Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03013422 2018-08-01
WO 2018/134657 PCT/IB2017/057607
1
Description
Title of Invention : COMPOSITE CONICAL SLEEVE
Technical Field
[1] The present invention relates to devices for repairing pipelines, in
particular, for
repairing defective areas and welded joint defects of pipelines without
stopping
pipage (of water, oil, natural gas and other liquids and gases), as well as
for
reinforcing welded joints at the stage of pipeline construction.
Background Art
[2] Different devices are used for repairing pipelines including those having
a side
wall consisting of two parts connected to each other and mounted around the
pipeline defective area with a gap between the inner surface of the side wall
and
the outer surface of a pipe, which is filled with an uncured composite
material (RU
113811 Ul, 02.27.2012, RU 129593 Ul, 06.27.2013, RU 2191317 C2, 10.20.2002,
RU 2378560 Cl, 01.10.2010, SK 1995 A3, 11.06.1996, GB 2210134 A,
06.01.1989). This method of repairing is referred to as "Composite sleeve
technology", CST for short.
[3] CST has a variety of disadvantages, the main of which are:
[4] 1) a risk of non-uniform filling the space between a pipe and the side
wall with
the composite material, which does not provide guaranteed quality of repair,
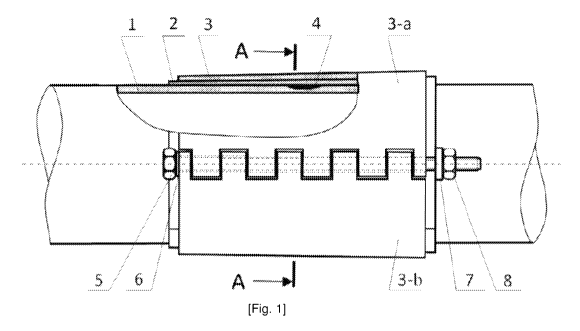
due to
the air bubbles which can be formed during injection of a liquid composite
material, particularly over the defect, which subsequently can cause pressing
out
metal into the cavity appeared and unsealing the pipeline;
[5] 2) the complexity of conducting arc welding of the outer metal side wall
halves
under the water, which constrains application of the given method for
repairing
underwater pipelines;
CA 03013422 2018-08-01
WO 2018/134657 PCT/IB2017/057607
2
[6] 3) the necessity for providing active protection of the metal side wall
against soil
con-osion;
[7] 4) while having relatively low cost of materials and components of the
repair
structure, the high cost of organizational and technical measures for its
installation,
making repair in whole expansive.
[8] A polymeric sleeve for repairing pipes with localized corrosion defects,
lacking
those disadvantages, consists of several layers of glass tape connected to
each
other by means of an adhesive layer and covers the pipeline circumferentially,
wherein the sleeve is made of two separate preformed halves provided with
hinged
units engaged into each other at the ends and concatenated by means of the
coupling shafts oriented in parallel in relation to the pipeline axis (RU
2219423 C2,
12.20.2003). However, this repair structure has the other drastic
disadvantages.
Thus, due to the absence of the metal side wall this sleeve does not allow for
bringing area being repaired to a defect free extent, since pretension, which
is
provided initially by heating the fiberglass sleeve and then by shrinkage
thereof
due to cooling down, is insufficient for fiberglass strength development to
stop
progression of the defect under the sleeve up to through hole. The reason for
this is
that the modulus of elasticity of fiberglass is at least seven times lower
than the
modulus of elasticity of steel. Furthermore, heating of a bulk fiberglass
structure
up to a temperature of about 160 C is rather difficult in the field
environment.
[9] According to RU2224169 C2, 02.20.2004, a sleeve for repairing a pipeline
is
known, wherein the sleeve comprises a tape, made of the preformed composite
material in the form of two halfsleeves having a wavelike profile
circumferentially,
and an elastic pad facing the tape, and a smooth profile facing the pipeline.
[10] The main disadvantage of such sleeve is utilising teclmical rubber having
service life 200 000 hours, that is about 23 years, as elastic pad. Acting
Russian
norms and specifications for construction, exploitation and repair of main
pipelines
require that service life of materials used for these purposes is not less
than 30
CA 03013422 2018-08-01
WO 2018/134657 PCT/1132017/057607
3
years. Therefore, the structure according to RU2224169 C2, 02.20.2004, can not
be considered as means for continuous repair of main pipelines.
