Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CONTROLLED RELEASE ENTERIC SOFT CAPSULES OF FUMARATE ESTERS
TECHNICAL FIELD
Described herein are pharmaceutical compositions comprising fumarate esters,
methods for making the same, and methods for treating subjects in need
thereof. In
particular, oral pharmaceutical compositions comprising controlled release
enteric soft
capsules and matrices comprising fumarate esters are described.
BACKGROUND
Fumaric acid esters (FAE; fumarate esters, e.g., alkyl or dialkyl fumarate
esters
such as dimethyl fumarate or monomethyl fumarate) are pharmacologically active
substances used for treating hyperproliferative, inflammatory, or autoimmune
disorders.
They were first used to treat psoriasis and were licensed for this indication
in Germany in
1995 as Fumaderm (Biogen Idec, Inc., Cambridge, MA, USA). Fumaderm produces
various undesirable side effects, including flushing, headaches, dizziness,
eructation,
nausea, vomiting, abdominal and intestinal cramps, and diarrhea. High
concentrations of
the drug released in the stomach are believed to be responsible for such side
effects.
After oral intake, the main component of Fumaderm , dimethyl fumarate (DMF),
is
hydrolysed by esterases to monomethyl fumarate (MMF), the bioactive
metabolite. After
absorption in the small intestine, MMF is believed to interact with
immunocytes in the
bloodstream. The primary plasma metabolitcs of DMF are monomethyl fumarate,
fumaric acid, citric acid, and glucose. Monomethyl fumarate is further
metabolized in the
tricarboxylic acid cycle to carbon dioxide and water.
1
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
An oral formulation of DMF was developed and approved for the treatment of
multiple
sclerosis. This formulation, TECFIDERA (Biogen Idec, Inc.), is available as
hard gelatin
delayed-release capsules containing 120 mg or 240 mg of granulated dimethyl
fumarate
enterically coated minitablets. See International Patent Application
Publication No.
WO 2013/119677 and U.S. Patent No. 6,509,376. TECFIDERA was intended to
reduce the
undesirable side effects by preventing release of DMF in the stomach.
The enterically coated DMF granules in TECFIDERA , however, lack uniformity in
shape and size, and the enteric coating may not be evenly distributed over the
minitablets. This
lack of homogeneity can diminish the enteric properties and affect the acid-
resistance,
dissolution, and release rates. In addition, the integrity of the acid-
resistant coating fails when
the coating cracks or flakes off This leads to DMF release in the stomach and
can cause
flushing and the negative gastrointestinal side effects.
A subject's stomach content also affects delivery of DMF from TECFIDERA. A
meal
was shown to decrease Cmax by 40% and delay Tin. from 2.0 hours to 5.5 hours;
the AUC was
unaffected. See WO 2006/037342. A reduction in the incidence of flushing by
approximately
25% in the postprandial state was also observed. See TECFIDERA Prescribing
Information
03/2013 (Biogen Idec Inc.).
In addition, DMF sublimes at relatively low temperatures. About 15-20% of the
DMF
active ingredient is lost owing to sublimation during the wet-granulation
processing used to
manufacture TECFIDERA . See WO 2013/076216. Sublimation also causes loss of
DMF
during storage and unused TECFIDERA capsules must be discarded 90 days after
a bottle of
the capsules is opened.
Accordingly, it is desirable to develop oral controlled release formulations
of fumarate
esters that: (1) prevent flushing and the undesirable GI side effects
associated with oral
administration of fumarate esters; (2) reduce or eliminate fumarate ester
sublimation during
manufacturing and storage; (3) increase the long-tem' stability of the
pharmaceutical
composition; and (4) provide a variety of different release profiles, dosage
forms, and dosing
regimens.
2
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
SUMMARY
Described herein are controlled release pharmaceutical compositions comprising
one or
more fumarate esters suspended in a lipid or lipophilic matrix. The
pharmaceutical composition
is encapsulated in an enteric soft capsule. The oral enteric soft capsules
comprising controlled
release matrix compositions prevent release of the fumarate ester active
ingredient in the gastric
environment, but release the active ingredient in the intestine in a
controlled manner. The
compositions can be tailored to provide one or more release profiles,
including immediate
release, controlled release, delayed release, or extended release
pharmacokinctics by the
composition of the matrix fill. The formulations described herein comprise
solid micronized
particles of fumarate esters suspended in a matrix. The controlled release
enteric capsule
comprising a matrix of fumarate esters reduce, ameliorate, or eliminate the
undesirable
gastrointestinal side effects observed with prior fumarate ester
pharmaceuticals. Further, the
formulations preclude or reduce sublimation of the fumarate ester during
manufacturing and
storage.
One embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition
comprising a
controlled release composition of one or more fumarate esters, including, but
not limited to,
dialkyl fumarates, alkyl fumarates, dimethyl fumarate (DMF), monomethyl
fumarate (MMF), or
combinations thereof. In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition
comprises a
controlled release enteric soft capsule shell encapsulating a matrix
comprising one or more
fumarate esters. In one aspect, the matrix comprises a lipid or lipophilic
vehicle, a neutralizing
agent, and solid particles of fumarate esters. In another aspect, the matrix
comprises a lipid or
lipophilic vehicle, a neutralizing agent, excipients, and solid particles of a
fumarate ester. In
another aspect, the matrix comprises a lipid or lipophilic vehicle, a
neutralizing agent,
surfactants, and solid particles of a fumarate ester. In one aspect, the lipid
or lipophilic vehicle
comprises polyvinylpyrrolidones, mono- and di-glycerides, and oils. In another
aspect, the
surfactant can comprise polysorbate 80 or polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil.
In another
aspect, the solid particles of fumarate ester comprise milled or micronized
particles. In another
aspect, the milled or micronized particles of one or more fumarate esters
comprise mean particle
distribution sizes of about 20 [tm to about 300 um, including all integers
within the specified
range. In another aspect, the solid particles of fumarate esters comprise mean
particle
distribution sizes of about 65 um to about 260 um, including all integers
within the specified
3
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
range. In another aspect, the solid microparticles of fumarate esters have
mean particle
distribution sizes of less than 260 vun. In another aspect, the solid
particles of fumarate esters
have mean particle distribution sizes of about 100 um. In another aspect, the
neutralizing agent
comprises an organic acid, ester, or salt. In another aspect, the neutralizing
agent comprises at
least one of lactate, fumarate, caprylate, caprate, oleate, maleate,
succinate, tartrate, citrate,
glutamate, gluconate, or esters or salts thereof, or combinations thereof. In
another aspect, the
matrix comprises one or more fumarate esters, a mixture of mono- and di-
glycerides,
polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and lactic acid.
In another embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition comprises a matrix fill
comprising about 10% to about 64% by weight of one or more fumarate esters
(FAE; PSD d90
<100 um); about 18% to about 70% by weight of a mixture of mono- and di-
glycerides; at least
about 1% to about 10% by weight polyvinylpyrrolidone; at least about 1% to
about 10% by
weight polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and at least about 1% to about 5%
by weight lactic
acid.
In another embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition comprises a matrix fill
comprising about 29% by weight of one or more fumarate esters (FAE; PSD d90
<100 um);
about 54% by weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; about 3% by
weight
polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 10 A by weight polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor
oil, and about 5%
by weight lactic acid. In one aspect, the composition has controlled release,
delayed release, or
extended release properties. In one aspect, the composition comprises one or
more FAEs in an
amount of about 80 mg to about 480 mg. In one aspect, the one or more FAEs
comprise about
90 mg to about 120 mg. In one aspect, the composition comprises one or more
FAEs in an
amount of about 180 mg to about 240 mg. In one aspect, the one or more FAEs in
an amount of
about 360 mg to about 480 mg. In one aspect, the composition comprises one or
more FAEs in
an amount of about 80 mg FAE, about 85 mg FAE, about 90 mg FAE, about 95 mg
FAE, about
100 mg FAE, about 105 mg FAE, about 110 mg FAE, about 115 mg FAE, about 120 mg
FAE,
about 125 mg FAE, about 130 mg FAE, about 135 mg FAE, about 140 mg FAE, about
145 mg
FAE, about 150 mg FAE, about 155 mg FAE, about 160 mg FAE, about 165 mg FAE,
about 170
mg FAE, about 175 mg FAE, about 180 mg FAE, about 185 mg FAE, about 190 mg
FAE, about
195 mg FAE, about 200 mg FAE, about 205 mg FAE, about 210 mg FAE, about 215 mg
FAE,
about 220 mg FAE, about 225 mg FAE, about 230 mg FAE, about 235 mg FAE, about
240 mg
4
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
FAE, about 245 mg FAE, about 250 mg FAE, about 255 mg FAE, about 260 mg FAE,
about 265
mg FAE, about 270 mg FAE, about 275 mg FAE, about 280 mg FAE, about 285 mg
FAE, about
290 mg FAE, about 295 mg FAE, about 300 mg FAE, about 305 mg FAE, about 310 mg
FAE,
about 315 mg FAE, about 320 mg FAE, about 325 mg FAE, about 330 mg FAE, about
335 mg
FAE, about 340 mg FAE, about 345 mg FAE, about 350 mg FAE, about 355 mg FAE,
about 360
mg FAE, about 365 mg FAE, about 370 mg FAE, about 375 mg FAE, about 380 mg
FAE, about
385 mg FAE, about 390 mg FAE, about 395 mg FAE, about 400 mg FAE, about 405 mg
FAE,
about 410 mg FAE, about 415 mg FAE, about 4 20 mg FAE, about 425 mg FAE, about
430 mg
FAE, about 435 mg FAE, about 440 mg FAE, about 445 mg FAE, about 450 mg FAE,
about 455
mg FAE, about 460 mg FAE, about 465 mg FAE, about 470 mg FAE, about 475 mg
FAE, or
about 480 mg FAE. In one aspect, the composition comprises one or more FAEs in
an amount
of about 0.5 mmol to about 4.0 mmol FAE. In another aspect, the composition
comprises one or
more FAEs in an amount of about 0.7 mmol to about 3.7 mmol FAE. In another
aspect, the
composition comprises DMF, MMF, or a combination thereof. In another aspect,
the
composition comprises DMF. In another aspect, the composition further
comprises one or more
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS). In one aspect, the composition
prevents
sublimation of the fumarate ester during manufacturing. In another aspect, the
composition
prophylactically reduces the onset or ameliorates the symptoms of any flushing
side effects. In
another aspect, the composition reduces the onset or ameliorates the severity
of any
gastrointestinal side effects. In another aspect, the composition is stable
for at least 1 year at
conditions comprising 25 C and 60% relative humidity. In another aspect, the
composition is
stable for at least 2 years at conditions comprising 25 C and 60% relative
humidity.
In one embodiment, the enteric soft capsule shell comprises one or more
enteric, acid-
insoluble polymers, and in a preferred embodiment additionally includes a film-
forming
polymer, a plasticizer, an alkali-neutralizing agent, a solvent, and
optionally, a coloring agent, a
flavoring, or a pharmaceutical excipient.
In another embodiment, the enteric soft capsule shell comprises about 20% to
about 36%
by weight of at least one film-forming polymer; about 8% to about 20% by
weight of at least one
enteric, acid-insoluble polymer; about 15% to about 20% by weight of at least
one plasticizer;
about 1% to about 5% by weight of at least one alkali-neutralizing agent;
about 20% to about
5
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
40% by weight of a solvent; optionally, about 1% to about 5% by weight of an
opacifying agent;
and optionally, about 0.05% to about 1% by weight of at least one coloring
agent.
In another embodiment, the enteric soft capsule shell comprises about 30% of
at least one
film-forming polymer; about 10% by weight of at least one enteric, acid-
insoluble polymer;
about 20% by weight of at least one plasticizer; about 1% by weight of at
least one alkali-
neutralizing agent; about 37% by weight of a solvent; and optionally, about
1.5% by weight of an
opacifying agent; and optionally, at least one coloring agent. In one aspect,
the enteric soft
capsule shell comprises gelatin, acrylic mcthacrylate copolymers, glycerol,
triethyl citrate,
ammonia, water, and titanium dioxide.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for manufacturing an oral
enteric soft
capsule shell encapsulating a matrix comprising a fumarate ester, the method
comprising: (i)
providing a matrix fill composition comprising any of the composition
described herein; (ii)
providing an enteric soft capsule shell composition comprising any of the
composition described
herein; (iii) casting the enteric soft capsule shell into films using heat-
controlled drums or
surfaces; and (iv) forming an enteric soft capsule shell encapsulating the
matrix fill composition
using rotary die encapsulation technology. In one aspect, the enteric soft
capsule matrix
comprises one or more fumarate esters produced by said method.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for manufacturing an oral
enteric soft
capsule shell encapsulating a matrix comprising a fumarate ester, the method
comprising: (i)
providing a matrix fill composition comprising: about 10% to about 64% by
weight of one or
more fumarate esters (FAE; PSD d90 <100 um); about 18% to about 70% by weight
of a mixture
of mono- and di-glycerides; about 1% to about 10% by weight
polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 2%
to about 12% by weight polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 1% to
about 5% by
weight lactic acid; (ii) providing an enteric soft capsule shell composition
comprising: about
20% to about 36% by weight of at least one film-forming polymer; about 8% to
about 20% by
weight of at least one enteric, acid-insoluble polymer; about 15% to about 20%
by weight of at
least one plasticizer; about 1% to about 5% by weight of at least one alkali-
neutralizing agent;
about 20% to about 40% by weight of a solvent; optionally, about 1% to about
5% by weight of
an opacifying agent; and optionally, about 0.05% to about 1% by weight of at
least one coloring
agent; (iii) casting the enteric soft capsule shell into films using heat-
controlled drums or
6
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
surfaces; and (iv) forming an enteric soft capsule shell encapsulating the
matrix fill composition
using rotary die encapsulation technology.
Another embodiment described herein is an enteric soft capsule comprising a
shell
encapsulating a fumarate ester matrix, wherein the matrix comprises: about 10%
to about 64%
by weight of one or more fumarate esters (FAE; PSD: <100 pm); about 18% to
about 70% by
weight of mono- and di-glycerides; at least about 1% to about 7% by weight of
polyvinylpyrrolidone; at least about 2% to about 10% by weight of polyoxyl 40
hydrogenated
castor oil, and at least about 1% to about 5% by weight of lactic acid; and
wherein the enteric
soft capsule shell comprises: about 20% to about 36% by weight of at least one
film-forming
polymer; about 8% to about 20% by weight of at least one enteric, acid-
insoluble polymer; about
15% to about 20% by weight of at least one plasticizer; about 1% to about 5%
by weight of at
least one alkali-neutralizing agent; about 20% to about 40% by weight of a
solvent; optionally,
about 1% to about 5% by weight of an pacifying agent; and optionally, about
0.05% to about
1% by weight of at least one coloring agent.
Another embodiment described herein is an enteric soft capsule comprising a
shell
encapsulating a fumarate ester matrix, wherein the matrix comprises: about 29%
by weight of
one or more fumarate esters (FAE; PSD d90 <100 pm); about 54% by weight of a
mixture of
mono- and di-glycerides; about 3% by weight polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 10% by
weight
polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 5% by weight lactic acid; and
wherein the enteric
soft capsule shell comprises: about 30% by weight of at least one film-forming
polymer; about
10% by weight of at least one enteric, acid-insoluble polymer; about 20% by
weight of at least
one plasticizer; about 1% by weight of at least one alkali-neutralizing agent;
about 37% by
weight of a solvent; optionally, about 1.5% by weight of an opacifying agent;
and optionally, at
least one coloring agent. In another aspect, the composition comprises DMF,
MMF, or a
combination thereof. In another aspect, the composition comprises DMF. In one
aspect, the
enteric soft capsule comprising a fumarate ester is resistant to dissolution
at about pH 1.2 for at
least about 2 hours. In another aspect, the enteric soft capsule comprising a
fumarate ester
begins dissolution at pH of about 6.8 within about 10 minutes. In one aspect,
the enteric soft
capsule has immediate release, controlled release, delayed release, or
extended release
properties. In another aspect, the enteric soft capsule comprising a fumarate
ester reduces the
onset or ameliorates the severity of any flushing or gastrointestinal side
effects.
7
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of multiple
sclerosis or psoriasis, comprising administering to a subject in need thereof
an oral
pharmaceutical composition comprising a controlled release enteric soft
capsule shell and matrix
comprising a fumarate ester. In one aspect, the pharmaceutical composition
comprises a
controlled release enteric soft capsule comprising a formulation of fumarate
ester. In another
aspect, the composition comprises DMF, MMF, or a combination thereof In
another aspect, the
composition comprises DMF.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of a general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an oral
pharmaceutical
composition comprising a controlled release formulation of a fumarate ester,
wherein the subject
achieves a reduction of annualized relapse rate relative to baseline without
substantially
experiencing one or more of flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea. In
one aspect, the
pharmaceutical composition comprises any of the compositions described herein.
In another
aspect, the composition comprises DMF, MMF, or a combination thereof In
another aspect, the
composition comprises DMF.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition as
described
herein that is useful for treating neurodegenerative disorders. In one aspect,
the pharmaceutical
composition is useful for treating multiple sclerosis or psoriasis. In one
embodiment described
herein, subjects that are administered the oral pharmaceutical composition as
described herein
exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Tmax of from about 1.5 hours to
about 3.5 hours.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition
useful for
treating, retarding the progression of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of,
amelioration of, or
reducing the symptoms of general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorders. In
another
aspect, the composition comprises DMF, MMF, or a combination thereof In
another aspect, the
composition comprises DMF.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of general
8
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorders. In another aspect, the composition
comprises
DMF, MMF, or a combination thereof. In another aspect, the composition
comprises DMF.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition
comprising
a controlled release composition comprising a formulation of a fumarate ester
useful for treating,
retarding the progression of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of,
amelioration of, or reducing
the symptoms of general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorders, including
but not limited
to, acute dermatitis, adrenal lcukodystrophy, AGE-induced genome damage,
Alexander's
disease, alopecia areata (totalis and univcrsalis), Alper's disease,
Alzheimer's disease,
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, angina pectoris, arthritis, asthma, autoimmune
diseases, balo
concentric sclerosis, Behcet's syndrome, bullous pemphigoid, Canavan disease,
cardiac
insufficiency including left ventricular insufficiency, central nervous system
vasculitis, Charcot-
Marie-Tooth disease, childhood ataxia with central nervous system
hypomyelination, chronic
active (lupoid) hepatitis, chronic dermatitis, chronic idiopathic peripheral
neuropathy, chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease, contact dermatitis, Crohn's disease and
cutaneous Crohn's
disease, cutaneous lupus, cutaneous sarcoidosis, diabetic retinopathy,
fibromyalgia, graft versus
host disease, granuloma annulare, granulomas including annulare, Grave's
disease, Hashimoto 's
thyroiditis, hepatitis C viral infection, herpes simplex viral infection,
human immunodeficiency
viral infection, Huntington's disease, inflammatory bowel disease, irritable
bowel disorder,
ischemia, juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus, Krabbe disease, lichen planus,
macular degeneration,
mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, monomelic amyotrophy, multiple sclerosis
(MS), myocardial
infarction, necrobiosis lipoidica, neurodegcneration with brain iron
accumulation,
neurodermatitis, neuromyelitis optica, neuropathic pain, neurosarcoidosis, NF-
1(13 mediated
diseases, optic neuritis, organ transplantation rejection, parancoplastic
syndromes, Parkinson's
disease, Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, pemphigus, pernicious anemia, primary
lateral sclerosis,
progressive supranu cl ear palsy, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, pyod erm a
gan greno sum , rad i cular
pain, radiculopathic pain, reperfusion injury, retinopathic pigmentosa,
rheumatoid arthritis (RA),
sarcoidosis, sarcoidosis, Schilder's disease, sciatic pain, sciatica,
Sjogren's syndrome, subacute
necrotizing my, elopathy, such as polyarthritis, Susac's syndrome, systemic
lupus erythematosus
(SLE), tumors, transverse myelitis, ulcerative colitis, or Zellweger syndrome.
In another aspect,
the composition comprises DMF, MMF, or a combination thereof. In another
aspect, the
composition comprises DMF.
9
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorders, including but not limited to, acute
dermatitis,
adrenal leukodystrophy, AGE-induced genome damage, Alexander's disease,
alopecia areata
(totalis and universalis), Alper's disease, Alzheimer's disease, amyotrophic
lateral sclerosis,
angina pectoris, arthritis, asthma, autoimmune diseases, balo concentric
sclerosis, Beheet's
syndrome, bullous pemphigoid, Canavan disease, cardiac insufficiency including
left ventricular
insufficiency, central nervous system vasculitis, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease,
childhood ataxia
with central nervous system hypomyelination, chronic active (lupoid)
hepatitis, chronic
dermatitis, chronic idiopathic peripheral neuropathy, chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease,
contact dermatitis, Crohn's disease and cutaneous Crohn's disease, cutaneous
lupus, cutaneous
sarcoidosis, diabetic retinopathy, fibromyalgia, graft versus host disease,
granuloma annulare,
granulomas including annulare, Grave's disease, Hashimoto 's thyroiditis,
hepatitis C viral
infection, herpes simplex viral infection, human immunodeficiency viral
infection, Huntington's
disease, inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel disorder, ischemia,
juvenile-onset diabetes
mellitus, Krabbe disease, lichen planus, macular degeneration, mitochondrial
encephalomyopathy, monomelic amyotrophy, multiple sclerosis (MS), myocardial
infarction,
necrobiosis lipoidica, neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation,
neurodermatitis,
neuromyelitis optica, neuropathic pain, neurosarcoidosis, NF-KB mediated
diseases, optic
neuritis, organ transplantation rejection, paraneoplastic syndromes,
Parkinson's disease,
Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, pcmphigus, pernicious anemia, primary lateral
sclerosis,
progressive supranuclear palsy, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, pyoderma
gangrenosum, radicular
pain, radiculopathic pain, reperfusion injury, retinopathic pigmcntosa,
rheumatoid arthritis (RA),
sarcoidosis, sarcoidosis, Schilder's disease, sciatic pain, sciatica,
Sjogren's syndrome, subacute
necrotizing my, elopathy, such as polyarthritis, Susac's syndrome, systemic
lupus erythematosus
(SLE), tumors, transverse myelitis, ulcerative colitis, or Zellweger syndrome
comprising
administering to a subject in need thereof an oral controlled release
pharmaceutical composition
comprising a fumarate ester. In one embodiment described herein, the oral
pharmaceutical
composition comprises an enteric soft capsule shell and matrix comprising a
fumarate ester. In
one aspect, the pharmaceutical composition comprises a controlled release
enteric soft capsule
comprising a formulation of a fumarate ester. In another aspect, the
pharmaceutical composition
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
is an immediate release, delayed release, controlled release, or extended
release formulation of a
fumarate ester. In another aspect, the composition comprises DMF, MMF, or a
combination
thereof. In another aspect, the composition comprises DMF.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition
comprising
a controlled release formulation of a fumarate ester. In one aspect, the
composition is provided
in a dosage form containing about 80 mg to about 120 mg of one or more
fumarate esters,
wherein subjects administered the dosage form four times daily exhibit one or
more
pharmacokinetic parameters comprising: (a) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate
C. ranging
from about 0.4 mg/L to about 2.41 mg/L; or (b) a mean plasma monomethyl
fumarate AUCoverall
ranging from about 3.2 h.mg/L to about 11.2 h-mg/L. In another aspect, the
composition is
provided in a dosage form containing about 120 mg to about 180 mg of one or
more fumarate
esters, wherein subjects administered the dosage form exhibit one or more
pharmacokinetic
parameters comprising: (a) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from
about 0.4
mg/L to about 2.41 mg/L; (b) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0-121,
ranging from
about 0.5 h=mg/L to about 2.5 h=mg/L; or (c) a mean AUC0-0 ranging from about
0.5 h=mg/L to
about 2.6 h=mg/L. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage
form containing a
total amount of about 180 mg to about 240 mg of one or more fumarate esters,
wherein subjects
administered the dosage form twice-daily exhibit one or more pharmacokinetic
parameters
comprising: (a) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about 1.0
mg/L to about
3.4 mg/L; (b) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCoveraa ranging from about
4.81 h=mg/L
to about 11.2 h=mg/L. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a
dosage form
containing about 180 mg to about 240 mg of one or more fumarate esters,
wherein subjects
administered the dosage form exhibit one or more pharmacokinetic parameters
comprising: (a) a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about 1.0 mg/T, to about 3.4
mg/T.; (b) a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0-12h ranging from about 1.0 h-mg/L to
about 5.5
h-mg/L; or (c) a mean AUC0-00 ranging from about 1.0 h-mg/L to about 5.6 h-
mg/L. In another
aspect, the fumarate ester formulation is encapsulated in an enteric soft
capsule. In another
aspect, the composition comprises DMF, MMF, or a combination thereof. In
another aspect, the
composition comprises DMF.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition
comprising
total amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of one or more fumarate esters,
wherein subjects
11
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
administered the capsule exhibit one or more pharmacokinetic parameters
comprising: (a) a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Timiõ of from about 1.5 hours to about 3.5
hours; (b) a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about 0.4 mg/L to about 2.41 mg/L;
(c) a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCo¨>i 2h ranging from about 0.5 h=mg/L to about
2.5 h=mg/L; or
(d) a mean AUC0, ranging from about 0.5 h=mg/L to about 2.6 h=mg/L. In another
aspect, the
composition comprises about 180 mg to about 240 mg of one or more fumarate
esters, wherein
subjects administered the capsule exhibit one or more pharmacokinetic
parameters comprising:
(a) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Tmax of from about 1.5 hours to about
3.5 hours; (b) a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about 1.0 mg/L to about 3.4
mg/L; (c) a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0_12h ranging from about 1.0 h-mg/L to
about 5.5
h-mg/L; or (d) a mean AUG¨. ranging from about 1.0 h-mg/L to about 5.6 h.mg/L.
In one
aspect, the composition comprises DMF, MMF, or a combination thereof. In
another aspect, the
composition comprises DMF.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of a general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, comprising orally administering to a subject in need thereof a
therapeutically effective
amount of one or more fumarate esters comprising any of the compositions
described herein and
a therapeutically amount of one or more non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
effective to
reduce flushing. In one aspect, the one or more non-steroidal anti-
inflammatory drug is aspirin,
ibuprofen, naproxene, diclofcnac, ketoprofen, celecoxib, or a combination
thereof.
Another embodiment described herein is a once or twice daily oral
pharmaceutical
composition comprising a delayed release, controlled release, or extended
release formulation of
a filmarate ester. In one aspect, the composition is provided in one or more
dosage forms
containing about 80 mg to about 480 mg of one or more fumarate esters, wherein
subjects
administered the dosage form once daily exhibit one or more pharmacokinetic
parameters
comprising: (a) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about 0.4
mg/L to about
5.2 mg/L; or (b) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0¨. ranging from about
0.5 h=mg/L
to about 15.5 Irmg/L. In another aspect, the composition is provided in one or
more dosage
forms containing about 80 mg to about 480 mg of one or more fumarate esters,
wherein subjects
administered the dosage form once daily exhibit one or more pharmacokinetic
parameters
12
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
comprising: (a) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Camx ranging from about 0.4
mg/L to about
5.2 mg/L, (b) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0-121, ranging from about
0.5 h=mg/L to
about 13.5 h=mg/L, or (c) a mean AUC0_õo ranging from about 0.5 h=mg/L to
about 15.5 h=mg/L.
In another aspect, the capsule contains a total amount of about 80 mg to about
480 mg of one or
more fumarate esters, wherein subjects administered the one or more capsules
exhibit one or
more pharmacokinetic parameters comprising: (a) a mean plasma monomethyl
fumarate Tmax of
from about 1.5 hours to about 10.5 hours; (b) a mean plasma monomethyl
fumarate Cmax ranging
from about 0.4 mg/L to about 5.2 mg/L; (c) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate
AUCo-12h
ranging from about 0.5 h-mg/L to about 13.5 h-mg/L; or (d) a mean AUCo¨c
ranging from about
0.5h .mg/L to about 15.5 h -mg/L.
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition as
described
herein, for oral administration to a subject having multiple sclerosis
containing one or more
fumarate ester compounds, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof that
metabolize to
monomethyl fumarate, wherein said administering the composition provides one
or more of the
following pharmacokinetic parameters: (a) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate
Toaax of from
about 1.5 hours to about 3.5 hours; (b) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate
Cniax ranging from
about 0.4 mg/L to about 3.4 mg/L; (c) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate
AUCoverall ranging
from about 3.2 h=mg/L to about 11.2 h=mg/L; (d) a mean plasma monomethyl
fumarate
AUC012h ranging from about 0.5 h=mg/L to about 5.5 h=mg/L; or (e) a mean
AUC0_,a, ranging
from about 0.5 h=mg/L to about 5.6 h=mg/L.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of a general
autoimmunc or neurodegencrative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, comprising administering to a subject in need thereof any one of
the compositions of
described herein, containing one or more fumarate ester compounds, or
pharmaceutically
acceptable salts thereof that metabolize to monomethyl fumarate, wherein said
administering the
composition provides one or more of the following pharmacokinetic parameters:
(a) a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate Tmax of from about 1.5 hours to about 3.5 hours;
(b) a mean plasma
monomethyl fumarate Cala, ranging from about 0.4 mg/L to about 3.4 mg/L; (c) a
mean plasma
monomethyl fumarate AUCoverall ranging from about 3.2 h=mg/L to about 11.2
h=mg/L; (d) a
13
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCO¨>12h ranging from about 0.5 h=mg/L to
about 5.5
h=mg/L; or (e) a mean AUCc_,, ranging from about 0.5 h=mg/L to about 5.6
h=mg/L.
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition as
described
herein, for oral administration to a subject having multiple sclerosis
containing one or more
fumarate ester compounds, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof that
metabolize to
monomethyl fumarate, wherein said administering the composition provides one
or more of the
following pharmacokinetic parameters: (a) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate T.
of from
about 1.5 hours to about 10.5 hours; (b) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C.
ranging from
about 0.4 mg/L to about 5.2 mg/L; (c) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate
AUCO¨>12h ranging
from about 0.5 h-mg/L to about 13.5 h-mg/L; or (d) a mean AUC0_, ranging from
about 0.5
h-mg/L to about 15.5 h.mg/L.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of a general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, comprising orally administering to a subject in need thereof any
one of the
compositions described herein comprising one or more fumarate ester compounds,
or
pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof that metabolize to monomethyl
fumarate, wherein said
administering the composition provides one or more of the following
pharmacokinetic
parameters: (a) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Tnia, of from about 1.5
hours to about 10.5
hours; (b) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about 0.4 mg/L to
about 5.2
mg/L; (c) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCowirall ranging from about 0.5
h=mg/L to
about 15.2 h=mg/L; (d) a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0¨>12h ranging
from about 0.5
h=mg/L to about 13.5 h=mg/L; or (e) a mean AUG, ranging from about 0.5 h=mg/L
to about
15.5 h -mg/L. In one aspect, the composition comprises DMF, MMF, or a
combination thereof.
In another aspect, the composition comprises DMF.
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition comprising
any
one of the pharmaceutical compositions described herein for oral
administration to a subject
having multiple sclerosis, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of
one or more fumarate
esters, wherein the administration is sufficient to achieve a reduction of
about 0.224 annualized
relapse rate relative to baseline in the subject without substantially
inducing one or more of
flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea in the subject. In one aspect,
the subject
14
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
experiences one or more of flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea at a
rate of less than
about 10%. In another aspect, the subject is a child. In one aspect, the child
is over 9 years of
age.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
.. of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of multiple
sclerosis, the method comprising the oral administration of a therapeutically
effective amount of
one or more fumarate esters comprising any one of the pharmaceutical
compositions described
herein, to a subject with multiple sclerosis, wherein the administration is
sufficient to achieve a
reduction of about 0.224 annualized relapse rate relative to baseline in the
subject without
substantially inducing one or more of flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and
nausea in the
subject. In one aspect, the subject experiences one or more of flushing,
abdominal pain,
diarrhea, and nausea at a rate of less than about 10%. In another aspect, the
subject is a child. In
one aspect, the child is over 9 years of age.
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition comprising
any
one of the pharmaceutical compositions described herein for oral
administration to a subject
having multiple sclerosis, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of
one or more fumarate
esters, wherein the administration is sufficient to achieve a reduction of
annualized relapse rate
relative to baseline in the subject without substantially inducing one or more
of flushing,
abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea in the subject. In one aspect, the
subject experiences one
or more of flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea at a rate of less
than about 10%. In
another aspect, the subject is a child. In one aspect, the child is over 9
years of age.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of a general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, the method comprising the oral administration of a therapeutically
effective amount of
one or more fumarate esters comprising any one of the phamiaceutical
compositions described
herein to a subject in need thereof, wherein the subject achieves a reduction
annualized relapse
rate relative to baseline without substantially experiencing one or more of
flushing, abdominal
pain, diarrhea, and nausea. In one aspect, the subject experiences one or more
of flushing,
.. abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea at an incidence rate of less than
about 10%. In another
aspect, the subject is a child. In one aspect, the child is over 9 years of
age.
