Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CONDUIT AND COMPONENT SUPPORT SYSTEM
FIELD OF INVENTION
[1] The invention is a conduit support system for use in supporting or
securing
piping, conduits and electrical wiring found in plumbing waste, water and
venting,
heating and air conditioning, gas lines in liquid and vapor states, oil
piping, pneumatic
and hydraulic piping, fire protection systems, electrical conduits and wires
or similar to
any of the previous mentioned all herein referred to as conduits. The support
system in
some aspects will include the support of the fittings and components used
within a
conduit; such fittings and components included but are not limited to 90
degree elbows,
45 degree elbows, T fittings, couplings, flanges, unions, valves, regulators,
junction
boxes, disconnects, meters, or any other fitting and component that might be
required
for use as part of a conduit system to complete the installation. The above
described
fittings and components herein may be refereed to as component.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[2] The background for the invention or device as described is based on
mechanical
executions including risk assessed engineering for supporting and securing
conduits
within or on one embodiment and for attaching or placing those conduits within
or on the
said embodiment to other structures or objects. Structures which may include
attachment and or placement on a roof, to a roof pipe support, a trusses,
beams, u-
channel, u-channel strut, angle iron, machinery or similar to those listed
above where
compensation is given for conduit expansion and contraction, corrosion
protection,
physical protection, wear, identification, vibrations, temperature transfer,
shock, ease of
installation, and cost savings. The device or invention can be used in
mechanical fields
including plumbing, heating, air conditioning, electrical, fire protection and
related trade
disciplines. The use of the word invention or device may be interchangeable
throughout
this writing or disclosure and the meaning is understood to describe the
invention or
device in the same manner.
1
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[3] Previous prior art show means or provide teaching for pipe supporting,
hanging
or similar and each add value to mechanical trades from US patent Lombard
2,166,916
to US patent SixSmith 9,903,512 prior art has provided individual solutions
for support
of a conduit, piping or similar. While each individual solution described and
illustrated in
prior arts solves problems or adds value, the present invention provides a
system which
creates a multi functional support and hanger for conduits. This now disclosed
invention
does not only recognize one or two challenges faced by designers, engineers
and
installers but focuses on the integration of expansion and contraction,
corrosion
protection, dielectric isolation, wear, physical protection, identification of
the conduit
including contents inside the conduit, vibrations with respect given to such
forces as
hydraulic shock and seismic movement, parallel positioning distance
protection, ease of
installation, critical support to the components such as couplings, 90 degree
elbows, T
fittings, valves, regulators, unions, junction box's other related or
associated mechanical
components herein referred to as component, or any such place that protection
or
support needs to be provided from load bearing forces external to or from the
conduits
themselves in one device or system of support.
[4] This invention, in one device or embodiment solves the above expansion
and
contraction including corrosion protection within the conduit. Engineering
tolerances
provided within the design wherein the conduits size is compensated for in
relation to
the conduit support area. Expansion and contraction due to temperature change
is a
factor considered through risk assessment in the engineering and design of
this
invention. Temperature changes are not only created externally from ambient
temperatures but also internal to the conduits themselves and therefore in
many cases
are not controllable, but manageable. This invention manages thermal expansion
and
contraction by allowing this natural effect to occur controlling it throughout
the entire
system. When conduits are suppressed from hanger to hanger or clip to clip by
tightly
fastening them not only do the conduits warp and bend between these hangers
but
sometimes hangers can be dislodged by thermal expansion forces or more
severely
conduits themselves can be damaged. While previous prior arts rely on moving
parts or
2
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
material selection for expansion and contraction, this invention prevents
damages
caused by thermal expansion and contraction by managing the effects with
engineering
tolerances designed within the invention where no actions are needed by the
installer to
accommodate for thermal expansion or contraction.
[5] Another advantage with certain aspects of this invention or device as
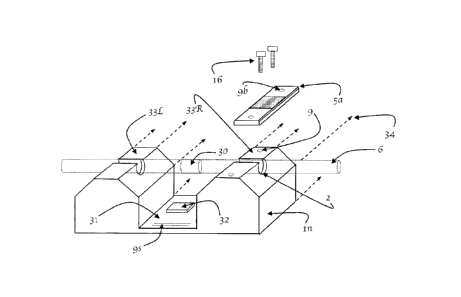
described
is the singular use of the hanger or support in one embodiment to where
attachment is
possible to different objects including attachment to open channel strut
without
additional retaining components. The device or invention as described and
illustrated in
the drawings continues with advantages where no pressure or force is imposed
on the
conduit itself for attachment. Many similar u-channel strut clamps or supports
tighten
conduits against open channel strut to secure a conduit. This invention or
device can be
friction fit where no pressure or force is applied by or applied to a conduit.
[6] Still another advantage of the invention is the physical protection
engineering as
part of the device. Many conduits are either installed outside a building
structure where
they travel to concrete pads or other structures beside or outside of the main
building
structure, on roof tops, beside or at machinery, inside or outside areas where
workers
must travel to complete inspections, work on or above conduits leaving
conduits
unprotected from physical damages. Prior US patent art Jentzsch 3,888,186;
Valeri
4,067,258 Martin 5,095,822; Herman 5,777,266; Berardi 6,499,410; Henry
6,878,811;
Lubanski 7,309,836; Henry 7,939,759; Lubanski 8,119,914 and Lioi 9,438,022;
describe
and teach of protection methods in the forms of ramps for heavy equipment or
foot
traffic at special events. This invention as disclosed is not meant for
protection of
vehicular traffic but from physical damages to the conduits caused by workers
standing
on conduits to gain access to other equipment, falling objects from workers
working
above conduits, from processes of equipment or those from such physical
damages that
can occur from moving or falling ice and snow loads. The design of this
invention has
built in tolerances for outside forces such as impact from falling objects,
foot traffic and
similar forces imposed on conduits while providing inspection access without
dismantling the protection device also providing identification to conduits.
Furthermore,
3
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
this invention will allow for simple attachment where conduits are installed
within or
around pipe racking. Many conduits require work to be completed within such
pipe
racking where workers have to build on site wooded structures or similar. The
invention
as described and illustrated in the drawing figures now solves physical
protection of a
conduit relative to size wherein now protection can be accomplished within or
around
equipment, in pipe racking, on roof areas, between buildings or similar to
those areas
above.
[7] Protection of a conduit is critical in the success of the functions in
which a conduit
performs and as such this invention through risk assessment provides not only
protection as described above but allowance and compensation for conduit
release from
structural objects. Extreme movement or fatigue of a structural object to
where a conduit
is attached can cause extreme harm to a conduit support, a conduit and to the
function
a conduit performs; now as disclosed this invention can manage extreme
conditions by
allowing a conduit to be released prior to critical fatigue of the conduit.
[8] Another advantage of the current invention is the support of semi rigid
conduits
where support is not only provided at strategically placed supports, but
throughout the
entire run of a conduit. Past practices have been the use of wooden planks
placed
beneath corrugated conduits for entire system support, this invention now
solves entire
system protection for semi rigid conduits as well.
[9] Vibrations within conduit systems including those apparent in liquid
system are
accounted for and protected from within this said invention or device.
Hydraulic shock is
due to flow being suddenly stopped within a conduit and should be accounted
for within
the designs of conduit protection. Devices like shock absorbers and expansion
tanks
provide internal relief for hydraulic shock as shown by US patent Tsai
9,004,110,
however, this does not protect the outside of the conduit if such devices
intended to
absorb inner shock are not installed, or depleted, undersized or not installed
in the
correct location. These vibrations due to hydraulic shock can cause conduits
to bang,
move or break. The effects caused by hydraulic shock if not suppressed or
managed
4
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
within a conduit can be lessened by this invention. This device itself
provides external
absorption of hydraulic shock not only dampening the sound of this condition
but
reducing effects such as wear of the conduit and conduit retainer. Internal
protection is
always recommended and cannot in itself be solved by supports or hangers,
however,
this invention can aid the internal measures required. US patent Mastro
5,261,633 does
make mention of providing a solution for the sound of "water hammer" by
separating a
conduit from a metal hanger, however this method of separation does not
correct or aid
in the condition of hydraulic shock. The invention as now described not only
solves the
sound of hydraulic shock, but more importantly allows the opposite action of
hydraulic
shock to happen naturally inside the conduit allowing the conduit and this
invention to
absorb the impact caused by hydraulic shock also providing protection impact
from
external physical forces and those that may occur due to settling of
structures and
vibrations which also includes vibrations which might occur due to seismic
activity.
[10] Still another advantage of the present invention is centerline measuring
provided
within the device where known measurements are provided from the center of the
conduit support area to the outside of the device. This known measurement
allows
installers precise measuring. This is not only important for straight parallel
conduit
guiding for appearances but for those installations that require precise
clearances from
other conduits such as a gas conduit distance from an electrical conduit.
[11] Visual identification is another advantage within this invention, not
only for
physical contact incidents but also as a visual working aid. This can be
accomplished by
coloring the invention differently and or labeling the invention. Color coding
or
identification of the device will give immediate notification to workers,
engineers, fire
fighters, safety personnel or similar what the conduit contains, if the
conduit is hot or
cold, the electrical current, voltage and phase, where a conduit is fed from
or where a
conduit begins or ends. This identification by color, numbering, lettering or
labelling
solves cost and hazards associated with the above. Prior US patent art lbey
6,772,634
teaches and solves the problem of identification of conduit ends by the use of
a sonic
transmitter and a sonic receiver; while this invention or prior art taught by
lbey is needed
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
and solves a great problem for the electrical industry, the marking system
which is
accomplished within this device allows for identification prior to or after
the invention of
lbey is used wherein the conduits should be identified. Moreover, many
conduits are
typically supported in the same areas, this identification can now from a
glance identify
the conduit. Such examples could be a blue colored device for compressed air
lines,
yellow color for flammable gasses in a vapor state, red for fire-quenching
fluids or
wording such as 600 volt. Current conduit hangers or supports in the basics of
the
design may not allow for such marking or labelling on the conduit hanger or
support and
rely on conduit marking in the form of banding on the conduit such as prior US
patent
art Piana 4,268,986; Clement 4,844,000; Niwa 5,138,784; or methods of marking
such
as US patent Bennett 9,446,877 or by painting the conduit a desired color. As
described
and shown conduit marking and identification is important and now with this
invention
expensive painting or marking of the conduit could be minimized as marking and
identification is provided within this device or invention.
[12] Another advantage over other prior art is the development of the "Insert
Single
Block" "Insert Double Block"," Double Block", "Insert 90 Block", "90 Block",
"Insert T
Block", and "T Block" that integrate a means of securing, supporting and
guiding
conduits and wire systems regardless of size or numbers with emphasis on code
compliance, public health and safety, mechanical impact protection and points
of joining
within a conduit system. The described devices may provide in some models
support
not only to the conduits but also where critical support to the components
such as
couplings, 90 degree elbows, T fittings, valves, regulators, unions, junction
box's or
other related to those described or other associated mechanical components
herein
referred to as component, or any such places that protection or support needs
to be
provided from load bearing forces external to or from the conduits themselves.
