Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR MONITORING SECURITY OF A POINT-OF-
SALE TERMINAL
FIELD
[0001] The embodiments described herein relate generally to point of
sale
terminals, and more specifically to methods and apparatus for monitoring point
of
sale terminals to attempt to detect when the point of sale terminals have been
tampered with.
BACKGROUND
[0002] Point of sale (POS) terminals enable merchants to receive
payments from customers using a variety of payment methods such as credit
cards, debit cards, smart cards, and gift cards, which are referred to herein
as
transaction cards. The use of POS terminals allows the customer the option of
choosing a payment method that suits them, and as a result POS terminals are
found at almost all merchant establishments.
[0003] Along with the increased deployment of POS terminals has come
an increase in the theft of transaction card data. Through use of the
merchant's
payment system, thieves may attempt to replace a legitimate POS terminal,
whether bank issued or otherwise, with a dummy device that can read and store
transaction card data (including card numbers, and any authentication
information entered by the users, names, etc.) from unsuspecting customers and
without knowledge of the merchant. After a period of time has elapsed the
dummy device can store considerable amounts of transaction card data and the
dummy device may then be removed and replaced with the legitimate POS
device. The data that is stored upon the dummy device can then be used to
perform fraudulent transactions through use of the unsuspecting customer's
account information. Where the thieves have not resorted to employing a
dummy device in the merchant's system, the legitimate POS terminal is often
modified or compromised by thieves to allow the transaction card data to be
- 1 -
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
diverted to added storage devices which may then be subsequently retrieved and
used for fraudulent purposes. Due to attempts made to compromise terminals
and steal transaction card data, there is a need for a system and method for
determining payment terminal fraud detection.
SUMMARY
[0004] In one aspect, this patent application describes a method for
monitoring security of a point-of-sale terminal. The method involves the point-
of-
sale terminal monitoring one or more security parameters associated with the
point-of-sale terminal. A violation of any one of the security parameters may
be
indicative of a compromise of the point-of-sale terminal.
[0005] The point-of-sale terminal detects a violation of any one of
the
security parameters, and transmits to a terminal management server data
regarding the any violation of the one or more of the security parameters.
[0006] One or more of the security parameters may include a network
connectivity status of the point-of-sale terminal. The point-of-sale terminal
may
maintain a network connection with the terminal management server, and the
detecting any violation of the any one of the security parameters may include
the
point-of-sale terminal detecting a termination of the network connection.
[0007] In response to the terminal management server classifying the
any
detected violation of the one or more of the security parameters as potential
fraudulent activity, the point-of-sale terminal receives from the terminal
management server a command disabling functionality of the point-of-sale
terminal.
[0008] In one embodiment, the security parameters may include a
status
of an access door to interior components of the point-of-sale terminal, and
the
detecting of any violation of the any one of the security parameters may
include
the point-of-sale terminal detecting an opening of the access door.
- 2 -
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
[0009] In one embodiment, the security parameters may include a
status
of at least one internal component of the point-of-sale terminal, and the
detecting
of any violation of the any one of the security parameters may include the
point-
of-sale terminal detecting removal of one of the internal components from the
point-of-sale terminal.
[0010] In one embodiment, the point-of-sale terminal may transmit to
the
terminal management server the data regarding the any violation of the one or
more of the security parameters together with transaction data generated by
the
point-of-sale terminal based on a payment transaction at the point-of-sale
terminal.
[0011] The point-of-sale terminal may transmit the data when the
point-of-
sale terminal is powered down by an authorized user and/or when the point-of-
sale terminal is powered up. The point-of-sale terminal may transmit the data
in
real time with the point-of-sale terminal detecting the any violation of the
one or
more security parameters.
[0012] The command disabling functionality may indicate the point-of-
sale
terminal is to be deactivated, and in response to the command disabling
functionality the point-of-sale terminal may discontinue processing of payment
transactions at the point-of-sale terminal until an override authentication
code is
entered into the point-of-sale terminal. In response to the command disabling
functionality, the point-of-sale terminal may discontinue processing of
payment
transactions at the point-of-sale terminal above a set monetary amount.
