Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Description
Title of Invention: RECEIVING DEVICE, TRANSMITTING
DEVICE, AND DATA PROCESSING METHOD
Technical Field
[0001] The present technology relates to a receiving device, a transmitting
device, and a data
processing method, and especially relates to a receiving device, a
transmitting device,
and a data processing method that can flexibly perform an operation related to
a
viewing history.
[0002] <CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS>
This application claims the benefit of Japanese Priority Patent Application JP
2015-125154 filed on June 22, 2015 .
Background Art
[0003] In the field of broadcasting, there is a case of performing an
operation related to a
viewing history such as collection and analysis of a viewing history of
content by a
user. For example, a technology for transmitting the viewing history
periodically or as
needed is disclosed (for example, see Patent Literature 1).
Citation List
Patent Literature
[0004] PTL 1: JP 2009-278651 A
Summary of Invention
Technical Problem
[0005] By the way, since a technical method for performing the operation
related to a
viewing history has not yet been established, proposals for flexibly
perfoiming the
operation related to a viewing history have been requested.
[0006] The present technology has been made in view of the foregoing, and
enables a
flexible operation related to a viewing history.
Solution to Problem
[0007] According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, there is
provided a receiving
device including circuitry configured to receive a digital broadcast stream.
The
circuitry is configured to acquire server information corresponding to a
viewing history
server that collects viewing history information related to a viewing history
of content.
The server information is included in the digital broadcast stream. The
circuitry is
further configured to control transmission of the viewing history information
to the
viewing history server based on the acquired server information.
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-11-18
2
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
[0008] According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, there is
provided a data
processing method of a receiving device. The method includes acquiring, by
circuitry
of the receiving device, server information corresponding to a viewing history
server
that collects viewing history information related to a viewing history of
content. The
server information is included in a digital broadcast stream. The method
further
includes controlling, by the circuitry of the receiving device, transmission
of the
viewing history information to the viewing history server based on the
acquired server
information.
[0009] According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, there is
provided a
transmitting device including circuitry configured to generate server
information corre-
sponding to a viewing history server that collects viewing history information
related
to a viewing history of content. The server information is included in a
digital
broadcast stream. The circuitry is further configured to transmit the digital
broadcast
stream including the generated server information and the content.
[0010] According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, there is
provided a data
processing method of a transmitting device. The method includes generating, by
circuitry of the transmitting device, server information corresponding to a
viewing
history server that collects viewing history information related to a viewing
history of
content. The server information is included in a digital broadcast stream. The
method
further includes transmitting, by the circuitry of the transmitting device,
the digital
broadcast stream including the generated server information and the content.
Advantageous Effects of Invention
[0011] According to the first and second aspects of the present technology,
the operation
related to a viewing history can be flexibly performed.
[0012] Note that the effects described here are not necessarily limited,
and any of the effects
described in the present disclosure may be exerted.
Brief Description of Drawings
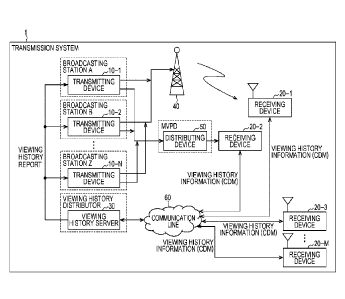
[0013] [fig.l]Fig. 1 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of an
embodiment of a
transmission system to which the present technology is applied.
[fig.2]Fig. 2 is a diagram illustrating a configuration example of a
transmitting device.
[fig.3]Fig. 3 is a diagram illustrating a configuration example of a receiving
device.
[fig.4]Fig. 4 is a diagram illustrating a functional configuration example of
a control
unit.
[fig.5]Fig. 5 is a diagram illustrating a configuration example of a viewing
history
server.
[fig.6]Fig. 6 is a diagram illustrating protocol stack of an lP transmission
method to
which the present technology is applied.
3
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
[fig.7]Fig. 7 is a diagram illustrating a collection example of viewing
history in-
formation (CDM).
[fig.8]Fig. 8 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of the CDM.
[fig.9]Fig. 9 is a diagram illustrating a related method of notifying a
viewing history
server URL.
[fig.10]Fig. 10 is a diagram illustrating a collection example of viewing
history in-
formation (CDM) in a case of transmitting a viewing history server URL using
signaling.
[fig.11]Fig. 11 is a diagram illustrating a method 1 of a method of notifying
a viewing
history server URL in a case of using signaling.
[fig.12]Fig. 12 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of an SLT.
[fig.13]Fig. 13 is a diagram illustrating an example of a descriptor arranged
in the SLT.
[fig.14]Fig. 14 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of a signaling
location
descriptor.
[fig.15]Fig. 15 is a diagram illustrating an example of URL type.
[fig.16]Fig. 16 is a flowchart for describing transmission processing.
[fig.17]Fig. 17 is a flowchart for describing viewing history server URL
notification
processing in a case of using signaling.
[fig.18]Fig. 18 is a flowchart for describing initial scan processing.
[fig.19]Fig. 19 is a flowchart for describing stream/SLT acquisition
processing.
[fig.20]Fig. 20 is a flowchart for describing SLT acquisition processing at
the time of
switching a service.
[fig.21]Fig. 21 is a flowchart for describing the SLT acquisition processing
at the time
of viewing.
[fig.22]Fig. 22 is a flowchart for describing viewing history information
recording
processing.
[fig.23]Fig. 23 is a flowchart for describing viewing history information
transmission
processing.
[fig.24]Fig. 24 is a flowchart for describing viewing history information
collection/
analysis processing.
[fig.25]Fig. 25 is a diagram illustrating a collection example of viewing
history in-
formation (CDM) in a case of transmitting a viewing history server URL using a
video
watermark.
[fig.26]Fig. 26 is a diagram illustrating a method of notifying a viewing
history server
URL in a case of using a video watermark.
[fig.27]Fig. 27 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of a watermark
payload.
[fig.28]Fig. 28 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of a WM
message.
[fig.29]Fig. 29 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of a URI
message.
4
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
[fig.30]Fig. 30 is a diagram illustrating an example of uri type.
[fig.31]Fig. 31 is a flowchart for describing viewing history server URL
notification
processing in a case of using a video watermark.
[fig.32]Fig. 32 is a flowchart for describing viewing history server URL
acquisition
processing in a case of using a video watermark.
[fig.33]Fig. 33 is a diagram of a collection example of viewing history
information
(CDM) in a case of transmitting a viewing history server URL using audio user
data.
[fig.34]Fig. 34 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of an SYS
metaframe.
[fig.35]Fig. 35 is a diagram illustrating an example of sysType.
[fig.36]Fig. 36 is a diagram illustrating an example of sysData.
[fig.37]Fig. 37 is a flowchart for describing viewing history server URL
notification
processing in a case of using audio user data.
[fig.38]Fig. 38 is a flowchart for describing viewing history server URL
acquisition
processing in a case of using audio user data.
[fig.39]Fig. 39 is a diagram illustrating a collection example of viewing
history in-
formation (CDM) in a case of transmitting a viewing history server URL using
metadata of a TTML document.
[fig.40]Fig. 40 is a diagram illustrating a description example of a TTML
document.
[fig.41]Fig. 41 is a flowchart for describing viewing history server URL
notification
processing in a case of using metadata of a TTML document.
[fig.42]Fig. 42 is a flowchart for describing viewing history server URL
acquisition
processing in a case of using metadata of a TTML document.
[fig.43]Fig. 43 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of an SLT in an
XML
format.
[fig.44]Fig. 44 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of an SLT in an
XML
format.
[fig.45]Fig. 45 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of an SLT in an
XML
format.
[fig.46]Fig. 46 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of an SLT in an
XML
format.
[fig.47]Fig. 47 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of a signaling
location
descriptor in an XML format.
[fig.48]Fig. 48 is a diagram illustrating a configuration example of a
computer.
Description of Embodiments
[0014] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present technology will be described
with reference
to the drawings. Note that the description will be given in the following
order.
[0015] 1. Configuration of System
5
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
2. Outline of Present Technology
3. Specific Operation Examples
(1) Method 1: Transmission of Viewing History Server URL Using Signaling
(2) Method 2: Transmission of Viewing History Server URL Using Video Watermark
(3) Method 3: Transmission of Viewing History Server URL Using Audio User Data
(4) Method 4: Transmission of Viewing History Server URL Using Metadata of
TTML
Document
4. Modification
5. Configuration of Computer
[0016] <1. Configuration of System>
[0017] (Configuration of Transmission System)
Fig. 1 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of an embodiment of a
transmission
system to which the present technology is applied. Note that a system refers
to a
plurality of logically collected devices.
[0018] A transmission system 1 is configured from transmitting devices 10-1
to 10-N (N is
an integer of 1 or more), receiving devices 20-1 to 20-M (M is an integer of 1
or more),
a viewing history server 30, a transmitting facility 40, and a distributing
device 50.
Further, the receiving devices 20-1 to 20-M and the viewing history server 30
are
mutually connected through a communication line 60.
[0019] The transmitting device 10-1 is a transmitter complying with a
digital broadcasting
standard such as the advanced television systems committee (ATSC), and
installed by
a broadcasting station A. The transmitting device 10-1 transmits a digital
broadcasting
signal including content (for example, a television program) and signaling
through the
transmitting facility 40. Further, the transmitting device 10-1 transmits the
digital
broadcasting signal including the content and the like to the distributing
device 50.
Note that the distributing device 50 is installed by multichannel video
programming
distributors (MVPD) that provides pay broadcasting such as a cable television
(CATV)
or satellite broadcasting, and distributes the content provided by the
transmitting
device 10-1.
[0020] The transmitting devices 10-2 to 10-N are installed by broadcasting
stations such as a
broadcasting station B and a broadcasting station Z. The transmitting devices
10-2 to
10-N transmit the digital broadcasting signals including content and signaling
through
the transmitting facility 40 or the distributing device 50. Note that, in the
description
below, when the transmitting devices 10-1 to 10-N do not need to be especially
dis-
tinguished, they are referred to as transmitting device 10 and description
will be given.
[0021] The receiving device 20-1 is a receiver complying with a standard of
digital
broadcasting such as the ATSC, and is, for example, a fixed receiver such as a
television receiver or a set-top box, or a mobile receiver such as a smart
phone, a
6
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
mobile phone device, or a tablet-type computer. Further, the receiving device
20-1 may
be a device mounted in an automobile, such as an on-vehicle television.
[0022] The receiving device 20-1 receives (directly receives), with an
antenna, the digital
broadcasting signal transmitted through the transmitting facility 40 as a
radio wave
tower from the transmitting device 10, and reproduces the content (for
example, the
television program or the like) according to a channel selection operation of
a service
(channel) by a user. Further, the receiving device 20-1 records (accumulates)
viewing
history information related to a viewing history of the content. Here, as the
viewing
history information, a consumption data message (CDM) defined by the ATSC can
be
used. The receiving device 20-1 transmits the viewing history information
(CDM) to
the viewing history server 30 through the communication line 60 according to a
uniform resource locator (URL) of the viewing history server 30.
[0023] Note that the URL of the viewing history server 30 (hereinafter,
referred to as
viewing history server URL) is included in the digital broadcasting signal and
transmitted from the transmitting device 10. Therefore, the receiving device
20-1
acquires and holds the viewing history server URL included in the digital
broadcasting
signal. As the method of transmitting the viewing history server URL, there
are a
method 1 that is a method using signaling, a method 2 that is a method using a
video
watermark, a method 3 that is a method using audio user data, and a method 4
that is a
method using metadata of a TTML document, and details of the methods will be
described below.
[0024] The receiving device 20-2 is a fixed receiver such as a television
receiver, a mobile
receiver such as a smart phone, or the like, similarly to the receiving device
20-1. The
receiving device 20-2 receives (indirectly receives) the content (the digital
broadcasting signal of the content) received from the transmitting device 10
through
the distributing device 50 of the MVPD, and reproduces the content according
to the
channel selection operation of a service.
[0025] Further, the receiving device 20-2 records (accumulates) the viewing
history in-
formation (CDM) of the content, and transmits the viewing history information
(CDM)
to the viewing history server 30 through the communication line 60 according
to the
viewing history server URL, similarly to the receiving device 20-1.
[0026] The receiving devices 20-3 to 20-M are, for example, a fixed
receiver such as a
television receiver, a mobile receiver such as a smart phone, or the like,
similarly to the
receiving device 20-1 and the receiving device 20-2.
[0027] The receiving devices 20-3 to 20-M receive (directly receive) the
digital broadcasting
signal transmitted from the transmitting device 10 through the transmitting
facility 40,
or receive (indirectly receive) the content (the digital broadcasting signal
of the
content) distributed through the distributing device 50 of the MVPD, and
reproduces
7
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
the content according to the channel selection operation of a service.
[0028] Further, the receiving devices 20-3 to 20-M record (accumulate) the
viewing history
information (CDM) of the content, and transmits the viewing history
information
(CDM) to the viewing history server 30 through the communication line 60
according
to the viewing history server URL, similarly to the receiving device 20-1 and
the
receiving device 20-2. When the receiving devices 20-1 to 20-M do not need to
be es-
pecially distinguished, they are referred to as receiving device 20, and
description will
be given.
[0029] The viewing history server 30 is a server that collects and
processes the viewing
history information (CDM) transmitted from the plurality of receiving devices
20. The
viewing history server 30 is provided by a viewing history provider such as a
sole
broadcasting provider, a joint management provider established by a plurality
of
broadcasting providers (for example, broadcasting stations A to Z), or a
provider by a
third party organization (for example, a representative organization that
specially
performs viewing rate investigation) that is irrelevant to a broadcasting
provider.
[0030] The viewing history server 30 receives and accumulates (collects)
the viewing
history information (CDM) transmitted from the receiving devices 20-1 to 20-M
through the communication line 60. The viewing history server 30 then performs
various types of processing such as an analysis of the viewing history, for
the collected
viewing history information (CDM). For example, the viewing history server 30
generates a viewing history report related to the viewing history of each
broadcasting
station, and provides the viewing history report to the transmitting device 10
of each
broadcasting station.
[0031] The configuration of the transmission system 1 has been described.
Next, con-
figuration examples of the transmitting device 10, the receiving device 20,
and the
viewing history server 30 that configure the transmission system 1 of Fig. 1
will be
described.
[0032] (Configuration of Transmitting Device)
Fig. 2 is a diagram illustrating a configuration example of the transmitting
device 10
of Fig. 1.
