Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
DRAINAGE FOIL FOR USE IN AN INSTALLATION FOR PRODUCING A
PAPER WEB WITH A FABRIC BELT, WHICH CAN BE MOVED OVER A
MULTIPLICITY OF DRAINAGE FOILS ORIENTED TRANSVERSELY
TO ITS DIRECTION OF MOVEMENT
The actual invention relates to a drainage foil for use in an installation for
producing a paper web with a fabric belt, which can be moved over a
multiplicity of
drainage foils oriented transversely to its direction of movement.
The actual invention further relates to a kit and an installation for
producing a
paper web.
Known installations for producing a paper web have a closed loop fabric belt
which
is kept circulating by means of transport rolls and onto which, at the start
of the
installation, a fibrous stock is sprayed. In a first region of the
installation, the
fabric belt is moved over drainage foils and over suction boxes formed with
drainage foils, by which liquid that has emerged from the fibrous stock is
stripped
off and sucked away. In further regions of the installation, the paper web
produced on the fabric belt is dried by means of felt belts.
The drainage foils found in such an installation, which are oriented
transversely to
the direction of movement of the fabric belt, are foils produced from metal or
from
plastic which, on their upper side which faces the fabric belt in the
operating
position, can be provided with an overlay of a wear-resistant material, in
particular
of plane-ground ceramic plates. The ceramic plates consist in particular of Al
oxide, of Zr oxide, of Si nitride and of Si carbide. The fabric belt is moved
over the
drainage foils at a speed of 1 m/s to 40 m/s. By means of the drainage foils,
firstly the fabric belt is supported. Secondly, the drainage foils serve to
strip off
from the fabric belt liquid that has escaped from the fibrous stock and is
found on
the underside of the fabric belt. By means of an oblique position of a first
group of
drainage foils with respect to the fabric belt, wedge-shaped interspaces can
be in
this case formed between the surfaces of the drainage foils and the fabric
belt,
which interspaces enlarge in the direction of movement of the fabric belt,
which
means that, because of the movement of the fabric belt, a suction action is
exerted
on the fibrous stock found on the latter, by means of which liquid found in
the
CA 3015246 2018-08-24
2
fibrous stock is sucked away. Underneath a second group of drainage foils
there
are suction boxes, by means of which a suction action is likewise exerted on
the
fibrous stock found on the fabric belt. The liquid that has escaped from the
fibrous
stock as a result is led away through the suction boxes.
During the movement of the fabric belt over the drainage foils, the fabric
belt rests
on the surfaces of the drainage foils or on the ceramic plates found on the
latter,
as a result of which high frictional resistances are caused, which have to be
overcome by the transport rolls. In addition, as a result the surfaces of the
drainage foils and the fabric belt are subjected to high wear, for which
reason the
drainage foils and the fabric belt have only short service lives.
The actual invention is based on the object of devising a drainage foil by
means of
which, during operation of such a fabric belt installation, the frictional
resistances
occurring between the fabric belt and the individual drainage foils are
reduced.
According to the invention, this object is achieved in that the surface of the
drainage foils is formed with a defined profiling, which has elevations and/or
depressions, wherein the vertical extent of the profiling is at least 0.1 mm.
Within
the scope of the invention, the elevations and the depressions can be
implemented
and/or distributed randomly or in a non-concretely defined manner. However, in
the invention it is preferred if the elevations and the depressions have a
defined
profiling and/or are distributed in a defined manner on the surface, since
more
specific influencing of the friction is therefore possible. Preferably but not
necessarily, the drainage foil is formed on its surface assigned to the fabric
belt in
the operating position with a multiplicity of ceramic plates located beside
one
another which, on their surface, are formed with defined profiling in the form
of
elevations and/or of depressions, wherein the vertical extent of the profiling
is at
least 0.1 mm.
According to a preferred embodiment of the invention, the vertical extent is
up to
3 mm, preferably up to 2.5 mm or up to 1.6 mm, in particular 0.2 mm up to
0.8 mm.
The surface of the drainage foil can be formed with profiling oriented in the
longitudinal extent of the drainage foil or enclosing an acute angle with the
latter.
CA 3015246 2018-08-24
3
The profiling preferably has the shape of ribs that are triangular in cross
section,
rectangular foils or wave-like foils, other profilings also being possible in
the
context of the invention, however. Furthermore, the profilings of ceramic
plates
located beside one another can be offset with respect to one another both in
and
also transversely to the longitudinal direction of the drainage foil and/or
different.
In addition, the longitudinal extent of the elevations and/or the depressions
can
enclose an angle of 0 to 80 with the longitudinal direction of the drainage
foil.