[0013] In another aspect, this patent application describes a method
for
monitoring security of a point-of-sale terminal that involves a terminal
management server receiving from the point-of-sale terminal data indicative of
a
violation detected by the point-of-sale terminal of one or more security
parameters, the violation being indicative of a compromise of the point-of-
sale
terminal.
- 3 -
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
[0014] One or more security parameters may include a network
connectivity status of the point-of-sale terminal. The point-of-sale terminal
may
maintain a network connection with the terminal management server, and the
detected violation may include a termination of the network connection.
[0015] The terminal management server classifies the detected violation of
the one or more of the security parameters as potential fraudulent activity,
and
sends a command to the point-of-sale terminal disabling functionality of the
point-
of-sale terminal.
[0016] In another aspect, this patent application describes a
terminal
management server that comprises a data transceiver and a data processor in
communication with the data transceiver. The data transceiver is configured to
receive from a point-of-sale terminal data indicative of a violation detected
by the
point-of-sale terminal of one or more security parameters. The violation is
indicative of a compromise of the point-of-sale terminal.
[0017] One or more of the security parameters may include a network
connectivity status of the point-of-sale terminal. The point-of-sale terminal
may
maintain a network connection with the terminal management server, and the
detected violation may include a termination of the network connection.
[0018] The data processor is configured to classify the detected
violation
as potential fraudulent activity, and to cause the data transceiver to send a
command to the point-of-sale terminal disabling functionality of the point-of-
sale
terminal.
[0019] One or more of the security parameters may include a
restoration
of the network connection, and the terminal management server may classify the
detected violation as potential fraudulent activity from a comparison of a
time
instant of the restoration of the network connection with an expected time
instant
for an authorized network reconnection.
- 4 -
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
[0020] One or more of the security parameters may include a power-up
event at the point-of-sale terminal, and the terminal management server may
classify the detected violation as potential fraudulent activity from a
comparison
of the time instant of a power-up event at the point-of-sale terminal with an
expected time instant for an authorized power-up event.
[0021] One or more of the security parameters may include a power-
down
event at the point-of-sale terminal, and the terminal management server may
classify the detected violation as potential fraudulent activity from a
comparison
of a time instant of the power-down event at the point-of-sale terminal with
an
expected time instant for an authorized power-down event.
[0022] The terminal management server may provide notice of the
detected violation. The notice of the detected violation may be provided by at
least one of an electronic mail or a SMS message to one or more recipients.
The
notice may be generated at and sent from the centralized terminal management
server to the one or more recipients.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING FIGURES
[0023] For a better understanding of the present invention and to
show
more clearly how it may be carried into effect, reference will now be made, by
way of example, to the accompanying drawings, which show a preferred
embodiment of the present invention and in which:
FIG. 1 is a block diagram of the components of a payment terminal
system;
FIG. 2a is a block diagram of the components of point of sale terminal;
FIG. 2b is a block diagram of the components of the base station of a
point of sale terminal;
FIG. 2c is a block diagram of the components of the key pad terminal of a
point of same terminal;
- 5 -
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
FIG. 3 is a block diagram of the components of the security application;
FIG. 4 is a block diagram of the components of the terminal management
server;
FIG. 5 is a block diagram of the components of a processing module;
FIG. 6 is a block diagram of the fields of the terminal database;
FIG. 7 is a flowchart illustrating the steps of a monitoring method security;
FIG. 8 is a flowchart illustrating the steps of an event processing method;
FIG. 9 is a sample screenshot of a terminal report screen.
FIG. 10 is a sample screenshot of a terminal report that identifies the
security parameters that are being monitored;
FIG. 11 is a sample screenshot of a terminal report that identifies the
number of violations that have been detected for each terminal; and
FIG. 12 is a sample screenshot of a terminal report that identifies the
security parameter violations that were detected for a specific terminal.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
[0024] It will be appreciated that, numerous specific details have
provided
for a thorough understanding of the exemplary embodiments described herein.
However, it will be understood by those of ordinary skill in the art that the
embodiments described herein may be practiced without these specific details.
In
other instances, well-known methods, procedures and components have not
been described in detail so as not to obscure the embodiments described
herein.
Furthermore, this description is not to be considered so that it may limit the
scope
of the embodiments described herein in any way, but rather as merely
describing
the implementation of the various embodiments described herein.