[0033] In Fig. 2, the transmitting device 10 is configured from a control
unit 111, a video
data acquiring unit 112, a video processing unit 113, an audio data acquiring
unit 114,
an audio processing unit 115, a caption data acquiring unit 116, a caption
processing
unit 117, a signaling generating unit 118, a signaling processing unit 119, a
multiplexer
120, a transmitting unit 121, and a communication unit 122.
[0034] The control unit 111 controls operations of respective units of the
transmitting device
10.
[0035] The video data acquiring unit 112 acquires video data (a component
of a video) of
8
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
the content (for example, a television program or the like) from an external
server, a
camera, a recording medium, or the like, and supplies the video data to the
video
processing unit 113. The video processing unit 113 applies processing such as
encoding processing conforming to a predetermined encoding method to the video
data
supplied from the video data acquiring unit 112, and supplies the processed
video data
to the multiplexer 120.
[0036] The audio data acquiring unit 114 acquires audio data (a component
of an audio) of
the content (for example, a television program or the like) from an external
server, a
microphone, a recording medium, or the like, and supplies the audio data to
the audio
processing unit 115. The audio processing unit 115 applies processing such as
encoding processing conforming to a predetermined encoding method to the audio
data
supplied from the audio data acquiring unit 114, and supplies the processed
audio data
to the multiplexer 120.
[0037] The caption data acquiring unit 116 acquires caption data (a
component of a caption)
of the content (for example, a television program or the like) from an
external server, a
recording medium, or the like, and supplies the caption data to the caption
processing
unit 117. The caption processing unit 117 applies processing such as encoding
processing conforming to a predetermined encoding method to the caption data
supplied from the caption data acquiring unit 116, and supplies the processed
caption
data to the multiplexer 120.
[0038] The signaling generating unit 118 generates signaling information
used in processing
such as channel selection or reproduction of the content, and supplies the
signaling in-
formation to the signaling processing unit 119. The signaling processing unit
119
processes the signaling information supplied from the signaling generating
unit 118,
and supplies the processed signaling information to the multiplexer 120. Here,
for
example, link layer signaling (LLS) signaling information, or service layer
signaling
(SLS) signaling information is generated and processed.
[0039] The multiplexer 120 multiplexes a video stream supplied from the
video processing
unit 113, an audio stream supplied from the audio processing unit 115, a
caption
stream supplied from the caption processing unit 117, and the signaling
information
supplied from the signaling processing unit 119, and supplies a multiplexed
stream
obtained as a result of the multiplexing to the transmitting unit 121.
[0040] The transmitting unit 121 transmits the multiplexed stream supplied
from the mul-
tiplexer 120 as a broadcasting wave (digital broadcasting signal) of the
digital
broadcasting through an antenna 131.
[0041] Further, the control unit 111 includes a viewing history server URL
generating unit
151. The viewing history server URL generating unit 151 generates the viewing
history server URL. The viewing history server URL generating unit 151
supplies the
9
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
generated viewing history server URL to the signaling generating unit 118, the
video
processing unit 113, the audio processing unit 115, or the caption processing
unit 117
according to the method from the method 1 to the method 4. The viewing history
server URL is included in the multiplexed stream multiplexed by the
multiplexer 120
according to the method from the method 1 to method 4.
[0042] The communication unit 122 exchanges data with the viewing history
server 30 (Fig.
1) through various networks (not illustrated) according to control from the
control unit
111. For example, the communication unit 122 receives the viewing history
report
transmitted from the viewing history server 30, and supplies the viewing
history report
to the control unit 111. The control unit 111 acquires the viewing history
report
supplied from the communication unit 122, and performs processing of
presenting the
viewing history report, for example.
[0043] (Configuration of Receiving Device)
Fig. 3 is a diagram illustrating a configuration example of the receiving
device 20 of
Fig. 1.
[0044] In Fig. 3, the receiving device 20 is configured from a control unit
211, a recording
unit 212, an input unit 213, a receiving unit 214, a demultiplexer 215, a
video
processing unit 216, a video output unit 217, an audio processing unit 218, an
audio
output unit 219, a caption processing unit 220, a display unit 221, a speaker
222, and a
communication unit 223. Fig. 3 illustrates the configuration including the
display unit
221 and the speaker 222. However, a configuration without the display unit 221
and
the speaker 222 may be employed.
[0045] The control unit 211 controls operations of the respective units of
the receiving
device 20. The recording unit 212 is, for example, a non-volatile memory such
as a
non-volatile RAM (NVRAM), and records various types of data according to
control
from the control unit 211. The input unit 213 supplies an operation signal to
the control
unit 211 according to an operation of the user.
[0046] The receiving unit 214 extracts and demodulates a signal according
to the channel
selection operation of a service from the broadcasting wave (digital
broadcasting
signal) of the digital broadcasting received through an antenna 231, and
supplies the
multiplexed stream obtained as a result to the demultiplexer 215.
[0047] The demultiplexer 215 separates the multiplexed stream supplied from
the receiving
unit 214 into the audio, video, and caption streams, and the signaling
information. The
demultiplexer 215 supplies the video data (the component of a video) to the
video
processing unit 216, the audio data (the component of an audio) to the audio
processing unit 218, the caption data (the component of a caption) to the
caption
processing unit 220, and the signaling information to the control unit 211,
respectively.
[0048] The control unit 211 controls the operations of the respective units
such as the de-
10
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
multiplexer 215 and the processing units of the respective components based on
the
signaling information supplied from the demultiplexer 215 in order to
reproduce the
content.
[0049] The video processing unit 216 applies processing such as decoding
processing
conforming to a predetermined decoding method to the video data supplied from
the
demultiplexer 215, and supplies the processed video data to the video output
unit 217.
The video output unit 217 outputs the video data supplied from the video
processing
unit 216 to the display unit 221. Accordingly, in the display unit 221, a
video of the
content (for example, a television program or the like) according to the
channel
selection operation of a service is displayed.
[0050] The audio processing unit 218 applies processing such as decoding
processing
conforming to a predetermined decoding method to the audio data supplied from
the
demultiplexer 215, and supplies the processed audio data to the audio output
unit 219.
The audio output unit 219 outputs the audio data supplied from the audio
processing
unit 218 to the speaker 222. Accordingly, an audio of the content (for
example, a
television program or the like) according to the channel selection operation
of a service
is output from the speaker 222.
[0051] The caption processing unit 220 applies processing such as decoding
processing
conforming to a predetermined decoding method to the caption data supplied
from the
demultiplexer 215, and supplies the processed caption data to the video output
unit
217. The video output unit 217 displays a caption corresponding to the caption
data
supplied from the caption processing unit 220 to be superimposed on the video
corre-
sponding to the video data supplied from the video processing unit 216.
Accordingly,
in the display unit 221, the caption superimposed on the video of the content
(for
example, a television program or the like) according to the channel selection
operation
of a service.
[0052] The communication unit 223 exchanges various types of data with the
viewing
history server 30 through the communication line 60 according to control from
the
control unit 211.
[0053] (Functional Configuration of Control Unit)
Fig. 4 is a diagram illustrating a functional configuration example of the
control unit
211 of Fig. 3.
[0054] In Fig. 4, the control unit 211 is configured from a broadcasting
control unit 251, a
communication control unit 252, a viewing history information managing unit
253, and
a viewing history server URL acquiring unit 254.
[0055] The broadcasting control unit 251 controls the respective units such
as the receiving
unit 214, the demultiplexer 215, and the processing units and output units of
the re-
spective components in order to reproduce the content included in the digital
11
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
broadcasting signal transmitted from the transmitting device 10.
[0056] The communication control unit 252 controls the communication unit
223 in order to
exchange various types of data with the viewing history server 30 through the
commu-
nication line 60.
[0057] The viewing history information managing unit 253 manages the
viewing history in-
formation (CDM) of the content. When it becomes timing to record the viewing
history
information (CDM), the viewing history information managing unit 253 records
(accumulates) the viewing history information (CDM) according to a viewing
state of
the content by the user to the recording unit 212.
[0058] The viewing history server URL acquiring unit 254 acquires the
viewing history
server URL included in the multiplexed stream to be separated by the
demultiplexer
215 according to the method from the method 1 to method 4, and records (holds)
the
viewing history server URL to the recording unit 212.
[0059] When it becomes timing to transmit the viewing history information
(CDM) to the
viewing history server 30, the viewing history information managing unit 253
reads the
viewing history information (CDM) and the viewing history server URL from the
recording unit 212, and supplies the viewing history information (CDM) and the
viewing history server URL to the communication control unit 252.
[0060] To the communication control unit 252, the viewing history
information (CDM) and
the viewing history server URL are supplied from the viewing history
information
managing unit 253. The communication control unit 252 controls the
communication
unit 223 so that the viewing history infoiniation (CDM) is transmitted to the
viewing
history server 30 through the communication line 60 based on the viewing
history
server URL.
[0061] (Configuration of Viewing History Server)
Fig. 5 is a diagram illustrating a configuration example of the viewing
history server
30 of Fig. 1.
[0062] In Fig. 5, the viewing history server 30 is configured from a
control unit 311, a com-
munication unit 312, and a viewing history information accumulating unit 313.
[0063] The control unit 311 controls operations of the respective units of
the viewing history
server 30. The control unit 311 is configured from a viewing history
information
managing unit 351 and a viewing history information analyzing unit 352. The
viewing
history information managing unit 351 manages the viewing history information
(CDM). The viewing history information analyzing unit 352 analyzes the viewing
history information (CDM).
[0064] The communication unit 312 receives the viewing history information
(CDM)
transmitted from the receiving device 20 through the communication line 60
according
to the control from the control unit 311, and supplies the viewing history
information
12
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
(CDM) to the control unit 311. The viewing history information managing unit
351
records (accumulates) the viewing history information (CDM) supplied from the
com-
munication unit 312 to the viewing history information accumulating unit 313.
Ac-
cordingly, in the viewing history information accumulating unit 313, the
viewing
history information (CDM) sequentially sent from the plurality of receiving
devices 20
is collected, and is accumulated for each broadcasting station.
[0065] When it becomes timing to analyze the viewing history information
(CDM), the
viewing history information analyzing unit 352 reads the viewing history
information
(CDM) of each broadcasting station from the viewing history information accu-
mulating unit 313 and analyzes the viewing history information (CDM). The
viewing
history information analyzing unit 352 generates the viewing history report of
each
broadcasting station based on an analysis result of the viewing history
information
(CDM), and supplies the viewing history report to the communication unit 312.
The
communication unit 312 transmits the viewing history report of each
broadcasting
station to the transmitting device 10 of the target broadcasting station
through various
types of networks (not illustrated) according to control from the control unit
311.
[0066] <2. Outline of Present Technology>
[0067] By the way, in the next-gen ATSC standard called ATSC 3.0, an IP
transmission
method is employed, and as data transmission, use of an Internet protocol
(IP)/user
datagram protocol (UDP) packet, that is, an IP packet including a UDP packet,
instead
of a transport stream (TS) packet, has been determined. Further, in
broadcasting
methods other than ATSC 3.0, use of an IP transmission method using an IP
packet in
the future is expected.
[0068] Further, in the ATSC 3.0, as transport protocols, real-time object
delivery over unidi-
rectional transport (ROUTE) and MPEG media transport (MMT) co-exist, and
streams
(of components) such as a video, an audio, and a caption are transmitted using
either
one of the transport protocols. Note that which of the ROUTE and MMT is used
as the
transport protocol is selected for each broadcasting provider.
[0069] Here, the ROUTE is a protocol of extended file delivery over
unidirectional transport
(FLUTE) that is a protocol suitable for unidirectional multicast transfer of a
binary file.
Further, the MMT is a transport method used on an Internet protocol (IP), and
can refer
to data of the video, the audio, and the like by setting an IP address or a
uniform
resource locator (URL) with control information.
[0070] Further, in the ATSC 3.0, as signaling, definition of link layer
signaling (LLS)
signaling information and service layer signaling (SLS) signaling information
is
expected, and the SLS signaling information of each service is acquired
according to
information described in the LLS signaling information acquired in advance.
[0071] Here, as the LLS signaling information, for example, metadata such
as a service list
13
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
table (SLT) is included. The SLT includes information (service configuration
in-
formation) that indicates configurations of a stream and a service in a
broadcasting
network, such as information necessary for channel selection of a service
(channel
selection information).
[0072] Further, as the SLS signaling information, for example, metadata
such as user service
description (USD), LCT session instance description (LSID), media presentation
de-
scription (MPD) is included. The USD includes information such as an
acquisition des-
tination of other metadata. The LSID is control information of a ROUTE
protocol. The
MPD is control information for managing reproduction of a stream of a
component.
Note that the metadata such as the USD, LSID, and MPD is described in markup
language such as extensible markup language (XML). Further, the MPD conforms
to
the standard of dynamic adaptive streaming over HTTP (MPEG-DASH).
[0073] (Protocol Stack)
Fig. 6 is a diagram illustrating a protocol stack of an IP transmission method
to
which the present technology is applied.
[0074] In Fig. 6, the lowest hierarchy is a physical layer. A higher
hierarchy adjacent to the
physical layer is a hierarchy of a layer 2 (Layer2), and a higher hierarchy
adjacent to
the hierarchy of the layer 2 is an IP layer. Further, a higher hierarchy
adjacent to the IP
layer is a UDP layer. That is, the IP packet (IP/UDP packet) including the UDP
packet
is arranged in a payload of a L2 packet (generic packet) of the layer 2, and
is en-
capsulated (encapsulation). Further, a Li frame (physical frame) of the
physical layer
is configured from a preamble and a data portion, and in the data portion,
data is
mapped, the data being obtained by performing processing related to the
physical layer
such as interleave and mapping, after adding error correction parity to a BB
frame
obtained by encapsulation of a plurality of L2 packets.
[0075] A higher hierarchy adjacent to the UDP layer is ROUTE, MMT, and SLT.
That is,
the video, audio, and caption streams, an SLS signaling information stream,
and an
NRT content stream, transmitted by an ROUTE session, are stored in the IP/UDP
packet and transmitted. Note that the NRT content is content distributed by
non real
time (NRT) broadcasting, and is accumulated in a storage of the receiving
device 20
once and reproduced. Further, a file other than the NRT content (for example,
a file of
an application) may be transmitted by the ROUTE session.
