Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
DUAL-FUNCTION CATHETER WITH TWO SLIDING SHEATHS
The present invention concerns a catheter and more particularly a
catheter for injecting fluid. It also concerns a dual function catheter as
well as a
device comprising at least one catheter for injecting fluid.
Conventionally, a catheter for injecting fluid comprises a sheath with
an injection nozzle, which is moreover connected to a reservoir of fluid
making it
possible, for example, to inject a fluid under pressure.
For example the document FR2830455 is known which describes a
catheter for injecting a fluid under pressure. The catheter comprises a sheath
with a retractable injection tool at its distal end, the injection tool being
a
perforating, cutting, or pricking injection tool.
However, in such a catheter, the injection of fluid actuates the
extension of the tool, which, although having the advantage of being able to
retract the perforating, cutting or pricking tool automatically, requires a
minimum
of pressure from the fluid in order to extend the tool. Furthermore, certain
applications may require more precise positioning of the tool before injecting
the
fluid. However, it is preferable to protect the organs or tissues from any
cutting
part, for example such as the tool. It is thus more prudent to insert a
catheter
comprising a cutting tool with the tool protected.
The present invention aims to mitigate at least some of the aforesaid
drawbacks and furthermore to give rise to other advantages.
To that end, according to a first aspect, a catheter for injecting fluid is
provided comprising a conduit, characterized in that it comprises:
= an inner sheath, forming the conduit, fastened by a proximal end
to a connector enabling the catheter to be connected to a fluid
reservoir,
= an injection nozzle fastened to a distal end of the inner sheath,
= and an outer sheath, surrounding the inner sheath, fastened to a
sleeve, the sleeve and the outer sheath sliding relative to the
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
2
inner sheath and adopting at least one pushed position in which the outer
sheath covers at least a part of the injection nozzle and a pulled position
in which the outer sheath exposes said part of the injection nozzle.
According to another aspect, there is provided a dual function catheter
comprising:
a conduit, wherein the conduit includes an inner sheath;
a connector comprising a fluidic connection, an electrical connection, and an
outlet
connection, wherein a proximal end of the inner sheath is in fluid
communication with
the outlet connection, and wherein the connector couples the catheter to a
fluid
reservoir;
an injection nozzle coupled to a distal end of the inner sheath;
an electrode;
an outer sheath, surrounding the inner sheath, wherein the outer sheath is
coupled to
a sleeve, the sleeve and the outer sheath sliding relative to the inner sheath
and
adopting at least one pushed position in which the outer sheath covers at
least a part
of the injection nozzle and a pulled position in which the outer sheath
exposes said part
of the injection nozzle, wherein the injection nozzle is electrically
conductive and forms
the electrode such that the injection nozzle and the electrode are grouped
together into
a single component, an annulus at a distal end of the injection nozzle and
blocking entry
of the distal end into the outer sheath; and
a tip ring at a distal end of the outer sheath and adapted to slide over said
part of the
injection nozzle, wherein the tip ring includes a channel for slidably
receiving said part
of the injection nozzle, the tip ring having a radially outer surface that
engages a radially
inner surface of the outer sheath, the tip ring comprising a head protruding
distally from
a distal end of the outer sheath.
According to another aspect, there is provided a catheter comprising:
an injection nozzle, wherein at least a portion of the injection nozzle is
conductive,
wherein the injection nozzle includes a proximal portion, a distal portion
adjacent to an
outlet orifice, wherein the distal portion includes a distal end portion with
an annulus;
and
a sheath and a tip ring at a distal end of the sheath, wherein at least one of
the injection
nozzle or the sheath is movable relative to the other of the injection nozzle
or the sheath
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-03-09
2a
such that in a first position the sheath and the tip ring cover a portion of
the injection
nozzle and in a second position the portion of the injection nozzle is exposed
beyond
the sheath and the tip ring, wherein the annulus at the annulus at the distal
end portion
of the injection nozzle has a width greater than a width of the portion of the
injection
nozzle, and wherein the width of the annulus of the distal end portion is
greater than a
width of a distal opening in the tip ring in order to block the distal end
portion from being
covered by the sheath and the tip ring.
Such a catheter thus gives independence between an injection of
fluid and a retraction of the nozzle, in a simple and safe manner, in
particular if the nozzle
is a pricking or cutting nozzle. In a general case, as a nozzle typically has
a very narrow
geometry, it is thus protected when the catheter is inserted to avoid it being
accidentally
damaged, or avoid it scratching or snagging a tissue
or an organ when the catheter is inserted.
"Fluid" here means any liquid, such as water, a saline solution or a liquid
having a high viscosity, as well as macromolecular compounds or therapeutic
compounds.
More particularly, the fluid under pressure is for example a saline 15
solution or a more viscous solution according to the requirements of the
application. Injecting a viscous fluid in particular enables slower resorption
into
a tissue than if the fluid is of very low viscosity.
The nozzle of such a catheter thus adopts two positions, a retracted
position in which it is at least partly covered by the outer sheath, and an
extended, protruding position, for a specific utilization.
The outer sheath, sliding on the inner sheath, is for example shorter
than the inner sheath.
In other words, the nozzle, the inner sheath and the connector form a
first assembly, and the outer sheath and the sleeve form a second assembly,
adapted to slide relative to the first assembly.
"Sleeve" here designates any member or part, optionally with a texture, that
facilitates gripping of the outer sheath to impart a pushed or pulled movement
to it. This
may be a textured region in the sheath or a plastics ring for example.
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-03-09
2b
In the pushed position, the sleeve is for example located away from the
connector relative to the pulled position in which it is for example located
towards the
connector.
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-03-09
Thus, when the catheter is introduced, for example into an organ, the
nozzle, at least partially retracted, enables safer insertion, that is to say
with
less risk of accidentally perforating or scratching part of the organ or
another
organ for example. Once a distal end of the catheter is in position, the
nozzle is
extended by pulling the outer sheath, via the sleeve, and it is then possible
to
adjust its position if necessary.
Organ is used here to mean any organ, tissue, vein or artery, or any
part of the body for which such a catheter would be required at least for an
injection of fluid.
