2016-12-20
tooth block with fasteners such as screws or bolts. The tooth block 11 is
supported by a fixed main
frame 1 that spans between existing supports already in place to hold the
conveyor pulley. The main
frame 1 has two base plates 2 with slotted holes which allow for installation
adjustment side to side. The
main frame may be fabricated from a common wide flange beam or welded plates.
The mount frames 7
have slotted holes 90 degrees to the base plates 2 allowing for frame
adjustment forward and back.
Once the Cleaner is located in position in the initial setup there is no need
for any further adjustment as
the cutter tooth 24 length is adjustable. The cutter tooth may have a wear
resistant surface on the
exposed tip that corresponds to the length the tooth can be extended,
providing improved tool life and
a visual indication when the tooth will need to be replaced. The Cleaner does
not need to be adjusted,
moved or shimmed once it is installed as the variable length tooth accounts
for this. Cutter tooth, tooth
block and main structure may be rigid, robust and designed for considerable
impact loading. The tooth
block may be supported by a fixed support structure that spans between
existing supports already in
place to hold the conveyor pulley.
[0031] FIGURE 2 is an isometric view with cover plates 3, 4, 5, 8, 9 and
seal channel block stop
or seal plates 25 hidden to show the Cleaner internal systems. The cutter
tooth may be held in the tooth
block and the tooth block may translate horizontally across the full width of
the pulley face in one
continuous motion. The tooth block 11 travels inside the main frame 1 driven
by a threaded linear
actuation shaft 18, drive train 21 and motor 20. The actuation shaft 18 is
supported on both ends with
bearing mounts 19. The tooth block 11 will start on the right side and move
left until it comes near the
left bearing mount 19. The cutter tooth may travel the full distance of the
pulley face, then reverse
direction and this cycle may be repeated. A limit switch or revolution counter
will trigger the motor to
reverse, changing the travel direction of the tooth block 11 to start heading
back to the starting position.
The same process will happen when the tooth block 11 gets near the right
bearing block 19. The tooth
block 11 will travel the full length of the pulley face back and forth which
constitutes the lathe function
of the Cleaner. The seal belt 14, which is secured to the tooth block 11, is
also hidden from this figure to
aid in showing the seal belt pulleys 15. The seal belt pulleys 15 are
supported with shafts 16 on the four
corners of the main structure 1. The seal belt pulleys 15 provide fixed points
for the seal belt 14 to travel
along while the tooth block 11 moves back and forth inside the main frame 1.
[0032] FIGURE 3 shows a side view for a cleaner with a right hand drive
option. The cleaner is
adaptable to either a left hand or right hand drive motor configuration. The
drive motor 20 is mounted
to a removable motor mount plate 3. The removable access hatch 5 allows for
inspection of the
internals and access to the drive train couplings 21. The back cover plates 4
may also be removed when
6
CA 02890531 2016-12-20
maintenance is required. The base plate 2 is welded to the main structure 1.
When the assembled items
1 & 2 are bolted to the mounting frame 7 there is flexibility in position that
can be selected due to
slotted holes in the base plate 2 and mounting frame 7. This flexibility is
only needed in the initial setup
as the variable length removable cutter tooth 24 can be adjusted to suit the
offset needed from the
pulley face. The cutter tooth can be released by removing the tooth
maintenance access plugs 23 and
loosening the tooth lock bolts 27 (shown on Figure 5).
[0033] FIGURE 4 shows a side view of the cleaner with the motor mount
plate 3 hidden to aid
in showing the internal components. The cutter tooth block 11 travels on the
internal faces of the main
frame 1 and the channel guide plates or seal plates 25. The tooth block 11 has
removable low friction
wear resistance pads 26 around its perimeter to aid in the horizontal
translation during operation. The
front deflector plate 6 protects the belt seal 14 from direct debris from
cutting. The heating
lines/elements 22 located in the top and bottom seal plates 25 keep the seal
14 from freezing in place if
the unit it shut down in sub-zero conditions. The seal 14 is maintained at set
elevation with internal seal
belt pulleys 15 that are mounted to fixed shafts 16. The rear shafts are
mounted to slider frames 17 that
allow for the ability to tension the seal 14. The seal is guided along the
back side of the main frame 1
with notched gussets 12 that have low friction wear pads 13 to prevent wear on
the seal. The gussets 12
also provide rigidity to the main structure when an impact load is
experienced. The input drive train 21
can also be seen in this view.