- 6 -
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
[0025] The embodiments of the apparatus, systems and methods
described herein may be implemented in hardware or software, or a combination
of both. Furthermore, the system, processes and methods of the described
embodiments are capable of being distributed as computer programming in a
computer program product comprising a computer readable medium that bears
computer usable instructions for execution on one or more processors.
[0026] The description which follows, and the embodiments described
therein, are provided for illustration by way of an example, or examples, of
particular embodiments of the principles of the present invention. These
principles are provided for purposes of explanation, and not limitation of
those
principles, and of the invention.
[0027] The embodiments described herein, as will be more fully
understood with the accompanying description, relate to methods and systems
for monitoring point of sale terminals for detecting fraudulent activity, and
thus
tending to reduce and deter theft of transaction card data. The term
transaction
card data as used herein is used to refer to specific information that is
contained
or associated with transaction cards and includes, but is not limited to,
account
numbers, expiry dates, names, pins, track one, track two, chip data or other
authentication information. The POS terminals described herein are provided to
a merchant or retailer by an issuing authority which for purposes of this
description is referred to as a bank. An issuing authority can be an
intermediary
service provider or other payment processing provider or service. Reference is
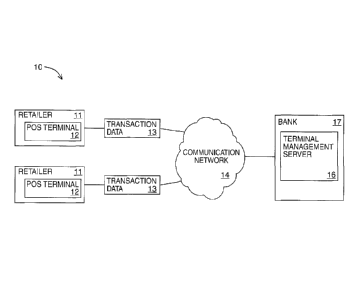
made now to FIG. 1, where a block diagram illustrating the components of a
fraud detection system 10 is shown in an exemplary embodiment. The fraud
detection system 10 in this exemplary embodiment is comprised of one or more
POS terminals 12 that are associated with a retailer 11, where the POS
terminals
12 generates transaction data 13 that is transmitted through a communication
network 14 to a terminal management server 16. One or more communication
devices 18 can be used to access the terminal management server 16 to set
- 7 -
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
parameters related to the operation of the system 10 as explained in detail
below, and to view reports and alerts regarding the POS terminals 12. The
fraud
detection system 10, as explained in further detail below, monitors the status
of
the member POS terminals 12 with regards to one or more security parameters.
The security parameters are monitored to detect if a POS terminals 12 is
compromised, such as where either a terminal 12 is being removed from
operation or an attempt to remove is made, or where malicious code or devices
are being installed upon a terminal. The security parameters can measure
whether any component of the POS terminals are removed, or deactivated or
where a connection that the POS terminal requires has been removed. The
security parameters may include, but are not limited to, the removal of
network
connectivity from the terminal, the loss of power to the terminal, the removal
of
any internal component of the terminal 12 (including but not limited to IC
boards,
circuits, batteries, screens), and/or the opening of access doors or other
tampering of the external casing for the terminal 12.
[0028] The POS terminals 12 transmit transaction data 13 to a
terminal
management server 16 through communication network 14. The transaction
data 13 may be any data that is generated by the POS terminal based on a
transaction and includes any data that is used specifically by the system 10
when
attempting to determine whether the terminal may have been tampered with.
The communication network 14 in an exemplary embodiment is the Internet.
Proprietary or private networks can also be used. Communication over the
network 14 can be encrypted, provided over a virtual private network, or
otherwise secured. The communication network 14 receives data from the POS
terminal 12 and transmits it to terminal management server 16. The terminal
management server 16 receives data and processes the data from the POS
terminals 12. In and embodiment, the terminal management server 16 receives
the transaction data 13 and allows the merchants to view the security
parameter
related data, and also processes the data so that the POS terminal 12 may be
- 8 -
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
disabled where it is suspected that the POS terminal has been compromised.
The components of the terminal management server 16 are described in further
detail below with regards to FIG. 4. Communication device 18 can allow users
of
the system 10 to access reports and receive alerts from the terminal
management server 16. The communication devices, including device 18, may
be any computing devices that have network capabilities, including, but not
limited to desktop, laptop computers, handheld devices, and mobile devices.