[11] According to US 2014048164 Al, 02.20.2014, a method for repairing
pipelines
is provided, wherein one or more compression straps are installed around the
outer
circumferential surface of a pipe in the repair zone, corrosion-resistant
coating is
applied over the installed compression straps and the surface of the pipe in
the
repair zone, and a composite outer cover is wound around the corrosion-
resistant
(ground) coating applied in the repair zone.
[12] This method for repairing does not provide a uniform pretension of the
whole
repair structure and tight squeezing of the pipeline defect area, therefore
providing
a uniform transfer of the radial load from the defect area to the outer sleeve
cover
can not be guaranteed, which is a drastic disadvantage of this repair
structure.
[13] The prototype for the provided invention is a sleeve (RU 148064 Ul,
07.14.2014), which comprises a sleeve mounted on a pipeline consisting of two
halfsleeves, made of a cured composite material, and having a cylindrical
inner
surface corresponding to the pipeline diameter, and a conical outer surface,
on the
top of which a metallic side wall is mounted, the metallic side wall having a
tapered shape, con-esponding to the outer surface of the composite sleeve, and
consisting of two halves preliminarily connected by means of arc welding. The
composite sleeve resists compression and provides full load transfer from the
defect area to the metallic side wall.
[14] While the solution disclosed in the prototype for the provided invention
lacks
two of the most important CST disadvantages (1 and 4) described above, but it
still
has two disadvantages peculiar for CST, which are:
[15] the complexity of conducting arc welding of the outer metal side wall
halves
under the water, which constrains application of the given method for
repairing
underwater pipelines;
[16] the necessity for providing active protection of the metal side wall
against soil
corrosion.
CA 03013422 2018-08-01
WO 2018/134657 PCT/IB2017/057607
4
[17] The provided invention is intended to eliminate the disadvantages,
described
above.
Summary of Invention
[18] The technical result archived by the provided invention consists in
improving
performance reliability of the pipeline being repaired by means of a device
for
repairing pipelines, comprising a sleeve adhered to the pipeline, said sleeve
being
made of a cured composite material in the form of a truncated cone with a
cylindrical passage passing along the axis, the diameter of the passage being
equal
to the outer diameter of the pipeline being repaired, and a side wall, the
inner
surface of the side wall corresponding to the outer surface of the sleeve,
wherein
the side wall is made of a cured composite material.
[19] The composite material, of which the sleeve and the side wall are made,
is
selected from a group of: fiberglass, carbon fiber reinforced plastic, basalt
plastics.
[20] The sleeve is made of a composite material having compression strength
equal
to at least 70 MPa, which corresponds to JSC "Transneft" requirements for
composite materials in the cured condition, used for repairing main oil
pipelines in
accordance with the composite sleeve technology.
[21] The side wall is made of the composite material having a modulus of
elasticity
equal to at least 130 GPa, which is at most similar to the value of a modulus
of
elasticity of pipe steels.
[22] The length of the side wall is less than the length of the sleeve by the
value
selected depending on the diameter of the pipeline being repaired in the range
of
50-200 mm.
[23] In the operating state ends of the sleeve are project with regard to ends
of the
side wall.
[24] The sleeve and the side wall consist of at least two parts being
connected to
each other during mounting on the pipeline.
CA 03013422 2018-08-01
WO 2018/134657 PCT/1B2017/057607
[25] The parts of the side wall comprise hinges on the edges thereof by means
of
which they are connected to each other, the hinges alternating with grooves
for the
respective hinges, wherein the hinges are provided with inner bushings, the
parts
of the side wall are configured to connect to each other by means of coupling
shafts fed through the said inner bushings, when the parts of the side wall
coincide
such that the hinges enter into the respective grooves, wherein the coupling
shafts
have a smooth cylindrical part, equal to the length of the side wall, having a
diameter which does not exceed the inner diameter of the bushings, and a
threaded
part which, in the operating state, protrudes outside of the side wall not
less than
by 50-100 mm, the coupling shafts are provided with a stop member at one end
and with a screw nut at the other one, screwed with a calibrated force on the
threaded part of the shaft through a washer abutted against the abutting end
of the
sleeve.