This is of
particular importance in systems where threaded or grooved ends of conduits
have
removed base metals in the process of such actions or in systems where
attachments
are glued or attached with screws or connectors. Such systems which are, but
not
limited to electrical, gas, plumbing, refrigeration and air conditioning. By
supporting all
conduit ends where components are attached the invention creates a total
system of
6
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
support to any conduit system. Prior US patent art Rook 9,528,271, Brown
9,523,380,
Krovates 8,312,692 Hillman D692,393 and Tally D738,711 and others provide
support
as a singular block that can only support one area at a time and means of
support is
only for a pipe and not the complete system in which only a single support is
used and
placed at locations randomly or not placed in critical areas such as joints or
changes of
direction leaving one or more attachment points unprotected, unsupported or
incorrectly
installed or easily moved accidentally during renovations, repairs or other
such actions
after the conduits have been installed, supported and inspected. This
invention or
support system complete with the "Insert Double Block", "Double Block",
"Insert 90
Block", "90 Block", "Insert T Block" and "T Block" are singular supports in
design but
encompass all sides of a component providing support at both or all sides of
associated
components held within a conduit system, in turn not only providing full
support of the
conduit system but also the associated components within a single block or
support.
National codes make reference to supporting ends of threaded piping and
providing
correctly mounted, braced and supported conduits. This invention solves
support of
conduits as per Codes while enabling those installing conduits and supports to
do so
more efficiently and safely with proper planning and engineering provided
within this
invention.
[13] This invention as disclosed solves through risk assessed engineering not
only
one or two challenges for mechanical trades but provides advantages and solves
conditions or effects of thermal expansion and contraction, corrosion
protection,
dielectric protection, physical protection, component inspection, wear,
identification,
vibrations and shock and ease of installation. Providing support to all
aspects of conduit
systems as a whole by providing weakest link protection in component support
by the
invention of "Insert Double Block", "Double Block", "Insert 90 Block", "90
Block", "Insert
T Block" and "T Block" while incorporating inspection and testing areas this
invention is
not only a conduit support but a managed system of support; an invention
focused on
conforming to Codes, Standards and good engineering practices by eliminating
the
hazard.
7
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
SUMMARY
[14] The now disclosed invention and support system as described is a general
summary of the invention, and is not a comprehensive disclosure of all of its
features. The invention now disclosed may in one embodiment or parts formed
within an
embodiment or added to a embodiment provide advantages or solve conditions or
effects of thermal expansion and contraction, corrosion, component protection,
dielectric
and galvanic actions, physical protection, wear protection, identification of
the invention
and a conduit, vibrations or shock, ease of installation for supporting,
securing or
guiding, and attaching conduits as disclosed in descriptions or illustrations
throughout
this document.
[15] The main embodiment of the invention or device can be made of non
metallic
elastomeric material or similar, which can be made of recycled material, which
may
have other elements when desired for attachment, marking and labelling,
protection and
lighting. The device is used as a support for supporting, protecting and
identifying
conduits and components as previously described in the Abstract. This
invention will
have allowances for expansion and contraction without the use of moving parts.
Expansion and contraction is managed by or within the unique engineered
support
conduit area or conduit cradle as mentioned in the description. The support
area is
designed with specific engineered tolerances based on the coefficient of
thermal
expansion and contraction of conduit materials and the invention. However,
some
models may appear without a conduit cradle area allowing for a conduit to be
directly
placed on top of the invention. The shape and size of the conduit area is a
factor of risk
assessment and engineering tolerances surrounding the conduit; the conduit
support
area may in other words be slightly larger with a specific contact footprint
for conduit
support within the embodiment while providing allowances for multi-directional
expansion and contraction of the conduit supported by the invention. The
tolerances
formulated are dependent upon the size and material of the conduit being
supported
and risk assets activities or functions of the invention not based solely on
the rate or
coefficient of expansion for any particular conduit material which may include
8
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
allowances for air circulation around the conduit, the invention and
surrounding areas.
The shape and size of the conduit support area may differ when required
dependent
upon those factors listed previous as well factors which can be site specific.
The
invention will not have metallic materials in contact with the conduits
however metallic
materials are given allowance for depending upon installation activities.
Metallic material
may be part of the invention or provided as an option to the installer. The
metallic parts
may include but are not limited to, a base, a base clip, a wedge, screws or
bolts, a slide,
top clip or cover or conduit protector. The invention can be secured to other
structures
by the use of conventional screws, threaded rod, bolts or adhesives alone or
in
conjunction with those conventional means described above. Areas for
attachment can
be pre set by means of hole(s) part way through or entirely through or simply
marked or
labelled "attachment point", "anchor point" or in language that will be
familiar and
understood by the installer which may only include instructions wherein
numbering or
lettering is used to describe the locations. However, options to the installer
are left to
those trained to locate the specific positions of attachment based on the
experience and
need of the installer to where no instruction is provided.
[16] The invention will have allowances for one, or more than one conduit to
be
supported within one embodiment where means of conduit attachment to the
invention
may require no tools to complete. The conduit may simply be inserted into the
invention
by way of an insert opening or passing the conduit through a pre-sized opening
where
protection of the conduit can be accomplished by the material of the main
embodiment
at each side of the conduit. The insert opening may have a cover for
attachment after
the conduit is placed inside the conduit support area. The cover and invention
may
include a structural fatigue design wherein the cover and or the invention can
release a
conduit if undue stresses occur. The cover as described can be fitted with
lighting and
conduit protection methods further to or in addition to those described for
side
protection. Options for protection and the method used to provide this
protection can
also be used to ensure other similar devices stay within installation distance
tolerances.
9
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[17] The invention can incorporate other convention means of direct attachment
for
conduits above or beside when conduit separation is required for such
installation as
gas conduit separation from electrical conduits or simply to save space. This
separation
of conduits may also isolate conduits from one another creating air gaps
impairing
temperature transfer from conduit to conduit or from conduit to building or
similar.
[18] The invention or device may have a flat bottom to rest on top of flat
surfaces or
be placed on objects such as roof blocking or be notched to be placed over
smaller
objects with additional options including those with strut like adaptions made
within the
device to be pushed, slid or clamped into u-channel strut. Discrimination is
not given to
the numbers of conduits or the size of conduits held or supported within the
invention.
However, a typical length that could be anticipated would not be longer than
three feet
which may include areas within the main embodiment where break away sections
are
provided between areas where a conduit is supported, this may allow for longer
sections to be separated with ease. The size of the invention is based on the
size of the
conduit being supported or held within. The typical largest size of a conduit
could be
Nominal Pipe Size 3 inch, however special considerations are given to larger
sized
conduits and are to be considered within the scope.
[19] The
inventions can be installed in any position but it is the intent that with
larger
conduits the invention be installed with the base at the bottom with the
conduit insert
opening facing upward.
[20] The color of the invention is expected to be black, however optional
colors are
possible depending on the installation requirements. Such examples could be
those set
forth by codes and standards followed by jurisdictional requirements which
could
include yellow for natural gas or red for fire suppression. The invention can
be color
coded as mentioned with additional means of identification by numbering,
lettering or
labelling which are dependent upon the use. These can be provided as
attachments to
the invention including push pins or push inserts. Identification is also
possible by where
stored energy lighting is provided within the invention or within the
inventions slide or
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
clip or cover. For areas of snow fall identification flagging can be provided
and inserted
into parts of the invention when desired.
[21] The invention, as described is for use as a support, attachment piece,
hanger,
adaptor or component including roof supports to where adaptation can be
accommodated for existing supports by either placing on top, inside or around
any
support base provided without being directly placed on the roof surface but on
a support
already on the roof surface. However, direct placement on a roof surface is
possible
with such certain models if so desired and sense can be made by the installer
or user.
The invention also may be used inside or around or place directly on where
sense can
be made for attachment to objects like or similar to roof trusses, u channel,
strut,
beams, electrical panels, machinery or similar for the installation as
described or
illustrated within other aspects of this disclosure.
[22] The invention may have models where an opening or openings between the
support areas have allowance for inspection or testing of conduit components.
The
invention can incorporate specialized specific types such as "Double Blocks"
for
couplings, valves, junction boxes, regulator or similar when required and
"Single Blocks"
configured to accommodate support where chosen, "T Blocks" for angles that
form tee
connections and "90 Block" for perpendicular changes in direction. Regardless
of the
configuration of the device or invention components have inspection and
testing areas
built within the device and support will be within close proximity to a
component at
joining points. The lowered area of the invention can accommodate for lighting
and
storage of components required for the purpose of lighting, however, lighting
may be
attached wherever needed on the main embodiment of the device which would
include
single block styles where no lower area is formed as part of the device.
[23] Alterations and further modifications of the inventive features described
within
this document which would normally occur to one skilled in the relevant art
and having
possession of this disclosure, are to be considered within the scope of the
invention
claimed. A portion of the disclosure of this patent document contains material
which is
11
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
subject to copyright protection as such those including but not limited to
"Single Block"
"Double Block" "90 Block" and "T Block" are reserved by the named inventor
appearing
within this document.
BREIF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[24] Reference is made herein to the accompanying drawings or illustrations,
which
are not drawn to scale.
[25] Figure 1 and Figure la are exploded front views of the present invention
or side
views in relation to a perpendicular support member in relation to a conduit.
[26] Figure 2 is a perspective view of the present invention illustrating
the flat bottom
attachment.
[27] Figure 3 is a perspective view illustrating the flat bottom attachment to
where no
discrimination is given to the number of conduits that may be in one
embodiment of the
present invention.
[28] Figure 4 is a perspective view illustrating a clip bottom attachment.
[29] Figure 5 is a perspective view illustrating the clip bottom attachment to
where no
discrimination is given to the number of conduits that may be in one
embodiment of the
present invention.
[30] Figure 6 is a perspective view of the present invention illustrating
the solid
grooved bottom attachment.
[31] Figure 7 is a perspective view illustrating the solid grooved bottom
attachment to
where no discrimination is given to the number of conduits that may be in one
embodiment of the present invention.
12
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[32] Figure 8 is a perspective view illustrating the open grooved bottom
attachment.
[33] Figure 9 is a perspective view illustrating the open grooved bottom
attachment to
where no discrimination is given to the number of conduits that may be in one
embodiment of the present invention.
[34] Figure 10 is a perspective view illustrating the universal grooved bottom
attachment.
[35] Figure 11 is a perspective view illustrating the universal grooved
bottom
attachment to where no discrimination is given to the number of conduits that
may be in
one embodiment of the present invention.