For
example, where the terminal management server 16 and its on board processing
suspects that a terminal has been compromised, the merchant may receive
electronic notification of such suspicious activity where they may then
investigate
further. Electronic notification may be provided through use of an electronic
mail
message, SMS or automated phone call.
[0029] Reference is now made to FIG. 2A-2C, where the POS terminals
12 are described in greater detail. Reference is now made to FIG. 2A where a
block diagram illustrating the components of the POS terminal 12 in one
embodiment is shown. In one embodiment, the POS terminals 12 comprise a
base station 20 and a keypad terminal 22. Where the POS terminals comprise
both a base station 20 and a keypad terminal 22, the base station 20 is used
by
the merchant to enter the relevant transaction information and the keypad
terminal 22 is then used by the customer to confirm the transaction by
entering
appropriate authentication information (i.e., a PIN number). It will be
understood
by one of skill in the art, that the POS terminal 12 may also be comprised of
one
unit with the functions of the base terminal 20 and keypad terminal 22
combined
in one unit, as appropriate.
[0030] Reference is now made to FIG. 2B where the components of the
base station 20 are shown in an exemplary embodiment. The base station 20, in
an exemplary embodiment comprises a card reader 30, a base station keypad 31
a power interface 32, a network interface 34, a processor 35, a memory store
36
- 9 -
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
which has resident upon it or associated with it a security application 38.
The
base station 20 may also have one or more peripheral devices 39.
[0031] The card reader 30 allows the information imprinted on
transaction
cards to be read by the POS terminal 12. In embodiments, multiple card readers
or a multi-function reader can be provided, such as for reading magnetic
stripes,
integrated chips, or for reading radio-frequency or other wireless information
from
a transaction card. The base station key pad 31 allows the merchant to enter
the
transaction information along with providing other input that may be required
by
the POS terminal 12. In some embodiments, the base station can also be used
by a customer of the merchant providing the transaction card to enter
information, such as to authenticate a purchase (especially in embodiments in
which there is no separate keypad terminal 22). The power interface 32 may
comprises an external power input 32A, and an internal power output 32B. The
external power input 32A allows for the base station 20 to be connected to an
external power source. The Internal power output 32B provides a wired
connection in an exemplary embodiment to the keypad terminal that powers the
operation of the keypad terminal 22. The network interface 34 provides a
connection to a communication network or to a gateway that can provide
communication with a communication network 14. In an exemplary embodiment,
the network interface 34 is a phone connection, but may also in alternative
embodiments be an Ethernet connection, or any other similar connection that
provides for connectivity with a communication network 14. The processor 35
controls the processing operations of the POS terminal 12. The memory store 36
provides memory storage that stores the security application 38. The security
application 38 monitors the transactions that are processed by the POS
terminal
and transmits transaction data, monitors the security parameters, as well as
restricts access to the POS terminals when certain security parameters have
been detected and/or when particular activity or pattern of activities are
deemed
to have occurred. The peripheral devices 38 of the POS terminal allow for
-10-
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
connectivity with devices such as printers, memory devices, monitors and other
such devices.
[0032] Reference is now made to FIG. 20, where the components of the
keypad terminal 22 are shown in an exemplary embodiment. The keypad
terminal 22 may comprise a card reader 40, a power and connectivity interface
42, and a keypad 44. The card reader 40 may be used where the customer is
required, or wishes to, swipe their transaction card themselves as opposed to
having their transaction card swiped, inserted or otherwise read by the
merchant
using the base station 20. Where the transaction card handling is done by the
customer, the merchant would then upon the base .station keypad 31 enter
information related to the amount of the transaction, and where appropriate
the
customer would then enter their authentication information upon the base
station
keypad terminal 40. The power and connectivity interface in an exemplary
embodiment is one connection that is provided from the base station, where the
base station powers the keypad terminal and connects through a USB
connection in an exemplary embodiment. In alternative embodiments, the power
and connectivity interfaces may be separate components and/or via other types
of connections.
[0033] Reference is now made to FIG. 3, where the components of the
security application 38 are illustrated in greater detail. The security
application
38 allows for monitoring of the security parameters. The security application
38
in an exemplary embodiment comprises a monitoring module 50, a reporting
module 52 and the security module 54. The operation of the various components
of the security application 39 is described in further detail with regards to
FIG. 7.
