Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
LOWER LIMB AUTOMATIC REGULATING PLATFORM FOR WAIST REHABILITATION
TRAINING AND TRAINING METHOD
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to the technical field of medical rehabilitation
training instruments, in
particular to a lower limb automatic regulating platform for waist
rehabilitation training and a training
method thereof.
BACKGROUND ART
In today's society, there are more and more patients that suffer from waist
dyskinesia due to
paroxysmal diseases or accidents, but the conventional rehabilitation therapy
mainly relies on
rehabilitation therapists, which has low efficiency and high cost. Hence,
there is a higher demand for waist
rehabilitation training. To meet the demand in the society, the inventor has
filed a patent application
which discloses a six-DOF (Degree of Freedom) in-parallel waist
rehabilitation training device that utilizes pneumatic artificial muscle to
drive waist bending rehabilitation
training; in the device, a lower limb rehabilitation regulating platform is
driven by ropes so as to change the
spatial position and posture of the platform and thereby enables the legs of a
patient to bend and rotate in
relation to the waist, to attain an effect of lumbar spinal rehabilitation
training. Though the technical
scheme and device structure in this application has innovative breakthroughs,
it is found in clinical
examination that the rehabilitation training device disclosed in this patent
application
has many problems when it is used for training to simulate lower limb
exercise:
Firstly, the patient stands on the standing platform and there is no support
or connection between
the lower limbs and the rehabilitation training device; consequently, in the
rehabilitation training, the lower
limb movement driven by the movement of the platform in relation to the waist
is not stable and has poor
smoothness, and may cause secondary injuries to the patient;
Secondly, the lower limb movement is realized by driving the standing platform
with a motor via
ropes; since the motor has rotation errors and the ropes has deformation
caused by expansion and
shrinkage, the standing platform can't attain preset spatial positions and
postures, causing compromised
rehabilitation training effect;
CA 2950546 2018-05-30
Finally, in the rehabilitation training, the standing platform drives the two
legs to make spatial
movement, so that the two legs move in relation to the hip joints and thereby
realize rehabilitation training
of lumbar spine; however, since the thigh and shank of the patient may bend in
the training process,
assistance is required to enable the legs of the patient to bend so as to
attain a better waist rehabilitation
training effect. Hence, it is necessary to further improve the mechanical
structure disclosed in this
application.
CONTENTS OF THE INVENTION
The object of the present invention is to provide a lower limb automatic
regulating platform for
waist rehabilitation training and a training method thereof, so as to solve
the lower limb jointing problem in
the existing waist rehabilitation training devices.
To attain the object described above, the present invention employs the
following technical
scheme:
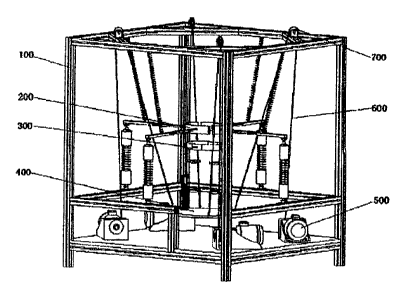
A lower limb automatic regulating platform for waist rehabilitation training,
comprising an
aluminum alloy profile frame 100 in a rectangular shape and fixed to the
floor. In addition:
a lower limb automatic regulating platform unit 300, a standing platform 400,
motor units 500,
ropes 600, and pulley units 700 are arranged in the aluminum alloy profile
frame 100.
Four pulley units 700 are arrange at the top of the aluminum alloy profile
frame 100. One motor
unit 500 is arranged below each of the pulley units 700. The drum shaft of
each motor unit 500 is connected
with one flexible rope 600. Each flexible rope 600 runs around a pulley unit
700 and then is connected to
the standing platform 400. Namely, the direction of the flexible rope 600 is
changed via the pulley unit 700,
and the length of the flexible rope 600 is changed via the motor unit 500:
thus, the spatial position and
posture of the connected standing platform 400 are changed, and thereby the
postures of the patient in
standing state and moving state are regulated.
The lower limb automatic regulating platform unit 300 is arranged on the
standing platform 400.
The lower limb automatic regulating platform unit 300 is movably connected
with the legs of the patient, so
as to restrain, support, and regulate the leg postures of the patient in
standing state and waist movement
state. Namely, through the supporting, restraining, and regulating of the
lower limb automatic regulating
2
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
platform unit 300, ,the legs of the patient can bend and straighten within the
working range of the lower
limb automatic regulating platform unit 300.
In other words, by means of the joint movement of the standing platform 400
and the lower limb
automatic regulating platform unit 300, the leg postures of the patient
standing on the standing platform
400 are regulated when the waist of the patient is in straightening state or
bending state.
