Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
1
METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR TAGGING PACKETS ROUTED TO CUSTOMER
PREMISES DEVICES VIA CLUSTERS OF DEDICATED CUSTOMER INTERFACES
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates generally to the delivery of telecommunications
services such as voice, video and data to customer premises devices, and more
specifically to a method and system for tagging packets routed to customer
premises
devices via clusters of dedicated customer interfaces.
BACKGROUND
Telecommunication companies all over the world are continuously striving to
enhance their infrastructure in order to provide better broadband services and
therefore
meet the expectations of their customers.
A popular implementation for delivering broadband services is the xDSL-based
infrastructure, as it uses existing copper wires. This ensures that the copper
investment
is not wasted while at the same time keeps deployment costs relatively low.
However,
as the xDSL-based infrastructure becomes more complicated (e.g., due to the
requirement to deliver broadband services at a higher bandwidth), its use
ceases to be
cost-effective. In particular, switching components in the remote (outside
plant) unit are
required to operate at higher speeds, leading to increased cost,
The architectural design of the remote unit also suffers from another major
issue,
namely heat. In particular, excessive heat is generated by components of the
remote
unit operating at high frequencies, such as switching components, optical
devices and so
on. The heat generated by these devices will increase the ambient temperature
within
the remote unit. in the summer or in countries with a tropical climate,=the
remote unit
might fail to function properly as the ambient temperature of the remote unit
meets
and/or exceeds its maximum rated operating temperature.
Another major issue plaguing the existing design of an xDSL-based
infrastructure
is quality of service (QoS), particularly as the number of users increases
(e.g., as a result
of an increase in population density). The current paradigm calls for
implementing QoS
at the network core. However, traffic congestion is almost negligible at this
point
because of the presence of high capacity-links in the network core. Instead,
it can be
observed that traffic congestion actually occurs closer to the periphery of
the network,
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
Our Ref.: 86955-7
2
namely at the links branching out to the various remote units that service
individual neighborhoods.
These links have a fixed bandwidth and cannot readily cope with traditional
QoS management
mechanisms that rely on external factors to prioritize traffic, such as
service level agreements (SLAs)
reached with individual customers or end user applications that autonomously
(and often greedily)
assign a priority level to their own packets.
As a result, when packets associated with multiple services being delivered to
one or more
customers over a shared physical link compete for bandwidth resources on that
link, a reduction in
service performance or QoS is likely to occur in an unpredictable fashion,
leading to a degraded
customer experience.
Therefore, there is a need in the industry to address certain shortcomings of
the
conventional approach to delivering broadband services over an xDSL-based
infrastructure.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
According to a first broad aspect, the present invention seeks to provide a
method of routing
traffic to a plurality of customer premises devices (CPDs), each of the CPDs
being reachable via a
respective one of a plurality of dedicated customer interfaces (DCIs), wherein
the DCIs are grouped
into clusters included in respective outside plant units (OPUs). The method
comprises receiving
traffic via an input interface, the traffic comprising packets, each of said
packets being destined for
one of said CPDs; determining a destination DCI and a destination OPU for each
of the packets, the
destination DCI for a particular packet destined for a particular CPD being
determined by identifying
the DCI via which the particular CPD is reachable and the destination OPU for
the particular packet
being determined by identifying the OPU that includes the destination DCI; for
each particular OPU
that is the destination OPU for one or more packets, buffering the one or more
packets and
transmitting the buffered packets via an OPU interface uniquely associated
with the particular OPU;
and for each particular DCI that is the destination DCI for one or more
packets, tagging each of the
one or more packets with an indication of the particular DCI; and for a
particular one of said
clusters, receiving upstream traffic via an access interface for a particular
one of the DCIs in said
particular cluster, the traffic comprising upstream packets, each of said
upstream packets
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
Our Ref.: 86955-7
3
originating from at least one of the CPDs reachable via said particular DCI;
sending the upstream
packets towards a head-end unit over a communication link; and for said
particular DCI, receiving
additional upstream traffic from an adjacent one of the DC's in said
particular cluster, the additional
upstream traffic comprising additional upstream packets, each of said
additional upstream packets
originating from at least one of the CPDs reachable via ones of said DC's in
said particular cluster
other than the particular DCI; and aggregately sending said upstream packets
and said additional
upstream packets to a designated one of the DCIs in said particular cluster
that is connected to the
communication link and that is responsible for releasing the upstream traffic
towards the head-end
unit.
According to a second broad aspect, the present invention seeks to provide an
apparatus for
use in regulating traffic flow to a plurality of customer premises devices
(CPDs), each of the CPDs
being reachable via a respective one of a plurality of dedicated customer
interfaces (DCIs), wherein
the DC's are grouped into clusters included in respective outside plant units
(OPUs). The apparatus
comprises an input interface over which is received traffic, the traffic
comprising packets, each of
said packets being destined for a respective one of said CPDs; a plurality of
OPU interfaces, the
OPU interfaces being uniquely associated with respective ones of said OPUs and
connectable
thereto; a plurality of output buffers respectively associated with the OPU
interfaces, each of the
output buffers being configured to temporarily store packets for release via
the respective one of the
OPU interfaces towards the OPU uniquely associated therewith; and a
distribution/routing engine
configured to determine a destination DCI and a destination OPU for each of
the packets, the
destination DCI for a particular packet destined for a particular CPD being
determined by identifying
the DCI via which the particular CPO is reachable and the destination OPU for
the particular packet
being determined by identifying the OPU that includes the destination DCI. The
distribution/routing
engine is further configured to tag each of the packets with an indication of
the destination DCI for
the packet. Also, the distribution/routing engine is further configured to
route the tagged packet
towards the output buffer respectively associated with the destination OPU for
the packet. The
packets in the buffer respectively associated with a particular OPU interface
include first packets
and second packets, wherein the first packets carry traffic in a first
category of traffic and the
second packets carry traffic in a second category of traffic. The apparatus
further comprises an
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
Our Ref.: 86955-7
4
output buffer control entity configured to regulate packet flow via the OPU
interface by prioritizing
transmission of the first packets over transmission of the second packets.
According to a third broad aspect, the present invention seeks to provide an
apparatus for
routing traffic to a plurality of customer premises devices (CPDs), each of
the CPDs being
reachable via a respective one of a plurality of dedicated customer interfaces
(DCIs), wherein the
DCIs are grouped into clusters included in respective outside plant units
(OPUS). The apparatus
comprises means for receiving traffic via an input interface, the traffic
comprising packets, each of
said packets being destined for one of said CPDs; means for determining a
destination DCI and a
destination OPU for each of the packets, the destination DCI for a particular
packet destined for a
particular CPD being determined by identifying the DCI via which the
particular CPD is reachable
and the destination OPU for the particular packet being determined by
identifying the OPU that
includes the destination DCI; means for buffering packets and transmitting the
buffered packets via
an OPU interface uniquely associated with the OPU for which the buffered
packets are destined;
and means for tagging individual packets with an indication of the DCI for
which the individual
packets are destined, and for a particular one of said clusters, means for
receiving upstream traffic
via an access interface for a particular one of the DCIs in said particular
cluster, the traffic
comprising upstream packets, each of said upstream packets originating from at
least one of the
CPDs reachable via said particular DCI; and means for sending the upstream
packets towards a
head-end unit over a communication link; for said particular DCI, means for
receiving additional
upstream traffic from an adjacent one of the DCIs in said particular cluster,
the additional upstream
traffic comprising additional upstream packets, each of said additional
upstream packets originating
from at least one of the CPDs reachable via ones of said DC's in said
particular cluster other than
the particular DCI; and means for aggregately sending said upstream packets
and said additional
upstream packets to a designated one of the DCIs in said particular cluster
that is connected to the
communication link and that is responsible for releasing the upstream traffic
towards the head-end
unit.
According to a fourth broad aspect, the present invention seeks to provide a
method for
routing traffic to a plurality of customer premises devices (CPDs), each of
the CPDs being
reachable via a respective one of a plurality of dedicated customer interfaces
(DCIs), wherein the
DCIs are grouped into clusters included in respective outside plant units
(OPUs), the method
CA 2913681 2017-02-24
,
Our Ref.: 86955-7
4a
comprising receiving traffic via an input interface, the traffic comprising
packets, each of said
packets being destined for one of said CPDs; determining a destination DCI and
a destination
OPU for each of the packets, the destination DCI for a particular packet
destined for a particular
CPD being determined by identifying the DCI via which the particular CPD is
reachable and the
destination OPU for the particular packet being determined by identifying the
OPU that includes
the destination DCI; for each particular OPU that is the destination OPU for
one or more packets,
buffering the one or more packets and transmitting the buffered packets via an
OPU interface
uniquely associated with the particular OPU; and for each particular DCI that
is the destination DCI
for one or more packets, tagging each of the one or more packets with an
indication of the
particular DCI; wherein buffering the one or more packets comprises placing
the packets into a
buffer for the particular OPU.
