Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
ADJUSTABLE ADDITIVE DELIVERY SYSTEMS AND METHODS
PRIORITY CLAIM AND REFERENCE TO RELATED
APPLICATIONS
Priority is claimed under all applicable laws, treaties, conventions and
regulations, based on United States Provisional Application No. 62/303,376,
titled
CARTRIDGE RESERVOIR SYSTEMS, filed on March 4, 2016; United States
Provisional Application No. 62/363,177, titled ADJUSTABLE ADDITIVE
CARTRIDGE SYSTEMS, filed on July 15, 2016; and pending US Application No.
15/358,087, titled ADJUSTABLE ADDITIVE CARTRIDGE SYSTEMS, filed
November 21, 2016. The subject matter described in all applications is
incorporated
herein by reference in its entirety. Where an element or subject matter of
this
application or a part of the description, claims or drawings in the
aforementioned
applications are not otherwise contained in this application, that element,
subject
matter or part is incorporated by reference in this application for the
purposes of any
and all applicable rules, procedures or laws.
BACKGROUND
1. Technical Field
[0001] The disclosure relates to dispensing and delivery systems for beverages
and
other products. The disclosure further relates to dispensing and delivery
systems in
which an additive, such as flavorings, concentrates or supplements, may be
provided
in replaceable cartridges and mixed with a base fluid, such as water, as the
base fluid
is dispensed and/or consumed from a container and wherein one-way flow of base
fluid is provided to prevent additive from mixing with the base fluid supply,
which
may thus be used with different additive delivery systems. The disclosure
further
relates to dispensing and delivery systems and additive delivery systems that
provide
for user adjustment of the amount of additive that is mixed with the base
fluid. The
disclosure further relates to reservoir assemblies for storage of additives
and for use in
such additive delivery systems, and to methods for making and using such
systems.
1
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
2. Prior Art
The prior art includes various devices for providing additives to a base
liquid. Such
devices include pre-mix systems, such as those described in U.S. Pat. No.
7,306,117,
in which a predetermined amount of additive is dispensed into a base liquid
within the
container and mixed therewith prior to consumption. Prior art systems also
include
devices in which an additive is provided to a base fluid as it is dispensed
from a
container. Such delivery systems are exemplified by U.S. Pat. No. 8,230,777,
which
describes a dispensing system in which a base liquid flows through a
supplement area
containing solid supplements, and U.S. Pat. No. 8,413,844, which describes a
water
dispenser (pitcher) having a filter and an additive chamber in which the
additive is
dispensed as water is poured from the dispenser. There is a need in the art
for
systems and methods that improve upon these prior art undertakings.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0002] According to one aspect of the disclosure, an additive delivery system
may
incorporate a cartridge system, including a container cap and an additive
reservoir
assembly that provides for storage of an additive. The container cap may be
secured to
a base fluid container. A mixing nozzle is cooperatively associated with the
container
cap for mixing of the additive with a base fluid as the base fluid flows from
the base
fluid container through the cartridge. A one-way valve prevents backflow of
base
fluid and/or mixed base fluid/additive from an area downstream of the mixing
nozzle
such that the base fluid supply remains in a pure state. These features permit
different
cartridge assemblies, containing different respective additives, to be used
with a given
supply of base fluid. Moreover, this feature permits a given additive to be
used with a
given supply of base fluid without requiring the entire supply of base fluid
to be used
or consumed in a mixed state. A leftover supply of base fluid may remain
unmixed
2
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
and used in other applications, such as with other flavorings or supplements.
The
additive delivery systems enable more efficient use of both additive and base
fluid.
[0003] According to another aspect of the invention, an additive delivery
system may
incorporate a cartridge system and provide for adjustable flow of additive and
adjustable mixing of additive with a base fluid as the base fluid flows
through the
additive delivery system. An adjustment actuator may be moved by a user to
cause a
corresponding adjustment in valve components incorporated into the additive
delivery
system. The valve components may include a metering component, which may have
a
conical portion that cooperates with a mixing nozzle having a correspondingly
shaped
seat to provide precise control of additive flow. Movement of the adjustment
actuator
by a user results in movement of the metering component in precise fashion to
increase or decrease the flow of additive that occurs when base fluid is
dispensed
through the cartridge. Indicia may be included to indicate relative degrees of
additive
flow and mixing to the user. This feature permits a user to achieve a desired
and
repeatable mixing proportion of additive to base fluid.
