Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
1
Method for hot or warm forming a workpiece and production plant for hot or
warm forming a workpiece
Technical Field
The present disclosure concerns a method for hot or warm forming of a
workpiece and a production plant for hot
or warm forming of a workpiece.
Background
In hot and warm forming, uncoated or coated materials are generally used. To
avoid corrosion during transport, a
semifabricated piece in the form of a coil or a sheet can be provided
partially, preferably entirely, with a corro-
sion protection oil or with lubricants. In addition, a contamination with dust
or the like, especially in a coil or
sheet warehouse, can likewise hardly be avoided as a rule.
Caused by thermal processes which occur upon reaching the desired temperature
for the tempering process, a
thermal decomposition of the substances which have been deposited on the
semifabricated piece occurs. As a
result of this thermal decomposition, contaminants remain on the
semifabricated piece, which in turn reduce the
quality of the fabricated semifabricated piece. A mechanical cleaning, such as
by shot blasting, cannot always
entirely remove the residues which occur, or it may in particular impair
semifabricated pieces which are coated.
Furthermore, large oil residues, such as those due to a large oil film, may
lead to an intensified hydrogen absorp-
tion in the material during the processing of the semifinished piece. This may
result in material embrittlement on
account of the high strength. In the case of a micro-oiling, this behavior is
not found, but then no adequate corro-
sion protection can be assured.
Summary
One object of selected embodiments is to provide a method for hot or warm
forming of a workpiece with which
the quality of the piece fabricated by the hot or warm forming is further
improved beyond that of the prior art.
An exemplary embodiment provides a method for hot or warm forming of a
workpiece, comprising the follow-
ing method steps:
providing of the workpiece,
at least partial pretreating of the workpiece,
at least partial heating of the workpiece to a target temperature in a heating
station and
at least partial forming and/or hardening of the workpiece,
CA 2961869 2017-07-26
2
wherein the workpiece is at least partially cleaned in a cleaning step between
the pretreating and the heating of
the workpiece.
Another exemplary embodiment provides a method for hot or warm forming of a
workpiece, comprising the
following steps: providing of the workpiece, at least partial pretreating of
the workpiece, wherein the workpiece
is coated with a protective material and/or coated with a corrosion protection
oil or with a lubricant or cutting oil.
at least partial heating of the workpiece to a target temperature in a heating
station and at least partial forming
and/or hardening of the workpiece, wherein the workpiece is at least partially
cleaned in a cleaning step between
the pretreating and the heating of the workpiece, characterized in that the
workpiece in the cleaning step is at
least partially thermally treated, wherein the workpiece in the cleaning step
is heated by a burner to a cleaning
temperature.
In another embodiment there is provided a production plant for hot or warm
forming of a workpiece, wherein the
production plant comprises a clean-ing station for cleaning a workpiece, a
heating station for heating the cleaned
workpiece and a forming and/or hardening die for forming and/or hardening the
heated workpiece, wherein the
cleaning station is suitable for a thermal treatment, wherein the cleaning
station comprises a burner.
As compared to the prior art, the workpiece is cleaned after the pretreating
and before the heating for the forming
and/or hardening and in particular is thereby freed of residues which have
become deposited due to the pretreat-
ment on the workpiece. In this way, the quality of the part fabricated after
the forming of the workpiece is im-
proved, since the likelihood of a depositing of contaminants which form from
the residues during the heating of
the workpiece and thus the likelihood of a permanent impairment of the
workpiece is reduced. Furthermore,
other contaminations such as dust can be removed from the workpiece in the
cleaning step.
Preferably, it is provided that the cleaning step is done immediately before
the heating. It is furthermore prefera-
bly provided that the workpiece as a finished part after the forming and/or
hardening is a structural or chassis
part of a motor vehicle. In particular, the workpiece is provided as a sheet
metal piece, especially a flat metal
sheet (direct hot forming) or a formed part having practically its final
geometry (indirect hot forming), and the
pretreatment is at least part of the manufacturing process for the sheet metal
piece. Furthermore, it is preferably
provided that the partial region of the workpiece which is supposed to be
heated during the heating to the target
temperature, preferably the entire workpiece, is specifically cleaned in the
cleaning step. But it is also conceiva-
ble to clean specifically those partial regions of the workpiece for which an
improved surface quality is desired
on the finished part.
According to a further embodiment, it is provided that the workpiece in the
cleaning step is at least partially
chemically, mechanically and/or thermally treated. The chosen cleaning method
is thereby preferably adapted to
the workpiece such that the cleaning leaves the properties of the workpiece
substantially unimpaired. In this way,
one can advantageously ensure that no steps are taken with the cleaning step
which endanger the quality of the
subsequently fabricated part.