According to a fifth broad aspect, the present invention seeks to provide an
apparatus for
routing traffic to a plurality of customer premises devices (CPDs), each of
the CPDs being
reachable via a respective one of a plurality of dedicated customer interfaces
(DCIs), wherein the
DC's are grouped into clusters included in respective outside plant units
(OPUs), the apparatus
comprising means for receiving traffic via an input interface, the traffic
comprising packets, each of
said packets being destined for one of said CPDs; means for determining a
destination DCI and a
destination OPU for each of the packets, the destination DCI for a particular
packet destined for a
particular CPD being determined by identifying the DCI via which the
particular CPD is reachable
and the destination OPU for the particular packet being determined by
identifying the OPU that
includes the destination DCI; means for buffering packets and transmitting the
buffered packets
via an OPU interface uniquely associated with the OPU for which the buffered
packets are
destined; and means for tagging individual packets with an indication of the
DCI for which the
individual packets are destined; wherein the means for buffering the one or
more packets
comprises means for placing the packets into a buffer for the particular OPU.
According to a sixth broad aspect, the present invention seeks to provide an
outside plant
unit. The outside plant unit comprises a cluster of dedicated customer
interfaces (DCIs) serially
interconnected in a chain, a designated one of the DCIs being connectable to a
head-end unit over
a communication link, wherein each of the DCIs is connected to one or more
respective customer
CA 2913681 2017-02-24
Our Ref.: 86955-7
4b
premises devices (CPDs) over respective communication links; and at least one
of the DC's
comprising a drop/forward unit configured to (a) receive a packet from the
head-end unit that has
been tagged with a tag indicative of a destination DCI, (b) carry out a
comparison of the
destination DCI with a predetermined identifier associated with that DCI, (c)
forward the packet to
an adjacent one of the DC's if the destination DCI does not match the
predetermined identifier
associated with that DCI, and (d) determine a destination CPD for the packet
and route the packet
to the destination CPD if the destination DCI matches the predetermined
identifier associated with
the at least one of the DCIs.
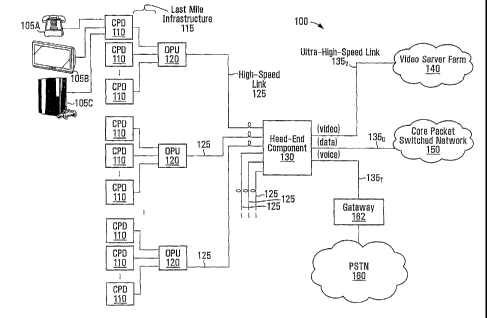
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure 1 is a block diagram showing components of a system for service-based
regulation
of traffic flow to customer premises devices according to a non-limiting
example of implementation
the invention, the system including a head-end component and a plurality of
Outside Plant Units
(OPUs);
Figure 2 is a block diagram showing components of the head-end component
included
within the system illustrated in Figure 1;
Figure 3 is a block diagram showing components of a Dedicated Customer
Interface (DCI)
module located within one embodiment of the Outside Plant Unit (OPU);
Figure 4 is a block diagram showing components of an aggregator sub-component
forming
part of the head-end component illustrated in Figure 2;
Figure 5 is a block diagram showing components of the DCI module;
Figure 6 is a block diagram showing multiple DCI modules within another
embodiment of
the OPU; and
Figure 7 is a block diagram showing how certain components of the aggregator
sub-
component in the head-end component tag downstream packets to identify a
particular DCI module
for which they are destined.
CA 2913681 2017-02-24
s.
Our Ref.: 86955-7
4c
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
In accordance with a non-limiting embodiment of the present invention, and
with reference
to Figure 1, a system 100 for the service-based regulation of traffic flow to
customer premises
devices (CPDs) is presented. The system 100 includes a plurality of CPDs 110
that are distributed
throughout a particular geographic region, such as an urban, sub-urban or
rural area. Examples of
geographic regions throughout which the CPDs 110 may be distributed include
residential areas
(e.g., apartment buildings, housing developments), commercial areas (e.g.,
individual retail stores,
shopping malls, office buildings) and industrial areas (e.g., factories,
warehouses, industrial parks).
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100 5
PCT/MY2009/000080
The system 100 also includes a plurality of Outside Plant Units (OPUs) 120.
Each of the OPUs 120 is connected to a subset of the CPDs 110 in a particular
geographic area. This connection is achieved over a so-called "last-mile"
infrastructure
115, which belongs to or is managed by a network access provider. The last-
mile
infrastructure 115 that connects each of the CPDs 110 to a respective one of
the OPUs
120 may include a wired component (such as copper twisted-pair cable or a
power line)
and/or a wireless component, such as a proximate cellular base station or a
wireless
WAN (e.g., WiMAX) installation.
The CPDs 110 each comprise certain communications equipment for
communicating with respective ones of the OPUs 120. The implementation of the
CPDs
110 and, in particular, their communications equipment, depends on the last-
mile
infrastructure 115. For example, where the last-mile infrastructure 115 is
based on
copper twisted-pair cable, the CPDs 110 may each comprise a broadband modem
that is
designed to communicate over such an infrastructure. Other possibilities exist
and are
within the scope of the present invention.
A particular one of the CPDs 110 may comprise a distribution/aggregation
device
(not shown), allowing multiple end user devices 105A, 105B, 105c to share the
use of the
connection between the particular one of the CPDs 110 and the respective one
of the
OPUs 120. Non-limiting examples of a distribution/aggregation device include a
router,
splitter and/or residential gateway, whereas non-limiting examples of an end
user device
include television set top boxes, computers, gaming devices and/or telephones.
The system 100 also comprises a head-end component 130 (or "head-end unit").
The head-end component 130 may be connected via one or more ultra high-speed
links
135v, 135, 135r to certain resources that are provided by, or made accessible
to, the
network access provider. Such resources may include a video server farm 140, a
core
packet-switched network 150 (such as the Internet), and/or a Public Switched
Telephone
Network (PSTN) 160 (accessible via a PSTN gateway 162).
The OPUs 120 are connected to the head-end component 130 via respective
high-speed links 125. Individual ones of the high-speed links 125 may be bi-
directional
or formed from pairs of unidirectional links. For example, an optical fiber
link can be
used for downstream traffic travelling from the head-end component 130 to a
given one
of the OPUs 120, as well as for upstream traffic travelling in the other
direction (i.e., from
the given one of the OPUs 120 to the head-end component 130). Where the high-
speed
links 125 are formed from pairs of unidirectional links, the same or different
linking media
CA 02 913 681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100 6
PCT/MY2009/000080
may be used for each unidirectional link. For example, a linking medium that
is wired
(e.g., an optical fiber link) can be used for downstream traffic travelling
from the head-
end component 130 to a given one of the OPUs 120, whereas a linking medium
that is
wireless (e.g., a WilVIA)( connection or a satellite link) can be used in the
opposite
direction (i.e., from the given one of the OPUs 120 to the head-end component
130). It
should be appreciated that communications along the high-speed links 125 may
be
carried out in accordance with any suitable communications protocol. Examples
of such
protocols that will be well known to those skilled in the art include the
SONET and SDH
multiplexing protocols, as well as the 10, 100 and 1000 Gigabit Ethernet (GbE)
protocols,
among others.
In some non-limiting embodiments, it is expected that the high-speed links 125
will be bandwidth-constrained. Constraints on bandwidth can be inherent due to
the
linking media and signaling protocol used, or they may be artificially imposed
by the
network access provider. In particular, bandwidth constraints may be
artificially imposed
on the high-speed links 125 in order to limit the processing power required by
the OPUs
120 to levels that keep the heat generated from their casings during operation
to within
acceptable bounds. In this way, the OPUs 120 can be designed in a cost-
effective way
and/or such that the unsightly addition of cooling equipment otherwise needed
to
dissipate excess heat generated during operation can be avoided.
Head-End Component
Figure 2 shows a possible configuration of the head-end component 130, in an
example non-limiting embodiment. In particular, Figure 2 shows that the head-
end
component 130 includes various sub-components including an aggregator sub-
component 200 and a switching sub-component 260, as well as a set of internal
high-
speed links 255v, 255, 255i that facilitate communications between these two
sub-
components. The switching sub-component 260 can be connected to any number of
instances of an aggregator sub-component. In fact, Figure 2 shows two (2)
instances of
an aggregator sub-component as being connected to the switching sub-component
260.
However, to simplify the description, unless otherwise noted, the remainder of
the
description will consider only the aggregator sub-component 200.
The aggregator sub-component 200 may represent the portion of the head-end
component 130 that can be connected to the OPUs 120 via the high-speed links
125.
The aggregator sub-component 200 can be thought of as having a "customer side"
that
is connected to the OPUs 120, as well as a "network side", which is connected
to the
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
7
switching sub-component 260. The aggregator sub-component 200 includes a set
of
customer-side ports 210, a set of customer-side interfaces 220 (or "OPU
interfaces"), a
processing entity 230, a set of network-side interfaces 240v, 240o, 240T and a
set of
network-side ports 250v, 250o, 250.
The "customer side" of the aggregator sub-component 200 typically includes the
aforementioned customer-side ports 210 and customer-side interfaces 220. The
customer-side ports 210 terminate respective ones of the high-speed links 125
that
connect the head-end component 130 to its subtending OPUs 120. In the
illustrated
embodiment, the aggregator sub-component 200 includes three (3) customer-side
ports
210, although this number should not be considered as a limitation of the
invention.