[0004] According to another aspect, an additive delivery system may utilize a
cartridge system that provides improved flow geometries that enhance mixing of
additive and base fluid as the additive and base fluid flow from the
cartridge. Such
flow geometries may include a central flow component for the additive and a
surrounding or radially displaced flow component for the base fluid. They may
also
include one or more convergence zone in the additive flow path. Such flow
geometries may also be used in conjunction with one or more agitating or
turbulence
creating elements incorporated into a dispensing spout downstream of a mixing
area
in the cartridge assembly to further enhance the mixing of the additive and
base fluid
3
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
prior to use or consumption. Such flow geometries and agitating or turbulence
creating elements provide for thorough mixing of additive and base fluid.
[0005] According to one aspect of the disclosure, a reservoir assembly for use
with an
additive delivery system and cartridge may include a flexible reservoir such
as a
pouch, bag, bladder or other flexible reservoir structure. This reservoir
assembly
structure provides improved flow and mixing characteristics by reducing or
eliminating vacuum in the reservoir as additive is dispensed. A protective
cage or
solid walled protective housing may enclose the reservoir to protect it during
sale/shipping. In the case of a protective cage or other external element with
apertures
or holes, such flexible reservoir structures may also permit external pressure
to be
applied to the additive reservoir, such as pressure created when a user
squeezes or
otherwise applies pressure to a container, i.e., water bottle, in which the
cartridge is
housed. This interaction between the flexible cartridge reservoir structure
and the
interior conditions may facilitate more uniform or consistent dispensing of
additive
from the cartridge and more uniform mixing with a base fluid.
[0006] According to another aspect, a cartridge assembly is packaged and
distributed
as a unit that includes a reservoir assembly and adjustable mixing cap, such
that the
cartridge assembly may be installed on a user's own bottle of base fluid, such
as a
water bottle purchased separately. A frangible protective outer safety
membrane,
such as a shrink wrap, or foil pouch, may seal the entire cartridge assembly
package
for quality and safety control.
[0007] Unless otherwise defined, all technical and scientific terms used
herein have
the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to
which
the described invention pertains. Although other implementations, methods and
materials similar to those described herein can be used to practice the
invention,
4
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
suitable and example implementations, methods and materials are described
below.
All publications, patent applications, and other references mentioned herein
are
incorporated by reference in their entirety. In case of conflict, the present
specification, including definitions, will control. In addition, the
materials, methods
and examples are illustrative only and are not intended to be limiting in any
way. The
details of one or more example implementations of the invention are set forth
in the
accompanying drawings and the description below. Other features, objects and
advantages of the invention will be apparent from the description and
drawings, and
from the claims.
DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0008] The above and other attendant advantages and features of the invention
will be
apparent from the following detailed description together with the
accompanying
drawings, in which like reference numerals represent like elements throughout.
It will
be understood that the description and embodiments are intended as
illustrative
examples and are not intended to be limiting to the scope of invention, which
is set
forth in the claims appended hereto.
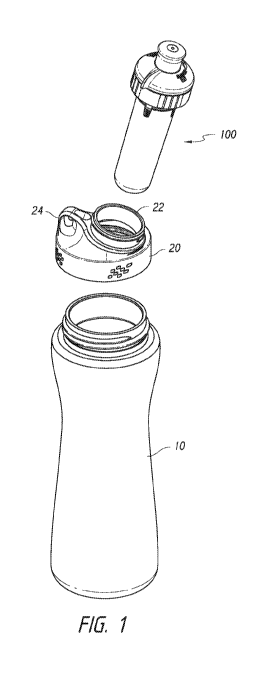
[0009]FIG. 1 is an exploded perspective view of an example dispensing and
delivery
system including an additive delivery system, both according to an aspect of
the
disclosure.
[0010]FIG. 2 is an exploded upper perspective view of an example cartridge
assembly
for an additive delivery system according to an aspect of the disclosure.
[0011]FIG. 3 is an exploded lower perspective view of the example cartridge
assembly of FIG. 2.
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
[0012] FIG. 4 is an exploded cutaway view of the example cartridge assembly of
FIG.
2.
[0013] FIG. 5 is perspective view of an example additive adjustment actuator
according to an aspect of the disclosure.
[0014] FIG. 6 is a top view of the example additive flow adjustment actuator
of FIG.
5.
[0015] FIG. 7 is a sectional view taken in plane A-A in FIG. 6.