A training method utilizing the lower limb automatic regulating platform for
waist rehabilitation
training according to the present invention is executed through the following
steps:
Step 1: powering up an industrial PC and the motors in the motor units 500,
controlling pressure
sensors 801, laser ranging sensors 802 and encoders 803 to feedback signals,
and resetting thigh pneumatic
artificial muscles 316, shank pneumatic artificial muscles 310, rotation joint
pneumatic artificial muscles
311, shank springs 307, rotation joint springs 312, and thigh springs 317;
Step 2: inputting thigh and shank length information of the patient to the
industrial PC; inputting
preset spatial positions and postures and allowable error ranges to the
industrial PC, wherein, the preset
spatial positions and postures are rehabilitation actions and postures to be
exercised by the patient on the
waist rehabilitation training device;
Step 3: instructing the patient to stand on the standing platform 400;
controlling the shank
pneumatic artificial muscles 310 to inflate or deflate at first according to
the leg information of the patient
inputted to the industrial PC in the step 2 to adjust the length of the shank
modules, detecting the length of
the shank springs 307 with laser ranging sensors 802 in the shank modules in
real time, and transmitting the
detection data to the industrial PC for computation and judgment, till the
rotation joints 306 are aligned to
the knee joints of the patient at the same level;
then, controlling the thigh pneumatic artificial muscles 316 via the
industrial PC to inflate or
deflate, so as to adjust the length of the thigh modules, detecting the
lengths of the thigh springs 317 in real
time via the laser ranging sensors 802 in the thigh modules at the same time,
and transmitting the detection
data to the industrial PC for computation and judgment, so that elastic hip
joint straps 301 are positioned at
the hip joints of the patient;
3
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
Step 4: tying elastic leg straps 303 in the thigh modules and elastic leg
straps 303 in the shank
modules to the thighs and shanks of the patient respectively, and tying the
elastic hip joint straps 301 to the
hip joints of the patient, so as to prepare for making rehabilitation
movements;
Step 5: controlling the motors in the motor units 500 to rotate by the
industrial PC, so that the
flexible ropes 600 extend and retract and thereby the standing platform 400
moves, Controlling the air inlet
valve and air outlet valve for the two rotation joint pneumatic artificial
muscles 311 in real time through the
industrial PC to open or close according to the spatial position and posture
of the standing platform 400, so
as to control the shank joints to rotate and thereby drive the standing
platform 400 to move; at the same
time, making angle compensation for the rotation of the rotation joints 306
via the industrial PC according
to the angles of rotation of the shank modules fed back in real time by the
encoders 803, so that the position
and posture of the patient standing on the standing platform 400 matches the
preset spatial position and
posture inputted in the step 2;
Step 6: monitoring the real-time pressure information of the thigh pneumatic
artificial muscles
316, real-time pressure information of the shank pneumatic artificial muscles
310, real-time pressure
information of the rotation joint pneumatic artificial muscles 311, and real-
time spatial position and posture
information of the standing platform 400 with pressure sensors 801 and visual
sensors respectively, and
transmitting the real-time pressure information and real-time spatial position
and posture information via a
data acquisition card to the industrial PC; stopping the rehabilitation
training immediately and alarming for
device check if an error goes beyond the allowable error range set in the step
2, to avoid any accident of the
patient during the rehabilitation training;
Step 7: removing the elastic leg straps 303 and the elastic hip joint straps
301 manually and
instructing the patient to get off the standing platform 400 after the
rehabilitation training is finished;
Step 8: resetting the lower limb automatic regulating platform 300, turning
off the power of the
motor units 400, the pneumatic artificial muscles and the industrial PC.
= 4
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
BENEFICIAL EFFECTS Qf THE PRESENT INVENTION:
1. The present invention simulates the leg structures of human and designs
a lower limb movement
device based on pneumatic artificial muscles and springs, which connects the
lower limbs of a patient with
a waist training device, and attains an effect of fixing and supporting the
lower limbs of the patient.
2. The thigh modules and shank module in the device provided in the present
invention employ
pneumatic artificial muscles and springs which are connected in series, so
that the pneumatic artificial
muscles drive the flexible rope compression springs to decrease the height of
the device, or the height of
the device is increased by the spring force; at the same time, the variation
of the heights of the springs is
monitored in real time with laser ranging sensors; thus, the heights of the
thigh device and the shank device
can be regulated automatically according to the leg information of the
patient, and the device has excellent
flexibility, provides shock absorption and damping functions, and thereby
effectively protects the waist
and prevents secondary injuries in the rehabilitation training.
3. The device provided in the present invention employs pneumatic
artificial muscles and springs to
drive in parallel and utilizes the engagement transmission between the
synchronous belt and the belt pulley
to drive the joints to rotate; specifically, the pneumatic artificial muscles
are inflated and thereby contract
to stretch the springs and thereby drives the pulley to rotate, so that the
knee joints rotate; in addition, the
pulleys can rotate in a reversed direction under the action of the spring
force, so that the knee joint rotate in
the reversed direction; in addition, encoders are mounted on the rotation
shafts to detect the angles of
rotations to ensure the knee joints to rotate accurately in the rehabilitation
training process, and thereby
assist the standing platform to attain preset change of spatial positions and
postures, and the legs of the
patient bend in relation to the waist more accurately; thus, a better waist
rehabilitation training effect is
attained.
4. The lower limb automatic regulating platform in the device provided in
the present invention
employs a bionic design, and it not only can be used as a lower limb
supporting and regulating device for a
waist training device, but also can be used for lower limb rehabilitation
training in medical rehabilitation,
and has high expansibility.
The structural advantages of device provided in the present invention also
include:
5
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
The aluminum alloy profile frame 100 in the present invention is constructed
by a plurality of
aluminum alloy profiles and panels, to fix and support the units and thereby
accomplish a rehabilitation
training process. Four waistband units 200 are fixed to the pneumatic
artificial muscles on the front, rear,
left, and right sides of the aluminum alloy profile frame 100 to provide axial
driving force respectively,
which acts on the waist of a patient via connecting devices; the springs in
the waistband units 200 are used
to balance off the gravity of the connecting devices. The entire structure is
simple and robust, and can
operate stably and reliably.
The four motor units 500 in the present invention comprise a motor and a drum
connected with the
output shaft of the motor, and the four motor units 500 are evenly distributed
and fixedly mounted on the
panels of the aluminum alloy profile frame 100. The mounting shaft at the
bottom end of the pulley in the
pulley unit 700 is in interference fit with the inner ring of a crossed taper
roller bearing, the outer ring of the
crossed taper roller bearing is fixedly mounted on the top of the aluminum
alloy profile frame 100 via the
support, so that the pulley can rotate freely. The power is output in a simple
and efficient way.
