Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02966809 2017-05-04
WO 2016/087162 PCT/EP2015/076064
APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CUTTING OR EMBOSSING COATINGS
Field of the invention
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for making a frozen
confectionery
product with a peelable confectionery coating. In particular the invention
relates to an apparatus
and method for automatically applying cutting or embossing lines to a
confectionery coating,
especially a gel coating, during the production on an industrial manufacturing
line.
Background
Frozen confectionery products consisting entirely of frozen gel or comprising
a frozen gel
coating are known and are popular in particular with children.
One example is a frozen confectionery product comprising a core consisting of
a frozen
confection said core being at least partially coated with a frozen flexible
edible gel coating or
layer. Such a frozen confectionery product is sold by Nestle Thailand under
the brand name
"Eskimo Monkey". This product comprises an ice-cream core being coated with a
frozen
flexible edible gel layer. This gel layer can be peeled off by the consumer
and eaten separately.
Since the gel is resistant to liquefaction, even in the defrosted state, the
product parts that have
been peeled off by the consumer remain intact without melting and dripping. To
facilitate the
peeling, four longitudinal cutting lines are provided in the gel layer, so
that four flaps of peel can
be peeled off One thereby achieves a banana-style peeling effect.
W02013064376 discloses a product with a core of ice cream which is coated with
at least two
visually distinct layers of jelly. The patent application mentions that when
the two gel layers are
frozen in two separate steps, they show little adhesion between each other, so
that they can be
peeled off separately by a consumer. However, due to the very close
characteristic, both jelly
shell and core, or the different layers of jelly, can be found to adhere to
each other and may be
difficult to peel apart from each other during consumption in particular for
children who enjoy
these kinds of composite frozen confectionery products. For example, thinner
layers of coating
may be more difficult to peel off To facilitate the peeling of the gel coating
it is important that
the product has well defined pre-cuts in the gel coating.
To cut spiral cutting line into the gel coating, a cutting tool as described
in the International
Patent Application PCT/CN11/077465 filed on July 22nd, 2011 can be used.
1
CA 02966809 2017-05-04
WO 2016/087162 PCT/EP2015/076064
When manufacturing a shell and core products on a standard industrial
production line in a first
production step, a liquid, jelly-like material is dosed into a mold cavity. As
the mold is
suspended into a cold brine solution, the jelly material starts to solidify
and freeze. Once a thin
layer of the jelly material has become frozen, the remaining unfrozen material
is sucked out of
the mold, creating a shell of frozen jelly. Into this jelly-shell, the core
material, such as ice cream
mix, is dosed and allowed to freeze. Prior to full completion of freezing, a
stick is inserted and
the product is completely frozen. Subsequently, the outside of the mold is
sprayed with a warm
liquid to soften or melt a thin surface-layer of the product. Using grippers
the product is pulled
out of the mold by it's stick. The product, suspended from the grippers, is
then transported
towards other process steps, and finally to a wrapping machine.
To manufacture a peelable stick, an additional process steps is included to
apply of cuts to the
jelly-shell. These cuts are essential for a proper working of the peelable
effect, which means that
the consumer can easily pull down slices of jelly material using his or her
teeth. The role of the
cut lines is to guide the separation of the jelly to form e.g. banana-type
slices. Without the cut
lines, the jelly skin would rather be torn-off in pieces, which does not
reflect a banana-type
peeling experience. The industrial application of such cut lines, however,
constitutes a technical
challenge.
CN200976814 describes frozen confection products characterized by an ice cream
core and a
gel-like shell on various overall shapes. The shell part can be peeled off by
the consumer and
consumed. The utility model does not specify how to apply the cut lines.
W02014/079848 specifies compositional details of the shell material that can
be used to create
a gel-type shell that can be subsequently sliced and displays graphics of a
frozen confection
exhibiting a spiral-type peeling option. The patent mentions a cutting action
to apply lines of
weakness to guide the spiral-type peeling action. The cut is applied by two
set of blades, which
are pressed from opposite sides against the surface in a horizontal movement.
During the
process, the frozen confection is vertically suspended by the stick via
grippers.