[36] Figure 12 is a perspective view illustrating a lowered upper plateau of a
main
embodiment's top and description to where allowance is made for combination of
bases.
[37] Figure 13 is a prospective view illustrating a lowered upper plateau to
where no
discrimination is given to the number of conduits that may be in one
embodiment of the
present invention. And where allowance is made for combination of bases.
[38] Figure 14 is a perspective view illustrating the flat bottom
attachment base and a
closure clip.
[39] Figure 15 is an exploded perspective view illustrating a support block to
where
attachment is made of the present invention with the flat bottom.
[40] Figure 16 is a perspective view illustrating the completed movements of
Figure
15.
13
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[41] Figure 17 illustrates an exploded perspective view illustrating the
flat bottom
attachment to a support block where the top of the support has a u-channel
strut.
[42] Figure 18 is a perspective view illustrating the completed movements of
Figure
17.
[43] Figure 19 is a perspective view illustrating the open grooved bottom
attachment
base.
[44] Figure 20 is an exploded perspective view illustrating the open grooved
bottom
attachment base with a u-channel strut including the use of a securing tapered
wedge.
[45] Figure 21 is a perspective view of the securing tapered wedge with a pull
tight
draw mechanism.
[46] Figure 22 is a perspective view illustrating the position of the
tapered wedge after
insertion.
[47] Figure 23 is a perspective view illustrating the completed movements of
Figure
20.
[48] Figure 24 is a perspective view illustrating the open grooved bottom
attachment
over an object.
[49] Figure 25 is a perspective view illustrating a clip bottom attachment
over an
object.
[50] Figure 26 is a prospective view illustrating the wrap around bottom
attachment
over an object.
14
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[51] Figure 27 is an exploded perspective view of components for use in
figures 28
through Figure 30.
[52] Figure 28 is a perspective view illustrating a protection method.
[53] Figure 29 is a perspective view illustrating a protection method on a
support
block.
[54] Figure 30 is a perspective view illustrating the protection covers
installed
including marking means for the conduit.
[55] Figure 31 is an exploded perspective view illustrating a cover protector
and
protection platform.
[56] Figure 32 is a perspective view illustrating a cover protector and
protection
platform with an elongated side of a protection platform and lights on the
cover
protectors.
[57] Figure 33 is a perspective view illustrating the main embodiment of the
invention
without the cover protector and protection platform.
[58] Figure 34 is a perspective view illustrating the cover protector and
protection
platform installed over the main embodiment of the invention illustrating a
conduit being
protected.
[59] Figure 35 is an exploded perspective view illustrating the lower plateau
of the
main embodiment with cover protector, protection platform, conduit base
support and
underside protection of a conduit.
[60] Figure 36 is a perspective view illustrating physical protection using
only the
protection platforms.
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[61] Figure 37 is a perspective view illustrating physical protection with
side and top
protection platforms including conduit identification and covers including
lighting.
[62] Figure 38 is a front view illustrating the conduit holding area and
the top insert
area with an opening for a protection method.
[63] Figure 39 illustrates an exploded perspective view of one means to
provide a
protection slot to accept a protection platform incorporated within a main
embodiment.
[64] Figure 40 is a front view illustrating the conduit holding area for
cover slides.
[65] Figure 41 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or
"Insert Single
Block".
[66] Figure 42 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "Insert
Double
Block".
[67] Figure 43 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "Double
Block".
[68] Figure 44 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "Insert
90
Block".
[69] Figure 45 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "90
Block".
[70] Figure 46 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "Insert
T
Block".
[71] Figure 47 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "T
Block".
16
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[72] Figure 48 is an exploded perspective view illustrating a main embodiment
or
"Insert Single Block" with a cover plate and conduit.
[73] Figure 49 is a perspective view illustrating the completed movements of
Figure
48.
[74] Figure 50 is a perspective view of a main embodiment or "Insert Single
Block"
with a conduit inserted into the main embodiment and a conduit attached to the
top of
the main embodiment.
[75] Figure
51 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "Insert Single
Block" with a conduit inserted into the main embodiment and a conduit attached
to the
top of the main embodiment at a higher elevation with the use of threaded rod.
[76] Figure 52 is an exploded perspective view illustrating a main embodiment
or
"Insert Double Block" with a cover plate, lighted area, structural attachment
area,
component and a conduit inserted into the main embodiment.
[77] Figure 53 is an exploded perspective view illustrating a main embodiment
or
"Insert Double Block" with a cover plate, cover clip, lighted area, structural
attachment
area, component and a conduit inserted into the main embodiment with a conduit
elevated above the main embodiment.
[78] Figure 54 is an exploded perspective view illustrating a main embodiment
or
"Insert Double Block" with a protection platform, cover clip protector,
component and a
conduit inserted into the main embodiment.
[79] Figure 55 is a perspective view illustrating the completed movements of
Figure
54.
17
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[80] Figure 56 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "Double
Block"
with a conduit attached to the top of the main embodiment.
[81] Figure 57 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "Double
Block"
illustrating a conduit where attachment of a conduit is made using u-channel
and a clip.
[82] Figure 58 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "Double
Block"
illustrating conduit attachment using threaded rod elevating u-channel.
[83] Figure 59 is an exploded perspective view illustrating a main embodiment
or
"Insert 90 Block" with a lighted area, structural attachment area, component,
a conduit
inserted into the main embodiment and a cover plate.
[84] Figure 60 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "90
Block" with
a conduit attached to the top of the main embodiment.
[85] Figure 61 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "90
Block" with
a conduit attached to the top of the main embodiment.
[86] Figure 62 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "90
Block" with
an elevated conduit attached to the top of the main embodiment using threaded
rod.
[87] Figure 63 is an exploded perspective view illustrating a main embodiment
or
"Insert T Block" with a cover plate, conduit, component, lighted area and
structural
attachment area.
[88] Figure 64 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "Insert
T Block"
with a cover plate, a conduit inserted into the main embodiment and a conduit
supported by the main embodiment but elevated above the main embodiment with
the
use of threaded rod.
18
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[89] Figure 65 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "T
Block" with a
conduit attached to the top of the main embodiment.
[90] Figure 66 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "T
Block" with a
conduit attached to the top of the main embodiment.
[91] Figure 67 is a perspective view illustrating a main embodiment or "T
Block" with
an elevated conduit attached to the top of the main embodiment using threaded
rod.
[92] Figure 68 is a plan view illustrating a main embodiment or "Insert
Single Block"
[93] Figure 69 is a plan view illustrating either main embodiment "Insert
Double Block"
or "Double Block"
[94] Figure 70 is a plan view illustrating either main embodiment "Insert
90 Block" or
"90 Block"
[95] Figure 71 is a plan view illustrating either main embodiment "Insert T
Block" or "T
Block"
[96] Figure 72 is a plan view illustrating the top of an upper ridge in
where the upper
ridge may be of any embodiment.
[97] Figure 73 is a plan view illustrating the bottom or underside of an
upper ridge in
where the upper ridge illustrated can be of any embodiment.
[98] Figure 74 is a plan view illustrating the top of an upper ridge in
where the upper
ridge may be of any embodiment.
[99] Figure 75 is a plan view illustrating the bottom or underside of an
upper ridge in
where the upper ridge illustrated can be of any embodiment.
19
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[100] Figure 76 is a side view illustrating a cover plate complete with push
pins.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[101] In the following description with the use of the figures or
illustrations, numerical
and or alphabetical references may refer to similar components and elements.
The
components, elements and or embodiments may also be identified numerically,
alphabetically, or a combination of both described or configured to point to
one element,
component or embodiment; where this appears, the meaning may be for all that
appear
as illustrated and described where sense can be made. The embodiments,
components, configurations and materials illustrated in the figures or
described within
this description are preferred embodiments only and are given solely for
explanation
purposes. Where similar depictions or drawings are made these similar
descriptions
where sense can be made are to be understood without duplication of such
descriptions
for each Illustration. Descriptions of well-known components are omitted so as
to not
unnecessarily obscure the principle features of the invention. It is noted
that
combinations of main embodiments and the means of attachment are
interchangeable
and depictions within the drawings or illustrations do not limit the usage of
other main
embodiments, as such, drawings are basic forms of each. It should be
understood that
no limitation of the scope of the invention is thereby intended. Terminology
used herein
is for the purpose of describing embodiments only and is not intended to be
limiting of
the invention. As used herein, the use of singular terms may include plural or
plural may
be singular where sense can be made. No discrimination is given to the design
for the
numbers of repetitions of conduit 6 attachments, or other descriptions, this
is shown in
dotted extension 34 throughout as a continuation of noted remarks in a mirror
like
fashion.
[102] The present invention and the components of the invention may be
fabricated of
any suitable materials, including plastics, composites, metals and recycled
materials,
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
and may be fabricated using suitable techniques, including molding, casting,
machining
or similar to achieve the results required.
{103} Referring now to the figures and the inventions which are composed of
several
different elements or components completing one embodiment depending on the
use or
function. Figure 1 is a front view illustrating a conduit 6 supported within
the main
embodiment 1 of the conduit insert invention which is held or supported in the
uniquely
engineered conduit cradle 2 (as described in the summary as conduit area)
which may
have a top section of pliable overlaying materials 4 which may be formed as
part of the
main embodiment 1 which is intentionally separated by a void or conduit insert
opening
3. The overlaying material 4 may be straight cut or have an angular shape
where the
opposing ends facing inward are discontinued. The discontinued overlaying
material 4 is
intentionally done so that the conduit 6 may have a shorter path of travel to
its final
installed position within the conduit cradle 2. The conduit 6 is to be
inserted without the
use of tools through the conduit insert opening 3 even when ambient
temperatures are
not favorable. This overlaying material 4 when moved in an inward direction
towards the
conduit cradle 2 allows the conduit 6 to be inserted with ease by defecting
the
overlaying material 4 in a downward manner. It is now mentioned that
overlaying
material 4 is optional and may in some cases not be formed in part or in whole
of the
device(s) or a main embodiment. After the action of inserting the conduit 6
through the
conduit insert opening 3 the overlaying material 4 returns to its original
position. The
overlaying material 4 is not anticipated to hold fast the conduit 6 in designs
that are
engineered with expansion and contraction considerations. The shape of the
conduit
cradle 2 is noticeably not round and this feature is intentional for designs
when required
expansion and contraction considerations are given, however, the conduit 6
could be of
the same size as the conduit cradle 2. The overlaying material 4 may not be
the only
holding member of the main embodiment 1 to where the conduit 6 is enclosed.
The
main embodiment 1 may have a cover plate 5a, cover clip 5op or cover clip 5
for
attachment over the insert opening 3 or be left uncovered without the cover
plates 5 and
5a or similar in Figure la. Figure 1 further illustrates attachment areas 8
which may be
drilled or formed hollow at the time of manufacturing or marked or labeled or
similar.