[26] The stop member can be implemented as a bolt head with a washer.
[27] Depending on the material, type, operating conditions and service life of
the
pipeline being repaired inner bushings, coupling shafts, washers and screw
nuts are
made of metal or composite material selected from a group of: fiberglass,
carbon
fiber reinforced plastic, basalt plastics.
[28] The inner bushings, the coupling shafts, the washers and the screw nuts,
made
of metal or a composite material, are used in combination in one repair
structure.
Brief Description of Drawings
[29] The invention is described with reference to drawings.
Fig.1
[30] [Fig.1] shows a front view with a cut-out in the region of a defect of
the device
according to the present invention mounted at the area of the pipeline with
the
defect;
Fig.2
CA 03013422 2018-08-01
WO 2018/134657 PCT/1132017/057607
6
[31] [Fig.2] shows a side view in section of the device according to the
present
invention without one of the coupling shafts.
Description of Embodiments
[32] A device for repairing pipelines comprises a sleeve 2, mounted on a
pipeline 1,
with a cylindrical inner surface corresponding to the diameter of the
pipeline, and a
side wall 3 configured to be mounted with its inner surface on the respective
outer
surface of the sleeve. The sleeve is made of a cured composite material which
resists compression and provides a transfer of a radial load from the defect
area to
the side wall, which is made of a composite material having a modulus of
elasticity
with a value similar to that of the steel, i.e. having a bad stretchability.
During the
manufacturing process cavities 11 in the side wall are filled with a material
of
which the sleeve is made (for example, fiberglass).
[33] The outer surface of the sleeve 2 and the inner surface of the side wall
3 are
formed in the form of a cone. The outer surface of the side wall can be of any
shape, in particular, conical. The sleeve 2 (see Fig. 1) consists of at least
two
component parts being connected to each other during mounting on the pipeline
1
with a defect 4. In the embodiment shown, the sleeve consists of two component
parts 2-a and 2-b (see Fig. 2). When repairing pipelines of big diameter to
optimize
mounting work, the parts of the repair structure are lightened. To this end
the
sleeve and the side wall can consist of three and more parts.
[34] The side wall 3 is made of at least two component parts. In the
embodiment
shown, the side wall consists of two parts 3-a and 3-b connected to each other
by
means of shafts 5 with stop members, for example, in the form of a bolt head,
arranged at one end of the shafts. The shafts 5 pass through the hinges 9,
inside of
which the bushings 10 are arranged. The bushings are intended to eliminate
gaps
between the inner surface of the hinges and the shafts, which can result in
generation of bending stresses within the hinges and formation of cracks
therein.
The stop member is separated from the side wall by a washer 6. The washer 7
and
a screw nut 8, put on the other end of the shaft 5, together with the shaft 5,
except
CA 03013422 2018-08-01
WO 2018/134657 PCT/IB2017/057607
7
for the fixing function, act as an arrangement 12 for tightening the side wall
on the
sleeve and a calibrated squeezing of the repair structure around the defect
area of
the pipeline. To this end the washer 7 is provided with a reinforced, for
example,
square shape having rounded corners.
[35] The shafts 5, the washers 6 and 7, as well as the screw nuts 8 and the
bushings
can be made of metal and/or composite and polymeric materials, particularly
depending on conditions and remaining time of the pipeline areas being
repaired.
[36] The sleeve 2 has a length longer then a length of the side wall 3 for
placing, at
the edges of the sleeve, provisional means, for example, compression straps
with
ratchets and/or strip clamps for pressing and fixing the sleeve during
adhesive
attaching to the pipeline. With tightening the side wall on the sleeve,
compression
straps with ratchets and/or strip clamps are removed alternately.
[37] When using the device according to the present invention, repairing the
pipeline with the defect is implemented as follows.