[0016] FIG. 8 is a sectional view taken in plane B-B in FIG. 6.
[0017] FIG. 9 a bottom view of the example additive flow adjustment actuator
of FIG.
5.
[0018] FIG. 10 is a perspective view of an example additive flow metering
insert
according to an aspect of the disclosure.
[0019] FIG. 11 is a top view of the example additive flow metering insert of
FIG. 10.
[0020] FIG. 12 is a sectional view taken in plane A-A in FIG. 11.
[0021] FIG. 13 is a bottom view of the example additive flow metering insert
of FIG.
10.
[0022] FIG. 14 is a perspective view of an example mixing nozzle according to
an
aspect of the disclosure.
[0023] FIG. 15 is a top view of the mixing nozzle of FIG. 14.
[0024] FIG. 16 is a sectional view taken in plane A-A of FIG. 15.
[0025] FIG. 17 is a perspective view of an example cartridge cap base
according to an
aspect of the disclosure.
[0026] FIG. 18 is a top view of the example cartridge cap base of FIG. 17.
[0027] FIG. 19 is a sectional view in plane A-A of FIG. 18.
[0028] FIG. 20 is a bottom view of the example cartridge cap base of FIG. 17.
[0029] FIG. 21 is a perspective view of an example flexible pouch reservoir
and pouch
reservoir spout according to an aspect of the disclosure.
6
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
[0030] FIG. 22 is a top view of the flexible pouch reservoir and pouch
reservoir spout
of FIG. 21.
[0031] FIG. 23 is a side view of the flexible pouch reservoir and pouch
reservoir spout
of FIG. 21.
[0032] FIG. 24 is a sectional view of an example assembled additive delivery
system
cartridge assembly according to an aspect of the disclosure.
[0033] FIG. 25 is an example dilution/concentration variance curve that may be
achieved with example cartridge systems according to an aspect of the
disclosure.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0034] FIG. 1 is an exploded perspective view of an example beverage
dispensing
system utilizing an example additive delivery system according to an aspect of
the
disclosure. A bottle 10 may include a bottle lid 20 for sealing an interior
space of the
bottle 10. Threads, which are integrally molded on the bottle 10 cooperate
with
internal threads molded on bottle lid 20 to provide sealed fastening between
the two
components. A handle 24 may be molded into the lid 20 and an umbrella check
valve
or vent (not shown in FIG. 1) may be provided in the lid 20 in a known manner
to
reduce or eliminate vacuum in the bottle interior and prevent base fluid from
leaking
out of the vent when a base fluid is dispensed therefrom. Lid 20 includes a
cartridge
receiving mouth 22 having a threaded fastener formed on an exterior surface
thereof
for receiving an additive delivery system, such as the example additive
delivery
system, also referred to herein as a cartridge, generally referenced 100 in
FIG. 1.
[0035] Referring additionally to FIGS. 2-4, which are exploded views of an
example
cartridge assembly providing an additive delivery system according to an
aspect of the
disclosure, the system may include a number of components that are assembled
in a
7
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
generally stacked arrangement using snap-fit or threaded connections that
facilitate
quick assembly, as will be described in more detail below. The components may
include a cartridge cap comprising an additive flow adjustment actuator 200
cooperating with and mounted for limited rotational movement relative to a
cartridge
cap base 250. Additive flow adjustment actuator may include a dispensing spout
and
a push-pull closure 230 mounted thereon for selectively permitting and
preventing
egress of mixed fluid from the cartridge. Disposed between the additive flow
adjustment actuator 200 and cartridge cap base 250 are an additive flow
metering
component 300, which cooperates with a mixing nozzle 350. An annular one-way
base fluid flow sealing element 320 provides for one-way flow of base fluid
through
the cartridge, preventing backflow, as will be described. A reservoir assembly
including a pouch reservoir spout 400, reservoir (see FIGS. 21 and 23) and
protective
outer housing 500, may be secured to the mixing nozzle 350, and thus the cap
base
250 as will be explained. The pouch may be a flexible pouch containing an
additive
supply and fastened in sealing engagement to pouch reservoir spout 400. The
reservoir assembly may be secured using snap fittings or other fastening
elements,
such as threaded fasteners or friction fastening, within the cartridge cap
base 250 and
also fit to mixing nozzle 350 in a manner that will be explained. The
reservoir
protective housing 500, which may be a cage or a solid-walled (illustrated)
cover, may
be snap-fit to a flange of the pouch reservoir spout 400 to protect the
interior flexible
reservoir pouch containing additive. The reservoir housing 500 and reservoir
pouch
may be made of a transparent or translucent material to permit a user to view
and
identify the nature of the additive supply. Details regarding each of the
above-
described example components as well as their cooperating relationships will
now be
described.