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition comprising
any
one of the pharmaceutical compositions described herein, for oral
administration to a subject
having a general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not
limited to
multiple sclerosis, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of one or
more fumarate esters,
wherein the administration is sufficient to achieve a reduction of annualized
relapse rate relative
to baseline in the subject without substantially inducing one or more of
flushing, abdominal pain,
diarrhea, and nausea in the subject; and wherein the administration does not
require titration of
the pharmaceutical composition. In one aspect, the subject experiences one or
more of flushing,
abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea at an incidence rate of less than about
10%. In another
.. aspect, the subject is a child. In one aspect, the child is over 9 years of
age.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of a general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis, the
method comprising the oral administration of a therapeutically effective
amount of one or more
fumarate esters comprising any one of the pharmaceutical compositions
described herein, to a
subject in need thereof, wherein the administration is sufficient to achieve a
reduction of
annualized relapse rate relative to baseline in the subject without
substantially inducing one or
more of flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea in the subject; and
wherein the
administration does not require titration of the pharmaceutical composition.
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition comprising
any
of the pharmaceutical compositions described herein for oral administration to
a subject having a
general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple
sclerosis, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of one or more
fumarate esters, wherein
the administration is sufficient to achieve a reduction of about 0.224
annualized relapse rate
relative to baseline in the subject without substantially inducing one or more
of flushing,
abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea in the subject and wherein the
administration does not
require titration of the pharmaceutical composition. In one aspect, the
subject experiences one or
more of flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea at a rate of less than
about 10%. In
another aspect, the subject is a child. In one aspect, the child is over 9
years of age.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of a general
16
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis, the
method comprising the oral administration of a therapeutically effective
amount of one or more
fumarate esters comprising any of the pharmaceutical compositions described
herein to a subject
in need thereof, wherein the administration is sufficient to achieve a
reduction of about 0.224
annualized relapse rate relative to baseline in the subject without
substantially inducing one or
more of flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea in the subject and
wherein the
administration does not require titration of the pharmaceutical composition.
In one aspect, the
subject experiences one or more of flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and
nausea at an
incidence rate of less than about 10%. In another aspect, the subject is a
child. In one aspect, the
child is over 9 years of age.
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition comprising
any
one of the pharmaceutical compositions described herein, for oral
administration to a subject
having a general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not
limited to
multiple sclerosis or psoriasis, comprising a therapeutically effective amount
of one or more
.. fumarate esters, wherein the subject achieves a reduction of annualized
relapse rate relative to
baseline without substantially experiencing one or more of flushing, abdominal
pain, diarrhea,
and nausea in the subject and wherein the administration does not require
titration of the
pharmaceutical composition.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of a general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, the method comprising the oral administration of a therapeutically
effective amount of
one or more fumarate esters comprising any one of the pharmaceutical
compositions described
herein, to a subject in need thereof, wherein the subject achieves a reduction
of annualized
relapse rate relative to baseline without substantially experiencing one or
more of flushing,
abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea in the subject and wherein the
administration does not
require titration of the pharmaceutical composition.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition
comprising
any of the compositions described herein for administration to a subject
having a general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis or
17
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
psoriasis, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of one or more
fumarate esters, wherein
the pharmaceutical composition is stable at 25 C and 60% RH for at least 1
year.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition
comprising
any of the compositions described herein comprising a therapeutically
effective amount of one or
more fumarate esters for administration to a subject diagnosed with multiple
sclerosis or
psoriasis.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of a general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, comprising orally administering to a subject in need thereof a
therapeutically effective
amount of one or more fumarate esters comprising any of the pharmaceutical
compositions
described herein.
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition comprising
any
one of the compositions described herein, for oral administration to a subject
of less than 17
years of age having a general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder,
including but not
limited to multiple sclerosis or psoriasis, comprising a therapeutically
effective amount of one or
more fumarate esters.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of a subject
of less than 17 years of age having a general autoimmune or neurodegenerative
disorder,
including but not limited to multiple sclerosis or psoriasis, comprising
orally administering to a
subject in need thereof having an age less than 17 a therapeutically effective
amount of one or
more fumarate esters comprising any one of the pharmaceutical compositions
described herein.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of a general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, comprising orally administering to a subject in need thereof a
therapeutically effective
amount of a fumarate ester comprising any of the pharmaceutical compositions
described herein
and a therapeutically effective amount of a leukotriene receptor antagonist.
In one aspect, the
leukotriene receptor antagonist comprises montelukast or zafirlukast.
18
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition comprising
a
matrix fill comprising any of the compositions described herein in Tables 1,
2, 5-24, and 26-28.
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition for
treating,
retarding the progression of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of,
amelioration of, or reducing
the symptoms of a general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including
but not limited
to multiple sclerosis or psoriasis, comprising a fumarate ester, wherein the
pharmaceutical
composition exhibits an in vitro dissolution rate (% dissolution per minute)
at pH 6.8, as shown
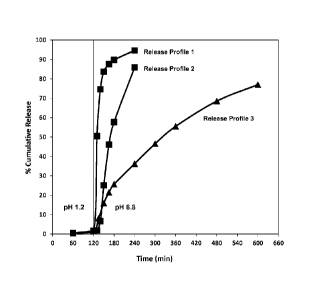
in any of Drawings 2-14 described herein.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of a general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, comprising orally administering to a subject in need thereof a
therapeutically effective
amount of one or more fumarate esters comprising any of the pharmaceutical
compositions
described herein, wherein the composition exhibits an in vitro dissolution
rate (% dissolution per
minute) at pH 6.8, as shown in any of Drawings 2-14described herein.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition for
treating,
retarding the progression of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of,
amelioration of, or reducing
the symptoms of general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorders, including
but not limited
to multiple sclerosis or psoriasis, comprising one or more fumarate esters,
wherein the
pharmaceutical composition exhibits a plasma monomethyl fumarate C. of about
1321.3 +
618.9 ng/mL.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorders, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, comprising orally administering to a subject in need thereof a
therapeutically effective
amount of one or more fumarate esters comprising any of the pharmaceutical
compositions
described herein, wherein the pharmaceutical composition exhibits a plasma
monomethyl
fumarate Cma, of about 1321.3 618.9 ng/mL.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition for
treating,
retarding the progression of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of,
amelioration of, or reducing
the symptoms of general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorders, including
but not limited
19
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
to multiple sclerosis or psoriasis, comprising one or more fumarate esters,
wherein the
pharmaceutical composition exhibits a plasma monomethyl fumarate C,õ,õ as
shown herein in
Drawing 15.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorders, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, comprising orally administering to a subject in need thereof a
therapeutically effective
amount of one or more fumarate esters comprising any of the pharmaceutical
compositions
described herein, wherein the pharmaceutical composition exhibits a plasma
monomethyl
fumarate Cmax as shown herein in Drawing 15.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition for
treating,
retarding the progression of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of,
amelioration of, or reducing
the symptoms of a general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including
but not limited
to multiple sclerosis or psoriasis, comprising one or more fumarate esters,
wherein the
pharmaceutical composition exhibits an in vitro dissolution rate at pH 6.8
comprising about 10%
to about 80% dissolution after about 10 minutes to about 480 minutes.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of, amelioration of, or reducing the
symptoms of general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorders, including but not limited to
multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, comprising orally administering to a subject in need thereof a
therapeutically effective
amount of one or more fumarate esters comprising any of the pharmaceutical
compositions
described herein, wherein the pharmaceutical composition is administered
without titration of the
pharmaceutical composition and without substantially inducing one or more of
flushing,
abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea in the subject.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition for
treating,
retarding the progression of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of,
amelioration of, or reducing
the symptoms of general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorders, comprising
one or more
fumarate esters, wherein the pharmaceutical composition is administered
without titration of the
pharmaceutical composition and without substantially inducing one or more of
flushing,
abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea in the subject.
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition
comprising
a controlled release enteric soft capsule shell encapsulating a matrix
comprising: about 10% to
about 64% by weight of one or more fumarate esters (FAE; PSD d90 <100 i_tm);
about 18% to
about 70% by weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; about 3% by
weight of
polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 10% by weight of polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor
oil, and about
5% by weight of lactic acid. In one aspect, the matrix comprises about 13% to
about 16%; about
27% to about 32%; or about 53% to about 64%, each by weight of one or more
FAEs. In another
aspect, the mixture of mono- and di-glycerides is present in an amount of
about 66% to about
69%; about 50% to about 55%; or about 18% to about 29%, each by weight. In
another aspect,
the one or more FAEs comprise about 80 mg to about 480 mg FAE. In another
aspect, the
matrix comprises about 80 mg to about 105 mg FAE, about 90 mg to about 110 mg
FAE, about
95 mg to about 115 mg FAE, about 100 mg to about 120 mg FAE; about 180 mg to
about 230
mg FAE; about 200 mg to about 240 mg FAE; about 270 mg to about 360 mg FAE;
about 360
mg to about 480 mg FAE; or about 400 to about 480 mg FAE. In another aspect,
the matrix
comprises about 90 mg to about 120 mg FAE. In another aspect, the matrix
comprises about 180
mg to about 230 mg FAE. In another aspect, the matrix comprises about 200 mg
to about 220
mg FAE. In another aspect, the matrix comprises about 215 mg FAE. In another
aspect, the
matrix comprises about 0.5 to about 3.5 mmol FAE. In another aspect, the
matrix comprises
about 0.6 to about 1.7 mmol FAE. In another aspect, the matrix comprises DMF,
MMF, or a
combination thereof. In another aspect, the matrix comprises DMF.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of a
composition comprising one or more fumarate esters in an amount of about 90 mg
to about 120
mg FAE or about 1 80 mg to about 240 mg FAR, wherein the one or more doses
comprise a
controlled release pharmaceutical composition that releases the contents at a
physiological pH of
about pH 6.8.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of one
or more fumarate esters comprising about 90 mg to about 120 mg FAE or about
180 mg to about
240 mg FAE wherein the FAE comprises a prodrug of methyl hydrogen fumarate or
methyl
hydrogen fumarate.
21
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of one
or more fumarate esters wherein methyl hydrogen fumarate activates a nuclear
erythroid 2-
related factor 2 (nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2; Nrf2)
transcriptional pathway. In one
aspect, the dose comprises an oral controlled release composition comprising:
about 10% to
about 64% by weight of one or more fumarate esters (FAE; PSD d90 <100 lAm);
about 18% to
about 70% by weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; about 3% by
weight of
polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 10% by weight of polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor
oil, and about
5% by weight of lactic acid. In another aspect, the dose comprises one or more
FAEs in an
amount of about 80 mg to about 480 mg. In another aspect, the dose comprises
one or more
FAEs in an amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg. In another aspect, the dose
comprises one
or more FAEs in an amount of about 180 mg to about 240 mg. In another aspect,
a daily total
dose comprises one or more FAEs in an amount of about 360 mg to about 480 mg.
In another
aspect, the fumarate ester comprises MMF, DMF, or a combination thereof. In
another aspect,
the fumarate ester comprises DMF.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral controlled release
pharmaceutical
composition comprising a soft capsule shell and a matrix, the matrix
comprising about 10% to
about 64% by weight of one or more fumarate esters (FAE; PSD d90 <100 !Am);
about 18% to
about 70% by weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; about 1% to about
10% by weight
polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 2% to about 10% by weight polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated
castor oil,
and about 1% to about 5% by weight lactic acid. In one aspect, the soft
capsule shell is an
enteric soft capsule comprising about 30% by weight of gelatin; about 10% by
weight of
methylacrylic acid copolymer; about 18% by weight of glycerol; about 1 % by
weight of triethyl
citrate; about 1.5% by weight of ammonia; and about 37% by weight of water.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of an
oral controlled release pharmaceutical composition comprising a soft capsule
shell and a matrix,
the matrix comprising about 10% to about 64% by weight of one or more fumarate
esters (FAE;
PSD d90 <100 ?Am); about 18% to about 70% by weight of a mixture of mono- and
di-glycerides;
about 1% to about 10% by weight polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 2% to about 10% by
weight
polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 1% to about 5% by weight lactic
acid.
22
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Another embodiment described herein is an oral controlled release
pharmaceutical
composition comprising a soft capsule shell and a matrix, the matrix
comprising about 28% by
weight of FAE; about 53% by weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides;
about 10% by
weight of polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 3% by weight of polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated
castor oil, and
about 5% by weight of lactic acid. In one aspect, the soft capsule shell is an
enteric soft capsule
shell comprising about 30% by weight of gelatin; about 10% by weight of
methylacrylic acid
copolymer; about 18% by weight of glycerol; about 1% by weight of triethyl
citrate; about 1.5%
by weight of ammonia; and about 37% by weight of water.
Another embodiment described herein is method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a subject
in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or more
doses of an oral
controlled release pharmaceutical composition comprising a soft capsule shell
and a matrix, the
matrix comprising about 28% by weight of FAE; about 53% by weight of a mixture
of mono-
and di-glycerides; about 10% by weight of polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 3% by
weight of
polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 5% by weight of lactic acid.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of an
oral controlled release pharmaceutical composition comprising a soft capsule
shell and a matrix,
the matrix comprising about 28% by weight of DMF; about 53% by weight of a
mixture of
mono- and di-glycerides; about 10% by weight of polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 3%
by weight of
polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 5% by weight of lactic acid.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral controlled release
pharmaceutical
composition comprising a soft capsule shell and a matrix, the matrix
comprising about 75 mg,
about 80 mg, about 85 mg, about 90 mg, about 95 mg, about 100 mg, about 105
mg, about 108
mg, about 110 mg, about 115 mg, about 120 mg, about 180 mg, about 200 mg,
about 210 mg,
about 216 mg, about 220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg, about 360 mg, about
400 mg, about
420 mg, about 432 mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about 480 mg of FAE;
about 53% by
weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; about 10% by weight of
polyvinylpyrrolidone;
about 3% by weight of polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 5% by
weight of lactic
acid.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral controlled release
pharmaceutical
composition comprising a soft capsule shell and a matrix, the matrix
comprising about 75 mg,
23
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
about 80 mg, about 85 mg, about 90 mg, about 95 mg, about 100 mg, about 105
mg, about 108
mg, about 110 mg, about 115 mg, about 120 mg, about 180 mg, about 200 mg,
about 210 mg,
about 216 mg, about 220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg, about 360 mg, about
400 mg, about
420 mg, about 432 mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about 480 mg of DMF;
about 53% by
weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; about 10% by weight of
polyvinylpyrrolidone;
about 3% by weight of polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 5% by
weight of lactic
acid.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral controlled release
pharmaceutical
composition dosage form comprising a daily total amount of FAE of about 180
mg, about 200
mg, about 210 mg, about 216 mg, about 220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg,
about 360 mg,
about 400 mg, about 420 mg, about 432 mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about
480 mg.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral controlled release
pharmaceutical
composition dosage form comprising a daily total amount of DMF of about 180
mg, about 200
mg, about 210 mg, about 216 mg, about 220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg,
about 360 mg,
about 400 mg, about 420 mg, about 432 mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about
480 mg.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition
providing a
daily total amount of DMF of about 180 mg, about 200 mg, about 210 mg, about
216 mg, about
220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg, about 360 mg, about 400 mg, about 420 mg,
about 432
mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about 480 mg DMF; about 53% by weight of a
mixture of
mono- and di-glycerides; about 10% by weight of polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 3%
by weight of
polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 5% by weight of lactic acid.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of a
pharmaceutical composition providing a daily total amount of FAE of about 180
mg, about 200
mg, about 210 mg, about 216 mg, about 220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg,
about 360 mg,
about 400 mg, about 420 mg, about 432 mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about
480 mg.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of a
pharmaceutical composition providing a daily total amount of DMF of about 180
mg, about 200
mg, about 210 mg, about 216 mg, about 220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg,
about 360 mg,
about 400 mg, about 420 mg, about 432 mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about
480 mg.
24
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition
comprising
a controlled release enteric soft capsule shell and matrix comprising: about
10% to about 64% of
one or more fumarate esters (FAE; PSD <100 [tm); about 18% to about 70% by
weight of a
mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; at least about 3% by weight of
polyvinylpyrrolidone; at least
about 10% by weight of polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and at least about
5% by weight of
lactic acid. In one aspect, the composition comprises one or more FAEs in an
amount of about
13% to about 16% by weight; about 27% to about 32% by weight; or about 53% to
about 64%
by weight. In another aspect, the composition comprises mono- and di-
glycerides in an amount
of about 66% to about 69% by weight; about 50% to about 55% by weight; or
about 18% to
about 29% by weight. In another aspect, the composition comprises one or more
FAEs in an
amount of about 80 mg to about 480 mg FAE. In another aspect, the composition
comprises one
or more FAEs in an amount of about 80 mg to about 100 mg FAE; about 90 mg to
about 110 mg
FAE, about 100 mg to about 120 mg FAE; about 180 mg to about 220 mg FAE; about
200 mg to
about 240 mg FAE; or about 400 to about 480 mg FAE. In another aspect, the
composition
comprises one or more FAEs in an amount of about 90 mg to about 110 mg FAE. In
another
aspect, the composition comprises one or more FAEs in an amount of about 100
mg to about 120
mg FAE. In another aspect, the composition comprises one or more FAEs in an
amount of about
200 mg to about 220 mg FAE. In another aspect, the composition comprises one
or more FAEs
in an amount of about 210 mg to about 220 mg FAE. In another aspect, the
composition
comprises one or more FAEs in an amount of about 215 mg FAE. In another
aspect, the
composition comprises one or more FAEs in an amount of about 1.5 to about 1.7
mmol FAE. In
another aspect, the matrix comprises DMF, MMF, or a combination thereof. In
another aspect,
the matrix comprises DMF.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of one
or more fumarate esters in an amount of about 180 mg to about 220 mg FAE,
wherein the one or
more doses comprise a controlled release pharmaceutical composition that
releases the contents
at a physiological pH of about pH 6.8.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of one
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
or more fumarate esters in an amount of about 180 mg to about 220 mg FAE,
wherein the FAE
comprises a prodrug of methyl hydrogen fumarate or methyl hydrogen fumarate.
Another embodiment described herein is an method of treating multiple
sclerosis in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of one
or more fumarate esters wherein methyl hydrogen fumarate activates a nuclear
erythroid 2-
related factor 2 (nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2; Nrf2)
transcriptional pathway. In one
aspect, the one or more doses of fumarate esters comprise an oral controlled
release composition
comprising: about 10% to about 64% by weight of one or more fumarate esters
(FAE; F'SD <100
inm); about 18% to about 70% by weight of a mixture of mono- and di-
glycerides; at least about
3% by weight polyvinylpyrrolidone; at least about 10% by weight polyoxyl 40
hydrogenated
castor oil, and at least about 5% by weight lactic acid. In another aspect,
the dose comprises one
or more FAEs in an amount of about 80 mg to about 480 mg. In another aspect,
the dose
comprises one or more FAEs in an amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg. In
another aspect,
the dose comprises one or more FAEs in an amount of about 180 mg to about 240
mg. In
another aspect, a daily total dose comprises one or more FAEs in an amount of
about 360 mg to
about 480 mg. In another aspect, the FAE comprises MMF, DMF, or a combination
thereof In
another aspect, the FAE comprises DMF.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral controlled release
pharmaceutical
composition comprising a soft capsule and a matrix, the matrix comprising
about 10% to about
64% by weight of one or more fumarate esters (FAE; PSD d90 <100 pm); about 18%
to about
70% by weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; about 1% to about 10%
by weight
polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 2% to about 10% by weight polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated
castor oil,
and about 1% to about 5% by weight lactic acid. In one embodiment, the FAE is
dimethyl
fumarate. In one embodiment, the soft capsule is an enteric soft capsule shell
comprising about
30% by weight of gelatin; about 10% by weight of methylacrylic acid copolymer;
about 18% by
weight of glycerol; about 1 % by weight of triethyl citrate; about 1.5% by
weight of ammonia;
and about 37% by weight of water.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of an
oral controlled release pharmaceutical composition comprising a soft capsule
shell and a matrix,
the matrix comprising about 10% to about 64% by weight of one or more fumarate
esters (FAE;
26
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
PSD d90 <100 [tm); about 18% to about 70% by weight of a mixture of mono- and
di-glycerides;
about 1% to about 10% by weight polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 2% to about 10% by
weight
polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 1% to about 5% by weight lactic
acid.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral controlled release
pharmaceutical
composition comprising a soft capsule shell and a matrix, the matrix
comprising about 28% by
weight of fumarate esters; about 53% by weight of a mixture of mono- and di-
glycerides; about
10% by weight of polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 3% by weight of polyoxyl 40
hydrogenated castor
oil, and about 5% by weight of lactic acid. In one embodiment, the fumarate
ester is dimethyl
fumarate. In one embodiment, the soft capsule is an enteric soft capsule
comprising about 30%
by weight of gelatin; about 10% by weight of methylacrylic acid copolymer;
about 18% by
weight of glycerol; about 1 % by weight of triethyl citrate; about 1.5% by
weight of ammonia;
and about 37% by weight of water.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of an
oral controlled release pharmaceutical composition comprising a soft capsule
shell and a matrix,
the matrix comprising about 28% by weight of fumarate esters; about 53% by
weight of a
mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; about 10% by weight of
polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 3% by
weight of polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 5% by weight of
lactic acid.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of an
oral controlled release pharmaceutical composition comprising a soft capsule
shell and a matrix,
the matrix comprising about 28% by weight of DMF; about 53% by weight of a
mixture of
mono- and di-glycerides; about 10% by weight of polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 3%
by weight of
polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 5% by weight of lactic acid.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral controlled release
pharmaceutical
composition comprising a soft capsule and a matrix, the matrix comprising
about 75 mg, about
80 mg, about 85 mg, about 90 mg, about 95 mg, about 100 mg, about 105 mg,
about 108 mg,
about 110 mg, about 115 mg, about 120 mg, about 180 mg, about 200 mg, about
210 mg, about
216 mg, about 220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg, about 360 mg, about 400 mg,
about 420
mg, about 432 mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about 480 mg of FAE and about
53% by
weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; about 10% by weight of
polyvinylpyrrolidone;
27
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
about 3% by weight of polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 5% by
weight of lactic
acid. In one embodiment, the soft capsule is an enteric soft capsule
comprising about 30% by
weight of gelatin; about 10% by weight of methylacrylic acid copolymer; about
18% by weight
of glycerol; about 1 % by weight of triethyl citrate; about 1.5% by weight of
ammonia; and about
37% by weight of water.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral controlled release
pharmaceutical
composition comprising a soft capsule and a matrix, the matrix comprising
about 75 mg, about
80 mg, about 85 mg, about 90 mg, about 95 mg, about 100 mg, about 105 mg,
about 108 mg,
about 110 mg, about 115 mg, about 120 mg, about 180 mg, about 200 mg, about
210 mg, about
216 mg, about 220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg, about 360 mg, about 400 mg,
about 420
mg, about 432 mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about 480 mg of DMF and about
53% by
weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; about 10% by weight of
polyvinylpyrrolidone;
about 3% by weight of polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 5% by
weight of lactic
acid. In one embodiment, the soft capsule is an enteric soft capsule
comprising about 30% by
weight of gelatin; about 10% by weight of methylacrylic acid copolymer; about
18% by weight
of glycerol; about 1 % by weight of triethyl citrate; about 1.5% by weight of
ammonia; and about
37% by weight of water.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral controlled release
pharmaceutical
composition dosage forms comprising a daily total amount of FAE of about 180
mg, about 200
mg, about 210 mg, about 216 mg, about 220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg,
about 360 mg,
about 400 mg, about 420 mg, about 432 mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about
480 mg.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral controlled release
pharmaceutical
composition dosage form comprising a daily total amount of DMF of about 180
mg, about 200
mg, about 210 mg, about 216 mg, about 220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg,
about 360 mg,
about 400 mg, about 420 mg, about 432 mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about
480 mg.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical compositions
providing
a daily total amount of FAE of about 180 mg, about 200 mg, about 210 mg, about
216 mg, about
220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg, about 360 mg, about 400 mg, about 420 mg,
about 432
mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about 480 mg FAE; about 53% by weight of a
mixture of
mono- and di-glycerides; about 10% by weight of polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 3%
by weight of
polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 5% by weight of lactic acid.
28
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical compositions
providing
a daily total amount of DMF of about 180 mg, about 200 mg, about 210 mg, about
216 mg,
about 220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg, about 360 mg, about 400 mg, about
420 mg, about
432 mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about 480 mg DMF; about 53% by weight
of a mixture
of mono- and di-glycerides; about 10% by weight of polyvinylpyrrolidone; about
3% by weight
of polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and about 5% by weight of lactic acid.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of a
pharmaceutical composition providing a daily total amount of FAE of about 180
mg, about 200
mg, about 210 mg, about 216 mg, about 220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg,
about 360 mg,
about 400 mg, about 420 mg, about 432 mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about
480 mg. In
one embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition comprises about 28% by weight
of FAE;
about 53% by weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; about 10% by
weight of
polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 3% by weight of polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor
oil, and about 5%
by weight of lactic acid.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating multiple sclerosis
in a
subject in need thereof comprising orally administering to the subject one or
more doses of a
pharmaceutical composition providing a daily total amount of DMF of about 180
mg, about 200
mg, about 210 mg, about 216 mg, about 220 mg, about 230 mg, about 240 mg,
about 360 mg,
about 400 mg, about 420 mg, about 432 mg, about 440 mg, about 460 mg, or about
480 mg. In
one embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition comprises about 28% by weight
of DMF;
about 53% by weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; about 10% by
weight of
polyvinylpyrrolidone; about 3% by weight of polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor
oil, and about 5%
by weight of lactic acid.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition for
treating
multiple sclerosis in a subject in need thereof comprising one or more
fumarate esters comprising
DMF, MMF, or a combination thereof.
Another embodiment described herein is an oral pharmaceutical composition for
treating
multiple sclerosis in a subject in need thereof comprising one or more
fumarate esters comprising
DMF.
29
Another embodiment described herein is any of the foregoing composition or
methods wherein the fumarate ester comprises a therapeutically effective
amount of
DMF, MMF, or a combination thereof.
Another embodiment described herein is any of the foregoing composition or
methods wherein the fumarate ester comprises a therapeutically effective
amount of
DM F.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to an oral pharmaceutical
composition comprising an immediate releasing single-phase non-aqueous liquid
vehicle comprising 90 mg to 120 mg of monomethyl fumarate.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the oral pharmaceutical composition
comprises a controlled release enteric soft capsule shell encapsulating a
matrix
comprising the immediate releasing single-phase non-aqueous liquid vehicle
comprising
the monomethyl fumarate.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the matrix comprises a single-phase
lipid or
lipophilic vehicle, a neutralizing agent, excipients, and solid particles of
monomethyl
fumarate.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the lipid or lipophilic vehicle
comprises
polyethylene glycols, polyvinylpyrrolidones, oils, or surfactants.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the surfactant comprises polysorbate
80 or
polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the solid particles of monomethyl
fumarate
comprise milled or micronized particles.
CA 2962916 2020-02-27
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the solid particles of monomethyl
fumarate
comprise mean particle distribution sizes of 20 pm to 300 pm.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the solid particles of monomethyl
fumarate
comprise mean particle distribution sizes of 65 pm to 260 pm.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the solid particles of monomethyl
fumarate
comprise mean particle distribution sizes having a d90 of less than or equal
to 100 pm.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the neutralizing agent comprises an
organic
acid, ester, or salt.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the neutralizing agent comprises at
least one
of lactate, fumarate, caprylate, caprate, oleate, maleate, succinate,
tartrate, citrate,
glutamate, gluconate, or esters or salts thereof, or combinations thereof.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the matrix comprises solid particles
of
monomethyl fumarate, a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides,
polyvinylpyrrolidone,
polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and lactic acid.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the matrix comprises:
10% to 64% by weight of monomethyl fumarate;
18% to 70% by weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides;
1% to 10% by weight polyvinylpyrrolidone;
2% to 12% by weight polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and
1% to 5% by weight lactic acid.
30a
CA 2962916 2020-02-27
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, further comprising one or more non-steroidal
anti-
inflammatory drugs.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the oral pharmaceutical composition
prevents sublimation of monomethyl fumarate during manufacturing.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the oral pharmaceutical composition
reduces
the onset of any flushing side effects.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the oral pharmaceutical composition
reduces
the onset of any gastrointestinal side effects.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition defined hereinabove, wherein the oral pharmaceutical composition
is
stable for at least 1 year at 25 C.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to a use of a composition for
treating or reducing the symptoms of multiple sclerosis or psoriasis in a
subject, the
composition comprising an oral pharmaceutical composition comprising an
immediate
releasing single-phase non-aqueous liquid vehicle comprising 90 mg to 120 mg
of
monomethyl fumarate, wherein the subject achieves a reduction of annualized
relapse
rate relative to baseline without substantially experiencing one or more of
flushing,
abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the use composition defined
hereinabove, wherein the oral pharmaceutical composition is as defined defined
hereinabove.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to an oral pharmaceutical
composition comprising an immediate releasing single-phase non-aqueous liquid
30b
CA 2962916 2020-02-27
,
,
vehicle comprising 90 mg to 120 mg of monomethyl fumarate for use in treating
or
reducing the symptoms of multiple sclerosis or psoriasis.
Another embodiment of the invention relates to the oral pharmaceutical
composition for the use defined hereinabove, wherein the oral pharmaceutical
composition is as defined hereinabove.
30c
CA 2962916 2020-02-27
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Further advantageous features of the present disclosure will become more
apparent with
the following detailed description when taken with reference to the
accompanying drawings,
each according to an aspect of the present disclosure:
FIGURE 1. Scheme for manufacturing enteric soft capsules comprising a DMF
matrix.
FIGURE 2. Dissolution of enteric soft capsules comprising two DMF
formulations.
FIGURE 3. DMF enteric soft capsule stability.
FIGURE 4. DMF release in enteric soft capsules.
FIGURE 5. Surfactant affects DMF release rate.
FIGURE 6. Polyvinylpyrrolidone concentration affects DMF release rate.
FIGURE 7. DMF enteric soft capsules are amenable to controlled or extended
release.
FIGURE 8. DMF particle size affects release rate.
FIGURE 9. Two-stage dissolution of application batches.
FIGURE 10. Two-stage dissolution of GMP batch compared to application batches.
FIGURE 11. Effects of Povidone K30 and PEG 600 on DMF release rate.
FIGURE 12. Two-stage dissolution of 120 mg DMF enteric soft capsule.
FIGURE 13. DMF enteric soft capsule stability at To and after 3- and 6-month
conditions.
FIGURE 14. Two-stage dissolution of BLS-11 (-215 mg) enteric soft capsule.
FIGURE 15. Mean plasma concentration of MMF over time following dose
administration.
31
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
Described herein are pharmaceutical compositions of fumarate esters such as
dimethyl
fumarate, monomethyl fumarate, other pharmacologically active fumarate esters,
or
combinations thereof.
The pharmaceutical compositions described herein provide matrix fills of
fumarate esters,
di-alkyl fumarates, mono-alkyl fumarates, such as dimethyl fumarate,
monomethyl fumarate, or
combinations thereof, and methods for preparation thereof. Also described
herein are
compositions and methods for manufacturing controlled, delayed, or extended
release fumarate
esters, dimethyl fumarate, monomethyl fumarate, or combinations thereof as
soft capsule dosage
forms. In one embodiment described herein, the fumarate ester pharmaceutical
composition is
encapsulated within an enteric soft capsule shell. In another embodiment, the
fumarate ester is in
the form of solid microparticles of defined size within a matrix comprising a
lipid or lipophilic
vehicle. In some aspects, described herein, the lipid or lipophilic vehicle
may comprise an
amount of one or more hydrophilic polymers, but as described herein, is
considered a lipid or
lipophilic vehicle.
As used herein, the terms "fumarate ester" or "FAE" refers to any
pharmacologically
active mono- or di-alkyl fumarate ester, such as monomethyl fumarate, dimethyl
fumarate, or
other fumarate esters, acids, salts, or derivatives thereof, and combinations
or mixtures of any of
the foregoing.
The terms "active ingredient" or "active pharmaceutical ingredient" as used
herein refer
to a pharmaceutical agent, active ingredient, compound, or substance,
compositions, or mixtures
thereof, that provide a pharmacological, often beneficial, effect.
The terms "dosage" or "dose" as used herein denote any form of the active
ingredient
formulation that contains an amount sufficient to produce a therapeutic effect
with a single
administration. The dosage form used herein is for oral administration. The
preferred oral
dosage forms are soft capsules, or preferably, enteric soft capsules.
The terms "soft capsule" or "enteric soft capsule" as used herein refer to a
soft capsule
shell encapsulating a liquid or semisolid "matrix" or "fill" comprising
vehicles, pharmaceutically
acceptable excipients, and one or more active pharmaceutical ingredients.
The terms "active pharmaceutical ingredient load" or "drug load" as used
herein refers to
the quantity (mass) of the active pharmaceutical ingredient comprised in a
single soft capsule fill.
32
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
The terms "formulation" or "composition" as used herein refers to the drug in
combination with pharmaceutically acceptable excipients.