Each of the customer-side ports 210 corresponds to a respective one of the
customer-side interfaces 220 that converts signals received along the high-
speed links
125 into signals compatible with the remainder of the head-end component 130
using
methods that are known in the art. For example, in the case where the high-
speed links
125 are based on optical fiber, the customer-side interfaces 220 may comprise
optical-
to-electrical conversion circuitry for converting optical signals originating
from respective
ones of the OPUs 120 to electrical signals that can be processed by the
processing
entity 230 of the aggregator sub-component 200.
The "network side" of the aggregator sub-component 200 includes the
aforementioned network-side interfaces 240v, 240, 240T and network-side ports
250v,
250o, 250T. The network-side ports 250v, 250o, 250T terminate the internal
high-speed
links 255v, 255o, 255T between the aggregator sub-component 200 and the
switching
sub-component 260. Specifically, each of the network-side ports 250v, 250,
250T
corresponds to a respective one of the network-side interfaces 240v, 240o,
240T that
processes, converts and/or encodes signals or data to be sent by the
aggregator sub-
component 200 into a form compatible with the internal high-speed links 255v,
255o,
255T and the switching sub-component 260 using methods known in the art.
Each of the network-side interfaces 240v, 240o, 240T is designed to handle a
particular "category" (or "type") of traffic. A common category of traffic
includes traffic
which, while different in terms of actual content, has sufficient commonality
such that it
requires a common degree of treatment with respect to one or more parameters
such as
bandwidth, priority, loss, delay, etc. An examples of a traffic category is
video traffic,
which may have certain high-bandwidth, low-loss requirements. Another category
is
voice, which has less stringent bandwidth and loss requirements but requires
low delay.
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
8
Another category is data which can have relaxed bandwidth and delay
requirements but
might tolerate very little loss. These requirements and general
characterizations are
merely examples and are not to be taken as limiting.
In accordance with a specific non-limiting embodiment of the present
invention, at
least two (2) of the network-side interfaces 240v, 240D, 240T are
distinguishable from one
another and are dedicated to handling different categories of traffic. For
example,
network-side interface 240v may be used to handle traffic in the video
category, network-
side interface 240D may be used to handle traffic in the data category and
network-side
interface 240T may be used to handle data in the voice category.
In the illustrated embodiment, the three (3) network-side interfaces 240v,
240o,
240T are respectively connected to the three (3) network-side ports 250v, 250,
250T. As
with the network-side interfaces 240v, 240, 240T, the network-side ports 250v,
250,
250T are similarly allocated to distinct categories of traffic traveling
between the
aggregator sub-component 200 and the switching sub-component 260.
Specifically,
network-side port 250v carries video traffic, network-side port 250D carries
data traffic
and network-side port 250T carries voice traffic. In other embodiments,
however, traffic
in different categories may be multiplexed onto a single internal high-speed
link (via a
single network-side port), in which case the network-side interfaces 240v,
240, 240T in
the aggregator sub-component 200 may connect to multiplexing/demultiplexing
circuitry
that allows co-existence of multiple traffic types on a single physical link.
The processing entity 230 conceptually straddles the customer-side and network-
side portions of the aggregator sub-component 200. The processing entity 230
can be
implemented in hardware, software or a combination of hardware and software
that
executes code which implements a control logic function. The processing entity
230
performs several functions that will be discussed later on.
The switching sub-component 260 forms the other main component within the
head-end component 130. The switching sub-component 260 is comprised of a
control
unit 262, a switching unit 264, a set of aggregator interfaces 270v, 270o, 270-
r, 275v,
275D, 275T and a set of core network interfaces 280v, 280D, 280T.
As with the aggregator sub-component 200, the switching sub-component 260
can be thought of as having a "customer side" and a "network side". On the
"customer-
side", the switching sub-component 260 connects to the aggregator sub-
component 200
(rather than directly to the OPUs 120) over the internal high-speed links
255v, 255,
255T. It should be noted that unlike the bandwidth-constrained high-speed
links 125 that
CA 02 913 681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
9
connect the OPUs 120 to the aggregator sub-component 200, the internal high-
speed
links 255v, 255o, 255T between the switching sub-component 260 and the
aggregator
sub-component 200 can be assumed to always have sufficient bandwidth, as they
are
under the full control of the network access provider.
The "customer side" of the switching sub-component 260 includes the
aforementioned aggregator interfaces 270v, 270o, 270T, 275v, 275o, 275T. In
the case of
aggregator interfaces 270v, 270, 270T, these terminate the internal high-speed
links
255v, 255o, 255T connecting the switching sub-component 260 to the aggregator
sub-
component 200. Each of the aggregator interfaces 270v, 270o, 270T is connected
to a
respective one of the network-side ports 250v, 250o, 250T of the aggregator
sub-
component 200. Each of the aggregator interfaces 270, 270o, 270T is designed
to
handle a distinct category of traffic between the switching sub-component 260
and the
aggregator sub-component 200. Specifically, aggregator interface 270v handles
video
traffic, aggregator interface 270o handles data traffic and aggregator
interface 270T
handles voice traffic. In other embodiments, traffic in different categories
may be
multiplexed onto a single internal high-speed link, in which case the
aggregator
interfaces 270v, 270o, 270T in the aggregator sub-component 200 may connect to
multiplexing/demultiplexing circuitry that allows co-existence of multiple
traffic types on a
single physical link.
The "network side" of the switching sub-component 260 includes the
aforementioned core network interfaces 280v, 280o, 2801. The core network
interfaces
280v, 280o, 280T allow traffic to be processed and transferred via the ultra
high-speed
links 135v, 135o, 135T between the head-end component 130 and other components
of
the system 100, such as the video server farm 140, the core packet-switched
network
150 and/or the PSTN 160.
In the illustrated embodiment, the switching sub-component 260 includes three
(3) core network interfaces 280v, 280, 280T. In the illustrated embodiment,
the core
network interfaces 280v, 280o, 280T are designed to handle distinct categories
of traffic
traveling between the switching sub-component 260 and the core packet-switched
network 150, the video server farm 140 and/or the PSTN 160 via distinct
physical ports.
In other embodiments, traffic in different categories may be multiplexed onto
a single
ultra high-speed link, in which case the core network interfaces 280v, 280o,
280T may
connect to multiplexing/demultiplexing circuitry that allows co-existence of
multiple traffic
types on a single physical link.
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
The implementation of individual ones of the core network interfaces 280v,
280o,
280T depends on the type of ultra high-speed links 135v, 135o, 135T used to
connect the
switching sub-component 260 to the other components of the system 100. For
example,
a particular one of the core network interfaces 280v, 280D, 280T may provide
electrical-to-
5 optical conversion (and vice versa) and SONET frame assembly/disassembly
if the ultra-
high speed connection to the core packet-switched network 150, the video
server farm
140 and/or the PSTN 160 is composed of a SONET link. Another one of the core
network interfaces 280v, 280, 280T may provide 10GBE encapsulation/de-
encapsulation
if the ultra-high speed connection to the core packet-switched network 150,
the video
10 server farm 140 and/or the PSTN 160 is composed of a 10GBE link.
As stated earlier, the switching sub-component 260 includes a control unit 262
and a switching unit 264. The switching unit 264 carries out switching of
packets
received from the internal high-speed links 255v, 255D, 255- (in an upstream
direction)
and from the ultra high-speed links 135v, 13511 1351- (in a downstream
direction). In this
way, packets destined to or from the OPUs 120 (via the aggregator sub-
component 200)
and/or destined to or from the video server farm 140, the core packet-switched
network
150 and/or the PSTN 160 can be switched appropriately.
The control unit 262 controls the functionality of the switching unit 264. The
control unit 262 can be implemented as dedicated hardware, software or a
combination
of dedicated hardware and software that executes code which implements a
control logic
function.
In one non-limiting embodiment of the invention, the switching unit 264 is
used to
route traffic arriving from the video server farm 140, the core packet-
switched network
150 and/or the PSTN 160 via the associated one of the ultra high-speed links
135v,
135D, 1351- to the aggregator sub-component 200. For example, a packet from
the video
server farm 140 that represents a video frame (hereinafter, a "downstream
video
packet") arrives along ultra high-speed link 135v and is processed by core
network
interface 280v. The control unit 262 knows that the received packet is a
downstream
video packet (as opposed to a downstream data packet or a downstream voice
packet)
based upon the particular core network interface (in this case, core network
interface
280v) at which was received. The downstream video packet may be converted by
core
network interface 280v into a form that may be analyzed by the control unit
262 and
redirected by the switching unit 264 onto the appropriate internal high-speed
link.
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100 11
PCT/MY2009/000080
Specifically, based on the content of the downstream video packet, the control
unit 262 can identify whether the downstream video packet should be directed
to one
aggregator sub-module or another. For example, the downstream video packet may
include a header and a payload, where the header includes information about a
particular CPD for which the packet is destined (e.g., in the form of an IP
address for the
particular CPD). Based on this information and on knowledge of how the CPDs
110 are
distributed geographically, the control unit 262 instructs the switching unit
264 to direct
the downstream video traffic to aggregator interface 270v or aggregator
interface 275v,
both of which are configured to handle downstream video packets but are
associated
with different aggregator sub-components serving different geographic regions.
In this case, the downstream video packet representing the video frame can be
sent towards the aggregator sub-component 200 on internal high-speed link
255v, which
is dedicated to carrying video traffic. Naturally, aggregator interface 270v
may convert
the downstream video packet into a form suitable for transmission across
internal high-
speed link 255v. It should be appreciated that in other embodiments, a certain
amount of
multiplexing may be performed in order to transport the downstream video
packet
together with downstream packets in other traffic categories over the same
internal high-
speed link. In any event, the downstream video packet then arrives at core
network port
250v of the aggregator sub-component 200.