8
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
[0036] Referring now to FIGS. 5-9, these figures illustrate an example
additive flow
adjustment actuator 200. This component may include a main body portion 202
with
an actuation tab 204 to enable a user to rotate the actuator 200. A spout
portion 206
extends upward from the main body portion 202 and provides for flow of mixed
fluid
from the cartridge. The spout portion 206 and may include an integral
retaining ring
208 formed in a top portion thereof for retaining a push-pull cap (FIGS. 2-4)
thereon.
A circular projection 210 is disposed on the top of the spout 206 and
supported by
three spoke elements 212. Projection 210 functions to provide a seal with the
push-
pull cap 230 (FIGS. 2-4) and to provide agitation or turbulence as mixed fluid
exits
the cartridge. A number of axially extending guide rails 216 are defined on an
interior
of the spout portion 206 and define guide channels therebetween, which
cooperate
with and guide complementarily-shaped elements on additive flow metering
component 300 (FIGS. 2-4), as will be explained. A window or aperture 218 is
defined in the main body portion to enable a user to view an adjustment
setting
indicating the relative position of the actuator 200 and associated level of
additive
flow. Indicia 220 may be provided as molded elements on the actuator 200 to
indicate
directions for increasing additive (FLAVOR) or base fluid (WATER). A pair of
recesses 222 may be provided in the main body portion 202 for facilitating
molding of
the actuator 200. Retaining tabs 224 and an outer annular wall 226 and inner
annular
wall 228 provide for mating and rotational engagement and support of the
actuator
202 with the cartridge cap base 250, as will be explained.
[0037] Referring additionally to FIGS. 10-13, these figures illustrate details
of an
example additive flow metering component 300 according to an aspect of the
disclosure. The metering component may be provided as a generally cylindrical
element having a cylindrical body portion 302 and a conical metering
projection or
element 318 (FIG. 12). An annular additive flow passage 312 is defined on the
9
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
additive flow metering component 300. A number of projections 306 and 310 are
defined on an outer surface of the main body portion 302 and define guide
channels
308. These elements cooperate with the rails and channels defined in the
actuator
200, as described above with reference to FIGS. 5-9) to permit the component
300 to
move axially (upward/downward) in a guided cooperative relationship with the
actuator 200 but to also cause the component 300 to rotate with the actuator
200. The
generally annular additive flow passage 312 is defined between the main body
portion
302 and conical metering element 318 to permit flow of additive through the
component. Metering element 318 defines a metering surface 314 (FIG. 12),
which
cooperates with a surface on mixing nozzle 350 (FIGS. 2-4) to provide precise
flow
control of additive flowing through the cartridge. Meterig component 300
includes
internal threads 316 which cooperate with threads on mixing nozzle 350 to
provide
axial movement of the metering surface 314 relative to the counterpart surface
on
mixing nozzle 350 when the component 300 is rotated relative to the mixing
nozzle
350. A shoulder 319 (FIG. 12) is defined in an upper area of conical element
318 to
provide a food safety seal when the conical element is in a closed and sealed
position
within the mixing nozzle 350. The shoulder may deform to facilitate a tight
seal. A
positive locking projection 321 (FIG. 13) extends radially inward on a lower
portion
of the component 300. This projection cooperates with a detent channel (368 in
FIG.
14) to provide for positive locking of the component 300 within the mixing
nozzle
350 during an assembly and packaging operation and to positively indicate that
the
component 300 has been installed in (rotated to) a consistent and
predetermined
position on the mixing nozzle, with the component 300, by virtue of shoulder
319 and
the conical surface 314 then providing a standard food-safety grade seal with
the
mixing nozzle 350.
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
[0038] FIGS. 14-16 illustrate details of an example mixing nozzle 350
according to
an aspect of the disclosure. Mixing nozzle 350 may include a generally
cylindrical
main body portion 352, having a flattened area 353 to facilitate proper
orientation and
alignment within a complementarily shaped recess in cap base 250 during
assembly.
Extending upward from main body portion 352 is a generally circular, raised
snap-fit
projection 354, including a rounded edge for permitting a sealing and snap fit
engagement with a mating portion of the cartridge cap base 250 (FIGS. 2-4 and
FIG.