CA 2961869 2018-11-02
2a
According to a further embodiment, it is provided that the workpiece in the
cleaning step is at least partially
cleaned in a cleaning bath. During this chemical treatment of the workpiece,
the contaminants are advantageous-
ly bound in a liquid of the cleaning bath. It is conceivable that the liquid
in the cleaning bath will be exchanged
by bringing the liquid into the cleaning bath and draining it out once more,
for example it is pumped in a liquid
circuit into the cleaning bath and again pumped out from the cleaning bath.
Thanks to the binding of the contam-
inants to the liquid, it is advantageously prevented that the contaminants
spread via the air and become deposited
for example on plant parts. Furthermore, it is conceivable that the wet
workpiece will be dried, for example with
hot air, before the heating.
According to a further embodiment, it is provided that the workpiece is in the
cleaning step brushed. For this
mechanical treatment in the cleaning step, it is conceivable that the
workpiece is brought into contact with the
brush and the workpiece is moved in the longitudinal direction, while the
brush extends substantially along the
transverse direction of the workpiece. In this way, the cleaning step can be
advantageously integrated in the
transport of the workpiece to the heating station, without the cleaning step
occasioning any significant delay in
CA 2961869 2018-11-02
3
the hot or warm forming. It is also conceivable that the brush or a system of
brushes are arranged at the entrance
to the heating station and in this way the cleaning of the workpiece is
provided immediately before the heating.
Alternatively, it is conceivable that the workpiece is cleaned manually. In
manual cleaning with a brush, residues
visible to the naked eye can be advantageously removed without major
additional effort.
According to a further embodiment, it is provided that the workpiece in the
cleaning step is heated by a burner to
a cleaning temperature. Preferably the workpiece is heated by one or more
burners, preferably on both sides,
especially all around and uniformly. It is conceivable that the burner is
moved during the heating along the
transverse direction or the longitudinal direction of the workpiece,
preferably in oscillating manner. Thanks to
the heating already done during the cleaning of the workpiece, relatively
little heating energy is required to attain
the target temperature in the heating station. Preferably the cleaning station
with its burner is physically separate
from the heating station in order to prevent contaminants which are present in
the exhaust gases occurring during
the heating to the cleaning temperature from depositing on the plant parts
during the heating to the target tem-
perature. But it is also conceivable that the cleaning step is carried out in
the heating station by the burner re-
sponsible for the heating first heating the workpiece to the cleaning
temperature and then to the target tempera-
ture, the target temperature being greater than the cleaning temperature. It
is preferably provided that the air
surrounding the workpiece is drawn off during the heating of the workpiece to
a cleaning temperature, for exam-
ple by means of an exhaust hood, in order to carry away the contaminants.
According to a further embodiment, it is provided that the workpiece is
transported or moved during the cleaning
step. In this way, the cleaning step can be advantageously integrated in the
hot or warm forming of the
workpiece such that potential delays due to the cleaning step are kept as
short as possible. If the cleaning step
involves a thermal treatment, it is conceivable that the workpiece is moved by
a burner belt along the convey-
ance direction past a burner, with the burner heating the workpiece as it
moves past it. In particular, the
workpiece is moved with a conveying mechanism along a conveyance direction and
in this process it passes in
succession through the cleaning station, the heating station, and reaches the
forming and/or hardening die.
According to a further embodiment, it is provided that the workpiece is
transported from a cleaning station to a
heating station between the cleaning step and the heating step. In the case of
thermal cleaning, it is preferably
provided that the transport path is covered in a shortest possible time in
order to prevent the workpiece from
cooling down again. In particular, it is conceivable that the conveying
mechanism comprises heating elements
which ensure that the workpiece basically maintains its cleaning temperature.
Preferably, the workpiece is trans-
ported such that the workpiece does not become polluted or contaminated once
more. In particular, the
workpiece is moved with a conveying mechanism along a conveyance direction and
thereby passes in succession
through the cleaning station, the heating station, and reaches the forming
and/or hardening die.
CA 2961869 2017-07-26
4
According to a further embodiment, it is provided that the workpiece is heated
during the heating for the forming
and/or hardening with an additional burner to the target temperature.
Preferably, the target temperature chosen is
a temperature between 600 C and 900 C. If a manganese-boron steel material
is used preferably, it is prefera-
bly provided that the target temperature is reached above AC3, in order to
transform the microstructure com-
pletely into austenite. If the target temperature lies below AC3 and above Ad,
a mixed microstructure of aus-
tenite and ferrite is obtained. For example, it is provided that the speed
with which the workpiece is heated to the
cleaning temperature when using a burner is greater than the speed with which
the workpiece is heated to the
target temperature, especially when using a radiant furnace.