Furthermore, the profiling can be formed by depressions located at a distance
from
one another, in particular by cut-outs that are concave in cross section or
cylindrical holes.
According to the invention, the surface of the drainage foils can also have a
convex
curvature in the section transverse to the longitudinal extent of the drainage
foil,
wherein, in the invention, it is preferred for the curvature to have a radius
of
100 mm to 500 mm, preferably of 200 mm to 350 mm.
Finally, it is preferred in the invention if the side edges of the surface of
the
drainage foil are rounded in cross section with a radius of 0.5 mm to 5 mm,
preferably of 1 mm to 3 mm.
In known drainage foils, the surfaces that face the fabric belt in the
operating
position, which, in particular, are coated with ceramic plates, are plane-
ground,
having surface roughness values Ra of 0.15 pm to 0.7 pm. Because of the plane
grinding of the surfaces of the ceramic plates and the low roughness values
achieved hereby, according to the known prior art the frictional resistances
occurring between the surfaces of the drainage foils, in particular the
surfaces of
the ceramic plates, and the fabric belt moved over the latter should be
minimized.
By contrast, the actual invention is based on the finding that, with a
substantially
intensified profiling of the surfaces with defined elevations and depressions,
bow
waves occur in the liquid which is located in the depressions as a result of
the
fabric belt moved over the drainage foils, by means of which waves the fabric
belt
in the regions of the elevations is raised above the latter, there being a
layer of
liquid between the fabric belt and the elevations, by means of which the
frictional
CA 3015246 2018-08-24
4
resistances occurring between the fabric belt and the elevations are reduced
significantly.
Further preferred embodiments of the invention are the subject matter of the
remaining subclaims.
Further features and advantages of the invention are gathered from the
following
description of preferred exemplary embodiments of the invention, not
restricting
the protective scope, with reference to the attached drawings, in which:
FIG.1 shows a section of an installation for producing a paper web with a
fabric
belt, which is moved over drainage foils and a suction box located
underneath, in a section located in the longitudinal direction of the
movement of the fabric belt,
FIG.1A shows the detail X from FIG.1, on a scale highly enlarged with respect
to
FIG.1,
FIG.2 shows a first embodiment of a drainage foil according to the
invention in
an axonometric illustration,
FIG.3 shows the drainage foil according to FIG.2 in a cross section, on a
scale
highly enlarged with respect to FIG. 2,
FIG.3A shows an illustration corresponding to FIG.1A to explain the mode of
action of the drainage foil according to FIG.3, on a scale highly enlarged
with respect to FIG.3,
FIG.4, FIG.4A and FIG.4B show three further embodiments of a drainage foil
according to the invention, each in cross sections,
FIG.5 and FIG.5A show a further embodiment of a drainage foil according to the
invention in plan view and in section according to the line V-V from
FIG.5,
FIG.6, FIG.6A and FIG.6C show two further embodiments of a drainage foil
according to the invention in plan view and in sections according to the
line VI-VI from FIG.6,
FIG.7 shows design variants of the drainage foil according to the
invention
according to FIG.2, in a cross section and on a scale enlarged with
respect to FIG.2,
CA 3015246 2018-08-24
5
FIG.8 shows a section of an installation for producing a paper web,
formed with
drainage foils according to the invention, with a fabric belt moved over
the drainage foils and with a further formation of the surfaces of the
drainage foils, in cross section, and
FIG.8A shows the detail Y from FIG.8, on a scale highly enlarged with respect
to
FIG.8.
FIG.1 illustrates a section of a fabric belt 1 in an installation for
producing a paper
web, on which a layer of a fibrous stock 2 is found and which is moved in the
direction of the arrow M over a group of drainage foils 3. The fibrous stock 2
is
sprayed onto the fabric belt 1 at the start of the latter. The drainage foils
3 are
each formed on their upper side with an overlay 4 made of a wear-resistant
material. Underneath the drainage foils 3 there is a suction box 5, in the
interior
51 of which there is a vacuum of about -2 mbar to -700 mbar. The drainage
foils 3
are located on a supporting frame 52, which is detachably fixed to the upper
side
of the suction box 5.
The fabric belt 1, which extends over a length of up to about 50 m and can
have a
width of 2 m up to 12 m, is moved over the drainage foils 3 at a speed of, for
example, 1 m/s to 40 m/s by means of transport rolls located in the
installation.