21
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
These attachment areas 8 can be filled after installation with push marking
pins 8a
which also can function as a marking or labelling system which could be words,
letters,
numbers, shapes with words, colors or letters, bar coding, numbers or similar
embossed, cast or formed as part thereof. The use of stickers or other could
be adhered
to the push marking pins 8a for the purpose of marking or labelling also. A
notched area
7 which may be any length or size is illustrated now extending the entire
length of the
main embodiment 1 illustrated as a dotted line which is for the purpose of
marking and
labelling where more precise labelling is required in such models that
provisions are
made in this manner. Such means for marking and labelling could be provided as
a
push tab 7a and will perform and be created in a similar manner as those
described for
the push marking pin 8a. The notched area 7 may further function as a support
member
or groove for attachment into u-channel strut which will become more clear and
obvious
as the descriptions and illustrations continue throughout other figures and
explanations
including those of Figure 6 and Figures 19 through 23. Marking and labelling
as
described within Figure 1 is similar throughout the writing and from now when
not
shown or described elsewhere will be similar to those described within this
Figure 1 or
where other mention is made.
[104] Figure la as illustrated provides the same basic components and
functions as
Figure 1 for the elements of the conduit 6, conduit cradle 2, attachment area
8,
overlaying material 4, conduit insert opening 3, notched area 7, push tab 7a
and push
marking pins 8a but now representation is illustrated for overlaying vibration
material 4a
which may be used as a vibration dampener or similar which can be in contact
with the
conduit 6 where it may also function as a pressure release for the cover plate
5a, a
cover plate 5a which may include as an option the overlaying vibration
material 4a as
part of the cover plate 5a when overlaying material 4 is not part of the main
embodiment
1 and a recessed lower plateau llb which is a lower elevation change in
comparison to
the higher plateau 11c of the main embodiment 1. This lower plateau llb can be
formed as part of main embodiment 1 to allow for a recessed cover clip 5a and
other
protection methods that will become more obvious in other illustrations
including those
of Figures 35 through 37. Figure la also includes a light 5c which can be
formed in part
22
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
or in whole of the cover plate 5a. The light 5c could also utilize means of
reflective
material when required alternate to a light 5c or similar. A holding tab 4b is
now shown
which represents an option of providing within the higher plateau 11c an area
to slide
the cover plate 5a into without the use of tools to secure the cover plate 5a,
this option
is also illustrated with use of push pins 5d where the push pins 5d can be
inserted and
held by friction or with outward ridges at the base of the push pins 5d into
push holes 5e
within the main embodiment 1. This is provided as an option for where physical
attachment to a structural object could be compromised by extreme movement or
fatigue of the attached object to where the main embodiment 1 or conduit
support is
placed allowing for the cover plate 5a to be dislodged and the conduit 6 to be
released.
Centerline cl is shown for reference to the length from the centerline of the
conduit
cradle 2 to the outside of the embodiment 1 which may be used for installation
purposes
where the known length can be adopted as a measuring device to aid in conduit
6 being
installed in straight or parallel lines to each other. This distance from the
center line of
the conduit cradle 2 also now illustrates side physical protection to the
conduit 6
wherein the main embodiment 1 has a thickness engineered to withstand physical
impact, this protection is also provided by design if more than one conduit 6
is
accommodated in one main embodiment 1. Push pins 5d are described as
cylindrical
tapered pins which may be formed in part or in whole of the cover plate 5a or
similar for
insertion into push holes 5e within the main embodiment 1 to secure the cover
plate 5a
to the main embodiment 1. The push pins 5d will will have a void or voids as
part of the
push pins 5d extending from the bottom tip to the underside of the cover to
allow for
inward deflection of the pin material when pressed into the recessed area or
push holes
5e of the main embodiment. When extreme external forces are imposed on the
main
embodiment 1 or conduit 6 the push pins 5d can become dislodge from the main
embodiment 1 releasing the cover plate 5a and in turn the conduit. This action
of
dislodging the cover plate 5a can be critical in such designs where a conduit
6 needs to
be released form the main embodiment 1 during times where the structural
support the
main embodiment 1 is attach has critical failure; this might occur during an
earthquake
or similar.
23
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[105] Figure 2 now illustrates the main embodiment as 1a which later will
become
apparent with the introduction of similar main embodiments all starting with 1
but with
the addition of letters following the number. This change of main embodiments
is
intentional for recognition of the base or attachment means in which the main
embodiment transforms to accommodate attachment means. Further to describe
Figure
2 which now illustrates the main embodiment la with an insert point for top
clip 5 of
Figure 1 which may be slid through or into slide clip insert 4a opening or
slot which is
shown above the conduit cradle 2 and under the insert opening 3. This top clip
5 of
Figure 1 can be reflective material which also may function as a measuring
device for
attachment of screws or similar into the attachment area 9 when the design or
instructions have the installer leaving the attachment screws slightly
elevated allowing
for movement. The main embodiment la shows attachment area 9, this area can be
as
describe as a drilled or formed hollow opening at the time of manufacturing
which may
be provided for the purpose of attaching the main embodiment la to a
structure. The
attachment area 9 can provide for expansion and contraction when the hole is
elongated. This attachment area if not formed in whole at the time of
manufacturing can
be marked or labeled or similar where notification is given to the installer
for its purpose.
[106] Figure 3 is illustrated showing the same attachment means or flat bottom
as the
main embodiment la of Figure 2 but now with more than one conduit cradle 2 in
the
main embodiment lb where no discrimination is given to the numbers of conduit
cradles
2 that might be within one main embodiment lb. The main embodiment lb can have
multiple conduit cradles sized equally in circumference, however the size of
conduit
cradle 2 may differ as shown in conduit cradle 2b, this is probable in such
conduit
systems similar to potable water lines where the water system includes a hot
line, a cold
line, and a recirculation line wherein the hot and cold lines could be equal
in size shown
as conduit cradles 2 and 2a but having a recirculation line sized smaller held
within
conduit cradle 2b; these are given as examples only, and other similar
examples could
be predicted where conduit size changes are needed. Conduit cradles 2, 2a and
2b
could replicate in numbers depending on the installation. Insert openings 3,3a
and 3b
are shown in relation to the conduit cradles 2, 2a and 2b wherein the same
previous
24
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
described actions of insertion are required for a conduit to be inserted
through insert
openings 3,3a and 3b. Attachment area 9 is shown at the ends of the main
embodiment
lb, however it is conceivable that with longer main embodiments lb composed of
multiple conduit cradles 2 these attachment areas 9 could be more numerous and
allowances within the conduit cradle 2 bottom are given for addition
attachment areas 9.
Small holes may be added in the bottom of any conduit cradle 2 for this
purpose, these
holes may also function as drainage holes for water or condensate or similar.
[107] Figure 4 illustrates a void 10 within the main embodiment lc at the
bottom for the
purpose of fitting the main embodiment lc overtop of other surfaces which
could include
2x4 or 2x6 or similar wood planking or studs, strut u-shaped channel or
similar
rectangular objects. Attachment areas 8 are now shown for the purpose of side
attachment to the similar above mentioned objects also including attachment
area 9
which are for the purpose of downward attachment. Both attachment areas may be
drilled or formed hollow at the time of manufacturing or marked or labeled or
similar for
the installer to drill out. Attachment areas 8 can be filled after
installation with push pins
8a of Figure 1 and Figure la which also function as a marking or a labelling
system
which could be words, letters, numbers, shapes with words, colors or letters,
numbers,
bar coding or similar embossed, cast or formed as part thereof as described in
Figure 1.
The conduit insert opening 3 and conduit cradle 2 are shown with the same
functions as
those previously describe.
[108] Figure 5 is illustrated as a replication of elements previously
described in Figure
3 as attachment area 9, conduit cradles 2, 2a and 2b and insert openings 3,3a
and 3b.
The main embodiment 1d now shows the same void 10 as described in Figure 4.
Figure
is shown now with attachment areas 8 for the side attachment a described in
Figure 4.
With multiple conduit cradles 2, 2a and 2b as described in Figure 3 the
importance of
the marking systems described previously becomes apparent. Attachment areas 8
complete with the push pins 8a of Figure 1 could be attached inside the
attachment
area 8 providing identification for the conduits being supported within any
given conduit
cradle 2, 2a and 2b. It is possible for these attachment areas 8 to be more
numerous
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
than the actual need for attachment locations to an object, however these
attachment
areas may still be part of the main embodiment 1d strategically placed for
only the
purpose of identification with the use of the push pins 8a of Figure 1.
[109] Figure 6 illustrates the main embodiment le now with a notched groove 11
which
runs the entire lateral length of the main embodiment le with further
proximity to the
bottom. This notched area may be sized exactly or within given tolerances to
allow for
the sliding or pushing of the main embodiment le inside a u-channel strut. An
arrow
shaped end or similar may be formed within the base of the main embodiment le
shown as angle cut lla for the purpose of providing less resistance for direct
placement
downward into u-channel strut when the u-channel strut is upright or the open
end is
facing the main embodiments le bottom. The main embodiment le may either be
pushed inside a u-channel strut or slide into such strut when the outward
ridge of the u-
channel strut matches up or line up with the inward notched groove 11 of the
main
embodiment.
[1101 Figure 7 illustrates a main embodiment if to where now the same notched
groove 11 is shown but in combination with multiple conduit cradles 2, 2a and
2b and
insert openings 3,3a and 3b this is again given as an example of more than one
conduit
cradle 2 and is not intended to limit the numbers or size of either. The same
base of the
main embodiment if and angle cut 11 a and notched groove 11 complete or
performs
the same duty and or function as described in Figure 6. The main element
change of
this figure is the inclusion of push pin openings 8b. The push pin openings 8b
are
formed in part or in whole of the main embodiment If for the purpose of
attachment of
push pins 8a of Figure 1 only as attachment to objects is not from the side
for this main
embodiment if. The intention is that the push pins 8a of Figure 1 are to be
inserted into
the push pin openings 8b of this figure for the purposes as described in
Figure 1 as a
marking or labelling system which could be words, letters, numbers, shapes
with words,
colors or letters, numbers or similar embossed, cast or formed as part
thereof. The use
of stickers or other could be adhered to the push pins 8a of Figure 1 for the
purpose of
marking or labelling also.
26
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[111] Figure 8 is a main embodiment 1g showing a conduit cradle 2 and insert
opening
3 with a base of the main embodiment 1g similar to that shown in Figure 6,
except that
the base is now open continuously throughout the main embodiment 1g
illustrated at the
base opening 12. The base opening 12 is provided or given as an allowance for
ease of
installation into u-channel strut where the base opening 12 allows for inward
movement
of the base legs 12a when inserted into u-channel strut. After the
installation, when the
inward notched groove 11 fits into the u-channel strut and around or mated
with the u-
channel strut outward groove the base legs 12a that were deflected inward at
the initial
time of installation return to the original resting state locking the main
embodiment 1g
into the u-channel strut. Marking and labelling will be accounted for within
the main
embodiment as described in the previous figures but is not shown in Figure 8,
this is
intentional. The base legs 12a may be formed where the bottoms have an angle
cut to
allow for ease of installation as illustrated in angle cut 11a.