While other shapes of cut lines than a spiral can principally be manufactured
using that process,
it has been found this procedure has limitations when applied to vertical cut
lines for generally
cylinder-shaped products. In particular, the process meets limitations if more
than two cut lines,
such as 3, 4 or more lines, are to be produced with the lines evenly
distributed around the
circumference of the product. The problems arise from the fact that on modern
production lines,
2
CA 02966809 2017-05-04
WO 2016/087162 PCT/EP2015/076064
the products are arranged in rows of typically 4 to 20 or more products side-
by-side. The
products are suspended from their stick and there is little space between the
products available
to arrange cutting mechanisms in the gap between adjacent frozen confections.
Even if the gap is
large enough to accommodate such mechanisms, such a procedure would require a
complex
mechanical installation.
One problem with the current cutting mechanisms is that it provides mechanical
stress on the
production line when products are moved up and down.
Furthermore, for frozen confection products in the form of a stick with
longitudinal cut lines, it
was found that the products tend to remain stuck in the cutter or they that
may break apart
during the process of cutting of the coating.
None of the documents describe a solution to improve the cutting of a gel
layer of a frozen
confection.
There is therefore a need to improve on the cutting of the gel coatings both
for single and
composite products with multiple gel layers.
Object of the invention
It is the objective of this invention to provide a tool and a method to apply
such cut lines on the
frozen confection coating while avoiding the aforementioned disadvantages.
Summary of the invention
It was found that a combination of separate rotatable side knives in
combination with an end
knife provides a solution to the above-discussed drawbacks.
Accordingly, the present invention relates to a coating cutting tool for
frozen confection
comprising
a frame defining a product void for receiving a product at least partly
coated,
a set of side knives comprising at least two knifes mounted on the frame
opposite of the
product void, wherein the knives are rotatable arranged on the frame such that
they can be
rotated into a product coating cutting position for cutting the coating on the
side of the product
and out of such a position to a non-engaging position to allow the product to
be moved passed
3
CA 02966809 2017-05-04
WO 2016/087162 PCT/EP2015/076064
the knives, and
an end knife for cutting the coating on the end of the frozen confection.
The invention while providing well defined cutting pattern also reduces the
force needed to pull
or push a product into the cutting mechanism. It has the further advantage
that products that
accidentally get stuck inside knives assembly may easily be released.
According to a second aspect the invention relates to a method for cutting or
embossing a
coating on a frozen confection comprising
providing a coating cutting tool as described in this application,
providing a frozen confection being at least partially coated,
inserting the frozen confection preferably vertically into the coating cutting
tool product
void until the coating of the end of the frozen confection engages at least
partly with the end
knife or knives,
cutting the coating on the frozen confection on the sides with the first pair
of side
knives, and removing the frozen confection again, and
wherein the cutting of the coating on the side of the product is due to the
relative
movement between the coated frozen confection and the side knives.
Brief description of the figure
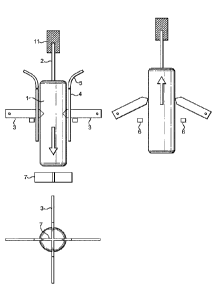
Fig. 1 shows schematically a coating cutter with knives that swing upwards
during product
removal.
Fig. 2 shows schematically a coating cutter with knives that swing downwards
during product
removal. The end knife arrangement (not shown) is the same as depicted in fig.
1.
Fig. 3 shows schematically a coating cutter with a set of knives including an
end knife which
moves up and down for cutting. The product is static. The end knife
arrangement (not shown) is
as in Fig. 1.
Fig. 4 shows schematically a coating cutter for irregular product shapes. The
knives can
individually follow the contour of the product, supported by a spring
mechanism. Cutting depth
is adjusted through regulator plates. The end knife arrangement (not shown) is
the same as
depicted in fig. 1.
Fig. 5 shows schematically a coating cutter with a plunger for clearing stuck
products.
Fig. 6 shows schematically a coating cutter mounted on a rail to remove the
knives to clear out
stuck products.
4
CA 02966809 2017-05-04
WO 2016/087162 PCT/EP2015/076064
Detailed description of the invention
In the present context the coating on the frozen confectionery product is a
flexible
coating. In a preferred embodiment of the invention the coating is a gel
coating.
In a preferred embodiment of the invention the position of the set of side
knives and the end
knife are arranged such that the cutting lines on side of the products and
cutting lines at the end
of the product are aligned. This allows e.g. peels running from the top of the
product and along
the sides to be formed. For example, a banana type peels can be made. The
cutting lines of the
1 0 side and top cut may be aligned so that they are directly abutting and
form a common groove in
the coating or may be positioned with a space or abutting however still
allowing a continuous
peel to be formed when the top coating is being pulled.