This term includes orally
administrable formulations as well as formulations administrable by other
means.
The term "titration" as used herein refers to the incremental increase in drug
dosage to a
level that provides the optimal therapeutic effect.
The term "controlled release" as used herein encompasses the terms "immediate
release,"
"modified release," "sustained release," "extended release," and "delayed
release."
The terms "extended release" or "sustained release" as used herein refers to a
composition that releases an active ingredient according to a desired profile
over an extended
period under physiological conditions or in an in vitro test. By "extended
period" it is meant a
continuous period of time of at least about 1 hour; about 2 hours; about 4
hours; about 6 hours;
about 8 hours; about 10 hours; about 12 hours; about 14 hours; about 16 hours;
about 18 hours;
about 20 hours about 24 hours; or even longer; specifically over a period of
about 18 hours under
physiological conditions or in an in vitro assay.
The term "modified release" as used herein refers to a composition that
releases an active
ingredient at a slower rate than does an immediate release formulation under
physiological
conditions or in an in vitro test.
The term "delayed" release" as used herein refers to a composition that
releases an active
ingredient after a period of time, for example minutes or hours, such that the
active ingredient is
not released initially. A delayed release composition may provide, for
example, the release of a
drug or active ingredient from a dosage form, after a certain period, under
physiological
conditions or in an in vitro test.
The term mean "particle size distribution" (PSD) as used herein refers to the
mean
particle size from a statistical distribution of a range of particle sizes as
described herein. The
distribution may be a Gaussian, normal distribution, or a non-normal
distribution.
The terms "d90," "d50," and "d10" refer to the percentage (90%, 50%, or 10%,
respectively) of particle sizes that are less than a specified size, range, or
distribution. For
example, d90 < 90 tm as specified means that 90% of the particle sizes within
a distribution of
particles are less than or equal to 90 [im.
33
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
The term "Co." as used herein refers to the maximum observed blood (plasma,
serum, or
whole blood) concentration or the maximum blood concentration calculated or
estimated from a
concentration to time curve, and is expressed in units of mg/L or ng/mL, as
applicable.
The term "Cnia," as used herein refers to the minimum observed blood (plasma,
serum, or
whole blood) concentration or the minimum blood concentration calculated or
estimated from a
concentration to time curve, and is expressed in units of mg/L or ng/mL, as
applicable.
The term "Cavg" as used herein refers to the blood (plasma, scrum, or whole
blood)
concentration of the drug within the dosing interval, is calculated as
AUC/dosing interval, and is
expressed in units of mg/L or ng/mL, as applicable.
The term "Tmax" as used herein refers to the time after administration at
which (max
occurs, and is expressed in units of hours (h) or minutes (min), as
applicable.
The term "AUCo," as used herein refers to area under the blood (plasma, serum,
or
whole blood) concentration versus time curve from time zero to time tau (r)
over a dosing
interval at steady state, where tau is the length of the dosing interval, and
is expressed in units of
h=mg/L or h=ng/mL, as applicable. For example, the term AUC0¨,12 as used
herein refers to the
area under the concentration versus time curve from 0 to 12 hours.
The term "AUC0¨.," as used herein refers to the area under the blood (plasma,
serum, or
whole blood) concentration versus time curve from time 0 hours to infinity,
and is expressed in
units of h=mg/L or h=ng/mL, as applicable.
The term "AUCoverall" as used herein refers to the combined area under the
blood (plasma,
scrum, or whole blood) concentration versus time curve, and is expressed in
units of h=mg/L (or
h=ng/mL) for at least one or more doses of the pharmaceutical compositions
described herein. In
one aspect, the "AUCoverall" refers to the combined area under the blood
concentration versus
time curve for at least two doses of the pharmaceutical compositions described
herein
The term "treating" refers to administering a therapy in an amount, manner, or
mode
effective (e.g., a therapeutic effect) to improve a condition, symptom,
disorder, or parameter
associated with a disorder, or a likelihood thereof
The term "prophylaxis" refers to preventing or reducing the progression of a
disorder,
either to a statistically significant degree or to a degree detectable to one
skilled in the art.
The term "substantially" as used herein means to a great or significant
extent, but not
completely.
34
As used herein, all percentages ( /0) refer to weight percent unless noted
otherwise.
The term "about" as used herein refers to any values, including both integers
and fractional components that are within a variation of up to 10% of the
value
modified by the term "about."
As used herein, "a" or "an" means one or more unless otherwise specified.
Terms such as "include," "including," "contain," "containing," "having," and
the like mean "comprising."
The term "or" can be conjunctive or disjunctive.
One embodiment described herein, is a controlled release pharmaceutical
composition comprising an enteric soft capsule shell encapsulating a matrix
fill
comprising one or more fumarate esters.
In another embodiment, the enteric soft capsule provides controlled release
properties.
In another embodiment, the matrix fill provides controlled release
properties. Such controlled release matrix fills are described in
International Patent
Application Publication No. WO 2005/009409; U.S. Patent Application
Publication No.
US 2006/0115527; U.S. Patent Nos. 8,293,270; and 8,333,989. In one aspect, the
matrix is configured to provide controlled release, extended release,
sustained release,
delayed release, or combinations thereof.
In another embodiment, the matrix comprises a lipid or lipophilic vehicle that
provides a suspension of fumarate ester microparticles having defined sizes.
In one
aspect, an enteric soft capsule comprising a suspension of fumarate ester
microparticles provides controlled release delivery of the fumarate ester.
The fumarate ester particles described herein (e.g., dimethyl fumarate or
monomethyl fumarate) may be generated by any particle size reduction or
particle
growth methodology known to one having ordinary skill the art. Exemplary and
non-
limiting methods may comprise a "top-down" reduction in particle size
including
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
mechanical micronization techniques, wherein a larger particle is crushed,
bashed, or
ground into a smaller particle through techniques, such as jet milling, ball
milling, or
high pressure homogenization; or particle engineering techniques such as
cryogenic
spraying or crystal engineering. In addition, "bottom-up" processing may be
used to
build a suitable size of particles as described herein using dual solvent/anti-
solvent
rapid precipitation techniques. See, Handbook of Pharmaceutical Granulation
Technology, CRC Press, 3rd Edition, 2010. In one aspect described herein,
fumarate
ester particles of a specified size distribution are produce using a milling
technique.
In another embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition comprises
matrix fills for fumarate esters, such as dimethyl fumarate, monomethyl
fumarate, or
derivatives thereof, based on lipids or lipophilic vehicles. The described
matrices have
a hydrophobic (lipophilic) surface in contact with the hydrophilic soft
enteric capsule
shell to minimize any potential shell¨fill interactions, such as when enteric
soft
capsules are filled with hydrophilic vehicles.
Described herein are methods for manufacturing matrix fills comprising
fumarate esters, such as dimethyl fumarate, monomethyl fumarate, or
derivatives
thereof, in a controlled release enteric soft capsule in the form of a
suspension, where
part or all of the fumarate ester is suspended within the matrix. Also
provided are
compositions and formulations where the fumarate ester is incorporated into a
one-
phase or two-phase matrix.
Also described herein are methods for manufacturing matrix fills comprising
fumarate esters or derivatives thereof, in a delayed release enteric soft
capsule in the
form of a suspension, where part or all of the fumarate ester is suspended
within the
matrix.
Described herein are methods for manufacturing matrix fills comprising
fumarate
esters or derivatives thereof, in an extended release enteric soft capsule in
the form of
a suspension, where part or all of the fumarate ester is suspended within the
matrix.
Another embodiment described herein is a controlled, delayed, or extended
release enteric soft capsule having a shell and a matrix fill, wherein the
matrix fill
36
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
includes fumarate esters such as dimethyl fumarate, monomethyl fumarate, or
derivatives thereof, suspended as solid particles in a lipid or lipophilic
vehicle. In
another embodiment, the lipid or lipophilic vehicle comprises a vegetable oil,
hydrogenated vegetable oil, fatty acid, wax, fatty acid ester, or combination
thereof.
Exemplary matrix lipid or lipophilic vehicles comprise mineral oil; light
mineral oil;
natural oils (e.g., vegetable, corn, canola, sunflower, soybean, olive,
coconut, cocoa,
peanut, almond, cottonseed, persic, sesame, squalane, castor, cod liver)
hydrogenated
vegetable oil; partially hydrogenated oils; beeswax; polyethoxylated beeswax;
paraffin;
normal waxes; medium chain monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides;
higher
aliphatic alcohols; higher aliphatic acids; long chain fatty acids; saturated
or
unsaturated fatty acids; hydrogenated fatty acids; fatty acid glycerides;
polyoxyethylated oleic glycerides; monoglycerides and diglycerides; mono-, bi-
or
tri-substituted glycerides; glycerol mono-oleate esters; glycerol mono-
caprate;
glyceryl monocaprylate; propylene glycol dicaprylate; propylene glycol
monolaurate; glyceryl palmitostearate; glyceryl behenate; diethyleneglycol
palmitostearate; polyethyleneglycol stearate; polyoxyethyleneglycol
palmitostearate;
glyceryl mono palmitostearate; cetyl palmitate; polyethyleneglycol
palmitostearate;
dimethylpolysiloxane; mono- or di-glyceryl behenate; fatty alcohols associated
with
polyethoxylate fatty alcohols; cetyl alcohol; octyl dodecanol; myristyl
alcohol; isopropyl
myristate, isopropyl palmitate, stearic acid, or stearyl alcohol, inter alia,
or combinations
thereof.
In one embodiment, the matrix comprises a solvent or solubility enhancing
agent.
Exemplary solvents or solubility enhancing agents useful for the matrix fills
described
herein include Capmul MCM, Captex 355, Cremophor RH 40, Croscarmellose,
Crospovidone, Crospovidone CL, Crospovidone CL-F, Crospovidone CL-M, I mwitor
742, Kollidon CL, Kollidon CL-F, Kollidon CL-M, LabrafacTM Lipophile WL
1349,
Labrafil M2125CS, Labrasol , Lutrol F 68, MaisineTM 35-1, mannitol, Miglyol
812,
Pearlitol Flash, Peceol , polyethylene glycol 400, polyethylene glycol 600,
polyethylene glycol 3350, Plurol Oleique CC 497, Povidone K 17, Povidone K
30,
propylene glycol, or combinations thereof.
37
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
In one embodiment, the matrix comprises solid particles of fumarate ester
suspended in a lipid or lipophilic vehicle of vegetable oil, hydrogenated
vegetable oil,
fatty acid, fatty acid ester, or a combination thereof. The matrix can also
comprise
solvents and suspension agents such as polyethylene glycols of molecular
weight
ranging from about 200 to about 8000 (MN, number average molecular weight),
polyvinylpyrrolidone, or combinations thereof.
In another embodiment, the matrix fill comprises a release regulator such as a
fatty acid salt, fatty acid ester, or fatty acid polyoxyethylene derivative.
The release
regulator can also be a surfactant having a hydrophilic/lipophilic balance
(HLB) value
between about 2 and about 40. The HLB characteristic of surfactants can be
determined in accordance with "Physical Pharmacy: Physical Chemical Principles
in
the Pharmaceutical Sciences," Fourth Edition, pp. 371-373, A. Martin, Ed.,
Lippincott
Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia (1993).
In another embodiment, the matrix comprises emulsifying or solubilizing agents
such as acacia, cholesterol, diethanolamine, glyceryl monostearate, lanolin
alcohols,
lecithin, mono- and
37a
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
di-glycerides, monoethanolamines, oleic acids, oleyl alcohols, poloxamer,
polyoxyethylene 50
stearate, polyoxyl 35 castor oil, polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil,
polyoxyl 10 oleyl ether,
polyoxyl 20 cetostearyl ether, polyoxyl 40 stearate, polysorbate 20,
polysorbate 40, polysorbate
60, polysorbate 80, propylene glycol diacetate, propylene glycol monostearate,
sodium lauryl
sulfate, sodium stearate, sorbitan monolaurate, sorbitan monooleate, sorbitan
monopalmitate,
sorbitan monostearate, stearic acid, trolamine, emulsifying wax, or
combinations thereof.
In another embodiment, the matrix comprises a neutralizing agent. Without
being bound
to any theory, the neutralizing agent stabilizes the fumarate ester in the
matrix fill by preventing
hydrolysis. In addition, without being bound by any theory, the neutralizing
agent stabilizes the
enteric soft capsule shell by forming salts with the methylacrylate moieties
from the capsule
shell. In one aspect, the neutralizing agent comprises an organic acid, ester,
or salt. In another
aspect, the neutralizing agent comprises at least one of lactate, fumarate,
caprylate, caprate,
oleate, maleate, succinate, tartrate, citrate, glutamate, gluconate, esters or
salts thereof, or
combinations thereof. In one aspect, the neutralizing agent is lactic acid.
In another embodiment, the matrix includes a hydrophilic internal phase and a
lipid or
lipophilic external phase. The hydrophilic internal phase can comprise
polypropylene glycol or
polyethylene glycol of molecular weight ranging from about 200 to about 8000
(MN, number
average molecular weight). In another embodiment, the internal phase comprises
hydroalcoholic
solutions of cellulose derivatives, polyacrylates, polyvinyl polymers, or
combinations thereof. In
one embodiment, the internal phase comprises polymers such as methylcellulose,
hydroxypropylmcthylccllulosc, polymcthylmethacrylate, or polyvinylpyrrolidonc
(PVP). In one
embodiment, the internal phase of the matrix state is "fluid" or "structured."
A "fluid" internal
phase, as used herein, means a completely flowable liquid whose globules can
aggregate to make
a larger globule. A "structured" internal phase, as used herein, means a
solid, semisolid, or a gel
whose shape is relatively stable and does not usually aggregate to form a
large globule. A
structured internal phase can provide controlled drug release and stabilize
the physical state of
the matrix. Without being bound to any theory, the structured nature of the
matrix impedes
solvation or diffusion of the fumarate ester out of the matrix. In another
embodiment, the
external phase comprises a vegetable oil, hydrogenated vegetable oil, fatty
acid, fatty acid ester,
wax, or a combination thereof. In another embodiment, fumarate ester is
dispersed in the
internal phase as a suspension form.
38
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
In another embodiment, the matrix fill is an emulsion type, where the fumarate
ester is
distributed in one or both of the external (lipophilic) and internal
(hydrophilic) phases. The
external phase of the emulsion matrix fill comprises lipid or lipophilic
vehicles similar to those
described herein. The fumarate ester can be dispersed in the internal phase as
a solution or as a
suspension. For example, one portion of the fumarate ester in the form of a
powder is
incorporated in the internal phase, while another portion is dispersed in the
external phase as
solid particles. An emulsion-type matrix may comprise a surfactant or
combination of
surfactants having HLB values ranging from about 2 to about 40, including all
integers within
the specified range. In one aspect, the HLB range comprises from about 8 to
about 20, including
all integers within the specified range.
In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition described herein comprises
an
enteric soft capsule comprising a matrix comprising a lipid or lipophilic
vehicle that provides a
suspension of a fumarate ester. In one embodiment described herein, the
fumarate ester is a
mono-or di-alkyl fumarate of Formula I:
Ri
wherein RI and R2, which may be the same or different, independently represent
linear,
branched, or cyclic, saturated or unsaturated C1_20 alkyl radical, which may
be optionally
substituted with halogen (Cl, F, I, Br), hydroxy, C1_4 alkoxy, nitro, or cyano
for preparing a
pharmaceutical composition as described herein.
The C1_20 alkyl radicals, C1_8 alkyl radicals, and C4_5 alkyl radicals are,
for example,
methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl,sec-butyl, t-butyl, pentyl,
cyclopentyl, 2-ethyl hexyl,
hexyl, cyclohexyl, heptyl, cycloheptyl, octyl, vinyl, allyl, 2-hydroxyethyl, 2
or 3-hydroxy propyl,
2-methoxy ethyl, methoxy methyl or 2- or 3-methoxy propyl. In one aspect, at
least one of Rl or
R2 is a C1_5 alkyl, especially methyl or ethyl. In another aspect, RI and R2
are the same or
different C1_5 alkyl radicals such as methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, or t-butyl. In
one aspect, RI and R2
are the same or different C1_5 alkyl radicals such as methyl and ethyl. In one
aspect, Rl and R2
are identical and are methyl or ethyl. In one aspect, the fumarate ester is
monomethyl fumarate,
dimethyl fumarate, methyl ethyl fumarate, or diethyl fumarate. In one aspect,
the fumarate ester
39
is monomethyl fumarate, dimethyl fumarate, or a combination thereof. In one
aspect,
the fumarate ester is monomethyl fumarate. In another aspect, the fumarate
ester is
dimethyl fumarate.
In one embodiment, the fumarate ester is:
0
0
H i..,, CH3
113., 0
0
In one embodiment, the fumarate ester is:
0
HO /CH3
0
0
In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical compositions described herein comprise
pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the active ingredient. The term
"pharmaceutically
acceptable salts" of an active ingredient includes alkali metal salts such as,
sodium or
potassium salts, alkaline earth metal salts such as, for example, calcium and
magnesium salts, and salts with organic or inorganic acid such as, for
example,
hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, phosphoric
acid, citric acid,
formic acid, maleic acid, succinic acid, tartaric acid, methanesulphonic acid,
toluenesulphonic acid, inter alia. In another embodiment, the active
ingredient may also
be in the form of pharmaceutically acceptable uncharged or charged molecules,
molecular complexes, solvates, or anhydrates thereof, and, if relevant, single
isomers, enantiomers, racemic mixtures, or mixtures thereof. In another
embodiment,
the active pharmaceutical ingredient may be in any of its crystalline,
polymorphous,
semi-crystalline, amorphous or polyamorphous forms, or mixtures thereof.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
The fumarate esters described herein can be prepared by processes known in
the art. See, e.g., EP 0 312 697 and U.S. Patent Application Publication Nos.
US
2013/0295169; US 2014/0179779; and US 2014/0200363.
In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition comprises an active
ingredient or drug. In one embodiment, the active ingredient or drug is a
pharmacologically active fumarate ester. In one embodiment described herein,
the
active ingredient is a dialkyl fumarate. In one
40a
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
embodiment described herein, the active ingredient is a fumarate ester or
combination of
fumarate esters. In one embodiment described herein, the active ingredient is
dimethyl fumarate.
In another embodiment described herein, the active ingredient is monomethyl
fumarate. In
another embodiment described herein, the active ingredient is a combination of
dimethyl
fumarate and monomethyl fumarate. In another embodiment described herein, the
active
ingredient is a combination of dimethyl fumarate, monomethyl fumarate, and
other
pharmacologically active fumarate esters, acids, salts, or derivatives
thereof. In another
embodiment, the active ingredient or drug comprises dimethyl fumarate,
monomethyl fumarate,
other pharmacologically active fumarate esters, acids, or salts, derivatives
thereof, or
combinations thereof. In another embodiment, the active ingredient comprises
dimethyl
fumarate, monomethyl fumarate, or derivatives thereof, combined with aspirin,
ibuprofen,
naproxene, diclofenac, ketoprofen, celecoxib, other non-steroidal anti-
inflamatory active drugs
(NSAIDs), or combinations thereof. In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical
composition
comprises a fumarate ester combined with aspirin.
In another embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition comprises a fumarate
ester
combined with one or more leukotriene receptor antagonists. In another
embodiment, the
pharmaceutical composition comprises a fumarate ester combined with
montelukast (Singulair )
or zafirlukast (Accolate). In another embodiment, the pharmaceutical
composition comprises a
fumarate ester combined with montelukast or zafirlukast and an NSAID. In
another
embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition comprises a fumarate ester combined
with
montelukast or zafirlukast and aspirin.
In one embodiment, the fumarate ester-to-matrix ratio range comprises from
about 1:50
to about 1:1 by weight, including all ratios within the specified range. In
another embodiment,
the fumarate ester-to-matrix ratio range comprises from about 1:10 to about
1:1 by weight,
including all ratios within the specified range. In one aspect, the fumarate
ester-to-matrix ratio
comprises about 1:9 to about 1:1 by weight, including all ratios within the
specified range. In
another aspect, the fumarate ester-to-matrix ratio range comprises from about
1:5 to about 1:1 by
weight, including all ratios within the specified range. In another aspect,
the fumarate ester-to-
matrix ratio is about 1:5; about 1:4; about 1:3; about 1:2; about 1:1; or
about 0.5:1. In other
aspects, the fumarate ester-to-matrix ratio is 1:3.5; 1:3.1; 1:2.9; 1:2.3; or
1:1.5.
41
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
In one embodiment, the active ingredient comprises about 1% to about 70% of
the
matrix, including all integers and fractions within the specified range. In
another embodiment,
the active ingredient comprise about 70%; about 60%; about 50%; about 40%;
about 30%; about
20%; about 15%; about 10%; about 5%; about 2%; or about 1% of the matrix fill.
In one aspect,
the active ingredient comprises about 64% of the matrix. In another
embodiment, the active
ingredient comprises about 57% of the matrix. In another embodiment, the
active ingredient
comprises about 50% of the matrix. In another embodiment, the active
ingredient comprises
about 32% of the matrix. In another embodiment, the active ingredient
comprises about 30% of
the matrix. In another embodiment, the active ingredient comprises about 28%
of the matrix. In
another embodiment, the active ingredient comprises about 25% of the matrix.
In one embodiment, the solid fumarate ester particles are milled or
micronized. In one
embodiment, the fumarate ester comprises a particle size range of about 1 pm
to about 500 [tm,
including all integers and fractions within the specified range. In one
aspect, the micronized
solid fumarate ester particles have a particle size of about 1 pm, 2 pm, about
5 m, about 10 pm,
about 15 pm, about 20 m, about 25 [tm, about 30 pm, about 35 pm, about 40 pm,
about 45 1..tm,
about 50 pm, about 55 m, about 60 pm, about 65 pm, about 70 pm, about 75 m,
about 80 1..tm,
about 85 pm, about 90 pm, about 95 pm, about 100 pm, about 105 pm, about 110
pm, about 115
pm, about 120 pm, about 125 pm, about 130 pm, about 135 pm, about 140 pm,
about 145 pm,
about 150 pm, about 155 pm, about 160 pm, about 165 pm, about 170 pm, about
175 pm, about
180 pm, about 185 pm, about 190 pm, about 195 [tm, about 200 pm, about 205 m,
about 210
pm, about 215 pm, about 220 pm, about 225 pm, about 230 pm, about 235 pm,
about 240 pm,
about 245 pm, about 250 pm, about 255 pm, about 260 pm, about 265 pm, about
270 pm, about
275 pm, about 280 pm, about 285 pm, about 290 [tm, about 295 pm, about 300 m,
about 305
pm, about 310 pm, about 315 pm, about 320 pm, about 325 pm, about 330 pm,
about 335 pm,
about 340 pm, about 345 pm, about 350 pm, about 355 pm, about 360 pm, about
365 pm, about
370 pm, about 375 pm, about 380 pm, about 385 m, about 390 pm, about 395 m,
about 400
pm, about 405 pm, about 410 pm, about 415 pm, about 420 pm, about 425 pm,
about 430 pm,
about 435 pm, about 440 pm, about 445 pm, about 450 pm, about 455 pm, about
460 pm, about
465 pm, about 470 pm, about 475 pm, about 480 pm, about 485 pm, about 490 pm,
about 495
pm, about 500 pm, or even larger. In another aspect, the solid particles of
fumarate ester
42
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
comprise a distribution of particle sizes, comprising particles of any of the
foregoing particle
sizes.
In another embodiment, the solid fumarate ester particles have mean particle
size
distributions (PSD) ranging from about 20 [rm to about 300 pm, including all
integers and
fractions within the specified range. In one aspect, the solid particles of
fumarate ester comprise
mean particle size distributions of about 20 pm, about 30 pm, about 40 pm,
about 50 pm, about
60 )tm, about 70 )tm, about 80 )tm, about 90 pm, about 100 [tm, about 120 pm,
about 140 pm,
about 160 pm, about 180 pm, about 190 pm, about 200 pm, about 220 pm, about
240 pm, about
260 tim, about 280 pm, or about 300 [rm. In one aspect, the solid particles of
fumarate ester have
a mean particle size distribution of about 260 pm. In one aspect, the solid
particles of fumarate
ester have a mean particle size distribution of about 170 pm. In one aspect,
the solid particles of
fumarate ester have a mean particle size distribution of about 140 pm. In one
aspect, the solid
particles of fumarate ester have a mean particle size distribution of about 90
1..tm. In one aspect,
the solid particles of fumarate ester have a mean particle size distribution
of about 80 pm. In one
aspect, the solid particles of fumarate ester have a mean particle size
distribution of about 25 pm.
In another embodiment, the solid fumarate ester particles have a particle size
distribution
with a d90 of less than or equal to about 500 pm. In one aspect, the particle
size distribution of
solid particles of fumarate ester have a d90 of - to about 20 pm, about 30
pm, about 40 pm,
about 50 pm, about 60 pm, about 70 pm, about 80 pm, about 90 pm, about 100
jim, about 120
pm, about 140 pm, about 160 pm, about 180 pm, about 190 pm, about 200 pm,
about 220 pm,
about 240 pm, about 260 pm, about 280 pm, about 300 pm, or about 400 pm. In
one aspect, the
solid particles of fumarate ester have a particle size distribution with a d90
of < about 260 pm
(d90 <260 pm). In one aspect, the solid particles of fumarate ester have a
particle size
distribution with a d90 of < about 170 pm (d90 <170 pm). In one aspect, the
solid particles of
fumarate ester have a particle size distribution with a d90 of < about 140 pm
(d90 <140 pm). In
one aspect, the solid particles of fumarate ester have a particle size
distribution with a d90 of <
about 100 pm (d90 <100 pm). In one aspect, the solid particles of fumarate
ester have a particle
size distribution with a d90 of < about 90 pm (d90 <90 pm). In one aspect, the
solid particles of
fumarate ester have a particle size distribution with a d90 of < about 80 pm
(d90 <80 )tm). In
one aspect, the solid particles of fumarate ester have a particle size
distribution with a d90 of <
about 25 pm (d90 <25 pm).
43
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
In another embodiment, the solid fumarate ester particles have a mean particle
size
distribution comprising a range of particle sizes with a d10 of <10 [tm and a
d90 of <500 pm. In
one aspect, the solid particles of fumarate ester have a particle size
distribution with a d10 of < to
about 10 pm and a d90 of < to about 400 pm, a d10 of < to about 10 pm and a
d90 of < to about
300 pm, a d10 of < to about 10 pm and a d90 of < to about 250 m, a d10 of <
to about 10 pm
and a d90 of < to about 200 pm, a dl 0 of < to about 10 pm and a d90 of < to
about 150 pm, a d10
of < to about 10 pm and a d90 of < to about 100 pm. In one aspect, the solid
particles of
fumarate ester have a particle size distribution with a d10 of < to about 10
[tm and a d90 of < to
about 100 pm, a d10 of < to about 20 pm and a d90 of < to about 100 pm, a d10
of < to about 30
pm and a d90 of < to about 100 pm, a dl 0 of < to about 40 pm and a d90 of <
to about 100 pm, a
d10 of < to about 50 pm and a d90 of < to about 100 tarn, a d10 of < to about
60 pin and a d90 of
< to about 100 pm, a d10 of < to about 70 1..tm and a d90 of < to about 100
pm, a d10 of < to
about 80 [im and a d90 of < to about 100 pm.
In another embodiment, the solid particles of fumarate ester comprise multiple
.. distributions of particle sizes. In one aspect, the solid particles of
fumarate ester may comprise a
plurality of independently combined mean particle size distributions, wherein
each independent
mean particle size distribution ranges from about 20 pm to about 300 pm,
including all integers
and fractions within the specified range. In another aspect, the plurality of
mean particle size
distributions can comprise a mean particle size distribution of about 261 pm,
a mean particle size
.. distribution of about 168 pm, a mean particle size distribution of about
148 pm, a mean particle
size distribution of about 90 pm, a mean particle size distribution of about
80 pm, or a mean
particle size distribution of about 26 pm. In another aspect, the plurality of
mean particle size
distributions can comprise combinations of independent mean particle size
distributions, wherein
each independently combined mean particle size distribution is about 261 pm,
about 168 pm,
about 148 pm, about 90 pm, about 80 pm, or about 26 pm. In another aspect, the
solid particles
of fumarate ester comprise a combination of independently combined mean
particle size
distributions of about 30 pm to about 260 pm in a single matrix fill. Any of
the foregoing
particle size distributions may be combined to provide the desired controlled
release profile.
The forgoing sizes of fumarate ester particles may be determined using
standard
techniques known to one of ordinary skill in the art. The exemplary techniques
that can be used
for measuring the size of fumarate ester particles may include laser
diffraction analysis, light
44
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
scattering (e.g., dynamic light scattering), microscopic particle image
analysis, elutriation, or
aerosol mass spectrometry. The sample of fumarate ester particles may be
measured as a dry
sample or a wet sample. Any commercially available instrument for measuring
particle sizes
may be used, including instruments from Cilas; Brookhaven Instruments
Corporation; Malvern
Instruments; Horiba Scientific; or Wyatt following the recommended operating
procedures
according to the manufacturer's instructions.
The measured particle sizes using the techniques described herein may be
expressed as a
derived diameter with a normal distribution or non-normal distribution with a
mean, median
(e.g., mass median diameter), and mode of particle diameter sizes. The
particle size distribution
may be expressed as a diameter number distribution, a surface area
distribution, or a particle
volume distribution. The mean of the particle size distribution may be
calculated and expressed
in various ways, such as the volume mean diameter (D[4,3] or d43), mean
surface area diameter
(D[3,2] or d32) or the mean number particle diameter (D[1,0] or d10). Because
the particle size
distribution values vary depending on the measurement methodology and how the
distribution is
expressed, the comparison of different mean particle size distributions must
be calculated by the
same methodology in order to have an accurate comparison. For example, a
sample with a
measured and calculated volume mean diameter must be compared with a second
sample having
a measured and calculated volume mean diameter, ideally measured using the
same measuring
instrument under the same conditions. Thus, the specific particle size
distributions described
herein are not intended to be limited to any one type of method for measuring
or calculating a
particle size distribution (e.g., a diameter number distribution, a surface
area distribution, or a
particle volume distribution), but rather indicate particle size values and
distributions thereof for
each method of measuring particle sizes described herein.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for manufacturing a matrix
fill for a
controlled release soft enteric capsule comprising particles of fumarate
esters such as dimethyl
fumarate or monomethyl fumarate of defined sizes. In one aspect, the particles
are of a similar
size distribution. In one aspect, the fumarate ester particles comprise varied
size distributions.
In another aspect, the fumarate ester particles comprise several size
distributions. In another
aspect, the fumarate ester particles comprise a mixture of smaller and larger
size distributions.
Without being bound to any theory, smaller particles are generally solubilized
and released more
rapidly than larger particles. The release rate can be adjusted to achieve a
specific therapeutic
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
window over a defined period and produce controlled release, delayed release,
or extended
release compositions by combining multiple fumarate ester particle sizes or
distributions.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for manufacturing a
pharmaceutical
composition comprising fumarate ester(s) where the fumarate ester does not
sublime during
processing, manufacturing, after production, or during storage. Soft enteric
capsules comprising
fumarate ester in the matrix fills described herein are stable for months or
years. Without being
bound to any theory, it is believed that suspending solid fumarate ester in a
lipid or lipophilic
vehicle comprising an organic acid prevents or retards sublimation and
stabilizes the fumarate
ester. In one aspect, the pharmaceutical compositions described herein are
stable at 25 C and
60% relative humidity (RH) for about 1 month, about 2 months, about 3 months,
about 4 months,
about 5 months, about 6 months, about 9 months, about 10 months, about 11
months, about 12
months, or even longer. In another aspect, the pharmaceutical compositions
described herein are
stable for 1 year or longer at 25 C and 60% RH. In another aspect, the
pharmaceutical
compositions described herein are stable for 2 years or longer at 25 C and
60% RH.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for preparing a pharmaceutical
matrix
comprising a fumarate ester. An exemplary scheme of a manufacturing process is
shown in
Figure 1. The method comprises applying heat to the matrix components during
mixing or prior
to mixing at about the melting point of the matrix fill composition; and then
mixing the fumarate
ester with the lipid or lipophilic matrix ingredients using mechanical or
ultrasonic forces to form
the matrix fill. The matrix fill is flowable such that it can be encapsulated
using a rotary die
encapsulation machine. In one embodiment, the matrix components are heated to
a temperature
in the range of from about 25 C to about 70 C. In another embodiment, the
matrix components
are heated to a temperature in the range of from about 25 C to about 30 C.
In one embodiment, the matrix comprises a lipid or lipophilic vehicle, a
neutralizing
agent, excipients, and sold particles of fumarate ester. In another aspect,
the matrix comprises
polyethylene glycols, polyvinylpyrrolidones, oils, and surfactants. In one
aspect, the surfactant
comprises polysorbate 80 or polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil. In another
aspect, the matrix
comprises dimethyl fumarate, a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides,
polyvinylpyrrolidone,
polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, and lactic acid.
46
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
In one embodiment, the matrix comprising fumarate ester comprises the
composition
shown in Table 1 including all possible iterations of the specified ranges
that provide 100% for
the total weight percentage of the composition.