The fact that it is the outer sheath which is movable facilitates any
formation of a sealing connection between the inner sheath in which a fluid is
to
flow and a reservoir of fluid or other elements. This therefore makes it
possible
to reduce the production costs.
The nozzle next penetrates a superficial layer of the organ, for
example a mucosa. It is then possible to raise and separate a polyp or a
lesion
of a mucosa relative to an underlying muscle layer, in order then to remove
the
polyp or lesion for example. The injection of the fluid separates the mucosa
from the muscle and raises the polyp situated in the mucosa, which is then
potentially cut and dissected by the fluid under high pressure and optionally
assisted by an electrode connected to an electricity generator (for example an
ESU, standing for "electrical surgical unit", i.e. an electrical surgical unit
for
endoscopic surgery).
The injection nozzle is optionally a perforating nozzle to facilitate the
injection of a fluid under a membrane or a mucosa covering a muscle layer for
example.
The inner and outer sheaths preferably exhibit pliability and/or
flexibility over their length, in order to be easily introduced into a vein,
an artery
or some other organ and in a medical tool such as an endoscope. However, it is
preferable to be able to avoid causing the sheaths to fold, and to limit
irreversible deformations of a section of the sheaths that would obstruct the
passage of the fluid (for example buckling, in particular of the inner sheath
if
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
4
that sheath is flexed). For this, the sheaths are for example produced from
biocompatible polymers.
According to an example embodiment, the inner sheath is of PEBA.
According to an example embodiment, the outer sheath is of Teflon.
Such a catheter makes it possible to limit or even avoid losses of
pressure and exhibits high flexibility without naturally enabling easy
irreversible
folding (plasticity).
Thanks to its flexibility, it also enables fluids of greater or lesser
viscosity to be injected using straight view or retroflexion when it is
inserted, for
example, in an endoscope exhibiting plasticity that enables it to be sharply
bent.
Thus, according to an aspect that is original per se, independently of
any sliding between the sheaths, a catheter for injecting fluid is also
provided
comprising a conduit, characterized in that it comprises an inner sheath
produced from PEBA which forms the conduit, and an outer sheath produced
from Teflon, surrounding the inner sheath. The inner sheath is optionally
fastened by a proximal end to a connector enabling the catheter to be
connected to a fluid reservoir. An injection nozzle is also, for example,
fastened
to a distal end of the inner sheath.
According to an example embodiment, the catheter comprises a tip
ring fastened to a distal end of the outer sheath adapted to slide over at
least
part of the injection nozzle.
Such a tip ring for example provides surface continuity with the
nozzle that is retracted at least partly to facilitate the introduction of the
catheter.
It moreover facilitates guiding between the inner sheath and the outer sheath
when they slide relative to each other. Lastly, such a tip ring is for example
an
insulator, it enables the movements of the nozzle to be controlled, it also
optionally serves as a seal to avoid the fluid infiltrating between the inner
sheath
and the outer sheath.
For example, the tip ring is of ceramic, because ceramic is an easy
material to employ (molding or machining for example), and is both
biocompatible and electrically insulating. Other materials may of course be
envisioned, for example polymers.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
:' `=
The tip ring for example has a head of rounded distal shape. Such a
shape is better ergonomically for the insertion of the catheter when the
nozzle is
retracted at least partially.
According to an advantageous embodiment, the injection nozzle
furthermore forms an electrode such that the catheter is a dual function
catheter.
A dual function catheter is thus also provided comprising:
= a conduit,
= a connector comprising a fluidic connection and an electrical
connection,
= an inner sheath, forming the conduit, fastened by a proximal end
to an outlet connection of the connector enabling the catheter to
be connected to a fluid reservoir,
= an injection nozzle fastened to a distal end of the inner sheath,
= an electrode,
= and an outer sheath, surrounding the inner sheath, fastened to a
sleeve, the sleeve and the outer sheath sliding relative to the
inner sheath and adopting at least one pushed position ("b") in
which the outer sheath covers at least a part of the injection
nozzle and a pulled position ("a") in which the outer sheath
exposes said part of the injection nozzle.
characterized in that the injection nozzle forms the electrode such
that the nozzle and the electrode are grouped together into a single
component.
Such a dual function catheter thus makes it possible to raise and
detach a polyp or a lesion from a muscle layer below and to remove the polyp
or lesion with a single tool having among others the advantages cited above,
for
example such as insertion of the catheter that is rendered safe since the
nozzle
(also serving as an electrode) is retracted at least partially. The
perforation of
the tissue for the injection of the fluid may then also be carried out by the
nozzle, next introduced under the tissue for the injection of the fluid, which
may
thus dispense with a beveled shape for example. After injection, it is also
the
nozzle which can then cut up the polyp or the lesion in order to remove them.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
0
A dual function catheter here designates a catheter for injection and
dissection by electrical surgery i.e. a catheter making it possible to inject
a fluid
under pressure under a tissue or a mucosa, and to cut the tissue or the mucosa
with the electrode in the same tool. Thus, the electrode considered here is an
.. electrical surgical dissection electrode.
In other words, such a catheter makes it possible to inject a fluid
under pressure through a nozzle present in an electrode.
According to a preferred example embodiment, the jet of fluid passes
through the center of the electrode.
The electrode, which is thus also the nozzle, comprises for example
a central channel, configured to inject fluid.
A central jet is better adapted for injecting fluid to swell a zone (for
example detach the mucosa from the muscle in order to cut up the mucosa
more easily without risking damage to the muscle), whereas when a jet is at
the
periphery of an electrode, the jet is better adapted for washing the zone for
example. The nozzle and the electrode thus grouped together into a single
component are thus centered relative to each other. The component forming the
riuLcle arid the electrode exliibil axial symmetry for example.
According to an example embodiment, the electrode comprises an
annulus in the form of a holed circular plate to be fastened at a distal end
of the
electrode.
According to an example embodiment, the connector comprises a
fluidic connection and an electrical connection.