In the present context a product void for receiving a product is an open space
within the cutting
1 5 tool wherein the product can be inserted.
Further in the present context a frame is a structure or housing onto which
the side knives are
mounted and which defines the void. The frame may comprise an inlet funnel
and/or a side
guide. The inlet funnel ensures that products which are not perfectly centred
above the set of
20 side knifes become aligned prior to be inserted into said set of side
knifes. The side guide is a
tubular shaped member which keeps the product centred during the cutting step.
It helps to
achieve equal cutting depths of the knives. The funnel and side guide shown in
to fig. 1 may be
used in the other embodiments of the coating cutting tool shown in this
application except for
the embodiment of fig.4, where the side guide is not needed.
The side knives are preferably blades of metal. The preferred thickness of the
blades is from 0.5
to 5 mm for that part of the blade that is inserted into the coating, with the
cutting edge being a
sharp edge.
The side knives are rotatable arranged on the frame by means of an axis that
holds each knife
and allows rotation and blocking means which restricts the rotation movement
of the knife in one
direction.
Further in the present context an end knife is a knife which may have one or
more cutting
blades. In a preferred embodiment the end knife has 2 to 6 blades arranged in
a cross or a star.
5
CA 02966809 2017-05-04
WO 2016/087162 PCT/EP2015/076064
In the present context "cutting" means cutting, embossing, providing notches
or scores.
In one advantageously embodiment of the coating cutter the side knives are
rotatable to the
product cutting position when the product is moved out of the product void. In
this embodiment
a frozen confectionery is first introduced into the void, cut by the end
knives and then the side
knives are moved into a cutting position, and the cutting of the side coatings
takes place as the
frozen confection is moved out of the void.
In another advantageously embodiment of the coating cutter the knives are
rotatable to a product
cutting position when the product is introduced into the product void. In this
embodiment the
knives are pushed into cutting position by the product descending into the
void and the coating is
cut until it reaches the end knife. Then the side knives are rotated to a non-
engaging position and
the product can be freely moved out of the cutter.
To secure the side knives during the engagement with the product coating, the
cutter may further
comprise blocking means statically fixing the rotation of the side knives when
they are in the
product cutting position.
In a method according to the invention the side knives are rotated into a
fixed product cutting
position before the product is introduced into the product void and released
from this cutting
position when the product is moved out of the product void again. This
provides precise cutting
line.
In a another method according to the invention the side knives are rotated
into a product cutting
position when the product has reached the end knife and engages with the
coating of product
when the product is moved out of the void. This also has the advantage that
precise cutting lines
are obtained. This further has the advantage that the product and the stick by
which it is
suspended is not compressed during the cutting step, thus avoiding possible
breaking due to
compression.
The insertion of the product into the coating cutting tool is done by a
providing a fixed coating
cutting tool frame and moving the frozen confection into the void of the tool.
Alternatively, the
insertion of the product into the coating cutting tool is done by moving the
coating cutting tool
frame to enclose the frozen confection in the void.
6
CA 02966809 2017-05-04
WO 2016/087162 PCT/EP2015/076064
In a preferred embodiment of the coating cutter the side cutting knives have a
counterweight at
the end of the knives not engaging with the product, which counterweight is
situated on the
opposite of the knives points of rotation. The counterweight pushes the side
knives into
engagement with the coating and ensures a continuous cut in the coating.
Alternatively, the
knives may be spring loaded to push the knives into engagement position.
The present invention is particular advantageous for cutting gel coating along
the products axis.
In a preferred embodiment the coating cutter has a first set of side knives to
cut the coating of a
cylindrical product along its longitudinal axis.
When the side knifes are engaged in the cutting position, the cut reaches
through the
full thickness of the coating to the desired cutting depth. This is desirable
when the
coating need to be fully cut to ensure a smooth peeling effect. A preferred
depth of the
cut in the coating for confectionery coatings is in the range between 0.5 and
7 mm.
In order to ease or fasten the removal of a product engaged with the knives in
the coating cutter,
the coating cutter may comprise a movable plunger which preferably is mounted
on the frame to
assist in the release of the frozen confection from the knife or knives of the
coating cutter.