The regulating device for assisting leg movement in the lower limb automatic
regulating unit 300
comprises a shank module and a thigh module. The bottom of the shank support
309 is mounted on the
standing platform 400, a top protrusion part of the shank support 309 has a
slotted hole, a bottom protrusion
part of the rotation joint 306 forms an insertion plate, which can be inserted
into the slotted hole freely. A
top protrusion part of the thigh support 304 has a slotted hole, a bottom
protrusion part of the elastic hip
joint strap support 319 forms an insertion plate, which can be inserted into
the slotted hole freely. The
bottom side walls of the thigh support 104 have two holes respectively for
mounting bearings 305. The
rotation shaft 315 is mounted in the inner rings of the bearings 305, and is
connected with the rotation joint
306 via a flat key 320, and the protruding end of the rotation shaft 315 is
connected with the synchronous
belt pulley 314 by interference fit. The three components are connected
compactly, and the length is
adjustable, to meet the demand for rehabilitation of patients with different
leg shape.
The waistband unit 200 not only can assist the patient to attain a waist
rehabilitation training effect,
but also can fix and support the upper body of the patient, so that the upper
body of the patient is kept in
balance.
6
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
In the present invention, the motor units 500 drive the flexible ropes 600 to
extend and retract, and
thereby drive the standing platform 400 to move. The spatial position and
posture of the standing platform
400 varies as the lengths of the four flexible ropes 600 vary.
In the present invention, the elastic hip joint straps 301 are fixedly tied on
the hip joint part of the
patient, the elastic leg straps 303 are fixedly tied on the thighs and shanks
of the patient, so as to fix and
support the lower limbs of the patient, without limiting the degree of freedom
of lower limb movement of
the patient.
The device provided in the present invention can automatically check and
correct any error in the
actual spatial position and posture of the standing platform 400 compared with
the preset spatial position
and posture, so that the legs of the patient can reach preset positions; thus,
the bending of the legs of the
patient in relation to the hip joints is more accurately realized, and the
effect of waist rehabilitation training
is ensured.
By utilizing the sensors, the present invention not only ensures accurate and
safe rehabilitation
training, but also realizes automation of the device. The pressures on the
pneumatic artificial muscles is
monitored in real time with the pressure sensors 801; thus, a potential safety
hazard of output force
variation resulted from pressure change on the pneumatic artificial muscles is
prevented, and the safety of
rehabilitation training is ensured. The heights of the thigh modules and the
shank modules are detected with
the laser ranging sensors 802; so that automatic height regulation is
realized. The rotation angles of the
shank modules are detected by the encoders 803, and thereby the accuracy of
rehabilitation training is
ensured.
DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of the overall structure according to the
present invention;
Fig. 2 is a front view of the overall structure according to the present
invention;
Fig. 3 is a top view of the overall structure according to the present
invention;
Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of the overall structure of the lower limb
regulating platform
according to the present invention;
7
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
Fig. 5 is a front view of the lower limb regulating platform according to the
present invention;
Fig. 6 is a top view of the lower limb regulating platform according to the
present invention;
Fig. 7 is a partial schematic diagram of the shank module in the lower limb
regulating platform
according to the present invention;
Fig. 8 is a partial schematic diagram of the thigh module in the lower limb
regulating platform
according to the present invention;
Fig. 9 is a partial schematic diagram of the rotation joint in the tower limb
regulating platform
according to the present invention;
Fig. 10 is a schematic diagram of the rotation shaft in the lower limb
regulating platform according
10. to the present invention;
Fig. 11 is a schematic diagram of the mechanical structure for lower limb
movement according to
the present invention;
Fig. 12 is a schematic diagram of the thigh support in the lower limb
regulating platform according
to the present invention;
Fig. 13 is a schematic diagram of the rotation joint in the lower limb
regulating platform according
to the present invention; '
Fig. 14 is a schematic installation diagram of the sensors in the lower limb
regulating platform
according to the present invention;
Fig. 15 is a schematic installation diagram of the laser ranging sensors in
the lower limb regulating
platform according to the present invention;
Fig. 16 is a system control flow chart of the lower limb regulating platform
according to the present
invention;
In the figures: 100 - aluminum alloy profile frame; 200 - waistband unit; 300 -
lower limb
automatic regulating platform unit; 301 - elastic hip joint strap; 302 -
elastic leg strap support; 303 - elastic
8
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
leg strap; 304- thigh support; 305 - bearing; 306 - rotation joint; 307 -
shank spring; 308 - shank flexible
rope; 309- shank support; 310- shank pneumatic artificial muscle; 311 -
rotation joint pneumatic artificial
muscle; 312 - rotation joint spring; 313 - synchronous belt 314 - synchronous
belt pulley; 315 = rotation
shaft; 316- thigh pneumatic artificial muscle; 317- thigh spring; 313- thigh
flexible rope; 319- elastic hip
joint strap support; 320 - flat key; 400 - standing platform; 500 - motor unit
600 ¨ flexible rope; 700 -
pulley unit; 800- detection unit; 801 - pressure sensor; 802 - laser ranging
sensor; 803 - encoder
EMBODIMENTS
Hereunder the structural features of the present invention will be described
in detail with reference
to the accompanying drawings.
As shown in Fig. 1, the waist rehabilitation training device comprises an
aluminum alloy profile
frame 100, which is a rectangular frame constructed with aluminum alloy
profiles and is fixed to the floor.