[0076] Meanwhile, the video, audio, and caption streams and the SLS
signaling information
stream transmitted by an MMT session are stored in the IP/UDP packet and
transmitted. Further, the SLT is stored in the IP/UDP packet and transmitted.
[0077] In the IP transmission method to which the present technology is
applied, when the
above protocol stack is employed, the receiving device 20 acquires the SLS
signaling
information transmitted by the ROUTE session according to the channel
selection in-
14
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
formation included in the SLT at the time of the channel selection of a
service
(channel) provided by the streams of the components transmitted by the ROUTE
session (S1-1, S1-2). The receiving device 20 is then connected with the
streams of the
components of the selected service according to the metadata such as the USD,
LSID,
and MPD (S1-3). Accordingly, the receiving device 20 outputs a video and an
audio of
content (for example, a television program) according to the channel selection
operation of the service.
[0078] Further, the receiving device 20 acquires the SLS signaling
information transmitted
by the MMT session, according to the channel selection information included in
the
SLT, at the time of the channel selection of a service provided by the streams
of the
components transmitted by the MMT session (S2-1, S2-2). The receiving device
20 is
then connected with the streams of the components of the selected service
according to
the metadata such as the USD, LSID, and MPD (S2-3). Accordingly, the receiving
device 20 outputs a video and an audio of content (for example, a television
program)
according to the channel selection operation of the service.
[0079] (Collection Example of Viewing History Information)
Fig. 7 is a diagram illustrating a collection example of the viewing history
in-
formation (CDM) in the transmission system 1 of Fig. 1. Note that, in Fig. 7,
"CDM
Server" means the viewing history server 30, and the same applies to other
drawings
described below.
[0080] In Fig. 7, the receiving device 20 receives (directly or indirectly
receives) the digital
broadcasting signal transmitted from the transmitting device 10, and
reproduces the
content according to the channel selection operation of the service. Further,
in the
receiving device 20, the viewing history information (CDM) is recorded
(accumulated)
according to viewing of the content by the user, and the viewing history
information
(CDM) is transmitted to the viewing history server 30 through the
communication line
60.
[0081] Here, to access the viewing history server 30 through the
communication line 60 and
transmit the viewing history information (CDM) by the receiving device 20, the
receiving device 20 needs to acquire the URL (viewing history server URL) of
the
viewing history server 30 in advance.
[0082] In the present technology, a technology for causing the transmitting
device 10 to
include the viewing history server URL to the digital broadcasting signal and
transmit
the signal, thereby to cause the receiving device 20 that receives the digital
broadcasting signal to acquire (hold) the viewing history server URL is
proposed. To
be specific, as the methods of transmitting the viewing history server URL,
the method
1 as a method using signaling, the method 2 as a method using a video
watermark, the
method 3 as a method using audio user data, and the method 4 as a method using
15
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
metadata of a TTML document are proposed. Details will be described below.
[0083] Fig. 7 illustrates a case in which the broadcasting station A, the
broadcasting station
B, and the broadcasting station C jointly manage the viewing history server
30. At this
time, in the receiving device 20, the content distributed from the
transmitting device
10-1 of the broadcasting station A, the content distributed from the
transmitting device
10-2 of the broadcasting station B, and the content distributed from the
transmitting
device 10-3 of the broadcasting station C are viewed by the user, and the
viewing
history information (CDM) of the content is accumulated.
[0084] Further, the digital broadcasting signal including the viewing
history server URL is
transmitted from the transmitting device 10 of each broadcasting station
according to
any method of the method 1 to method 4. Therefore, the receiving device 20
acquires
and holds the viewing history server URL. Here, the viewing history server 30
is
jointly managed by the broadcasting station A, the broadcasting station B, and
the
broadcasting station C. Therefore, each of the transmitting devices 10-1 to 10-
3
notifies the same viewing history server URL (for example, a URL of
"http://cdmServer.com/cdm") for accessing the viewing history server 30.
[0085] The receiving device 20 can receive the digital broadcasting signals
from the
transmitting devices 10-1 to 10-3, and acquire and hold the viewing history
server
URL included in the digital broadcasting signals. Accordingly, when it becomes
timing
to transmit the viewing history information (CDM) to the viewing history
server 30,
the receiving device 20 can access the viewing history server 30 through the
commu-
nication line 60 according to the held viewing history server URL (for
example, the
URL of "http://cdmServer.com/cdm"), and transmit the viewing history
information
(CDM).
[0086] The viewing history server 30 receives and accumulates the viewing
history in-
formation (CDM) transmitted from the receiving device 20 through the
communication
line 60. In the example of Fig. 7, only one receiving device 20 is
illustrated. However,
in reality, the viewing history information (CDM) is transmitted from the
plurality of
receiving devices 20 (the receiving devices 20-1 to 20-M). Therefore, the
viewing
history server 30 accumulates the viewing history information (CDM) collected
from
the plurality of receiving devices 20.
[0087] In the viewing history server 30, analysis processing and the like
are applied to the
viewing history information (CDM) collected from the plurality of receiving
devices
20, as described above, and the viewing history report of each broadcasting
station is
generated. The viewing history report of each broadcasting station is
transmitted to the
transmitting device 10 of each broadcasting station. Accordingly, each
broadcasting
station can confirm the viewing history report provided by the viewing history
server
30.
16
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
[0088] Further, the viewing history server 30 can request the transmitting
device 10 of each
broadcasting station to change the viewing history server URL. When having
received
the request to change the viewing history server URL from the viewing history
server
30, the transmitting device 10 of each broadcasting station changes the
viewing history
server URL to be included in the digital broadcasting signal so that the
viewing history
server URL (for example, a URL of "http://cdmServer_2.com/cdm") after change
is
transmitted.
[0089] Here, the viewing history server URL is expected to be periodically
or irregularly
changed in operation. Therefore, the viewing history server URL after change
is
requested to be reliably notified to the receiving device 20. In the case of
employing
the method 1 to method 4 of notifying the viewing history server URL included
in the
digital broadcasting signal by push, the viewing history server URL can be dy-
namically changed and notified to many unspecified receiving devices 20-1 to
20-M,
using broadcasting properties, immediacy, expandability (scalability) that are
charac-
teristics of the digital broadcasting signal, and can respond to the request.
Further, ac-
cordingly, the viewing history server URL for accessing the viewing history
server 30
can be periodically changed or instantly changed as needed. Therefore, for
example,
security can be enhanced, such as avoidance of denial of service attack (DoS
attack)
against the viewing history server 30.
[0090] Note that, in the example of Fig. 7, a case where the viewing
history server 30 is
jointly managed by the plurality of broadcasting stations including the
broadcasting
station A, the broadcasting station B, and the broadcasting station C has been
described. However, the viewing history server 30 may be managed by a single
broadcasting station.
[0091] In this case, the transmitting device 10-1 of the broadcasting
station A notifies the
viewing history server URL (for example, a URL of "http://cdmServer
A.com/cdm")
for accessing a viewing history server 30A managed by the broadcasting station
A to
the receiving device 20. Similarly, the transmitting device 10-2 of the
broadcasting
station B notifies the viewing history server URL (for example, a URL of
"http://cdmServer B.com/cdm") for accessing a viewing history server 30B
managed
by the broadcasting station B, and the transmitting device 10-3 of the
broadcasting
station C notifies the viewing history server URL (for example, a URL of
"http://cdmServer_C.com/cdm") for accessing a viewing history server 30C
managed
by the broadcasting station C.
[0092] That is, in this case, the transmitting devices 10-1 to 10-3 notify
the different viewing
history server URLs for accessing the viewing history servers 30 (for example,
the
viewing history server 30A, the viewing history server 30B, and the viewing
history
server 30C) of the respective broadcasting stations to the receiving device 20
by the
17
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
digital broadcasting signals.
[0093] As described above, the viewing history server 30 is expected to be
managed by the
single broadcasting station or jointly managed by the plurality of
broadcasting stations.
In the notification of the viewing history server URL by the method 1 to the
method 4,
the notification of the viewing history server URL can be performed according
to a
management form of the viewing history server 30. Therefore, the viewing
history
server URL can be notified without depending on the broadcasting station. For
example, as illustrated in Fig. 7, even in the case where the plurality of
broadcasting
stations jointly manages the viewing history server 30, (the transmitting
device 10 of)
each broadcasting station transmits the same viewing history server URL, so
that such
operation can be handled.
[0094] In the transmission system 1 of Fig. 1, the collection and analysis
of the viewing
history information (CDM) are performed as described above. That is, in the
transmission system 1 of Fig. 1, the service (channel) the viewing history
information
(CDM) of which is recorded and the notification of the viewing history server
URL of
the viewing history server 30 that transmits the viewing history information
(CDM) are
associated with each other. Therefore, specification of the viewing history
server 30
that transmits the viewing history information (CDM) on a broadcasting station
by
broadcasting station basis can be easily realized.
[0095] Further, the viewing history server URL of the viewing history
server 30 is notified
by push by the broadcasting wave (digital broadcasting signal) of the digital
broadcasting, whereby a possibility of falsification of the viewing history
server URL
along the way of the path between the transmitting device 10 and the receiving
device
20 can be decreased. Therefore, for example, security of the viewing history
in-
formation (CDM) that is personal information can be enhanced, such as
prevention of
erroneous transmission (forcible transmission) of the viewing history
information
(CDM) to a third party server.
[0096] Further, methods of receiving a television service in the receiving
device 20 are
roughly classified into a method of performing reception (direction reception)
with an
antenna, and a method of performing reception (indirect reception) through
(the dis-
tributing device 50 of) the MVPD such as a cable television (CATV). In the
former
case of the direct reception, all of the information such as the streams of
the component
(for example, the video, audio, caption, and the like), and the metadata (for
example,
the signaling information) included in the digital broadcasting signal
distributed by
(the transmitting device 10 of) the broadcasting station are acquired by the
receiving
device 20. However, in the latter case of the indirect reception, there is a
possibility
that the metadata and the like may be removed (filtered) by (the distributing
device 50
of) the MVPD.
18
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
[0097] Even in such a case, in the transmission system 1 of Fig. 1, by
employment of the
method 2(the method using a video watermark), the method 3 (the method using
audio
user data), or the method 4 (the method using metadata of a TTML document),
the
viewing history server URL can be notified regardless of the metadata.
Therefore,
various reception environments such as the direct reception with an antenna
and the
indirect reception through the MVPD can be handled.
[0098] (Syntax of CDM)
Fig. 8 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of the consumption data
message (CDM) in the XML format. Note that, among elements and attributes in
Fig.
8, "@" is attached to the attributes. Further, indented elements and
attributes are
specified for higher elements thereof.
[0099] In Fig. 8, a CDM element as a route element is a higher element of a
protocolVersion
attribute, an AVChannel element, and an NRTService element. As the protocol
Version
attribute, a protocol version of the CDM is specified.
[0100] As the AVChannel element, information related to the viewing history
of each
channel (service) of the distributed content is specified. The AVChannel
element is a
higher element of a channelNum attribute, a serviceType attribute, and a
ViewInterval
element. As the ChannelNum attribute, a channel number (service ID) is
specified. As
the serviceType attribute, for example, a type of the service such as normal
broadcasting or broadcasting of an audio only is specified.
[0101] The ViewInterval element is a higher element of a startTime
attribute, an endTime
attribute, a usageType attribute, a timeShift attribute, a viewStartTime
attribute, a
viewEndTime attribute, and a DOInterval element. Further, the DOInterval
element is
a higher element of a doId attribute, a startTime attribute, and an endTime
attribute. In
the ViewInterval element, information related to the viewing history of each
channel
(service) is specified by these elements and attributes.
[0102] As the NRTService element, information related to the viewing
history about an
NRT service is specified. The NRTService element is a higher element of a
serviceID
attribute and an NRTInterval element. As the serviceID attribute, a service ID
is
specified.
[0103] The NRTInterval element is a higher element of a startTime
attribute, an endTime
attribute, and an NRTItem element. Further, the NRTItem element is a higher
element
of a contentItemId attribute, a startTime attribute, and an endTime attribute.
In the
NRTInterval element, information related to the viewing history is specified
for each
NRT service by these elements and attributes.
[0104] The CDM is defined by ATSC 2Ø Fig. 9 illustrates a method of
notifying the
viewing history server URL in the ATSC 2Ø As illustrated in Fig. 9, in the
ATSC 2.0,
the viewing history server URL is arranged in private data (PrivateData) (as a
payload)
19
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
of a service #6 defined by the ATSC as the standards developing organization
(SDO)
in a caption (CC: closed caption) among components that configure content.
[0105] Here, the IP transmission method employed in the ATSC 3.0 or the
like is different
from the transmission method in the ATSC 2Ø Therefore, even in the IP
transmission
method, a method of notifying the viewing history server URL to the receiving
device
20 is requested, and in the present technology, the viewing history server URL
can be
notified by the transmission methods of the method 1 to method 4 described
below.
[0106] <3. Specific Operation Examples>
[0107] (1) Method 1: Transmission of Viewing History Server URL Using
Signaling
[0108] (Collection Example of Viewing History Information)
Fig. 10 is a diagram illustrating a collection example of viewing history
information
(CDM) in a case of transmitting the viewing history server URL using
signaling.
[0109] In Fig. 10, the transmitting device 10 of each broadcasting station
includes the
viewing history server URL to the digital broadcasting signal and transmits
the signal
by the method 1 using signaling. To be specific, the viewing history server
URL is
described in a signaling location descriptor (inet signaling location
descriptor)
arranged in the SLT that is the LLS signaling information.
[0110] Here, the viewing history server 30 is jointly managed by the
broadcasting station A,
the broadcasting station B, and the broadcasting station C. Therefore, the
transmitting
devices 10-1 to 10-3 notify the same viewing history server URL (for example,
the
URL of "http://cdmServer.com/cdm") for accessing the viewing history server 30
by
the signaling location descriptors of the SLTs transmitted by the digital
broadcasting
signals.
[0111] The receiving device 20 can receive the digital broadcasting signals
from the
transmitting devices 10-1 to 10-3, and acquire and hold the viewing history
server
URL described in the signaling location descriptors of the SLTs. Accordingly,
the
receiving device 20 can access the viewing history server 30 through the commu-
nication line 60 and transmit the viewing history information (CDM) according
to the
held viewing history server URL (for example, the URL of
"http://cdmServer.com/cdm") when it becomes timing to transmit the viewing
history
information (CDM) to the viewing history server 30.