[112] Figure 9 similar to Figures 3, 5 and 7 illustrates multiple conduit
cradles 2, 2a and
2b and insert openings 3,3a and 3b now for main embodiment lh. The narrative
or
descriptive writing will be similar to those given previous as is the
intention of those
noted above. Base legs 12a, base opening 12 and angle cut lla function in
relation to
or with the notched groove 11 and u-channel strut as described previous.
[113] Figure 10 now shown with a main embodiment as 1i with a knock out 13
that
when removed provides and acts like the base opening 12 of Figure 8. The knock
out
13 when intact and not removed functions and acts like the solid base of
Figure 6. This
intentional knock out 13 provides features of two bases within one base of the
main
embodiment 1i. Conduit cradle 2 and insert opening 3 are typical as described
elsewhere as is the notched groove 11 and angle cut 11a.
[114] Figure 11 as shown provides multiple conduit cradles 2, 2a and 2b and
insert
openings 3,3a and 3b without discrimination to numbers or sizes as described
previous.
27
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
The main embodiment 1j is shown now with the same knock out 13 as in Figure 10
with
notched groove 11 and angle cut 11a also described previous.
[115] Figure 12 shows a main embodiment 1k with a noticeable lower top section
or
lower plateau llb with raised ends or higher plateau 11c. The lower plateau
llb can be
formed within the main embodiment 1k for the purpose of recessing the cover
plate 5a
of Figure la. The recessed cover plate 5a of Figure la is anticipated to have
a level top
with the higher plateau 11c providing a streamline feature and a shallower or
lower
profile. This lower plateau lib as shown also acts as a holding area for cover
plate 5a
of Figure la and or platform 27 of Figure 35 which will be noticed and become
apparent
in later Figures 35 through 37 along with the lower plateau notch 1 1 f of
Figure 35. The
main embodiment lk has multifunctional means of attachment or bottoms or bases
which is shown as multi base lie in where any of the previous bottoms or bases
shown
are also included within main embodiment 1k, these are represented in Figures
2,4,6,8,
and 10. Conduit cradle 2 and insert opening 3 are shown with the same
representation
as those described previous.
[116] Figure 13 illustrates the same lower plateau 11 b and higher plateau 11c
of the
main embodiment lk of Figure 12. Now illustrated are multiple conduit cradles
2, 2a and
2b and insert openings 3,3a and 3b of main embodiment 11 which are shown again
without any discriminations as previously described in the above detailed
description of
the illustrations, including now the same multi base 11e.
[117] Figure 14, 15 and 16 illustrate the attachment of the main embodiment la
starting from Figure 14 which is a main embodiment la and cover plate 5a.
Figure 15 is
an exploded perspective view of the main embodiment la to where attachment
elements are being shown in what could be interpreted where attachment bolt
hardware
16 could be inserted through attachment area 9 and again through an optional
base
plate 14 through attachment area 9a into the top area 15a of a block type of
support 15
where the bottom area 15c could be resting or placed on a roof surface. The
cover clip
of Figure 14 could be reflective and an option is given for cover plates 5a of
Figure lb
28
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
wherein a light is also optional for areas when lighting is required or
desired, this is also
shown in Figure 17 and Figure 18. Other cover clip methods such as those in
later
descriptions are possible when so required or needed for protection or marking
as
shown in such figures as Figures 27 through Figure 34. Figure 16 shows a main
embodiment la attached to a block type of support 15.
[118] Figure 17 and Figure 18 perspective views showing elements of attachment
to a
block type of support 15a where Figure 17 is an exploded view and Figure 18 is
what
could be anticipated to be the final look of the completed attachment.
Starting now with
Figure 17 and the block type of support 15a which has a u-channel strut 17
attached.
The main embodiment la is shown with a flat bottom and will not recess or be
inserted
in the u-channel strut 17, this will be accomplished with the use of
conventional strut
clips 20 or a clip manufactured for this intention shown as base clip 19. The
intention of
the base clip 19 is for insertion into the u-channel strut 17 where the top
sides of the
base clip 19 mate with the outward elongated ridges 18 of the u-channel strut
17. A clip
tab 19a is provided for ease of installation giving the installer a grasping
point for
holding as the bolt hardware 16 is started into the clip threads 19b. The bolt
hardware
16 when inserted through the main embodiment la's attachment area 9 and the
base
plate 14 through the attachment area 9a may be threaded into the base clip 19
at clip
threads 19b or similar where the bolt hardware 16 could be tightened pulling
the base
clip 19 upward toward the elongated ridges 18 of the u-channel strut 17
simultaneously
drawing downward the main embodiment la and base plate 14 to where a hold fast
state is provided to the u-channel strut 17. The cover plate 5a which is shown
with a
light 5c could be fastened to the main embodiment la through openings that
might be
provided or marked as such at attachment area 9b. Figure 18 shows a main
embodiment la attached to u-channel strut 17 which is attached to a block type
of
support 15a in where the main embodiment la uses the base clip 19 of Figure
17. The
cover plate 5a is now shown on the top of the main embodiment la to where
representation is given for the bolt hardware 16 to be attached to the main
embodiment
la through attachment area 9b.
29
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[119] Figure 19 through 23 now show a main embodiment 1i which could be
inserted
into or inside or slid into a u-channel strut 17 then secured within that u-
channel strut 17
using an insert wedge 20 that is placed within the base opening 12. Figure 19
is shown
as a main embodiment 1i with attachment area 9, a notched groove 11 and angle
cut
11a having a base opening 12. Figure 20 shows an attachment means starting
with bolt
hardware 16 in which can be inserted through attachment area 9 which could be
located
at the outsides of the main embodiment 1i and or attachment area 9a which also
could
be provided inside conduit cradles 2 of the main embodiment 1i. Bolt hardware
16 which
is or could be threaded into wedge top opening 20a of Figure 21.Continuing now
with
Figure 20 the main embodiment 1i could be slid into a u-channel strut 17 or
pushed
through the top of a u-channel strut 17 to where an inward deflection is
assumed for
base legs 12a and base legs 12b. With the main embodiment 1i pushed into the u-
channel strut 17 and the inward notched groove 11 fitted into the u-channel
strut 17 and
around or mated with the u-channel strut 17 outward groove or elongated ridges
22 the
base legs 12a and base legs 12b that were deflected inward at the initial time
of
installation return to the original resting state locking the main embodiment
1i into the u-
channel strut 17. With the main embodiment 1i now established within the u-
channel
strut 17 the insert wedge 20 could be used as an extra measure to secure the
main
embodiment 1i. The insert wedge 20 could be placed within the base opening 12
and
then tightened by means of bolt hardware 16 which could be threaded into the
wedge
top opening 20a (illustrated in Figure 21) to where tightening downward within
the insert
wedge 20 the insert wedge 20 could be drawn upward into the base opening 12 of
Figure 20. The actions of the insert wedge 20 as described above will cause an
outward
force on the base legs 12a and base legs 12b toward the outside of the u-
channel strut
17 at the sidewalls 23a and sidewalls 23b of the u-channel strut 17. When bolt
hardware
16 is tightened the actions should also pull the base legs top 12c upward
toward the
elongated ridges 22 pressing the base legs top 12c against the bottom of the
elongated
ridges 22 at ridge bottom 22a of the u-channel strut 17 simultaneously drawing
downward the main embodiment 1i. Figure 21 as described above illustrates the
push
tab 7a, insert wedge 20, bolt hardware 16, wedge top opening 20a and wedge
bottom
opening 20b with the addition of pull tab 20c, pull tab grip 20e, pull tab top
20d. Figure
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
21 is now described with an option to the bolt hardware 16 in that of a pull
tab 20c. The
pull tab top 20d could be fed through the wedge bottom opening 20b and through
attachment area 9a of Figure 20 with the pull tab grip 20e ending at wedge
bottom
opening 20b. The pull tab 20c could after installation be simply rolled over
the push tab
7a and pulled upwards or away from the insert wedge 20; when the pull tab 20c
is
pulled to the engineered fatigue resistance release tolerance of pull tab grip
20e the pull
tab 20c would release and be pulled out of the insert wedge 20 and through the
main
embodiment 1i and attachment area 9a of Figure 20 securing the insert wedge 20
in
place. The elements of this Figure could be assembled prior to insertion into
u-channel
strut 17 for installation ease. Figure 22 shows now the main embodiment 1i
secured into
a u-channel strut 17 in which insert wedge 20 can be seen as a dotted outline.
Figure
23 illustrates the completed actions described above where the main embodiment
1i is
installed into u-channel strut 17.
[120] Figure 24 illustrates a main embodiment 1g attached to or placed over a
rectangular object 23 which could be metal or wood or similar. The main
embodiment
1g is illustrated with a rectangular object 23 inside the base opening 12 to
where secure
attachment is possible by the use of bolt hardware 16 which can pass through
attachment areas 9 or attachment areas 8 but friction fitting is possible to
where means
of conventional attachment is overruled. The notched area 11 can be provided
for push
tab 7a marking and labeling as described in Figure 1. Similar marking and
labelling is
possible in attachment area 8 also described in Figure 1.
[121] Figure 25 illustrates a main embodiment 1d attached to or placed over a
rectangular object 23 which could be metal or wood or similar, which could be
2x2, 2x4,
2x6 or similar. The main embodiment 1g is drawn with a rectangular object 23
inside the
base opening 12 to where secure attachment is possible by the use of bolt
hardware 16
which can pass through attachment areas 8 to where marking and labelling is
possible
by the use of push pins 8a where description is given in Figure 1.
31
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[122] Figure 26 main embodiment 1k is illustrated now with a front side lr and
backside elongated downward to encapsulate objects which is shown within this
figure
as a u-channel strut 17. The extended main embodiment lk appears now with a
top
bottom 1q and an outer bottom in which may be made of pliable material. The
outer
bottom in can have a spreadable interlock lm that can be manipulated and
opened
outward to accept an object such as u-channel strut 17. Once the actions of
opening
and placing the main embodiment 1k over the u-channel strut 17 the manipulated
material will again regain its original shape which can be pressed and locked
in place
with the interlock lm and secured with a screw or similar if so desired.
Marking and
labelling is now possible from the sides as shown in notched area 11 or in
attachment
area 8 but also now from the underside of the outer bottom In making labelling
or
marking visible from the bottom of the main embodiment lk.