The connector is for example a Y-connector or a T-connector with a
fluidic connection for the fluid reservoir and an electrical connection, in
addition
to a so-called "outlet" connection, connecting it to the inner sheath
According to a particular example embodiment, the electrode is
connected to the electrical connection by a conductive wire running in the
inner
sheath. The conductive wire is electrically conductive, and is for example a
metal wire.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
7
In other words, the dual function catheter comprises a conductive
wire disposed inside the inner sheath and linked both to the electrode, that
is to
say to the nozzle, and to the electrical connection.
Furthermore, the inner sheath links the connector to the electrode,
.. which serves as a nozzle. Thus in practice, the fluid to inject passes from
the
fluidic connection, into the inner sheath, to the electrode, by virtue of its
channel. The conductive wire is then immersed in the fluid to inject.
Thus, for example, contrary to other devices in which the electrode is
connected by a metal tube passing along the whole length of the catheter,
itself
.. capable of forming the conduit, such a catheter has the advantage of
pliability
and/or flexibility, and makes it possible to avoid blockages (by folding of
the
metal tube leading to buckling), head losses and pressure losses or jamming in
translation of the outer sheath relative to the inner sheath.
The present invention also concerns a device comprising a pulsed jet
generator comprising a reservoir and a catheter, characterized in that the
catheter is a catheter as defined above having firstly a connection to the
pulsed
jet generator by a fluidic connection of the connector.
The device generates the fluid under pressure (for example a saline
solution), sends it via the catheter and injects it by the nozzle situated at
one
.. end of the catheter into a soft tissue (such as the mucosa or a sub-
mucosa).
If the catheter is dual function, the device then comprises an injection
nozzle and an electrode connected to an electricity generator (an "ESU"
standing for "electro surgical unit"), the electrode and the nozzle then being
produced in a single component. The catheter then furthermore has secondly a
connection to an electricity generator by an electrical connection of the
connector.
According to an advantageous example embodiment, the pulsed jet
generator is a high pressure pulsed jet generator for generating fluid pulses
under high pressure from at least one fluid contained in a flexible bag
forming
the reservoir placed in a pressurized fluid-tight chamber, the chamber having
at
least one outlet for fluids, the generator comprising:
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
8
= a pressurization device for the chamber which comprises a source
of gas under pressure which supplies a gas under pressure
entering the chamber to increase its internal pressure,
= a pressure regulating device which regulates the pressure inside
the chamber,
= at least one joining connector for joining a flexible bag to a
connection conduit, this joining connector and the connection
conduit being disposed in the chamber,
= a hydraulic sequencer comprising at least:
- an inlet into which enters at least the connection conduit, and
an outlet to which is connected an outlet conduit communicating
hydraulically with the outside of the generator,
- a flexible deformable envelope provided in a hydraulic
connection, all of this being exposed to the pressure inside the
chamber,
- at least one hydraulic obturating valve in the hydraulic
connection,
- a means for actuating the hydraulic obturating valve,
= and the fluid-tight outlet conduit between the outlet of the
sequencer and the outlet of the chamber connected to a conduit
for external connection with the catheter.
Such a generator is described in the international application
W02011/148333.
For example, the generator is adapted to generate a pulse of fluid at
a pressure comprised between 2 and 30 bars.
The pressure of the fluid is for example 10 bars (i.e. approximately
145 psi) for a saline solution (-water), and 20 bars (i.e. approximately 290
psi)
when the fluid is viscous.
For example, the generator is adapted to generate a pulse of fluid
with a volume of fluid per pulse comprised between 100 pL and 10 m L.
The pulse is controlled by an on-off solenoid valve (often called a
clamp valve, which enables pulses to be generated, in contrast to a continuous
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
9
jet for example) situated in the pressurized chamber itself controlled for
example by a user interface. The solenoid valve for example forms at least one
hydraulic obturating valve situated upstream of the flexible deformable
envelope.
Flexible deformable envelope is used here to mean that part of the
hydraulic connection deforms according to the variation in pressure inside the
chamber. It is for example formed thanks to a narrowed wall portion of the
hydraulic connection, or by a bulb formed in the hydraulic connection.
According
to another example, the flexible deformable envelope is also optionally an
independent component, the hydraulic connection then comprising a part that is
upstream and a part that is downstream relative to the flexible deformable
envelope.
Such a device thus makes it possible to limit or even avoid the risks
of perforating the muscle and has a low production cost.
Thus such a device makes it possible to cut and dissect soft tissues
in open surgery, as well as by endoscopy and/or laparoscopy.
According to another aspect, there is provided a catheter, comprising:
an electrode coupled to the inner sheath, wherein at least a portion of the
electrode is conductive, wherein the electrode includes a proximal portion,
and
a distal portion, wherein the distal portion includes a distal end portion
with an
annulus; and an outer sheath and a tip ring at a distal end of the outer
sheath,
wherein the outer sheath and the tip ring surround at least a portion of the
inner
sheath, wherein at least one of the inner sheath or the outer sheath is
movable
relative to the other inner sheath or the outer sheath such that in a first
position
the outer sheath and the tip ring covers a portion of the electrode and in a
second
position the portion of the electrode is exposed beyond the outer sheath and
the
tip ring, wherein the distal end portion with the annulus of the electrode has
a
width greater than a width of the portion of the electrode, and wherein the
width
of the distal end portion with the annulus is wider than a distal opening in
the tip
ring in order to block the distal end portion from being covered by the outer
sheath and the tip ring.
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-03-09
9a
According to another aspect, there is provided a catheter, comprising
an electrode, wherein at least a portion of the electrode is conductive,
wherein
the electrode includes a proximal portion, and a distal portion, wherein the
distal
portion includes a distal end portion with an annulus; and a sheath, wherein
at
least one of the electrode or the sheath is movable relative to the other of
the
electrode or the sheath such that in a first position the sheath covers a
portion
of the electrode and in a second position the portion of the electrode is
exposed
beyond the sheath; and a handle connected to the sheath, wherein the handle
includes an electrical connection, wherein movement of a portion of the handle
controls movement of one of the electrode or the sheath relative to the other
of
the electrode or the sheath.