[0112] The viewing history server 30 receives and accumulates the viewing
history in-
formation (CDM) transmitted from the plurality of receiving devices 20 through
the
communication line 60. The viewing history server 30 applies analysis
processing and
the like to the viewing history information (CDM) collected from the plurality
of
receiving devices 20, thereby to generate the viewing history reports of the
respective
broadcasting stations.
[0113] (Method of Notifying Viewing History Server URL)
20
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
Fig. 11 is a diagram illustrating a method of notifying the viewing history
server URL
in a case of using signaling.
[0114] In Fig. 11, the transmitting device 10 transmits the signaling
information such as the
SLT by the digital broadcasting signal together with the streams of (the
components
of) the video, audio, and caption. The receiving device 20 processes the
streams of the
components and reproduces the content based on the signaling information
transmitted
by the digital broadcasting signal from the transmitting device 10. Further,
in the
receiving device 20, the viewing history information (CDM) of the content is
recorded
(accumulated).
[0115] Here, the transmitting device 10 describes the viewing history
server URL (for
example, the URL of "http://cdmServer.comicdm") to the signaling location
descriptor
(inet signaling location descriptor) arranged in the SLT so that the viewing
history
server URL is transmitted by the digital broadcasting signal. The receiving
device 20
acquires and records (holds) the viewing history server URL from the signaling
location descriptor arranged in the SLT transmitted by the digital
broadcasting signal
from the transmitting device 10. The receiving device 20 then can access the
viewing
history server 30 through the communication line 60 and transmit the viewing
history
information (CDM) according to the held viewing history server URL (for
example,
the URL of "http://cdmServer.com/cdm").
[0116] (Syntax of SLT)
Fig. 12 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of an SLT in a binary
format.
[0117] In 8-bit table id, an identifier of a table to which a section of
the SLT belongs is
specified. In 4-bit SLT section_version, a version of the section of the SLT
is
specified. In 12-bit SLT section length, a section length of the SLT is
specified. In
8-bit SLT_protocol_version, a protocol version of the SLT is specified.
[0118] In 16-bit broadcast stream id, a broadcast ID is specified. In 4-bit
SLT section number and last SLT section_number, a section number of the SLT is
specified.
[0119] In 8-bit num_service, the number of services is specified. The
service loop is
repeated according to the number of services. In the service loop, contents
below are
specified.
[0120] In 16-bit service id, a service ID is specified. In 3-bit SLT
service seq number, a
sequence number of the service is specified. In 1-bit protected, encryption
information
that indicates protection of the service is specified.
[0121] In 10-bit major, channel number, a major channel number is
specified. In 10-bit
minor, channel number, a minor channel number is specified. In 4-bit
service_category, a category of the service is specified.
[0122] In 4-bit short service name length, the length of a short service
name is specified.
21
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
In 8*m-bit short_service_name(), the short service name is specified. In 1-bit
broadcast_signaling_present, whether the SLS signaling information has been
transmitted is specified.
[0123] In 1-bit SLS source IP address present, whether an IP address of a
transmission
source (source) exists is specified. In 1-bit broadband_access_reuired,
whether an
access to the communication line (broad band) is necessary is specified. In 4-
bit
SLS protocol type, a type of the protocol of the SLS signaling information is
specified.
[0124] When the broadcast_signaling_present indicates that the SLS
signaling information
has been transmitted, as information for acquiring the SLS signaling
information,
SLS PLP ID, SLS destination IP address, SLS destination UDP port, and
SLS protocol version are specified.
[0125] However, when the SLS_source_IP_address_present indicates that the
IP address of
the transmission source (source) exists, SLS_source_IP_address is specified.
[0126] In 8-bit SLS PLP ID, an ID of a PLP to which the SLS signaling
information is
transmitted is specified. In 32-bit SLS destination IP address, an IP address
of a des-
tination is specified. In 16-bit SLS_destination_UDP_port, a port number of
the des-
tination is specified.
[0127] In 32-bit SLS source IP address, an IP address of a transmission
source (source) is
specified. In 8-bit SLS protocol version, a version of the protocol of the SLS
signaling information is specified.
[0128] When num ext lenght bits is specified, an area reserved for future
extension is
secured as reserved 1. Further, an area reserved for future expansion can be
secured as
reserved2 by ext length.
[0129] In 4-bit num_service_level_descriptors, the number of descriptors of
a service level
is specified. A service level descriptor loop is repeated according to the
number of de-
scriptors of a service level. As illustrated by the frame A in Fig. 12, in the
service level
descriptor loop, a service level descriptor (service level descriptor) is
arranged.
[0130] Next to the service loop, num_SLT_level_descriptors is arranged
following the 4-bit
reserved. In 4-bit num SLT level descriptors, the number of descriptors of an
SLT
level is specified. An SLT level descriptor loop is repeated according to the
number of
descriptors of an SLT level. As illustrated by the frame B in Fig. 12, in the
SLT level
descriptor loop, an SLT level descriptor (SLT_level_descriptor) is arranged.
[0131] Next to the SLT level descriptor loop, reserved3 for future
expansion is specified.
[0132] (Example of Descriptor of SLT)
Fig. 13 is a diagram illustrating an example of a descriptor arranged in the
SLT.
[0133] In the SLT, a signaling location descriptor
(inet_signaling_location_descriptor), de-
scriptors such as a service language descriptor (service language descriptor),
and a ca-
22
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
pability descriptor (capabilities_descriptor) are arranged.
[0134] In the signaling location descriptor, location infoimation such as
information that
indicates an acquisition destination of the signaling information acquired
through com-
munication is specified. For example, in a case of employing the method 1, the
viewing history server URL is described in the signaling location descriptor.
[0135] This signaling location descriptor can be arranged in both of the
service level de-
scriptor loop of Fig. 12A and the SLT level descriptor loop of Fig. 12B. That
is, in a
case where the signaling location descriptor is arranged in the service level
descriptor
loop (Fig. 12A) of the SLT, the service and the viewing history server URL can
be as-
sociated. In this case, the viewing history server URL can be specified for
each service.
Meanwhile, in a case where the signaling location descriptor is arranged in
the SLT
level descriptor loop (Fig. 12B) of the SLT, a common viewing history server
URL can
be specified for all of services.
[0136] In the service language descriptor, information related to language
of the service is
specified. This service language descriptor can be arranged in both of the
service level
descriptor loop of Fig. 12A and the SLT level descriptor loop of Fig. 12B.
[0137] In the capability descriptor, information related to capability is
specified. This ca-
pability descriptor can be arranged in both of the service level descriptor
loop of Fig.
12A and the SLT level descriptor loop of Fig. 12B.
[0138] (Syntax of Signaling Location Descriptor)
Fig. 14 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of the signaling
location de-
scriptor (inet signaling location descriptor) of Fig. 13C.
[0139] In 8-bit descriptor_tag, a descriptor tag of the descriptor is
specified. In 8-bit de-
scriptor length, a descriptor length of the descriptor is specified.
[0140] In 8-bit URL_type, a type of a URL is specified. URL_bytes() is made
of
8*(descriptor length-1) bits, and in URL bytes(), a URL according to the type
of a
URL specified in URL type is specified.
[0141] For example, Fig. 15 illustrates that a URL of a signaling server
that provides the
signaling information is specified in URL_bytes() in a case where "0x00" is
specified
as URL type. Further, Fig. 15 illustrates that a URL of an ESG server that
provides
electronic service guide (ESG) information is specified in URL_bytes() in a
case where
"Ox01" is specified as URL type.
[0142] Further, Fig. 15 illustrates that the URL (viewing history server
URL) of the viewing
history server 30 is specified in URL_bytes() in a case where "0x02" is
specified as
URL type. That is, in the method 1, when notifying the viewing history server
URL
using the signaling location descriptor arranged in the SLT, the URL specified
in
URL_bytes() is identified as the URL (viewing history server URL) of the
viewing
history server 30 by specification of "0x02" as URL type.
23
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
[0143] Note that, in URL_type, "0x03" to "OxFF" are values reserved for
future expansion.
[0144] Next, details of processing executed in the devices that configure
the transmission
system 1 of Fig. 1 in a case where the method 1 is employed will be described
with
reference to the flowcharts of Figs. 16 to 24.
[0145] (Transmission Processing)
First, a flow of transmission processing executed by the transmitting device
10 of
Fig. 1 will be described with reference to the flowchart of Fig. 16.
[0146] In step S101, component/signaling processing is performed.
[0147] In the component/signaling processing, various types of processing
for the video
stream (video bitstream) processed in the video processing unit 113 and the
like, the
audio stream (audio bitstream) processed in the audio processing unit 115 and
the like,
the caption stream processed in the caption processing unit 117 and the like,
and the
signaling information processed in the signaling processing unit 119 and the
like are
performed, and the streams of the respective components and the signaling
information
are made transmittable as the digital broadcasting signal.
[0148] In step S102, the transmission processing is performed by the
transmitting unit 121,
and the streams of the respective components and the signaling information
processed
in the processing of step S101 are transmitted through the antenna 131 as the
digital
broadcasting signal. When the processing of step S102 is terminated, the
transmission
processing of Fig. 16 is terminated.
[0149] The flow of the transmission processing has been described.
[0150] (Viewing History Server URL Notification Processing)
Next, a flow of viewing history server URL notification processing in a case
of using
signaling will be described with reference to the flowchart of Fig. 17. Note
that this
viewing history server URL notification processing is processing executed in
parallel
to the processing of step S101 of Fig. 16 by the transmitting device 10 of
Fig. 1.
[0151] In step S111, the control unit 111 determines whether it is timing
to notify the
viewing history server URL.
[0152] In step S111, when it is determined not to be the timing to notify
the viewing history
server URL, the determination processing of step S111 is repeated. Meanwhile,
when
it is determined to be the timing to notify the viewing history server URL,
the
processing proceeds to step S112.
[0153] In step S112, the viewing history server URL generating unit 151
generates the
viewing history server URL of the target viewing history server 30. The
viewing
history server URL generated as described above is supplied to the signaling
generating unit 118 in the case of the method 1.
[0154] In step S113, the signaling generating unit 118 adds the viewing
history server URL
generated in the processing of step S112 to the signaling location descriptor
arranged
24
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
in the service level descriptor loop of the SLT or the SLT level descriptor
loop, in
generating the SLT.
[0155] Note that, at this time, in the signaling location descriptor,
"0x02" is specified as
URL type. Further, for example, as illustrated in Fig. 10, in a case where the
viewing
history server 30 is jointly managed by the broadcasting station A, the
broadcasting
station B, and the broadcasting station C, "http://cdmServer.com/cdm" is
described in
URL bytes() of the signaling location descriptor of the SLT as the viewing
history
server URL, in the transmitting devices 10-1 to 10-3 of the broadcasting
station A, the
broadcasting station B, and the broadcasting station C.
[0156] The flow of the viewing history server URL notification processing
has been
described. In this viewing history server URL notification processing, URL
type as
"0x02" and URL bytes() in which the viewing history server URL is specified
are
described in the signaling location descriptor. Then, the SLT in which the
signaling
location descriptor is arranged in the service level descriptor loop or the
SLT level de-
scriptor loop is generated (S101 of Fig. 16), and is included in the digital
broadcasting
signal and transmitted (S102 of Fig. 16).
[0157] (Initial Scan Processing)
Next, a flow of initial scan processing executed by the receiving device 20 of
Fig. 1
will be described with reference to the flowchart of Fig. 18.
[0158] In step S201, an operation signal and the like from the input unit
213 are monitored
by the control unit 211, and when a start event of initial scan processing is
generated,
the initial scan processing is started, and the processing proceeds to step
S202.
[0159] In step S202, the receiving unit 214 performs frequency scan
processing according to
the control from the broadcasting control unit 251. In step S203, whether
frequency
scan has succeeded is determined by the frequency scan processing of step
S202.
[0160] In step S203, when the frequency scan is determined to have failed,
the processing is
returned to the processing of step S202, and the frequency scan processing is
perfoimed again. Meanwhile, in step S203, when the frequency scan is
determined to
have succeeded, the processing proceeds to step S204.
[0161] In step S204, stream/SLT acquisition processing is executed. In this
stream/SLT ac-
quisition processing, the SLT transmitted with a multiplexed stream is
acquired, and is
recorded in the recording unit 212. Note that details of the stream/SLT
acquisition
processing will be described with reference to the flowchart of Fig. 19.
[0162] When the stream/SLT acquisition processing is terminated, the
processing proceeds
to step S205. In step S205, whether scan of all of frequency bands has been
completed
is determined.
[0163] In step S205, when the scan of all of frequency bands is determined
not to be
completed, the processing is returned to step S202, and the processing of step
S202 and
25
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
the subsequent steps is repeated. Accordingly, the frequency scan processing
in each
frequency band is performed, and the SLT is acquired for each frequency band
and
recorded in the recording unit 212. Then, in step S205, when scan of all of
the
frequency bands is determined to be completed, the initial scan processing of
Fig. 18 is
terminated.
[0164] The flow of the initial scan processing has been described. In this
initial scan
processing, the scan of each frequency band is perfoimed, and the information
(for
example, the channel selection information) obtained from the SLT acquired for
each
frequency band is recorded in the recording unit 212.
[0165] (Stream/SLT Acquisition Processing)
Here, details of the stream/SLT acquisition processing corresponding to the
processing of step S204 of Fig. 18 will be described with reference to the
flowchart of
Fig. 19.
[0166] In step S211, the receiving unit 214 performs demodulation
processing for the digital
broadcasting signal, extracts (acquires) the L2 packet from the Li frame of
the
physical layer, and extracts (acquires) the IP/UDP packet encapsulated in the
payload
of the L2 packet.
[0167] In step S212, whether the SLT is included in the IP/UDP packet
extracted in the
processing of step S211, that is, whether the SLT has been transmitted is
determined.
[0168] In step S212, when it is determined that the SLT has been
transmitted, the processing
proceeds to step S213. In step S213, the broadcasting control unit 251
acquires the
SLT included in the IP/UDP packet. Further, in step S214, the broadcasting
control
unit 251 records the service configuration information included in the SLT
acquired in
the processing of step S213 to the recording unit 212.
[0169] In step S215, the broadcasting control unit 251 determines whether
the signaling
location descriptor (inet signaling location descriptor) exists in the SLT,
and "0x02"
has been specified as URL_type, that is, whether the viewing history server
URL is
described in the SLT.