Although the above description focused on packets belonging to the video
traffic
category, similar operations would take place in the case of traffic from
other categories,
such as packets representing telephone conversations (i.e., downstream voice
packets)
and/or packets representing data received via the core packet switched network
150
(i.e., downstream data packets). In each case, knowledge of the traffic
category to which
a particular received downstream packet belongs is obtained from knowledge of
the core
network interface at which the packet was received, and in each case the
correspondence between a particular packet's traffic category and the identity
of the
aggregator interface that processes the particular packet is preserved.
Outside Plant Unit
By way of illustrative non-limiting embodiment, Figure 3 shows certain
components of a particular one of the OPUs 120, hereinafter denoted 120A. OPU
120A
includes at least one instance of a dedicated customer interface (DCI) module,
which
may also be referred to as a "line card" or simply as a "DCI". OPU 120A may
contain a
cluster of one (1) or more DCI modules 300 within a single physical structure
(e.g.,
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100 12
PCT/MY2009/000080
chassis). In the illustrated embodiment, three (3) DCI modules 300 are shown,
but this is
not to be considered as a limitation of the present invention.
In one embodiment of OPU 120A, it may be beneficial to implement certain
switching functionality between the DCI modules 300 in order to direct traffic
more
efficiently. In such a case, a "switching sub-component" (not shown) is
interconnected to
the plurality of DCI modules 300 via a backplane (not shown). In another
embodiment of
OPU 120A, no dedicated switching hardware is used. Instead, the plurality of
DCI
modules 300 are connected to form a "daisy chain" that removes the need for
dedicated
hardware to perform switching between cards. This embodiment will be described
in
more detail later.
The DCI modules 300 will now be described in further detail. For simplicity,
let it
be assumed that OPU 120A contains a single DCI module denoted 300A. The DCI
module 300A is comprised of a set of customer-side ports 310, an access
network
interface 320, a processing entity 330, a network-side interface 340, and a
network-side
port 350.
The DCI module 300A may be thought of as having a "customer side" and a
"network side". The "customer side" of the DCI module 300A is in communication
with
the various CPDs 110 that are serviced by OPU 120A, while the "network side"
of DCI
module 300A is communicatively coupled to the head-end component 130.
The "network side" of the DCI module 300A includes the network-side interface
340 and the network-side port 350. The network-side interface 340 allows
communication over a respective one of the high-speed links 125 via the
network-side
port 350. For example, if the high-speed links 125 are optical fiber links,
the network-
side interface 340 may include electrical-to-optical (and optical-to-
electrical) conversion
circuitry in order to convert electrical signals to optical signals and vice-
versa. The
network-side interface 340 may also comprise formatting of electrical signals
into a
format that is compatible with the other components of the DCI module 300A,
and in
particular with the processing entity 330 and/or the access network interface
320.
The 'customer side" of the DCI module 300A includes the customer-side ports
310 and the access network interface 320. The customer-side ports 310 include
one
port for each CPD that is served by the DCI module 300A. The access network
interface
320 implements a signaling protocol compatible with the last-mile
infrastructure 115
deployed between OPU 120A and the CPDs 110 it serves. For example, in the case
where the last-mile infrastructure 115 is comprised of twisted-pair copper
cable, the
=
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
13
access network interface 320 may implement an xDSL encoding and modulation
scheme. Where the last-mile infrastructure 115 is comprised of wireless links
(such as
WiFi or WiMAX links, or WCDMA, BFA or 3G micro base stations), the access
network
interface 320 may implement wireless protocols suitable for use with WiFi or
WiMAX
receivers. Where the last-mile infrastructure 115 is based on power-line
connections,
the access network interface 320 may be equipped with suitable BPL receivers.
Indeed,
the last-mile infrastructure 115 may be formed of a mix of wired and wireless
media (e.g.,
a wired portion for proximate CPDs and a wireless portion for less-proximate
CPDs).
The access network interface 320 and the customer-side ports 310 can be
suitably
adapted to such circumstances.
The processing entity 330 analyzes and processes packets received from both
the customer-side ports 310 and the network-side port 350. In the case where a
downstream packet is received from the network-side port 350, the processing
entity 330
can be used to analyze the downstream packet to identify a destination CPD,
i.e., one of
the CPDs 110 towards which the downstream packet is destined. This information
can
be learned by consulting a header of the packet. Once the destination CPD has
been
determined for the downstream packet, the processing entity 330 can formulate
the
packet such that when it is interpreted by the access network interface 320,
the latter will
know to release it via the correct one of customer-side ports 310 (i.e., the
one leading to
the destination CPD).
The processing entity 330 can also process packets travelling in the opposite
(i.e., upstream) direction, namely an upstream packet that was sent from a
particular one
of the CPDs 110 and that arrives at one of the customer-side ports 310. In
this case, the
access network interface 320 aggregates many such received upstream packets
and
sends them towards the processing entity 330. The processing entity 330 then
may
simply channel the upstream packets towards the network-side interface 340 for
transmission to the head-end component 130 via the network-side port 350.
Thus, it will be appreciated that individual ones of the high-speed links 125
carry
traffic in various traffic categories that is destined for (and originating
from) multiple
CPDs 110. The traffic categories may include video, voice and/or data, as well
as
possibly additional or alternate traffic categories. However, bandwidth
constraints on the
high-speed links 125 can cause the potential for a traffic bottleneck to
develop at both
ends of a given one of the high-speed links 125 as packets from the different
traffic
categories that are destined for (or originating from) different CPDs 110
(and/or different
end user devices) vie for transfer along the given one of the high-speed
links. The
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100 14
PCT/MY2009/000080
development of such a bottleneck may impact the quality of service (QoS) of
one or
more services (e.g., related to voice, data and/or video communication) as
perceived by
one or more of the end user devices that share the bandwidth available on the
given one
of the high-speed links 125.
Service Hierarchy
The head-end component 130 functions to deliver traffic in the various traffic
categories to the CPDs 110 at an acceptable quality of service in each traffic
category
despite the existence of bandwidth constraints (whether inherent or
artificially imposed)
on the high-speed links 125. According to an embodiment of the invention,
therefore,
QoS management can be achieved by implementing a "service hierarchy", whereby
one
category of traffic is prioritized over others. In this embodiment, packets
that belong to
the prioritized traffic category receive preferential access to the high-speed
links 125 that
would allow their transfer and delivery to become more regular and predictable
than
would otherwise be the case.
In a non-limiting example of a service hierarchy, packets in a first traffic
category
are given priority over packets in any other traffic category. For example,
"video
packets' (e.g., packets belonging to the video traffic category and that may
represent
encoded video frames of a movie or television show) can be given priority over
both
"voice packets" (e.g., packets belonging to the voice traffic category and
that may
represent encoded speech frames) and "data packets" (e.g., packets belonging
to the
data traffic category and that may represent data obtained from a server on
the packet-
switched network) which belong to the voice and data traffic categories,
respectively.
Other service hierarchies are of course possible, including multi-level
service hierarchies,
whereby packets in a first traffic category are given priority over packets in
a second
traffic category and traffic in the second traffic category are given priority
over packets in
a third traffic category.
The service hierarchy can be used to regulate the flow of the traffic along
the
high-speed links 125 through careful design of the processing entities 230 and
330
which, as previously described, belong respectively to the aggregator sub-
component
200 in the head-end component 130 and to the DCI module 300A within OPU 120A.
In
particular, the processing entity 230 in the aggregator sub-component 200 is
designed
for regulating "downstream traffic", which refers to packets currently at the
head-end
component 130 that are destined for the various OPUs 120 to which it is
connected.
Analogously, the processing entity 330 in the DCI module 300A can be designed
for
=
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100 15
PCT/MY2009/000080
regulating "upstream traffic", which refers to packets originating from the
subtending
CPDs 110 that are awaiting transmission from OPU 120A to the head-end
component
130.
Aggregator Sub-Component Detailed Operation
Figure 4 shows the design of the aggregator sub-component 200, and in
particular, shows the processing entity 230 and the network-side interfaces
240v, 240D,
240T that are respectively associated with the network-side ports 250v, 250,
250-r
Where the internal high-speed links 255v, 255D, 255T are bidirectional, each
of the
network-side interfaces 240v, 240D, 240T includes a respective
splitter/combiner 410 in
addition to optical-to-electric and electric-to-optical conversion circuitry.
The
splitter/combiner 410 allows downstream traffic in a particular traffic
category to co-exist
with upstream traffic on the same internal high-speed link (i.e., one of the
internal high-
speed links 255v, 255, 255T between the aggregator sub-component 200 and the
switching sub-component 260). A similar spliffer/combiner may also be provided
by the
customer-side interfaces 220 connected to the high-speed links 125 leading to
the OPUs
120.
Downstream
Operation of the processing entity 230 in the context of handling packets
travelling in a downstream direction and in an upstream direction will be
discussed
separately. To begin with, in the context of downstream traffic, the
processing entity 230
in the aggregator sub-component 200 may implement, for each traffic category,
a
downstream input buffer and a distributor/router. As a non-limiting example,
for the
video traffic category, the processing entity 230 may implement a downstream
input
buffer 420v and a distributor/router 430v. Similarly, for the data traffic
category, the
processing entity 230 may implement a downstream input buffer 420D and a
distributor/router 430D. Finally, for the voice traffic category, the
processing entity 230
may implement a downstream input buffer 420T and a distributor/router 430T.