According to another aspect, there is provided a catheter, comprising
an injection nozzle, wherein at least a portion of the injection nozzle is
conductive, wherein the injection nozzle includes a proximal portion and a
distal
portion, wherein the distal portion includes a distal end portion with an
annulus; a
sheath and a tip ring at a distal end of the sheath, wherein at least one of
the
injection nozzle or the sheath is movable relative to the other of the
injection
nozzle or the sheath such that in a first position the sheath and the tip ring
covers
a portion of the injection nozzle and in a second position the portion of the
injection nozzle is exposed beyond the sheath and the tip ring; and a handle
connected to the sheath, wherein the handle includes a fluid connection,
wherein
movement of a portion of the handle controls movement of one of the injection
nozzle or the sheath relative to the other of the injection nozzle or the
sheath.
According to another aspect, there is provided a catheter, comprising
an inner sheath; an electrode coupled to the inner sheath, wherein at least a
portion of the electrode is conductive, wherein the electrode includes a
proximal
portion, a distal portion adjacent to an outlet orifice, wherein the distal
portion
includes a distal end portion with an annulus; asheath, surrounding at least a
portion of the inner sheath, wherein at least one of the inner sheath or the
outer
sheath is movable relative to the other of the inner sheath or the outer
sheath
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-03-09
9b
such that in a first position the outer sheath and the tip ring covers a
portion of
the electrode and in a second position the portion of the electrode is exposed
beyond the outer sheath; and a handle connected to the sheath, and a handle
connected to the sheath, wherein the handle includes a fluid connection,
wherein
movement of a portion of the handle controls movement of one of the electrode
or the outer sheath relative to the other of the electrode or the outer
sheath.
According to another aspect, there is provided a device, comprising
an inner sheath; an electrode coupled to the inner sheath, wherein at least a
portion of the electrode is conductive, wherein the electrode includes a
proximal
portion, a distal portion, and a distal end portion; and an outer sheath
surrounding at least a portion of the inner sheath, wherein at least one of
the
inner sheath or the outer sheath is movable relative to the other of the inner
sheath or the outer sheath such that in a first position the outer sheath
covers a
portion of the electrode and in a second position the portion of the electrode
is
exposed beyond the outer sheath, wherein the annulus at the distal end portion
of the electrode has a width greater than a width of the portion of the
electrode,
and wherein the width of the annulis of the distal end portion is greaterthan
a
width of a distal opening in the tip ring in order to block the distal end
portion
from being covered by the sheath and the tip ring.
According to another aspect, there is a provided A medical device,
comprising an electrode, wherein at least a portion of the electrode is
conductive,
wherein the electrode includes a proximal portion and a distal portion,
wherein
the distal portion includes a distal end portion with an annulus; a sheath and
a
tip ring at a distal end of the sheath, wherein at least one of the electrode
or the
sheath is movable relative to the other of the electrode or the sheath such
that
in a first position the sheath and the tip ring covers a portion of the
electrode and
in a second position the portion of the electrode is exposed beyond the sheath
and the tip ring; and a handle connected to the sheath, wherein the handle
includes an electrical connection, wherein movement of a portion of the handle
controls movement of one of the electrode or the sheath relative to the other
of
the electrode or the sheath.
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-03-09
9c
According to another aspect, there is provided a dual function
catheter, comprising a conduit, wherein the conduit includes an inner sheath,
a
connector comprising a fluidic connection, an electrical connection, and an
outlet
connection, wherein a proximal end of the inner sheath is in fluid
communication
with the outlet connection, and wherein the connector couples the catheter to
a
fluid reservoir, an injection nozzle coupled to a distal end of the inner
sheath and
including an annulus at a distalmost end, an electrode, an outer sheath,
surrounding the inner sheath, wherein the outer sheath is coupled to a sleeve,
the sleeve and the outer sheath sliding relative to the inner sheath and
adopting
at least one pushed position in which the outer sheath covers at least a part
of
the injection nozzle and a pulled position in which the outer sheath exposes
said
part of the injection nozzle, characterized in that the injection nozzle is
electrically conductive and forms the electrode such that the injection nozzle
and
the electrode are grouped together into a single component, wherein the
distalmost end of the injection nozzle has a width greater than a width of
said
part of the injection nozzle that is selectively covered and exposed by
sliding of
the outer sheath, the width of the distalmost end blocking entry of the
distalmost
end into the outer sheath, and a tip ring at a distal end of the outer sheath
and
adapted to slide over said part of the injection nozzle, wherein the tip ring
includes a passage for slidably receiving said part of the injection nozzle,
the tip
ring comprising a cylindrical proximal stem received in the outer sheath, the
cylindrical proximal stem having a radially outer surface that engages a
radially
inner surface of the outer sheath, and a distal head protruding distally from
a
distalmost end of the outer sheath, and radially outwardly from the
cylindrical
proximal stem.
According to another aspect, there is provided a dual function
catheter, comprising a conduit, a connector comprising a fluidic connection
and
an electrical connection, an inner sheath forming the conduit fastened by a
proximal end to an outlet connection of the connector, the connector enabling
connecting the catheter to be connected to a fluid reservoir, an injection
nozzle
fastened to a distal end of the inner sheath, an electrode, an outer sheath,
surrounding the inner sheath, the outer sheath being fastened to a sleeve, the
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-03-09
9d
sleeve and the outer sheath sliding relative to the inner sheath and adopting
at
least on position in which the outer sheath covers at least a part of the
injection
nozzle and a pulled position in which the outer sheath exposes said part of
the
injection nozzle, characterized in that the injection nozzle is electrically
conductive and forms the electrode such that the injection nozzle and the
electrode are grouped together into a single component, in which the most
distal
end to the injection nozzle comprises an annulus having an width larger than
the
width of said part of the injection nozzle which is selectively covered and
exposed by sliding the outer sheath.
The invention, according to an example embodiment of the invention,
will be well understood and its advantages will be clearer on reading the
following description, given by way of illustrative example that is in no way
limiting, with reference to the accompanying drawings.