According to a further embodiment, it is provided that the workpiece is coated
with a protective material and/or
in particular it is coated at least partially with a corrosion protection oil
in order to prevent corrosion during
transport.
According to a further embodiment, it is provided that the burner and/or the
additional burner is operated with a
fuel gas and an oxygen-containing gas. Preferably, the heating power of the
burner and/or the additional burner
is adjusted by the mix ratio of the fuel gas and the oxygen-containing gas. In
particular, an oxygen content is
used to establish the maximum temperature in a burning flame of the burner
and/or the additional burner. It is
provided for example that a technical oxygen mixture is supplied to the
additional burner wherein the oxygen
content is preferably greater than 70% or especially preferably greater than
90%. Furthermore, it is provided that,
in order to reach the target temperature with a desired speed at which the
workpiece is heated, the distance be-
tween burner and workpiece, the oxygen content, and/or a conveying speed of
the workpiece being transported
along the conveyance direction are adjusted accordingly.
According to a further embodiment, it is provided that the workpiece is
arranged in a forming/hardening die for
the forming and/or hardening. Preferably, the forming/hardening die is at
least partially cooled and thereby ad-
vantageously ensures, for example, a partial hardening of the workpiece.
According to a further embodiment, it is provided that the workpiece used is a
flat metal sheet. For example, the
workpiece is a workpiece fabricated substantially from a manganese-boron
steel, especially 22MnB5, or it is a
flat metal sheet with higher carbon content.
Another embodiment provides a production plant for hot or warm forming of a
workpiece, especially for carry-
ing out a method as described above, wherein the production plant comprises a
cleaning station for cleaning a
workpiece and a heating station for heating the cleaned workpiece.
As compared to the prior art, the production plant has the advantage that, as
a result of the cleaning station, it can
be ensured that possible residues from a pretreatment of the workpiece are
removed and thus the quantity of
potential contaminants which might impair the quality of the subsequently
fabricated part is reduced in
advantageously reduced.
CA 2961869 2017-07-26
5
According to a further embodiment, it is provided that the production plant
comprises a conveying mechanism.
With the conveying mechanism, the workpiece can be advantageously transported
through the cleaning station
and the heating station to the forming/hardening die. It is conceivable that
the conveying mechanism comprises
conveying rollers.
According to a further embodiment, it is provided that the cleaning station is
structurally separate from the heat-
ing station. In this way, it can be advantageously ensured that the
contaminants loosened by the heating of the
workpiece to the cleaning temperature are distributed through the air and then
become deposited on the plant
parts of the heating station.
Further details, features and benefits of embodiments will emerge from the
drawings as well as the following
specification of preferred embodiments with the aid of the drawings. The
drawings only illustrate sample
embodiments which do not limit the notions of the invention.
Brief description of the figures
Figures la to id show a method for hot or warm forming of a workpiece
according to a sample embodiment of
the present invention.
Detailed Description
In the various figures, the same parts are always provided with the same
reference number and therefote as a rule
will respectively only be mentioned or designated once.
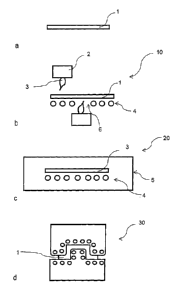
Figures la to Id represent a method for hot or warm forming of a workpiece 1
according to a sample embodi-
ment of the present invention. For example, this involves a structural or
chassis part of a motor vehicle, the
workpiece I being provided as a semifabricated part, especially in the form of
a tailored rolled blank or a metal
sheet as shown in Figure 1. The workpiece I consists, for example, of a
material fabricated at least partially from
a boron-manganese steel, especially 22MnB5. Thanks to the hot or warm forming,
it is preferably provided that
the workpiece 1 is converted into its final form as a component part. In order
not to influence the properties
and/or the form of the component fabricated afterwards, the workpiece 1 is
subjected to a pretreatment. One
example of such a pretreatment is the coating of the workpiece I with a
corrosion protection oil or with a lubri-
cant in order to prevent corrosion during the transport of the workpiece.
Another example of the pretreatment is
the application of a cutting oil to the workpiece I in order to facilitate a
possible cutting of the sheet to size in
advance of the hot or warm forming. Due to the pretreatment and other external
circumstances, residues remain
behind on the workpiece 1, such as those of the corrosion protection oil, the
lubricant and/or the cutting oil. Up-
on heating of the workpiece 1 required for the hot or warm forming, these
residues as contaminants would result
in damage or impairment of the finished part, for example in the form of a
material embrittlement. In order to
avoid such impairment, it is provided that the pretreated workpiece 1 is
cleaned, preferably directly before the
CA 2961869 2017-07-26
CA 02961869 2017-03-20
6
140419PlOWO
heating of the workpiece 1 in a heating station 20, in a cleaning step.