[0170] In step S215, when it is determined that the viewing history server
URL is described
in the SLT, the processing proceeds to step S216. In step S216, the viewing
history
server URL acquiring unit 254 acquires the viewing history server URL included
in
(the signaling location descriptor of) the SLT according to a processing
result of step
S215, and records the viewing history server URL to the recording unit 212.
[0171] Meanwhile, in step S215, it is determined that the viewing history
server URL is not
described in the SLT, the processing of step S216 is skipped. Further, in step
S212,
when it is determined that SLT has not been transmitted, the processing from
steps
S213 to S216 is skipped.
[0172] Following that, the processing is returned to the processing of step
S204 of Fig. 18,
26
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
and the processing of step S204 and the subsequent steps is executed.
[0173] The flow of the stream/SLT acquisition processing has been
described. In this
stream/SLT acquisition processing, the SLT is acquired when the SLT has been
transmitted, and the viewing history server URL is acquired and recorded when
the
viewing history server URL is described in the signaling location descriptor
of the
SLT.
[0174] (SLT Acquisition Processing at the time of Switching Service)
Next, a flow of SLT acquisition processing at the time of switching a service
executed by the receiving device 20 of Fig. 1 will be described with reference
to the
flowchart of Fig. 20.
[0175] In step S221, the operation signal and the like from the input unit
213 are monitored
by the control unit 211, and the processing stands by until a service channel
selection
event is generated. In step S222, when it is determined that the service
channel
selection event has been generated, the processing proceeds to step S223.
[0176] In step S223, the broadcasting control unit 251 acquires the service
ID (channel
number) corresponding to the selected service. Further, in step S224, the
broadcasting
control unit 251 refers to the recording unit 212, and determines whether the
channel
selection information has been recorded and acquired.
[0177] In step S224, when it is determined that the channel selection
information has been
acquired, the processing proceeds to step S225. In step S225, the broadcasting
control
unit 251 reads and acquires the channel selection information (the channel
selection in-
formation corresponding to the service ID of the selected service) recorded in
the
recording unit 212.
[0178] Meanwhile, in step S224, when it is determined that the channel
selection in-
formation has not yet been acquired, the processing proceeds to step S226. In
step
S226, reception processing is performed by the control unit 211 and the
receiving unit
214, and the SLT included in the IP/UDP packet is acquired. Accordingly, the
broadcasting control unit 251 can acquire the channel selection information
(the
channel selection information corresponding to the service ID of the selected
service)
from the SLT acquired in the processing of step S226 (S225).
[0179] Note that, here, when the signaling location descriptor exists in
the SLT acquired in
the processing of step S226, and "0x02" is specified as URL type, the viewing
history
server URL included in the SLT may be acquired and recorded in the recording
unit
212. Further, when the viewing history server URL has already been recorded in
the
recording unit 212, the viewing history server URL may be overwritten and
updated.
[0180] When the channel selection information has been acquired by the
processing of step
S225, the processing proceeds to step S227.
[0181] In step S227, the broadcasting control unit 251 performs selection
processing by con-
27
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
trolling the operations of the respective units based on the channel selection
in-
formation acquired by the processing of step S225. By the channel selection
processing, the content of the service selected in the processing of steps
S221 and S222
is reproduced, and the service being in channel selection is switched.
[0182] The flow of the SLT acquisition processing at the time of switching
a service has
been described. In this SLT acquisition processing at the time of switching a
service,
the SLT is acquired when the channel selection information has not yet been
acquired,
and the viewing history server URL is acquired and recorded when the viewing
history
server URL is described in the signaling location descriptor of the SLT, at
the time of
switching a service.
[0183] (SLT Acquisition Processing at the time of Viewing)
Next, a flow of SLT acquisition processing at the time of viewing executed by
the
receiving device 20 of Fig. 1 will be described with reference to the
flowchart of Fig.
21.
[0184] In step S231, the reception processing is performed by the control
unit 211, the
receiving unit 214, and the like, and the transmission port of the SLT is
monitored
(S232).
[0185] In step S233, the broadcasting control unit 251 determines whether
the SLT
transmitted by the IP/UDP packet has been updated, based on a monitoring
result of
the processing of step S232.
[0186] In step S233, when it is determined that the SLT has not yet been
updated, the
processing is returned to step S231, and the monitoring processing from steps
S231 to
S233 is repeated. Meanwhile, in step S233, when it is determined that the SLT
has
been updated, the processing proceeds to step S234.
[0187] In step S234, the broadcasting control unit 251 refers to the
recording unit 212, and
updates the service configuration information (or a parameter thereof)
included in the
updated SLT.
[0188] In step S235, the broadcasting control unit 251 determines whether
the viewing
history server URL has been updated when the signaling location descriptor
(inet signaling location descriptor) exists in the updated SLT, and "0x02" is
specified
as URL_type.
[0189] In step S235, when it is determined that the viewing history server
URL has been
updated, the processing proceeds to step S236. In step S236, the viewing
history server
URL acquiring unit 254 acquires the viewing history server URL included in the
SLT
according to a processing result of step S235, and updates the viewing history
server
URL recorded in the recording unit 212.
[0190] Note that, in step S235, when it is determined that the viewing
history server URL
has not yet been updated, the processing of step S236 is skipped, and the
processing
28
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
proceeds to step S237. Further, when the viewing history server URL is not
recorded in
the recording unit 212, a newly acquired viewing history server URL is
recorded in the
recording unit 212 as it is.
[0191] In step S237, whether the viewing by the user is terminated is
determined. In step
S237, when it is determined that the viewing is not terminated, the processing
is
returned to step S231, and the processing of step S231 and the subsequent
steps is
repeated. Meanwhile, in step S237, when it is determined that the viewing is
terminated, the SLT acquisition processing at the time of viewing of Fig. 21
is
terminated.
[0192] The flow of the SLT acquisition processing at the time of viewing
has been
described. In this SLT acquisition processing at the time of viewing, the SLT
is
acquired when the transmitted SLT is updated, the viewing history server URL
is
acquired when the viewing history server URL is described in the signaling
location
descriptor of the SLT, and the viewing history server URL is updated.
[0193] (Viewing History Information Recording Processing)
Next, a flow of viewing history information recording processing executed by
the
receiving device 20 of Fig. 1 will be described with reference to the
flowchart of Fig.
22.
[0194] In step S241, the viewing history information managing unit 253
determines whether
it is timing to record the viewing history information (CDM).
[0195] In step S241, when it is determined not to be the timing to record
the viewing history
information (CDM), the determination processing of step S241 is repeated.
Meanwhile, in step S241, when it is determined to be the timing to record the
viewing
history information (CDM), the processing proceeds to step S242.
[0196] In step S242, the viewing history information managing unit 253
records
(accumulates) the viewing history information (CDM) of the content to the
recording
unit 212. When the processing of step S242 is terminated, the viewing history
in-
formation recording processing of Fig. 22 is terminated.
[0197] The flow of the viewing history information recording processing has
been
described. In this viewing history information recording processing, the
viewing
history information (CDM) is recorded at predetermined timing, so that the
viewing
history information (CDM) of each service (channel) is sequentially
accumulated in
the recording unit 212, for example.
[0198] (Viewing History Information Transmission Processing)
Next, a flow of viewing history information transmission processing executed
by the
receiving device 20 of Fig. 1 will be described with reference to the
flowchart of Fig.
23.
[0199] In step S251, the viewing history information managing unit 253
determines whether
29
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
it is timing to transmit the viewing history information (CDM) to the viewing
history
server 30.
[0200] In step S251, when it is determined not to be the timing to transmit
the viewing
history information (CDM) to the viewing history server 30, the determination
processing of step S251 is repeated. Meanwhile, in step S251, when it is
determined to
be the timing to transmit the viewing history information (CDM) to the viewing
history
server 30, the processing proceeds to step S252.
[0201] In step S252, the viewing history information managing unit 253
reads and acquires
the viewing history information (CDM) from the recording unit 212. Note that
this
viewing history information (CDM) is the viewing history information (CDM)
recorded (accumulated) in the recording unit 212 by the viewing history
information
recording processing of Fig. 22.
[0202] In step S253, the viewing history information managing unit 253
reads and acquires
the viewing history server URL from the recording unit 212. Note that the
viewing
history server URL is the viewing history server URL recorded in the recording
unit
212 in the processing of step S216 of Fig. 19, or the viewing history server
URL
updated in the processing of step S236 of Fig. 21.
[0203] In step S254, the communication control unit 252 controls the
communication unit
223 to transmit the viewing history infoiniation (CDM) acquired in the
processing of
step S252 to the viewing history server 30 through the communication line 60
based on
the viewing history server URL acquired in the processing of step S253. When
the
processing of step S254 is terminated, the viewing history information
transmission
processing of Fig. 23 is terminated.
[0204] The flow of the viewing history information transmission processing
has been
described. In this viewing history information transmission processing, the
viewing
history server URL and the viewing history information (CDM) appropriately
recorded
in the recording unit 212 are read at predetermined timing, and the viewing
history in-
formation (CDM) is transmitted to the viewing history server 30 according to
the
viewing history server URL.
[0205] In the above description, a case where the viewing history
information (CDM) appro-
priately recorded in the recording unit 212 is transmitted to the viewing
history server
30 has been described. However, the viewing history information (CDM) may be
instantly transmitted to the viewing history server 30 at timing when the
viewing
history information (CDM) is generated, without being recorded to the
recording unit
212.
[0206] (Viewing History Information Collection/Analysis Processing)
Finally, a flow of viewing history information collection/analysis processing
executed by the viewing history server 30 of Fig. 1 will be described with
reference to
30
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
the flowchart of Fig. 24.
[0207] In step S301, whether the viewing history information (CDM) from the
receiving
device 20 has been transmitted through the communication line 60 is
determined.
[0208] In step S301, when it is determined that the viewing history
information (CDM) has
been transmitted from the receiving device 20, the processing proceeds to step
S302. In
step S302, the communication unit 312 receives the viewing history information
(CDM) transmitted from the receiving device 20 through the communication line
60
according to the control from the control unit 311.
[0209] In step S303, the viewing history information managing unit 351
accumulates the
viewing history information (CDM) received in the processing of step S302 to
the
viewing history information accumulating unit 313.
[0210] When the processing of step S303 is terminated, the processing
proceeds to step
S304. Note that, in step S301, when it is determined that the viewing history
in-
formation (CDM) is not transmitted from the receiving device 20, the
processing of
steps S302 and S303 is skipped, and the processing proceeds to step S304.
[0211] In step S304, whether analyzing the viewing history information
(CDM) ac-
cumulated in the viewing history information accumulating unit 313 is
determined.
[0212] In step S304, when it is determined not to analyze the viewing
history information
(CDM), the processing is returned to step S301, and the processing of step
S301 and
the subsequent steps is repeated. That is, by repetition of the processing
from steps
S301 to S304, the viewing history information (CDM) transmitted from the
plurality of
receiving devices 20 is collected, and the viewing history information (CDM)
of each
service (channel) is accumulated in the viewing history information
accumulating unit
313.
[0213] Meanwhile, in step S304, when it is determined to analyze the
viewing history in-
formation (CDM), the processing proceeds to step S305. In step S305, the
viewing
history information analyzing unit 352 reads the viewing history information
(CDM)
from the plurality of receiving devices 20 accumulated in the viewing history
in-
formation accumulating unit 313 by the processing of step S303, and analyzes
the
viewing history information (CDM).
[0214] In step S306, the viewing history information analyzing unit 352
generates the
viewing history report of each broadcasting station based on an analysis
result of the
processing of step S305.
[0215] In step S307, the communication unit 312 transmits the viewing
history report of
each broadcasting station generated in the processing of step S306 to the
transmitting
device 10 of each broadcasting station according to the control from the
control unit
311. When the processing of step S307 is terminated, the viewing history
information
collection/analylsis processing of Fig. 24 is terminated.
31
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
[0216] The flow of the viewing history information collection/analylsis
processing has been
described. In this viewing history information collection/analylsis
processing, the
viewing history information (CDM) from the plurality of receiving devices 20
is se-
quentially accumulated, and analysis of the accumulated viewing history
information
(CDM) is performed at predetermined timing, and the viewing history report is
generated.
[0217] When the method 1 that is a method of using signaling is employed as
the method of
transmitting the viewing history server URL, the viewing history server URL is
included in the signaling location descriptor arranged in the SLT, so that the
viewing
history server URL is notified from the transmitting device 10 to the
receiving device
20. Further, when the method 1 is employed, the receiving device 20 that
performs
direct reception with an antenna can reliably acquire the metadata (the
signaling in-
formation such as the SLT) included in the digital broadcasting signal, and
the
metadata (the signaling information such as the SLT) is transmitted to the
receiving
device 20 that performs the indirect reception through the MVPD, depending on
the
operation. Therefore, the viewing history server URL included in the SLT can
be
acquired and used at the time of transmitting the viewing history information
(CDM)
in various reception environments.
[0218] (2) Method 2: Transmission of Viewing History Server URL Using Video
Watermark
[0219] (Collection Example of Viewing History Information)
Fig. 25 is a diagram illustrating a collection example of the viewing history
in-
formation (CDM) in a case of transmitting the viewing history server URL using
a
video watermark.
[0220] In Fig. 25, the transmitting device 10 of each broadcasting station
includes the
viewing history server URL to the digital broadcasting signal and transmits
the signal
by the method 2 using a video watermark. To be specific, the viewing history
server
URL is described in a watermark payload transmitted in the video stream as the
video
watermark.
[0221] Here, the viewing history server 30 is jointly managed by the
broadcasting station A,
the broadcasting station B, and the broadcasting station C. Therefore, the
transmitting
devices 10-1 to 10-3 notify the same viewing history server URL (for example,
the
URL of "http://cdmServer.com/cdm") for accessing the viewing history server 30
by
the video watermarks of the video streams transmitted by the digital
broadcasting
signals.
[0222] The receiving device 20 can receive the digital broadcasting signals
from the
transmitting devices 10-1 to 10-3, and acquire and hold the viewing history
server
URL described in the watermark payload transmitted in the video stream as the
video
32
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
watermark. Accordingly, the receiving device 20 can access the viewing history
server
30 through the communication line 60 according to the held viewing history
server
URL (for example, the URL of "http://cdmServer.com/cdm") and transmit the
viewing
history information (CDM) when it becomes timing to transmit the viewing
history in-
formation (CDM) to the viewing history server 30.
