Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02950698 2016-11-29
Petroleum product storage tank and floating element for said tank
The present invention refers to a tank construction and may be used for the
construction of storage tanks for light ends of petroleum products and
preferably for
gasoline storage.
In petroleum product storage tanks currently operated for storage of petroleum
products without a floating cover or pontoons, the intensive evaporation of
petroleum
products occurs on a liquid surface, which results in the formation of
explosive and
flammable vapor mixture in the gas space of a tank. Even with the use of
modern lighting
protection systems, we cannot avoid lighting striking to the tank. If lighting
strikes any
tanks filled with petroleum products, explosions and fires occur, which lead
not only to
significant losses but also result in injuries and death of people.
There are known methods of production of single-disc floating covers with a
circular pontoon, radial and circular floats or a ring pontoon and point
floats, in which a
central part of the floating covers is delivered to a construction site as
individual sheets,
ring pontoon, radial, ring buoys are delivered as individual elements,
respectively:
hermetically sealed units (compartments), profile or box girders, bottomless
boxes. Radial,
circular, point floats are located evenly over the entire cover area
/RU2200120,
B65D88/34, 10.03.2003; GB1191461A, B65D88/34, 13.05.1970, RU2127216 Cl,
B65D88/34, 10.03.1999, RU2163559 Cl, B65D88/34, 27.02.2001/. On the racks
above the
bottom, a frame and floating cover pontoons are collected. By the frame layers
of the
central part are spread, welded together. On the spreading central part of the
floating cover,
radial and circular or point floats are welded. The finished central part of
the floating cover
is welded to the pontoon ring.
The main disadvantages of such covers are significant labor intensity of the
construction, low portability and, moreover, large metal intensity. In tanks
using such
pontoons, the problem of formation of explosive and flammable vapor mixture is
significantly reduced but also remains. In such tanks in the event of lighting
or the
discharge-load of petroleum products, the pontoon may be skewed within the
tank, and it
stops to perform its protective functions (so called rigid pontoons).
Invention /EP 2530032 Al, B65D88/34, 01.06.2012/ includes a cover, which
consists of independent flexible compartments in which spherical bodies are
located. The
specified spherical bodies may have a different diameter to overlap densely a
liquid margin
by evaporation to the gas space of a tank. However, as practice shows
spherical bodies
CA 02950698 2016-11-29
2
with a lower diameter due to gravity action, as well present vibrations,
always drop below
the bodies with a large diameter and do not overlap the space between the
bodies with a
big diameter. Moreover, by chaotic filling of compartments with the bodies of
various
diameters, they would not form an ordered structure with the minimum size of
an empty
cell formed by the surfaces of the spherical bodies. But perforated cover
compartments will
decrease but not prevent liquid evaporation. Moreover, according to our
studies, not only
overlapping of liquid surface by the cover, which is located in the plane of a
liquid surface,
is of great importance, but also an overlap in the gas space above the liquid
surface plays
its role. At that in case of any collapsing of constructions into the liquid,
for example, the
elements of automatic fire extinguishing systems, what most likely occurs in
explosions in
the gas space of the tank, for example, with lighting strike, such cover will
be submerged
and stop playing protective role in the reduction of evaporation to the tank
gas space
combusted.
There is known the invention /US12533218, B65D88/34, 31.07.2008/ that
represents a floating barrier to reduce evaporation of liquid product, which
contains
floating elements, which have a cross-sectional polyhedron form. This
invention like the
previously described one solves the problems of reduced evaporation, but does
not solve
the problem of combustion processes phlegmatization in the possible combustion
of liquid
and air mixture. In the specified invention, the problem of liquid surface
overlapping on
the tank walls is not also solved. On tank walls the increased evaporation of
liquid product
will occur, and hazardous liquid and air mixture will be collected in the gas
space of the
tank. Moreover, by chaotic filling of the tank with the floating elements
specified in the
invention, it is rather highly probable that the correct order of dense
element installation
"brink to the brink" will be impaired that inevitably will result in the
increase of liquid
evaporation rate.