In the present context a gel coating may be a layer of gel which completely or
partly covers a
frozen confectionery core. It may have any form e.g. being a stripe or stripes
or rods.
Further in the present context unless otherwise indicated % of a component
means the % of
weight based on the weight of the composition, i.e. weight/weight %.
In a preferred embodiment of the invention the gel coating has a total solid
content from 20 to
45% based on weight of the gel (wt) and comprises 0.2 to 2 % wt of a gelling
agent or
combination of gelling agents, more preferably from 0.3 to 1.5% wt of gelling
agent or agents.
The solid content and the gelling agent provide a gel coating which is both
flexible and resilient
enough that it can be peeled off the frozen confection core or from other gel
coatings without
breakage.
Preferably the gel coating comprises gelling agent selected from the group
consisting of konjac,
carrageenan, xanthan, locust bean gum, gellan gum, pectins, alginates, agar,
gelatine and starch
or a combinations thereof
7
CA 02966809 2017-05-04
WO 2016/087162 PCT/EP2015/076064
The gel coating composition of the present invention may further include one
or more additional
ingredients such as flavors, sweeteners, colorants, setting salts, acids,
buffer salts or a
combination thereof
Sweeteners can include, for example, sucrose, fructose, dextrose, maltose,
dextrin, levulose,
tagatose, galactose, corn syrup solids and other natural or artificial
sweeteners. Sugarless
sweeteners can include, but are not limited to, sugar alcohols such as
maltitol, xylitol, sorbitol,
erythritol, mannitol, isomalt, lactitol, hydrogenated starch hydrolysates, and
the like, alone or in
combination. Usage level of the flavors, sweeteners and colorants will vary
greatly and will
depend on such factors as potency of the sweetener, desired sweetness of the
product, level and
type of flavor used and cost considerations. Combinations of sugar and/or
sugarless sweeteners
may be used.
In a preferred embodiment of the frozen confectionery product the at least one
gel coating
comprises 25 to 45 % wt of sweetener, preferably from 30 to 43 % wt.
Advantageously, the
sweetener is sucrose or glucose syrup or a combination thereof In a further
preferred
embodiment of the invention, the sweetener consists of 15% wt sugar and 18% wt
glucose
syrup.
The frozen confectionery product according to the invention may comprise one
or more
additional gel coating(s) on top of or beneath the gel coating, which
additional gel coatings at
least partly overlaps with the other gel coating.
The frozen confection product according to the invention may be provided with
at least two
cutting line allowing peeling off the gel-coating at least partially. With
only one cutting line, the
product needs to be supported at the opposite side, which may damage the
coating. The cutting
line does not necessarily have to extend through the complete gel coating. In
particular,
according to one embodiment of the invention, it is possible that the depth of
the cutting line or
lines corresponds to the thickness of an outer gel layer. In this case, the
gel coating can be
peeled off partially, i.e. only the outer gel layer can be peeled off, while
the inner gel layer,
which is not provided with any cutting lines, remains intact.
According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, several cutting lines
extending
longitudinally across the gel coating are provided, so that the coating can be
peeled off by
pulling down stripes, similar to peeling a banana. As mentioned above, it is
possible that all of
8
CA 02966809 2017-05-04
WO 2016/087162 PCT/EP2015/076064
the layers constituting the coating or only an outer layer or several outer
layers are peeled off
It is further preferred that the product comprises a stick, such as a wooden
or plastic stick,
having one portion which is inserted into the core and another portion by
which the product can
be handled and fixed in the coating cutter. Further, this allows easy handling
of the product
during manufacturing and consumption. The consumer can hold the stick with one
hand, and
peel off the gel layer with the other hand or using the teeth. Alternatively,
it is also possible to
make products without a stick, for example in a dome shape or in a shape
imitating the shape of
a fruit such as an apple or a pear. These products can then be consumed as a
dessert using a
plate and a spoon.
According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, the gel layer comprises
one or more
gelling hydrocolloids, in particular a polyanionic gelling hydrocolloid. This
leads to the desired
consistency and peelablity. Gelling properties can be achieved by various
stabilisers and
combinations thereof An overview of stabilisers used in ice cream and
indications on its gelling
properties can be found in literature such as "Ice Cream, Sixth Edition, R.T.