As shown in Fig. 2, a lower limb automatic regulating platform unit 300, a
standing platform 400,
motor units 500, flexible ropes 600, and pulley units 700 are arranged in the
aluminum alloy profile frame
100.
As shown in Fig. 1, four pulley units 700 are arrange on the top of the
aluminum alloy profile
frame 100. One motor unit 500 is arranged below each of the pulley units 700.
The drum shaft of each
motor unit 500 is connected with one flexible rope 600. As shown in Fig. 3,
each flexible rope 600 runs
around a pulley unit 700 and then is connected to the standing platform 400.
Namely, the direction change
of flexible rope 600 is realized via the pulley unit 700, and the length
change of the flexible rope 600 is
realized via the motor unit 500; thus, the spatial position and posture of the
connected standing platform
400 are changed, and thereby the postures of the patient in standing state and
movement state are regulated.
In other words, each of the four motor units 500 comprises a motor, a bevel
gear pair drive chain connected
with the output shaft of the motor, and a drum connected e,oaxially with the
big bevel gear, and the four
motor units 500 are evenly distributed and fixedly mounted on the panels of
the aluminum alloy profile
frame 100. The mounting shaft at the bottom end of the pulley in the pulley
unit 700 is in interference fit
with the inner ring of a crossed taper roller bearing, the outer ring of the
crossed taper roller bearing is
fixedly mounted on the top of the aluminum alloy profile frame 100 via the
support, so that the pulley can
rotate freely. One end of the flexible rope 600 is connected to the drum in
the motor unit 500, and the other
9
=
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
end of the flexible rope 600 is connected to the standing platform 400 via the
pulley in the pulley unit 700.
Namely, the motor in the motor unit 500 rotates and drives the connected drum
to rotate, so that the rope
600 wound around the drum extends or retracts, and thereby drives the standing
platform 400 to move. The
spatial position and posture of the standing platform 400 varies as the
lengths of the four flexible ropes 600
vary.
As shown in Fig. 1, four waistband units 200 are fixed to the pneumatic
artificial muscles on the
front, rear, left, and right sides of the aluminum alloy profile frame 100 to
provide axial driving force,
which acts on the waist of a patient via connecting devices; the springs in
the waistband units 200 are used
to balance off the gravity of the connecting devices.
As shown in Fig. 2, furthermore, the waistband unit 200 not only can assist
the patient to attain a
waist rehabilitation training effect, but also can fix and support the upper
body of the patient, so that the
upper body of the patient is kept in balance.
As shown in Fig. 4, the lower limb automatic regulating platform unit 300 is
arranged on the
standing platform 400. The lower limb automatic regulating platform unit 300
is movably connected with
the legs of the patient, so as to restrain, support, and regulate the leg
postures of the patient in standing state
and waist movement state. Namely, through the supporting, restraining, and
regulation functions of the
lower limb automatic regulating platform unit 300, the legs of the patient can
bend and straighten within
the working range of the lower limb automatic regulating platform unit 300, as
shown in Fig. 11.
In other words, by means of the joint movement of the standing platform 400
and the lower limb
automatic regulating platform unit 300, the leg postures of different patients
standing on the standing
platform 400 and the leg postures of the patient during waist rehabilitation
training are regulated.
Furthermore, a detection unit 800 is arranged on the lower limb automatic
regulating platform unit
300. The working postures of the lower limb automatic regulating platform unit
300 are fed back by the
detection unit 800 to the industrial PC; length of the legs of the patient and
the bending angle of the tower
limb automatic regulating platform unit 300 are obtained through calculation
via the industrial PC.
The industrial PC associates the movement execution parameters inputted
manually, with the
length of the legs of the patient and the bending angle of the lower limb
automatic regulating platform unit
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
300 obtained through calculation, to drive the lower limb automatic regulating
platform unit 300, the
standing platform 400 and the motor units 500 to move respectively.
As shown in Fig. 1, a set of waistband units 200 is arranged in the aluminum
alloy profile frame
100. The waist of the patient is assisted to bend and straighten by the
restraining and length adjustment of
the waistband units 200.
In other words, by means of the joint movement of the standing platform 400,
the lower limb
automatic regulating platform unit 300 and waistband units 200, the leg
postures of the patient standing on
the standing platform 400 are regulated when the waist of the patient is in
straightening state or bending
state.
As shown in Fig. 5, the lower limb automatic regulating platform unit 300
comprises elastic hip
joint straps 301, elastic hip joint strap supports 319, and two regulating
devices for assisting leg movement.
The elastic hip joint straps 301 are straps that have an approximately
elliptical shape and are made
of an elastic material. Preferably, the elastic hip joint straps 301 are
leather straps or rubber straps. One
elastic hip joint strap support 319 is connected at each end of the elastic
hip joint strap 301 in the long axis
direction. The elastic hip joint strap support 319 is in a Y-shape. A pair of
hip joint insertion plates are
arranged on the bottom of each elastic hip joint strap support 319. The hip
joint insertion plates are inserted
in the adjacent regulating device for assisting leg movement. The regulating
devices for assisting leg
movement are in a strip shape, and can bend, extend and retract, as shown in
Fig. 11.
The bottom of each regulating device for assisting leg movement is connected
to the top surface of
the standing platform 400 respectively, as shown in Fig. 6.
As shown in Fig. 5, each regulating device for assisting leg movement
comprises a shank module
and a thigh module.
As shown in Fig. 9, the bottom end of the shank module is fixedly connected to
the top surface of
the standing platform 400. The length of the shank module can be adjusted by
extending/retracting.
11
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
As shown in Fig. 8, the top of the shank module is movably connected to the
bottom end of the
thigh module. The length of the thigh module can be adjusted by
extending/retracting. The bottom end of
the thigh module can rotate around the top of the shank module.