24). A plurality, in this case four, base fluid ports 358 are defined in the
mixing
nozzle 350 to permit flow of base fluid and at least partially define a base
fluid flow
path through the mixing nozzle 350 and cartridge 100. A mixing nozzle stem 360
extends upward from the snap-fit projection 354 and includes integral threads
362 on
an exterior surface thereof Mixing nozzle stem 360 defines at least a portion
of an
additive flow path by way of an internal mixing nozzle additive flow passage
363. A
seal retaining ring 364 is formed on a lower portion of mixing nozzle spout
360 for
securing an internal end of annular one-way base fluid flow seal 320 (FIGS. 2-
4 and
FIG. 24) in place. As best seen in FIG. 16, additive flow passage 363 is
defined in
part by an upper conical interior surface 365 which is shaped complementarily
to the
conical projection on additive flow metering component 300 to define an
adjustable
metering zone through which the additive flows. According to an aspect of the
disclosure, the flow geometry of the example mixing nozzle 350 may include a
lower
conical surface 367 defining a first converging additive flow zone, a middle
cylindrical or slightly expanding interior surface 369 defining a second flow
zone
extending to the upper conical surface 365 which defines in part a metering
zone.
Applicants have found that characteristics of this flow geometry provides
advantageous flow and mixing of additive with base fluid. As described above,
a
detent channel 368 is defined by projections 366 and 368 (FIG. 14) on a lower
portion
of the stem 360 to provide for a positive locking interaction with metering
component
11
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
300 when it is threaded onto the metering nozzle in an initial assembly
operation to
provide a food safety grade seal.. A number of reservoir spout retaining arms
374
having snap-fit projections 372 formed on an end thereof may be formed on a
lower
portion of the mixing nozzle to secure an upper end of the reservoir spout
within the
cartridge assembly (see FIG. 24). A lower annular wall 378 provides a channel
380
for receiving an end of the reservoir spout for additional sealing engagement.
As will
be recognized, the example mixing nozzle 350 defines a base fluid flow path,
represented by arrows "B" in FIGS. 16 and 26, and an additive flow path
represented
by arrows "A" in FIGS. 16 and 26, it being recognized that the sectional view
in FIG.
16 shows the ports 358 in dotted (hidden) lines. More particularly, the
additive flow
path is defined by a centrally or axially located passage, while the base
fluid flow path
includes passages that are disposed outward from the central location at least
partially
surrounding the additive fluid flow path. This flow geometry provides
advantageous
mixing and flow characteristics.
[0039] FIGS. 17-20 illustrate details of an example cartridge cap base 250
according
to aspects of the disclosure. Base cap 250 includes a generally cylindrical
internally
threaded base portion 254 and a generally annular raised indicator portion 252
having
a contoured upper surface with indicia 258 for indicating an additive mixing
level to a
user. The position of the indicia 258 is such that a selected indicia appears
within the
window in additive flow adjustment actuator. Indicator portion 252 fits within
a
channel formed in the underside of additive flow adjustment actuator 200 (see
FIG.
24). Cap base includes an annular seat 272 for an outer edge of base flow one-
way
valve is 320 and an annular snap-fit ridge 274 for retaining the mixing nozzle
300 (see
FIG. 24). Cap base includes an annular recess with a flat area (FIG. 20) for
ensuring
that the mixing nozzle is installed with correct orientation relative to the
cap base. A
number of ribs extend radially inward for supporting an annular wall.
12
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
[0040] FIGS. 21-23 illustrate details of a flexible pouch reservoir and pouch
reservoir
spout according to an aspect of the disclosure. Spout 400 may include a stem
portion
402 defining an interior additive flow passage. A first flange 404 may be
provided
with slots for receiving the reservoir retaining arms 374 of the mixing nozzle
300. A
snap fit ridge or ring (FIG. 24) is formed on a lower portion of the stem 402
and
cooperates with an internal ridge on a lower portion of the mixing nozzle. A
second
and third flange 406 and 408 extend from the stem 402 for use by automated
filling
equipment. The series of flanges on the spout may also be utilized in a
cartridge
assembly operation where the housing 500 is snap-fit on a first of the flanges
during a
first assembly operation, and then moved upward to snap fit onto a next higher
flange
in a second assembly operation. The flanges may also provide additional
sealing
interfaces with corresponding ridges defined on the housing interior, which
the
reservoir is filled with automated equipment. A bottom flange 410 provides a
snap fit
within housing or cage 50. The pouch reservoir is shown in a flat, unfilled
state in
FIGS. 21-23. As will be recognized, when filled with additive, pouch may
assume a
cylindrical shape and fit within housing 500. The pouch may be fastened by
heat
welding or other fastening techniques to a fastening adapter portion 412 of
the
reservoir spout 400 to seal the pouch walls to the pouch reservoir spout 400.