[123] Figure 27 through 30 are illustrated giving drawing details for
attachment of a
protection method which is possible to be formed within the said inventions
embodiment
but here shown as an attachment cover clip protector 5b,5d, and 5e. Mention
was given
previous to protection means in Figure 1a and will now be described with
alternate
methods throughout Figure 27 to Figures 34. Figure 27 is now described as
cover clip
protector 5b and cover clip protector 5d in which the outside end walls are
solid and the
inside end walls have rod hollows 5f to where square rods 25a or pipe 25, or
similar can
be inserted. Bolt hardware 16 can be used to attach the cover clip protectors
5b or 5d
not only to the main embodiment la shown in Figure 29 but also could be
utilized and
attached to any similar device where sense can be made for physical protection
or can
be used as a marking system by where signage 26 can easily be attached to one
or
more of the square rods 25a or pipe 25. The use of signage 26 and the
inclusion of a
light 5c greatly improves keeping conduit systems noticeable and protected.
Figure 28
provides a detail in which square rods 25a and pipe 25 are inserted into the
corresponding square hollows 5g and rod hollows 5f where cover clip protector
5b and
cover clip protector 5d are used. Figure 29 now introduces the use of cover
clip through
protector 5e where it is possible to run or pass square rods 25a and pipes 25
32
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
completely through the cover clip through protector 5e. Conduit 6 is now shown
under
the cover clip protectors 5b and cover clip through protector 5e where conduit
6a
represents the continuation of conduit 6 to under cover clip protector 5d.
Cover clip
protectors 5b, cover clip through protector 5e and cover clip protector 5d are
installed
on a main embodiment 1a which is installed on a support 15c where bolt
hardware 16
can pass through attachment area 9 into the support 15c. Figure 30 gives a
detail to
one form of completed installation of cover clip protector 5b and cover clip
protector 5d
using pipe 25 installed over a main embodiment la as the protection medium for
a
conduit 6 which is installed inside the main embodiment 1a on a block type of
support
15c. Signage 26 is now shown attached to a protection pipe 25 providing
notification of
the conduit type, style, contents or similar. Figure 30 also provides in the
completed
installation a way to secure main embodiments 1a and block type of support 15c
together providing additional protection to conduit 6 components.
[124] Figure 31 through Figure 34 now illustrate another means of conduit
protection
where in Figure 31 a protection platform 27 is shown ready to install into
platform cover
clip protector 5g and platform cover clip protector 5h by way of the
installation slot 27a.
Attachment areas 9 are shown where Bolt hardware 16 can be inserted. Figure 32
provides an example of the use of platform cover clip protector center 5i
which is
installed between platform cover clip protector 5g and platform cover clip
protector 5h
where a light 5c is illustrated as an option. Platform 27 is illustrated now
with an option
of side protection 27a wherein platform 27 extends at a downward angle
illustrated as
perpendicular, but similar is possible. This now illustrated side protection
27a area may
include marking or labelling means for identification of the conduit and or
the conduits
contents or the conduits use. Vent air flow areas or inspection areas 27b may
be
provided. Figure 33 is shown with a conduit 6 installed within a main
embodiment la to
where the main embodiment la is installed on a block type of support 15c
without a
protection method. Attachment area 9 is formed as part thereof the main
embodiment
la or marked "attachment point" is illustrated to show where attachment points
are
possible to a block type of support 15c. Figure 34 is shown as a
representation of what
a completed installation of this means of protection could look like. A
protection platform
33
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
27 is shown installed between platform cover clip protector 5g and platform
cover clip
protector 5h to where protection is now provided to a conduit 6 which is
installed in a
main embodiment la attached to a block type of support 15c. Figure 34 also
provides in
the completed installation a way to secure single block type supports 15c
together
providing additional protection to conduit 6 components.
[125] Figure 35 through Figure 37 illustrates a protection method similar to
that shown
in Figures 31 through Figure 34 with noticeable changes. Further to those
protection
methods previously illustrated Figure 35 now illustrates an elongated device
described
as an under support 27a which can be used as a means to provide protection
from the
underside of conduit 6. The under support 27a also functions as a support for
semi
ridged conduits 6 wherein this elongated channel under support 27a may be
attached to
and between main embodiments lka and 1kb providing underlying support and
protection for entire lengths of semi ridged conduits 6. Under support 27a can
also be
marked and labeled on the underside for conduit 6 identification. Further to
under
support 27 Figure 35 now illustrates, a lower top section or lower plateau llb
with
raised ends or a higher plateau 11c, this is formed in the main embodiment lka
or 1kb
to allow for the protection platform 27 or the cover plate 5a to be set or to
rest within the
main embodiment lka or lkb. The lower plateau llb may have a lower plateau
notch
1 lf in which accommodation can be made for thicker structural member 11g if
provided
within a protection platform 27. This is now shown and may replicate within
any
embodiment as described or shown in drawings or figures of this DETAILED
DESCRIPTION. Figure 35 continues with description of the cover plate 5a where
an
attachment area 9 may be provided to aid in the attachment of bolt hardware
16. The
cover plate 5a may have a light 5c for visual indication or identification if
so desired. The
protection platform 27 may have attachment areas 16a provided as part of the
platform,
the attachment area 16a holes may be recessed to allow for flush mounting for
the bolt
hardware 16 if made of material that is solid; however, if expanded type
metals or other
materials are chosen or used the bolt hardware 16 would be chosen for each
material
type used. Attachment areas 9b can be provided to match or line up with the
attachment
areas 9b of the cover plate 5a and the attachment areas 16a of the protection
platform
34
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
27, or notification can be given to the particular area where bolt hardware 16
is to be
attached to remove mistakes made by the installer where damages could occur to
the
conduit 6. Figure 36 now shows a conduit 6 supported in a main embodiment lk
with
physical protection of the conduit 6 by means of the protection platform 27
which is
shown attached to the main embodiment lk with bolt hardware 16b. The above
description is shown to provide details of conduit 6 protection and as seen in
Figure 36
the flat top provides physical protection while providing a flat work surface
where
conduits 6 might be installed where workers might happen to stand or walk on
the
protection platform 27. Centerline cl illustrates physical side impact
protection wherein
any main embodiment or now illustrated as main embodiment lk has material
substance or a clear physical distance separation from the conduit 6. Figure
37 shows
another method of attachment of a cover plate 5a which is shown at cover plate
5w
wherein the cover plate 5w is without a light 5c of Figure 35 allowing for a
lower profile.
This lower profile can also be accomplished and installed level with the
protection
platform 27 when the cover plate 5a is manufactured to accept a protection
platform 27
that is formed to fit a lower inside of the lower plateau lib of Figure 35.
Figure 37 also
provides in the completed installation a way to secure main embodiments la
together
providing additional protection to conduit 6 components. Signage 26 is shown
where
additional labelling or marking can be provided or incorporated as part of
side protection
27c where signage is shown at 26a. Flagging 26c is also possible where
attachment is
possible when fitted into the main embodiment.
[126] Figure 38 illustrates a conduit 6 being supported within a conduit
cradle 2 where
now a protection insert opening 28a is illustrated with representation of
where a
protection platform 27 could be inserted. The protection insert opening 28a is
between
insert opening 3 and upper insert opening 3a Overlaying material 4 will not be
affected
by this now newly formed protection insert opening 28a.
[127] Figure 39 illustrates protection as formed in part or in whole of the
invention or a
main embodiment where cover plate 5a is illustrated having a light 5c. Cover
plate 5a
may be used to cover the main embodiment lm providing protection for conduit 6
or in
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
conjunction with the protection platform 27 which provides conduit 6
protection outside
of the main embodiment lm as well the conduit 6 within the main embodiment lm.
The
protection platform may have supporting structural members 11g which fit into
lower
plateau notch 1 1 f of the main embodiment 1m. After placement or fitting of
protection
platform 27 a filler cap 28 could be inserted into upper insert opening 3a of
the main
embodiment 1m.
[128] Figure 40 illustrates a conduit 6 being supported within a conduit
cradle 2 where
the top section above the conduit can be fitted with a slide cover 29 which
has an
elongated upper ridge 29c or a flat top side cover 29a without the elongated
upper ridge
29c. These covers as described can be fitted or slid into slide clip 4a
opening also
illustrated in Figure 2 where use is possible in any of the mentioned main
embodiments
throughout. Attachment will not affect overlaying material 4 when used.
[129] Figure 41 is a main embodiment 1m or "Single Block" in where a conduit
can be
inserted into the main embodiment lm as described previous within this
disclosure
including descriptions given in Figure 1 and Figure la.
[130] Figure 42 is described as a main embodiment in or "Insert Double Block"
in
where a conduit can be inserted into the main embodiment lm as previous
descriptions
disclosed within this writing in particularly in Figure 1 and Figure la.
Figure 42 illustrates
a lowered elevation within one support, device, or main embodiment described
now as
lower area 31 which is located between upper ridge 33R and upper ridge 33L;
this lower
elevation is intentional for the support of a conduit at two locations and for
support or
protection of a component attached to, or as part of a conduit such as a
coupling, valve,
union, flange, junction box, regulator, flow indicator or similar to these.
This intentional
lower area 31 now illustrated and described will be similar throughout the
writing and
the purpose is the same regardless of the main embodiments configuration, this
includes the lower area 31 of Figures 43 through Figure 47 and others as
reference or
illustrated. The lower area 31 will provide a controlled area for the purpose
of
component protection by supporting a component on all sides or attachment
points to a
36
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
conduit regardless of the attachment means of the component to a conduit. The
lower
area 31 will in addition provide an area for component inspection which
includes the
attachment methods used to attach the component such as welds, threads, clamps
or
similar, a testing area, which can include all aspects of testing such as leak
testing,
pressure testing, non destructive testing, bolt torque testing or similar to
these which
can include opening and closing of unions, junction boxes, valves or similar
to these.
The center to center distance from upper ridge to upper ridge or the center of
any upper
ridge to the middle or center of the lower area 31 dependent upon the conduit
circumference and the component attached to the conduit. The lower area 31
will
provide in addition to the above noted remarks as an option, lighting,
lighting
components, drainage areas or structural attachment points which may also
include
expansion and contraction provisions as described in Figure 52.
[131] Figure 43 can now be described similar to Figure 42 except now this main
embodiment 1p or "Double Block" does not cradle a conduit within the main
embodiment 1p; this "Double Block" is without conduit cradles 2 and insert
opening 3 as
illustrated and described in Figure 1 and la. This main embodiment provides
without
conduit insertion within one embodiment support for a conduit which can be
supported
at two locations while providing an open area for a component between the two
conduit
supporting areas within the same main embodiment 1p.
[132] Figure 44 can now be described as a main embodiment 1q or "Insert 90
Block" in
where a conduit can be inserted into the main embodiment lq as described
previous
including Figures 1 and Figure1a at two locations perpendicular to the first
while
providing an open area for a component between the two conduit supporting
areas
within the same main embodiment 1q.