Table 1. Exemplary Matrix Fill Composition
Ingredient mg/capsule "A weight
Fumarate Ester (Mean PSD 80 [un) 240 32
Capmul MCM 375 50
Povidone K 30 15-52.5 0.01-7
Cremophor RH 40 15-75 2-10
Lactic acid 7.5-37.5 1-5
TOTAL 750 mg 100%
In one embodiment, the matrix comprises about 32% by weight of fumarate ester
(PSD:
80 pm); about 50% by weight of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; at least
about 0.01-7%
by weight of polyvinylpyrrolidone; at least about 2-10% by weight of polyoxyl
40 hydrogenated
castor oil, and at least about 1-5% by weight of lactic acid, including all
iterations of the
specified ranges. In one aspect, the composition prevents sublimation of the
FAE during
processing and manufacturing. In one aspect, the composition reduces the onset
of symptoms of
gastrointestinal side effects. In another aspect, the composition is stable
for at least 6 months at
25 C and 60% relative humidity. In one aspect, the composition is stable for
at least 24 months.
In one embodiment, the matrix comprises the composition shown in Table 2
including all
possible iterations of the specified ranges that provide 100% for the total
weight percentage.
Table 2. Exemplary Matrix Fill Composition
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight
Fumarate ester
480 48-60
PSD: d90 < 100 pm
Capmul MCM 216-470 25-48.0
Cremophor RH 40 7.3-120 0.85-12.0
Povidone K 30 7.3-50 0.85-5.0
Lactic acid 21.7-50 2.55-5.0
TOTAL 750 mg-1000 mg 100%
In another embodiment the matrix fill comprises about 32% of fumarate ester
(PSD: < 90
pm); about 25% to about 47% of a mixture of mono- and di-glycerides; at least
about 0.01-7%
47
polyvinylpyrrolidone; at least about 0.85-12% polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor
oil, and
at least about 1-5% lactic acid, including all iterations of the specified
ranges. In one
aspect, the composition prevents sublimation of the FAE during processing and
manufacturing. In another aspect, the composition reduces the onset of
symptoms of
any gastrointestinal side effects. In another aspect, the composition is
stable for at
least 6 months at 25 C and 60% relative humidity. In another aspect, the
composition
is stable for at least 24 months at 25 C and 60% relative humidity.
In one embodiment, the fumarate ester pharmaceutical composition comprises
a soft gelatin capsule shell comprising a matrix comprising a fumarate ester.
In one embodiment, the fumarate ester pharmaceutical composition comprises
an enteric soft capsule shell comprising a matrix comprising a fumarate ester.
Enteric
soft capsules are described in International Patent Application Publication
No. WO
2004/030658; U.S. Patent Application Publication No. US 2006/0165778; and U.S.
Patent No. 8,685,445. The enteric soft capsule shell may comprise one or more
film
forming polymers, one or more enteric acid-insoluble polymers, one or more
plasticizers, one or more alkali-neutralizing agents, one or more solvents,
optionally
one or more colorants, and optionally one or more flavorings or other
conventionally
accepted pharmaceutical excipients or additives.
Film-forming polymers that are useful for creating enteric soft capsules are
gelatin or hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC). In one aspect of the enteric
soft
capsule shell described herein, the film-forming polymer is gelatin.
Examples of enteric, acid-insoluble polymers are acrylic and
methacrylate acid copolymers, cellulose acetate phthalate (CAP), cellulose
acetate butyrate, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose phthalate (HPMCP), algenic
acid salts such as sodium or potassium alginate, or shellac. Poly(methacylic
acid-
co-methyl methacrylate) anionic copolymers based on methacrylic acid and
methyl
methacrylate are particularly stable and are preferred in some embodiments.
Poly(meth)acrylates (methacrylic acid copolymer), available under the trade
name
48
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
EUDRAGIT (Evonik Industries AG, Essen, Germany), are provided as powder or
aqueous dispersions. In another aspect, the methacrylic acid copolymer
comprises
EUDRAGIT L 30 D-55; EUDRAGIT L 100-55; EUDRAGIT L 100; EUDRAGIT L
12.5; EUDRAGIT S 100; EUDRAGIT S 12.5; EUDRAGIT FS 30 D; EUDRAGIT E
100;
48a
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
EUDRAGIT E 12.5; EUDRAGIT E PO; EUDRAGIT RL 100; EUDRAGIT RL PO;
EUDRAGIT RL 30 D; EUDRAGIT RL 12.5; EUDRAGIT RS 100; EUDRAGIT RS PO;
EUDRAGIT RS 30 D; EUDRAGIT RS 12.5; EUDRAGIT NE 30 D; EUDRAGIT NE 40
D; EUDRAGIT NM 30 D; other poly(meth)acrylate polymers; or a mixture thereof.
In one
aspect, the enteric polymer is EUDRAGIT L 100, a methacrylic acid copolymer,
Type A.
Acid-insoluble polymer specifications are detailed in the United States
Pharmacopoeia and in
various monographs.
In another embodiment described herein, the enteric polymer in the enteric
soft capsule
shell comprises poly(methacylic acid-co-ethyl acrylate) 1:1 (e.g., EUDRAGIT L
100-55). In
one embodiment described herein, the enteric polymer comprises poly(ethyl
acrylate-co-methyl
methacrylate) 2:1 (e.g., EUDRAGIT NE 40 D). In another embodiment described
herein, the
enteric polymer comprises poly(methyl acrylate-co-methyl methacrylate-co-
methacrylic acid)
7:3:1 (e.g., EUDRAGIT FS 30 D). In another embodiment described herein, the
enteric
polymer comprises a combination of poly(methacylic acid-co-ethyl acrylate) 1:1
and
poly(methyl acrylate-co-methyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) 7:3:1. In
another
embodiment, the enteric polymer comprises a combination of poly(methacylic
acid-co-ethyl
acrylate) 1:1 and poly(ethyl acrylate-co-methyl methacrylate) 2:1. In another
embodiment, the
enteric polymer comprises a combination of poly(methacylic acid-co-ethyl
acrylate) 1:1,
poly(ethyl acrylate-co-methyl methacrylate) 2:1, and poly(methyl acrylate-co-
methyl
methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) 7:3:1.
In another embodiment, plasticizers that are useful for creating enteric soft
capsules as
described herein are glycerol, sorbitol, Sorbitol Special , maltitol, corn
syrup, propylene glycol,
poly-alcohols with 3 to 6 carbon atoms, polyethylene glycol, citric acid,
citric acid esters, such as
tri-ethyl citrate, or combinations thereof. The weight ratio between the film-
forming polymer,
the enteric acid-insoluble polymer, and plasticizer is adjusted so that the
gel mass is flowable and
not too viscous, and can be made into soft capsules using rotary die
encapsulation methods.
In one embodiment, enteric soft capsule shell compositions are made by
dissolving the
enteric acid-insoluble polymer in an aqueous solution of an alkali-
neutralizing agent such as
ammonia, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, or liquid amines such as tri-
ethanol amine or
ethylene diamine. The amount of alkali is adjusted to give a final pH value of
the gel mass less
than or equal to about pH 9Ø In one embodiment, the final pH does not exceed
8.5. The
49
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
volatile alkali-neutralizing agent, ammonia is preferred. The film-forming
polymer can then be
combined with the plasticizer and solvent and then blended with the acid-
insoluble gel to make a
final homogeneous mix in a heat-controlled vessel with degassing by vacuum.
The fugitive
ammonia evaporates during degassing. Using the foregoing process, the alkali
concentrations do
not require heating or neutralizing with acid in order to neutralize the gel
mass.
In another embodiment described herein, the enteric soft capsule shell is made
using an
aqueous dispersion of the acid-insoluble polymer by adding an alkali-
neutralizing agent such as
ammonium, sodium, or potassium hydroxides, other alkalis, or a combination
thereof that will
cause the enteric acid-insoluble polymer to dissolve. The plasticizer-wetted,
film-forming
polymer can then be mixed with the solution of the acid-insoluble polymer. In
one embodiment,
enteric acid-insoluble polymers in the form of salts of the bases or alkalis
as described herein are
dissolved directly in water and mixed with the plasticizer-wetted, film-
forming polymer.
In one embodiment described herein, enteric acid-insoluble polymers in the
form of salts
of the bases or alkalis described herein are dissolved directly in water and
mixed with the
plasticizer-wetted, film-forming polymer. In another embodiment described
herein, an aqueous
dispersion of the acid-insoluble polymer or polymers is used, which obviates
the need for the
addition of the alkali-neutralizing agent described herein.
In one embodiment. the enteric soft capsule shell has the composition of Table
3,
including all possible iterations of the specified ranges that provide 100%
for the total weight
percentage, including or excluding the optional, excipients, opacifiers,
colorants, and flavorings.
Table 3. Enteric Soft Capsule Shell Composition
Component Exemplary Component Composition Range
(%)
Film-folming polymer Gelatin 20-36
Enteric, acid-insoluble polymer
Methacrylic Acid Copolymer 8-20
Plasticizer Glycerol, sorbitol, Triethyl citrate 15-22
Alkali-neutralizing agents NH4OH (30%), NaOH 1-5
Solvent Water 20-40
Op acifier Titanium Dioxide 1-7.5
Colorant (optional) Various 0.05-1
Flavoring (optional) Various 0.05-2
Excipients (optional) Various 1-5
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
In one embodiment, the enteric soft capsule shell comprises a composition of
about 30%
film forming polymer; about 10% enteric, acid-insoluble polymer; about 20%
plasticizer; about
1% alkali-neutralizing agent; and about 37% solvent.
In another embodiment, the weight percentage range of total polymer content
(i.e., film
forming polymer and enteric acid-insoluble polymer) of the enteric soft
capsule described herein
is about 30% to about 45%, including all integers and fractions within the
specified range. In
one aspect, the total polymer weight percentage is about 40%. In another
aspect, the total
polymer weight percentage is about 42%. In another aspect, the total polymer
weight percentage
is about 45%. In another aspect, the total polymer weight percentage is about
38%.
In one embodiment, the weight percentage range of total plasticizer is about
15% to about
22%, including all integers and fractions within the specified range. In one
aspect, the total
plasticizer weight percentage is about 19%. In another aspect, the total
plasticizer weight
percentage is about 17.7%. In another aspect, the total plasticizer weight
percentage is about
18.9%. In another aspect, the total plasticizer weight percentage is about
19.3%.
In one embodiment, the alkali-neutralizing agent is ammonia (ammonium
hydroxide;
30% w/v) that is added to comprise a weight percentage of about 1% to about 5%
of the total
enteric soft capsule composition. In one aspect, 30% w/v ammonia is added to
comprise a
weight percentage of about 2%. In another aspect, 30% w/v ammonia is added to
comprise a
weight percentage of about 1.7%. In one aspect, ammonia is added to provide a
final pH of
about 9 in the enteric soft capsule composition. In another aspect, ammonia is
added to provide
a final pH of about 8.5 in the enteric soft capsule composition. In another
aspect, after the
capsules are filled and dried, the ammonia concentration is substantially
reduced, owing to the
fugitive nature of the volatile alkali-neutralizing agent. In another aspect,
practically all of the
ammonia is evaporated except for ammonium ions comprising salts with other
moieties in the
composition.
In one embodiment, the weight ratio range of film forming polymer to enteric
acid-
insoluble polymer (i.e., film forming : enteric) is about 25:75 (A.33) to
about 40:60 (0.67) (i.e.,
0.33-0.67), including all ratios within the specified range. In one aspect,
the ratio of film
forming polymer to enteric acid-insoluble polymer is about 30:70 (4.43). In
another aspect, the
ratio of film forming polymer to enteric acid-insoluble polymer is about 28:72
(4.38).
51
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
In one embodiment, the weight ratio of total plasticizer to film forming
polymer is about
20:40 to 21:30 (i.e., including all ratios within the specified range.
In one aspect, the
weight ratio of total plasticizer to film forming polymer is about 20:40
(4.5). In another aspect,
the weight ratio of total plasticizer to film forming polymer is about 21:30
(4.7). In another
aspect, the weight ratio of total plasticizer to film forming polymer is about
19:29 (4.65). In
another aspect, the weight ratio of total plasticizer to film forming polymer
is about 19.3:29.2
(4.66).
In one embodiment, the weight ratio of total plasticizer to enteric acid-
insoluble polymer
is about 1:1 to about 2:1 (z1-2), including all ratios within the specified
range. In one aspect,
the weight ratio of total plasticizer to enteric acid-insoluble polymer is
about 11:10 (z1.1). In
another aspect, the weight ratio of total plasticizer to enteric acid-
insoluble polymer is about
14:10 (z1.4). In another aspect, the weight ratio of total plasticizer to
enteric acid-insoluble
polymer is about 17:10 (z1.7). In another aspect, the weight ratio of total
plasticizer to enteric
acid-insoluble polymer is about 20:10 (---2). In another aspect, the weight
ratio of total plasticizer
to enteric acid-insoluble polymer is about 19.3:11.2 (z1.73).
In one embodiment, the weight ratio range of total plasticizer to total
polymer (film
forming and enteric acid-insoluble polymer) is about 18:45 to about 20:40
(i.e., 4.40-0.5),
including all ratios within the specified range. In one aspect, the weight
ratio range of total
plasticizer to total polymer is about 18:45 (4.40). In another aspect, the
weight ratio range of
total plasticizer to total polymer is about 19:40 (4.475). In another aspect,
the weight ratio
range of total plasticizer to total polymer is about 20:40 (4.5). In another
aspect, the weight
ratio range of total plasticizer to total polymer is about 19.3:40.4 (4.477).
In one embodiment, the solvent comprises about 20% to about 40% of the enteric
soft
capsule composition, including all integers and fractions within the specified
range. In one
embodiment, the solvent is water. The quantity of water in the composition
varies depending on
the quantities of the other ingredients. For example, the quantity of
opacifier, colorant,
flavoring, or other excipients can change the percentage of water present in
the composition. In
one embodiment, the weight percentage of water is as much as suffices to bring
the total weight
percentage to 100% (i.e., quantum sufficiat; q.s.). In another embodiment, the
water comprises
about 20%, about 25%, about 30%, about 35%, or about 40% of the enteric soft
capsule
52
composition. In another embodiment, water comprises about 35% to about 40% of
the
enteric soft capsule composition. In one embodiment, water comprises about 37%
of the
composition.
In one embodiment, the final moisture (water) content of the enteric soft
capsule is
from about 8% to about 15%, including all integers and fractions within the
specified range.
In another embodiment, the moisture content is about 8% to about 12%,
including all
integers and fractions within the specified range. In one aspect, the final
moisture content is
about 8%. In one aspect, the final moisture content is about 9%. In one
aspect, the final
moisture content is about 10%. In one aspect, the final moisture content is
about 11%. In
another aspect, the final moisture content is about 12%.
In one embodiment, the enteric soft capsule shell has the exemplary
composition shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Exemplary Enteric Soft Capsule Shell Composition
Component Percent weiaht (Vo)
Gelatin 29.2
Methacrylic Acid Copolymer (EUDRAGIT L 100) 11.2
Glycerol or Sorbitol 18.0
Triethyl citrate 1.3
Ammonium hydroxide 1.7
Titanium dioxide 1.5
Water 37.1
TOTAL 100%
Final pH 8.5-9.0
Total polymer A weight (gelatin + enteric) 40.4%
Gelatin A wt of total polymer (gelatin + enteric) 72.4%
Enteric A wt of total polymer (gelatin + enteric) 27.6%
Ratio of Enteric to Gelatin 11.2 : 29.2
(0.38)
Total plasticizer % weight (glycerol + triethyl citrate) 19.3%
Ratio of total plasticizer to total polymer 19.3 : 40.4
(0.48)
Ratio total plasticizer to gelatin 19.3 : 29.2
(0.66)
Ratio total plasticizer to enteric 19.3: 11.2
(1.73)
Water content in dried enteric soft capsule: 8-15%
In one embodiment, the enteric soft capsule shell comprises about 30% gelatin;
about 10% poly(methyl) acrylate copolymer; about 18% glycerol; about 1%
triethyl citrate;
about 1.5% ammonia; about 37% water; and about 1.5% titanium dioxide.
53
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
One embodiment described herein provides an enteric acid-insoluble polymer
dispersed within the film-forming polymer gel mass that provides the total
soft gel
composition with enteric acid-insoluble properties, at relatively low
concentrations of the
enteric acid-insoluble polymer (e.g., from about 8% to about 20% of the total
wet gel
mass composition) and without the need of excessive amounts of alkali, thus
avoiding
denaturation or degradation of the film-forming polymer that can weaken the
integrity of
the enteric soft capsule shell.
Films of the enteric soft capsule shell do not dissolve or disintegrate in
acids, such
as 0.1 N hydrochloric acid or simulated gastric fluid (ca. pH 1.2), despite
the fact that
the majority of the shell ingredients (i.e., greater than 50%) normally
dissolve in, or are
miscible with, acids. Enteric soft capsules made using the compositions
described
herein remain intact in hydrochloric acid or simulated gastric fluid for at
least two hours.
The capsules readily release the contents upon shifting the pH of the solution
to ca. 6.8,
such as that of simulated intestinal fluid.
In another embodiment, the final enteric capsule composition provides films of
increased strength without substantially compromising film elasticity.
Moreover, films
made from the enteric soft capsule compositions as described herein are sealed
at
normal temperature range typically used for making traditional soft gel
capsules. In one
aspect, enteric soft capsules are made using a rotary die apparatus as
described in
U.S. Patent Nos. 5,459,983; 5,146,730; and 6,482,516.
Another embodiment described herein includes a process of manufacturing
enteric soft capsules comprising the pharmaceutical composition as described
herein.
The process includes preparing a gel mass composition comprising a film-
forming,
water-soluble polymer and an enteric acid-insoluble polymer and mixing with
appropriate plasticizers and solvent; casting the gel mass into films or
ribbons using
heat-controlled drums or surfaces; and manufacturing a soft capsule comprising
a
matrix fill using rotary die technology. The thickness of the films or ribbons
that form the
enteric capsule shell is from about 0.010 inches (--- 0.254 mm) to about 0.050
inches (---
1.27 mm), including all integers and fractions within the specified range. The
shell
54
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
thickness comprises about 0.010 inch (.-- 0.254 mm), about 0.015 inch (.--
0.381 mm),
about 0.02 in (--- 0.508 mm), about 0.03 in (--- 0.762 mm), about 0.04 in (-.
1.02 mm), or
about 0.05 in (.-- 1.27 mm). In one embodiment, the thickness is about 0.02
inches (.--
0.508 mm) to about 0.040 inches (.-- 1.02 mm). In one embodiment, the shell
thickness
is about 0.028 inches (.-- 0.711 mm).
In another embodiment, the shell thickness is about 0.033 inches (.-- 0.838
mm). In
another embodiment, the shell thickness is about 0.038 inches (.-- 0.965 mm).
In one embodiment described herein, the enteric soft capsule shell described
herein, encapsulates a matrix fill as described herein. In another embodiment
described
herein, the enteric soft capsule shell and encapsulated matrix fill comprises
an outer
dimension from about 2 oval to about 30 oval including all iterations of
capsule size
within the specified range (e.g., 2 oval, 3 oval, 4 oval, 5 oval, 6 oval, 7
oval, 8 oval, 10
oval, 12 oval, 16 oval, 20 oval, or 30 oval). In another embodiment described
herein, the
enteric soft capsule shell and encapsulated matrix fill comprises an outer
dimension
from about 2 round to about 28 round including all iterations of capsule size
within the
specified range (e.g., 2 round, 3 round, 4 round, 5 round, 6 round, 7 round, 8
round, 10
round, 12 round, 16 round, 20 round or 28 round). In another embodiment
described
herein, the enteric soft capsule shell and encapsulated matrix fill comprises
an outer
dimension from about 2 oblong to about 22 oblong including all iterations of
capsule
size within the specified range (e.g., 2 oblong, 3 oblong, 4 oblong, 5 oblong,
6 oblong, 7
oblong, 8 oblong, 10 oblong, 11, oblong, 12 oblong, 14 oblong, 16 oblong, 20
oblong, or
22 oblong). Dimension specifications of soft capsules and tablets are known to
those of
ordinary skill in the art. See Remington's Essentials of Pharmaceutics,
Pharmaceutical
Press Publishing Company, London, UK, 1st Edition, 2013.
The enteric soft capsules described herein can contain a matrix fill that is
liquid,
semi-solid, or solid. Capsules prepared as described herein can contain a
hydrophobic
solution or suspension, such as vegetable oils or shortening, or waxes, or
combinations
thereof. The matrix fill can be formulated to prevent interaction with the
capsule shell
components and release the pharmaceutical composition at a specified rate.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
One embodiment described herein, is a pharmaceutical composition comprising a
matrix fill formulation comprising any of the formulations shown in the Tables
or
Examples described herein. Any of the components of the formulations shown in
the
Tables or Examples can be increased, decreased, combined, recombined,
switched, or
removed to provide for a formulation comprising about 100% by weight.
In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition described herein provides a
dosage of fumarate ester for administration to a subject. The dosage form can
be
administered, for example, to a subject, or a subject in need thereof. In one
aspect, the
subject is a mammal, or a
55a
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
mammal in need thereof. In one aspect, the subject is a human, or human in
need thereof. In one
aspect, the human or human in need thereof is a medical patient. In one
aspect, the human
subject is a child (-0-9 years old) or an adolescent (-10-17 years old). In
one aspect, the subject
is from about 0 to about 9 years of age. In another aspect, the human subject
is from about 10
years to about 17 years of age. In another aspect, the human subject is over
17 years of age. In
another aspect, the human subject is an adult (>18 years of age).
The dosage form can be administered, for example, lx, 2x, 3x, 4x, 5x, 6x, or
even more
times per day. One or more dosage form can be administered, for example, for
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
days, or even longer. One or more dosage forms can be administered, for
example, for 1, 2, 3, 4
weeks, or even longer. One or more dosage forms can be administered, for
example, for 1, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 months, 1 year, 2, years, 3 years, 4 years, 5
years, over 5 years, a
decade, multiple decades, or even longer. One or more dosage forms can be
administered at a
regular interval until the subject or subject in need thereof, does not
require treatment,
prophylaxis, or amelioration of any disease or condition including but not
limited to, general
autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorders.
In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition described herein is
administered in
multiple dosages simultaneously. For example, two or more identical dosages
are administered
at one time. In another embodiment, two or more different dosages are
administered at one time.
Such dual or different simultaneous doses can be used to provide an effective
amount of the
pharmaceutical composition to a subject in need thereof.
In another embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition described herein may be
used to
treat, prevent, retard the progression of, delay the onset, ameliorate, reduce
the symptoms of, or
prophylaxis of general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorders.
Neurodegenerative
disorders, as used herein, include multiple sclerosis (MS), which includes
relapsing remitting
multiple sclerosis (RRMS), secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (SPMS),
primary
progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS), progressive relapsing multiple
sclerosis (PPvMS),
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis,
Alzheimer's disease,
Parkinson's disease, or any combination thereof.
In one embodiment described herein, other conditions, disorders, or diseases
are
controlled by administration of fumarate esters. The administration of
pharmaceutical
compositions comprising fumarate esters, as described herein, may be used for
treating,
56
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
preventing, retarding the progression of, delaying the onset, ameliorating,
reducing the
symptoms of, or prophylaxis of general autoimmune or neurodegenerative
disorders, including
but not limited to, acute dermatitis, adrenal leukodystrophy, AGE-induced
genome damage,
Alexander's disease, alopecia areata (totalis and universalis), Alper's
disease, Alzheimer's
disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, angina pectoris, arthritis, asthma,
autoimmune diseases,
balo concentric sclerosis, Behcet's syndrome, bullous pemphigoid, Canavan
disease, cardiac
insufficiency including left ventricular insufficiency, central nervous system
vasculitis, Charcot-
Marie-Tooth disease, childhood ataxia with central nervous system
hypomyelination, chronic
active (lupoid) hepatitis, chronic dermatitis, chronic idiopathic peripheral
neuropathy, chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease, contact dermatitis, Crohn's disease and
cutaneous Crohn's
disease, cutaneous lupus, cutaneous sarcoidosis, diabetic retinopathy,
fibromyalgia, graft versus
host disease, granuloma annulare, granulomas including annulare, Grave's
disease, Hashimoto 'S
thyroiditis, hepatitis C viral infection, herpes simplex viral infection,
human immunodeficiency
viral infection, Huntington's disease, inflammatory bowel disease, irritable
bowel disorder,
ischemia, juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus, Krabbe disease, lichen planus,
macular degeneration,
mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, monomelic amyotrophy, multiple sclerosis
(MS), myocardial
infarction, necrobiosis lipoidica, neurodegeneration with brain iron
accumulation,
neurodermatitis, neuromyelitis optica, neuropathic pain, neurosarcoidosis, NF-
1d3 mediated
diseases, optic neuritis, organ transplantation rejection, paraneoplastic
syndromes, Parkinson's
disease, Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, pemphigus, pernicious anemia, primary
lateral sclerosis,
progressive supranucicar palsy, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, pyodcrma
gangrcnosum, radicular
pain, radiculopathic pain, reperfusion injury, retinopathic pigmentosa,
rheumatoid arthritis (RA),
sarcoidosis, sarcoidosis, Schilder's disease, sciatic pain, sciatica,
Sjogren's syndrome, subacute
necrotizing myelopathy, such as polyarthritis, Susac's syndrome, systemic
lupus erythematosus
(SLE), tumors, transverse myelitis, ulcerative colitis, or Zellweger syndrome.
One embodiment described herein comprises a method for orally administering a
dosage
form that provides a total amount of fumarate ester of about 20 mg to about
1000 mg (e.g., ¨20-
1000 mg), including all integers and fractions within the specified range.
In one embodiment described herein, the fumarate ester (FAE) dosage form can
comprise, but is not limited to about 50 mg FAE, about 55 mg FAE, about 60 mg
FAE, about 65
mg FAE, about 70 mg FAE, about 75 mg FAE, about 80 mg FAE, about 85 mg FAE,
about 90
57
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
mg FAE, about 95 mg FAE. about 100 mg FAE, about 105 mg FAE, about 110 mg FAE,
about
115 mg FAE, about 120 mg FAE, about 125 mg FAE, about 130 mg FAE, about 135 mg
FAE,
about 140 mg FAE, about 145 mg FAE, about 150 mg FAE, about 155 mg FAE, about
160 mg
FAE, about 165 mg FAE, about 170 mg FAE, about 175 mg FAE, about 180 mg FAE,
about 185
mg FAE, about 190 mg FAE, about 195 mg FAE, about 200 mg FAE, about 205 mg
FAE, about
210 mg FAE, about 215 mg FAE, about 220 mg FAE, about 225 mg FAE, about 230 mg
FAE,
about 235 mg FAE, about 240 mg FAE, about 245 mg FAE, about 250 mg FAE, about
255 mg
FAE, about 260 mg FAE, about 265 mg FAE, about 270 mg FAE, about 275 mg FAE,
about 280
mg FAE, about 285 mg FAE, about 290 mg FAE, about 295 mg FAE, about 300 mg
FAE, about
305 mg FAE, about 310 mg FAE, about 315 mg FAE, about 320 mg FAE, about 325 mg
FAE,
about 330 mg FAE, about 335 mg FAE, about 340 mg FAE, about 345 mg FAE, about
350 mg
FAE, about 355 mg FAE, about 360 mg FAE, about 365 mg FAE, about 370 mg FAE,
about 375
mg FAE, about 380 mg FAE, about 385 mg FAE, about 390 mg FAE, about 395 mg
FAE, about
400 mg FAE, about 405 mg FAE, about 410 mg FAE, about 415 mg FAE, about 420 mg
FAE,
about 425 mg FAE, about 430 mg FAE, about 435 mg FAE, about 440 mg FAE, about
445 mg
FAE, about 450 mg FAE, about 455 mg FAE, about 460 mg FAE, about 465 mg FAE,
about 470
mg FAE, about 475 mg FAE, or about 480 mg FAE. In one embodiment, the
foregoing dosages
comprise a partial dose, e.g., including but not limited to one dose of a
twice or thrice daily
regimen. In another embodiment, any of the foregoing dosages comprise a total
daily dose.
In another embodiment described herein, the fumarate ester (FAE) dosage form
can
comprise, but is not limited to about 50 mg FAE, about 52 mg FAE, about 54 mg
FAE, about 56
mg FAE, about 58 mg FAE, about 60 mg FAE, about 62 mg FAE, about 64 mg FAE,
about 66
mg FAE, about 68 mg FAE, about 70 mg FAE, about 72 mg FAE, about 74 mg FAE,
about 76
mg FAR, about 78 mg FAR, about 80 mg FAR, about 82 mg FAR, about 84 mg FAR,
about 86
mg FAE, about 88 mg FAE, about 90 mg FAE, about 92 mg FAE, about 94 mg FAE,
about 96
mg FAE, about 98 mg FAE. about 100 mg FAE, about 102 mg FAE, about 104 mg FAE,
about
106 mg FAE, about 108 mg FAE, about 110 mg FAE, about 112 mg FAE, about 114 mg
FAE,
about 116 mg FAE, about 118 mg FAE, about 120 mg FAE, about 122 mg FAE, about
124 mg
FAE, about 126 mg FAE, about 128 mg FAE, about 130 mg FAE, about 132 mg FAE,
about 134
mg FAE, about 136 mg FAE, about 138 mg FAE, about 140 mg FAE, about 142 mg
FAE, about
144 mg FAE, about 146 mg FAE, about 148 mg FAE, about 150 mg FAE, about 152 mg
FAE,
58
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
about 154 mg FAE, about 156 mg FAE, about 158 mg FAE, about 160 mg FAE, about
162 mg
FAE, about 164 mg FAE, about 166 mg FAE, about 168 mg FAE, about 170 mg FAE,
about 172
mg FAE, about 174 mg FAE, about 176 mg FAE, about 178 mg FAE, about 180 mg
FAE, about
182 mg FAE, about 184 mg FAE, about 186 mg FAE, about 188 mg FAE, about 190 mg
FAE,
about 192 mg FAE, about 194 mg FAE, about 196 mg FAE, about 198 mg FAE, about
200 mg
FAE, about 202 mg FAE, about 204 mg FAE, about 206 mg FAE, about 208 mg FAE,
about 210
mg FAE, about 212 mg FAE, about 214 mg FAE, about 216 mg FAE, about 218 mg
FAE, about
220 mg FAE, about 222 mg FAE, about 224 mg FAE, about 226 mg FAE, about 228 mg
FAE,
about 230 mg FAE, about 232 mg FAE, about 234 mg FAE, about 236 mg FAE, about
238 mg
FAE, about 240 mg FAE, about 242 mg FAE, about 244 mg FAE, about 246 mg FAE,
about 248
mg FAE, about 250 mg FAE, about 252 mg FAE, about 254 mg FAE, about 256 mg
FAE, about
258 mg FAE, about 260 mg FAE, about 262 mg FAE, about 264 mg FAE, about 266 mg
FAE,
about 268 mg FAE, about 270 mg FAE, about 272 mg FAE, about 274 mg FAE, about
276 mg
FAE, about 278 mg FAE, about 280 mg FAE, about 282 mg FAE, about 284 mg FAE,
about 286
mg FAE, about 288 mg FAE, about 290 mg FAE, about 292 mg FAE, about 294 mg
FAE, about
296 mg FAE, about 298 mg FAE, about 300 mg FAE, about 302 mg FAE, about 304 mg
FAE,
about 306 mg FAE, about 308 mg FAE, about 310 mg FAE, about 312 mg FAE, about
314 mg
FAE, about 316 mg FAE, about 318 mg FAE, about 320 mg FAE, about 322 mg FAE,
about 324
mg FAE, about 326 mg FAE, about 328 mg FAE, about 330 mg FAE, about 332 mg
FAE, about
334 mg FAE, about 336 mg FAE, about 338 mg FAE, about 340 mg FAE, about 342 mg
FAE,
about 344 mg FAE, about 346 mg FAE, about 348 mg FAE, about 350 mg FAE, about
352 mg
FAE, about 354 mg FAE, about 356 mg FAE, about 358 mg FAE, about 360 mg FAE,
about 362
mg FAE, about 364 mg FAE, about 366 mg FAE, about 368 mg FAE, about 370 mg
FAE, about
372 mg FAE, about 374 mg FAE, about 376 mg FAE, about 378 mg FAE, about 380 mg
FAE,
about 382 mg FAE, about 384 mg FAE, about 386 mg FAE, about 388 mg FAE, about
390 mg
FAE, about 392 mg FAE, about 394 mg FAE, about 396 mg FAE, about 398 mg FAE,
about 400
mg FAE, about 402 mg FAE, about 404 mg FAE, about 406 mg FAE, about 408 mg
FAE, about
410 mg FAE, about 412 mg FAE, about 414 mg FAE, about 416 mg FAE, about 418 mg
FAE,
about 420 mg FAE, about 422 mg FAE, about 424 mg FAE, about 426 mg FAE, about
428 mg
FAE, about 430 mg FAE, about 432 mg FAE, about 434 mg FAE, about 436 mg FAE,
about 438
mg FAE, about 440 mg FAE, about 442 mg FAE, about 444 mg FAE, about 446 mg
FAE, about
59
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
448 mg FAE, about 450 mg FAE, about 452 mg FAE, about 454 mg FAE, about 456 mg
FAE,
about 458 mg FAE, about 460 mg FAE, about 462 mg FAE, about 464 mg FAE, about
466 mg
FAE, about 468 mg FAE, about 470 mg FAE, about 472 mg FAE, about 474 mg FAE,
about 476
mg FAE, about 478 mg FAE, or about 480 mg FAE. In one embodiment, the
foregoing dosages
comprise a partial dose, e.g., including but not limited to one dose of a
twice or thrice daily
regimen. In another embodiment, any of the foregoing dosages comprise a total
daily dose.