Preferably the cleaning step begins 60 se-
conds, preferably 20 seconds and especially preferably 5 seconds before the
heating of the workpiece 1.
As an example of a cleaning step, the embodiment in Figures la to Id shows in
Figure lb a thermal treatment in
a cleaning station 10. In the present embodiment, the cleaning station 10
comprises a burner belt or roller con-
veyor 4, arranged underneath the workpiece I being delivered by the burner
belt or roller conveyor 4. Further-
more, the cleaning station 10 preferably comprises a burner 2, which is
arranged above and/or beneath the trans-
portable workpiece 1. It is furthermore provided that the burner 2 heats the
workpiece 1 to a cleaning tempera-
ture. For this, the burner 2 is operated in particular with a mixture of a
burner gas and an oxygen-containing gas.
Furthermore, when using a burner 2 for heating the workpiece 1 to the cleaning
temperature, a burner flame 3
occurs which makes direct contact with the workpiece 1 in the cleaning station
10, for example, or which is held
at a distance from the workpiece. In particular, the burner belt or roller
conveyor 4 has a recess 6 in one position
so that the burner flame 3 can heat the workpiece 1 unhindered. Furthermore,
it is provided that the workpiece I
is heated on both sides by one burner 2 apiece, in order to free as much of
the surface of the workpicce I as pos-
sible from residues. It is conceivable that the burner 2 is moved along a
direction running perpendicular to a
conveyance direction of the burner belt or roller conveyor 4, preferably in
oscillating manner, in order to realize
by this motion the heating along a transverse dimension of the workpiece 1. In
particular, it is conceivable that
the cleaning temperature is adjusted or realized by the determination of a
conveyance speed with which the
workpiece 1 is delivered by the burner belt or roller conveyor 4, the
determination of a distance of the burner 2
from the workpiece 1 and/or by the determination of an oxygen content of the
oxygen-containing gas mixed in
with the fuel gas. Furthermore, it is preferably provided that the burner
flame 3 of the burner 2 in the cleaning
station 10 heats the workpiece 1 homogeneously, i.e., uniformly along the
surface. Furthermore, it is conceivable
that the cleaning station 10 comprises an exhaust air system in order to carry
away the pollution gases arising
during the thermal treatment by the exhaust air system. In this way, it is
possible to prevent the pollutants con-
tained in the pollution gas from being deposited on the plant parts of the
cleaning station 10. In order to further
prevent the pollutants contained in the pollution gas from being deposited on
plant parts which are situated for
example in a heating station 20, the cleaning station 10 in the depicted
embodiment is structurally separate from
the heating station 20, as shown in Figure lc.
Figure lc shows a heating station 20 in the form of a furnace 5, the workpiece
1 being arranged for the heating
inside the preferably enclosed furnace 5. In particular, it is provided that
the target temperature is greater than the
cleaning temperature. Furthermore, it is provided that the workpiece 1 is
heated in the heating station 20 with an
additional burner or by radiant heating, the additional burner being operated
preferably with a mixture of a fuel
gas and an oxygen-containing gas. In particular, the additional burner in the
heating station 20 is operated with a
technical-grade oxygen whose oxygen content is preferably greater than 75 %,
especially preferably greater than
90%. For example, the heating in the heating station 20 can be used to adjust
material properties of the compo-
nent fabricated afterwards. For example, the workpiece 1 is specifically
heated in at least a first region to a tem-
perature below AC3, especially below Ad, in order to avoid a complete
austenitization and/or at least in a se-
cond region to a temperature above AC3, in order to bring about an
austenitization. It is also conceivable for the
workpiece 1 to be precoated after the cleaning step and before the heating in
order to ensure by this precoating
CA 02961869 2017-03-20
7
140419P10W0
the formation of an alloy layer on the surface of the workpiece 1.
Furthermore, it is provided that the cleaning
station 10 is connected to the heating station 20 via a conveying mechanism 4.
In particular, the cleaned
workpicce 1 is delivered by the conveying mechanism 4 to the furnace 5.
After the heating of the cleaned workpiece 1 it is provided that the workpieee
I is placed in a preferably cooled
forming and/or hardening die 30 and formed and/or hardened therein, as shown
in Figure Id. In particular, the
forming and/or hardening die 30 comprises a mold which is adapted to the
component to be fabricated. Further-
more, it is conceivable that the conveying mechanism delivers the workpiece 1
along the conveyance direction in
a production plant through the cleaning station 10 and the heating station 20
to the forming and/or hardening die
30.
CA 02961869 2017-03-20
8
140419P1OVVO
List of reference numbers
1 Workpiece
2 Burner
3 Burner flame
4 Conveying mechanism, burner belt, roller conveyor
Furnace
6 Recess
Cleaning station
Heating station
Forming and/or hardening die