[133] Figure 45 can now be described similar to Figure 44 except now this main
embodiment lr or "90 Block" does not cradle a conduit within the main
embodiment 1r;
this " 90 Block" is without conduit cradles 2 and insert opening 3 as
illustrated and
described in Figure 1 and la. Figure 45 can now be further described with
illustration of
37
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
the main embodiment lr or "90 Block" in where a conduit can be supported at
two
locations perpendicular to the first while providing an open area for a
component
between the two conduit supporting areas within the same main embodiment 1r.
[134] Figure 46 can now be described with illustration of a main embodiment is
or
"Insert T Block" in where a conduit can be inserted into the main embodiment
Is as
described previous including Figures 1 and Figure1a at three locations while
providing
an open area for a component between the three conduit supporting areas within
the
same main embodiment is.
[135] Figure 47 can now be described similar to Figure 46 except now this main
embodiment it or "T Block" does not cradle a conduit within the main
embodiment it;
this "T Block" is without conduit cradles 2 and insert opening 3 as
illustrated and
described in Figure 1 and la. Figure 47 can now be further described with
illustration of
a main embodiment it or "T Block" in where a conduit can be supported at three
locations while providing an open area for a component between the three
conduit
supporting areas within the same main embodiment it.
[136] Figure 48 is an illustration of a cover plate 5a and a main embodiment
1m where
the cover plate 5a can be attached to the main embodiment 1m by the use of
push pins
5d which are inserted into the push holes 5e located on the top of the main
embodiment
lm above the conduit 6. The conduit 6 is illustrated supported by the conduit
cradle 2
which is in the main embodiment lm. Dashed line segments 34 with arrow ends
are
included within the illustration to show a continuation of the support
including all
attributes of a main embodiment now and throughout the following or previous
descriptions or illustrations where sense can be made. For longer models where
repetitions are created break away cuts may be formed within a main embodiment
for
ease of separation and means to keep known distance separations constant. The
cover
plate 5a is illustrated with a light 5c incorporated as part of the cover
plate 5a as
described previous. Conduit 6 attachment to main embodiment lm is as described
in
38
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
the Summary and Descriptions of Figure 1 and Figure la or where similar
descriptions
are made.
[137] Figure 49 is described as a main embodiment lm in continuation of Figure
48 to
where now the cover plate 5a is attached to the main embodiment lm above
conduit 6
which is supported within the main embodiment lm by the conduit cradle 2
located
under the cover plate 5a. It is noticeable now the cover plate 5a provides
protection
above the conduit 6 where below and side protection is provided by the main
embodiment 1m.
[138] Figure 50 is illustrated to provide description for the use of other
hanger methods
which could be attached to a main embodiment lm. Parallel conduits 6 are
illustrated to
represent support methods where code, engineering or expansion of equipment or
conduits 6 require such attachment. This system of attachment is possible to
any aspect
or position of the main embodiment lm or other main embodiments where sense
can be
made including directly over top of another conduit 6 supported within or by
the main
embodiment lm as later described within other figures.
[139] Figure 51 is illustrated to provide description for the use u-channel
strut 17
supporting a conduit 6a above a conduit 6 which is installed in the main
embodiment
lm. The vertical distance may be decided depending on the length of threaded
rod 35
used to elevate the u-channel strut 17. Conduit 6 and conduit 6a separation by
vertical
distance in this manner or separation of conduits in general as illustrated
throughout the
drawings or illustrations in this disclosure provide improved methods for
distance
separation where heat gains or losses are possible when conduits are installed
in close
proximity to one and other or where distance separation could be enforced by
the
inspection body or authority having jurisdiction.
[140] Figure 52 describes a main embodiment in or "Insert Double Block" which
illustrates means of conduit 6 support at two locations upper ridge 33L, upper
ridge 33R
and where a component 30 is supported between the upper ridges on or within
one
39
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
support, device or main embodiment. This can be described now as main
embodiment
in which has two raised ridges at either side of a lower area 31. The
elevation change
or lower area 31 within the main embodiment in is intentional providing an
area for
inspection, testing or similar for components 30 within a conduit 6 while
providing
fundamental support on both sides of a component 30 at both ends of the
conduit 6.
Attachment of the conduit 6 can be made to the main embodiment ln for securing
a
conduit 6 which is placed inside the conduit cradles 2; critical areas are
supported with
equal respect providing in one conduit a support means to provide support at
two
locations of a conduit 6 while providing critical component support adding
strength to
the entire system. The lower area 31 may also provide a means for structural
fixed
attachment points 9s which may be incorporated at strategic places within the
lower
area 31 including the opposite side of those illustrated. The attachment
points 9s may
include a built in means for expansion and contraction engineering when so
desired or
required by code or hazard analysis. The fixed attachment points 9s built
within the
lower area 31 in one aspect can be accomplished by providing elongated slots
extending from one side to the other side where the length of the fixed
attachment
points 9s is determined by the coefficient of expansion for the particular
need.
Conventional attachment means such as screws, washers, glues, threaded rod,
nuts
and bolts or similar can be used as required for attachment through the
attachment
points 9s. The lower area 31 attachment points 9s may also function as
drainage areas
for water, condensate or similar. The lower area may be solid in formation
however ribs
or bosses may be added for strength or incorporated within to lessen the
overall
thickness. The thickness with additions of ribs or bosses throughout the lower
area 31
or main embodiment ln is possible to allow for a support of lighter overall
weight if so
desired without compromising the strength, durability, footprint for load
distribution,
drainage, vibration dampening, securing or other aspects of the invention. The
lower
area 31 may also provide an area for attachment of lighting and lighting
components
such as solar panels, batteries, and a light wherein description for all is
given as lighted
area 32. For areas in need of inspection or visibility during times of
impaired visibility
this lighted area 32 may be provided, this lighted area 32 also functions to
display areas
of notability such as maintenance tasks involving component manipulation or
similar is
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
required and or areas to where safe work practices must be maintained to avoid
trips,
falls or other hazards. Lighted area 32 may provide illumination by use of
stored energy
which can include solar lighting provided as an attachment to or be fixed
within the main
embodiment ln wherever so desired including mounting of lighting on upper
ridges or
vertical sides or slopes. No discrimination is given to the design for the
numbers of
repetitions of conduit 6 attachments or other descriptions, this is shown in
dotted
extension 34 as a continuation of the above noted remarks in a mirror like
fashion.
Further description can be described as given in Figure 1 and Figure 1a for
means of
conduit 6 insertion into the main embodiment in including but not limited to
cover
attachments, protection attachments, marking and similar aspects as sense
allows in
those descriptions as provided. Attachment of protection methods are possible
as
described through Figures 27 through 39. Cover attachment as illustrated in
this figure
are described as or with the use of a cover plate 5a which has or may have per-
determined attachment areas 9b or knockouts through which bolt hardware 16 can
be
inserted through the cover plate 5a into attachment areas 9 of the main
embodiment in.
The attachment areas at the main embodiment ln may be pre-drilled, marked or
indicated for its use or simply left to the installer to determine the
location as not all main
embodiments ln require a cover as shown at upper ridge 33L which is
intentionally
without a cover.
[141] Figure 53 is a main embodiment in or "Insert Double Block" where conduit
6a
stacking is illustrated using threaded rod 35 to elevate an additional conduit
6a above
conduit 6 which is supported within the main embodiment in. This allowance is
made
for space saving as well as when conduit 6 separation is required by designs
such as
gas conduit 6 separation from electrical conduits 6a. Threaded rod 35 or
similar may be
used for the elevation change which can be attached to the main embodiment ln
with
the use of nuts and washers 36. The nuts and washers 36 are additionally used
to
secure a cover plate 5a where the threaded rod 35 may pass through the cover
plate 5a
at attachment area 9. Alternative covers are possible as illustrated with the
use of cover
clip 5 which simply clips over the insert opening 3. The physical separation
for conduits
6 and conduit 6a may also be achieved within one embodiment without the
elevation
41
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
change if so desired with a replication of the main embodiment ln illustrated
as dotted
extension 34 as a continuation of the above noted remarks in a mirror like
fashion. This
allowance for the above noted may be used with some or all of the previous and
later
described main embodiments as determined by code and hazard assessments.
[142] Figure 54 is described with illustration of a main embodiment in having
protection provided by a protection platform 27 with the use of cover clip
protector 5h
and cover clip protector 5g. The assembly of the protection platform 27 with
cover clip
protector 5h and cover clip protector 5g is installed directly on the top
surface of the
main embodiment ln over the conduit 6 at either push holes 5e or alternatively
attachment areas 9. The push holes 5e or attachment areas 9 may be sized in
the same
manner to accept either push pins 5d or bolt hardware 16. If the method of
attachment
is with use of bolt hardware 16 the cover clip protector 5h may have openings
or
attachment area 9 for the bolt hardware 16 to pass through the cover clip
protector 5h
into the main embodiment ln or if the cover clip protector as shown on cover
clip
protector 5g has push pins 5d then attachment to the main embodiment in is
simply
completed by pushing the cover clip protectors 5g push pins 5d into the push
holes 5e
of the main embodiment in.
[143] Figure 55 is the completed movement of Figure 54 which is described now
as
"Insert Double Block" having complete protection for a conduit 6 with the
addition of the
protection platform 27 on the main embodiment in above the conduit 6. The
conduit 6 is
now protected from physical damages that might be occurred while allowing the
conduit
6 expansion and contraction flexibilities within the main embodiment in.
[144] Figure 56 described now wherein a main embodiment 1p or "Double Block"
illustrates means of conduit 6 support at two locations upper ridge 33L, upper
ridge 33R
providing component 30 support. The main embodiment 1p can be described as a
support which has two raised ridges at either side of a lower area 31. The
elevation
change or lower area 31 within the main embodiment 1p is intentional providing
an area
for inspection, testing or similar for components 30 within a conduit 6 while
providing
42
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
fundamental support on both sides of a component 30 at both attachment ends of
the
conduit 6. This now described main embodiment 1p is similar to that of the
"Insert
Double Block" of Figure 52 with the noticeable, now not included, insert
opening 3 or
conduit cradle 2 which is intentional to this design. The conduit of this main
embodiment
1p is to be supported on the top of upper ridge 33L and upper ridge 33R with
conventional hangers or similar while continuing to also provide support at
both sides of
a component 30. The support continues to have attributes such as lighted area
32,
attachment points 9s and lower area 31 as described in previous descriptions
of the
same. This as with other illustrations and descriptions is illustrated with
the use of
dotted extension 34 illustrating a continuation of the main embodiment and its
features.
[145] Figure 57 and 58 are illustrated and described to illustrate other forms
of support
of a conduit 6 on the upper ridge 33L and upper ridge 33R for main embodiment
1p;
whatever the attachment means to this main embodiment the design of the
support is
as described previous where component 30 is supported and protected including
two
points of contact on one main embodiment 1p for a conduit 6.