In one embodiment, the daily dosage is about 80 mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE
including all integers and fractions within the specified range. In another
embodiment, the daily
dosage is about 90 mg FAE to about 120 mg FAE, including all integers and
fractions within the
specified range. In another embodiment, the daily dosage is about 90 mg FAE to
about 240 mg
FAE, including all integers and fractions within the specified range. In
another embodiment, the
daily dosage is about 100 mg FAE to about 200 mg FAE, including all integers
and fractions
within the specified range. In another embodiment, the daily dosage is about
100 mg FAE to
about 240 mg FAE, including all integers and fractions within the specified
range. In another
embodiment, the daily dosage is about 180 mg FAE to about 240 mg FAE,
including all integers
and fractions within the specified range. In one embodiment, the daily dosage
is about 200 mg
FAE to about 240 mg FAE, including all integers and fractions within the
specified range. In
another embodiment, the daily dosage is about 360 mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE,
including all
integers and fractions within the specified range. In another embodiment, the
daily dosage is
about 400 mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE, including all integers and fractions
within the
specified range. In another embodiment, the daily dosage is about 480 mg FAE.
In another embodiment, the daily dosage form can comprise, but is not limited
to, a total
amount of FAE of about 80 mg FAE, about 82 mg FAE, about 84 mg FAE, about 86
mg FAE,
about 88 mg FAE, about 90 mg FAR, about 92 mg FAR, about 94 mg FAR, about 96
mg FAE,
about 98 mg FAE, about 100 mg FAE, about 102 mg FAE, about 104 mg FAE, about
106 mg
FAE, about 108 mg FAE, about 110 mg FAE, about 112 mg FAE, about 114 mg FAE,
about 116
mg FAE, about 118 mg FAE, about 120 mg FAE, about 122 mg FAE, about 124 mg
FAE, about
126 mg FAE, about 128 mg FAE, about 130 mg FAE, about 132 mg FAE, about 134 mg
FAE,
about 136 mg FAE, about 138 mg FAE, about 140 mg FAE, about 142 mg FAE, about
144 mg
FAE, about 146 mg FAE, about 148 mg FAE, about 150 mg FAE, about 152 mg FAE,
about 154
mg FAE, about 156 mg FAE, about 158 mg FAE, about 160 mg FAE, about 162 mg
FAE, about
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
164 mg FAE, about 166 mg FAE, about 168 mg FAE, about 170 mg FAE, about 172 mg
FAE,
about 174 mg FAE, about 176 mg FAE, about 178 mg FAE, about 180 mg FAE, about
182 mg
FAE, about 184 mg FAE, about 186 mg FAE, about 188 mg FAE, about 190 mg FAE,
about 192
mg FAE, about 194 mg FAE, about 196 mg FAE, about 198 mg FAE, about 200 mg
FAE, about
202 mg FAE, about 204 mg FAE, about 206 mg FAE, about 208 mg FAE, about 210 mg
FAE,
about 212 mg FAE, about 214 mg FAE, about 216 mg FAE, about 218 mg FAE, about
220 mg
FAE, about 222 mg FAE, about 224 mg FAE, about 226 mg FAE, about 228 mg FAE,
about 230
mg FAE, about 232 mg FAE, about 234 mg FAE, about 236 mg FAE, about 238 mg
FAE, about
240 mg FAE, about 242 mg FAE, about 244 mg FAE, about 246 mg FAE, about 248 mg
FAE,
about 250 mg FAE, about 252 mg FAE, about 254 mg FAE, about 256 mg FAE, about
258 mg
FAE, about 260 mg FAE, about 262 mg FAE, about 264 mg FAE, about 266 mg FAE,
about 268
mg FAE, about 270 mg FAE, about 272 mg FAE, about 274 mg FAE, about 276 mg
FAE, about
278 mg FAE, about 280 mg FAE, about 282 mg FAE, about 284 mg FAE, about 286 mg
FAE,
about 288 mg FAE, about 290 mg FAE, about 292 mg FAE, about 294 mg FAE, about
296 mg
FAE, about 298 mg FAE, about 300 mg FAE, about 302 mg FAE, about 304 mg FAE,
about 306
mg FAE, about 308 mg FAE, about 310 mg FAE, about 312 mg FAE, about 314 mg
FAE, about
316 mg FAE, about 318 mg FAE, about 320 mg FAE, about 322 mg FAE, about 324 mg
FAE,
about 326 mg FAE, about 328 mg FAE, about 330 mg FAE, about 332 mg FAE, about
334 mg
FAE, about 336 mg FAE, about 338 mg FAE, about 340 mg FAE, about 342 mg FAE,
about 344
mg FAE, about 346 mg FAE, about 348 mg FAE, about 350 mg FAE, about 352 mg
FAE, about
354 mg FAE, about 356 mg FAE, about 358 mg FAE, about 360 mg FAE, about 362 mg
FAE,
about 364 mg FAE, about 366 mg FAE, about 368 mg FAE, about 370 mg FAE, about
372 mg
FAE, about 374 mg FAE, about 376 mg FAE, about 378 mg FAE, about 380 mg FAE,
about 382
mg FAR, about 384 mg FAR, about 386 mg FAR, about 388 mg FAR, about 390 mg
FAR, about
392 mg FAE, about 394 mg FAE, about 396 mg FAE, about 398 mg FAE, about 400 mg
FAE,
about 402 mg FAE, about 404 mg FAE, about 406 mg FAE, about 408 mg FAE, about
410 mg
FAE, about 412 mg FAE, about 414 mg FAE, about 416 mg FAE, about 418 mg FAE,
about 420
mg FAE, about 422 mg FAE, about 424 mg FAE, about 426 mg FAE, about 428 mg
FAE, about
430 mg FAE, about 432 mg FAE, about 434 mg FAE, about 436 mg FAE, about 438 mg
FAE,
about 440 mg FAE, about 442 mg FAE, about 444 mg FAE, about 446 mg FAE, about
448 mg
FAE, about 450 mg FAE, about 452 mg FAE, about 454 mg FAE, about 456 mg FAE,
about 458
61
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
mg FAE, about 460 mg FAE, about 462 mg FAE, about 464 mg FAE, about 466 mg
FAE, about
468 mg FAE, about 470 mg FAE, about 472 mg FAE, about 474 mg FAE, about 476 mg
FAE,
about 478 mg FAE, or about 480 mg FAE. The daily dosage form can contain a
total amount of
fumarate ester effective for treatment of retarding the progression of,
prophylaxis of delaying the
onset of, amelioration of, or reducing symptoms of multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis or other
neurodegenerative disorders.
In one embodiment, the amount of fumarate ester can comprise about 80 mg to
about 500
mg (e.g., 80-500 mg) of fumarate ester, including all integers and fractions
within the specified
range. In one embodiment, the amount can comprise, but is not limited to,
about 80 mg to about
480 mg FAE, including all integers and fractions within the specified range.
In one embodiment,
the amount of fumarate ester can comprise about 80 mg FAE to about 85 mg FAE,
about 85 mg
FAE to about 90 mg FAE, about 85 mg FAE to about 100 mg FAE, about 90 mg FAE
to about
95 mg FAE, about 90 mg FAE to about 100 mg FAE, about 90 mg FAE, to about 105
mg FAE,
about 95 mg FAE to about 100 mg FAE, about 100 mg FAE to about 105 mg FAE,
about 100
mg FAE to about 110 mg FAE, about 100 mg FAE to about 115 mg FAE, about 100 mg
FAE to
about 120 mg FAE, about 100 mg FAE to about 200 mg FAE, about 100 mg FAE to
about 210
mg FAE, about 100 mg FAE to about 220 mg FAE, about 100 mg FAE to about 230 mg
FAE,
about 100 mg FAE to about 240 mg FAE, about 100 mg FAE to about 400 mg FAE,
about 100
mg FAE to about 420 mg FAE, about 100 mg FAE to about 430 mg FAE, about 100 mg
FAE to
about 440 mg FAE, about 100 mg FAE to about 460 mg FAE, about 100 mg FAE to
about 480
mg FAE, about 105 mg FAE to about 110 mg FAE, about 105 mg FAE to about 115 mg
FAE,
about 105 mg FAE to about 120 mg FAE, about 105 mg FAE to about 200 mg FAE,
about 105
mg FAE to about 210 mg FAE, about 105 mg FAE to about 220 mg FAE, about 105 mg
FAE to
about 230 mg FAR, about 105 mg FAR to about 240 mg FAR, about 105 mg FAR to
about 400
mg FAE, about 105 mg FAE to about 420 mg FAE, about 105 mg FAE to about 430 mg
FAE,
about 105 mg FAE to about 440 mg FAE, about 105 mg FAE to about 460 mg FAE,
about 105
mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE, about 110 mg FAE to about 115 mg FAE, about 110 mg
FAE to
about 120 mg FAE, about 110 mg FAE to about 200 mg FAE, about 110 mg FAE to
about 210
mg FAE, about 110 mg FAE to about 220 mg FAE, about 110 mg FAE to about 230 mg
FAE,
about 110 mg FAE to about 240 mg FAE, about 110 mg FAE to about 400 mg FAE,
about 110
mg FAE to about 420 mg FAE, about 120 mg FAE to about 430 mg FAE, about 110 mg
FAE to
62
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
about 440 mg FAE, about 110 mg FAE to about 460 mg FAE, about 110 mg FAE to
about 480
mg FAE, about 115 mg FAE to about 120 mg FAE, about 115 mg FAE to about 200 mg
FAE,
about 115 mg FAE to about 210 mg FAE, about 115 mg FAE to about 220 mg FAE,
about 115
mg FAE to about 230 mg FAE, about 115 mg FAE to about 240 mg FAE, about 115 mg
FAE to
about 400 mg FAE, about 115 mg FAE to about 420 mg FAE, about 115 mg FAE to
about 430
mg FAE, about 115 mg FAE to about 440 mg FAE, about 115 mg FAE to about 460 mg
FAE,
about 115 mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE, about 120 mg FAE to about 200 mg FAE,
about 120
mg FAE to about 210 mg FAE, about 120 mg FAE to about 220 mg FAE, about 120 mg
FAE to
about 230 mg FAE, about 120 mg FAE to about 240 mg FAE, about 120 mg FAE to
about 400
mg FAE, about 120 mg FAE to about 420 mg FAE, about 120 mg FAE to about 430 mg
FAE,
about 120 mg FAE to about 440 mg FAE, about 120 mg FAE to about 460 mg FAE,
about 120
mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE, about 200 mg FAE to about 210 mg FAE, about 200 mg
FAE to
about 220 mg FAE, about 200 mg FAE to about 230 mg FAE, about 200 mg FAE to
about 240
mg FAE, about 200 mg FAE to about 400 mg FAE, about 200 mg FAE to about 420 mg
FAE,
about 200 mg FAE to about 430 mg FAE, about 200 mg FAE to about 440 mg FAE,
about 200
mg FAE to about 460 mg FAE, about 200 mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE, about 210 mg
FAE to
about 220 mg FAE, about 210 mg FAE to about 230 mg FAE, about 210 mg FAE to
about 240
mg FAE, about 210 mg FAE to about 400 mg FAE, about 210 mg FAE to about 420 mg
FAE,
about 210 mg FAE to about 430 mg FAE, about 210 mg FAE to about 440 mg FAE,
about 210
mg FAE to about 460 mg FAE, about 210 mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE, about 220 mg
FAE to
about 230 mg FAE, about 220 mg FAE to about 240 mg FAE, about 220 mg FAE to
about 400
mg FAE, about 220 mg FAE to about 420 mg FAE, about 220 mg FAE to about 430 mg
FAE,
about 220 mg FAE to about 440 mg FAE, about 220 mg FAE to about 460 mg FAE,
about 220
mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE, about 230 mg FAE to about 240 mg FAR, about 230 mg
FAE to
about 400 mg FAE, about 230 mg FAE to about 420 mg FAE, about 230 mg FAE to
about 430
mg FAE, about 230 mg FAE to about 440 mg FAE, about 230 mg FAE to about 460 mg
FAE,
about 230 mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE, about 240 mg FAE to about 400 mg FAE,
about 240
mg FAE to about 420 mg FAE, about 240 mg FAE to about 430 mg FAE, about 240 mg
FAE to
about 440 mg FAE, about 240 mg FAE to about 460 mg FAE, about 240 mg FAE to
about 480
mg FAE, about 400 mg FAE to about 420 mg FAE, about 400 mg FAE to about 430 mg
FAE,
about 400 mg FAE to about 440 mg FAE, about 400 mg FAE to about 460 mg FAE,
about 400
63
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE, about 420 mg FAE to about 430 mg FAE, about 420 mg
FAE to
about 440 mg FAE, about 420 mg FAE to about 460 mg FAE, about 420 mg FAE to
about 480
mg FAE, about 430 mg FAE to about 440 mg FAE, about 430 mg FAE to about 460 mg
FAE,
about 430 mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE, about 440 mg FAE to about 460 mg FAE,
about 440
mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE, or about 460 mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE, including
all
integers and fractions within the specified ranges.
In another embodiment, the effective amount of fumaratc ester can comprise,
but is not
limited to, about 70 mg FAE to about 480 mg FAE (e.g., 70-480 mg FAE),
including all integers
and fractions within the specified range. In one aspect, the daily effective
amount can comprise,
but is not limited to, an effective amount of about 70 mg to about 90 mg FAE,
about 75 mg to
about 95 mg FAE, about 80 mg to about 100 mg FAE, about 85 mg to about 105 mg
FAE, about
90 mg to about 105 mg FAE, about 95 mg to about 108 mg FAE, about 100 mg to
about 110 mg
FAE, about 100 mg to about 115 mg FAE, about 100 mg to about 120 mg FAE, about
105 mg to
about 110 mg FAE, about 105 mg to about 115 mg FAE, about 105 mg to about 120
mg FAE,
about 105 mg to about 125 mg FAE, about 110 mg to about 120 mg FAE, about 110
mg to about
125 mg FAE, about 115 mg FAE to about 120 mg FAE, about 115 mg FAE to about
125 mg
FAE, about 100 mg to about 200 mg FAE, about 105 mg to about 210 mg FAE, about
110 mg to
about 220 mg FAE, about 115 mg FAE to about 230 mg FAE, about 120 mg to about
240 mg
FAE, about 200 mg to about 220 mg FAE, about 210 mg to about 240 mg FAE, about
220 mg to
about 250 mg FAE, about 400 mg to about 420 mg FAE; about 400 mg to about 430
mg FAE,
about 400 mg to about 440 mg FAE, about 400 mg to about 450 mg FAE, about 400
mg to about
460 mg FAE, about 400 mg to about 480 mg FAE, about 410 mg to about 420 mg
FAE; about
410 mg to about 430 mg FAE, about 410 mg to about 440 mg FAE, about 410 mg to
about 450
mg FAR, about 410 mg to about 460 mg FAR, about 410 mg to about 480 mg FAR,
about 420
mg to about 430 mg FAE, about 420 mg to about 440 mg FAE, about 420 mg to
about 450 mg
FAE, about 420 mg to about 460 mg FAE, about 420 mg to about 480 mg FAE, about
425 mg to
about 430 mg FAE, about 425 mg to about 440 mg FAE; about 425 mg to about 450
mg FAE,
about 425 mg to about 460 mg FAE, about 425 mg to about 480 mg FAE, about 430
mg to about
440 mg FAE, about 430 mg to about 450 mg FAE, about 430 mg to about 460 mg
FAE, about
430 mg to about 480 mg FAE, about 440 mg to about 450 mg FAE, about 440 mg to
about 460
64
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
mg FAE, or about 440 mg to about 480 mg FAE, including all integers and
fractions within the
specified ranges.
In one embodiment described herein, the FAE may comprise a solution or
suspension
having an active pharmaceutical ingredient load (e.g., drug load) of about 1%
to about 65% by
weight, including all integers and fractions within the specified range. In
one embodiment, the
drug load can comprise about 12% to about 16% by weight, including all
integers and fractions
within the specified range. In one embodiment, the drug load can comprise
about 24% to about
32% by weight, including all integers and fractions within the specified
range. In one
embodiment, the drug load can comprise about 48% to about 64% by weight,
including all
integers and fractions within the specified range. In one embodiment, the drug
load can
comprise about 1%, about 2%, about 2.5%, about 5%, about 10%, about 15%, about
20%, about
25%, about 30%, about 35%, about 40%, about 45%, about 40%, about 50%, about
60%, about
65%, or even higher, by weight. In one embodiment, the drug load can comprise
13.3%, 14.0%,
14.4%, 14.7%, 15.3%, 16.0%, 26.7%, 28.0%, 28.8%, 29.3%, 30.7%, 32.0%, 53.3%,
56.0%,
57.6%, 58.7%, 61.3%, or 64.0%, each by weight. In one aspect, the drug load is
about 20% by
weight. In one aspect, the drug load is about 30% by weight. In one aspect,
the drug load is
about 40% by weight. In one aspect, the drug load is about 50% by weight. In
one aspect, the
drug load is about 60% by weight. In one aspect, the drug load is about 28% by
weight. In one
aspect, the drug load is about 32% by weight. In one aspect, the drug load is
about 44% by
weight. In one embodiment, the drug load is about 48% by weight. In one
embodiment, the
drug load is about 56% by weight.
In one embodiment described herein, pharmaceutical composition can comprise
about 0.4
mmol FAE to about 4.0 mmol FAE, including all integers and fractions within
the specified
range. In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition comprises 0.4 mmol
FAR, 0.5 mmol
FAE, 0.6 mmol FAE, 0.7 mmol FAE, 0.8 mmol FAE, 0.9 mmol FAE, 1.0 mmol FAE, 1.1
mmol
FAE, 1.2 mmol FAE, 1.3 mmol FAE, 1.4 mmol FAE, 1.5 mmol FAE, 1.6 mmol FAE, 1.7
mmol
FAE, 1.8 mmol FAE, 1.9 mmol FAE, 2.0 mmol FAE, 2.1 mmol FAE, 2.2 mmol FAE, 2.3
mmol
FAE, 2.4 mmol FAE, 2.5 mmol FAE, 2.6 mmol FAE, 2.7 mmol FAE, 2.8 mmol FAE, 2.9
mmol
FAE, 3.0 mmol FAE, 3.1 mmol FAE, 3.2 mmol FAE, 3.3 mmol FAE, 3.4 mmol FAE, 3.5
mmol
FAE, 3.6 mmol FAE, 3.7 mmol FAE, 3.8 mmol FAE, 3.9 mmol FAE, or 4.0 mmol FAE.
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
One embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical dosage form comprising any
one
of the pharmaceutical compositions described herein for administration to a
subject having a
general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to
multiple
sclerosis, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of one or more
fumarate esters, wherein
the administration is sufficient to achieve a reduction of about 0.224
annualized relapse rate
relative to baseline in the subject without substantially inducing one or more
of flushing,
abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea in the subject; and wherein the
administration does not
require titration of the pharmaceutical composition.
Another embodiment described herein is a method for treating, retarding the
progression
of, prophylaxis of, delaying the onset of, ameliorating, or reducing the
symptoms of multiple
sclerosis or psoriasis comprising the administration of a therapeutically
effective amount of one
or more fumarate esters comprising any one of the pharmaceutical compositions
described herein
to a subject with multiple sclerosis, wherein the administration is sufficient
to achieve a
reduction of about 0.224 annualized relapse rate relative to baseline in the
subject without
substantially inducing one or more of flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and
nausea in the
subject. In one aspect, after administration of any one the pharmaceutical
compositions
described herein, the subject experiences one or more of flushing, abdominal
pain, diarrhea, and
nausea at a rate of less than about 10%. In another aspect, the endpoint may
be less than about
2%, about 5%, about 10%, about 15%, about 20%, about 25%, about 30%, about
35%, about
.. 45%, about 50%, or greater than about 50%.
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition and a
method for
treating, retarding the progression of, delaying the onset of, prophylaxis of,
amelioration of, or
reducing the symptoms of a general autoimmune or neurodegenerative disorder,
including but
not limited to multiple sclerosis or psoriasis, the method comprising the
administration of a
.. therapeutically effective amount of one or more fumarate esters comprising
any one of the
pharmaceutical compositions described herein to a subject in need thereof,
wherein the subject
achieves a reduction of annualized relapse rate relative to baseline without
substantially
experiencing one or more of flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea. In
another aspect,
the endpoint may be less than about 2%, about 5%, about 10%, about 15%, about
20%, about
25%, about 30%, about 35%, about 45%, about 50%, or greater than about 50%,
relative to
baseline.
66
Endpoints for treating multiple sclerosis using fumarate esters are described
in the TECFIDERA Prescribing Information (Biogen ldec Inc.), and U.S. Patent
Application Publication No. US 2014/0163100. Other pharmaceutical compositions
and methods for treating multiple sclerosis are described in U.S. Patent Nos.
6,509,376; 7,320,999; 7,619,001; 7,803,840; 8,399,514; 8,524,773; and
8,759,393,
and International Patent Application Publication No. WO 2013/119677.
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition for
administration to a subject with multiple sclerosis or psoriasis comprising a
therapeutically effective amount of one or more fumarate esters, wherein the
subject
achieves a reduction of annualized relapse rate relative to baseline without
substantially experiencing one or more of flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea,
and
nausea. In one aspect the reduction of annualized relapse rate may be about
1%,
about 2%, about 5%, about 10%, about 15%, about 20%, about 25%, about 30%,
about 35%, about 45%, about 50%, or greater than about 50%.
For the treatment of multiple sclerosis (e.g., relapsing forms of MS such as
RRMS), the dosage form administered to the subject or subject in need thereof
comprises an enteric soft capsule comprising micronized solid particles of a
fumarate
ester as the only active ingredient or in combination with one or more NSAIDS
(e.g.,
AspirinTM) or leukotriene receptor antagonists (e.g., montelukast or
zafirlukast). In one
aspect, the effective amount of fumarate ester is about 360 mg to about 480 mg
FAE
per day and the subjects can receive the effective amount, e.g., about 80 mg
to about
120 mg FAE quater in die (QID), in the form of four capsules a day, to be
taken orally,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another
aspect, the
effective amount is about 80 mg to about 110 mg FAE quater in die (QID). In
another
aspect, the effective amount is about 90 mg to about 107 mg FAE quater in die
(QID).
In another aspect, the effective amount is about 102 mg to about 115 mg FAE
quater in
die (QID). In one aspect, the effective amount of fumarate ester is about 360
mg to
67
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
about 480 mg FAE per day and the subjects can receive the effective amount,
e.g.,
about 180 mg to about 240 mg FAE bis in die (BID), in the form of two capsules
a day,
to be taken orally, including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges. In
another aspect, the effective amount is about 205 mg to about 230 mg FAE BID.
In a
further aspect, the effective amount is about 210 mg to about 225 mg FAE BID,
or
about 215 mg to 220 mg FAE BID. In another aspect, the effective amount of FAE
is
67a
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
about 360 mg to about 480 mg FAE per day and the subjects can receive the
effective amount,
e.g., about 360 to about 480 mg FAE quaque die (QD), in the form of one
capsule a day, to be
taken orally, including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges.
In another embodiment, for the treatment of multiple sclerosis the daily
effective amount
of FAE is from 80 mg FAE to 85 mg FAE, 80 mg FAE to 90 mg FAE, 80 mg FAE to 95
mg
FAE, 85 mg FAE to 100 mg FAE, 85 mg FAE to 90 mg FAE, 85 mg FAE to 95 mg FAE,
90 mg
FAE to 100 mg FAE, 90 mg FAE to 105 mg FAE, 90 mg FAE to 95 mg FAE, 95 mg FAE
to
100 mg FAE, 95 mg FAE to 105 mg FAE, 95 mg FAE to 110 mg FAE, 100 mg FAE to
105 mg
FAE, 100 mg FAE to 110 mg FAE, 100 mg FAE to 115 mg FAE, 105 mg FAE to 110 mg
FAE,
105 mg FAE to 115 mg FAE, 105 mg FAE to 120 mg FAE, 110 mg FAE to 115 mg FAE,
110
mg FAE to 120 mg FAE, 110 mg FAE to 125 mg FAE, 115 mg FAE to 120 mg FAE, 115
mg
FAE to 125 mg FAE, 115 mg FAE to 130 mg FAE, 120 mg FAE to 125 mg FAE, 120 mg
FAE
to 130 mg FAE, 120 mg FAE to 135 mg FAE, 125 mg FAE to 130 mg FAE, 125 mg FAE
to 135
mg FAE, 125 mg FAE to 140 mg FAE, 130 mg FAE to 135 mg FAE, 130 mg FAE to 140
mg
FAE, 130 mg FAE to 145 mg FAE, 135 mg FAE to 140 mg FAE, 135 mg FAE to 145 mg
FAE,
135 mg FAE to 150 mg FAE, 140 mg FAE to 145 mg FAE, 140 mg FAE to 150 mg FAE,
140
mg FAE to 155 mg FAE, 145 mg FAE to 150 mg FAE, 145 mg FAE to 155 mg FAE, 145
mg
FAE to 160 mg FAE, 150 mg FAE to 155 mg FAE, 150 mg FAE to 160 mg FAE, 150 mg
FAE
to 165 mg FAE, 155 mg FAE to 160 mg FAE, 155 mg FAE to 165 mg FAE, 155 mg FAE
to 170
mg FAE, 160 mg FAE to 165 mg FAE, 160 mg FAE to 170 mg FAE, 160 mg FAE to 175
mg
FAE, 165 mg FAE to 170 mg FAE, 165 mg FAE to 175 mg FAE, 165 mg FAE to 180 mg
FAE,
170 mg FAE to 175 mg FAE, 170 mg FAE to 180 mg FAE, 170 mg FAE to 185 mg FAE,
175
mg FAE to 180 mg FAE, 175 mg FAE to 185 mg FAE, 175 mg FAE to 190 mg FAE, 180
mg
FAE to 185 mg FAE, 180 mg FAE to 190 mg FAE, 180 mg FAE to 195 mg FAR, 185 mg
FAR
to 190 mg FAE, 185 mg FAE to 195 mg FAE, 185 mg FAE to 200 mg FAE, 190 mg FAE
to 195
mg FAE, 190 mg FAE to 200 mg FAE, 190 mg FAE to 205 mg FAE, 195 mg FAE to 200
mg
FAE, 195 mg FAE to 205 mg FAE, 195 mg FAE to 210 mg FAE, 200 mg FAE to 205 mg
FAE,
200 mg FAE to 210 mg FAE, 200 mg FAE to 215 mg FAE, 205 mg FAE to 210 mg FAE,
205
mg FAE to 215 mg FAE, 205 mg FAE to 220 mg FAE, 210 mg FAE to 215 mg FAE, 210
mg
FAE to 220 mg FAE, 210 mg FAE to 225 mg FAE, 215 mg FAE to 220 mg FAE, 215 mg
FAE
to 225 mg FAE, 215 mg FAE to 230 mg FAE, 220 mg FAE to 225 mg FAE, 220 mg FAE
to 230
68
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
mg FAE, 220 mg FAE to 235 mg FAE, 225 mg FAE to 230 mg FAE, 225 mg FAE to 235
mg
FAE, 225 mg FAE to 240 mg FAE, 230 mg FAE to 235 mg FAE, 230 mg FAE to 240 mg
FAE,
230 mg FAE to 245 mg FAE, 235 mg FAE to 240 mg FAE, 235 mg FAE to 245 mg FAE,
235
mg FAE to 250 mg FAE, 240 mg FAE to 245 mg FAE, 240 mg FAE to 250 mg FAE, 240
mg
FAE to 255 mg FAE, 245 mg FAE to 250 mg FAE, 245 mg FAE to 255 mg FAE, 245 mg
FAE
to 260 mg FAE, 250 mg FAE to 255 mg FAE, 250 mg FAE to 260 mg FAE, 250 mg FAE
to 265
mg FAE, 255 mg FAE to 260 mg FAE, 255 mg FAE to 265 mg FAE, 255 mg FAE to 270
mg
FAE, 260 mg FAE to 265 mg FAE, 260 mg FAE to 270 mg FAE, 260 mg FAE to 275 mg
FAE,
265 mg FAE to 270 mg FAE, 265 mg FAE to 275 mg FAE, 265 mg FAE to 280 mg FAE,
270
mg FAE to 275 mg FAE, 270 mg FAE to 280 mg FAE, 270 mg FAE to 285 mg FAE, 275
mg
FAE to 280 mg FAE, 275 mg FAE to 285 mg FAE, 275 mg FAE to 290 mg FAE, 280 mg
FAE
to 285 mg FAE, 280 mg FAE to 290 mg FAE, 280 mg FAE to 295 mg FAE, 285 mg FAE
to 290
mg FAE, 285 mg FAE to 295 mg FAE, 285 mg FAE to 300 mg FAE, 290 mg FAE to 295
mg
FAE, 290 mg FAE to 300 mg FAE, 290 mg FAE to 305 mg FAE, 295 mg FAE to 300 mg
FAE,
295 mg FAE to 305 mg FAE, 295 mg FAE to 310 mg FAE, 300 mg FAE to 305 mg FAE,
300
mg FAE to 310 mg FAE, 300 mg FAE to 315 mg FAE, 305 mg FAE to 310 mg FAE, 305
mg
FAE to 315 mg FAE, 305 mg FAE to 320 mg FAE, 310 mg FAE to 315 mg FAE, 310 mg
FAE
to 320 mg FAE, 310 mg FAE to 325 mg FAE, 315 mg FAE to 320 mg FAE, 315 mg FAE
to 325
mg FAE, 315 mg FAE to 330 mg FAE, 320 mg FAE to 325 mg FAE, 320 mg FAE to 330
mg
.. FAE, 320 mg FAE to 335 mg FAE, 325 mg FAE to 330 mg FAE, 325 mg FAE to 335
mg FAE,
325 mg FAE to 340 mg FAE, 330 mg FAE to 335 mg FAE, 330 mg FAE to 340 mg FAE,
330
mg FAE to 345 mg FAE, 335 mg FAE to 340 mg FAE, 335 mg FAE to 345 mg FAE, 335
mg
FAE to 350 mg FAE, 340 mg FAE to 345 mg FAE, 340 mg FAE to 350 mg FAE, 340 mg
FAE
to 355 mg FAR, 345 mg FAR to 350 mg FAR, 345 mg FAR to 355 mg FAR, 345 mg FAR
to 360
mg FAE, 350 mg FAE to 355 mg FAE, 350 mg FAE to 360 mg FAE, 350 mg FAE to 365
mg
FAE, 355 mg FAE to 360 mg FAE, 355 mg FAE to 365 mg FAE, 355 mg FAE to 370 mg
FAE,
360 mg FAE to 365 mg FAE, 360 mg FAE to 370 mg FAE, 360 mg FAE to 375 mg FAE,
365
mg FAE to 370 mg FAE, 365 mg FAE to 375 mg FAE, 365 mg FAE to 380 mg FAE, 370
mg
FAE to 375 mg FAE, 370 mg FAE to 380 mg FAE, 370 mg FAE to 385 mg FAE, 375 mg
FAE
to 380 mg FAE, 375 mg FAE to 385 mg FAE, 375 mg FAE to 390 mg FAE, 380 mg FAE
to 385
mg FAE, 380 mg FAE to 390 mg FAE, 380 mg FAE to 395 mg FAE, 385 mg FAE to 390
mg
69
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
FAE, 385 mg FAE to 395 mg FAE, 385 mg FAE to 400 mg FAE, 390 mg FAE to 395 mg
FAE,
390 mg FAE to 400 mg FAE, 390 mg FAE to 405 mg FAE, 395 mg FAE to 400 mg FAE,
395
mg FAE to 405 mg FAE, 395 mg FAE to 410 mg FAE, 400 mg FAE to 405 mg FAE, 400
mg
FAE to 410 mg FAE, 400 mg FAE to 415 mg FAE, 405 mg FAE to 410 mg FAE, 405 mg
FAE
to 415 mg FAE, 405 mg FAE to 420 mg FAE, 410 mg FAE to 415 mg FAE, 410 mg FAE
to 420
mg FAE, 410 mg FAE to 425 mg FAE, 415 mg FAE to 420 mg FAE, 415 mg FAE to 425
mg
FAE, 415 mg FAE to 430 mg FAE, 420 mg FAE to 425 mg FAE, 420 mg FAE to 430 mg
FAE,
420 mg FAE to 435 mg FAE, 425 mg FAE to 430 mg FAE, 425 mg FAE to 435 mg FAE,
425
mg FAE to 440 mg FAE, 430 mg FAE to 435 mg FAE, 430 mg FAE to 440 mg FAE, 430
mg
FAE to 445 mg FAE, 435 mg FAE to 440 mg FAE, 435 mg FAE to 445 mg FAE, 435 mg
FAE
to 450 mg FAE, 440 mg FAE to 445 mg FAE, 440 mg FAE to 450 mg FAE, 440 mg FAE
to 455
mg FAE, 445 mg FAE to 450 mg FAE, 445 mg FAE to 455 mg FAE, 445 mg FAE to 460
mg
FAE, 450 mg FAE to 455 mg FAE, 450 mg FAE to 460 mg FAE, 450 mg FAE to 465 mg
FAE,
455 mg FAE to 460 mg FAE, 455 mg FAE to 465 mg FAE, 455 mg FAE to 470 mg FAE,
460
mg FAE to 465 mg FAE, 460 mg FAE to 470 mg FAE, 460 mg FAE to 475 mg FAE, 465
mg
FAE to 470 mg FAE, 465 mg FAE to 475 mg FAE, 465 mg FAE to 480 mg FAE, 470 mg
FAE
to 475 mg FAE, 470 mg FAE to 480 mg FAE, or 475 mg FAE to 480 mg FAE. The
effective
amount can be administered in one or more doses, once, twice, three, four, or
more times per
day.