Invention /US8616398 B2, 865D 90/22, 25.09.2012/ is the closest to the
declared
invention in which a floating barrier for the prevention of liquid evaporation
is made with
the set of floating bodies. But as in the invention /EP 2530032 Al, B65D88/34,
01.06.2012/, spherical bodies with a lower diameter, due to gravity action and
vibrations,
always drop below the bodies with a large diameter and do not overlap space
between the
bodies with a large diameter. As well by chaotic tank filling with the bodies
of various
diameters, they would not form an ordered structure with the minimum size of
an empty
cell formed by the surfaces of spherical bodies. But perforated cover
compartments will
CA 02950698 2016-11-29
3
decrease but not prevent liquid evaporation. Moreover, according to our
studies, not only
overlapping of liquid surface by the cover, which is located in the plane of a
liquid surface,
is of great importance but also an overlap in the gas space above the liquid
surface plays
the role. At that in case of any collapsing of constructions into the liquid,
for example, the
elements of automatic fire extinguishing systems, which most likely occurs in
explosions
in the gas space of the tank, for example, with lighting strike or static
discharge, even
preliminarily ordered installation of spherical bodies of various diameters
will be impaired.
Besides, in liquid discharge ¨ loading to the tank, the spherical bodies will
be shifted with
respect to each other, rotated in respect of geometrical axis, what results in
the adherence
of flammable liquid to their surface and increased evaporation. Moreover, the
wall multi-
layerness of the spheroid bodes declared in the invention /US8616398 B2, B65D
90/22,
25.09.2012/, with the use of various plastics and resins even with the applied
antistatic
coating may not completely prevent the accumulation of static electricity and
the
occurrence of discharge, which may cause ignition or explosion of vapor-air
mixture. It is
confirmed with the introduction of the appropriate amendments to the
regulatory
documents concerning prohibition to use plastic and other polymeric products
for tanks
and other tanks for petroleum products.
Therefore, the goal of the invention is to make the tank for the storage of
petroleum
products devoid of the disadvantages. The technical result is the following:
1) decrease of vapor mixture volume, which is formed with the evaporation of
petroleum products, i.e. the decrease of liquid vapor concentration in the gas
space of the
tank;
2) provision of combustion process phlegmatization in the event of fire,
lighting
strike;
3) prevention of the possible accumulation of static discharge and occurrence
of
spark discharge between the floating bodies.
To solve the assigned task, as well to achieve the declared technical result,
the
petroleum product storage tank is offered, which consists of a body, a shell
and a floating
protective coating from numerous floating elements. The floating elements are
made as
rotation bodies of the same shape. Some part of the floating elements in the
tank is located
below a liquid surface, and some of them ¨ in the tank gas space. The
distinctive feature of
the proposed invention is that the floating elements, which differ from each
other in size
for more than 5%. And the floating elements from which the floating protective
coating is
CA 02950698 2016-11-29
4
made have the flotation center offset from their geometric centre. All
elements of the
protective coating are made of non-sparkling metal.
It is also proposed to locate the floating elements in the gas space forming
not more
than four layers.
It is also proposed to locate the floating elements within a liquid forming
not less
than one and a half layers.
As well in the upper part of the tank, a grid with a cell less than the
floating
element diameter may be installed.
In the upper part of the tank, internal collaring may be also made.
In the lower part of the tank above a liquid discharge-load level, a grid with
a cell
smaller than the floating element diameter may be installed.
A floating element constituting a floating protective coating may be made of
aluminum or its alloy.
A floating element may be made with a ceramic coating of aluminum oxide or
stainless steel.
Hydrophobic coating may be applied to a floating element surface.
It is preferable that the ratio of a maximum diameter of a rotation body to
its wall
thickness is at least 60.
It is also proposed to make a floating element with the minimum diameter not
less
than 10 mm.
It is also proposed to make a floating element with the maximum diameter not
more
than 60 mm.
It is also proposed to make a floating element in a spheroid, ellipsoid or egg-
shaped
form.