[0223] The viewing history server 30 receives and accumulates the viewing
history in-
formation (CDM) transmitted from the plurality of receiving devices 20 through
the
communication line 60. The viewing history server 30 applies analysis
processing and
the like, for example, to the viewing history information (CDM) collected from
the
plurality of receiving devices 20 as described above, thereby to generate the
viewing
history report of each broadcasting station.
[0224] (Method of Notifying Viewing History Server URL)
Fig. 26 is a diagram illustrating a method of notifying the viewing history
server
URL in the case of using a video watermark.
[0225] As illustrated in Fig. 26, in one video frame, upper-side two lines
of a video display
area can be used as the video watermark. In these two lines used as the video
watermark, either standard data transmission that is a method of transmitting
1-bit in-
formation amount in one block, or two time magnification data transmission
that is a
method of transmitting 2-bit information amount in one block can be used.
[0226] For example, in Fig. 26, in a case of using the standard data
transmission, "1" is
stored in the head block, "1" is stored in the second block, "0" is stored in
the third
block, and "1" is stored in the fourth block, in sequence, and one bit of "0"
or "1" is
stored in each of the fifth and subsequent blocks, in sequence. Meanwhile, in
a case of
using the two time magnification data transmission, "11" is stored in the head
block,
"10" is stored in the second block, "01" is stored in the third block, and
"10" is stored
in the fourth block, in sequence, and 2 bits of a combination of "0" and "1"
is stored in
each of the fifth and subsequent blocks, in sequence.
[0227] Further, in the video watermark, the watermark payload is
transmitted using the two
lines of the video bitstream.
[0228] (Syntax of Watermark Payload)
Fig. 27 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of the watermark
payload.
[0229] In 16-bit run in pattern, a transmission pattern of the video
watermark and
resolution of one area illustrated in the range from white to black are
specified. As the
transmission pattern, one line or two lines are specified. Further, as the
resolution of
one area, 8 to 12 bits are specified.
[0230] wm message() represents a message area of the watermark. 8-bit zero
pad represents
zero padding.
[0231] (Syntax of WM message)
33
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
Fig. 28 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of WM message
(wm_message)
of Fig. 27.
[0232] In 8-bit wm message id, a WM message ID is specified. In 8-bit
wm message length, a WM message length is specified.
[0233] In 4-bit wm_message_sequence, a sequence of WM message is specified.
In 2-bit
fragment_number and 2-bit last_fragment, information related to fragment is
specified.
[0234] Here, in a case where "Ox01" is specified as WM message ID, a
content ID message
(content id message) is arranged. Further, in a case where "0x02" is specified
as WM
message ID, a channel ID message (channel_id_message) is arranged. Further, in
a
case where "0x03" is specified as WM message ID, a URI message (uri_message)
is
arranged.
[0235] Then, in a case where the viewing history server URL is described in
the watermark
payload, the URI message is used. Therefore, here, "0x03" is specified as WM
message ID.
[0236] Note that the WM message includes error-detecting codes such as
message CRC 32
and CRC 32.
[0237] (Syntax of URI Message)
Fig. 29 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of URI message
(uri_message)
of Fig. 28.
[0238] In 8-bit uri type, a type of a URI is specified. In 8-bit uri
strlen, a URI length is
specified. URI_string() is made of 8*uri_strlen bits, and in URI_string(), a
uniform
resource identifier (URI) according to the type of a URI specified in uri type
is
specified.
[0239] For example, Fig. 30 illustrates that TBD is specified in a case
where "Ox01" or
"0x02" is specified as uri_type. Further, Fig. 30 illustrates that the URL
(viewing
history server URL) of the viewing history server 30 is specified in a case
where
"0x03" is specified as uri type. Note that "0x00", and "0x04" to "OxFF" in uri
type
are values reserved for future expansion.
[0240] Next, details of processing executed in the devices that configure
the transmission
system 1 of Fig. 1 in a case where the method 2 is employed will be described
with
reference to the flowcharts of Figs. 31 and 32.
[0241] (Viewing History Server URL Notification Processing)
First, a flow of viewing history server URL notification processing in a case
of using
the video watermark will be described with reference to the flowchart of Fig.
31. Note
that this viewing history server URL notification processing is processing
executed in
parallel to the processing of step S101 of Fig. 16 by the transmitting device
10 of Fig.
1.
[0242] In step S121, the control unit 111 determines whether it is timing
to notify the
34
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
viewing history server URL.
[0243] In step S121, when it is determined not to be the timing to notify
the viewing history
server URL, the determination processing of step S121 is repeated. Meanwhile,
in step
S121, when it is determined to be the timing to notify the viewing history
server URL,
the processing proceeds to step S122.
[0244] In step S122, the viewing history server URL generating unit 151
generates a
viewing history server URL of a target viewing history server 30. The viewing
history
server URL generated as described above is supplied to the video processing
unit 113
in the case of employing the method 2.
[0245] In step S123, the video processing unit 113 adds (describes) the
viewing history
server URL generated in the processing of step S122 to (the URI message of the
WM
message of) the watermark payload transmitted as the video watermark of each
frame,
in processing the video stream.
[0246] At this time, in the URI message, "0x03" is specified as uri_type.
Further, for
example, as illustrated in Fig. 25, in a case where the viewing history server
30 is
jointly managed by the broadcasting station A, the broadcasting station B, and
the
broadcasting station C, "http://cdmServer.com/cdm" is described in
URI_string() of
the URI message as the viewing history server URL, in the transmitting devices
10-1
to 10-3 of the broadcasting station A, the broadcasting station B, and the
broadcasting
station C.
[0247] The flow of the viewing history server URL notification processing
has been
described. In the viewing history server URL notification processing, uri type
as
"0x03" and URI string() in which the viewing history server URL is specified
are
described in the URI message of the WM message of the watermark payload. Then,
the
video frame (video stream) including the video watermark of which the
watermark
payload including the URI message is to be transmitted is generated (S101 of
Fig. 16),
and is included in the digital broadcasting signal and transmitted (S102 of
Fig. 16).
[0248] (Viewing History Server URL Acquisition Processing)
Next, a flow of viewing history server URL acquisition processing in a case of
using
the video watermark will be described with reference to the flowchart of Fig.
32. Note
that the viewing history server URL acquisition processing is processing
executed
during viewing of the content of the service selected according to the channel
selection
operation by the user, in the receiving device 20 of Fig. 1.
[0249] In step S261, the operation signal and the like from the input unit
213 are monitored
by the control unit 211, and the processing stands by until the service
channel selection
event is generated. Then, in step S262, when it is determined that the service
channel
selection event has been generated, the processing proceeds to step S263.
[0250] In step S263, the broadcasting control unit 251 performs channel
selection processing
35
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
by controlling the operations of the receiving unit 214 and the like based on
the
channel selection information recorded in the recording unit 212.
[0251] In step S264, the broadcasting control unit 251 renders (the streams
of) the
components of the video, audio, and caption by controlling the video
processing unit
216, the audio processing unit 218, and the caption processing unit 220.
[0252] In step S265, whether to perform processing for the video watermark
is determined.
In step S265, when it is determined to perfolm the processing for the video
watermark,
the processing proceeds to step S266. In step S266, the video processing unit
216 de-
termines whether the viewing history server URL is described in (the URI
message of
the WM message of) the watermark payload transmitted as the video wateimark.
[0253] In step S266, when it is determined that the viewing history server
URL is described
in (the URI message of the WM message of) the watermark payload, the
processing
proceeds to step S267. In step S267, the viewing history server URL acquiring
unit 254
acquires the viewing history server URL described in (the URI message of the
WM
message of) the watermark payload according to a processing result of step
S266, and
records the viewing history server URL to the recording unit 212.
[0254] Meanwhile, in step S266, when it is determined that the viewing
history server URL
is not described in (the URI message of the WM message of) the watermark
payload,
the processing proceeds to step S268. In step S268, the video processing unit
216
performs another video watermark processing (for example, processing for the
content
ID message, the channel ID message, and the like).
[0255] When the processing of step S267 or the processing of step S268 is
terminated, the
processing proceeds to step S269. Further, in step S265, when it is determined
not to
perfolin the processing for the video watermark, the processing from steps
S266 to
S268 is skipped, and the processing proceeds to step S269.
[0256] In step S269, whether the viewing by the user is terminated is
determined. In step
S269, when it is determined that the viewing is not terminated, the processing
is
returned to step S264, and the processing of step S264 and the subsequent
steps is
repeated. Meanwhile, in step S269, when it is determined that the viewing is
terminated, the viewing history server URL acquisition processing of Fig. 32
is
terminated.
[0257] The flow of the viewing history server URL acquisition processing
has been
described. In the viewing history server URL acquisition processing, the
watermark
payload is transmitted with the video watermark when the service channel
selection
even has been generated or at the time of viewing the content, and the viewing
history
server URL is acquired and recorded when the viewing history server URL is
described in the URI message of the WM message.
[0258] Note that, in the viewing history server URL acquisition processing
of Fig. 32, a case
36
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
where the viewing history server URL described in the URI message is acquired
at the
time of viewing the content has been exemplarily described. However, the
viewing
history server URL transmitted using the video watermark may be acquired and
recorded (newly recorded or updated) at another timing.
[0259] Further, even in the case of employing the method 2, in the
receiving device 20, the
viewing history information transmission processing of Fig. 23 is executed,
and the
viewing history information (CDM) is transmitted to the viewing history server
30
through the communication line 60 based on the viewing history server URL
acquired
from (the URI message of the WM message of) the watermark payload transmitted
with the video watermark, when it becomes timing to transmit the viewing
history in-
formation (CDM) to the viewing history server 30.
[0260] In the case of employing the method 2 that is a method of using a
video watermark,
as the method of transmitting the viewing history server URL, as described
above, the
viewing history server URL is notified from the transmitting device 10 to the
receiving
device 20 by including the viewing history server URL to the video watermark.
Further, in the case of employing such a method 2, the receiving device 20
that
performs the direct reception with an antenna can process the watermark
payload
transmitted as the video wateiniark, and even the receiving device 20 that
performs the
indirect reception through the MVPD can process the watermark payload
transmitted
as the video watermark. Therefore, the viewing history server URL included in
(the
URI message of the WM message of) the watermark payload can be acquired and
used
at the time of transmitting the viewing history information (CDM), regardless
of a
reception environment.
[0261] In the above description, a case of including the viewing history
server URL to the
video watermark has been described. However, in a case where an audio
watermark
can be used, the viewing history server URL may be included to the watermark
payload using the audio watermark.
[0262] (3) Method 3: Transmission of Viewing History Server URL Using Audio
User Data
[0263] (Collection Example of Viewing History Information)
Fig. 33 is a diagram illustrating a collection example of the viewing history
in-
formation (CDM) in a case of transmitting the viewing history server URL using
audio
user data.
[0264] In Fig. 33, the transmitting device 10 of each broadcasting station
includes the
viewing history server URL to the digital broadcasting signal and transmits
the signal
by the method 3 using audio user data. To be specific, the viewing history
server URL
is described in the audio user data transmitted with an audio stream.
[0265] Here, the viewing history server 30 is jointly managed by the
broadcasting station A,
the broadcasting station B, and the broadcasting station C. Therefore, the
transmitting
37
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
devices 10-1 to 10-3 notify the same viewing history server URL (for example,
the
URL of "http://cdmServer.com/cdm") for accessing the viewing history server 30
by
the audio user data of the audio streams transmitted by the digital
broadcasting signals.
[0266] The receiving device 20 can receive the digital broadcasting signals
from the
transmitting devices 10-1 to 10-3, and acquire and hold the viewing history
server
URL described in the audio user data transmitted by the audio streams.
Accordingly,
the receiving device 20 can access the viewing history server 30 through the
commu-
nication line 60 and transmit the viewing history information (CDM) according
to the
held viewing history server URL (for example, the URL of
"http://cdmServer.com/cdm") when it becomes timing to transmit the viewing
history
information (CDM) to the viewing history server 30.
[0267] The viewing history server 30 receives and accumulates the viewing
history in-
formation (CDM) transmitted from the plurality of receiving devices 20 through
the
communication line 60. The viewing history server 30 can generate the viewing
history
report of each broadcasting station by applying analysis processing and the
like to the
viewing history information (CDM) collected from the plurality of receiving
devices
20 as described above.
[0268] (Syntax of SYS Metaframe)
Fig. 34 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of an SYS metaframe
(SysMetaFrame) defined by MPEG-H 3D Audio.
[0269] In 8-bit sysType, a type of a system is specified. In dataLen, a
data length is
specified. sysData is made of PdataLen bits, and in sysData, data according to
the
type specified in sysType is specified.
[0270] For example, Fig. 35 illustrates that data specified in sysData is
used by
"SYS_MP2TS", that is, a MPEG2 TS system, in a case where "1" is specified as
sysType. Further, Fig. 35 illustrates that data specified in sysData is used
by
"SYS MMT", that is, an MMT system, in a case where "2" is specified as
sysType.
[0271] Further, Fig. 35 illustrates that data specified in sysData is used
by "SYS DASH",
that is, an MPEG-DASH system, in a case where "3" is specified as sysType.
Note that
the value of sysType as "0" is undefined. Further, "4" to "127" in the value
of sysType
are values reserved for future use by the International Organization for
Standardization
(ISO). Further, "128" to "255" are values reserved for future expansion.
[0272] Here, for example, when "128" is specified as sysType by allocating
"128", among
the values for future expansion of "128" to "255", to "SYS ATSC3.0", use of
the data
specified in sysData by an ATSC 3.0 system can be illustrated.
[0273] Fig. 36 is a diagram illustrating an example of syntax of sysData
(sysData atsc3.0) in
a case where "SYS_ATSC3.0" is specified as sysType.
[0274] In 4-bit version, a version is specified. In 4-bit sys data type, a
data type is
38
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
specified. Here, in a case where "cdm_uri" is specified as sys_data_type,
cdm_uri_length and cdm_uri are specified.
[0275] In 16-bit cdm uri length, a URI length is specified. cdm_uri is made
of
8*cdrn uri length bits, and in cdm_uri, a URI as the viewing history server
URL is
specified.
[0276] Next, details of processing executed in the devices that configure
the transmission
system 1 of Fig. 1 in a case where the method 3 is employed will be described
with
reference to the flowcharts of Figs. 37 and 38.