As shown in Fig. 7, the top end of the thigh module is movably connected to
the adjacent elastic
hip joint strap support 319.
Namely, the height of the thigh module in relation to the standing platform
400 is adjustable. The
height of the elastic hip joint strap support 319 in relation to the standing
platform 400 is adjustable.
The thigh module and the elastic hip joint strap 301 connected with the thigh
module via the elastic
hip joint strap support 319 can rotate around the top of the shank module.
As shown in Fig. 7, the thigh module comprises an elastic leg strap support
302, an elastic leg strap
303, a thigh support 304, a bearing 305, a synchronous belt pulley 314, a
rotation shaft 315, a thigh
pneumatic artificial muscle 316, a thigh spring 317, and a thigh flexible rope
318.
= As shown in Fig. 12, the thigh support 304 is in a U-shape, and comprises
two thigh straight plates
and one thigh bottom plate. The two thigh straight plates are arranged
vertically and parallel to each other.
The bottoms of the two thigh straight plates are connected together via the
thigh bottom plate.
The top surface of each of the two thigh straight plates has one thigh slotted
hole. The thigh slotted
hole matches the hip joint insertion plate in shape. Namely, the hip joint
insertion plate is inserted into the
adjacent thigh slotted hole, as shown in Fig. 7.
One thigh cross plate is arranged between the two thigh straight plates above
the thigh bottom
plate. The thigh cross plate has a small hole.
As shown in Fig. 7, the top surface of the thigh bottom plate is fixedly
connected to the bottom of
the thigh pneumatic artificial muscle 316. The top end of the thigh pneumatic
artificial muscle 316 is
connected to one end of the thigh flexible rope 318. The other end of the
thigh flexible rope 318 passes
through the small hole in the thigh cross plate and then is connected to the
bottom surface of the elastic hip
joint strap support 319. The thigh spring 317 is fitted over the thigh
flexible rope 318 above the thigh cross
12
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
plate. The top of the thigh spring 317 is in contact with the bottom surface
of the elastic hip joint strap
support 319, and the bottom of the thigh spring 317 is in contact with the top
surface of a top plate.
As shown in Fig. 12, two thigh insertion plates are arranged on the bottom
surface of the thigh
bottom plate. Both of the thigh insertion plates extend vertically downwards,
and are parallel to each other.
Each of the thigh insertion plates has a round hole, a bearing 305 is fitted
into the round hole of each thigh
insertion plate, and a rotation shaft 315 is arranged for the two adjacent
bearings 305, as shown in Fig. 10.
An elastic leg strap support 302 is connected horizontally at the outer side
of the thigh straight
plate at one side of the thigh support 304. An elastic leg strap 303 is
arranged on the tail end of the elastic
leg strap support 302. The synchronous belt pulley 314 is arranged on the end
of the rotation shaft 315 at
the other side of the thigh support 304, as shown in Fig. 10.
As shown in Figs. 4, 7 and 11, when the thigh pneumatic artificial muscle 316
extends or retracts,
the elastic hip joint strap support 319 is driven by the thigh flexible rope
318 and the thigh spring 317 to do
telescopic Motion, and thereby the positions of the elastic leg strap support
302 and the elastic leg strap 303
connected with the thigh support 304 in relation to the elastic hip joint
strap support 319 and the elastic hip
joint strap 301 are regulated.
As shown in Fig. 9, the shank module comprises an elastic leg strap support
302, an elastic leg
strap 303, a rotation joint 306, a shank spring 307, a shank flexible rope
308, a shank support 309, a shank
pneumatic artificial muscle 310, a rotation joint pneumatic artificial muscle
3 II, a rotation joint spring 312,
a synchronous belt 313, a synchronous belt pulley 314, and a flat key 320,
wherein, as shown in Fig. 13, the
rotation joint 306 is a rectangular block. As shown in Fig. 13, a circular
tube is arranged on the top of the
rotation joint 306. The axial direction of the circular tube on the rotation
joint 306 is parallel to the width
direction of the rotation joint 306, as shown in Fig. 8. The circular tube on
the rotation joint 306 is fitted
over the adjacent rotation shaft 315, i.e., the top of the rotation joint 306
is movably connected with the
bottom of the thigh support 304, as shown in Fig. 8. As shown in Fig. 13,
rectangular holes are arranged on
the sides of the rotation joint 306, and the opening direction of the
rectangular holes on the sides of the
rotation joint 306 is in accordance with the axial direction of the circular
tube on the top of the rotation joint
306. Two joint insertion plates are arranged on the bottom of the rotation
joint 306. Both of the joint
13
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
insertion plates extend vertically downwards and are parallel to each other.
The joint insertion plates are
perpendicular to the end surface of the circular tube on the rotation joint
306.
As shown in Fig. 9, the shank support 309 is in a H-shape, and comprises two
shank'vertical plates
and one shank cross plate. The two shank vertical plates are connected
together via the shank cross plate.
The shank cross plate has a small hole.
The top surface of each shank vertical plate has a shank slotted hole. The
shank slotted hole
matches the joint insertion plate in shape. Namely, the joint insertion plate
is inserted into the adjacent
shank slotted hole.
The top ends of the two shank vertical plates of the shank support 309 are
fixedly connected with
the bottom tnds of the two joint insertion plates of the adjacent rotation
joint 306 respectively. The bottom
ends of the two shank vertical plates of the shank support 309 are connected
to the top surface of the
standing platform 400.