In addition, the processing entity 230 may implement a respective downstream
output buffer 440 and a respective output buffer control entity 450 for each
of the OPUs
120 to which the aggregator sub-component 200 is connected. For example, if
there are
five (5) OPUs connected to the aggregator sub-component 200, there can be five
(5)
downstream output buffers 440 and five (5) output buffer control entities 450.
It should
be appreciated that individual subsets of these entities can be combined into
a larger
structural or functional unit. Specifically, two or more of the downstream
output buffers
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
16
440 could be combined into a pooled hardware memory resource, or they can each
be
implemented as a separate dedicated hardware memory resource.
Each of the downstream output buffers 440 is specially designed to allow the
corresponding one of the output buffer control entities 450 to know the
traffic category of
each packet placed into that downstream output buffer.
In one embodiment, a given one of the downstream output buffers 440 can be
implemented as a plurality of micro-buffers, one for each traffic category and
having a
respective input connected to a respective output of a respective one of the
distributor/routers 430v, 430, 430T. In this case, the corresponding one of
the output
buffer control entities 450 can selectively read from one micro-buffer or
another
depending on the service hierarchy being implemented.
In another embodiment, a given one of the downstream output buffers 440 can
be implemented as a shared random access memory divided into a plurality of
reserved
blocks, one for each traffic category, where a packet is written to a
particular block
depending on which of the distributor/routers 430v, 430, 430T issued the
packet. In this
case, the corresponding one of the output buffer control entities 450 can
selectively read
from one block of memory or another depending on the service hierarchy being
implemented.
In yet another embodiment, each of the distributor/routers 430v, 430, 430r
appends auxiliary information to each of the packets it processes, where the
auxiliary
information is indicative of the traffic category of the packet. Thus, packets
entering a
given one of the downstream output buffers 440 will include an indication of
their own
traffic category. In this case, the corresponding one of the output buffer
control entities
450 can readily implement the service hierarchy by selectively choosing to
release
packets from the given one of the downstream output buffers 440 based on each
packet's auxiliary information.
In a further embodiment, each of the packets in a given one of the downstream
packets includes a virtual local area network (VLAN) identifier, and each VLAN
identifier
can correspond to a VLAN that is known to be associated with a particular
traffic
category. For example, a table can be kept in memory which associates VLAN
identifiers to traffic categories. In this way, the downstream
distribution/routing engine
431 may include a single distributor/router which receives packets along a
common
physical port. Here, the distinction between the network-side interfaces 240v,
240, 240-r
is logical rather than physical.
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100 17
PCT/MY2009/000080
It should be noted that the term "buffer" as used above is merely
representative,
since its implementation could be generally in the form of a temporary storage
area with
a corresponding memory management function that allows flexibility in writing
to and/or
reading from the storage area.
The distributor/routers 430v, 430, 4$0T provide distribution and routing
functionality for downstream packets in each respective traffic category. To
illustrate,
consider downstream video packets, which are received via network-side port
250, and
network-side interface 240v. Upon receipt of a given downstream video packet,
distributor/router 430v identifies a particular one of the OPUs 120 that the
given
downstream video packet is destined for. This can be done by analyzing a
header of the
given downstream video packet in order to identify a destination CPD, i.e.,
one of the
CPDs 110 towards which the given downstream video packet is destined. Then, on
the
basis of a mapping (which can be stored in a memory accessible to
distributor/router
430v), distributor/router 430v identifies the particular one of the OPUs 120
towards which
the given downstream video packet is destined. Subsequently,
distributor/router 430v
routes the given downstream video packet to a particular one of the downstream
output
buffers 440 that corresponds to the particular one of the OPUs 120 that was
identified.
The downstream video packet is then written to the appropriate micro-buffer or
memory
block associated with the video traffic category.
Similarly, consider downstream data packets that are received via network-side
port 250D and network-side interface 240D. Upon receipt of a given downstream
data
packet, distributor/router 430D identifies a particular one of the OPUs 120
that the given
downstream data packet is destined for. This can be done by analyzing a header
of the
given downstream data packet in order to identify a destination CPD, i.e., one
of the
CPDs 110 towards which the given downstream data packet is destined. Then, on
the
basis of a mapping (which can be stored in a memory accessible to
distributor/router
430D), distributor/router 430D identifies the particular one of the OPUs 120
towards which
the given downstream data packet is destined. Subsequently, distributor/router
430D
routes the given downstream data packet to a particular one of the downstream
output
buffers 440 that corresponds to the particular one of the OPUs 120 that was
identified.
The given downstream data packet is then written to the appropriate micro-
buffer or
memory block associated with the data traffic category.
Finally, consider downstream voice packets, which are received via network-
side
port 250T and network-side interface 240. Upon receipt of a given downstream
voice
packet, distributor/router 430T identifies a particular one of the OPUs 120
that the given
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100 18
PCT/MY2009/000080
downstream voice packet is destined for. This can be done by analyzing a
header of the
given downstream voice packet in order to identify a destination CPD, i.e.,
one of the
CPDs 110 towards which the given downstream voice packet is destined. Then, on
the
basis of a mapping (which can be stored in a memory accessible to
distributor/router
4301), distributor/router 430T identifies the particular one of the OPUs 120
towards which
the given downstream voice packet is destined. Subsequently,
distributor/router 430-r
routes the given downstream voice packet to a particular one of the downstream
output
buffers 440 that corresponds to the particular one of the OPUs 120 that was
identified.
The given downstream voice packet is then written to the appropriate micro-
buffer or
memory block associated with the voice traffic category.
It should be noted that the distributor/routers 430v, 430, 430T do not need to
analyze or otherwise process each downstream packet's header to ascertain the
traffic
category to which it belongs. This is because only downstream video packets
will arrive
at distributor/router 430v by virtue of their arrival via network-side port
250v, while only
downstream data packets will arrive at distributor/router 430D by virtue of
their arrival via
network-side port 250D, and only downstream voice packets will arrive at
distributor/router 4301 by virtue of their arrival via network-side port 250T.
It should also be noted that the distributor/routers 430v, 430D, 430T can be
implemented as separate physical devices or they can be individual software or
firmware
components forming part of a larger module. Indeed, the distributor/routers
430v, 430D,
430T can be conceptually thought of as forming an overarching downstream
distribution/routing engine 431.
At this point, it should be apparent that downstream packets in various
traffic
categories (i.e., video, data and voice) that are destined for a common one of
the OPUs
(associated with a given one of the downstream output buffers 440) will find
themselves
awaiting transmission in the same given one of the downstream output buffers
440.
These downstream packets compete for transmission along a common one of the
(bandwidth-constrained) high-speed links 125 leading to the common one of the
OPUs
120. To avoid or alleviate potential congestion caused by competition between
downstream packets for transmission on this link (and the likely negative
impact on
customer experience that such congestion would cause), the contents of the
given one
of the downstream output buffers 440 are released in accordance with a service
hierarchy that is implemented by the corresponding one of the output buffer
control
entities 450.
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100 19
PCT/MY2009/000080
Specifically, each of the output buffer control entities 450 is configured to
prioritize the manner in which the downstream packets in the corresponding one
of the
downstream output buffers 440 are transmitted to the corresponding one of the
customer-side interfaces 220 (and eventually via the corresponding one of the
customer-
side ports 210). By "prioritization", it is meant that one or more downstream
packets in
one traffic category (and identifiable as such by virtue of the micro-buffer
or memory
block in which it is located, or by other means) are released before
downstream packets
in another traffic category, even though both sets of packets await
transmission at the
same time. More specifically, "prioritization" can be interpreted to cover the
case where
all buffered packets in a first traffic category are released before any
buffered packets in
a second traffic category are released. In accordance with one non-limiting
alternative,
"prioritization" can be interpreted to cover the case where, on average, for
each buffered
packet in a second category that is released, a greater number of buffered
packets in a
first traffic category will be released.
Each of the output buffer control entities 450 may also be configured to carry
out
a prior step of determining whether prioritization is required and then
carrying out the
aforementioned prioritization as a function of whether or not it was
determined that
prioritization is required. In particular, if a situation was identified where
prioritization is
required, then prioritization may be carried out as previously described.
In order to identify situations where prioritization is required, a given one
of the
output buffer control entities 450 may be configured to detect the presence of
congestion
on the corresponding one of the high-speed links 125 leading from the
corresponding
one of the customer-side ports 210 to the corresponding one of the OPUs 120.
This can
be measured indirectly through monitoring of an "occupancy level" of the
corresponding
one of the downstream output buffers 440. The term "occupancy level" can refer
to an
indication of the number of packets that are currently awaiting transmission,
either on an
absolute basis (e.g., number of packets) or on a relative basis (e.g., as a
percentage of
total buffer capacity). In one approach, a certain threshold buffer occupancy
level could
be established which, when reached, indicates to the given one of the output
buffer
control entities 450 that prioritization of packets becomes necessary. In some
embodiments, prioritization can be triggered as soon as the threshold buffer
occupancy
level is exceeded by the occupancy level of the corresponding one of the
downstream
output buffers 440, whereas in other embodiments, it may be specified that the
threshold
buffer occupancy level needs to be continually exceeded for a certain amount
of time
before prioritization is triggered.