[0041] FIG. 24 illustrates a cutaway of an assembled additive delivery system
according to an aspect of the disclosure. In this figure, the additive
metering valve is
shown in a closed position. Generally, assembly may involve first inserting
and snap-
fitting the metering valve 350 in place on the cartridge cap base 250. In a
next step,
the one-way sealing valve 320 is placed onto the mixing nozzle 350 and fit
over the
retaining ridge and seated on outer annulus of the cap base. Next, the
additive flow
metering insert 300 is threaded onto the counterpart threads on mixing nozzle
350 and
positioned in proper rotational orientation. Additive adjustment actuator 200
is then
13
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
inserted onto the cartridge cap base in proper alignment with the additive
flow
metering insert. Additive adjustment actuator 200 is retained on cap base with
retaining tabs 224 (FIGS. 7-9) and may rotate with respect to the cap base to
enable
selection of an additive level and associated position of metering component
300.
Push-pull cap 230 may then be placed on the cartridge assembly. Pouch
reservoir
spout and pouch reservoir are then snap fit into the mixing nozzle lower
portion.
[0042] In operation, the additive flow adjustment actuator may be rotated
relative to
the cap base 250. Such rotation also causes rotation of the metering insert
300 relative
to the mixing nozzle 350, resulting in slight axial, i.e., upward or downward
movement of the insert 300 by way of cooperating threads between the insert
300 and
nozzle 350. Axial movement of the metering insert 300 results in a change of
additive
flow through the metering area between the conical portion of insert 300 and
the
corresponding surface on mixing nozzle 350. As base fluid flows into the
cartridge
assembly, resulting from pressure changes within the base fluid container,
i.e., from
squeezing of a flexible bottle and or by suction applied by a user during
consumption,
and/or inverting or tipping, such action results in flow of additive and base
fluid is
mixed with additive at the appropriate level determined by the rotational
position of
the additive flow adjustment actuator. The additive flow path is illustrated
by arrows
"A", it being recognized that because the metering element 300 is in a fully
closed
position in this figure, the arrows "A" are adjacent where flow would occur in
the
metering section in this figure. The base fluid flow path is generally
illustrated by
arrows "B", it being recognized that flow will occur at the interface of the
sealing
element 320 and annular seat 272 of cap base 250, rather than the exact
location of
arrows "B" near that area.
14
CA 03015532 2018-08-22
WO 2017/152192 PCT/US2017/021016
[0043] FIG. 25 illustrates an example change in concentration variance with
amount of
fluid dispensed achieved with flexible reservoirs such as those described
herein.
Curve 1 represents a somewhat inconsistent additive concentration as fluid is
depleted. Such inconsistent concentration is characteristic of rigid
reservoirs. Curve 2
represents a relatively consistent change in concentration as fluid is
dispensed as is
attainable with flexible pouch reservoirs according to aspects of the
disclosure. The
disclosure also contemplates rigid or semi-rigid reservoir structures which
provide for
prevention of vacuum as additive is dispensed therefrom.
[0044] The components described above may be made using injection molding or
other known techniques using thermoplastics, such as food grade polypropylene
or
like materials. The disclosure also contemplates other materials, such as
stainless steel
or other food grade or non-food grade materials.
[0045] It should be understood that implementation of other variations and
modifications of the invention in its various aspects may be readily apparent
to those
of ordinary skill in the art, and that the invention is not limited by the
specific
embodiments described herein. It is therefore contemplated to cover, by the
present
invention any and all modifications, variations or equivalents. For example,
while the
metering function of the additive delivery system has been described using a
conical
metering component or element, other structures may be used, such as flow
control
elements that utilize gate or ball valve or other components that provide
adjustment of
the metering area and flow passage based on user movement of an actuator. In
addition, while snap fittings have been described for components, it will be
recognized that other fastening structure or techniques may be used, such as
threaded
or screw fittings, friction fittings, or adhesive or welding techniques.