[38] At the area of the pipeline 1, having the defect 4, the isolation coating
is
removed to an extent, which exceeds the length of the sleeve 2. The surface of
the
pipeline 1 is cleared of residuals of isolation and corrosion. The cavity of
the
defect 4 is filled with a leveling material, such as Etal plasticine. An
adhesive
compound, such as Etal 45, is applied on the cleared surface of the pipeline 1
and
the sleeve 2 is mounted. The component parts of the sleeve 2 are adhesively
attached by side edges during mounting on the pipeline 1. Two parts 2-a and 2-
b of
the sleeve are pulled together by any arrangement, such as a compression strap
with a ratchet, are fixed at the ends by strip clamps, such as scotch, and
then the
straps are removed. The component parts 3-a and 3-b of the side wall are
connected by means of shafts 5 through the washers 6 and 7 to form a solid
side
wall 3, and the screw nuts 8 are screwed on the ends of the shafts 5. Upon
that an
adhesive compound is applied on the outer surface of the sleeve 2, and the
side
wall 3 is shifted along the axis of the pipeline 1 on the sleeve 2, such that
the
washers 7 move beyond the edge of the sleeve 2, and then further tightening
the
CA 03013422 2018-08-01
WO 2018/134657 PCT/1B2017/057607
8
side wall 3 on the sleeve 2 is carried out by means of screwing the screw nuts
8 up
to the complete coinciding of the inner surface of the side wall 3 with the
outer
surface of the sleeve 2 and reaching the value of the tightening rated force
of the
fixing screw nuts, indicated by a manufacturing company in a specification,
formulated for the repair structure being mounted, which depends on a material
of
the side wall 3 and a type and operating conditions of the pipeline 1 being
repaired.
The calibrated force for tightening is reached by means of a dynamometric
wrench
of predefined length. Pulling together component parts of the side wall 3 with
a
calibrated force is performed for pretension of the assembled repair structure
and
rated squeezing of the repair area with it in order to provide tight seal and
effective
transfer of the radial load from the weakened defect area through the sleeve 2
on
the composite side wall 3, which is non inferior to the strength
characteristics of a
defect-free steel pipe, during the whole service life of the pipeline.
[39] Thus, the side wall 3 is fixed on the sleeve 2 by means of the shafts 5
fed
through the hinges 9, provided with embedded bushings 10, on the side edges of
the component parts of the side wall using stop members 5, washers 6, 7 and
crew
nuts 8.
[40] Then repaired area is isolated, for example, by means of a heat
shrinkable tape
overlapping over the old isolation.
[41] Corrosion resistance, high strength characteristics, sealing and
dielectric
properties of the materials used in this device, the conical outer surface of
the
sleeve and the inner surface side wall together with the adhesive compound
ensure
the elimination of gaps between the sleeve and the side wall, and between the
pipeline and the sleeve, which increases the performance reliability of the
pipeline
being repair and bringing it to the level of defect free.
[42] The device for repairing pipelines according to the invention does not
require
any further arrangements for tightening the side wall on the composite sleeve
and
protection of the side wall against its crawling from the sleeve while in
operation.
These functions are performed by the coupling shafts having threading on their
CA 03013422 2018-08-01
WO 2018/134657 PCT/1B2017/057607
9
ends, with corresponding washers and screw nuts. With tightening with a
calibrated force on the outer surface of the cone composite sleeve pre-greased
with
the adhesive compound, the side wall, assembled of two or more parts, assumes
its
structural position and transfer resulting radial force to the cone sleeve,
which, in
turn, being adhesively attached to the defect area of the pipeline, transfers
said
force to it, thereby pre-tensioning the repair structure and squeezing the
pipeline
with the force determined by the calculation that together with corrosion
resistance,
high strength characteristics, sealing and dielectric properties of the
materials used
in this device, leads repaired area to the state of a defect free pipe for the
entire
remaining service life of the pipeline.
[43] The invention allows for repairing pipelines either on the ground and
underwater. The application of the sleeve according to the invention optimizes
time and costs of the repair operations, because welding, as well as lifting
and
other mechanisms are not required, since both the sleeve and the side wall
consist
of two or more parts, and are made in workshop conditions of the cured
composite
materials, which are by many times lighter than the similar parts made of
steel.
Furthermore, the provided device does not require usage of an active
protection
against soil corrosion, such as electric connection with the pipeline,
cathodic
protection station, or protector, which is necessary when using the outer
metallic
side wall, as in the prototype, or during the composite sleeve repair.
[44] A service life of the composites, used when manufacturing the provided
composite cone sleeve, indicated by manufacturing companies is not less than
30
years.