The monitoring module 50 monitors the various security parameters that the
monitoring module is adapted to search for. The reporting module 52 may
transmit data related to the security parameters at set instances of time
(i.e.
when the device is powered down by an authorized user and at power up which
will likely coincide with opening and closing times), and/or in real time with
the
-11-
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
detection of a violation of a security parameter (where a security parameter
has
been flagged as having been compromised). The disabling module 54 may
receive instructions from the terminal management server 16 to restrict access
to
the terminal 12 based on the processing of transaction data 13 that has
indicated
that the terminal may have been compromised. Also, the disabling module in
alternative embodiments upon the detection of a security event by the
monitoring
module may deactivate the terminal so that it can only be operated after an
override authentication code has been entered.
[0034] Reference is now made to FIG. 4, where a block diagram
illustrating the components of the terminal management system 16 is shown in
one embodiment. The terminal management server 16 in one embodiment
comprises a terminal database 60 and a processing module 62. The
management server comprises further processing capabilities through its use of
conventional transmitters and receivers, transmitters, processors and storage
mediums. The terminal management server 16 in an exemplary embodiment
may be any server type computing device. The terminal database 60 can be
used to store terminal and transaction data and security parameter data
transmitted from the POS terminals. An exemplary embodiment of the terminal
database 60 is illustrated in further detail with regards to FIG. 6. The
processing
module 62 allows for the users of the system 10 to specify the variables
associated with the security parameters that may be used to dictate whether
security alerts originate from the POS terminals 12. The variables allow for
acceptable timing thresholds to be established by which determinations of
whether violations of security parameters have taken place can be made. The
processing module 60 as described below can also process the transaction data
to determine whether terminal 12 has been compromised.
[0035] Reference is now made to FIG. 5, where the components of the
processing module 62 are illustrated in greater detail. The processing module
62
comprises various modules that are described for purposes of this application
as
-12-
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
separate modules, however it will be understood that the respective modules
described herein, may be combined to represent one module. In an exemplary
embodiment the security module 62 is comprised of a reporting module 70, a
security variable module 72 and a fraud detection module 74. The reporting
module as is described with reference to FIG. 9 allows the users of the system
to view reports related to the use of the POS terminal system 10, particularly
with respect to any security events associated with the POS system 10. The
security variable module 72 allows the users of the system 10, to determine
variables associated with the security parameters that will determine whether
a
10 security alert has occurred. For example, if the merchant determines
that the
threshold for a security event associated with the power connectivity of the
terminal 12 is to be 10 seconds, where the power is removed or otherwise
disconnected from the POS terminal 12 for less than 10 seconds this will not
be
flagged as a flagged security event, though this data may still be transmitted
to
the terminal management server 16 that can log and/or otherwise process this
data as described below to determine whether this incident may fit a pattern
that
would can trigger a flag indicating that the terminal may have been
compromised
or has been removed for any period of time. The fraud detection module 74
processes the terminal data and with its processing it can, highlight and
determine whether incidents of fraud are being perpetrated through
compromising of the POS terminal 12. The fraud detection module 74 in an
exemplary embodiment is described herein as monitoring various security
parameters associated with the terminal. The security parameters are any
feature of the terminal that can be monitored, such that any violations of the
security parameters can be reported through use of the system 10. Violations
may be recorded where an allowable time has been exceeded or where a
security parameter has been flagged. Further, checks can be performed with
regards to the state of the security parameters at specific instances of time.
For
example, checks that ensure that no terminal power downs have taken place at a
-13-
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
certain time or during a certain period of time, may also be performed and
used
to determine whether any specific instances of fraud have been detected and
where they have detected a violation. As an example, the system 10 may
classify as violations all instances of the detection of a reboot of a
terminal 10
outside of a pre-specified set of business hours. When detecting or reporting
on
security parameters, additional information can also be provided from the
terminal 10, including information regarding any identifications used by
operators
of the terminal both before and after a violation of a security parameter has
been
detected, and serial numbers of the respective components of the terminals.
This additional information may also be used in the processing of the data to
detect whether a violation has occurred or where further follow up is
required.