The drainage foils 3 are usually but not necessarily produced from acid-
resistant
stainless steel, from a plastic, e.g. from polyethylene, or from a glass fiber
reinforced plastic. The suction box 5 is generally likewise produced from acid-
resistant stainless steel. The overlays 4 found on the supporting bars 3 are
preferably plates made of a ceramic material, e.g. Al oxide (hardness HV 0.5
18,000 N/mm2), Zr oxide (hardness HV 0.5 12,700 N/mm2), Si nitride (hardness
HV 0.5 18,800 N/mm2), Si carbide (hardness HV 0.5 28,150 N/mm2).
As a result of the vacuum prevailing in the interior 51 of the suction box 5,
a
suction force is exerted on the fibrous stock 2, by means of which liquid 6
contained in the latter is extracted. The liquid 6 escaping from the fibrous
stock 2
passes through the fabric belt 1 and reaches the underside of the fabric belt
1,
CA 3015246 2018-08-24
6
from which, during the movement of the fabric belt 1 over the drainage foils
3, it is
stripped off the latter and reaches the suction box 5, through which it is led
away.
FIG.1A illustrates a drainage foil 3 having a wear-resistant overlay 4 and the
fabric
belt 1 moved over the latter, on which the fibrous stock 2 is found. As can be
seen
herefrom, the fabric belt 1, which consists of a fabric, e.g. of polyamide or
of
polyester, has warp threads la oriented in the longitudinal direction of the
fabric
belt 1 and weft threads lb oriented in the transverse direction of the fabric
belt 1.
During the movement of the fabric belt 1 over the drainage foils 3 in the
direction
of the arrow M, during which the fabric belt 1 rests on the surface of the
overlays 4
of the drainage foils 3, high frictional resistances occur, which have to be
overcome
by the transport rolls found in the fabric belt installation in order to move
the
fabric belt 1. In addition, in this case, high wear of the fabric belt 1 and
of the
drainage foils 3 and of the overlays 4 is caused, which means that the fabric
belt 1
and the drainage foils 3 have only short service lives. During the movement of
the
fabric belt 1 over the drainage foils 3, bow waves 61 are formed in the liquid
6 that
has escaped from the fabric belt 1, in front of the weft threads lb resting on
the
drainage foils 3.
According to the prior art, the drainage foils 3 can be formed on their upper
side,
facing the fabric belt 1 in the operating position, with a multiplicity of
ceramic
plates, which have lengths of, for example, 12 mm to 230 mm in the direction
of
the drainage foils and widths of, for example, 12 mm to 100 mm transverse to
the
drainage foils, and also heights of, for example, 2 mm to 10 mm. The
hardnesses
of said ceramic plates are preferably HVO,5 12,700 Nimm2 to HVO,5 28,150
N/ mm2. In order to keep the frictional resistances which occur during the
movement of a fabric belt 2 over the drainage foils 3 as low as possible, the
surfaces of the drainage foils 3, in particular the ceramic plates 4, are
plane-
ground according to the prior art, having surface roughness values Ra of 0.15
pm
to 0.7 pm.
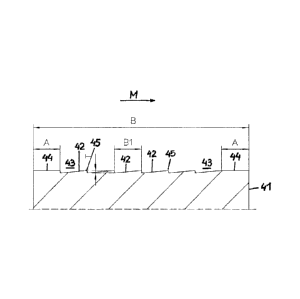
FIG. 2 shows a drainage foil 3 according to the invention. This drainage foil
3
differs from a drainage foil according to the prior art in the fact that the
ceramic
CA 3015246 2018-08-24
7
plates 41 found on its upper side are formed with elevations and/or
depressions
on their upper side facing the fabric belt 1 in an installation for producing
a paper
web, wherein the height difference of the elevations with respect to the
depressions
is 0.1 mm to 1.6 mm. Said elevations and depressions in embodiments of the
invention that are particularly preferred and described below in various
variants
have a profiling with a defined cross-sectional shape and distribution over
the
surface of the ceramic plates 4. The dimensions and the material of the
ceramic
plates 41 are preferably those according to the above-described known prior
art.
FIG.3 illustrates a first embodiment of a ceramic plate 41 found on a drainage
foil
3 according to the invention, which is formed with a profiling on its surface.
This
ceramic plate 41, which in the direction of movement M of the fabric belt 1
has a
width B of, for example, 8 mm to 70 mm, preferably of 12 mm to 25 mm, and a
height of, for example, 2 mm to 10 mm, is provided on its surface with ribs 42
extending in the longitudinal direction of the drainage foil 3, triangular or
saw-
tooth-like in cross section and having upper edges 45, wherein depressions 43
are
found in the regions of the flanks located between the edges 45. The width B1
of a
rib 42 is, for example, 1 mm to 16 mm, preferably 2 mm to 6 mm, and the height
difference T between the edges 45 of the ribs 42 and the bottom of the
depressions
43 is at least 0.1 mm, preferably up to 1.6 mm, particularly preferably 0.2 mm
to
0.8 mm. The lateral regions 44 of said ceramic plate 41, which have a width A
of,
for example, 1 mm to 8 mm, preferably of 2 mm to 6 mm, are likewise formed
flatly. Thus, the surface of said ceramic plate 41 is formed with a defined
profiling
according to the invention, consisting of elevations and depressions, wherein
the
ribs 42 that are saw-tooth-like in cross section form the elevations with the
edges
45, and the regions of the flanks of the saw-tooth-like ribs 42 located
between the
edges 45 form the depressions 43.