[0034] FIGURE 5 is a cross section view of the cleaner with the mount
frames 7 hidden. The
channel guides or seal plates 25 serve two functions, they provide restraint
the tooth block 11 for
normal operation conditions and the impact forces expected from this
application, and they also contain
grooves 35 for the seal belt 14 and seal belt heating lines 22. The lines can
be used for either liquid
based or electrical resistance heat input to the Cleaner. The seal belt rides
between the front plates 9
and the channel guides or seal plates 25 providing a seal from the outside
debris. The seal 14 wraps
around the belt pulleys 15 on each end and are guided along the back side of
the main frame 1 with
notched gussets 12 that have low friction wear pads 13. The rear of the
Cleaner is sealed by the back
cover plate 4. When a tooth extension is needed either because of tooth wear
or a new pulley offset
distance requirement, the compression bolt & stop bolt 27 are released and the
tooth is easily removed.
Once the cutter tooth 24 is removed the length can be adjusted as required and
re installed in the
reverse process as noted above. The tooth has a cutting portion 36 and a base
portion 37, and the
cutting portion is connected by a threaded connection 38 to the base portion,
and the length of the
tooth is increased by reducing the amount of the cutting portion which is
threaded into the base
7
CA 02890531 2016-12-20
portion. The tooth block 11 has low friction wear resistance pads 26 around
its perimeter which can be
replaced when needed. The linear actuation shaft 18 runs though the tooth
block 11 and transmits the
force to move the block via a threaded nut secured in the block.
[0035] FIGURE 6 shows a bottom view the Cleaner in a typical installation
with the existing
conveyor, conveyor equipment and associated structures shown in grey. The
conveyor pulley 28 is
mounted to the pillow block frame 30. The conveyor belt 29 wraps around the
conveyor pulley 28 and
extends on until the next conveyor pulley (not illustrated). The pillow block
frame 30 is a typical
arrangement, common on most conveyor systems. The Cleaner is adaptable and can
fit other existing
structures with modification to the mounting frame 7. It can be seen in this
view that the drive motor 20
and heating line ports are accessible well outside the active conveyor belt.
For maintenance on tooth
block 11 or for cutter tooth 24 change outs, the removable cover plates 3, 5,
and 8 can be taken off to
facilitate the maintenance.
[0036] FIGURE 7 shows a side view of the cleaner with existing structures
shown in grey. The
existing pillow block frame 30 is a typical dimensional constrain that is
common among conveyor
systems. In this side view it can be seen how cutter tooth 24 nearly contacts
the pulley 28. The
mounting frame 7 will be fit for purpose based on the specific dimensional
constraints of the conveyor
frame.
[0037] FIGURE 8 is a perspective view of the Cleaner assembly, the pillow
block frames 30 are
hidden for clarity. The front face of the Cleaner will experience the majority
of the debris during
operation. The seal belt 14 is protected from the majority of the direct
cuttings by the deflector plate 6.
[0038] FIGURE 9 is an exploded view with the main Cleaner components
shown. Some
hardware is hidden to provide clarity. The Cleaner symmetrical design allows
for the drive system 20 &
21 to be located on either the right or left hand side. In addition to this
the cutter tooth 24 can be
removed and rotated 180 degrees based on the top or bottom cut requirement.
[0039] The drawings show only one configuration for a right hand bottom
cut. Before the
cleaner is installed it can be easily changed for a either a right or left
hand drive configuration depending
on the required location. This change will need to be completed in the shop as
the motor and linear
actuator assembled need to be rotated 180 degrees. For a bottom cut, the
cutting tooth is rotated 180
degrees along its long axis. The Cleaner is scalable for a wide range of
conveyor belt widths.