For the treatment of autoimmune disorders, including multiple sclerosis and
psoriasis, the
dosage form administered to the subject or subject in need thereof comprises
an enteric soft
capsule comprising micronized solid particles of a fumarate ester as the only
active ingredient or
in combination with one or more NSA1DS (e.g., aspirin) or leukotriene receptor
antagonists (e.g.,
montelukast or zafirlukast). In one aspect, the effective amount of fumarate
ester is about 360
mg to about 480 mg FAE per day and the subjects can receive the effective
amount, e.g., about
80 mg to about 120 mg FAE quater in die (QID), in the form of four capsules a
day, to be taken
orally, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In
one aspect, the
effective amount of fumarate ester is about 360 mg to about 480 mg FAE per day
and the
subjects can receive the effective amount, e.g., about 180 mg to about 240 mg
FAE bis in die
(BID), in the form of two capsules a day, to be taken orally, including all
integers and fractions
within the specified ranges. In another aspect, the effective amount of
fumarate ester is about
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
360 mg to about 480 mg FAE per day and the subjects can receive the effective
amount, e.g.,
about 360 mg to about 480 mg FAE quaque die (QD), in the form of one capsule a
day, to be
taken orally, including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges.
Fumarate esters can cause flushing and gastrointestinal (GI) side effects in
some subjects.
While the side effects generally subside soon after subjects start on the
treatment, in one aspect
the starting dose is about 80 mg to about 120 mg FAE BID orally for the first
7 days, including
all integers and fractions within the specified range. The dose is increased
to the effective dose
of about 180 mg to about 240 mg FAE BID (e.g., about 360 mg to about 480 mg
FAE per day),
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another
aspect, the starting
.. dose is about 180 mg to about 240 mg FAE BID orally for the first 7 days,
including all integers
and fractions within the specified ranges. The dose is increased to the
effective dose of about
360 mg to about 480 mg FAE QD (e.g., about 360 mg to about 480 mg FAE per
day), including
all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. For those subjects who
experience GI or
flushing side effects, taking FAE with food can improve tolerability. In one
aspect described
herein, FAE is administered after a meal. In another aspect described herein,
FAE is
administered after a high-fat meal to reduce or ameliorate the one or more
symptoms of flushing,
abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea in the subject.
In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical compositions described herein can be
administered without titration of the pharmaceutical composition.
In one aspect, the
pharmaceutical compositions can be administered without titration and without
substantially
inducing one or more of flushing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea in the
subject.
In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition described herein does not
elicit the
flushing and gastrointestinal side effects when the dose is about 80 mg to
about 120 mg FAE
quater in die (QM) (e.g., 360 mg to about 480 mg FAE per day), including all
integers and
.. fractions within the specified ranges. In another embodiment, the
pharmaceutical composition
described herein does not elicit the flushing and gastrointestinal side
effects when the dose is
about 180 mg to about 240 mg FAE bis in die (BID) (e.g., 360 mg to about 480
mg FAE per
day), including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In one
embodiment, the
pharmaceutical composition described herein does not elicit the flushing and
gastrointestinal side
effects when the dose is about 360 mg to about 480 mg FAE quaque die (QD)
(e.g., 360 mg to
about 480 mg FAE per day), including all integers and fractions within the
specified ranges.
71
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition described herein does not
elicit
flushing and gastrointestinal side effects when the effective amount is about
180 mg FAE quaque
die (QD) (e.g., 180 mg FAE per day). In another embodiment, the pharmaceutical
composition
described herein does not elicit the flushing and gastrointestinal side
effects when the effective
amount is about 180 mg to about 240 mg FAE quaque die (QD) (e.g., 180 mg to
about 240 mg
FAE per day), including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges. In another
embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition described herein does not elicit
the flushing and
gastrointestinal side effects when the effective amount is about 360 mg to
about 480 mg FAE
quaque die (QD) (e.g., 360 mg to about 480 mg FAE per day), including all
integers and
fractions within the specified ranges.
In another aspect, the administration of about 325 mg of non-enteric coated
aspirin 30-
minutes prior to FAE dosing can reduce the occurrence and severity of
flushing. In one aspect,
subjects who experience flushing with gastrointestinal side effects may reduce
the dose to about
100 mg to about 120 mg FAE BID temporarily, including all integers and
fractions within the
specified range. Within a month, the effective dose of about 180 mg to about
240 mg FAE BID
should be resumed, including all integers and fractions within the specified
range. In another
aspect, subjects who experience flushing with gastrointestinal side effects
may reduce the dose to
about 180 mg to about 240 mg FAE BID temporarily, including all integers and
fractions within
the specified range. Within a month, the effective dose of about 360 mg to
about 480 mg FAE
QD should be resumed, including all integers and fractions within the
specified range.
In one embodiment, a subject administered a FAE pharmaceutical composition
described
herein may take one or more non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID)
before (for
example, about 10 minutes to an hour, e.g., about 30 minutes before) taking a
FAE
pharmaceutical composition described herein. In one embodiment, the subject
administered a
dosage form takes the one or more non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to
reduce flushing. In
one embodiment, the one or more non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs comprise
aspirin,
ibuprofen, naproxen, ketoprofen, celecoxib, or combinations thereof. The one
or more non-
steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be administered in an amount of about 50
mg to about 500
mg before taking the dosage form described herein. In one embodiment, a
subject takes 325 mg
aspirin about 30-minutes before taking the dosage forms described herein.
72
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
In another embodiment, a subject administered a FAE pharmaceutical composition
described herein may take one or more leukotriene receptor antagonists. In
another embodiment,
a subject administered a FAE pharmaceutical composition described herein may
take 10 to 20
mg of montelukast (Singulairg) or zafirlukast (Accolate).
In another embodiment described herein, subjects are orally administered one
or more
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs before taking the dosage form described
herein exhibit the
same pharmacokinetic properties (e.g., Cmax and AUC) as subjects orally
administered the dosage
form described herein without administering one or more non-steroidal anti-
inflammatory drugs
(e.g., aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, ketoprofen, celecoxib, or combinations
thereof). The NSAID
can be administered about 30-minutes before taking the dosage form described
herein.
In one embodiment described herein, a subject is administered one or more soft
capsules
containing about 80 mg to about 480 mg FAE, one or more times daily for a
total daily dose of
about 360 mg to about 480 mg, including all integers and fractions within the
specified range. In
one aspect, the pharmaceutical composition comprises an immediate release,
delayed release,
.. controlled release, or extended release formulation of a fumarate ester. In
one embodiment, the
matrix is a controlled release matrix. In another embodiment, the matrix is a
delayed release
matrix. In another embodiment, the matrix is an extended release matrix. In
another aspect, the
pharmaceutical composition comprises an enteric soft capsule.
In one embodiment, subjects having a general autoimmune or neurodegenerative
disorder, including but not limited to multiple sclerosis or psoriasis, are
administered one or
more enteric soft capsules containing about 80 mg to about 120 mg FAE, twice-
daily for a total
daily dose of about 360 mg to about 480 mg, wherein the enteric soft capsule
comprises solid
microparticles of FAE in a matrix, including all integers and fractions within
the specified
ranges. In one embodiment, the matrix is a controlled release matrix. In
another embodiment,
the matrix is a delayed release matrix. In another embodiment, the matrix is
an extended release
matrix.
In one embodiment, subjects having a general autoimmune or neurodegenerative
disorder, including but not limited to multiple sclerosis or psoriasis, are
administered one or
more enteric soft capsules containing about 180 mg to about 240 mg FAE, twice-
daily for a total
daily dose of about 360 mg to about 480 mg, wherein the enteric soft capsule
comprises solid
microparticles of FAE in a matrix, including all integers and fractions within
the specified
73
ranges. In one embodiment, the matrix is a controlled release matrix. In
another
embodiment, the matrix is a delayed release matrix. In another embodiment, the
matrix is an extended release matrix.
In one embodiment, subjects having a general autoimmune or
neurodegenerative disorder, including but not limited to multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, are administered an enteric soft capsule containing about 360 mg to
about
480 mg FAE, once daily for a total daily dose of about 360 mg to about 480 mg,
wherein the enteric soft capsule comprises solid microparticles of FAE in a
matrix,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In one
embodiment, the
matrix is a controlled release matrix. In another embodiment, the matrix is a
delayed
release matrix. In another embodiment, the matrix is an extended release
matrix.
Pharmacokinetics of fumarate esters, particularly DMF, are described by Sheikh
et al., Clinical Therapeutics 35(10): 1582-1594 (2013).
In one aspect, the pharmaceutical composition described herein is provided in
a dosage form containing a total amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a
fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage exhibit a mean plasma
monomethyl fumarate Cniõ ranging from about 0.2 mg/L to about 2.41 mg/L,
including
all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about 80
mg to
about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage
exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Cmõ ranging from about 0.4 mg/L to about 2.41
mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In
another
aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount
of
about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered
the
dosage exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Cmõ ranging from about 1.5
mg/L to about 3.4 mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the
specified ranges.
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total
amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Cmõ ranging
from about 1.03 mg/L to about 2.41
74
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In
another aspect,
the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of
about 80 mg
to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage
exhibit
a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Cmõ ranging from about 0.4 mg/L to
74a
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
about 0.75 mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges. In another
aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount
of about 80 mg to
about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage
exhibit a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about 0.76 mg/L to about 1.03 mg/L,
including
all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another aspect, the
composition is
provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about 80 mg to about
120 mg of a
fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage exhibit a mean plasma
monomethyl
fumarate C. ranging from about 1.04 mg/L to about 1.75 mg/L, including all
integers and
fractions within the specified ranges. In another aspect, the composition is
provided in a dosage
.. form containing a total amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate
ester, wherein
subjects administered the dosage exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C.
ranging
from about 1.75 mg/L to about 2.41 mg/L, including all integers and fractions
within the
specified ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage
form containing a
total amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein
subjects administered
the dosage exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Cmax of at least 0.4
mg/L, at least 0.5
mg/L, at least 0.6 mg/L, at least 0.7 mg/L, at least 0.8 mg/L, at least 0.9
mg/L, at least 1 mg/L, at
least 1.1 mg/L, at least 1.2 mg/L, at least 1.3 mg/L, at least 1.4 mg/L, at
least 1.5 mg/L, at least
1.6 mg/L, at least 1.7 mg/L, at least 1.8 mg/L, at least 1.9 mg/L, at least 2
mg/L, at least 2.1
mg/L, at least 2.2 mg/L, at least 2.3 mg/L, at least 2.4 mg/L, at least 2.5
mg/L, at least 2.6 mg/L,
at least 2.7 mg/L, at least 2.8 mg/L, at least 2.9 mg/L, at least 3 mg/L, at
least 3.1 mg/L, at least
3.2 mg/L, at least 3.3 mg/L, or at least 3.4 mg/L.
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount
of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage
form four times daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCoverall
ranging from
.. about 1.0 h-mg/L to about 15.2 h-mg/L, including all integers and fractions
within the specified
ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form
containing a total
amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the
dosage form four times daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate
AUCoveran ranging
from about 2.01 h=mg/L to about 5.2 irmg/L, including all integers and
fractions within the
specified ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage
form containing a
total amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein
subjects administered
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
the dosage form four times daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate
AUC0,eian ranging
from about 1.0 h-mg/L to about 5.2 h-mg/L, including all integers and
fractions within the
specified ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage
form containing a
total amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein
subjects administered
the dosage form four times daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate
AUCmeraii ranging
from about 11.3 h-mg/L to about 15.2 h-mg/L, including all integers and
fractions within the
specified ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage
form containing a
total amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein
subjects administered
the dosage form four times daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate
AUCoverall ranging
from about 3.2 h-mg/L to about 11.2 h-mg/L, including all integers and
fractions within the
specified ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage
form containing a
total amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein
subjects administered
the dosage form four times daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate
AUCO,emii ranging
from about 5.2 1-1-mg/L to about 11.2 Irmg/L, including all integers and
fractions within the
specified ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage
form containing a
total amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein
subjects administered
the dosage form four times daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate
AUCoverall at least
about 1.0 h-mg/L, at least 1.2 h-mg/L, at least 1.4 h-mg/L, at least 1.6 h-
mg/L, at least 1.8
h-mg/L, at least 2.0 h-mg/L, at least 2.3 h-mg/L, at least about 2.6 h-mg/L,
at least about 2.9
h-mg/L, at least 3.2 h-mg/L, at least 3.5 h-mg/L, at least 3.8 h-mg/L, at
least 4.1 h-mg/L, at least
4.4 h-mg/L, at least 4.7 h-mg/L, at least 5.0 h-mg/L, at least 5.3 h-mg/L, at
least 5.6 h-mg/L, at
least 5.9 h-mg/L, at least 6.2 h-mg/L, at least 6.5 h-mg/L, at least 6.8 h-
mg/L, at least 7.1
h=mg/L, at least 7.4 h=mg/L, at least 7.7 h=mg/L, at least 8.0 h-mg/L, at
least 8.3 h-mg/L, at least
8.6 h-mg/Tõ at least 8.9 h-mg/Iõ at least 9.2 h-mg/Tõ at least 9.5 h-mg/Iõ at
least 9.8 h -mg/1õ at
least 10.1 h-mg/L, at least 10.4-h-mg/L, at least 10.7 h-mg/L, at least 11.0 h-
mg/L, at least 11.3
h-mg/L, at least 11.6 h-mg/L, at least 11.9 It- mg/L, at least 12.2 h-mg/L, at
least 12.5 h-mg/L, at
least 12.8 h=mg/L, at least 13.1 h-mg/L, at least 13.3 h=mg/L, at least 13.6 h-
mg/L, at least 13.9
h-mg/L, at least 14.2 h-mg/L, at least 14.5 h-mg/L, at least 14.8 h-mg/L, or
at least 15.2 h-mg/L.
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount
of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage
form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCO->12h ranging from about
0.5 h-mg/L to
76
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
about 5.5 lumg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges. In another
aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount
of about 80 mg to
about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage
form exhibit a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCo-i2b ranging from about 0.5 lumg/L to about 2.5
lumg/L,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another
aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about 80
mg to about 120
mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form exhibit
a mean plasma
monomethyl fumarate AUCo-un ranging from about 2.6 lumg/L to about 5.5 lumg/L,
including
all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another aspect, the
composition is
provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about 80 mg to about
120 mg of a
fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage foim exhibit a mean
plasma
monomethyl fumarate AUCD-,12h of at least about 0.5 lumg/L, at least 1.0
lumg/L, at least 1.2
lumg/L, at least 1.4 Irmg/L, at least 1.6 lumg/L, at least 1.8 lumg/L, at
least 2.0 fumg/L, at least
2.1 lumg/L, at least 2.2 lumg/L, at least 2.3 lumg/L, at least 2.4 irmg/L, at
least 2.5 Irmg/L, at
least 2.6 lumg/L, at least 2.7 lumg/L, at least 2.8 lumg/L, at least 2.9
lumg/L, at least 3 lumg/L,
at least 3.1 lumg/L, at least 3.2 lumg/L, at least 3.3 lumg/L, at least 3.4
lumg/L, at least 3.5
lumg/L, at least 3.6 lumg/L, at least 3.7 lumg/L, at least 3.8 lumg/L, at
least 3.9 lumg/L, at least
4 lumg/L, at least 4.1 lumg/L, at least 4.2 lumg/L, at least 4.3 lumg/L, at
least 4.4 lumg/L, at
least 4.5 lumg/L, at least 4.6 lumg/L, at least 4.7 lumg/L, at least 4.8
lumg/L, at least 4.9
lumg/L, at least 5 lumg/L, at least 5.1 lumg/L, at least 5.2 lumg/L, at least
5.3 lumg/L, at least
5.4 h=mg/L, or at least 5.5 h=mg/L.
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount
of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage
form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUG- ranging from about 0.5 h -
mg/I. to
about 5.6 h-mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges. In another
aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount
of about 80 mg to
about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage
form exhibit a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCoõ ranging from about 0.5 lumg/L to about 2.6
lumg/L,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another
aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about 80
mg to about 120
mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form exhibit
a mean plasma
77
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
monomethyl fumarate AUCD-0, ranging from about 2.6 h=mg/L to about 5.5 h=mg/L,
including
all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another aspect, the
composition is
provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about 80 mg to about
120 mg of a
fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form exhibit a mean
plasma
monomethyl fumarate AUC0-. of at least about 0.5 h=mg/L, at least 1.0 h=mg/L,
at least 1.2
h=mg/L, at least 1.4 h=mg/L, at least 1.6 Irmg/L, at least 1.8 h=mg/L, at
least 2 h=mg/L, at least
2.1 h=mg/L, at least 2.2 h=mg/L, at least 2.3 h=mg/L, at least 2.4 h=mg/L, at
least 2.5 h=mg/L, at
least 2.6 h=mg/L, at least 2.7 h=mg/L, at least 2.8 h=mg/L, at least 2.9
h=mg/L, at least 3 h=mg/L,
at least 3.1 h.mg/L, at least 3.2 h.mg/L, at least 3.3 h-mg/L, at least 3.4 h-
mg/L, at least 3.5
Irmg/L, at least 3.6 h-mg/L, at least 3.7 h-mg/L, at least 3.8 h.mg/L, at
least 3.9 h-mg/L, at least
4 h.mg/L, at least 4.1 h-mg/L, at least 4.2 h-mg/L, at least 4.3 h.mg/L, at
least 4.4 h-mg/L, at
least 4.5 h=nag/L, at least 4.6 h=mg/L, at least 4.7 h=mg/L, at least 4.8
h=mg/L, at least 4.9
h=mg/L, at least 5 Irmg/L, at least 5.1 h=mg/L, at least 5.2 h=mg/L, at least
5.3 h=mg/L, at least
5.4 h=mg/L, or at least 5.5 irmg/L.
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount
of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage
form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Tmax ranging from about 1.5
hours to about
8.5 hours, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges.
In another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about 80
mg to about 120
mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form exhibit
a mean plasma
monomethyl fumarate T. ranging from about 1.6 hours to about 2.5 hours,
including all
integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another aspect, the
composition is provided
in a dosage form containing a total amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a
fumarate ester,
wherein subjects administered the dosage form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl
fumarate
T. ranging from about 2.6 hours to about 5 hours, including all integers and
fractions within
the specified ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a
dosage form containing
a total amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein
subjects
administered the dosage form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate T.
ranging from
about 5.1 hours to about 7.5 hours, including all integers and fractions
within the specified
ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form
containing a total
amount of about 80 mg to about 120 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the
78
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
dosage form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate T
- max ranging from about 7.6 hours to
about 8.5 hours, including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges. In another
aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount
of about 240 mg
to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage
form exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Tr., of at least 1.6 hours, at least 1.8
hours, at least 2 hours,
at least 2.2 hours, at least 2.4 hours, at least 2.6 hours, at least 2.8
hours, at least 3 hours, at least
3.2 hours, at least 3.4 hours, at least 3.6 hours, at least 3.8 hours, at
least 4 hours, at least 4.2
hours, at least 4.4 hours, at least 4.6 hours, at least 4.8 hours, at least 5
hours, at least 5.2 hours,
at least 5.4 hours, at least 5.6 hours, at least 5.8 hours, at least 6 hours,
at least 6.2 hours, at least
6.4 hours, at least 6.6 hours, at least 6.8 hours, at least 7 hours, at least
7.2 hours, at least 7.4
hours, at least 7.6 hours, at least 7.8 hours, at least 8 hours, at least 8.2
hours, or at least 8.4
hours.
In one embodiment described herein, a subject is administered a capsule
containing about
180 mg to about 240 mg FAE, twice daily for a total daily dose of about 360 mg
to about 480
mg, including all integers and fractions within the specified range. In one
aspect, the
pharmaceutical composition comprises an immediate release, delayed release,
controlled release,
or extended release formulation of a fumarate ester. In another aspect, the
pharmaceutical
composition comprises an enteric soft capsule.
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount
of about 180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage
form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumaratc C. ranging from about 0.4 mg/L
to about
2.41 mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges.
In another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
180 mg to about
240 mg of a fiimarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form
exhibit a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about 1.0 mg/L to about 3.4 mg/L,
including all
integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another aspect, the
composition is provided
in a dosage form containing a total amount of about 180 mg to about 240 mg of
a fumarate ester,
wherein subjects administered the dosage form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl
fumarate
C. ranging from about 1.03 mg/L to about 2.41 mg/L, including all integers and
fractions
within the specified ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in
a dosage form
containing a total amount of about 180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester,
wherein subjects
79
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
administered the dosage form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Cmax
ranging from
about 0.4 mg/L to about 0.75 mg/L, including all integers and fractions within
the specified
ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form
containing a total
amount of about 180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the
dosage form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about
0.76 mg/L to
about 1.03 mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges. In another
aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount
of about 180 mg
to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage
form exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about 1.04 mg/L to about 1.75
mg/L,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another
aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
180 mg to about
240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form
exhibit a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about 1.75 mg/L to about 2.41 mg/L,
including
all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another aspect, the
composition is
.. provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about 180 mg to
about 240 mg of a
fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form exhibit a mean
plasma
monomethyl fumarate C. of at least 0.4 mg/L, at least 0.5 mg/L, at least 0.6
mg/L, at least 0.7
mg/L, at least 0.8 mg/L, at least 0.9 mg/L, at least 1 mg/L, at least 1.1
mg/L, at least 1.2 mg/L, at
least 1.3 mg/L, at least 1.4 mg/L, at least 1.5 mg/L, at least 1.6 mg/L, at
least 1.7 mg/L, at least
1.8 mg/L, at least 1.9 mg/L, at least 2 mg/L, at least 2.1 mg/L, at least 2.2
mg/L, at least 2.3
mg/L, at least 2.4 mg/L, at least 2.5 mg/L, at least 2.6 mg/L, at least 2.7
mg,/L, at least 2.8 mg/L,
at least 2.9 mg/L, at least 3 mg/L, at least 3.1 mg/L, at least 3.2 mg/L, at
least 3.3 mg/L, or at
least 3.4 mg/L.
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount
of about 180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage
form twice-daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCoverall ranging
from about 1.0
h. mg/L to about 15.2 h=mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the
specified ranges. In
another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount of about
180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the
dosage form
twice-daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCoverall ranging from
about 2.01
h=mg/L to about 5.2 h=mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the
specified ranges. In
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount of about
180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the
dosage form
twice-daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCoverall ranging from
about 1.0
lrmg/L to about 5.2 Irmg/L, including all integers and fractions within the
specified ranges. In
another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount of about
180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the
dosage form
twice-daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCoverall ranging from
about 11.3
Irmg/L to about 15.2 Irmg/L, including all integers and fractions within the
specified ranges. In
another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount of about
180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the
dosage form
twice-daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCovema ranging from
about 4.8
Irmg/L to about 11.2 h. mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the
specified ranges. In
another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount of about
180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the
dosage form
twice-daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCoverall at least
about 1.0 Irmg/L, at
least 1.2 Irmg/L, at least 1.4 Irmg/L, at least 1.6 Irmg/L, at least 1.8
Irmg/L, at least 2.0
Irmg/L, at least 2.3 Irmg/L, at least about 2.6 Irmg/L, at least about 2.9
Irmg/L, at least 3.2
lrmg/L, at least 3.5 Irmg/L, at least 3.8 lvmg/L, at least 4.1 Irmg/L, at
least 4.4 frmg/L, at least
4.7 Irmg/L, at least 5.0 lrmg/L, at least 5.3 Irmg/L, at least 5.6 Irmg/L, at
least 5.9 lrmg/L, at
least 6.2 Irmg/L, at least 6.5 Irmg/L, at least 6.8 Irmg/L, at least 7.1
Irmg/L, at least 7.4
lrmg/L, at least 7.7 Irmg/L, at least 8.0 lvmg/L, at least 8.3 Irmg/L, at
least 8.6 Irmg/L, at least
8.9 Irmg/L, at least 9.2 frmg/L, at least 9.5 Irmg/L, at least 9.8 Irmg/L, at
least 10.1 Irmg/L, at
least 10.4=Irmg/L, at least 10.7 Irmg/L, at least 11.0 Irmg/L, at least 11.3
Irmg/L, at least 11.6
h -mg/I., at least 11.9 l -mg/L, at least 12.2 h-mg/iõ at least 12.5 h-mg/Tõ
at least 12.8 h.mg/Tõ at
least 13.1 h-mg/L, at least 13.3 h-mg/L, at least 13.6 h.mg/L, at least 13.9
frmg/L, at least 14.2
h-mg/L, at least 14.5 h-mg/L, at least 14.8 h-mg/L, or at least 15.2 h-mg/L.
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount
of about 180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage
form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCO->12h ranging from about
1.0 frrng/L to
about 5.5 frmg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges. In another
aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount
of about 180 mg
81
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage
form exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0_12h ranging from about 1.0 h=mg/L to
about 2.5
h=mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In
another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
180 mg to about
240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form
exhibit a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC012h ranging from about 2.6 h=mg/L to about 5.5
h=mg/L,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another
aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
180 mg to about
240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form
exhibit a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0_12h of at least about 1.0 h-mg/L, at least 1.2
h-mg/L, at
least 1.4 h.mg/L, at least 1.6 h.mg/L, at least 1.8 h.mg/L, at least 2.0 h-
mg/L, at least 2.1
h=mg/L, at least 2.2 h=mg/L, at least 2.3 Irmg/L, at least 2.4 h=mg/L, at
least 2.5 h=mg/L, at least
2.6 h=mg/L, at least 2.7 h=mg/L, at least 2.8 h=mg/L, at least 2.9 Irmg/L, at
least 3 h=mg/L, at
least 3.1 Irmg/L, at least 3.2 h=mg/L, at least 3.3 h=mg/L, at least 3.4
h=mg/L, at least 3.5
h=mg/L, at least 3.6 h=mg/L, at least 3.7 h=mg/L, at least 3.8 h=mg/L, at
least 3.9 h=mg/L, at least
4 h=mg/L, at least 4.1 h=mg/L, at least 4.2 h=mg/L, at least 4.3 h=mg/L, at
least 4.4 h=mg/L, at
least 4.5 h=mg/L, at least 4.6 h=mg/L, at least 4.7 h=mg/L, at least 4.8
h=mg/L, at least 4.9
h=mg/L, at least 5 h=mg/L, at least 5.1 h=mg/L, at least 5.2 h=mg/L, at least
5.3 h=mg/L, at least
5.4 h=mg/L, or at least 5.5 h=mg/L.
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount
of about 180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage
form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0_,õ, ranging from about 1.0
h=mg/L to
about 5.6 h=mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges. In another
aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount
of about 180 mg
to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage
form exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0_,.,, ranging from about 1.0 h-mg/L to
about 2.5
h=mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In
another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
180 mg to about
240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form
exhibit a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCoõ ranging from about 2.6 h=mg/L to about 5.5 h=
mg/L,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another
aspect, the
82
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
180 mg to about
240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form
exhibit a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0-õ, of at least about 1.0 h=mg/L, at least 1.2
h=mg/L, at least
1.4 h=mg/L, at least 1.6 h=mg/L, at least 1.8 h=mg/L, at least 2 h=mg/L, at
least 2.1 h=mg/L, at
least 2.2 h=mg/L, at least 2.3 h=mg/L, at least 2.4 h=mg/L, at least 2.5
h=mg/L, at least 2.6
h=mg/L, at least 2.7 h=mg/L, at least 2.8 Irmg/L, at least 2.9 h=mg/L, at
least 3 h=mg/L, at least
3.1 h=mg/L, at least 3.2 h=mg/L, at least 3.3 h=mg/L, at least 3.4 h=mg/L, at
least 3.5 h=mg/L, at
least 3.6 h=mg/L, at least 3.7 h=mg/L, at least 3.8 h=mg/L, at least 3.9
h=mg/L, at least 4 h=mg/L,
at least 4.1 h.mg/L, at least 4.2 h.mg/L, at least 4.3 h-mg/L, at least 4.4 h-
mg/L, at least 4.5
Irmg/L, at least 4.6 h-mg/L, at least 4.7 h-mg/L, at least 4.8 h.mg/L, at
least 4.9 h-mg/L, at least
5 h.mg/L, at least 5.1 h-mg/L, at least 5.2 h-mg/L, at least 5.3 h.mg/L, at
least 5.4 h-mg/L, at
least 5.5 h=mg/L, or at least 5.6 h=mg/L.
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount
of about 180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage
.. form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate T13x ranging from about 1.5
hours to about
8.5 hours, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges.
In another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
180 mg to about
240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form
exhibit a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate Trna, ranging from about 1.6 hours to about 2.5
hours, including all
integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another aspect, the
composition is provided
in a dosage form containing a total amount of about 180 mg to about 240 mg of
a fumarate ester,
wherein subjects administered the dosage form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl
fumarate
Tma, ranging from about 2.6 hours to about 5 hours, including all integers and
fractions within
the specified ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a
dosage form containing
a total amount of about 180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein
subjects
administered the dosage form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Tina),
ranging from
about 5.1 hours to about 7.5 hours, including all integers and fractions
within the specified
ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form
containing a total
amount of about 180 mg to about 240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the
dosage form exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Tnax ranging from about
7.6 hours to
about 8.5 hours, including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges. In one aspect,
83
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of
about 240 mg to about
240 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form
exhibit a mean
plasma monomethyl fumarate Tmax of at least 1.6 hours, at least 1.8 hours, at
least 2 hours, at
least 2.2 hours, at least 2.4 hours, at least 2.6 hours, at least 2.8 hours,
at least 3 hours, at least 3.2
hours, at least 3.4 hours, at least 3.6 hours, at least 3.8 hours, at least 4
hours, at least 4.2 hours,
at least 4.4 hours, at least 4.6 hours, at least 4.8 hours, at least 5 hours,
at least 5.2 hours, at least
5.4 hours, at least 5.6 hours, at least 5.8 hours, at least 6 hours, at least
6.2 hours, at least 6.4
hours, at least 6.6 hours, at least 6.8 hours, at least 7 hours, at least 7.2
hours, at least 7.4 hours,
at least 7.6 hours, at least 7.8 hours, at least 8 hours, at least 8.2 hours,
or at least 8.4 hours.
In one embodiment described herein, a subject is administered a capsule
containing about
360 to about 480 mg FAE, once daily for a total daily dose of about 360 to
about 480 mg,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In one
aspect, the pharmaceutical
composition comprises an immediate release, delayed release, controlled
release, or extended
release formulation of a fumarate ester. In another aspect, the pharmaceutical
composition
comprises an enteric soft capsule. In another aspect, the composition is
provided in a dosage
form containing a total amount of about 360 mg to about 480 mg of a fumarate
ester, wherein
subjects administered the dosage form once daily exhibit a mean plasma
monomethyl fumarate
C. ranging from about 0.4 mg/L to about 5.2 mg/L, including all integers and
fractions within
the specified ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a
dosage form containing
a total amount of about 360 mg to about 480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein
subjects
administered the dosage form once daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl
fumarate Cmax
ranging from about 1.5 mg/L to about 5.2 mg/L, including all integers and
fractions within the
specified ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage
form containing a
total amount of about 360 mg to about 480 mg of a fiimarate ester, wherein
subjects administered
the dosage form once daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C.
ranging from
about 0.4 mg/L to about 0.75 mg/L, including all integers and fractions within
the specified
ranges. In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form
containing a total
amount of about 360 mg to about 480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the
dosage form once daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging
from about
0.76 mg/L to about 1.03 mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the
specified ranges.
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount of
84
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
about 360 mg to about 480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage
form once daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Crna.õ ranging from
about 1.04
mg/L to about 1.75 mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the
specified ranges. In
another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount of about
360 mg to about 480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the
dosage form once
daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about 1.75
mg/L to about
2.41 mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges.