Figure 1 represents a dual function catheter according to an example
embodiment of the invention,
Figure 2 represents a view from above, in partial cross-section, of the
catheter of Figure 1,
Figure 3 an example embodiment in cross-section, of the catheter of
Figure 1,
Figures 4 to 15 illustrate example embodiments of different
components constituting the catheter of Figures 1 to 3:
Figures 4 and 5 represent an example embodiment of a
casing of the catheter, in two parts,
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-03-09
10
Figure 6 represents an example embodiment of a tube
enabling an inner sheath to be joined to a connector detailed in Figure
15,
Figure 7 represents an example embodiment of an
intermediate component for connecting a sleeve represented in Figure 10
to an outer sheath by virtue of a ring illustrated in Figure 9,
Figure 8 represents an example embodiment of an electrical
plug protector,
Figure 9 represents an example embodiment of the ring
enabling the outer sheath to be fastened to the intermediate component,
Figure 10 represents an example embodiment of the sleeve,
Figures 11a and 11 b respectively represent a perspective view
and a cross-section view of a tip ring of the outer sheath according to an
example embodiment of the present invention.
Figure 12 represents a nozzle according to an embodiment of
the present invention,
Figures 13a and 13b represent a nozzle, respectively not in
cross-section and in cross-section, according to another embodiment or
the present invention,
Figure 14 represents an annulus for a distal end of a nozzle
according to one embodiment of the present invention, the annulus
having the form of a holed circular plate adapted to be fastened to an end
of the nozzle as represented for example in Figures 13a and 13b,
Figure 15 illustrates an example embodiment of a connector
with two inlet passages,
Figure 16 illustrates a link between the position of the sleeve and the
outlet of the nozzle according to an example embodiment of the present
invention, and
Figure 17 illustrates a device according to an embodiment of the
invention.
= Identical components represented in Figures 1 to 17 are identified by
identical numerical references.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
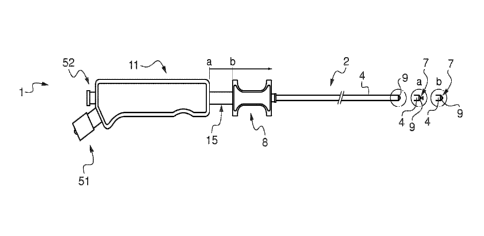
In the present example embodiment of the invention, a catheter 1 for
injecting fluid comprises a conduit 2 connected to a casing 11 comprising a
connector 5.
The conduit 2 comprises:
- an inner sheath 3 (visible for example in enlargement A of Figure
3), fastened by a proximal end to the connector 5 enabling the catheter 1 to
be
connected to a reservoir of fluid 6 (represented in Figure 17),
- an injection nozzle 7 fastened to a distal end of the inner sheath 3,
- and an outer sheath 4, surrounding the inner sheath 3, fastened to
a sleeve 8, the sleeve 8 and the outer sheath 4 sliding relative to the inner
sheath 3 and adopting at least one pushed position (position "b" illustrated
in
Figure 16) in which the outer sheath 4 covers at least a part of the injection
nozzle 7, and a pulled position (position "a" illustrated in Figure 16) in
which the
outer sheath 4 exposes said part of the injection nozzle 7.
The inner sheath 3 is for example produced from PEBA, and the
outer sheath 4 is for example produced from Teflon.
A tip ring 9 is here fastened to a distal end of the outer sheath 4 and
is adapted to slide over at least a part of the injection noz.Lle 7.
The tip ring 9 is for example of ceramic. It furthermore has a head 90
.. of rounded distal shape, as illustrated by Figures ha and lib.
In other words, the catheter 1 comprises two assemblies adapted to
slide relative to each other.
A first assembly, referred to here as "fixed assembly" comprises the
nozzle 7, the inner sheath 3, a tube 17, the connector 5, a plug protector 18
and
the electrical plug 14, and the casing 11.
A second assembly, referred to here as "movable assembly"
comprises the tip ring 9, the outer sheath 4, the sleeve 8, an intermediate
component 15, and a ring 16.
Of course, these definitions of assemblies are for ease of
understanding in the present description, and the attributes "fixed" and
"movable" are arbitrary here for defining one assembly relative to the other.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
12
With reference to the fixed assembly, as shown by enlargement A of
Figure 3, the nozzle 7 is sunk into the outer sheath 3. It is for example
bonded
inside the inner sheath 3 at its distal end.
As shown by Figures 12 to 14, the nozzle 7 here has a connecting
zone 70 promoting attachment between the nozzle 7 and the inner sheath 3.
The connecting zone 70 furthermore has grooves 71 and a flat 72. The grooves
71 are for example able to serve as spillways for adhesive if the assembly is
formed by bonding, in order to avoid adhesive overflowing, which furthermore
gives a sloppy and unaesthetic appearance. The grooves 71 also enable better
gripping between the nozzle 7 and the inner sheath 3, whereas the flat 72
serves as a fool-proof device for the Insertion of the nozzle 7 into the inner
sheath 3 and/or as a marker if it is preferable to insert the nozzle 7 with a
particular orientation. The flat 72 also enables the insertion of the nozzle 7
into
the inner sheath 3 to be facilitated since it gives rise to a reduction in
cross-
section. According to another embodiment not shown, it would however be
possible for there to be only one groove 71.
The nozzle 7 furthermore has a useful zone 73, outside the inner
sheath 3 when they are assembled together. The useful zone 73 has a distal
end 74a having an outlet orifice 75 by which the fluid is injected into or
under a
tissue where applicable. The distal end 74a is optionally a pricking or
cutting
end, or is for example beveled (not shown here).
In the example embodiment of Figures 13A and 13B, the useful zone
73 has a narrowed cross-section relative to the connecting zone 70. This makes
it possible to create a shoulder 76 serving for example as an abutment for the
tip ring 9 when that ring is in the pulled position, exposing the nozzle 7, as
for
example shown by element A of Figure 3. A smaller cross-section also enables
a smaller hole to be formed in the tissue when the nozzle penetrates a mucosa
to inject fluid, and this also enables the nozzle 7 to be inserted more easily
into
the tissue.