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
Another approach consists of the given one of the output buffer control
entities
450 monitoring a rate of change of the occupancy level of the corresponding
one of the
downstream output buffers 440. When the rate of change of the occupancy level
exceeds a certain predefined threshold, then prioritization may be triggered
by the given
5 one of the output buffer control entities 450, irrespective of the actual
occupancy level
within the corresponding one of the downstream output buffers 440. In some
embodiments, prioritization can be triggered as soon as the threshold is
exceeded by the
rate of change of the occupancy level of the corresponding one of the
downstream
output buffers 440, whereas in other embodiments, it may be specified that the
threshold
10 needs to be continually exceeded for a certain amount of time before
prioritization is
triggered.
The above techniques are non-limiting examples of how an individual one of the
output buffer control entities 450 may use the occupancy level of the
corresponding one
of the downstream output buffers 440 to implement a service hierarchy by
carrying out
15 packet prioritization. The above techniques can be supplemented by
adding multiple
threshold values that allow the individual one of the output buffer control
entities 450 to
control the packet prioritization process with a greater degree of refinement.
For example, attainment of a certain first threshold occupancy level may
trigger
prioritization of packets for a first traffic type, such as video packets,
with these packets
20 being given preferential access to the corresponding one of the high-
speed links 125. If
the occupancy level of the corresponding one of the downstream output buffers
440
continues to rise, it may attain a second threshold, at which point the
individual one of
the output buffer control entities 450 allows both video packets and, say,
voice packets
to benefit from preferential access to the corresponding one of the high-speed
links 125.
Through the use of such threshold values, the process of packet prioritization
may be
adjusted by the individual one of the output buffer control entities 450 based
on the
occupancy level of the corresponding one of the downstream output buffers 440.
Of course, those skilled in the art will recognize that further variants and
possibilities exist that would fall within the scope of the present invention.
For example, different ones of the output buffer control entities 450 may
implement different service hierarchies. In this way, the service hierarchy
can be
independently adjusted for each group of customers.
Also, still other techniques exist in order to identify situations where
prioritization
is required. For example, the need for prioritization of packets in certain
traffic
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100 21
PCT/MY2009/000080
categories may be based on statistical behaviour patterns during certain times
of day.
For example, during the daytime hours of the work week, it may be desirable to
prioritize
voice packets, whereas during evenings it may be desirable to prioritize video
packets,
and during weekends, it may be desirable to prioritize data packets. These are
merely
examples, and other possibilities exist without departing from the scope of
the present
invention.
By applying the above methodology at multiple ones of the downstream output
buffers 440 and corresponding output buffer control entities 450, a service
hierarchy can
be implemented for all traffic heading to the OPUs 120 that are connected to
the
aggregator sub-component 200. In particular, the network access provider can
achieve
control over the rate of downstream data entering the high-speed links 125
between the
head-end component 130 and the OPUs 120. Such control allows the network
provider
to provide true service-based QoS, which prioritizes some services at the
expense of
others when there is contention between packets for available bandwidth along
a high-
speed link, such as the high-speed links 125 between the head-end component
130 and
the OPUs 120.
Meanwhile, it will be observed that the manner in which the flow of packets is
regulated is independent of the higher-layer connections (e.g., at layer 3) to
which those
packets may belong. For example, assume that a user at a given one of the CPDs
110
has initiated a browser session (over the core packet-switched network 150),
is watching
a television show (delivered from the video server farm 140) and is on the
telephone
(using the PSTN 160). In this case, each individual application running on
each
individual end user device may make its own priority 'demands" for downstream
bandwidth. However, these demands are largely inconsequential since it is the
head-
end component 130 (and more particularly, the aggregator sub-component 200)
that
implements prioritization of packets. More specifically, the relevant output
buffer control
entity 450 can ensure that a desired service hierarchy is respected, which
could, but
need not, include the prioritization of video traffic over voice traffic, etc.
It should also be appreciated that the service hierarchy could be dynamic, in
the
sense that the traffic categories being given the highest (or lowest, etc.)
priority can
change overtime, as can the thresholds (e.g., occupancy level, rate of change
of
occupancy level, etc.) that may be used to trigger prioritization. All these
factors
contribute to allowing the network access provider to enter into true service
level
agreements (TSLAs) that reflect the implementation of a service hierarchy
(based on
traffic categories) rather than on providing access to a total amount of
bandwidth.
CA 02 913 681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
22
Upstream
Turning now to the case of upstream traffic, packets originating at a given
one of
the CPDs 110 travel to the corresponding one of the OPUs 120 and then to the
head-
end component 130. In the upstream direction, regulation of traffic flow is
optional. In
some cases, it may not even be required if the upstream bandwidth on the high-
speed
links 125 is sufficient. Where regulation of upstream traffic is carried out,
it can be
regulated at the OPUs 120 prior to packets entering the high-speed links 125.
Examples
of achieving such traffic control will be described later. For the time being,
assuming that
upstream packets have reached the head-end component 130, these will be
processed
by certain components of the aggregator sub-component 200.
Specifically, the aggregator sub-component 200 routes upstream traffic
according
to the traffic category to which each packet belongs. In particular, the
processing entity
230 includes a plurality of upstream input buffers 460, each of which
corresponds to one
of the OPUs 120 to which the aggregator sub-component 200 is connected. In
addition,
the processing entity 230 includes a plurality of upstream output buffers
480v, 480D,
480-1-, each of which corresponds to a respective traffic category, in this
case, video, data
and voice, respectively. Also, the processing entity 230 includes an upstream
distributor/router 470 that receives upstream packets from the upstream input
buffers
460 and routes the packets according to traffic type towards the upstream
output buffers
480v, 480D, 480T. In other words, the distributor/router 470 sends upstream
video
packets to upstream output buffer 480v, upstream data packets to upstream
output buffer
480 and upstream voice packets to upstream output buffer 480. Knowledge of the
traffic category to which an upstream packet belongs can be obtained from the
upstream
packet itself. For example, where the upstream packet includes a header or tag
indicative of a VLAN, the distributor/router 470 can look up the identity of
the VLAN in a
memory to identify the traffic category of the upstream packet. The
distributor/router 470
is assumed to have sufficient processing capacity to handle all the packets in
all the
upstream input buffers 460 without causing a build-up in any particular one of
the
upstream input buffers 460.
At the upstream output buffers 480v, 480D, 480, the upstream packets in the
relevant traffic category are released towards the respective one of the
network-side
interfaces 240v, 24011 240T. At the end of this process, the splitter/combiner
410 within
each of the network-side interfaces 240v, 240, 240T allows the upstream
packets to
proceed towards the switching sub-component 260 over the respective one of the
internal high-speed links 255v, 255D, 255. It can be assumed that available
bandwidth
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
23
on the internal high-speed links 255, 255, 255-r is sufficiently high that
contention for
bandwidth by upstream packets would be unlikely or insignificant. Such an
assumption
is reasonable, since the internal high-speed links 255v, 255, 255T exist
within the head-
end component 130 which is under the control of the network access provider.
Instead,
contention for bandwidth by upstream packets, if any, may occur when
considering the
high-speed links 125 between the OPUs 120 and the aggregator sub-component
200.
Dedicated Customer Interface (DCI) Module Detailed Operation
Reference is now made to Figure 5, which shows the design of certain
components of the DCI module 300A forming part of OPU 120A. Where the high-
speed
link between OPU 120A is bidirectional, the network-side interface 340
includes a
splitter/combiner 690 in addition to optical-to-electric and electric-to-
optical conversion
circuitry. The splitter/combiner 590 allows downstream traffic arriving from
the head-end
component 130 and destined for individual CPDs to co-exist with upstream
traffic on the
same high-speed link (i.e., one of the high-speed links 125 between OPU 120A
and the
aggregator sub-component 200). A similar splitter/combiner may also be
provided by the
customer-side interfaces 220 connected to the high-speed links 125 leading to
the OPUs
120.
Those skilled in the art will appreciate that a similar splitter/combiner (not
shown)
may also be implemented in the access network interface 320 in order to allow
downstream and upstream traffic to be exchanged with the CPDs 110 over the
last mile
infrastructure 115.
Upstream
Operation of the processing entity 330 in the context of handling packets
travelling in a downstream direction and in an upstream direction will be
discussed
separately. To begin with, in the context of upstream traffic, the processing
entity 330 in
OPU 120A may implement an upstream input buffer 520 for each of the CPDs 110
connected to the customer-side ports 310 via the last mile infrastructure 115.
in addition,
the processing entity 330 may also implement a multiplexer (MUX) 530, as well
as an
upstream output buffer 540 and an output buffer control entity 550. The
upstream output
buffer 640 has an output connected to the network-side interface 340 and, more
specifically, to the splitter/combiner 590.
Individual upstream packets could carry traffic in various traffic categories
(e.g,,
video, data, voice, etc.) and originate from various ones the CPDs 110.
However, in all
cases the upstream packets are destined for the same head-end component 130.
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100 24
PCT/MY2009/000080
Accordingly, the MUX 530 implements a multiplexing function for the upstream
packets.