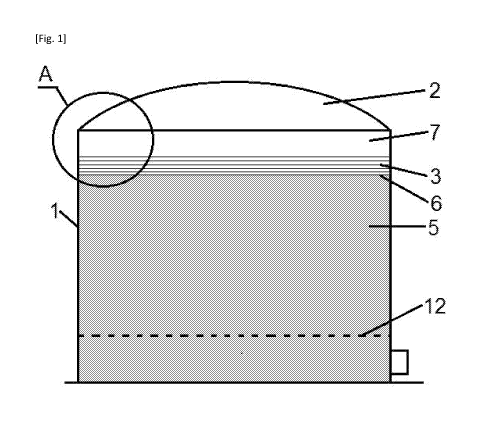
The invention essence is clarified by drawings where
on fig.1, the general appearance of a covered tank is provided; where it is
denoted:
1 ¨ the tank, 2 ¨ the tank cover, 3 ¨ the floating protective coating
consisting of numerous
floating elements 4, 5 ¨ the liquid (petroleum products), 6 ¨ the liquid
surface, 7 ¨ the gas
space, 8 ¨ the grid, 9 ¨ the collaring, 12 ¨ the lower grid.
on fig.2 and fig.3 - section A of fig. 1;
on fig.4,5,6,7 ¨ cross section of some possible forms of the floating
elements;
where it is denoted: 10 ¨ the flotation center of a floating element, 11 ¨ the
geometric
center of the floating element 4.
CA 02950698 2016-11-29
on fig.8¨ the flow charts of liquid evaporation rate in the tank are provided
depending on its configuration: 13 ¨ a curve for a tank without floating
elements, 14 ¨ a
curve for a rigid pontoon tank, 15 ¨ a curve for a tank with a floating
protective coating
from numerous floating elements.
5
The petroleum product storage tank 1 contains a cover 2, a floating protective
coating 3 consisting of numerous floating elements 4 some of which are located
in liquid 5,
i.e. below liquid surface 6, and some of them above liquid surface 6, i.e. in
gas space 7
(fig.1). In the upper part of the tank, a grid 8 (fig.2) or a collaring 9
(fig.3) are installed.
Flotation center 10 of the floating elements 4 is offset from their geometric
centre 11
(fig.4, 5, 6, 7). In the lower part of the tank above a drainage-load level,
the upper grid 12
is made with a perforation cell smaller than the floating element diameter 4.
The tank I with the cover 2 and the floating protective coating 3 acts in the
following way.
When the floating elements 4 are filled in to the tank 1 with the liquid 5
(petroleum
products), as well when the liquid 5 is loaded and discharged, they, being
chaotically
distributed in the tank, are placed in several layers forming the floating
protective coating 3
with dense packing.
In the event of oscillation of liquid surface 6 in loads and discharges or
explosion,
the floating protective coating 3 consisting of the numerous floating elements
4 as rotation
bodies of the same shape functions by the principle of tank duckweed. In the
event of
possible lighting strike or collapse of the cover constructions 2 within the
tank 1, the
floating elements 4 may diverge, even fly apart within the tank I. But then
chaotically
returning, they are placed to the structure with dense packaging (floating
protective coating
3) thereby they extinguish evaporation and evolving fire locus, as well
significantly
phlegmatize combustion process. To prevent the discharge of the floating
elements 4
beyond the tank 1 in the event of explosion, in its upper part, the grid 8 or
the collaring 9
are installed. The grid 8 has a cell smaller than the floating element
diameter 4. The
collaring 9 is installed as it is shown on fig.3, by the periphery of the
upper part of the tank
1. It allows to localize and extinguish fire quickly and with the lack of risk
of new
explosions. To reduce the risk of penetration of the floating elements to
drainage holes, in
the lower part of the tank above liquid discharge ¨load, the grid 5 is made
with a
perforation cell smaller than a floating element diameter.