In the example embodiment described here, the catheter 1 is a dual
function catheter, that is to say that the nozzle 7 also serves as an
electrode. -
Consequently, the nozzle 7 is for example produced from a conductive material,
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
13
for example a metal, and is connected by a conductive wire 10, for example of
metal, running in a channel 30 of the inner sheath 3, to an electrical plug 14
connected to an electrical connection 51 of the connector 5. The conductive
wire 10 is preferably soldered to a proximal end 74b of the nozzle 7.
In the case of a nozzle also serving as an electrode, it is for example
useful for the distal end 74a to be provided with an annulus 78 (represented
in
Figure 14). To provide better positioning of the annulus 78, it is then
advantageous for the distal end 74a of the nozzle 7 to have a narrowed portion
77 (represented here in the embodiment of Figure 13), forming another
shoulder, adapted to receive the annulus 78. Such a narrowed portion 77 could
also be formed at the distal end 74a of the nozzle 7 of Figure 12. The annulus
78 may however be fastened to the distal end 74a of the nozzle 7 without such
a narrowed portion, for example by bonding, but this configuration then
renders
its positioning more difficult.
The annulus 78 here takes the form of a holed circular plate so as to
fit the cross-section of the distal end 74a (i.e. of the useful end 73 or of
the
narrowed portion 77 if there is one).
From an internal point of view, as shown by Figure 13B, the nozzle 7
comprises a channel 79 enabling a fluid to be conveyed from the inner sheath 3
to the outlet orifice 75. In the example embodiment of Figure 13B, the channel
79 has a cross-section which, on average, narrows towards the outlet orifice
75.
More specifically, the channel 79, relatively centered in the nozzle 7,
here has the largest possible section 79a directly connected to the channel 30
of the inner sheath 3, a funnel-shaped section 79b, an intermediate section
79c
which is slightly wider here than the funnel-shaped section 79b, and an
injection
section 79d. These various sections are arranged so as to minimize turbulence
in the fluid flow while maintaining pressure of the fluid outletting from the
outlet
orifice 75 with a minimum of loss. It can be noted for example that sections
79a,
79b and 79c are arranged so as to form an ejection pipe.
At the other end of the inner sheath 3, at its proximal end, the inner
= sheath 3 is fastened to the tube 17, detailed in Figure 6.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
14
The tube 17 is in turn sunk into an outlet branch 53 of the connector
5.
In the present example embodiment, as detailed in Figure 6, the tube
17, of cylindrical general shape, has a groove 170 here extending lengthwise
over a major part of the tube 17. The groove 170 is for example able to serve
as
a spillway for adhesive if the assembly is formed by bonding, in order to
avoid
adhesive overflowing, which furthermore gives a sloppy and unaesthetic
appearance. The groove 170 also promotes gripping of the tube 17 in the
connector 5, which for example are assembled by bonding.
As mentioned earlier, the connector 5 here has an outlet branch 53.
It also comprises at least one branch 52 serving for a fluidic connection,
designated Hfluidic connection 52", and in the case of a dual function
catheter, it
further comprises a branch 51 serving for an electrical connection, designated
"electrical connection 51". Thus the connector 5 is a Y-connector here, with a
fluidic connection 52 for the fluid reservoir 6, an electrical connection 51
and an
outlet connection 53 connecting it to the inner sheath 3.
The connector 5 has a channel 56 enabling the fluid to be conveyed,
which is consequently in direct communication with the channel 30 of the inner
sheath 3.
To facilitate the insertion of the tube 17 into the outlet branch 53, the
outlet branch 53 here has a beveled end 54. It furthermore has an inclined
shoulder 55 forming an abutment for the tube 17.
The fluidic connection 52 here has a threaded end 52a for a Luer-
Lock connection for an arrival of fluid under pressure in the channel 56, of
which
a section 56a, at the location of the branch 52, is widened towards the
arrival of
the fluid, for example to limit turbulence in the flow when it arrives in the
catheter 1.
The branch 51 serving for the electrical connection receives the
electrical plug 14 connected to the conductive wire 10.
The electrical plug 14 is protected here by the plug protector 18,
which is for example held by its foot 180 between on one side the branches 51
and 52 of the connector, and on another side the casing 11 when the entire
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
15
catheter 1 is assembled. As regards the electrical plug 14, this is, for
example,
held in position by a thickened region 140 taken between the branch 51 and an
inner edge 181 of the plug protector 18.
Thus, the channel 56 of the connector 5, the channel 30 of the inner
sheath 3, and the channel 79 of the nozzle 7 enabling the fluid to inject to
be
conveyed from a reservoir, for example such as the reservoir 6 of a pulsed jet
generator 101, to the outlet orifice 75 of the nozzle 7.
In parallel, the conductive wire 10 passes along the channel 30 of the
inner sheath 3 and the channel 56 of the connector 5, forking into the branch
51.
Once assembled, the aforesaid components are then fixed in the
casing 11.
In comparison, the second assembly is considered as movable
relative to that first assembly.
The tip ring 9 (detailed in Figure 11) is fastened in a distal end of the
outer sheath 4, as shown by enlargement A of Figure 3. The tip ring 9 here
also
has a groove 91 promoting better gripping in the outer sheath 4 and is also
able
to serve as a spillway for adhesive if the assembly is formed by bonding, in
order to avoid adhesive overflowing, which furthermore gives a sloppy and
unaesthetic appearance. As mentioned earlier, the tip ring 9 has a rounded
distal shape forming a head 90 of the tip ring 9. Preferably, the head 90 of
the
tip ring 9 is slightly wider so as to provide continuity with an outside
surface of
the outer sheath 4 when they are assembled. The tip ring 9 lastly comprises a
channel 93 terminating with an orifice 92 formed at an apex of the head 90.
The
channel 93 has for example a diameter substantially equal to a diameter of the
useful zone 73 of a nozzle 7 to slide on that useful zone 73 while at the same
time enabling sealing between the nozzle 7 and the tip ring 9 to avoid fluid
or
anything else infiltrating between the inner sheath 3 and the outer sheath 4.