In another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about 2.42 mg/L to about 3.5
mg/L,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another
aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C. ranging from about 3.6 mg/L to about 5.2
mg/L,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another
aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate C. of at least about 1.0 mg/L, at least 1.1
mg/L, at least 1.2
mg/L, at least 1.3 mg/L, at least 1.4 mg/L, at least 1.5 mg/L, at least 1.6
mg/L, at least 1.7 mg/L,
at least 1.8 mg/L, at least 1.9 mg/L, at least 2.0 mg/L, at least 2.1 mg/L, at
least 2.2 mg/L, at least
2.3 mg/L, at least 2.4 mg/L, at least 2.5 mg/L, at least 2.6 mg/L, at least
2.7 mg/L, at least 2.8
mg/L, at least 2.9 mg/L, at least 3.0 mg/L, at least 3.1 mg/L, at least 3.2
mg/L, at least 3.3 mg/L,
at least 3.4 mg/L, at least 3.5 mg/L, at least 3.6 mg/L, at least 3.7 mg/L, at
least 3.8 mg/L, at least
3.9 mg/Iõ at least 4.0 mg/I, at least 4.1 m g/Iõ at least 4.2 mg/L, at least
4.3 mg/L, at least 4.4
mg/L, at least 4.5 mg/L, at least 4.6 mg/L, at least 4.7 mg/L, at least 4.8
mg,/L, at least 4.9 mg/L,
at least 5.0 mg/L, or at least 5.1 mg/L
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount
of about 360 mg to about 480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage
form once daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCO-,12h ranging
from about 1.0
Irmg/L to about 15.5 Irmg/L, including all integers and fractions within the
specified ranges. In
another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount of about
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
360 mg to about 480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the
dosage form once
daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0_121, ranging from about
1.0 h=mg/L to
about 2.5 h=mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges. In another
aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount
of about 360 mg
to about 480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage
form once daily
exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCO->12h ranging from about 2.6
h=mg/L to about
5.5 h=mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges.
In another aspect,
the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of
about 360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0_12h ranging from about 5.6 h-mg/L to
about 7.5
h-mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In
another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0_12h ranging from about 7.6 h=mg/L to
about 10.5
.. h=mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges.
In another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0_,12h ranging from about 10.5 h=mg/L to
about 15.5
h=mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In
another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0-,12h of at least about 1.0 h=mg/L, at
least 1.2 h=mg/L,
at least 1.4 h=mg/L, at least 1.6 h=mg/L, at least 1.8 h=mg/L, at least 2.0
h=mg/L, at least 2.3
h -mg/I, at least 2.6 h-mg/Tõ at least 2.9 h-mg/1õ at least 3.2 h.mg/1õ at
least 3.5 h-mg/Iõ at least
3.8 h.mg/L, at least 4.1 h-mg/L, at least 4.4 h-mg/L, at least 4.7 h-mg/L, at
least 5 h-mg/L, at
least 5.3 h.mg/L, at least 5.6 h.mg/L, at least 5.9 h.mg/L, at least 6.2 h-
mg/L, at least 6.5
Irmg/L, at least 6.8 Irmg/L, at least 7.1 h=mg/L, at least 7.4 h=mg/L, at
least 7.7 h.mg/L, at least
8.0 h=mg/L, at least 8.3 Irmg/L, at least 8.6 h=mg,/, at least 8.9 h=mg/L, at
least 9.2 h=mg/L, at
least 9.5 irmg/L, at least 9.8 Irmg/L, at least 10.1 h=mg/L, at least 10.4
Irmg/L, at least 10.7
Irmg/L, at least 11.0 h=mg/L, at least 11.3 Irmg/L, at least 11.6 irmg/L, at
least 11.9 h=mg/L, at
least 12.2 h=mg/L, at least 12.5 h=mg/L, at least 12.8 h=mg/L, at least 13.1
h=mg/L, at least 13.4
86
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
h=mg/L, at least 13.7 h=mg/L, at least 14 h=mg/L, at least 14.3 h=mg/L, at
least 14.6 h=mg/L, at
least 14.9 h=mg/L, at least 15.2 h=mg/L, or at least 15.5 h=mg/L.
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount
of about 360 mg to about 480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage
form once daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0_,õ, ranging
from about 1.0
h=mg/L to about 15.5 h=mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the
specified ranges. In
another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount of about
360 mg to about 480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the
dosage form once
daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0--,c, ranging from about
1.5 h-mg/L to
about 2.5 h-mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges. In another
aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount
of about 360 mg
to about 480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage
form once daily
exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0¨o,, ranging from about 2.6
h=mg/L to about
5.5 h=mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges.
In another aspect,
the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of
about 360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0_,õ ranging from about 5.6 h=mg/L to about
7.5
h=mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In
another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0õ ranging from about 7.6 h=mg/L to about
11.5
h=mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In
another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUC0¨,0 ranging from about 10.5 h.mg/L to
about 15.5
h-mg/L, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In
another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate AUCO_õo of at least about 1.0 h=mg/L, at least
1.2 h=mg/L, at
least 1.4 Irmg/L, at least 1.6 h=mg/L, at least 1.8 Irmg/L, at least 2.0
h=mg/L, at least 2.3
h=mg/L, at least 2.6 h=mg/L, at least 2.9 h=mg/L, at least 3.2 h=mg/L, at
least 3.5 h=mg/L, at least
87
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
3.8 h=mg/L, at least 4.1 h=mg/L, at least 4.4 h-mg/L, at least 4.7 h-mg/L, at
least 5 h-mg/L, at
least 5.3 h=mg/L, at least 5.6 h=mg/L, at least 5.9 h=mg/L, at least 6.2
h=mg/L, at least 6.5
h-mg/L, at least 6.8 h-mg/L, at least 7.1 h-mg/L, at least 7.4 h=mg/L, at
least 7.7 h=mg/L, at least
8.0 h=mg/L, at least 8.3 h-mg/L, at least 8.6 h-mg/L, at least 8.9 h-mg/L, at
least 9.2 h=mg/L, at
least 9.5 h-mg/L, at least 9.8 h-mg/L, at least 10.1 h-mg/L, at least 10.4
h=mg/L, at least 10.7
h-mg/L, at least 11.0 h-mg/L, at least 11.3 h-mg/L, at least 11.6 h-mg/L, at
least 11.9 h=mg/L, at
least 12.2 h-mg/L, at least 12.5 h-mg/L, at least 12.8 h=mg/L, at least 13.1 h-
mg/L, at least 13.4
h-mg/L, at least 13.7 h-mg/L, at least 14 h=mg/L, at least 14.3 h=mg/L, at
least 14.6 h-mg/L, at
least 14.9 h-mg/L, at least 15.2 h-mg/L, or at least 15.5 h-mg/L.
In another aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a
total amount
of about 360 mg to about 480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects
administered the dosage
form once daily exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate T. ranging from
about 1.5 hours
to about 10.5 hours including all integers and fractions within the specified
ranges. In another
aspect, the composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount
of about 360 mg
to about 480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage
form once daily
exhibit a mean plasma monomethyl fumarate T. ranging from about 1.6 hours to
about 2.5
hours, including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In
another aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate T. ranging from about 2.6 hours to about 5
hours,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another
aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Tma, ranging from about 5.1 hours to about 7.5
hours,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another
aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate T. ranging from about 7.6 hours to about 8.5
hours,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another
aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
88
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate T max ranging from about 8.6 hours to about
10.6 hours,
including all integers and fractions within the specified ranges. In another
aspect, the
composition is provided in a dosage form containing a total amount of about
360 mg to about
480 mg of a fumarate ester, wherein subjects administered the dosage form once
daily exhibit a
mean plasma monomethyl fumarate Tr., of at least 1.6 hours, at least 1.8
hours, at least 2 hours,
at least 2.2 hours, at least 2.4 hours, at least 2.6 hours, at least 2.8
hours, at least 3 hours, at least
3.2 hours, at least 3.4 hours, at least 3.6 hours, at least 3.8 hours, at
least 4 hours, at least 4.2
hours, at least 4.4 hours, at least 4.6 hours, at least 4.8 hours, at least 5
hours, at least 5.2 hours,
at least 5.4 hours, at least 5.6 hours, at least 5.8 hours, at least 6 hours,
at least 6.2 hours, at least
6.4 hours, at least 6.6 hours, at least 6.8 hours, at least 7 hours, at least
7.2 hours, at least 7.4
hours, at least 7.6 hours, at least 7.8 hours, at least 8 hours, at least 8.2
hours, at least 8.4 hours,
at least 8.6 hours, at least 8.8 hours, at least 9.0 hours, at least 9.2
hours, at least 9.4 hours, at
least 9.6 hours, at least 9.8 hours, at least 10 hours, at least 10.2 hours,
at least 10.4 hours, or at
least 10.6 hours.
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition for
treating,
prophylaxis, or amelioration of general autoimmune or neurodegenerative
disorders, comprising
a fumarate ester, wherein the composition exhibits an in vitro dissolution
rate (% dissolution per
minute) at pH 6.8, as described herein in any one of Drawings 2-12.
Another embodiment described herein is a pharmaceutical composition for
treating,
prophylaxis, or amelioration of general autoimmune or neurodegenerative
disorders, including
but not limited to multiple sclerosis or psoriasis, comprising a fumarate
ester, wherein the
composition exhibits an in vitro dissolution rate comprising about 10% to
about 80% dissolution
after about 5 minutes to about 480 minutes at pH 6.8, including all integers
and fractions within
the specified ranges of dissolution and time In another aspect, the in vitro
dissolution rate at pH
6.8 is about 50% after about 20 minutes to about 1080 minutes, including all
integers and
fractions within the specified ranges of dissolution and time. In one aspect,
the in vitro
dissolution rate at pH 6.8 is about 50% after about 5 min, is about 50% after
about 10 min, about
50% after about 20 min, about 50% after about 30 min, about 50% after about 40
min, about
50% after about 50 min, about 50% after about 60 min, about 50% after about 70
min, about
50% after about 80 min, about 50% after about 90 min, about 50% after about
120 min, about
50% after about 150 min, about 50% after about 180 min, about 50% after about
210 min, about
89
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
50% after about 240 min, about 50% after about 300 min, is about 50% after
about 330 min,
about 50% after about 360 min, is about 50% after about 390 min, about 50%
after about 420
min, about 50% after about 480 min, about 50% after about 540 min, about 50%
after about 600
min, about 50% after about 660 min, about 50% after about 720 min, about 50%
after about 780
min, about 50% after about 840 min, about 50% after about 900 min, about 50%
after about 960
min, or about 50% after 1080 min. In another aspect, the in vitro dissolution
rate at pH 6.8 is
about 50% after about 0.5 hour, about 50% after about 1 hour, about 50% after
about 2 hours,
about 50% after about 3 hours, about 50% after about 4 hours, about 50% after
about 5 hours,
about 50% after about 6 hours, about 50% after about 7 hours, about 50% after
about 8 hours,
about 50% after about 9 hours, about 50% after about 10 hours, about 50% after
about 11 hours,
about 50% after about 12 hours, about 50% after about 13 hours, about 50%
after about 14 hours,
about 50% after about 15 hours, about 50% after about 16 hours, about 50%
after about 17 hours,
or about 50% after about 18 hours. In one aspect, the in vitro dissolution
rate at pH 6.8 is about
50% after about 10 minutes. In another aspect, the in vitro dissolution rate
at pH 6.8 is about
50% after about 20 minutes. In another aspect, the in vitro dissolution rate
at pH 6.8 is about
50% after about 45 minutes. In another aspect, the in vitro dissolution rate
at pH 6.8 is about
50% after about 60 minutes. In one aspect, the in vitro dissolution rate at pH
6.8 is about 50%
after about 120 minutes. In another aspect, the in vitro dissolution rate at
pH 6.8 is about 50%
after about 180 minutes. In another aspect, the in vitro dissolution rate at
pH 6.8 is about 50%
after about 240 minutes. In one aspect, the in vitro dissolution rate at pH
6.8 is about 50% after
about 480 minutes.
Another embodiment described herein is a method of treating a neurological
disease,
neurodegenerativc disease, or autoimmunc disease comprising orally
administering one or more
doses of one or more fumarate esters described herein to a patient in need
thereof, wherein the
administration activates or modulates one or more cellular signaling pathways.
In one aspect, the
autoimmune disease comprises multiple sclerosis or psoriasis and the cellular
signaling pathway
comprises the nuclear erythroid-derived 2-like 2 (Nrf2) dependent antioxidant
response element
(ARE) pathway. Without being bound by any theory, it is believed that at least
one aspect of the
pharmacological activity of the fumarate esters described herein exert an anti-
inflammatory and
neuroprotective effect in patients with, for example, multiple sclerosis or
psoriasis, by activating
the Nrf2 cellular signaling pathway. Although not completely understood, the
Nrf2 pathway is
involved in the cellular response to oxidative stress, which has been linked
to neuronal
degeneration in multiple sclerosis and in other neurodegenerative or
autoimmune
diseases (e.g., HIV), see, e.g., Gao et al., Clin. PharmacoL 6:19-34 (2014).
It is currently thought that under basal conditions, Nrf2 is sequestered in
the
cytoplasm to the actin-bound Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keapl).
Keapl
associates with the Cullin3 ubiquitin ligase adaptor protein, which positions
Keapl and
its substrats in proximity (e.g., NRF2) to the E3 ubiquitin ligase Rbx 1.
Thus, under
normal conditions, the substrats (Nrf2) is polyubiquitinated and targeted for
degradation. In response to oxidative stress, Nrf2 is released from the
Keapl/Nrf2
complex, preventing its degradation resulting in the concomitant translocation
of NRF2
to the nucleus and activation of ARE-mediated gene transcription. Based on
this
understanding, any of the non-limiting methods for determining the activation
of Nrf2
may be used that are further described herein. See U.S. Patent No. 8,399,514.
Nrf2 activation may be determined by assessing the in vitro activation levels
of
Nrf2 and/or Nrf2 mRNA or protein expression levels. The sequence of the
promoter
region of the Nrf2 gene (-1065 to -35) is known. In vitro Nrf2 activation may
be
measured using a cell model system transfected or transduced with an
expression
construct containing the Nrf2 promoter element described above and an
artificial
reporter gene (e.g., luciferase or a fluorescent reporter gene (GFP, RFP, YFP
etc.,).
See, e.g., Chan et al., Proc. Natl. Aacd. Sci. USA 93:13943-13948 (1996) and
Kwak et
al., MoL Cell. BioL 22(9):2883-2892 (2002). Nrf2 activation may be assessed by
measuring reporter gene expression in treated vs. non-treated tells using
standard
imaging or fluorescence quantification techniques. Alternatively, PCR (e.g.,
qRT-PCR)
or Northern blotting may be used to determine expression levels of Nrf2 mRNA,
or
Western blotting to determine Nrf2 protein levels. See, e.g., Kwak et al., MoL
Cell. BioL
22(9):2883-2892 (2002) and Kwak et al., MoL Med. 7:135-145 (2001). Antibodies
against Nrf2 are can be produced by methods known in the art and are
commercially
available from, for example, StressGen.
In addition, Nrf2 activation may be assessed by determining the subcellular
localization and/or nuclear translocation of Nrf2 in treated vs. non-treated
tells. Such
91
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
assays include cell staining, or analysis of cytoplasmic versus nuclear cell
extracts. For
example, an Nrf2-green fluorescence protein (GFP) fusion protein construct can
be
introduced into cells and visualized as described in, e.g., Kraft et al., J.
Neurosci.
24:1101-1112 (2004) and in Satoh et al., Proc. Natl. Aacd. Sci. USA 103(3):768-
773
(2006).
Nrf2 activation may be determined through indirect measurement of the
expression levels and/or activity of one or more genes under the control of
Nrf2 in
treated vs. non-treated cells. For example, the expression levels of NADPH
dehydrogenase quinone 1 (NQ01) may be determined using, for example, qRT-PCR,
Northern blotting, or Western blotting, see, e.g., Wierinckx et al., J.
Neuroimmunology
166:132-143 (2005). Methods for measuring enzymatic activity of NQ01, using
menadione as a substrate, are described in Dinkova-Kostova et al., Proc. Nati.
Aacd.
Sci. USA 98:3404-09 (2001).
The cell type being contacted with the one or more fumarate esters described
herein may comprise a neuron or a neuronal cell line, a colon carcinoma cell
line (e.g.,
DLD1), a neuroblastoma cell line (e.g., SkNSH or IMR32), or a primary immune
cell
(e.g., a monocyte or T-lymphocyte or B-lymphocyte). The cell may be a cell in
culture
(in vitro) or be inside of a mammal (in vivo). Alternatively, endogenous Nrf2
activation
may be determined by measuring the levels of Nrf2 or a Nrf2 regulated gene
(e.g.,
NQ01) in a primary cell or cell population (e.g., a monocyte, T-lymphocyte, or
neuronal
cell) taken from a human patient having neurological disease,
neurodegenerative
disease, or autoimmune disease (e.g., multiple sclerosis or psoriasis).
It will be readily apparent to one of ordinary skill in the relevant arts that
suitable
modifications and adaptations to the compositions, methods, and applications
described herein can be made without departing from the scope of any
embodiments
92
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
or aspects thereof. The compositions and methods provided are exemplary and
are not
intended to limit the scope of any of the specified embodiments. All of the
various
embodiments, aspects, and options disclosed herein can be combined in any and
all
variations or iterations. The scope of the compositions, formulations,
methods, and
processes described herein include all actual or potential combinations of
embodiments, aspects, options, examples, and preferences herein described. The
ratios of the mass of any component of any of the formulations disclosed
herein to the
mass of any other component in the formulation or to the total mass of the
other
components in the formulation are hereby disclosed as if they were expressly
disclosed.
92a
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
EXAMPLES
Example 1
DMF Enteric Soft Capsule Fills
Based on results of dimethyl fumarate (DMF) solubility testing in various
lipid or
lipophilic vehicles (data not shown), two formulations were selected for
further studies and
encapsulated in enteric soft gelatin capsules: one having polyethylene glycol
and one with
medium chain mono- and diglycerides. Organic acids such as caprylic acid,
lactic acid, or oleic
acid, were incorporated into the matrix fill to prevent the hydrolysis of
dimethyl fumarate and to
retain enteric properties of the shell. Application batches of enteric soft
capsules were prepared
by rotary die encapsulation using the fill compositions shown in Table 5.
Table 5. DMF Fill Compositions
Capmul MCM Matrix (A413-A) PEG
Matrix (A413-B)
Ingredient mg/capsule % wt mg/capsule % wt
Dimethyl Fumarate
240 32.0 240 32.0
(Mean PSD: 80 (tm)
Capmul MCM 367.5 49.0
PEG 400 382.5 51.0
Povidone 1(30 52.5 7.0 37.5 5.0
Tween 80 75 10.0 75 10.0
Lactic acid 15 2.0 15 2.0
TOTAL 750 100% 750 100%
The enteric soft capsules comprising the matrix formulations shown in Table 5
were
subject to two-stage dissolution experiments in a USP Apparatus II (e.g.,
paddle method at 100
rpm). For these experiments, the capsules were introduced in to simulated
gastric fluid, 0.1 N
HCl, pH 1.2, for 2 hours. After 2 hours, the capsules were transferred to
simulated intestinal
fluid, phosphate buffer, pH 6.8. The results are shown in Figure 2. The
results show that the
capsules retain their enteric properties for at least 2 hours in simulated
gastric fluid at pH 1.2.
Both types of capsules released DMF shortly (-10 minutes) after being
transferred to simulated
intestinal fluid, pH 6.8. The enteric soft capsules comprising matrices
comprising PEG 400
released DMF more rapidly than those comprising Capmul MCM (ABITEC Corp.;
medium
chain mono- and di-glycerides).
93
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Example 2
Stability of the Enteric Soft Capsules over Time
The temporal stability of the dimethyl fumarate enteric soft capsule fill
formulation
shown in Table 6 was assessed. A sample of DMF enteric soft capsules was
subjected to
accelerated aging by a 1 month of exposure to 40 C and 75% relative humidity
conditions and
then evaluated in two-stage dissolution experiment. A second sample of DMF
enteric soft
capsules was subject to two-stage dissolution shortly after manufacturing.
Both sets of enteric
capsules remained intact in the acidic conditions for at least 2 hours. Figure
3. The freshly
manufactured capsules released DMF slightly faster than the age-accelerated
capsules when the
pH was shifted to 6.8 (phosphate buffer).
Table 6. DMF Fill Composition
Ingredient mg/capsule ./0 weight
Dimethyl fumarate
240 32.0
(Mean PSD: 80 [tm )
Capmul MCM 367.5 49.0
Povidone K 30 52.5 7.0
Tween 80 75 10.0
Lactic acid 15 2.0
TOTAL 750 mg 100%
Example 3
DMF Release in Enteric Soft Capsules
A developmental batch of enteric soft capsules comprising a Capmur MCM matrix
containing particles of dimethyl fumarate (Table 6) was subject to two-stage
dissolution at pH
1.2 in simulated gastric fluid for 2 hours, then the buffer was changed to
phosphate buffer, pH
6.8, containing 2% Cremophor RH 40. Figure 4. The enteric capsules remained
intact in the
acidic condition, and then began releasing DMF within 20 minutes of the pH-
shift to simulated
intestinal fluid.
Example 4
Surfactants Affect DMF Release Rate
Enteric soft capsules were prepared with matrices comprising 10% Tween 80
(Uniqema,
ICI Americas Inc; polyoxyethylene (80) sorbitan monooleate; e.g., polysorbate
80) or 10%
94
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133
PCT/US2015/047636
Cremophor RH 40 (BASF SE; polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil) (Table 7) and
then tested
in dissolution experiments at pH 6.8. Figure 5. The enteric soft capsules with
fills containing
Cremophor released DMF much more rapidly than those containing Tween 80.
Table 7. DMF Fill Compositions
Tween 80 Matrix Cremophor RH 40 Matrix
Ingredient mg/capsule A) wt mg/capsule A)
wt
Dimethyl Fumarate
240 32.0 240 32.0
(Mean PSD: 80 am)
Capmul MCM 367.5 49.0 367.5 49.0
Povidone K 30 52.5 7.0 52.5 7.0
Tween`R 80 75 10.0
Cremophor RH 40 75 10.0
Lactic acid 15 2.0 15 2.0
TOTAL 750 100% 750 100%
Example 5
Polyvinylpyn-olidone Concentration Affects DMF Release Rate
Enteric soft capsules prepared containing fills with of 3% or 5%
concentrations of
Povidone K30 (e.g., PVP; 30,000 average MW) (Table 8) were tested in
dissolution experiments
at pH 6.8. Figure 6. The enteric soft capsules with matrices containing 5%
Povidone K30
released DMF more rapidly at pH 6.8 than those with fills containing 3%
Povidone K30.
Table 8. DMF Fill Compositions
3% PVP 5% PVP
Ingredient mg/capsule "./9 wt
mg/capsule wt
Dimethyl Fumarate
240 32.0 240 32.0
(Mean PSD: 80 am)
Capmul MCM 397.5 53 382.5 51
Cremophor RH 40 75 10.0 75 10.0
Povidone K 30 22.5 3.0 37.5 5.0
Lactic acid 15 2.0 15 2.0
TOTAL 750 100% 750 100%
Viscosity: 43191 Cp 122000 Cp
Based on the foregoing formulation studies, the Capmul MCM-based formulation
was
selected for further analysis. A batch was manufactured using the formulation
below (Table 9).
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Table 9. DMF Fill Composition
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight
Dimethyl Fumarate
240 32
(Mean PSD: 80 um)
Capmul MCM 375 50
Crcmophor RH 40 75 10
Poyidone K 30 52.5 7
Lactic acid 15 2
TOTAL 750 mg 100%
Example 6
DMF Enteric Soft Capsules are Amenable to Controlled or Extended Release
The release profile of DMF is modified by varying the enteric soft capsule
shell
composition or by altering the fill composition or particle size of the active
ingredient. Three
different release profiles were observed under two-stage dissolution
experiments. All enteric
soft capsules were resistant to acid for at least 2 hours, and begin releasing
DMF upon transition
to pH 6.8. Figure 7. A release profile was observed in an enteric soft capsule
comprising a
matrix of Capmul MCM and Cremophor RH 40 (Table 10; Release Profile 1). A
different
release profile was observed with an enteric soft capsule shell comprising a
Capmul MCM and
Tween 80 matrix (Table 6; Release Profile 2). Another release profile was
observed with an
enteric soft capsule shell comprising a matrix of soybean oil, Tween 80, and
solid particles of
DMF having a mean particle distribution size of 148 [ini (Table 11; Release
Profile 3).
Table 10. DMF Fill Composition (P31)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight
Dimethyl fumarate
240 32.0
(Mean PSD: 80 um )
Cap mul MCM 367.5 49.0
Cremophor RH 40 75 10.0
Poyidone K 30 52.5 7.0
Lactic acid 15 2.0
TOTAL 750 mg 100%
96
Table 11. DMF Fill Composition (P6)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight
Dimethyl fumarate
240 43.6
(Mean PSD 148 pm)
Soybean oil 285.25 51.9
Aerosil 200TM 75 10.0
Tween 80 11 2.0
Caprylic acid 11 2.0
TOTAL 550 mg 100%
97
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-08-24
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133
PCT/US2015/047636
Example 7
DMF Particle Size Affects Release Rate
Enteric soft capsules comprising matrices with DMF particles of differing mean
particle
size distributions as shown in Table 12 were subject to dissolution at pH 6.8.
Figure 8.
Table 12. Matrices with Varying DMF Particle Sizes
Formulation
A (P7) B (P8) C (P9)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule A) weight mg/capsule A
weight
DMF Mean PSD:
240 43.6
168 gm
DMF Mean PSD:
240 43.6
148 gm
DMF Mean PSD:
240 43.6
90 pm
PEG 400 244 44.4 244 44.4 244 44.4
Povidone K30
Tween'g' 80 55 10 55 10 55 10
Caprylic acid 11 2 11 2 11 2
Lactic acid
TOTAL 550 100 550 100 550 100
Formulation
D (P25) E (P15) F (P23)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight
DMF Mean PSD:
240 34.3
76 gm
DMF Mean PSD.
240 28.2 240 28.2
26 pm
PEG 400 355 50.7 508 59.8 482 56.8
Povidone K30 21 3 ¨ 26 3
Twcen 80 70 10 85 10 85 10
Caprylic acid 17 2 17 2
Lactic acid 14 2
TOTAL 700 100 850 100 850 100
98
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133
PCT/US2015/047636
Example 8
Enteric soft capsules comprising various matrices comprising DMF particles
having
particle size distribution of d90 < 90 [tm were prepared and analyzed in two
stage (pH 1.2 and
pH 6.8) or single stage (pH 6.8) dissolution experiments (data not shown).
(Tables 13-15).
Table 13. Various DMF Fill Compositions
Formulation
A (P32) B (P33) C (P34)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule "A
weight
DMF
240 32.0 240 32.0 240
32.0
PSD: d90 < 90 ttm
Capmul MCM 360 48.0 322.5 43.0 352.5
47.0
Cremophor RH 40 112.5 15.0 150 20.0 112.5
15.0
Lactic acid 37.5 5.0 37.5 5.0 37.5 5.0
TOTAL 750 100 750 100 750 100
D (P35) E (P37) F (P38)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule %
weight
DMF
240 32.0 240 32.0 240
32.0
PSD: d90 < 90 lam
Capmul MCM 315 42.0 360 48.0 360
48.0
Cremophor RH 40 150 20.0 75 10.0 75
10.0
Lactic acid 37.5 5.0 37.5 5.0 37.5 5.0
Povidone K 30 7.5 1.0
PEG 400 - - , 37.5 5.0 - -
Polypropylene glycol 37.5 5.0
TOTAL 750 100 750 100 750 100
G (P39) II (P41) I (P43)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule %
weight
DMF
240 28.2 240 28.2 240
28.2
PSD: d90 < 90 vini
Capmul MCM 482.5 56.8 397.5 46.8 397.5
46.8
Cremophor RH 40 85 10.0 85 10.0
Lactic acid 42.5 5.0 42.5 5.0 42.5 5.0
Labrasolg' 85 10.0 170
20.0
TOTAL 850 100 850 100 850 100
99
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Table 14. Various DMF Fill Compositions
Formulation
A (P44) B (P45) C (P46)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight
DMF
PSD: d9090 tim
240 28.2 240 28.2 240 28.2
<
Capmul MCM 372 43.8 355 41.8 329.5 38.8
Cremophor RH 40 85 10.0 85 10.0 85 10.0
Lactic acid 42.5 5.0 42.5 5.0 42.5 5.0
Labrasor 85 10.0 85 10.0 85 10.0
Povidone K 30 25.5 3.0 25.5 3.0
Mannitol 42.5 5.0 42.5 5.0
TOTAL 850 100 850 100 850 100
D (P47) E (P48) F (P49)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule A weight mg/capsule % weight
DMF
240 28.2 240 28.2 240 28.2
PSD: d90 < 90 pn
Capmur MCM 384.75 45.3 284.195 33.43 312.5 36.76
Cremophor RH 40 85 10.0 85 10.0 85 10.0
Lactic acid 42.5 5.0 42.5 5.0 42.5 5.0
Povidone K 30 12.75 1.5
Labrasor 85 10.0 85 10.0
PEG 3350 85 10.0 113.305 13.33 85 10.00
TOTAL 850 100 850 100 850 100
G (P50) H (P51) I (P52)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight
DMF
240 28.2 240 28.2 240 28.2
PSD: d90 < 90 pn
Camila MCM 333.75 39.26 287 33.76 333.75 39.26
Cremophor RH 40 85 10.0 85 10.00 85 10.00
Lactic acid 42.5 5.0 42.5 5.0 42.5 5.0
Labrasor 85 10.0 85 10.0 85 10.00
PEG 3350 63.75 7.50
Povidone K 17 25.5 3.00
Mannitol 85 10.00
Crospovidone-CL 63.75 7.50
TOTAL 850 100 850 100 850 100
100
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Table 15. Various DMF Fill Compositions
Formulation
A (P53) B (P54) C (P55)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight
DMF
PSD: d9090 tim
240 28.24 240 28.24 240 28.24
<
Capmul MCM 397.5 46.76 397.5 46.76 390.7 45.96
Cremophor RH 40 85 10.00 85 10.00 85 10.00
Lactic acid 42.5 5.00 42.5 5.00 42.5 5.00
PEG 3350 85 10.00
PEG 400 42.5 5.00
Lutror F 68 85 10.00
Sodium lauryl sulfate 49.3 5.80
TOTAL 850 100 850 100 850 100
D (P56) E (P57) F (P58)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight
DMF
PSD: d90 < 90 i.tin 240 28.24 240 28.24 240 28.24
Capmul MCM 355 41.76 363.5 42.76 355 41.76
Cremophor RH 40 85 10.00 85 10.00 85 10.00
Lactic acid 42.5 5.00 42.5 5.00 42.5 5.00
PEG 400 85 10.00 85 10.00 85 10.00
Crospovidone CL 42.5 5.00
Cruspuvidone CL-F 34 4.00
Crospovidonc CL-M 42.5 5.00
TOTAL 850 100 850 100 850 100
G (P59) H (P60) I (P61)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight
DMF
PSD: d90901Am
240 28.24 240 28.24 240 28.24
<
Capmur MCM 312.5 36.76 355 41.76 329.5 38.76
CI emophor RH 40 85 10.00 85 10.00 85 10.00
Lactic acid 42.5 5.00 42.5 5.00 42.5 5.00
Labrasor 85 10.00 85 10.00 85 10.00
Pearlitol Flash 85 10.00 42.5 5.00
Croscarmellose
42.5 5.00 25.5 3.00
Sodium
TOTAL 850 100 850 100 850 100
101
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Example 9
Capsule Shell Thickness Affects Release Rate
Application batches of enteric soft capsules with shell thicknesses of 0.028
inches or
0.033 inches were prepared comprising DMF particles having particle size
distributions of d90 <
90 um in various matrices (Table 16) and analyzed in two stage (pH 1.2 and pH
6.8) dissolution
experiments (Figure 9).
Table 16. DMF Fill Compositions
A (APP021214) B (APP020714)
(0.028 inch ribbon) (0.033 inch ribbon)
Ingredient mg/capsule "A wt mg/capsule A wt
Dimethyl Fumarate
240 28.2 240 28.2
PSD: d90 < 90 ?Am
Capmul MCM 440 51.8 465.5 54.8
Cremophor RH 40 85 10.0 85 10.0
Povidone K30 42.5 5.0 42.5 5.0
PEG 400 42.5 5.0
Crospovidone-CL 17 2.0
TOTAL 850 100% 850 100%
C (APP022414-A) D (APP022414-B)
(0.028 inch ribbon) (0.028 inch ribbon)
Ingredient mg/capsule % wt mg/capsule % wt
Dimethyl Fumarate
240 28.24 240 28.24
PSD: d90 < 90 !Am
Capmul MCM 312.5 36.76 312.5 36.76
Cremophor RH 40 85 10.0 85 10.0
Povidone K30 42.5 5.0 42.5 5.0
PEG 600 127.5 15.0
Crospovidone-CL 42.5 5.0
Labrasol 85 10.0
Pearlitol Flash 85 10.0
TOTAL 850 100% 850 100%
102
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Example 10
A GMP batch of enteric soft capsules (0.038-inch shell thickness) comprising
DMF
particles having a particle size distribution of PSD: d90 < 90 1..im was
prepared with the matrix
composition shown in Table 17 and analyzed in two stage (pH 1.2 and pH 6.8)
dissolution
experiments (Figure 10) and compared to application batches (Table 15).