An elastic leg strap support 302 is connected horizontally at the outer side
of the shank vertical
plate at one side of the shank support 309. An elastic leg strap 303 is
arranged at the tail end of the elastic
leg strap support 302.
As shown in Fig. 9, the shank pneumatic artificial muscle 310 is arranged on
the standing platform
400 below the shank cross plate. The top of the shank pneumatic artificial
muscle 310 is connected to one
end of the shank flexible rope 308. The other end of the shank flexible rope
308 passes through the small
hole in the shank cross plate and then is fixedly connected to the bottom of
the rotation joint 306.
As shown in Fig. 9, the shank spring 307 is fitted over the shank flexible
rope 308 above the shank
cross plate. The bottom of the shank spring 307 contacts with the top surface
of the shank cross plate, and
the top of the shank spring 307 contacts with the bottom of the rotation joint
306.
AS shown in Fig. 5 or 9, a rotation joint pneumatic artificial muscle 31Iand a
rotation joint spring
312 are arranged on the standing platform 400 at the other side of the shank
support 309. The top of the
rotation joint pneumatic artificial muscle 311 is connected with the top of
the rotation joint spring 312 via
the synchronous belt 313. The synchronous belt 313 is wound around the
synchronous belt pulley 314.
14
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
As shown in Fig. 10, a flat key 320 Is arranged on the rotation shaft 315, a
corresponding key slot is
arranged on the inner wall of the circular tube on the rotation joint 306, so
that the rotation shaft 315 is
connected with the rotation joint 306. When the rotation joint pneumatic
artificial muscle 311 extends or
retracts, the rotation joint pneumatic artificial muscle 311, the rotation
joint spring 312, the synchronous
belt 313, the synchronous belt pulley 314, and the flat key 320 jointly drive
the shank module to move in
relation to the thigh module.
When the shank pneumatic artificial muscle 310 extends or retracts, the
rotation joint 306 is pulled
via the shank spring 307 and the shank flexible rope 308 to extend or retract
in relation to the shank support
309, and thereby the positions of the elastic leg strap support 302 and the
elastic leg strap 303 connected
with the shank support 309 in relation to the elastic hip joint strap support
319 and the elastic hip joint strap
301 are regulated.
As shown in Fig. 5, in the n-shaped structural part formed by the elastic hip
joint strap support 319,
the elastic hip joint strap 301 and the regulating device for assisting leg
movement via connection:
Both the elastic leg strap support 302 connected with the thigh support 304
and the elastic leg strap
support 302 connected with the shank support 309 are arranged at the inner
side of the n-shaped structural
Part.
The synchronous belt pulleys 314 connected with the ends of the rotation shaft
315 in the thigh
support 304 are arranged at the outer side of the n-shaped structural part.
Furthermore, the thigh pneumatic artificial muscle 316 is a DMSP-20-100N
pneumatic muscle
tendon from Festo.
The shank pneumatic artificial muscle 310 is a DMSP-20-130N pneumatic muscle
tendon from
Festo.
The rotation joint pneumatic artificial muscle 311 is a DMSP-20-130N pneumatic
muscle tendon
from Festo.
As shown in Fig. 14, the detection unit 800 comprises six pressure sensors
801, four laser ranging
sensors 802, and two absolute type encoders 803, which are: ISE30A-01-N
pressure switches from SMC,
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
Q4XTBLAF300-Q8 laser ranging sensors from BANNER, and E6CP-A absolute type
encoders from
OMRON respectively. As shown in Fig. 14, the pressure sensors 801 are mounted
at the orifices of air inlet
tubes of the thigh pneumatic artificial muscles 316, the orifices of air inlet
tubes of the shank pneumatic
artificial muscles 310, and the orifices of air inlet tubes of the rotation
joint pneumatic artificial muscles
311, detect the value of the pressures on the pneumatic artificial muscles in
real time, and transmit the
detection data via a data acquisition card to the industrial PC.
As shown in Fig. 15, the laser ranging sensor 802 comprises a laser sensing
head and a reflector,
wherein, the laser sensing heads of the laser ranging sensors 802 are mounted
on the top of the shank
supports 309 and on the top of the thigh supports 304 respectively; the
reflectors of the laser ranging
sensors 802 are mounted an the bottom of the elastic hip joint strap supports
319 and on the bottom of the
rotation joints 306 respectively; the laser sensing heads mounted on the top
of the thigh supports 304
correspond to the reflectors mounted on the bottom of the elastic hip joint
strap supports 319 respectively.
The laser sensing heads mounted on the top of the shank supports 309
correspond to the reflectors mounted
on the bottom of the rotation joints 306 respectively.
The lengths of the thigh springs 317 and the shank springs 307 are measured
and transmitted via
the data acquisition card to the industrial PC respectively, and the
industrial PC calculate the total heights
of the thigh modules and the shank modules on the basis of known support
height.
An encoder 803 is mounted on the tail end of each rotation shaft 315, the
rotation angle of the
rotation joint 306 is detected by the encoder 803 and is transmitted via the
data acquisition card to the
industrial PC. The rotation angle of the rotation joint 306 corresponds to the
rotation angle of the shank
module.
Furthermore, the detection unit 800 further comprises a visual sensor. The
visual sensor is
mounted on the aluminum alloy profile frame 100 and is connected to the
industrial PC, and is configured
to detect the spatial position and posture of the standing platform 400.
The visual sensor comprises an OMRON FH-SCO4 high speed CMOS camera and Sysmac
Studio
control software installed in the industrial PC. The industrial PC executes
the Sysmac Studio control
software to analyze and output the images captured by the high speed CMOS
camera.