Furthermore, in pulled position ("a") the tip ring 9 for example abuts a
distal end of the inner sheath 3, or even also of the shoulder 76 if it
exists, and
in pushed position ("b") the tip ring 9 by its head 90 abuts the annulus 78 if
the
nozzle 7 is provided therewith_
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
16
At another end, its proximal end, the outer sheath 4 is fastened into
the intermediate component 15 by the ring 16, as shown by the element B of
Figure 3.
The intermediate component 15 here is a slender component
represented diagrammatically in Figures 2 and 3, and detailed in Figure 7.
The outer sheath 4 passes here within the intermediate component
15, and around a body 160 of the ring 16. In order for the ring 16 to be
inserted
more easily into the outer sheath 4, it has for example a beveled first end
161.
Furthermore, the ring 16 also enables an abutment to be formed when the
movable assembly is in pulled position ("a") by coming to bear for example on
a
reinforcing member 130 of the casing 11. For this, the ring 16 advantageously
has a head 162 wider than the body 160.
The head 162 furthermore serves as an abutment for the
intermediate component 15 when the ring 16, surrounded by the outer sheath 4,
is sunk into it. Lastly, the ring 16 has a channel 163 of diameter
substantially
equal to a diameter of the inner sheath 3 to be able to slide along the inner
sheath 3.
The intermediate component 15 here has a first zone 151 adapted to
cooperate with the sleeve 8, and a second zone 152 adapted to be positioned
inside the casing 11.
The first zone 151 has a flat 150, for example over its whole length,
adapted to cooperate with a flat 80 of the sleeve 8 for example to give rise
to an
obligatory mounting orientation for the sleeve 8 on the intermediate component
15. This is for example useful if the sleeve 8 comprises indications, for
example
such as arrows illustrating the positions "a" and "b" to extend or retract the
nozzle 7.
The first zone 151 also has grooves 153 to promote gripping with the
sleeve 8. The grooves 153 are also able to serve as spillways for adhesive if
the
assembly is formed by bonding, in order to avoid adhesive overflowing, which
for example gives a sloppy and unaesthetic appearance. The first zone 151
= here has a diameter generally less than a diameter of the second zone 152
so
as to form a shoulder 154 able to serve as an abutment on insertion of the
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
17
sleeve 8. The first zone 151 lastly has a transition zone 155 enabling the
diameter of the first zone 151 to be reduced progressively relative to a
diameter
of the outer sheath. According to one option not shown, a flexible envelope,
for
example of elastomer, may be present between the intermediate component 15
and the sleeve 8 such that the sleeve 8 Is force fitted, for example over the
flexible envelope applied over the intermediate component 15. The flexible
envelope may for example extend on each side beyond the first part 151.
Once the assembly has been formed, the sleeve 8 is for example in
abutment against the casing 11 when the catheter is in pulled position ("a").
The second zone 152 furthermore has here two pairs of depressions
157a, 157a' and 157b, 157b' adapted to cooperate with two posts 120, 120'
formed in the casing 11. The two depressions of a pair (157a and 157a', and
157b and 157b') are preferably formed diametrically oppositely such that the
two posts 120, 120' thus enable holding and guiding of the intermediate
component 15 in the casing 11. However, other configurations may be
envisioned which would for example only rely on a single depression at a time.
The two pairs of depressions 157a, 157a' and 157b, 157b' in
particular here enable indexing of pulled position ("a") or pushed position
("b").
More particularly, in pulled position, the pair 157a, 157a' cooperates with
the
posts 120, 120' whereas in pushed position, it is the pair 157b, 157b' that
cooperates with the posts 120, 120'. On passage from one position to the
other,
the intermediate member 15 is then slightly compressed between the posts 120,
120' which gives the user a slight sensation of resistance until one of the
two
pairs of depressions are face to face with the posts 120, 120'. Furthermore,
the
positioning of the depressions relative to the posts 120, 120' is ensured
thanks
to the various abutments presented above (for example such as between the tip
ring 9 and the annulus 78 or between the tip ring 9 and the inner sheath 3, or
the ring 16 against the reinforcing member 130, or furthermore the sleeve 8
against the casing 11) which prevents a user from pulling or pushing more than
necessary, which could for example damage the various adhesive joints or
assemblies of parts, or the parts themselves.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
18
Furthermore, the intermediate component here also comprises a
trough 156. The trough 156 for example is of length equal to or slightly
greater
than a separation between the two pairs of depressions 157a, 157a' and 157b,
157b'. The trough 156 here cooperates with a finger 121 of the casing 11. The
cooperation between the trough 156 and the finger 121 makes it possible not
only to render safe the movements of the movable assembly to avoid a user
pulling beyond the pulled position or pushing beyond the pushed position, but
also to prevent a rotation, or even torsion, of the movable assembly relative
to
the fixed assembly. Preferably, the finger 121 is then of a diameter
substantially
equal to a width of the trough 156. In the present example embodiment, the
trough 156 is positioned between the two posts of the same pair and at equal
distances between them. The finger 121 is here slightly offset relative to the
posts 120, 120' as shown by Figures 2 and 5. Thus, in pulled position ("a"),
the
pair of depressions 157a, 157a' cooperates with the posts 120, 120' while the
finger 121 is close to, or even in contact with to form an abutment, a bottom
156a of the trough 156. In pushed position ("b"), not shown in detail here,
the
pair of depressions 157b, 157b' would cooperate with the posts 120, 120' while
the finger 121 would be close to, or even in contact with to form an abutment,
a
bottom 156b of the trough 156.
Even though the different components are not represented at the
same scale, it can nevertheless be noted that the separation between the pair
157a, 157a', and the pair 157b, 157b' is substantially greater than a length
of a
part of the useful zone 73 of the nozzle 7 which can be exposed or retracted.
This is in particular due to an effect of structure (existence of play,
elasticity of
the mounting), as well as to the elastic properties of the different parts and
of
the materials constituting them. It is to be recalled for example that the
conduit 2
typically measures more than a meter in length for a maximum diameter of
approximately 2.5 mm, or even less.