[0040] The tooth block 11 is shown with an internal acme nut and acme
shaft for translation,
but alternate modes of achieving this full horizontal translation can also
utilize the following; ball screw,
8
CA 02890531 2016-12-20
wire rope and a winch, driven from the seal belt, rack and pinion, hydraulic
rams, scissor mechanisms,
telescoping rod or magnetic driven plates.
[0041] Shown in Fig. 8 is a subsystem consisting of a dribble belt 31
placed under the Cleaner.
The dribble belt would be added for a top cut application to help move
cuttings away from the main
conveyor belt to prevent the recirculation of debris. Dribble belts are
commonly used in material
handling applications and in and of itself is not a new technology. However
current pulley cleaners do
not employ dribble belts and incorporating them would represent a significant
improvement to the
elimination of debris for pulley cleaners.
[0042] Shown in Fig. 9 is a "go/no-go" gauge 33 that is used to ensure
that the tooth length is
properly adjusted to ensure maximum debris removal without damaging the pulley
face. The gauge
would consist of a small structural member that would be positioned on the
base plates 2 to interfere
with the tooth if it were over extended towards the pulley face. Conversely
maintenance personnel can
observe the offset distance from the gauge to the tip of the tooth to
determine when the tooth should
be lengthened.
[0043] For installation considerations, a mono rail with a beam crawler
can be used in between
the existing pillow blocks 30. In current installation practice, multiple
rigging points are used which is
both cumbersome and time consuming.
[0044] The Cleaner may be used in conveyor belt systems where pulleys
experience material
build up.The cleaner is intended to be used at facilities that mine and convey
earth materials. The
Cleaner would be mounted on intermediate drive, snub and take up conveyor
pulleys that are prone to
material build up.
[0045] The cutter tooth, tooth block and main frame may be rigid, robust
and designed for
considerable impact loading. The cutter tooth may have a wear resistant
surface on the exposed tip that
corresponds to the length the tooth can be extended, providing improved tool
life and a visual
indication when the tooth will need to be replaced.
ITEM DESCRIPTION
1 MACHINED MAIN STRUCTURE
2 BASE PLATE WITH ADJUSTMENT SLOTS
3 REMOVABLE MOTOR MOUNT PLATE
4 BACK COVER PLATE
REMOVABLE ACCESS HATCH
6 DEBRIS DEFLECTOR PLATE
7 MOUNTING FRAME
9
CA 02890531 2016-12-20
8 REMOVABLE FRONT COVER PLATE
9 FRONT COVER PLATE
BELT SCRAPER PLATE ASSEMBLY
11 TOOTH BLOCK
12 STRUCTURAL GUSSET AND BELT GUIDE
13 LOW FRICTION BELT GUIDE
14 SEAL BELT
SEAL BELT GUIDE PULLEYS
16 GUIDE PULLEY SHAFT
17 GUIDE PULLEY TENSION ADJUSTER
18 LINEAR ACTUATION DEVICE / SHAFT
19 LINEAR ACTUATION SHAFT BEARING
MOUNT
DRIVE MOTOR
21 LINEAR ACTUATOR DRIVE TRAIN
22 SEAL BELT HEATING LINE
23 TOOTH MAINTENANCE ACCESS PLUGS
24 VARIABLE LENGTH CUTTER TOOTH
CHANNEL GUIDE PLATE
26 LOW FRICTION REMOVABLE WEAR PAD
27 TOOTH COMPRESSION AND LOCK BOLTS
28 EXISTING PULLEY ASSEMBLY
29 EXISTING CONVEYOR BELT
EXISTING PULLEY PILLOW BLOCK FRAME
31 DRIBBLE BELT
32 END PORTION OF MAIN FRAME
33 TOOTH BLOCK LIMIT SWITCH
34 SLOT
LOW FRICTION COATED GROOVE
36 CUTTER PORTION OF TOOTH
37 BASE PORTION OF TOOTH
38 THREADED CONNECTION OF TOOTH