Table 17. GMP DMF Fill Composition
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight
Dimethyl fumarate
240 32.0
PSD: d90 < 90 um
Capmul MCM 375 50.0
Cremophor RH 40 75 10.0
Povidonc K 30 22.5 3.0
Lactic acid 37.5 5.0
TOTAL 750 mg 100%
103
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133
PCT/US2015/047636
Example 11
Povidone K30 and PEG 600 affect DMF release rate
DMF matrices were prepared with and without Povidone K30 or PEG 600 (Table 18)
and analyzed in single stage (pH 6.8) dissolution experiments (Figure 11).
Table 18. DMF Fill Compositions
A (P62) B (P63)
Ingredient mg/capsule `)/0 weight mg/capsule
% weight
Dimethyl fumarate
240 28.2 240 28.24
PSD: d90 < 90 pn
Capmul MCM 482.5 56.8 384.75 45.26
Cremophor RH 40 85 10.0 85 10.00
Poyidone K 30 12.75 1.50
PEG 600 85 10.00
Lactic acid 42.5 5.0 42.5 5.0
TOTAL 850 mg 100% 850 mg 100%
C (P64) D (P65)
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight mg/capsule % weight
Dime-thy' fumaratc
240 28.24 240 28.24
PSD: d90 < 90 [an
Capmul MCM 457 53.76 372 43.76
Cremophor RII 40 85 10.00 85 10.00
Poyidone K 30 25.5 3.00 25.5 3.00
PEG 600 85 10.00
Lactic acid 42.5 5.00 42.5 5.00
TOTAL 850 mg 100% 850 mg 100%
104
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Example 12
A batch of enteric soft capsules (0.038 inch shell thickness) comprising DMF
particles
having particle size distribution of PSD: d90 < 90 [tm was prepared with the
matrix composition
shown in Table 19 and analyzed in two stage (pH 1.2 and pH 6.8) dissolution
experiments
(Figure 12). This example provides a lower dose of DMF (120 mg) compared with
that shown
in Table 6 (240 mg).
Table 19. DMF Fill Composition
Ingredient mg/capsule `)/0 weight
Dimethyl fumarate PSD: d90 < 90 im 120 28.2
Capmul MCM 228.5 53.8
Cremophor RH 40 42.5 10.0
Povidone K 30 12.75 3.0
Lactic acid 21.25 5.0
TOTAL 425 mg 100%
Example 13
A batch of enteric soft capsules (0.038 inch shell thickness) comprising
monomethyl
fumarate (MMF) particles having particle size distribution of PSD: d90 < 90
pin was prepared
with the matrix composition shown in Table 20. This example provides MMF (240
mg).
Table 20. MMF Fill Composition
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight
Monomethyl fumarate PSD: d90 < 90 um 240 28.2
Capmul MCM 457 53.8
Cremophor RH 40 85 10.0
Povidone K 30 25.5 3.0
Lactic acid 42.5 5.0
TOTAL 850 mg 100%
105
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Example 14
A batch of enteric soft capsules (0.038 inch shell thickness) comprising
monomethyl
fumarate (MMF) particles having particle size distribution of PSD: d90 < 90
pin was prepared
with the matrix composition shown in Table 21. This example provides MMF (480
mg).
Table 21. MMF Fill Composition
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight
Monomethyl fumarate PSD: d90 < 90 I..tm 480 48-56.4
Capmul MCM 216-470 25.5-47
Cremophor RH 40 7.3-120 0.85-12
Povidone K 30 7.3-50 0.85-5
Lactic acid 21.7-50 2.55-5
TOTAL 850 mg-1000 mg 100%
Example 15
Enteric soft capsules comprising particles of dimethyl fumarate, monomethyl
fumarate,
or a combination thereof having particle size distribution of PSD: d90 < 90
vim can be prepared
with an 850 mg matrix in the compositions shown in Table 22. This example
provides DMF or
MMF in a QD formulation (-480 mg).
Table 22. DMF or MMF 850 mg Fill Compositions
Percent Weight (%)
Ingredient EX1 EX2 EX3 EX4 EX5 EX6
Dimethyl fumarate or Monomethyl fumarate
PSD: d90 90
56.4 56.4 56.4 56.4 56.4
56.4
< !Am
Caprnul MCM 30.6 39.95 28.9 28.9
25.5 32.7
Cremophor RH 40 8.5 0.85 8.5 8.5 10.2
6.1
Povidone K 30 0.85 0.85 2.55 2.55 4.25
1.8
Lactic acid 4.25 2.55 4.25 4.25 4.25
3.0
TOTAL 100 100 100 100 100 100
106
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Example 16
Enteric soft capsules comprising particles of dimethyl fumarate, monomethyl
fumarate,
or a combination thereof having particle size distribution of PSD: d90 < 90
[ma can be prepared
with a 1000 mg matrix in the compositions shown in Table 23. This example
provides DMF or
MMF in a QD formulation (-480 mg).
Table 23. DMF or MMF 1000 mg Fill Compositions
Percent Weight (/o)
Ingredient EX1
EX2 EX3 EX4 EX5 EX6
Dimethyl fumarate or Monomethyl fumarate
48 48 48 48 48 48
F'SD: d90 < 90 pn
Capmul MCM 44 36 47 34 34
38.9
Cremophor RH 40 2 10 1 10 10 7.2
Povidone K 30 1 1 1 3 3 2.2
Lactic acid 5 5 3 5 5 3.6
TOTAL 100 100 100 100 100 100
107
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Example 17
Stability of the Enteric Soft Capsules over Time
The temporal stability of the dimethyl fumarate enteric soft capsule
pharmaceutical
composition shown in Table 24 was assessed under three ICH conditions. A
sample of DMF
enteric soft capsules was subject to chemical analysis and two-stage
dissolution shortly after
manufacturing (T0). Samples of DMF enteric soft capsules were subjected to
Room Temperature
Conditions (25 C and 60% relative humidity) for 1 month, 2, months, 3 months,
and 6 months.
Other samples of DMF enteric soft capsules were subjected to Intermediate
Conditions (30 C
and 65% relative humidity) for 1 month, 2 months, and 3 months. Additional
samples of DMF
enteric soft capsules were subjected to Accelerated Conditions (40 C and 75%
relative
humidity) for 1 month and 2 months. After the designated incubation period,
the capsules were
chemically analyzed and evaluated in two-stage dissolution experiments at pH
1.2 and 6.8 as
described herein if conditions permitted (i.e., non-leaking capsules). Two-
stage dissolution
results for DMS enteric soft capsules at To, and after 3- and 6-months at Room
Temperature
Conditions (25 C and 60% RH) are shown in Figure 13.
Table 24. GMP DMF Fill Composition
Ingredient mg/capsule % weight
Dimethyl fumarate PSD: d90 < 90 gm 240 32.0
Capmul MCM 375 50.0
Cremophor RH 40 75 10.0
Povidonc K 30 22.5 3.0
Lactic acid 37.5 5.0
TOTAL 750 mg 100%
108
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133
PCT/US2015/047636
Table 25. GMP DMF Stability
Initial 25 C, 60% Relative Humidity
To 1M 2M 3M 6M
Assay 101.2% 101.0% 102.4% 101.25 98.8%
Degradation Products To 1 M 2 M 3 M 6 M
Monomethyl Fumarate 0.14% 0.13% 0.14% 0.16% 0.18%
RRT 0.74 ND ND 0.07% 0.09% 0.18%
RRT 1.61 0.05% ND ND ND ND
RRT 2.18 ND ND ND <0.05% 0.09%
Total Degradation Products 0.19% 0.13% 0.21% 0.25% 0.45%
30 C, 65% Relative Humidity 40 C, 75% Rel. Humid.
1M 2M 3M 1M 2M
Assay 100.1% 99.4% 99.5% 99.3%
113.1%*
Degradation Products 1 M 2 M 3 M 1 M 2 M
Monomethyl Fumarate 0.14% 0.17% 0.22% 0.22% 0.26%
RRT 0.74 0.14% 0.22% 0.28% 0.3% 0.46%
RRT 1.61 0.06% 0.11% 0.14% 0.15% 0.35%
RRT 2.18 0.34% 0.5% 0.64% 0.67% 1.07%
Total Degradation Products 0.14% 0.17% 0.22% 0.22% 0.26%
*Data were collected on fill extracted from leaking capsules.
Note: Leaking capsules were observed at the 2- and 3-month time points for the
accelerated condition (40
C, 75% RH). This was expected for the enteric soft gelatin capsules. The
intermediate condition (30 C,
65% RH) and long-term condition (25 C, 60%RH) will be assessed at the 12-
month and 24-month time
points to assess chemical stability.
109
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Example 18
Fill compositions with increasing amounts of one or more fumarate esters
(e.g., dimethyl
fumarate, monomethyl fumarate, or a combination thereof ranging from about 0.5
mmol to about
4.0 mmol) haying a particle size distribution of PSD: d90 < 100 [tm in a 750
mg fill are shown in
Table 26. Millimole values for DMF or MMF (shaded rows) specify the millimoles
of the
respective species at the specified mass (mg). These fill compositions may be
encapsulated by
any of the capsule shell compositions (e.g., an enteric soft capsule shell) as
described herein. In
one embodiment, the one or more fumarate esters comprise about 0.5 mmol to
about 3.7 mmol
FAE. In one embodiment, the fumarate ester (FAE) comprises DMF. In another
embodiment,
the fumarate ester comprises MMF. In another embodiment, the fumarate ester
comprises MMF,
DMF, or a combination thereof.
Table 26. Fumarate Ester 750 mg Fill Compositions
mg/capsule
Ingredient EX1
EX2 EX3 EX4 EX5 EX6
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 100 tim 80 85 90 95 97 100
mmol DMF 0.56 0.59 0.62 0.66 0.67
0.69
mmol MMF 0.61 0.65 0.69 0.73 0.75
0.77
Capmul MCM 535 530 525 520 518 515
Cremophork RH 40 75 75 75 75 75 75
Povidone K 30 22.5 22.5 22.5 22.5 22.5
22.5
Lactic acid 37.5 37.5 37.5 37.5 37.5
37.5
TOTAL 750
750 750 750 750 750
Ratio FAE to Fill 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.15 0.15
0.15
Percent Weight (%)
Fumaratc Ester PSD: d90 < 1001.tm 10.7 11.3 12 12.7 12.9
13.3
Capmul MCM 71.3 70.7 70 69.3 69.1
68.7
Crernophor RH 40 10 10 10 10 10 10
Povidone K 30 3 3 3 3 3 3
Lactic acid 5 5 5 5 5 5
TOTAL 100 100 100 100 100 100
110
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133
PCT/US2015/047636
Table 26. Fumarate Ester 750 mg Fill Compositions Cont.
mg/capsule
Ingredient EX7 EX8
EX9 EX10 EX11 EX12
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 100 gm 105 107 108 110 115 120
intnol DMF 0.73 0.74 0.75 0.76 0.80
0.83
mmol MMF 0.81 0.82 0.83 0.85 0.88
0.92
Capmukk) MCM 510 508 507 505 500 495
Cremophort RH 40 75 75 75 75 75 75
Povidonc K 30 22.5 22.5 22.5 22.5 22.5
22.5
Lactic acid 37.5 37.5 37.5 37.5 37.5
37.5
TOTAL 750 750
750 750 750 750
Ratio FAE to Fill 0.16 0.17 0.17 0.17 0.18
0.19
Percent Weight (/0)
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 100 gm 14 14.3 14.4 14.7 15.3 16
Capmul MCM 68 67.7 67.6 67.3 66.7 66
Cremophoe RH 40 10 10 10 10 10 10
Povidone K 30 3 3 3 3 3 3
Lactic acid 5 5 5 5 5 5
TOTAL 100 100 100 100 100 100
Table 26. Fumarate Ester 750 mg Fill Compositions Cont.
mg/capsule
Ingredient EX13 EX14 EX15 re h
EX17 EX18
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 100 gm 160 170 180 190 194 200
mmol DMF 1.11 1.18 1.25 1.32 1.35
1.39
mmol MMF 1.23 1.31 1.38 1.46 1.49
1.54
Capmul(R) MCM 455 445 435 425 421 415
Cremophorg RH 40 75 75 75 75 75 75
Povidone K 30 22.5 22.5 22.5 22.5 22.5
22.5
Lactic acid 37.5 37.5 37.5 37.5 37.5
37.5
TOTAL 750 750
750 750 750 750
Ratio FAE to Fill 0.27 0.29 0.32 0.34 0.35
0.36
Percent Weight (/0)
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 100 gm 21.3 22.7 24 25.3 25.9 26.7
Capmue MCM 60.7 59.3 58 56.7 56.1 55.3
Crcmophor RH 40 10 10 10 10 10 10
Povidone K 30 3 3 3 3 3 3
Lactic acid 5 5 5 5 5 5
TOTAL 100 100 100 100 100 100
111
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133
PCT/US2015/047636
Table 26. Fumarate Ester 750 mg Fill Compositions Cont.
mg/capsule
Ingredient EX19
EX20 EX21 EX22 EX23 EX24
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 100 gm 210 214 216 220 230 240
mmol DMF 1.46 1.48 1.50 1.53 1.60
1.67
mmol MMF 1.61 1.64 1.66 1.69 1.77
1.84
Capmukk) MCM 405 401 399 395 385 375
Cremophort RH 40 75 75 75 75 75 75
Povidonc K 30 22.5 22.5 22.5 22.5 22.5
22.5
Lactic acid 37.5 37.5 37.5 37.5 37.5
37.5
TOTAL 750 750
750 750 750 750
Ratio FAE to Fill 0.39 0.40 0.40 0.42 0.44
0.47
Percent Weight (/0)
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 100 gm 28 28.5 28.8 29.3 30.7 32
Capmue MCM 54 53.5 53.2 52.7 51.3 50
Cremophoe RH 40 10 10 10 10 10 10
Povidone K 30 3 3 3 3 3 3
Lactic acid 5 5 5 5 5 5
TOTAL 100 100 100 100 100 100
Table 26. Fumarate Ester 750 mg Fill Compositions Cont.
mg/capsule
Ingredient EX25
EX26 EX27 EX28 EX29 EX30
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 100 p.m 320 340 360 380 388 400
mmol DMF 2.22 2.36 2.50 2.64 2.69
2.78
mmol MMF 2.46 2.61 2.77 2.92 2.98
3.07
Capmul(R) MCM 295 275 255 235 227 215
Cremophorg RH 40 75 75 75 75 75 75
Povidone K 30 22.5 22.5 22.5 22.5 22.5
22.5
Lactic acid 37.5 37.5 37.5 37.5 37.5
37.5
TOTAL 750 750
750 750 750 750
Ratio FAE to Fill 0.74 0.83 0.92 1.03 1.07
1.14
Percent Weight (/0)
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 100 gm 42.7 45.3 48 50.7 51.7
53.3
Capmue MCM 39.3 36.7 34 31.3 30.3
28.7
Crcmophor RH 40 10 10 10 10 10 10
Povidone K 30 3 3 3 3 3 3
Lactic acid 5 5 5 5 5 5
TOTAL 100 100 100 100 100 100
112
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133
PCT/US2015/047636
Table 26. Fumarate Ester 750 mg Fill Compositions Cont.
mg/capsule
Ingredient EX31
EX32 EX33 EX34 EX35 EX36
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 100 gm 420 428 432 440 460 480
intnol DMF 2.91 2.97 3.00 3.05 3.19
3.33
mmol MMF 3.23 3.29 3.32 3.38 3.54
3.69
Capmukk) MCM 195 187 183 175 155 135
Cremophort RH 40 75 75 75 75 75 75
Povidone K 30 22.5 22.5 22.5 22.5 22.5
22.5
Lactic acid 37.5 37.5 37.5 37.5 37.5
37.5
TOTAL 750 750
750 750 750 750
Ratio FAE to Fill 0.74 0.83 0.92 1.03 1.07
1.14
Percent Weight (/0)
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 100 [tm 56 57.1 57.6 58.7 61.3 64
Capmul MCM 26 24.9 24.4 23.3 20.7 18
Cremophoe RH 40 10 10 10 10 10 10
Povidone K 30 3 3 3 3 3 3
Lactic acid 5 5 5 5 5 5
TOTAL 100 100 100 100 100 100
113
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Example 19
Fill compositions having one or more fumarate esters (e.g., dimethyl fumarate,
monomethyl fumarate, or a combination thereof ranging from about 0.5 mmol to
about 3.5
mmol) having a particle size distribution of PSD: d90 < 100 1..tm with a
constant weight ratio of
fumarate ester to fill (e.g., about 0.40) are shown in Table 27. Millimole
values for DMF or
MMF (shaded rows) specify the millimoles of the respective species at the
specified mass (mg).
These fill compositions may be encapsulated by any of the capsule shell
compositions (e.g., an
enteric soft capsule shell) as described herein. In one embodiment, the
fumarate ester comprises
DMF. In another embodiment, the fumarate ester comprises MMF. In another
embodiment, the
fumarate ester comprises MMF, DMF, or a combination thereof.
Table 27. Fumarate Ester Fill Compositions
Percent Weight (/0) mg/capsule
Ingredient
EXI-EX4 EXI EX2 EX3 EX4
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 1001.tm 28.5 80 85 160
170
mmol DMF N/A 0.56 0.59 1.11
1.18
mmol MMF N/A 0.61 0.65 1.23
1.31
Capmulk MCM 53.5 150 159 300
318
CremophorR RH 40 10 28 29.8 56
59.5
Povidone K 30 3 8.4 8.9 16.8
17.9
Lactic acid 5 14 14.9 28
29.8
TOTAL 100 280 298 560
595
Table 27. Fumarate Ester Fill Compositions Cont.
Percent Weight (%) mg/capsule
Ingredient
EX5-EX8 EX5 EX6 EX7 EX8
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 1001.tm 28.5 90 95 180
190
mmol DMF N/A 0.62 0.66 1.25
1.32
mmol MMF N/A 0.69 0.73 1.38
1.46
Capmur MCM 53.5 169 178 337
356
Cremophor RH 40 10 31.5 33.3 63
66.5
Povidone K 30 3 9.5 10 18.9 20
Lactic acid 5 15.8 16.6 31.5
33.3
TOTAL 100 315 333 630
665
114
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Table 27. Fumarate Ester Fill Compositions Cont.
Percent Weight (/0) mg/capsule
Ingredient EX9-EX12 EX9 EX10 EX11 EX12
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 100 gm 28.5 100 107 200 214
mtnol DMF N/A 0.69 0.74 1.39 1.48
mmol MMF N/A 0.77 0.82 1.54 1.64
CapmulR MCM 53.5 187 201 375 401
Cremophor RH 40 10 35 37.5 70.1 75
Povidonc K 30 3 10.5 11.3 21 22.5
Lactic acid 5 17.5 18.8 35.1 37.5
TOTAL 100 350 375 701 750
Table 27. Fumarate Ester Fill Compositions Cont.
Percent Weight CYO mg/capsule
Ingredient EX13-EX16 EX17 EX18 EX19 EX20
Fumaratc Ester PSD: d90 < 100 gm 28.5 105 110 210 220
mmol DMF N/A 0.73 0.76 1.46 1.53
mmol MMF N/A 0.81 0.85 1.61 1.69
Capmul' MCM 53.5 197 206 393 412
Cremophor8- RH 40 10 36.8 38.5 73.5 77.0
Povidone K 30 3 11.0 11.6 22.1 23.1
Lactic acid 5 18.4 19.3 36.8 38.5
TOTAL 100 368 385 735 770
Table 27. Fumarate Ester Fill Compositions Cont.
Percent Weight mg/capsule
Ingredient EX13-EX16 EX17 EX18 EX19 EX20
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 <100 jam 28.5 115 120 230 240
mmol DMF N/A 0.80 0.83 1.60 1.67
mmol MMF N/A 0.88 0.92 1.77 1.84
Cap mul' MCM 53.5 215 225 431 449
Cremophor RH 40 10 40.3 42.0 80.5 84.0
Povidone K 30 3 12.1 12.6 24.2 25.2
Lactic acid 5 20.1 21.0 40.3 42.0
TOTAL 100 403 420 805 840
115
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Table 27. Fumarate Ester Fill Compositions Cont.
Percent Weight (/0) mg/capsule
Ingredient
EX13¨EX16 EX13 EX14 EX15 EX16
Fumarate Ester PSD: d90 < 100 gm 28.5 350 375 400 428
intnol DMF N/A 2.42 2.6 2.78 2.97
mmol MMF N/A 2.68 2.88 3.07 3.29
CapmulR MCM 53.5 655 702 750 802
Cremophor RH 40 10 123 131 140 150
Povidone K 30 3 36.8 39.4 42.1 45
Lactic acid 5 61.3 65.6 70.1 75
TOTAL 100 1225 1313 1402 1500
116
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Example 20
A batch of enteric soft capsules (0.038-inch shell thickness) comprising BSL-
11 particles
having particle size distribution of PSD: d90 < 90 [tm were prepared with the
matrix composition
shown in Table 28.
Table 28. BLS-11 Fill Composition
Fill Ingredients Percent Weight ("/0) Mass/capsule
(mg)
BLS-11, PSD: d90 < 90 lam 28.50 214
Capmul MCM 53.50 401
Cremophor RH 40 10.00 75
Povidone K 30 3.00 23
Lactic Acid 5.00 38
Total Fill Weight 100.0% 750
Total Capsule Weight 1116
Samples from a batch of enteric soft capsules comprising the composition shown
in
Table 28 were subject to two-stage dissolution experiments in a USP Apparatus
11 with the
parameters shown in Table 29. For these experiments, the capsule was
introduced in to
simulated gastric fluid, 0.1 N HC1, pH 1.2, for 2 hours. After 2 hours, the
capsule was
transferred to simulated intestinal fluid, phosphate buffer, pH 6.8. The
results are shown in
Figure 14. The results show that the capsules retain their enteric properties
for at least 2 hours
in simulated gastric fluid at pH 1.2. The capsules began releasing BLS-11
within ¨10 minutes
after being transferred to simulated intestinal fluid, pH 6.8, and achieved
100% dissolution after
120 minutes at pH 6.8.
Table 29. Two-stage Dissolution Analysis Parameters
USP Apparatus II
Agitation Rate 100 RPM
Temperature 37.0 0.5 C
Media/Volume
0.1 N HC1, pH 1.2, 500 mL
Phosphate buffer, pH 6.8, 500 mL
Sample Profile:
Samples obtained at 60 min and 120 mm in 0.1 N HCl
Samples obtained at 10, 20, 30, 45, 60, 120 min in phosphate buffer pH 6.8
117
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Example 21
Method for Measurement of Fumarate Ester Particles Size Distribution
Fumarate ester particles (dimethyl fumarate or mono methyl fumarate) in the
form of a
dry powder were measured using a Malvern Mastersizer 2000 instrument equipped
with vacuum
unit and air pressure following manufacturer instructions; see, e.g. The
Mastersizer 2000
Operators Guide; MAN0247-2-0, Malvern Instruments Ltd. (1999), which is
incorporated by
reference herein for such teachings. Approximately 1.0 gram of the test sample
was introduced
into the dry powder feeder and measured under the parameters shown in Table
28, and the
volume size distribution and the volume mean diameter were determined. In one
aspect,
described herein, the particle size distribution is expressed as a particle
volume distribution and
the mean particle size of the distribution is expressed as a volume mean
diameter.
Table 30. Particle Size Distribution Measurement Parameters
Analysis Model General Purpose
Sensitivity Normal
Particle RI 1.468
Vibration feed rate 60%
Dispersive air pressure 1.3 bars
Absorption 0.1
Measurement time 6 seconds
Measurement snaps 6,000
Background time 6 seconds
Background snaps 6,000
No. of measurements 1 per cycle
Obseuration 0.5% to 6.0%
118
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Example 22
Clinical Study of Test Pharmaceutical Compositions Comprising Fumarate Esters
Patient Population
Non-smoking male or females (n = 24) within the age range of 18 to 65 years,
having a
Body Mass Index (BMI) greater than or equal to 18.5 kg/m2 and less than or
equal to 29.9 kg/m2
and having given their written informed consent were at the Period-I check-in
of the study. The
patient demographics and number of patients dosed is provided in Table 31.
They did not have
any significant diseases or clinically significant abnormal findings during
screening, medical
history, physical and clinical examinations, laboratory evaluation, 12-lead
ECG recording and
vital sign measurement. Female volunteers had a negative pregnancy test.
Volunteers who meet
all the inclusion and exclusion criteria were enrolled into the study.
All the subjects willing to participate in the study were screened no more
than 28 days
before the first drug administration in order to assess their eligibility by
satisfying all of the
inclusion and exclusion criteria. During screening, the medical history of the
subjects was
elicited and they underwent a general clinical examination, measurement of
blood pressure, heart
rate, body temperature, respiratory rate, 12-Lead ECG, clinical laboratory
evaluations,
immunological tests for HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus), HBsAg (Hepatitis B
Surface
Antigen) and HCV (Hepatitis C Virus), Alcohol screen, Nicotine screen and
Screen for drugs of
abuse. Urine pregnancy test was performed for all female subjects. Subjects
were selected for
inclusion in the study no more than 28 days before the first drug
administration.
Table 31. Study Population Inclusion Numbers and Parameter Information
No. Planned for Inclusion 24
34
Enrolled and Checked-in
(Subject Nos. 1001-1024 and 10 standby subjects)
D Period-I 24
osed
Period-II (7 days later) 23
Dismissed 01
Analyzed 23
Considered for statistical analysis 23
Parameters Dosed Subjects (24)
Completed Study (23)
Age (years) 42.2 12.81 42.2
13.10
Height (cm) 171.14 8.668 171.32
8.817
Weight (kg) 75.05 1 10.135 75.35 1
10.258
BMI (kg/m2) 25.55 2.280 25.60
2.320
119
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
Study Methodology
The performed study was a randomized, pilot, two-way crossover, open-label,
single-
dose, fasting study, with a screening period of 28-days prior to the first
dose administration. In
each study period, 19 blood samples, including one pre-dose blood sample, were
collected from
each subject except for the subject who did not complete the study to analyze
the
pharmacokinetic profile of the Test pharmaceutical composition as well as the
Reference
pharmaceutical product.
Based on the elimination half-life of dimethyl fumarate, a washout period of 7-
days was
kept in between the successive dosing days. Multiple blood samples were
collected to assess the
bioequivalence between the Test and the Reference product. For this study with
a crossover
design, each subject except for one dismissed subject received both the
products (Test Product-T
and Reference Product-R) during the study. Hence, every subject acted as his
own control and
no separate group of subjects was required to act as the control group.
Subjects were dosed
according to the treatment sequence provided in Table 32. The duration of the
clinical part of
the study was about 9 days (one day prior to the drug administration in Period-
I until the last
study procedure in Period-II).
Table 32. Treatment Sequence
Period-I Period-II
Sequence 1 Treatment-R (Reference) Treatment-T (Test)
Sequence 2 Treatment-T (Test) Treatment-R (Reference)
After an overnight fast of at least 10 hours, a single oral dose (240 mg) of a
Test
pharmaceutical composition comprising dimethyl fumarate or a Reference
dimethyl fumarate
composition was administered to the subjects in sitting posture with 240 mL of
drinking water at
ambient temperature. The administration was as per the randomization schedule
and under open-
label conditions.
Dosing water was measured and poured into individual containers before dosing.
The
containers were then covered and allowed to remain at ambient temperature
until used. The drug
was provided to the subjects in unit-dose containers. A visual inspection of
each subject's mouth
and hands was performed immediately after dosing to ensure drug ingestion.
120
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
During the first 4 hours post-dose, subjects were encouraged to stay awake,
seated in an
upright position, and allowed to rise under supervision only for brief periods
of time, in order to
comply with study-related activities and to use the washroom. Subjects were
permitted to lie
down for treatment of any adverse event.
No water ingestion was permitted from 1.0 hour pre-dose to 1.0 hour post-dose,
with the
exception of the 240 mL of dosing water.
No food was allowed for at least 4 hours post-dose. Standardized meals with
beverages
were provided to the subjects at the following times: between 4.5 and 5.5
hours post-dose;
between 9.5 and 10.5 hours post-dose; and at 13.5 hours post-dose.
All meals and beverages were free of alcohol, grapefruit products, xanthine,
and caffeine
and were identical between the study periods.
Safety was assessed from the screening period to the end of the study. It was
assessed
through clinical examinations, vital signs assessment, 12-lead
electrocardiogram (ECG), clinical
laboratory parameters (e.g., biochemistry, hematology, immunology, and urine
analysis),
pregnancy test (for female subjects), subjective symptomatology, and
monitoring of adverse
events.
A total of 19 pharmacokinetic blood samples (6 ml, each) were drawn in each
period
according to the following schedule: 0 (pre-dose), and at intervals of 0.33,
0.67, 1, 1.25, 1.5,
1.75, 2, 2.25, 2.5, 2.75, 3, 3.33, 3.68, 4, 4.5, 5, 6, and 8 hours post-dose.
The plasma samples of subjects were analyzed using a validated LC-MS/MS method
for
monomethyl fumarate. Calibration curve using an 8-point calibration curve
standards, with
concentrations ranging from 21.35 ng/mL to 4967.75 ng/mL were used to
determine the
concentrations of monomethyl fumarate in the samples of various subjects.
Pharmacokineti c Parameter Calculations
The pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated from the drug concentration
versus time
point by non-compartmental model using WinNonlin Professional Software Version
5.3
(Pharsight Corporation, USA) for monomethyl fumarate. Statistical comparison
of the
pharmacokinetic parameters of the two products (Test, Reference) was performed
using PROC
MIXED of SAS Version 9.3 (SAS Institute Inc., USA).
121
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133 PCT/US2015/047636
The maximum measured plasma concentration (C.) and the time of observing the
peak
concentration (T,õ,,x) was taken directly from the plasma concentration versus
time profile of the
individual subjects.
Area under plasma concentration versus time curve (AUCo-T) in hmg/mL from time
zero
to the last measurable concentration as calculated by the linear trapezoidal
rule.
Area under the plasma concentration versus time curve (AUG) in hmg,/mL from
time
zero to infinity; where AUG-. = AUG, + Ct/Xz; G is the last measurable
concentration and Xz
is the terminal rate constant. The AUG-, was the sum of measurable and
extrapolated parts.
First order rate constants associated with the terminal (log-linear) portion
of the curve
were estimated via linear regression of time versus log concentration This
parameter was
calculated by linear least squares regression analysis using last three or
more non-zero plasma
concentration values. The units of k, were hours-1 (1/h).
The terminal half-life was calculated using the formula: 0.693/4 The unit of
tv, was hour
(h).
The residual area in percentage was determined by the formula:
RAUCo, - AUG,)/AUG¨,1 x 100.
The pharmacokinetic parameters of monomethyl fumarate for Test Product-T and
Reference Product-R are summarized in Table 33. The mean plasma concentration
versus time
curve over eight hours is shown in Figure 15.
Table 33. Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Monomethyl Fumarate; Test Product-T
and Reference
Product-R
Mean SD
Pharmacokinetic Parameters (Un-transformed data)
Test Product-T Reference Product-R
Tina, (h) 2.5 (1-5) 2.5 (1-5)
Cmax (ng/mL) 1321.3 + 618.9 1174.7 433.9
AUG-, lyng/mL 1818.415 + 532.5886 1907.405 + 525.7948
AUCõ 1919.247 533.8147* 2119.693 688.1376
(1/11) 1.323 0.3573* 1.103 0.3930"
trõ (It) 0.563 + 0.1586* 0.864 0.8508"
Residual Area in Percentage 1.799 + 1.0276* 6.481 + 14.0612
*n = 20
An = 22
122
CA 02962916 2017-03-28
WO 2016/057133
PCT/US2015/047636
Statistical Methods
Descriptive statistics were calculated and reported for all pharmacokinetic
parameters of
monomethyl fumarate. ANOVA, power, and ratio analysis for 1n-transformed
pharmacokinetic
parameters Crnax, AUC0, and AUC0¨ were calculated and reported for monomethyl
fumarate.
The 90% confidence interval for the ratio of the geometric least-squares means
were calculated
for the ln-transformed pharmacokinetic parameters, Cm., AUCo¨T, and AUCo¨oo
for
monomethyl fumarate. All statistical analyses for Monomethyl Fumarate were
performed using
F'ROC MIXED of SAS Version 9.3 (SAS Institute Inc., USA).
The relative bioavailability analysis (e.g., geometric least squares means,
ratios, 90%
confidence interval, intra subject CV, and power) of Test Product-T versus
Reference Product-R
for monomethyl fumarate is summarized in Table 34.
Table 34. Relative Bioavailability Results for Monomethyl Fumarate (n = 23)
Geometric Least Squares Means 90% Intra
Parameters Test Reference Ratio Confidence
Subject Power(
%)
Product-T P ro du ct-R (T/R)% Interval CV (%)
Cnia, 1189.160 1102.137 107.9 92.04-126.49
32.1 75.3
AUC0, 1747.744 1847.786 94.6 87.59-102.14
15.2 99.8
1875.657* 2034.147 92.2 85.17-99.82 14.3 99.7
= 20
^n = 22
123