More specifically, the MUX 530 combines upstream packets from various ones of
the
CPDs 110 in order to place them into the upstream output buffer 540. These
upstream
packets compete for transmission along the individual one of the high-speed
links 125
leading to the head-end component 130. To avoid or alleviate potential
congestion
caused by competition between upstream packets for transmission on this link
(and the
likely negative impact on customer experience that such congestion would
cause), the
contents of the given one of the upstream output buffer 540 are released in
accordance
with a service hierarchy that is implemented by the corresponding one of the
output
buffer control entities 550.
Specifically, the output buffer control entity 550 is configured to prioritize
the
manner in which the upstream packets in the upstream output buffers 540 are
transmitted to the network-side interface 340 (and eventually via the network-
side port
350). By "prioritization', it is meant that one or more upstream packets in
one traffic
category are released before upstream packets in another traffic category,
even though
both sets of packets await transmission at the same time. In order to allow
the output
buffer control entity 550 to determine the traffic category of a given
upstream packet, the
given upstream packet can include a VLAN identifier corresponding to a VLAN
that is
known to be associated with a particular traffic category. A table can be kept
in memory
which associates VLAN identifiers to traffic categories.
In particular, the "prioritization" carried out by the output buffer control
entity 550
can cover the case where all buffered packets in a first traffic category are
released
before any buffered packets in a second traffic category are released. In
accordance
with one non-limiting alternative, "prioritization" can be interpreted to
cover the case
where, on average, for each buffered packet in a second category that is
released, a
greater number of buffered packets in a first traffic category will be
released.
The output buffer control entity 550 may also be configured to carry out a
prior
step of determining whether prioritization is required and then carrying out
the
aforementioned prioritization as a function of whether or not it was
determined that
prioritization is required. In particular, if a situation was identified where
prioritization is
required, then prioritization may indeed be carried out as previously
described.
In order to identify situations where prioritization is required, the output
buffer
control entity 550 may be configured to detect the presence of congestion on
the
particular one of the high-speed links 125 leading from OPU 120A to the
aggregator sub-
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
component 200 of the head-end component 130. This can be measured indirectly
through monitoring of an "occupancy level" of the upstream output buffer 540.
The term
"occupancy level" can refer to an indication of the number of packets that are
currently
awaiting transmission, either on an absolute basis (e.g., number of packets)
or on a
5 relative basis (e.g., as a percentage of total buffer capacity). In one
approach, a certain
threshold buffer occupancy level could be established which, when reached,
indicates to
the output buffer control entity 550 that prioritization of packets becomes
necessary. In
some embodiments, prioritization can be triggered as soon as the threshold
buffer
occupancy level is exceeded by the occupancy level of the upstream output
buffer 540,
10 whereas in other embodiments, it may be specified that the threshold
buffer occupancy
level needs to be continually exceeded for a certain amount of time before
prioritization
is triggered.
Another approach consists of the output buffer control entity 550 monitoring a
rate of change of the occupancy level of the upstream output buffer 540. When
the rate
15 of change of the occupancy level exceeds a certain predefined threshold,
then
prioritization may be triggered by the output buffer control entity 550,
irrespective of the
actual occupancy level within the upstream output buffer 540. In some
embodiments,
prioritization can be triggered as soon as the threshold is exceeded by the
rate of change
of the occupancy level of the upstream output buffer 540, whereas in other
20 embodiments, it may be specified that the threshold needs to be
continually exceeded
for a certain amount of time before prioritization is triggered.
The above techniques are non-limiting examples of how the output buffer
control
entity 550 may use the occupancy level of the upstream output buffer 540 to
carry out a
service hierarchy and trigger packet prioritization. The above techniques can
be
25 supplemented by adding multiple threshold values that allow the output
buffer control
entity 550 to control the packet prioritization process with a greater degree
of refinement.
For example, attainment of a certain first threshold occupancy level may
trigger
prioritization of packets for a first traffic type, such as video packets,
with these packets
being given preferential access to the particular one of the high-speed links
125. If the
occupancy level of the corresponding upstream output buffer 540 continues to
rise, it
may attain a second threshold, at which point the output buffer control entity
550 allows
both video packets and, say, voice packets to benefit from preferential access
to the
particular one of the high-speed links 125. Through the use of such threshold
values,
the process of packet prioritization may be adjusted by the output buffer
control entity
550 based on the occupancy level of the upstream output buffer 540.
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
26
Of course, those skilled in the art will recognize that further variants and
possibilities exist that would fall within the scope of the present invention.
Also, still other techniques exist in order to identify situations where
prioritization
is required. For example, the need for prioritization of packets in certain
traffic
categories may be based on statistical behaviour patterns during certain times
of day.
For example, during the daytime hours of the work week, it may be desirable to
prioritize
voice packets, whereas during evenings it may be desirable to prioritize video
packets,
and during weekends, it may be desirable to prioritize data packets. These are
merely
examples, and other possibilities exist without departing from the scope of
the present
invention.
By applying the above methodology, a service hierarchy can be implemented for
all traffic heading from OPU 120A to the head-end component 130. In
particular, control
over the rate of upstream data entering the particular high-speed link 125
between OPU
120A and the head-end component 130 can be established. Such control allows
the
network provider to provide true service-based QoS, which prioritizes some
services at
the expense of others when there is contention between packets for available
bandwidth
along the high-speed link between OPU 120A and the head-end component 130.
Meanwhile, it will be observed that the manner in which the flow of packets is
regulated is independent of the higher-layer connections (e.g., at layer 3) to
which those
packets may belong. For example, assume that a user at a given one of the CPOs
110
has initiated a browser session (over the core packet-switched network 150),
is watching
a television show (delivered from the video server farm 140) and is on the
telephone
(using the PSTN 160). In this case, each individual application running on
each
individual end user device may make its own priority "demands" for upstream
bandwidth.
However, these demands are largely inconsequential since it is the individual
OPUs 120
that implement prioritization of packets. More specifically, the relevant
output buffer
control entity 550 can ensure that a desired service hierarchy is respected,
which could,
but need not, include the prioritization of video traffic over voice traffic,
etc.
it should also be appreciated that the service hierarchy could be dynamic, in
the
sense that the traffic categories being given the highest (or lowest, etc.)
priority can
change overtime, as can the thresholds (e.g., occupancy level, rate of change
of
occupancy level, etc.) that may be used to trigger prioritization. All these
factors
contribute to allowing the network access provider to enter into true service
level
CA 02 913 681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
27
agreements (TSLAs) that reflect the implementation of a service hierarchy
(based on
traffic categories) rather than on providing access to a total amount of
bandwidth.
It should further be noted that the term "buffer" as used above is merely
representative, since its implementation could be generally in the form of a
temporary
storage area with a corresponding memory management function that allows
flexibility in
writing to and/or in reading from the storage area.
Downstream
In the context of downstream traffic, the processing entity 330 in OPU 120A
may
implement a downstream input buffer 560 and a de-multiplexer (DMUX) 570. In
addition,
the processing entity 330 may also implement a downstream output buffer 580
for each
of the CPDs 110 connected to the customer-side ports 310 via the last mile
infrastructure
115. The downstream input buffer 560 temporarily stores downstream packets
that
arrive from the head-end component 130.
Individual downstream packets could be destined for various ones the CPDs 110.
Accordingly, the DMUX 570 implements a demultiplexing function for the
downstream
packets. More specifically, for each downstream packet, the DMUX 570
identifies a
destination CPD (i.e., one of the subtending CPDs 110 for which the downstream
packet
is destined). This can be achieved by examining the header of the downstream
packet.
Once the destination CPD for the downstream packet has been determined, the
downstream packet is sent to the particular one of the downstream output
buffers 580
that is associated with the destination CPD. At the particular one of the
downstream
output buffers 580, the downstream packet awaits transmission to the
destination CPD
over the last mile infrastructure 115 via the access network interface 320 and
the
corresponding one of the customer-side ports 310.
It can be assumed that available bandwidth in the last mile infrastructure 115
towards individual ones of the CPDs 110 is sufficiently high that contention
for bandwidth
by downstream packets would be unlikely or insignificant. Such an assumption
is
reasonable, since the overall bandwidth of the last mile infrastructure 115
(between OPU
120A and the CPDs 110) is likely to be significantly greater than the
bandwidth of the
individual one of the high-speed links 125 between OPU 120A and the head-end
component 130. Where temporary congestion may occur, appropriate sizing of the
downstream output buffer 580 could mitigate its impact.
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
28
It should be appreciated that the above description of the DCI module 300A
applies to other ones of the DCI modules 300 that may be housed within a
single one of
the OPUs 120 in order to service a greater number of the CPDs 110,
Serial Interconnection of Dedicated Customer Interface (DCI) Modules
Figure 6 shows an embodiment of an OPU 120B that contains multiple (i.e., two
or more) DCI modules 6021...N arranged in a serial interconnection that can be
referred to
as a "daisy chain" arrangement. This allows a single high-speed link 125
between the
OPU 120B and the head-end component 130 to be shared by multiple DCI modules
6021..N, in contrast to the situation in Fig. 3. The DCI modules 6021...N
include a
designated "first" DCI module 6021, a last DCI module 602N and a set of zero
or more
intermediate DCI modules 6022,..N1. The "first" DCI module 6021 is so named
only
because it is closest to the particular one of the high-speed links 125 that
connects OPU
120B to the head-end component 130. Thus, the first DCI module 6021 is indeed
the
first one of the DCI modules 602i...N to receive downstream traffic from the
head-end
component 130.