[0277] (Viewing History Server URL Notification Processing)
First, a flow of viewing history server URL notification processing in a case
of using
the audio user data will be described with reference to the flowchart of Fig.
37. Note
that this viewing history server URL notification processing is processing
executed in
parallel to the processing of step S101 of Fig. 16 by the transmitting device
10 of Fig.
1.
[0278] In step S131, the control unit 111 determines whether it is timing
to notify the
viewing history server URL.
[0279] In step S131, when it is determined not to be the timing to notify
the viewing history
server URL, the determination processing of step S131 is repeated. Meanwhile,
in step
S131, when it is determined to be the timing to notify the viewing history
server URL,
the processing proceeds to step S132.
[0280] In step S132, the viewing history server URL generating unit 151
generates a
viewing history server URL of a target viewing history server 30. The viewing
history
server URL generated as described above is supplied to the audio processing
unit 115
in a case of employing the method 3.
[0281] In step S133, the audio processing unit 115 adds the viewing history
server URL
generated in the processing of step S132 to the audio user data (sysData of
the SYS
metaframe) in processing an audio stream.
[0282] Note that, at this time, in the SYS metaframe (SysMetaFrame), "128"
("SYS_ATSC3.0") is specified as sysType, and sysData_atsc3.0 is used as
sysData.
Further, in sysData atsc3.0, "cdm_uri" is specified as sys data type. Further,
for
example, as illustrated in Fig. 33, in a case where the viewing history server
30 is
jointly managed by the broadcasting station A, the broadcasting station B, and
the
broadcasting station C, "http://cdmServer.com/cdm" is described in cdm_uri of
sysData atsc3.0 of the SYS metaframe as the viewing history server URL, in the
transmitting devices 10-1 to 10-3 of the broadcasting station A, the
broadcasting
station B, and the broadcasting station C.
[0283] The flow of the viewing history server URL notification processing
has been
described. In this viewing history server URL notification processing, sys
data type as
39
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
"cdm_uri" and cdm_uri in which the viewing history server URL is specified are
described in sysData_atsc3.0 of the SYS metaframe. Then, the audio stream
including
the SYS metaframe including the sysData_atsc3.0 is generated (S101 of Fig.
16), and
is included in the digital broadcasting signal and transmitted (S102 of Fig.
16).
[0284] (Viewing History Server URL Acquisition Processing)
Next, a flow of viewing history server URL acquisition processing of a case of
using
the audio user data will be described with reference to the flowchart of Fig.
38. Note
that the viewing history server URL acquisition processing is, for example,
processing
executed during viewing of the content of the service selected according to
the channel
selection operation by the user, in the receiving device 20 of Fig. 1.
[0285] In step S271, the operation signal and the like from the input unit
213 are monitored
by the control unit 211, and the processing stands by until the service
channel selection
event is generated. Then, in step S272, when it is determined that the service
channel
selection event has been generated, the processing proceeds to step S273.
[0286] In step S273, the broadcasting control unit 251 performs channel
selection processing
by controlling the operation of the receiving unit 214 and the like based on
the channel
selection information recorded in the recording unit 212.
[0287] In step S274, the broadcasting control unit 251 renders (the streams
of) the
component of the video, audio, and caption by controlling the video processing
unit
216, the audio processing unit 218, and the caption processing unit 220.
[0288] In step S275, whether to perform processing for the audio user data
of the audio
stream is determined. In step S275, when it is determined to perform the
processing for
the audio user data, the processing proceeds to step S276. In step S276, the
audio
processing unit 218 determines whether the viewing history server URL is
described in
the audio user data (sysData_atsc3.0 of the SYS metaframe).
[0289] In step S276, when it is determined that the viewing history server
URL is described
in the audio user data (sysData_atsc3.0 of the SYS metaframe), the processing
proceeds to step S277. In step S277, the viewing history server URL acquiring
unit 254
acquires the viewing history server URL described in the audio user data
(sysData_atsc3.0 of the SYS metaframe) according to a processing result of
step S276
and records the viewing history server URL to the recording unit 212.
[0290] Meanwhile, in step S275, when it is determined not to perform the
processing for the
audio user data, or in step S276, when it is determined that the viewing
history server
URL is not described in the audio user data (sysData_atsc3.0 of the SYS
metaframe),
the processing proceeds to step S278.
[0291] In step S278, whether the viewing by the user is terminated is
determined. In step
S278, when it is determined that the viewing is not terminated, the processing
is
returned to step S274, and the processing of step S274 and the subsequent
steps is
40
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
repeated. Meanwhile, in step S278, when it is determined that the viewing is
terminated, the viewing history server URL acquisition processing of Fig. 38
is
terminated.
[0292] The flow of the viewing history server URL acquisition processing
has been
described. In this viewing history server URL acquisition processing, when the
service
channel selection event has been generated, that is, at the time of viewing of
the
content, the viewing history server URL is acquired and recorded when the
viewing
history server URL is described in the audio user data (sysData atsc3.0 of the
SYS
metaframe).
[0293] In the viewing history server URL acquisition processing of Fig. 38,
a case where the
viewing history server URL described in sysData atsc3.0 of the SYS metaframe
is
acquired at the time of viewing the content has been exemplarily described.
However,
the viewing history server URL transmitted using the audio user data may be
acquired
and recorded (newly recorded or updated) at another timing.
[0294] Further, even in the case of employing the method 3, in the
receiving device 20, the
viewing history information transmission processing of Fig. 23 is executed,
and the
viewing history information (CDM) is transmitted to the viewing history server
30
through the communication line 60 based on the viewing history server URL
acquired
from the audio user data (sysData atsc3.0 of the SYS metaframe) when it
becomes
timing to transmit the viewing history information (CDM) to the viewing
history server
30.
[0295] In the case of employing the method 3 that is a method using audio
user data, as the
method of transmitting the viewing history server URL, as described above, the
viewing history server URL is notified from the transmitting device 10 to the
receiving
device 20 by including the viewing history server URL to the audio user data.
Further,
in the case of employing such a method 3, the receiving device 20 that
performs the
direct reception with an antenna can process the audio user data, and even the
receiving device 20 that performs the indirect reception through the MVPD can
process the audio user data. Therefore, the viewing history server URL
included in the
audio user data (sysData atsc3.0 of the SYS metaframe) can be acquired and
used at
the time of transmitting the viewing history information (CDM), regardless of
a
reception environment.
[0296] In the above description, a case of including the viewing history
server URL in the
audio user data (sysData atsc3.0 of the SYS metaframe) has been described.
However,
the viewing history server URL may be included using the video user data in a
case
where the video user data can be used.
[0297] (4) Method 4: Transmission of Viewing History Server URL Using
Metadata of
TTML Document
41
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
[0298] (Collection Example of Viewing History Information)
Fig. 39 is a diagram illustrating a collection example of the viewing history
in-
formation (CDM) in a case of transmitting the viewing history server URL using
metadata of a TTML document.
[0299] In Fig. 39, the transmitting device 10 of each broadcasting station
includes the
viewing history server URL to the digital broadcasting signal and transmits
the signal
by the method 4 using metadata of a TTML document. To be specific, the viewing
history server URL is described in the metadata of the TTML document
transmitted
with a caption stream.
[0300] Here, the viewing history server 30 is jointly managed by the
broadcasting station A,
the broadcasting station B, and the broadcasting station C. Therefore, the
transmitting
devices 10-1 to 10-3 notify the same viewing history server URL (for example,
the
URL of "http://cdmServer.com/cdm") for accessing the viewing history server 30
by
the metadata of the TTML documents of the caption streams transmitted by the
digital
broadcasting signals.
[0301] The receiving device 20 can receive the digital broadcasting signals
from the
transmitting devices 10-1 to 10-3, and acquire and hold the viewing history
server
URL described in the metadata of the TTML document transmitted by the caption
stream. Accordingly, the receiving device 20 can access the viewing history
server 30
through the communication line 60 and transmit the viewing history information
(CDM) according to the held viewing history server URL (for example, the URL
of
"http://cdmServer.com/cdm") when it becomes timing to transmit the viewing
history
information (CDM) to the viewing history server 30.
[0302] The viewing history server 30 receives and accumulates the viewing
history in-
formation (CDM) transmitted from the plurality of receiving devices 20 through
the
communication line 60. The viewing history server 30 can generate the viewing
history
report of each broadcasting station by applying analysis processing and the
like to the
viewing history information (CDM) collected from the plurality of receiving
devices
20, as described above.
[0303] (Description Example of TTML Document)
Fig. 40 is a diagram illustrating a description example of the TTML document
in an
XML format.
[0304] In Fig. 40, a cdmUri element for describing the viewing history
server URL is
described in metadata element of a head element described in the TTML
document.
Here, a name space of ATSC (ATSC 3.0) as the organization for standardization
is
defined, and the cdmUri element is caused to belong to the name space of ATSC
3.0,
so that the metadata of the TTML document is expanded.
[0305] "http://cdmServer.com/cdm" is described between a start tag and an
end tag of the
42
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
cdmUri element as the viewing history server URL. The cdmUri element is
expanded
in the metadata element in this way, so that the viewing history server URL
can be
described as the metadata of the TTML document.
[0306] Next, details of processing executed in the devices that configure
the transmission
system 1 of Fig. 1 in a case where the method 4 is employed will be described
with
reference to the flowcharts of Figs. 41 and 42.
[0307] (Viewing History Server URL Notification Processing)
First, a flow of viewing history server URL notification processing in a case
of using
the metadata of the TTML document will be described with reference to the
flowchart
of Fig. 41. Note that this viewing history server URL notification processing
is
processing executed in parallel to the processing of step S101 of Fig. 16 by
the
transmitting device 10 of Fig. 1.
[0308] In step S141, the control unit 111 determines whether it is timing
to notify the
viewing history server URL.
[0309] In step S141, when it is determined not to be the timing to notify
the viewing history
server URL, the determination processing of step S141 is repeated. Meanwhile,
in step
S141, when it is determined to be the timing to notify the viewing history
server URL,
the processing proceeds to step S142.
[0310] In step S142, the viewing history server URL generating unit 151
generates a
viewing history server URL of a target viewing history server 30. The viewing
history
server URL generated as described above is supplied to the caption processing
unit 117
in a case of employing the method 4.
[0311] In step S143, the caption processing unit 117 adds the viewing
history server URL
generated in the processing of step S142 to the metadata of the TTML document,
in
processing the caption stream.
[0312] However, for example, as illustrated in Fig. 39, in a case where the
viewing history
server 30 is jointly managed by the broadcasting station A, the broadcasting
station B,
and the broadcasting station C, "http://cdmServer.com/cdm" is described
between the
start tag and the end tag of the cdmUri element of the metadata element in the
head
element of the TTML document, in the transmitting devices 10-1 to 10-3 of the
broadcasting station A, the broadcasting station B, and the broadcasting
station C.
[0313] The flow of the viewing history server URL notification processing
has been
described. In this viewing history server URL notification processing, the
viewing
history server URL is described between the start tag and the end tag of the
cdmUri
element of the metadata element in the head element of the TTML document.
Then,
the caption stream including the TTML document including the metadata element
is
generated (S101 of Fig. 16), and is included in the digital broadcasting
signal and
transmitted (S102 of Fig. 16).
43
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
[0314] (Viewing History Server URL Acquisition Processing)
Next, a flow of viewing history server URL acquisition processing in a case of
using
the metadata of the TTML document will be described with reference to the
flowchart
of Fig. 42. Note that this viewing history server URL acquisition processing
is
processing executed during viewing of the content of the service selected
according to
the channel selection operation of the user, by the receiving device 20 of
Fig. 1.
[0315] In step S281, the operation signal and the like from the input unit
213 are monitored
by the control unit 211, and the processing stands by until the service
channel selection
event is generated. Then, in step S282, when it is determined that the service
channel
selection event has been generated, the processing proceeds to step S283.
[0316] In step S283, the broadcasting control unit 251 performs channel
selection processing
by controlling the operations of the receiving unit 214 and the like based on
the
channel selection information recorded in the recording unit 212.
[0317] In step S284, the broadcasting control unit 251 renders (the streams
of) the
components of the video, audio, and caption by controlling the video
processing unit
216, the audio processing unit 218, and the caption processing unit 220.
[0318] In step S285, whether to perform the processing for the metadata of
the TTML
document is determined. In step S285, when it is determined to perform the
processing
for the metadata of the TTML document, the processing proceeds to step S286.
In step
S286, the caption processing unit 220 determines whether the viewing history
server
URL is described in the metadata (the cdmUri element of the metadata element)
of the
TTML document.
[0319] In step S286, when it is determined that the viewing history server
URL is described
in the metadata (the cdmUri element of the metadata element) of the TTML
document,
the processing proceeds to step S287. In step S287, the viewing history server
URL
acquiring unit 254 acquires the viewing history server URL described in the
metadata
(the cdmUri element of the metadata element) of the TTML document according to
a
processing result of step S286, and records the viewing history server URL to
the
recording unit 212.
[0320] Meanwhile, in step S285, when it is determined not to perform the
processing for the
metadata of the TTML document, or in step S286, when it is determined that the
viewing history server URL is not described in the metadata (the cdmUri
element of
the metadata element) of the TTML document, the processing proceeds to step
S288.
[0321] In step S288, whether the viewing by the user is terminated is
determined. In step
S288, when it is determined that the viewing is not terminated, the processing
is
returned to step S284, and the processing of step S284 and the subsequent
steps is
repeated. Meanwhile, in step S288, when it is determined that the viewing is
terminated, the viewing history server URL acquisition processing of Fig. 42
is
44
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
terminated.
[0322] The flow of the viewing history server URL acquisition processing
has been
described. In this viewing history server URL acquisition processing, the
viewing
history server URL is acquired and recorded when the viewing history server
URL is
described in the metadata (the cdmUri element of the metadata element) of the
TTML
document, when the service channel selection event has been generated, that
is, at the
time of viewing the content.
[0323] In the viewing history server URL acquisition processing of Fig. 42,
a case where the
viewing history server URL described in the metadata of the TTML document is
acquired at the time of viewing the content has been exemplarily described.
However,
the viewing history server URL transmitted using the metadata of the TTML
document
may be acquired and recorded (newly recorded or updated) at another timing.