In the present example embodiment illustrated here, the casing 11 is
formed from a male part 12 (represented in Figure 5) and from a female part 13
(represented in Figure 4). The posts 120, 120' are here formed in the male
part.
12. In Figure 3, illustrating the positioning of the different components of
the
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
19
catheter 1 in the female part 13 of the casing 11, the posts 120 and 120' have
however been represented in dashed line to illustrate their positioning
relative to
the pairs of depressions 157a, 157a' and 157b, 157b'.
Once the different components of the catheter 1 have been
positioned for example in the female part 13, the casing 11 may be closed
again
by the male part 12, for example by welding or by bonding. The casing Ills for
example formed from plastics material, for example by molding. For this
assembly, the female part 13 for example has a rim 13' and the male part 12
for
example has a rim 12' adapted to be juxtaposed against the rim 13' in the
.. female part 13.
As shown by Figures 4 and 5, the casing 11 further comprises
different pairs of assembly projections 122, 132 (in this case six pairs)
comprising a male projection 122 in the male part 12 and a female projection
132 in the female part 13 of the casing 11.
The casing also includes reinforcing members, such as reinforcing
member 130, cooperating with a reinforcing member 123 of the male part. The
reinforcing members 130 and 123 respectively have a cavity 134 and 124
adapted lu receive the inner sheath 3 to keep it in position. The cavities 134
and
124 consequently have a curvature substantially equal to a curvature of a
cross-
section of the inner sheath 3. The male part furthermore has a reinforcing
member 125 provided with a cavity 126, and the female part has a reinforcing
member 135 complementary to the reinforcing member 125, provided with a
cavity 136. As regards the cavities 126 and 136, these have a curvature
substantially equal to a curvature of a cross-section of the second zone 152
of
the intermediate component 15 in order to keep it in position while enabling
it to
slide.
Lastly, the casing comprises cut-outs 127 and 137 for the passage of
the second zone 152 of the intermediate component 15 to keep it in position
while enabling it to slide, cut-outs 128, 138 for the passage of the fluidic
connection 52 of the connector 5, and cut-outs 129, 139 for the passage of the
electrical connection 51 of the connector 5 surrounded by the plug protector
18.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
20
Figure 17 provides a diagrammatic presentation of a device 100
according to an embodiment of the present invention.
The device 100 comprises at least one generator 101 and a catheter
1 according to the invention, for example as described above with reference to
Figures 1 to 16.
Such a generator is described in detail in the document
W02011/148333 but its main characteristics are described here.
The generator 101 is a high pressure pulsed jet generator for
generating fluid pulses under high pressure from at least one fluid contained
in
a reservoir here formed by a flexible bag 6, placed in a fluid-tight chamber
102,
pressurized for example thanks to a cylinder 103 containing gas under
pressure.
The chamber 102 here has at least one outlet for fluid 104, and an
inlet 105 for gas under pressure.
To be pressurized, the generator 101 comprises a pressurization
device for the chamber 102 which comprises a source of gas under pressure,
for example here the cylinder 103 situated outside the chamber 102, which
supplies a gas under pressure entering the chamber 102 by the inlet 105 fur
gas under pressure to increase the internal pressure of the chamber 102. A
pressure regulating device 106 enables the pressure inside the chamber 10210
be regulated. For this, the pressure regulating device 106 is disposed at the
inlet 105 for gas under pressure, just upstream, for example outside the
chamber 102.
The generator 101 furthermore comprises a fluid circuit which
comprises a bag 6 having an outlet for the fluid it contains, a joining
connector
107, and a connection conduit 108 itself connected to the bag 6 by the joining
connector 107. The joining connector 107, the connection conduit 108 as well
as the bag 6 are disposed in the chamber 102.
The fluid circuit further comprises a hydraulic sequencer 109 the inlet
of which is connected to at least the connection conduit 108, and the outlet
of
which is connected to an outlet conduit 110 connected the fluid outlet 104 of
the
chamber 102.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
21
The hydraulic sequencer 109 comprises in particular:
- a flexible deformable envelope (not shown), formed in a hydraulic
connection which connects the connection conduit 108
to the outlet conduit 110 inside the sequencer 109, all of
this being exposed to the pressure inside the chamber
102,
- at least one hydraulic obturating valve (not shown) in the hydraulic
connection, which may be situated upstream or
downstream of the flexible deformable envelope, or even
one upstream and another downstream,
- and a means (not shown) for actuating the various hydraulic
obturating valves.
The outlet conduit 110 is in turn connected to an external connection
conduit 112 for connection with the catheter 1.
To ensure sealing at the location of the outlet for fluid 104 of the
chamber 102, the outlet for fluid 104 is preferably provided with a cone
connector 111 for example of which a tapered part is preferably directed
towards the outside of the chamber 102 such that the internal pressure of the
chamber 102 tends to sink the cone further when the pressure increases.
In the present example embodiment, the hydraulic sequencer 109
with its associated actuating means are advantageously included in a
replaceable and interchangeable cassette, here placed inside the chamber 102.
According to the present example embodiment, the generator 101 is
adapted to generate a pulse of fluid at a pressure comprised between 2 and 30
bars, and with a volume of fluid per pulse comprised between 100 pl.. and
10 mL. For this, it is then preferable for the flexible deformable envelope to
have
a corresponding volume.
Of course, several bags 6 could be placed in the chamber 102 if
necessary, all connected to the sequencer 109.
The catheter 1 thus firstly has a connection to the generator of high
= pressure jets 101 by the fluidic connection 52 of the connector 5. In the
case of
a dual function catheter as described above, the device 100 further comprises
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28
22
an electricity generator 200 with which the catheter 1 then secondly has a
connection, for example by a cable 201 connected to the electrical connection
51 of the connector 5. The electricity generator 200 is generally designated
by
the term "ESU".
Naturally, the present invention is not limited to the preceding
description, but extends to any variant within the scope of the following
claims.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-05-28