[0036] Reference is now made to FIG. 6, where the fields of the
terminal
database 60 are illustrated in greater detail in one embodiment. The database
60
allows for the processing module 70 and the fraud detection module 74 to
access
data as required to perform their respective functions. The terminal database
60
in one embodiment comprises a terminal ID field 80, a serial number field 82,
an
event field 84, an access field 86, and a parameters field. The terminal ID
field
80 stores an unique terminal identifier that is assigned to each POS terminal
12.
The serial number field 82 stores the serial number of the POS terminal,
including both the serial number for the POS terminal 12 and a serial number
that
may be assigned to the keypad. The events field 84 stores the security event
data along with the start time 84A and end time 84B (where applicable
associated with each security event) of the event. The events fields 84 allows
the terminal management system to track and report on the security events
associated with each terminal 12 that is part of the terminal management
system
10. The access field 86 contains a flag that is used to determine whether the
POS terminal 12 has been deactivated or locked as a result of any suspected
instances of tampering. Where a flag indicates that the suspected instances of
tampering may have occurred, the POS terminal 12 in one embodiment may be
- 14-
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
locked out such that the terminal 12 may not be used until an authorization
code
associated with the POS terminal 12 is entered by an authorized user. The
parameters field 88 comprises parameter settings that determine whether a
security event has occurred.
[0037] Reference is now made to FIG. 7, where a flowchart illustrating the
steps of a monitoring method 100 is shown in one embodiment. The monitoring
method 100 monitors the POS terminal to determine whether a security event
has occurred and appropriately reports that security event to the terminal
management server 16. The monitoring method 100 can operate continuously
upon each of the POS terminals 12. Method 100 begins at step 102, where the
POS terminal 12 is initialized. During the initialization process, the
terminal 12
provides the serial number and terminal identification number. Method 100 then
proceeds to step 104, where the variables associated with the security
parameters are retrieved from the terminal management server 16. Method 100
then proceeds to step 106, where the various components or connections
associated with the security parameters are monitored. Upon the detection of a
security event, such as for example where a security event is indicative of a
disconnect having been detected, method 100 proceeds to step 110, where the
timing of the security event is recorded. Method 100 then proceeds to step
112,
where the end timing of the security event may be recorded (e.g. the time at
which connectivity is restored). Method 100 then proceeds to step 112, where a
check is performed to determine whether a flagged security event has occurred.
The check performed at step 112 determines whether the security parameter
timing has been exceeded. Where it is determined that the timing has been
exceeded, the security event is characterized as a flagged security event.
Where
a flagged security event has been detected, method 100 then proceeds to step
114, where the terminal management server 16 is notified of the occurrence of
a
flagged security event. Upon informing the terminal management server of the
occurrence of a flagged security event, method 100 returns to step 106, where
-15-
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
the POS terminal 12 is monitored for the occurrence of any other security
event.
The security events for purposes of this example have been described as those
that have an allowable elapsed time associated with them. It should be
understood that the operation of the system 10 is not limited to such
instances
and that a flagged security event may be generated upon the detection of any
disconnect without the requirement that a certain amount of time pass.
[0038] Reference is now made to FIG. 8, where a flowchart
illustrating the
steps of a security parameter processing method 150 is shown in one
embodiment. The security parameter processing method 150 is used to process
security parameter data that is transmitted from the respective point of sale
terminals. The security parameter processing method 150 is executed to secure
the POS terminal 12 to prevent use of the POS terminal where a suspected case
of tampering of the POS terminal 12 exists. Method 150 begins at step 152,
where data regarding violation of a security parameter is received. As
described
above, flagged security event data can be received where the security
parameters associated with the POS terminal are being been monitored and, for
example, it has been determined that a disconnect of one or more components
or connections has been determined (that may exceed an acceptable period of
time). Where information has been provided that a component or connection
may have been disconnected, the system 10 can factor into account that the
disconnection may have been inadvertent or accidental, or system 10 can
determine that it has been perpetrated deliberately and that the POS terminal
12
may be compromised. Therefore, method 150 then proceeds to step 154 and
security information is retrieved. The security information determines where
the
occurrence of a detected violation of a security parameter should lead to
access
to the terminal being restricted and whether the merchant should be sent an
electronic notice regarding the potential compromise of the POS terminal 12.