[0324] Further, even in the case of employing the method 4, in the
receiving device 20, the
viewing history information transmission processing of Fig. 23 is executed,
and the
viewing history information (CDM) is transmitted to the viewing history server
30
through the communication line 60 based on the viewing history server URL
acquired
from the metadata (the cdmUri element of the metadata element) of the TTML
document, when it becomes timing to transmit the viewing history information
(CDM)
to the viewing history server 30.
[0325] In the case of employing the method 4 that is a method using
metadata of a TTML
document, as the method of transmitting the viewing history server URL, as
described
above, the viewing history server URL is notified from the transmitting device
10 to
the receiving device 20 by including the viewing history server URL to the
metadata of
the TTML document. Further, in the case of employing such a method 4, the
receiving
device 20 that performs the direction reception with an antenna can process
the
metadata of the TTML document, and even the receiving device 20 that performs
the
indirect reception through the MVPD can process the metadata of the TTML
document. Therefore, the viewing history server URL included in the metadata
of the
TTML document can be acquired and used at the time of transmitting the viewing
history information (CDM), regardless of a reception environment.
[0326] <4. Modification>
[0327] In the above description, the ATSC that is the method employed in
the US has been
described as the standard of terrestrial digital television broadcasting.
However, the
present embodiments may be applied to the integrated services digital
broadcasting
(ISDB) that is the method employed in Japan and the like or the digital video
broadcasting (DVB) that is the method employed by European countries. Further,
the
present embodiments are employed not only in the terrestrial digital
television
broadcasting, but also in satellite digital television broadcasting, digital
wired
45
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
television broadcasting, and the like.
[0328] Further, in the above description, the SLT in a binary format has
been described.
However, the SLT may be in a text format such as the XML folinat. Figs. 43 to
46 il-
lustrate examples of the syntax of the SLT in the XML format. Similarly, the
de-
scriptor arranged in the SLT is not limited to the binary format, and can be
the text
format such as the XML foiniat. Fig. 47 illustrates an example of the syntax
of the
signaling location descriptor in the XML format.
[0329] <5. Configuration of Computer>
[0330] The above-described series of processing can be executed by
hardware, or can be
executed by software. When the series of processing is executed by software, a
program that configures the software is installed to a computer. Fig. 48 is a
diagram il-
lustrating a configuration example of hardware of the computer that executes
the series
of processing by the program.
[0331] In a computer 900, a central processing unit (CPU) 901, a read only
memory (ROM)
902, a random access memory (RAM) 903 are mutually connected by a bus 904. An
input/output interface 905 is further connected to the bus 904. An input unit
906, an
output unit 907, a recording unit 908, a communication unit 909, and a drive
910 are
connected to the input/output interface 905.
[0332] The input unit 906 is made of a keyboard, a mouse, a microphone, and
the like. The
output unit 907 is made of a display, a speaker, and the like. The recording
unit 908 is
made of a hard disk, a non-volatile memory, and the like. The communication
unit 909
is made of a network interface, and the like. The drive 910 drives a removable
medium
911 such as a magnetic disk, an optical disk, a magneto-optical disk, or a
semi-
conductor memory.
[0333] In the computer 900 configured as described above, the CPU 901 loads
the program
recorded in the ROM 902 or the recording unit 908 to the RAM 903 through the
input/
output interface 905 and the bus 904 and executes the program, so that the
above-
described series of processing is performed.
[0334] The program executed by the computer 900 (CPU 901) can be recorded
in the
removable medium 911 as a package medium and provided. Further, the program
can
be provided through a wired or wireless transmission medium such as a local
area
network, the internet, or digital satellite broadcasting.
[0335] In the computer 900, the program can be installed to the recording
unit 908 through
the input/output interface 905 by attaching the removable medium 911 to the
drive
910. Further, the program can be received by the communication unit 909
through the
wired or wireless transmission medium, and installed to the recording unit
908. In
addition, the program can be installed to the ROM 902 or the recording unit
908 in
advance.
46
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
[0336] Here, in the present specification, the processing performed by the
computer
according to the program is not necessarily performed in time series along the
order
described as the flowcharts. That is, the processing performed by the computer
according to the program includes processing executed in parallel or in an
individual
manner (for example, parallel processing or processing by objects). Further,
the
program may be processed by one computer (processor), or may be processed in a
dis-
tributed manner by a plurality of computers.
[0337] Note that embodiments of the present technology are not limited to
the above-
described embodiments, and various modification can be made without departing
from
the gist of the present technology.
[0338] Further, the present technology can employ following configurations.
[0339] (1)
A receiving device including:
circuitry configured to
receive a digital broadcast stream;
acquire server information corresponding to a viewing history server that
collects
viewing history information related to a viewing history of content, the
server in-
formation being included in the digital broadcast stream; and
control transmission of the viewing history information to the viewing history
server
based on the acquired server information.
(2)
The receiving device according to (1), in which
the digital broadcast stream includes first control information, the first
control in-
formation including channel selection information for the content,
the server information is included in the first control information, and the
circuitry is
configured to acquire the server information from the first control
information.
(3)
The receiving device according to (2), in which
the first control information specifies the server information for each of a
plurality of
services provided in the digital broadcast stream, or specifies the server
information to
be common among the plurality of services, and
the content is included in one of the plurality of services.
(4)
The receiving device according to (2) or (3), in which
the first control information is
arranged in a user datagram protocol (UDP) packet included in an IP packet,
and
acquired ahead of second control information transmitted by a real-time object
delivery over unidirectional transport (ROUTE) session or an MPEG media
transport
47
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
(MMT) session.
(5)
The receiving device according to (1), in which
the server information is included in a video or audio watermark that is
inserted in the
content, and
the circuitry is configured to acquire the server information from the
watermark.
(6)
The receiving device according to (1), in which
the server information is included in video or audio user data of the content,
and
the circuitry is configured to acquire the server information from the user
data.
(7)
The receiving device according to (1), in which
the server information is included in metadata of a timed text markup language
(TTML) document for displaying closed caption text associated with the
content, and
the circuitry is configured to acquire the server information from the
metadata of the
TTML document.
(8)
The receiving device according to any one of (1) to (7), in which the
circuitry is
configured to:
manage the viewing history information.
(9)
The receiving device according to any one of (1) to (8), in which
the server information is a uniform resource locator (URL) of the viewing
history
server, and
the viewing history information is a consumption data message (CDM)including a
service identifier field associated with a single virtual channel or non-real-
time service
and an individual consumption data record.
(10)
A data processing method of a receiving device, the method including:
acquiring, by circuitry of the receiving device, server information
corresponding to a
viewing history server that collects viewing history information related to a
viewing
history of content, the server information being included in a digital
broadcast stream;
and
controlling, by the circuitry of the receiving device, transmission of the
viewing history
information to the viewing history server based on the acquired server
information.
(11)
A transmitting device including:
circuitry configured to
48
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
generate server information corresponding to a viewing history server that
collects
viewing history information related to a viewing history of content, the
server in-
formation being included in a digital broadcast stream; and
transmit the digital broadcast stream including the generated server
information and
the content.
(12)
The transmitting device according to (11), in which
the digital broadcast stream includes first control information, the first
control in-
formation including channel selection information for the content, and
the server information is included in first control information.
(13)
The transmitting device according to (12), in which
the first control information specifies the server information for each of a
plurality of
services provided in the digital broadcast stream, or specifies the server
information to
be common among the plurality of services, and
the content is included in one of the plurality of services.
(14)
The transmitting device according to (12) or (13), in which
the first control information is
arranged in a user datagram protocol (UDP) packet included in an IP packet,
and
acquired ahead of second control information transmitted by a real-time object
delivery
over unidirectional transport (ROUTE) session or an MPEG media transport (MMT)
session.
(15)
The transmitting device according to (11), in which
the server information is included in a video or audio watermark that is
inserted in the
content.
(16)
The transmitting device according to (11), in which
the server information is included in video or audio user data of the content.
(17)
The transmitting device according to (11), in which
the server infoiniation is included in metadata of a timed text markup
language
(TTML) document for displaying closed caption text associated with the
content.
(18)
The transmitting device according to any one of (11) to (17), in which
the circuitry is configured to change the server information according to a
request to
change the server information.
49
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
(19)
The transmitting device according to any one of (11) to (18), in which
the server information is a uniform resource locator (URL) of the viewing
history
server, and
the viewing history information is a consumption data message (CDM) including
a
service identifier field associated with a single virtual channel or non-real-
time service
and an individual consumption data record.
(20)
A data processing method of a transmitting device, the method including:
generating, by circuitry of the transmitting device, server information
corresponding to
a viewing history server that collects viewing history information related to
a viewing
history of content, the server information being included in a digital
broadcast stream;
and
transmitting, by the circuitry of the transmitting device, the digital
broadcast stream
including the generated server information and the content.
(21)
A receiving device including:
a receiving unit configured to receive a broadcasting wave of digital
broadcasting
using an Internet protocol (IP) transmission method;
an acquiring unit configured to acquire destination information indicating a
destination
of a viewing history server that collects viewing history information related
to a
viewing history of content, the destination information being transmitted with
the
broadcasting wave; and
a control unit configured to control transmission of the viewing history
information to
the viewing history server through a communication line based on the acquired
des-
tination information.
(22)
The receiving device according to (21), wherein
the destination information is included in first control information including
in-
formation for controlling channel selection processing of the content and is
transmitted, and
the acquiring unit acquires the destination information included in the first
control in-
formation.
(23)
The receiving device according to (22), wherein
the first control information specifies the destination information for each
of services
of the content, or specifies the destination infoiniation to be common among
the
services.
50
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
(24)
The receiving device according to (22) or (23), wherein
the first control information
is arranged in a user datagram protocol (UDP) packet included in an IP packet
and is
transmitted, and
is acquired ahead of second control information transmitted by a real-time
object
delivery over unidirectional transport (ROUTE) session or a MPEG media
transport
(MMT) session.
(25)
The receiving device according to (21), wherein
the destination information is included in a video or audio watermark that
configures
the content and is transmitted, and
the acquiring unit acquires the destination infonnation included in the
watermark.
(26)
The receiving device according to (21), wherein
the destination information is included in video or audio user data that
configures the
content and is transmitted, and
the acquiring unit acquires the destination infoiniation included in the user
data.
(27)
The receiving device according to (21), wherein
the destination information is included in metadata of a timed text markup
language
(TTML) document in a TTML format for displaying a caption that configures the
content and is transmitted, and
the acquiring unit acquires the destination information included in the
metadata of the
TTML document.
(28)
The receiving device according to any one of (21) to (27), further including:
a managing unit configured to manage the viewing history information.
(29)
The receiving device according to any one of (21) to (28), wherein
the IP transmission method conforms to advanced television systems committee
(ATSC) 3.0,
the destination information is a uniform resource locator (URL) of the viewing
history
server, and
the viewing history information is a consumption data message (CDM) defined by
the
ATSC.
(30)
A data processing method of a receiving device, the method including the steps
of:
51
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
acquiring, by the receiving device, destination information indicating a
destination of a
viewing history server that collects viewing history information related to a
viewing
history of content, the destination information being transmitted with a
broadcasting
wave of digital broadcasting using an IP transmission method; and
controlling, by the receiving device, transmission of the viewing history
information to
the viewing history server through a communication line based on the acquired
des-
tination information.
(31)
A transmitting device including:
a generating unit configured to generate destination information indicating a
des-
tination of a viewing history server that collects viewing history information
related to
a viewing history of content, the destination information being transmitted
with a
broadcasting wave of digital broadcasting using an IP transmission method; and
a transmitting unit configured to transmit the generated destination
information with
the broadcasting wave together with the content.
(32)
The transmitting device according to (31), wherein
the destination information is included in first control information including
in-
formation for controlling channel selection processing of the content and is
transmitted.
(33)
The transmitting device according to (32), wherein
the first control information specifies the destination information for each
of services
of the content, or specifies the destination infoiniation to be common among
the
services.
(34)
The transmitting device according to (32) or (33), wherein
the first control information
is arranged in a UDP packet included in an IF packet and is transmitted, and
is acquired ahead of second control information transmitted by a ROUTE session
or an
MMT session.
(35)
The transmitting device according to (31), wherein
the destination information is included in a video or audio watermark that
configures
the content and is transmitted.
(36)
The transmitting device according to (31), wherein
the destination information is included in video or audio user data that
configures the
52
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137 PCT/JP2016/002770
content and is transmitted.
(37)
The transmitting device according to (31), wherein
the destination information is included in metadata of a TTML document in a
TTML
format for displaying a caption that configures the content and is
transmitted.
(38)
The transmitting device according to any one of (31) to (37), wherein
the generating unit changes contents of the destination information according
to a
change request of the destination infoimation.
(39)
The transmitting device according to any one of (31) to (38), wherein
the IP transmission method confoinis to ATSC 3.0,
the destination information is a URL of the viewing history server, and
the viewing history information is a CDM defined by the ATSC.
(40)
A data processing method of a transmitting device, the method including the
steps of:
generating, by the transmitting device, destination information indicating a
destination
of a viewing history server that collects viewing history information related
to a
viewing history of content, the destination information being transmitted with
a
broadcasting wave of digital broadcasting using an IP transmission method; and
transmitting, by the transmitting device, the generated destination
information with the
broadcasting wave together with the content.
Reference Signs List
[0340] 1 Transmission system
Transmitting device
Receiving device
Viewing history server
Transmitting facility
Distributing device
Communication line
111 Control unit
112 Video data acquiring unit
113 Video processing unit
114 Audio data acquiring unit
115 Audio processing unit
116 Caption data acquiring unit
117 Caption processing unit
53
CA 02980882 2017-09-25
WO 2016/208137
PCT/JP2016/002770
118 Signaling generating unit
119 Signaling processing unit
120 Multiplexer
121 Transmitting unit
122 Communication unit
151 Viewing history server URL generating unit
211 Control unit
212 Recording unit
213 Input unit
214 Receiving unit
215 Demultiplexer
216 Video processing unit
217 Video output unit
218 Audio processing unit
219 Audio output unit
220 Caption processing unit
221 Display unit
222 Speaker
223 Communication unit
251 Broadcasting control unit
252 Communication control unit
253 Viewing history information managing unit
254 Viewing history server URL acquiring unit
311 Control unit
312 Communication unit
313 Viewing history information accumulating unit
351 Viewing history information managing unit
352 Viewing history information analyzing unit
900 Computer
901 CPU