Adjacent ones of the DCI modules 6021., N are connected by a respective one of
a
plurality of DCI-to-DCI connections 605. The medium and signaling protocol
used for the
DCI-to-DCI connections 605 could be identical to the medium and signaling
protocol
used by the first DCI module 6021 to communicate with the head-end component
130
over the particular one of the high-speed links 125. This can serve to enhance
modularity.
Also provided in OPU 120B is a connection between the last DCI module 602N
and the first DCI module 6021, which is referred to as a "loop back" 660. The
loop back
660, which is optional, may be used to facilitate inter-DCI-module
communication and
provide redundancy.
Each of the DCI modules 6021õ,N includes an access-network interface 620, a
processing entity 630 and a drop/forward unit 642. The drop/forward unit 642
in any
given one of the DCI modules 6021...N includes or has access to a memory 644,
which in
a non-limiting example of implementation can be a content-addressable memory
(CAM).
The memory 644 stores an identifier that is uniquely associated with the given
one of the
DCI modules 6021.,,N. The identifier may be assigned during manufacture (e.g.,
a MAC
address) or can be assigned during an initialization phase.
In operation, each of the DCI modules 6021...N operates in substantially the
same
way. Thus, the following description will focus on the first DCI module 6021,
which is the
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
29
first one of the DCI modules 6021...N to receive downstream traffic from the
head-end
component 130. Specifically, the drop/forward unit 642 in the first DCI module
6021
determines whether a given packet received from the head-end component 130 is
destined for the first DCI module 6021. This can be achieved by reading a
special "tag"
that is associated with the given packet. Details regarding how the head-end
component
130 associates tags with packets will be provided later on. For now, it is
sufficient to
understand that the destination DCI module for the given packet can be
identified by
virtue of the tag associated with the given packet. In particular, when the
given packet is
destined for a particular one of the DCI modules 6021...N, the tag associated
with the
given packet specifies the aforesaid identifier of the particular one of the
DCI modules
6021...N.
Thus, by examining the tag associated with the given packet and comparing it
to
the identifier stored in its memory 644, the drop/forward unit 642 in the
first DCI module
6021 can determine whether the given packet is indeed destined for first DCI
module
6021. The use of the CAM is a particularly efficient way of obtaining a quick
binary (i.e.,
yes or no) answer to the question of whether or not the given packet is
destined for first
DCI module 6021. In particular, where the DCI-to-DCI connections 605 are
optical, an
optical CAM can be used for this purpose. However, it should be understood
that a
conventionally addressable memory could also be used instead of a CAM.
If the drop/forward unit 642 in the first DCI module 6021 finds a match
between
the tag associated with the given packet and the identifier stored in its
memory 644, the
drop/forward unit 642 in the first DCI module 6021 can conclude that the given
packet is
indeed destined for first DCI module 6021. In this case, the drop/forward unit
642 sends
the given packet to the processing entity 330 of the first DCI module 6021
where
processing is carried out as previously described. It should be noted that the
tag can be
removed prior to sending the given packet to the processing entity 330.
However, if the drop/forward unit 642 in the first DCI module 6021 finds no
match
between the tag associated with the given packet and the identifier stored in
its memory
644, the drop/forward unit 642 in the first DCI module 6021 can conclude that
the given
packet is not destined for first DCI module 6021. In this case, the
drop/forward unit 642
sends the given packet to the next adjacent DCI module (in this case, the
second DCI
module 6022) via the corresponding one of the DCI-to-DCI connections 605. At
the
second DCI module 6022, similar processing occurs as has been described above
having regard to the first DCI module 6021.
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100 30
PCT/MY2009/000080
In the case of upstream traffic, it should be appreciated that packets
arriving from
the various CPDs 110 at a "recipient DCI module" of OPU 120B do not need to be
tagged. Rather, the packets can be blindly routed from the recipient DCI
module to the
first DCI module 6021 via zero or more of the intermediate DC1 modules
6022...N and/or
via the loop back 660. For example, at each intervening DCI module, the
upstream
traffic received from another DCI module in the daisy chain may be aggregated
with its
own upstream traffic. Ultimately, the first DCI module 6021 releases the
aggregate
upstream traffic towards the head-end component 130 over the particular one of
the
high-speed links 125.
Tagging of Downstream Packets at Head-End Component
Reference is now made to Figure 7, which depicts the manner in which
downstream packets 7021_10 , 7121...10, 722-1...ic, may be tagged by the
aggregator sub-
component 200, and more specifically, by a plurality of distributor/routers
730v, 730D,
730T. Distributor/router 730v is used for routing downstream video packets
distributor/router 730D is used for routing downstream data packets 7121...w
and
distributor/router 730T is used for routing downstream voice packets 7221_10.
It should
be appreciated that the depiction of ten (10) packets per traffic category is
merely for
illustrative purposes.
The distributor/routers 730v, 730D, 730T are similar to the
distributor/routers 430v,
430, 430T described previously, except that they have been modified to include
a
tagging functionality. In particular, distributor/router 730v is configured to
identify a
"destination DCI module" for each of the downstream video packets 7021...1,3
received
over internal high-speed link 255v. The "destination DCI module" for a given
downstream video packet can be determined by identifying the specific one of
the CPDs
110 for which the given downstream video packet is destined, and then
consulting a
mapping that indicates which CPDs 110 are connected to which DCI modules in
which
OPUs. Such a mapping can be stored in a memory (not shown) and maintained by
the
network access provider.
In order to identify the specific one of the CPDs 110 for which the given
downstream video packet is destined, distributor/router 730v can examine the
header of
the given downstream video packet. For example, if the header includes an IP
address,
then this address can be mapped to one of the CPDs 110, which can then be
mapped to
a destination DCI module. Thus, for instance, knowing that the given
downstream
packet is destined for a particular CPD , and upon learning that the
particular CPD is
CA 02913681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
31
connected to DCI module 6023, the destination DCI module for the given
downstream
packet would be DCI module 6023. It should be appreciated that
distributor/router 730v
will already be configured to examine the headers of the downstream video
packets
7021_10 because the destination OPU for each such packet will need to be
determined,
as previously described, in order to ensure routing to the appropriate
downstream output
buffer 440.
Having determined the destination DCI module for the given downstream video
packet, distributor/router 730v tags the packet with an indication of the
destination DCI
module. The indication of a particular DCI module may correspond to the
aforementioned identifier that is uniquely associated with the particular DCI
module
(which is stored in its memory 644) and that is also known to the network
access
provider.
In Figure 7, by way of non-limiting example, downstream video packets 7021,
7023 and 7026 are all destined for CPDs that are served by various ones of the
DCI
modules 6021...N in OPU 12013. In particular, downstream video packet 7021 is
destined
for a CPD that is served by DCI module 6021 (and includes a tag indicative of
DCI
module 6021), downstream video packet 7023 is destined for a CPD that is
served by DCI
module 6024 (and includes a tag indicative of DCI module 6024) and downstream
video
packet 7025 is destined for a CPD that is served by DCI module 6023 (and
includes a tag
indicative of DCI module 6023). Meanwhile, downstream video packets 7023, 7025
and
7027 are destined for CPDs serviced by DCI modules in another one of the OPUs
120,
while downstream video packets 7024, 7025 and 70210 are destined for CPDs
serviced by
DCI modules in yet another one of the OPUs 120, and each such downstream video
packet has a tag indicative of its destination DCI module.
In order to tag the given downstream video packet, distributor/router 730, can
encapsulate the given downstream video packet within the payload of a super-
packet
and insert the identifier of the destination DCI module into a header of the
super-packet.
Alternatively, distributor/router 730v can modify one or more bits in the
existing header of
the given downstream video packet. Still other techniques for tagging the
given
downstream video packet exist and will occur to those of ordinary skill in the
art as being
within the scope of the present invention.
It should be noted that the "tag" that is applied to a particular downstream
video
packet in order to identify its destination DCI module may, but need not,
modify the
format of the particular downstream packet. In other words, if the particular
downstream
CA 02 913 681 2015-11-30
WO 2010/151100
PCT/MY2009/000080
32
packet is an IP packet, then the tagged version of the particular downstream
packet
could remain an IP packet. In a specific non-limiting example, the MAC address
of the
destination OPU for the particular downstream packet may be enhanced to
identify not
only the OPU but also the DCI module to which the particular downstream packet
is
destined. This can be referred to as MAC address extension.
Once tagged, distributor/router 730v sends the tagged version of each given
downstream video packet to the downstream output buffer 440 corresponding to
the
OPU to which the given downstream video packet is destined.
It should be understood that the above discussion of distributor/router 730v
in
relation to downstream video packets 7021,..10 also applies to
distributor/router 730D and
distributor/router 7301- in relation to downstream data packets 7121...w and
downstream
voice packets 722.1..,10, respectively.
Optionally, the tag associated with a given downstream packet could also
include
information indicative the traffic category to which the given downstream
packet belongs
in order to assist the output buffer control entity 450 in implementing the
previously
described service hierarchy.
Those skilled in the art will appreciate that certain adaptations and
modifications
of the described embodiments can be made. Therefore, the above discussed
embodiments are to be considered illustrative and not restrictive.