The described formation of the surface of the drainage foils 3, in particular
of the
surfaces of the ceramic plates 41, particularly preferably but not necessarily
with a
defined profiled surface, is based on the finding that, as a result of the
relatively
large elevations and depressions formed according to the invention, the
frictional
resistances occurring during the movement of the fabric belt 1 over the
drainage
foils are reduced down to about 50%, which means firstly that a significant
CA 3015246 2018-08-24
8
reduction in the drive power for the fabric belt 1 can be achieved and
secondly the
service lives of the fabric belt 1 and of the drainage foils 3 are
substantially
prolonged.
As can be seen from FIG. 3A, which corresponds to the illustration of FIG. 1A,
this
action is achieved in that firstly the fabric belt 1 in the regions of the
depressions
43 does not rest on the surface of the drainage foil 3 or the surfaces of the
ceramic
plates 41, which means that no frictional resistances occur in these regions,
and
that, secondly, because of the movement of the fabric belt 1, bow waves 61
occur
in the liquid 6 found in the depressions 43, by means of which the fabric belt
1 in
the regions of the elevations 42, in particular the edges 45, is lifted over
the latter,
and by means of which liquid gets between the elevations and the fabric belt
1, by
means of which the frictional resistances between the elevations and the
fabric belt
1 are reduced highly.
FIG. 4 illustrates a further embodiment of a ceramic plate 41a profiled in a
defined
manner according to the invention and having a width B, in which, between the
lateral regions 44a which form the elevations and which have a width A of, for
example, 1 mm to 8 mm, preferably of 2 mm to 6 mm, there is a depression 43a,
the depth of which with respect to the lateral regions 44a is at least 0.1 mm
to
preferably 2.5 mm, particularly preferably 0.2 mm to 0.8 mm.
In the further embodiment, illustrated in FIG. 4A, of a ceramic plate 4 lb
according
to the invention having a width B, elevations in the form of ribs 42b of
rectangular
cross section and depressions in the form of rectangular grooves 43b, which
have
widths B2 and B3 of, for example, 1 mm to 10 mm, preferably 2 mm to 8 mm, are
located between the lateral regions 44b having a width A, wherein the height
difference T2 between the elevations formed by the ribs 42b and the
depressions
formed by the grooves 43b is at least 0.1 mm to preferably 3.0 mm,
particularly
preferably 0.2 mm to 0.8 mm.
In the further embodiment, illustrated in FIG. 4B, of a ceramic plate 41c
according
to the invention having a width B, there is a wave-like profiling with ribs
42c and
depressions 43c that are concave in cross section located in between two
lateral
CA 3015246 2018-08-24
9
regions 44c having a width A, wherein the distance B4 between two depressions
43c is, for example, 1 mm to 20 mm, preferably 2 mm to 8 mm, and the height
difference T3 between the upper sides of the ribs 42c and the bottoms of the
depressions 43c is at least 0.1 mm to preferably 3.0 mm, particularly
preferably
0.2 mm to 0.8 mm.
The elevations 44a, 42b, 42c and depressions 43a, 43b, 43c of the embodiments
of
the invention illustrated in FIG.4 to FIG.4B are oriented in the longitudinal
direction of the drainage foil 3 and preferably extend over the entire length
of the
ceramic plates 41a, 41b, 41c.
In the further embodiment of a ceramic plate 41d according to the invention,
illustrated in FIG.5 and FIG.5A, the defined profiling is formed by elevations
in the
form of rectangular ribs 42d and depressions located in between in the form of
rectangular grooves 43d, which have widths B5 and B6 of, for example, 1 mm to
mm, preferably of about 2 mm to 8 mm, and a height difference T4 of at least
0.1 mm to preferably 3.0 mm, particularly preferably of 0.2 mm to 0.8 mm. The
longitudinal extent of the ribs 42d and the depressions 43d found in between
encloses an angle W1 of 00 to 80 , preferably of 30 to 55 , with the
longitudinal
extent of the drainage foil 3.