Method 150 then proceeds to step 156 where a check is performed to determine
whether the violation of a security parameter indicates that the POS terminal
12
-16-
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
may have been compromised. Optionally, the violation may be categorized to
indicate a severity level, where a security event may be flagged as a low,
medium or high level violation. If it is determined at step 156 that POS
terminal
may have been compromised, method 156 proceeds to step 160 where the use
of the POS terminal may be restricted in that it may not process transactions,
or
that only certain functions or transactions are performed (such as, for
example,
for transactions of particular dollar amounts or less). Additionally, an
electronic
notification may be sent to one or more authorized individuals associated with
the
merchant to inform them of the flagged security event. Such a notification
would
allow a merchant to inspect the device and make a determination as to whether
the device has been compromised thus potentially averting fraudulent activity
that may have taken place as a result of the compromised terminal.
[0039] Reference is now made to FIG. 9, where a sample screen shot of
a
report generation window 200 is shown in an exemplary embodiment. The report
generation window 200 provides an example of the functionality that is
presented
to the user with regards to reviewing the security events associated with a
specific POS terminal 12. FIGS. 10-12 further describe the functionality that
is
present in the system 10, with reference to the reports that may be requested
by
and generated for, a user. As will be understood by one of ordinary skill in
the art,
the sample report window shown in FIG. 9 is meant to provide an example of the
types of reports that may be generated. Report generation window 200 in one
embodiment comprises a terminal identifier field 202, a date field 204, an
events
field 206, and start time and end time fields 208 and 210 respectively. The
terminal identifier field will display the unique terminal id that is
associated with
the terminal 12 that will allow the merchant to appropriately identify the
terminal.
The date field 204 stores date information with regards to the dates
associated
with the report. The events field 206 displays information regarding the
various
flagged security events that took place between the dates specified in the
date
field, and where appropriate the length or duration associated with the
flagged
-17-
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
security events are specified in the respective start and end time date fields
208
and 210 respectively.
[0040]
Reference is now made to FIG. 10, where a sample report request
window 220 is shown in one embodiment. The request window 220 allows a
user to request specific reports, though use of the security report menu 222.
For
purposes of example, window 220 is shown where the user has chosen to
request a device security report. The device security report allows the user
to
request a report based on the various types of security parameters that are
monitored, and allows for a date range to be specified. Additional reports
that
may be requested, include but are not limited to, device inventory reports and
exception reports. The
exception reports provide the user with specific
information with regards to security parameters that have been monitored. The
device inventory reports will specify for each device a history of the
monitoring
that has taken place. For purposes of describing the functionality associated
with
the report generating functions, figures that further describe the device
security
report are shown in FIGS. 11 and 12. Reference is now made to FIG. 11, where
a sample of a device security report window 230 is shown. The device security
report window 230 in an exemplary embodiment provides the user with a report
where based on each terminal that is being monitored, the number of violation
that have been detected for each terminal. For each terminal, where the user
desires to obtain more information for a specific terminal, the user can
select the
specific terminal they require more information regarding. Reference is now
made to FIG. 12, where a terminal incident report 240 is shown in one
embodiment. The terminal incident report is generated for a terminal based on
a
user selection, where the user requires more information regarding a specific
terminal. In an
exemplary embodiment, the terminal incident report 240
generates a detailed report regarding the security parameter violations that
were
detected for a specific terminal, including where applicable their duration
(or
timing of incident detection where the duration is not applicable).
-18-
CA 02956329 2017-01-27
[0041] While the foregoing invention has been described in some
detail for
purposes of clarity and understanding, it will be appreciated by those skilled
in
the relevant arts, once they have been made familiar with this disclosure,
that
various changes in form and detail can be made without departing from the true
scope of the invention in the appended claims. The invention is therefore not
to
be limited to the exact components or details of methodology or construction
set
forth above. Except to the extent necessary or inherent in the processes
themselves, no particular order to steps or stages of methods or processes
described in this disclosure, including the Figures, is intended or implied.
In
many cases the order of process steps may be varied without changing the
purpose, effect, or import of the methods described.
-19-