Marshall, H. D.
Goff, R.W. Hartel eds., Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, 2003. Optionally
the gel layer
can comprise a gelation controller or inhibitor. This reduces the texture
degradation that
normally occurs when a gel is stored hot in its liquid state for a longer
time, or when it is cooled
down and then reheated.
Preferably each gel layer has a thickness of between 2 and 5 mm. A gel layer
which is too thin
makes the peeling difficult, since the gel layer may rupture. A gel layer
which is too thick is not
desirable as it is more difficult to peel, and because of the relatively high
sugar content of the gel
which has a negative impact on the nutritional characteristics of the product.
It should also be noted that the gel layer does not have to cover the core
completely, but may
cover only a part or parts of the product.
The frozen confection with a gel coating can be produced with a method for
manufacturing
comprising the following steps:
- filling a first jelly mix into a mould, freezing the jelly mix so that it
forms a first frozen gel
coating in the mould and sucking off the unfrozen jelly mix,
- optionally filling a second jelly mix into a mould, freezing the jelly
mix so that it forms a
second frozen gel coating in the mould and sucking off the unfrozen jelly mix,
thereby obtaining a shell consisting of two frozen gel coatings,
9
CA 02966809 2017-05-04
WO 2016/087162 PCT/EP2015/076064
- filling a third mix forming the core consisting of a frozen confection
into said shell,
- freezing and de-moulding the product,
-optionally inserting a stick into the core of the frozen confection.
In a further embodiment of the invention the cutting line does not extend
through the complete
gel coating. In particular, it is possible that the depth of the cutting line
or lines corresponds to
the thickness of an outer gel coating. In this case, the gel coating can be
peeled off partially, i.e.
only the outer gel coating can be peeled off, while the inner gel layer, which
is not provided with
any cutting lines, remains intact.
It should be noted that, although the cutting lines preferably extend through
the entire gel
coating, so that it can be peeled off entirely, they can also only cut through
an outer gel layer,
leaving an inner gel layer intact. This results then in a product where only
the outer gel layer can
be peeled off, revealing an inner gel layer (having preferably a different
color). It is also possible
to have different cutting lines in the inner layer that have been cut or
created in a previous step.
The frozen confection forming the core can comprise ice cream, milk ice, water
ice, sherbet,
sorbet or a gel.
In a desirable design to facilitate the peeling, four longitudinal cutting
lines are provided in the
gel layer, so that four flaps of peel can be peeled off One thereby achieves a
banana-style
peeling effect. The number of flaps may vary e.g. being 3 to 5 or more for
different product
designs.
Alternatively, the frozen confectionery product may be produced by extruding
the core and then
the adding gel coating(s) done by dipping, enrobing or spraying.
EXAMPLES
By way of example and not limitation, the following examples are illustrative
of various
embodiments of the present disclosure.
Several examples of the process of the invention will be given to demonstrate
the invention and
variants of it. If not otherwise stated, the application of the cuts applies
for peelable sticks of
generally cylindrical shape. It further applies to products situated at the
production line, right
CA 02966809 2017-05-04
WO 2016/087162 PCT/EP2015/076064
after demolding, typically at the location of the coating dipping station. The
products are
suspended from grippers on their stick in a row of several products and
perform down/up
movements typically used for dipping into coating. If not stated otherwise,
the coating dip tank
has been replaced by a set of knife assemblies as described in detail in the
examples below. The
end knife is shown in fig.1 only, but the same principle applies to the other
drawings as well.
Example 1
Fig. 1 shows a coating cutter with a set of the side knives (3) into which the
product (1) is
introduced and subsequently retracted. The number of knives (3) can be one or
more. Typically,
the number of knifes is 4. The knives consist of sharp blades with a pointed
or rounded end, that
reach through the skin layer of the product (1) up to the core layer. The
blades are fixed
statically horizontally when the product is pushed into the knives until the
desired length of the
cut is achieved. The figures shows a side view of product (1) hold on the
stick (2) by a gripper
(11). The end knife (7) is located beneath the product (1). Also shown is a
schematic top view
showing 4 side knives (3) and the cross shaped end knife (7). To apply the end
cuts, the end
knifes are fixed beneath the side knives. When the product is pushed into the
side knives and
close to the end point of the down movement, the end of the product is
inserted into the knifes at
a depth corresponding to the desired cut depth, typically the thickness of the
gel layer
The embodiment of the invention shown in Fig. 1 uses knifes, the ends of which
can swing
upwards around their axis but are blocked from swinging downwards by blocking
means (6).