In the further embodiments of two ceramic plates 41e, 41f, according to the
invention, illustrated in FIG.6, FIG.6A and FIG.6B, said plates are formed
with
profilings in the form of concave cut-outs 43e and cylindrical cut-outs 43f
located
close beside one another on a substantially flat surface, possibly somewhat
curved
as described below, which are spaced apart from one another. The distances B7
between the centers of two cut-outs 43e and 43f located beside one another
are,
in this case for example, 1 mm to 20 mm, preferably 2 mm to 12 mm, and the
depths T5 of the cut-outs are at least 0.1 mm to preferably 3.0 mm,
particularly
preferably 0.2 mm to 0.8 mm.
The cut-outs can also have another shape, both in plan view and also in cross
section, in particular an elongate or elliptical shape.
CA 3015246 2018-08-24
10
The ceramic plate 41g according to the invention illustrated in FIG. 7
corresponds
to the embodiment according to FIG. 3, having ribs 42g that are saw-tooth-like
in
cross section and having edges 45g which form the elevations, and depressions
43g in the regions of the flanks of the saw-tooth-like ribs 42g, wherein the
lateral
regions 44g having a width F of, for example, 1 mm to 20 mm, preferably of 2
mm
to 8 mm, are formed so as to fall obliquely toward the outside with an angle
of, for
example, 2 to 100, preferably of 3 to 6 , and, in addition, the outer edges
are
rounded with a radius R of, for example, 0.5 mm to 5 mm, preferably of 1 mm to
3
mm.
A further embodiment of a drainage foil according to the invention is
explained
below:
According to the known prior art, the surfaces of drainage foils are formed
flat and
the surfaces of drainage foils found on suction boxes are located in a common
plane. However, as a result of the fact that a suction action is exerted by
the
suction boxes on the fabric belt in the interspaces found between the drainage
foils, the fabric belt is drawn into the interspaces found between the
drainage foils.
In this way, the two lateral regions of the surfaces of the drainage foils, in
particular of the overlays of a wear-resistant material found on the latter,
for
example ceramic plates, are loaded more highly than is the case for the
central
regions of the surfaces of the drainage foils, located in between.
In order to achieve a uniform pressure distribution over the width of the
drainage
foils 3a, as can be seen from FIG. 8 and FIG. 8a, the surfaces of the ceramic
plates
4a found on the drainage foils 3a have a curvature or are formed convexly in
cross
section, which means that the fabric belt 1 overall assumes a wave-like
course.
The drainage foils 3a are located on a supporting frame 52a, which is
detachably
fixed to the suction box 5.
As can also be seen from FIG. 8A, the radius R1 of the curved surfaces of
convex
cross section of the ceramic plates 4a located on the drainage foils 3a is,
for
example, 100 mm to 500 mm, preferably 200 mm to 350 mm. In addition, the side
edges of the drainage foils 3a are rounded, the radius R2 of the rounding of
the
side edges being, for example, 0.5 mm to 5 mm, preferably 1 mm to 3 mm.
CA 3015246 2018-08-24
11
By means of such a formation of the surfaces of the drainage foils 3a, in
particular
of ceramic plates 4a found on the latter, a uniform distribution of the
pressure
exerted by the fabric belt 1 over the width of the drainage foils 3a is
effected, which
likewise means firstly that the frictional resistances and secondly the wear
of the
fabric belt 1 and of the drainage foils 3a are reduced.
This further formation of the drainage foils 3a is in particular combined with
the
profiling of the surface of the drainage foils, which can be provided with a
wear-
resistant overlay 4a, e.g. with ceramic plates, as is explained above by using
FIG.2
to FIG.7.
The formation of drainage foils according to the invention is in particular
advantageous in those drainage foils which are located on a suction box.
The drainage foils can be provided with overlays of ceramic plates. However,
the
drainage foils can also be produced overall from polyethylene, not being
coated
with ceramic plates. In addition, the surfaces, in this case, are formed with
a
profiling in the form of elevations and/or depressions with a vertical extent
of at
least 0.1 mm to preferably 3.0 mm.
As soon as the elevations have been ground off by the use of the drainage
foils, the
surfaces are re-machined to the effect that the height differences between the
elevations and depressions required for the specified action are reproduced.
All the embodiments described in conjunction with overlays of a wear-resistant
material, in particular ceramic, can also be used within the context of the
invention in drainage foils which have overlays of another material, in
particular
materials not having such good wear properties, and likewise in drainage foils
which have no overlays, in which the elevations and depressions are applied to
or
formed directly on the drainage foils.
All the embodiments illustrated and described can be combined wholly or partly
with one another and with embodiments which have not actually been illustrated
and described.
CA 3015246 2018-08-24