CA 02950698 2016-11-29
6
To reduce the concentration of liquid vapors in the gas space 7 of the tank 1
and
provide phlegmatization of combustion process as the protective coating 3, the
floating
elements 4 are used which are made as rotation bodies, with the flotation
center 10 offset
from their geometric centre 11. E.g., as fig.4, 5, 6, 7 show, the floating
element 4 may have
a spherical, ellipsoid or egg-shaped form. Further considerations would be
made in relation
to the floating elements 4 having spherical form. However, it should be
understood that
such considerations also cover other rotation bodies. With the tank discharge
and loading,
the spherical floating elements 4 may touching each other turn about its
geometrical center
and touching the liquid 5 have a liquid film on its surface. The film may
evaporate and
vapors will penetrate to the gas space of the tank 7. To prevent this the
spherical floating
elements 4 are made so that their gravity center 10 is offset from their
geometric centre 11
(fig.4-8). Hereby the spherical floating elements 4 will be constantly
oriented in relation to
the liquid surface 6 and in the event of the tank discharge-load may only
fluctuate slightly
in relation to their position. So a dry surface of the spherical floating
element 4 will not be
immersed to the liquid 5, and, respectively, have a liquid film. Moreover,
hydrophobic
coating may be applied to the surface of the floating element 4, which
prevents a capillary
effect. It will significantly reduce evaporation.
To prevent static electricity and possible spark discharge in the mass of the
spherical floating elements 4, these elements should be made from non-
sparkling metal,
mainly from aluminum or its alloys. In this case, the necessary buoyancy of
the elements 4
of the floating protective coating 3 may be provided. The criterion for
selection of the
floating element size 4 is the ratio:
n=D It,
where D ¨the external diameter of the spherical floating element 4,
t ¨ wall width of the spherical floating element 4.
The ratio of the floating element diameter n D to its wall thickness t should
be at
least 60. The preferred ratio is n=80...110. The larger ratio is undesirable
as the floating
wall element 4 will be too thin and not resistant to mechanic exposures. For
the same
reasons, the minimum diameter of the floating diameter D should be at least 10
mm. The
maximum diameter of the floating element D should be not more than 60 mm. In
this case
the size of a cell formed by the surfaces of the floating elements 4, densely
located will be
less than the critical value, i.e. sufficient to break a chain reaction
(explosion) of
stoichiometric petroleum product and air mixture (see Semenov N.N., Chain
reactions, M.,
CA 02950698 2016-11-29
7
Nauka, 1986). In other words, vapor ¨air mixture within such a cell will not
explode being
exposed to any ignition source (static electricity spark, lightning strike,
open fire exposure,
etc.).
Our studies have shown that a minimum number of layers of the floating
elements
4 located in gas space to reduce the dramatically flammable liquid evaporation
5 and,
respectively, entry of liquid vapors to the gas space 7 of the tank 1 should
be at least four.
Hereby combustion in the gas space 7 of the tank 1, even if it occurs for any
reasons,
would be phlegmatic. It is explained by the fact that the liquid evaporation
rate 5 would be
minimized due to overlapping of the liquid surface 6 and the gas space 7 above
the surface
6 with several layers of the floating elements 4.
Our calculations and tests have shown that the number of layers of the
floating
elements 4 located in the liquid 5 is of the same importance. After possible
explosion in the
gas space 7 and spread of the floating elements 4 located in the gas space 7,
they first,
being emerged, overlap the liquid surface 6 and thereby phlegmatize
combustion. And as
the tests have shown the floating elements 4 scattered in the tank 1
completely recover the
floating protective coating 3. The number of layers of the floating elements 4
in the liquid
5 should be at least one and a half.
Reduction of evaporation rate is well illustrated by the diagram of
relationship
between the level of excessive pressure and achievement time in the tank 1 in
which
pressure is released (fig. 8), where 13 ¨ a curve for a tank without the
floating elements, 14
¨ a curve for a rigid pontoon, 15 ¨ a curve for a tank with the floating
protective coating 3
from the numerous floating elements 4. The diagram on fig. 8 shows that with
the presence
of the floating protective coating 3 in which the floating elements 4 are
placed in several
layers, an excessive pressure is achieved for a longer time.
To prevent the surface corrosion of the floating elements 4, a layer of
aluminum or
its alloys should be applied to their surface. The preferred coating
composition for the
floating elements is A1203. Our studies have shown that the ceramic surface
coating of the
floating elements 4 makes effective corrosive protection of metallic surface
for the
overwhelming majority of petroleum products both of original manufacture and
having
various types of additives. The studies have shown high corrosive resistance
of such
coating in relation to a variety of flammable liquids and for benzenes it
fully protects the
surface of the floating aluminum elements 4 from corrosion.
So the assigned goal and the technical result are achieved.