16
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
As shown in Figs. 5 and II, the structure and working principle of the device
provided in the
present invention are briefly described as follows: in the thigh module, the
bottom end of the thigh
pneumatic artificial muscle 316 is fixedly mounted on the thigh support 304,
and the top end of the thigh
pneumatic artificial muscle 316 is connected to one end of the thigh flexible
rope 318. The thigh flexible
rope 318 passes through the hole in the top of the thigh support 304 and the
middle part of the thigh springs
317 and is connected to the bottom of the elastic hip joint strap support 319.
The bottom end of the thigh
spring 317 is fixedly mounted on the thigh support 304, and the top end of the
thigh spring 317 is connected
with the elastic hip joint strap support 319. A top protrusion part of the
thigh support 304 has a slotted hole,
a bottom protrusion part of the elastic hip joint strap support 319 forms an
insertion plate, which can be
inserted into the slotted hole freely. In the shank module, the bottom end of
the shank pneumatic artificial
muscle 310 is fixedly mounted on the standing platform 400, and the top end of
the shank pneumatic
artificial muscle 310 is connected to one end of the shank flexible rope 308.
The shank flexible rope 308
passes through the hole in the top of the shank support 309 and the middle
part of the shank spring 307 and
is connected to the bottom of the rotation joint 306. The bottom end of the
shank spring 307 is fixedly
mounted on the shank support 309, and the top end of the shank spring 307 is
connected to the bottom of
the rotation joint 306. The bottom of the shank support 309 is mounted on the
standing platform 400, a top
protrusion part of the shank support 309 has a slotted hole, a bottom
protrusion part of the rotation joint 306
= forms an insertion plate, which can be inserted into the slotted hole
freely. One end of the rotation joint
pneumatic artificial muscle 311 is fixedly mounted on the standing platform
400, the other end of the
rotation joint pneumatic artificial muscle 311 is connected to the synchronous
belt 313; the synchronous
belt 313 is engaged with the synchronous belt pulley 314, and the other end of
the synchronous belt 313 is
connected to the rotation joint spring 312 fixedly mounted on the standing
platform 400. The bottom side
walls of the thigh support 304 have two holes respectively for mounting
bearings 305. The rotation shaft
315 is mounted in the inner rings of the bearings 305, and is connected with
the rotation joint 306 via a flat
key 320, and the protruding end of the rotation shaft 315 is connected with
the synchronous belt pulley 314
by interference fit.
In use, the elastic leg strap supports 302 in the thigh modules and the shank
modules are fixedly
mounted on the thigh supports 304 and the shank supports 309 respectively, and
the outer ends of the
elastic leg strap supports 302 are tied on the thighs and shanks of the
patient via the elastic leg straps 303 to
provide a fixing function. The elastic hip joint straps 301 are fixedly tied
on the hip joint part of the patient,
17
=
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
the elastic leg straps 303 are fixedly tied on the thighs and shanks of the
patient, so as to fix and support the
lower limbs of the patient, without limiting the degree of freedom of lower
limb movement of the patient.
When the rotation joint pneumatic artificial muscles 311 are inflated and
thereby contract, the
synchronous belts 313 moves and the rotation joint springs 312 are tensioned;
at the same time, the
synchronous belt pulleys 314 engaged with the synchronous belts 313 are driven
to rotate, and thereby the
rotation shafts 315 rotate and drive the rotation joints 306 fitted with it
via the flat keys 320 to rotate. When
the rotation joint pneumatic artificial muscles 311 are deflated and thereby
extend, the rotation joint springs
312 reset under the action of the spring force, the synchronous belts 313 move
in a reversed direction, and
drives the synchronous belt pulleys 314 engaged with the synchronous belts 313
to rotate in a reversed
direction at the same time; thus, the rotation shafts 315 rotate in a reversed
direction, and drive the rotation
joints 306 fitted with it via the flat keys 320 to rotate in a reversed
direction, and thereby the purpose of
assisting the shanks to rotate backwards and return is attained.
When the shank pneumatic artificial muscles 310 in the shank modules are
inflated and thereby
contract, the entire leg device is driven by the shank flexible ropes 308 to
compress the shank springs 307
IS and move downwards. When the shank pneumatic artificial muscles 310 are
deflated and thereby extend,
the entire leg device moves upwards under the spring force of the compressed
shank springs 307; thus, the
heights of the elastic leg straps 303 in the shank module in relation to the
standing platform 400 are
regulated, to meet the demand of patients with shanks of different length.
When the thigh pneumatic artificial muscles 316 in the thigh modules are
inflated and thereby
contract, the elastic hip joint strap supports 319 and the connected elastic
hip joint straps 301 are driven by
the thigh flexible ropes 318 to compress the thigh springs 317, so that the
elastic hip joint strap supports
319 move downwards. When the thigh pneumatic artificial muscles 316 are
deflated and thereby extend,
the elastic hip joint strap supports 319 and the connected elastic hip joint
straps 301 move upwards under
the spring force of the compressed thigh springs 317; thus, the heights of the
elastic hip joint straps 301 in
relation to the elastic leg straps 303 in the thigh modules are regulated, and
the demand of patients with
thighs of different length is met.
In the present invention, the elastic hip joint straps in the lower limb
automatic regulating platform
are tied on the hip joints of the patient. Since the elastic hip joint straps
have elasticity, their effect on the
18
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
hip joints of the patient is similar to the effect of ball hinge, and the knee
joints in the platform can also
rotate; in addition, four waistband units 200 are arranged above the waist of
the patient to fix and support
the upper body of the patient. Therefore, the entire structure of lower limb
movement machine can be
simplified to the structure as shown in Fig. II. Thus, the standing platform
400 is driven by the ropes, and
the two legs of the patient can move in relation to the hip joints.