These knives allow to reduce the resistance of the knifes towards retraction
after the cut is
applied. To this end, the knife blades are oriented without load in a
horizontal position
(engaged), when the product moves downwards and being cut. When the products
are retracted,
however, the knives swing upwards and sideways around their axis. They no
longer interfere
with the confectionery coating, reducing the force needed to pull the product
out from the cutting
tool. This is of advantage in case of products accidentally getting stuck
inside the knives . Such
products have to be manually pushed out, e.g. by means of a stick or a hook.
Doing so against
the resistance of the static knifes is hard. With the knives swinging out of
the way, this action is
greatly facilitated, making handling of such irregularities easier.
Example 2
The embodiment of the invention shown in Fig. 2 involves principally a knife
as described in
Example 1. However, said knife assembly with the knife capable of swinging out
of the way
upon product retraction, is installed upside-down. Consequently, this set-up
allows inserting the
products into the coating cutter without performing any cutting, since the
knife has swung out of
11
CA 02966809 2017-05-04
WO 2016/087162 PCT/EP2015/076064
way. When pulling back the product out of the coating cutter, then the knives
engage and are
forced into the gel layer by means of a counterweight (8), or a spring and the
force exerted by
the up-moving product. The cuts are therefore applied during the up-movement
of the product.
Therefore, no pressure is applied on the product and on the stick by which it
is kept, but the
force is a pull-force. This procedure reduces the risk of products getting
stuck in knives in the
coating cutter in case of breakage of the stick from insertion pressure.
Example 3
The embodiment of the invention shown in Fig. 3 relates to the movement of the
knife assembly
along the product axis while applying the cuts. In this example, the product
is not lowered into
the coating cutter. Instead, the coating cutter is raised to become inserted
into the static product.
After application of the cut, the coating cutter is retracted back down. The
advantage of this set-
up consists in eliminating the need to forcefully lower and raise the product,
thereby avoiding
any mechanical stress on the production line.
Example 4
The embodiment of the invention shown in Fig. 4 relates to a coating cutter
capable of cutting
products having a stronger conicity or more irregular shape which would make
it impossible to
obtain a continuous cut through the skin layer by means of the cutting
mechanisms explained
previously. This is achieved by allowing some lateral movement of the
individual blades during
the cutting process. This way they can adapt to changing surface profiles of
the product. Such a
knife is preferably pushed against the product surface by a mechanical spring
(12) and can be
equipped with a cutting depth regulator plate (10) controlling the cutting
depth. The side knives
are rotatable arranged in the coating cutter in a way that allows lateral
movement to follow the
product profile.
Example 5
The embodiment of the invention shown in Fig. 5 relates to a coating cutter
comprising a
mechanism for removing products that get accidentally stuck inside the coating
cutter during the
cutting process. One or more rods or plungers (13) are located at the bottom
of the coating
cutter, beneath the end cutter (see also top view in fig 5). Once the product
has been introduced
into the coating cutter and is being retracted, said rods or plungers are
pushed upwards by an
actuator, following the retracting product. Products that got stuck inside the
knife assembly or
product parts remaining inside the assembly are then pushed out by the rod(s),
clearing the
assembly for the next product. The rods' pushing action may be activated on
demand by a
manual switch or can be automatically applied at each cutting cycle.
12
CA 02966809 2017-05-04
WO 2016/087162 PCT/EP2015/076064
Example 6
The embodiment of the invention shown in Fig. 6 shows a further mechanism to
facilitate
removal of products that got stuck inside the cutting unit during cutting.
This mechanism
comprises the installation of the coating cutter on a short rail (14). Using
an air cylinder or
another actuator, this mechanism allows to push away the coating cutter from
the path of the
products' up/down movement. The coating cutter can then conveniently be
cleared before being
pushed back to the original position.
1 0 It should be understood that various changes and modifications to the
presently preferred
embodiments described herein will be apparent to those skilled in the art.
Such changes and
modifications can be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the
present subject
matter and without diminishing its intended advantages. It is therefore
intended that such
changes and modifications be covered by the appended claims.
13