Furthermore, since the knee joints have
pneumatic artificial muscles to provide a driving force, the knee joints are
assisted to bend. Thus, the
bending accuracy of the two legs are ensured, and discomfort and potential
safety hazard incurred by
forward straightening of the shanks of the patient in relation to the knee
joints in the training process can be
prevented.
In the rehabilitation training process, the industrial PC controls the motors
to rotate, so that the
ropes extend or retract, and thereby drive the standing platform 400 to
realize preset spatial positions and
postures change; at the same time, the spatial position and posture of the
standing platform 400 is
monitored with a visual sensor and the data is transmitted to the industrial
PC. If there is any error in the
actual spatial position and posture of the standing platform 400 compared with
the preset spatial position
and posture, the industrial PC can control the air inlet valves and air outlet
valves of the two rotation joint
pneumatic artificial muscles 311 in the lower limb automatic regulating
platform unit 300 to open and
close, and thereby provide a driving force to control the rotation of the
shank joints and thereby drive the
standing platform 400 to move, so that the standing platform 400 reaches the
preset spatial position and
posture; thus, the legs of the patient can reach preset positions and can bend
in relation to the hip joints in a
better way, and thereby the effect of waist rehabilitation training is
ensured.
Utilizing the sensors, the lower limb automatic regulating platform provided
in the present
invention not only ensures accurate and safe rehabilitation training, but also
realizes automation of the
device. The pressures on the pneumatic artificial muscles is monitored in real
time with the pressure
sensors 801; thus, a potential safety hazard of output force variation
resulted from change of pressure on
the pneumatic artificial muscles is prevented, and the safety of
rehabilitation training is ensured. The
heights of the thigh modules and the shank modules are detected with the laser
ranging sensors 802, so that
automatic height regulation is realized. The rotation angles of the shank
modules are detected by the
encoders 803, and thereby the accuracy of rehabilitation training is ensured.
19
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
As shown in Fig. 16, a waist rehabilitation training method utilizing the
device for waist
rehabilitation training according to the present invention is executed through
the following steps:
Step 1: powering on an industrial PC and the motors in the motor units 500,
controlling pressure
sensors 801, laser ranging sensors 802 and encoders 803 to feedback signals,
and resetting thigh pneumatic
artificial muscles 316, shank pneumatic artificial muscles 310, rotation joint
pneumatic artificial muscles
311, shank springs 307, rotation joint springs
Step 2: inputting thigh and shank length information of the patient to the
industrial PC; inputting
preset spatial positions and postures and allowable error ranges to the
industrial PC, wherein, the preset
spatial positions and postures are rehabilitation actions and postures to be
exercised by the patient on the
waist rehabilitation training device;
Step 3: instructing the patient to stand on the standing platform 400;
controlling the shank
pneumatic artificial muscles 310 to inflate or deflate first according to the
leg information of the patient
inputted to the industrial PC in the step 2 to adjust the lengths of the shank
modules, detecting the lengths of
the shank springs 307 with laser ranging sensors 802 in the shank modules in
real time, and transmitting the
detection data to the industrial PC for computation and judgment, till the
rotation joints 306 are flush with
the knee joints of the patient;.
then, controlling the thigh pneumatic artificial muscles 316 via the
industrial PC to inflate or
deflate to adjust the length of the thigh modules, detecting the lengths of
the thigh springs 317 in real time
via the laser ranging sensors 802 in the thigh modules at the same time, and
transmitting the detection data
to the industrial PC for computation and judgment, so that elastic hip joint
straps 301 are positioned at the
hip joints of the patient;
Step 4: tying elastic leg straps 303 in the thigh modules and elastic leg
straps 303 in the shank
modules to the thighs and shanks of the patient respectively, and tying the
elastic hip joint straps 301 to the
hip joints of the patient, so as to prepare for making rehabilitation
exercise;
Step 5: controlling the motors in the motor units 500 by the industrial PC to
rotate, so that the
flexible ropes 600 extend or retract and thereby the standing platform 400
moves. Controlling the air inlet
valve and air outlet valve for the two rotation joint pneumatic artificial
muscles 311 in real time throuth the
CA 2950546 2017-06-07
industrial PC to open or close according to the spatial position and posture
of the standing platform 400, so
as to control the shank joints to rotate and thereby drive the standing
platform 400 to move; at the same
time, making angle compensation for the rotation of the rotation joints 306
via the industrial PC according
to the angles of rotation of the shank modules fed back in real time by the
encoders 803, so that the position
and posture of the patient standing on the standing platform 400 matches the
preset spatial position and
posture inputted in the step 2;
Step 6: monitoring the real-time pressure information of the thigh pneumatic
artificial muscles
316, real-time pressure information of the shank pneumatic artificial muscles
310, real-time pressure
information of the rotation joint pneumatic artificial muscles 311, and real-
time spatial position and posture
information of the standing platform 400 with pressure sensors 801 and visual
sensors respectively, and
transmitting the real-time pressure information and real-time spatial position
and posture information via a
data acquisition card to the industrial PC; stopping the rehabilitation
training immediately and alarming for
device examination if an error goes beyond the allowable error range set in
the step 2, to avoid any accident
of the patient during the rehabilitation training;
Step 7; removing the elastic leg straps 303 and the elastic hip joiM straps
301 manually and
instructing the patient to get off the standing platform 400 after the
rehabilitation training is finished;
Step 8: resetting the lower limb automatic regulating platform 300, cutting
off the power supply to
the motor units 400, the pneumatic artificial muscles and the industrial PC.
=
21
CA 2950546 2017-06-07