[146] Figure 59 is described now with illustration wherein a main embodiment
1q or
"Insert 90 Block" illustrates means of conduit 6 support in which support is
provided to
directional change of conduits 6 including support of the components 30. The
main
embodiment 1q can be described as a support with two raised portions upper
ridge 33L
and upper ridge 33R perpendicular to one and another with one or more lower
areas
described as lower area 31 and lower area 31a. The lower areas are intentional
providing an area for inspection and testing or similar for components 30
within a
conduit 6 while providing fundamental support on both sides of a component 6
where
attachments can be made to the main embodiment 1q for securing a conduit 6
into a
conduit cradle 2; critical areas are supported with equal respect providing in
one conduit
support a means to provide support at two locations while providing component
protection adding strength to the entire system in this embodiment that
provides support
at directional changes. The lower area 31 or lower area 31a may also provide a
means
for structural fixed attachment points 9s which may be incorporated at
strategic places
43
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
including opposite of those illustrated on lower area 31 including lower area
31a which
may also include built in expansion and contraction engineering for both lower
areas
when so desired or required by code or hazard analysis. Lower area 31a as
illustrated
could be omitted in some cases. The fixed attachment points 9s may be built
within the
lower area 31 and or lower area 31a, this can be accomplished by providing
elongated
slots extending from one side to the other side where the length of the fixed
attachment
points 9s are determined by the coefficient of expansion for the particular
need.
Conventional attachment means such as screws, washers, glues, threaded rod,
nuts
and bolts or similar can be used as required for attachment through the
attachment
points 9s. The lower area 31 and lower area 31a attachment points 9s may also
function as drainage areas for water, condensate or similar. The lower areas
may be
solid in formation, however, ribs or bosses may be added for strength or
incorporated
within to lessen the overall thickness. The thickness with additions of ribs
or bosses
throughout the lower area 31, lower area 31a, or main embodiment lq is
possible to
allow for a support of lighter overall weight if so desired without
compromising the
strength, durability, footprint for load distribution, drainage, vibration
dampening,
securing or other aspects of the invention. The lower area 31 and lower area
31a can
be described in the same as described for lower area 31 of Figure 52 for
lighted area 32
and attachment points 9s. No discrimination is given to the design for the
numbers of
repetitions of conduit 6 attachments or other descriptions, this is
illustrated in dotted
extension 34 as a continuation of the above noted remarks in a mirror like
fashion.
Raised portions, upper ridge 33L and upper ridge 33R may incorporate other
conduit
support means above the conduit 6 which is inserted into the conduit cradle 2
as
described elsewhere within this writing. Cover plate 5a is illustrated above
the main
embodiment 1q; however, to have upper ridge 33R unobstructed in the
illustration the
cover plate 5a of the illustration is not attached to the main embodiment lq
and
direction is given now that attachment is possible in the same manner as
previous
descriptions provided for such attachment.
[147] Figure 60 is a main embodiment lr or "90 Block" illustrating means of
conduit 6
support in which support is provided to directional change of conduits 6
including the
44
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
protection of components 30. The main embodiment lr is similar to that of the
"Insert 90
Block" of Figure 59 with the noticeable, now not included, insert opening 3 or
conduit
cradle 2 which is intentional to this design. The conduit 6 is now shown
supported on
the top of upper ridge 33L and upper ridge 33R with conventional hangers or
similar and
as illustrated now with u-channel strut 17 while continuing to also provide
support at
both sides of a component 30. The support continues to have attributes such as
lighted
area 32, attachment points 9s, lower area 31 and lower area 31a as described
previous
including those descriptions in Figure 59. Attachment points 9s when included
function
and perform the same as those in previous description including dotted
extension 34 as
a continuation of the above noted remarks in a mirror like fashion.
[148] Figure 61 and Figure 62 are illustrated and described to illustrate
other forms of
support of a conduit 6 on the upper ridge 33L and upper ridge 33R for main
embodiments 1r; whatever the attachment means, main embodiment lr provides the
same protection and support as described previous where component 30 is
supported
including two points of contact on one main embodiment lr for a conduit 6.
[149] Figure 63 is described as a main embodiment is or "Insert T Block" which
illustrates means of conduit 6 support in three locations upper ridge 33R,
upper ridge
33L and upper ridge 33M where a change of direction of a conduit 6 extends
outward at
a 90-degree angle or branch line forming a tee intersection where conduit 6
continues in
a same directional path as the original directional path from upper ridge 33R
to upper
ridge 33L. The main embodiment Is is now described illustrating an elevation
change or
lower area 31, lower area 31a and lower area 31b illustrated in Figure 71. The
lower
areas are intentional providing an area for inspection, testing, lighting, or
similar to those
listed for components 30 within a conduit 6 system as described previous
including
descriptions in Figure 42 for lower area 31. Upper ridge 33R, upper ridge 33L
and upper
ridge 33M provide fundamental support on three sides of a component 6 where
attachments can be made to the main embodiment is for securing a conduit 6;
critical
areas are supported with equal respect providing in one main embodiment is a
means
to provide support at three locations while providing complete component
protection
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
adding strength to the entire system. The lower area 31 of this figure and
lower areas
31a and 31b illustrated in Figure 71 now described create three lower areas
which may
when required also provide a means for structural fixed attachment points 9s
which may
be incorporated at strategic places including opposite of those illustrated on
lower area
31 including diagonal lower areas which may also include built in expansion
and
contraction engineering for all lower areas when so desired or required by
code or
hazard analysis. Diagonal lower areas to lower area 31 could be omitted in
some cases
or made angular. The fixed attachment points 9s may be built within the lower
areas 31,
and 31a and 31b illustrated in Figure 71, this can be accomplished by
providing
elongated slots extending from one side to the other side where the length of
the fixed
attachment points 9s are determined by the coefficient of expansion for the
particular
need. Attachment means such as screws, washers, glues, threaded rod, nuts and
bolts
or similar can be used as required for attachment through the attachment
points 9s. The
lower areas 31 and 31a and 31b as described in Figure 71 including lower areas
attachment points 9s may also function as drainage areas for water, condensate
or
similar. The lower areas may be solid in formation, however, ribs or bosses
may be
added for strength or incorporated within to lessen the overall thickness. The
thickness
with additions of ribs or bosses throughout the lower areas including the
upper ridge
33R, upper ridge 33L and upper ridge 33M is possible to allow for a main
embodiment
is of lighter overall weight if so desired without compromising the strength,
durability,
footprint for load distribution, drainage, vibration dampening, securing or
other aspects
of the main embodiment is. The lower area 31 may also provide an area for
attachment
of lighting and lighting components such as solar panels, batteries, and a
light wherein
description for all is given as lighted area 32. For areas in need of
inspection or visibility
during times of impaired visibility this lighted area 32 may be provided, this
lighted area
32 also functions to display areas of notability such as maintenance tasks
involving
component manipulation or similar is required and or areas to where safe work
practices must be maintained to avoid trips, falls or other hazards. Lighted
area 32 may
provide illumination by use of stored energy which can include solar lighting
provided as
an attachment to or be fixed within the main embodiment in wherever so desired
including mounting of lighting on upper ridges or vertical sides or slopes or
other lower
46
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
areas of this main embodiment is. Figure 63 is now described further to
illustrate the
conduit 6 attachment to main embodiment is by the same description given
previous
including Figures 1 and la. The main embodiment is or "Insert T Block" as
illustrated is
represented showing a flat top with sloping sides which progress downward to
the base
with straight lines, this illustration is a basic shape and is to be described
as a general
design. Regardless of the shape a critical aspect is the main embodiment is
upper
ridges on all connecting points of a component 30. In some aspects of the
inventive
features other shaped main embodiments is are included within the design which
perform the same support on all sides of a component 30. The main embodiment
is or
"Insert T Block" may in some models be square shaped, rectangular shaped, or
of a
shape that allows component 30 support with the above noted features and
allowance
is made for lower areas to be angular shaped or similar.
[150] Figure 64 is described similar to that of Figure 63 in that the main
embodiment is
provides component protection while supporting a conduit system at three
locations.
Figure 64 is with the addition of conduit 6a which is elevated above conduit 6
with the
use of u-channel strut 17, threaded rod 35 where attachment to the main
embodiment
is at upper ridges 33R and 33L is with the use of nuts and washers 36. Cover
plate 5a
is installed on upper ridge 33M.
[151] Figure 65 describes a main embodiment it or "T Block" which illustrates
means
of conduit 6 support in where a change of direction is possible while
supporting the
conduit in a same directional path as the original, thus providing support for
the conduit
6 at three positions while protecting a component 30. The main embodiment it
can be
described as a support with three raised sections or upper ridges as
illustrated in Figure
71 and described in previous including the description of Figure 63 for the
upper ridges
and with one or more lower portions or lower area 31 and lower areas 31a and
31b
illustrated in Figure 71 also described previous including the description
given in Figure
63.The main embodiment it in all respects can be described the same as Figure
63
except that now illustrated with the intentional omission of the insert
opening 3 and
conduit cradle 2. This omission of insert opening 3 and conduit cradle 2 is
done
47
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
purposefully to form a main embodiment for conduit 6 attachment on the top of
the
upper ridges wherein a conduit is not supported within a conduit cradle and
now
illustrated using hanger hardware 17a.
[152] Figure 66 and Figure 67 are described and illustrated to show other
methods of
hanger hardware 17a and attachment for conduits 6 to the main embodiment it
where a
component 30 is between three conduit 6 attachment points.
[153] Figures 68 through Figure 71 are now described and illustrated in plan
view to
show main embodiments "Insert Single Block", "Insert Double Block", "Double
Block",
"Insert 90 Block", "90 Block" "Insert T Block" or "T Block". These are general
examples
only; however, one can see the function and importance through these examples
of how
the components 30 are supported in close proximities to conduits 6, 6a or 6b
attachment points to or within upper ridge 33R or upper ridge 33L or upper
ridge 33M
provided within one main embodiment. These illustrations are general and
illustrations
as such are described generally as to not limit the intentions of the
inventive features as
described within this disclosure. However, a plan view of the main embodiments
could
provide another view of the use of the main embodiments. The conduits within
this
description for the purpose of illustration are named as; Conduit 6 is a
threaded type
where the attachment to the component 30 is screwed. Conduit 6b is a socket
weld type
where the attachment to the component 30 is welded. Conduit 6a is a wire.
These
Figures 68 through Figure 71 may all have a lighted area 32 near or under a
component
30 in the lower area 31 with the exception of the singular main embodiment of
Figure 68
in which a light 5c is illustrated as part of a cover plate 5a which is
installed over the
conduit 6 or 6a. The attachment points 9s are shown through the illustrations
mainly in
the lower areas however with a singular support these attachment points 9s are
on the
sides of a main embodiment. Lower areas 31a and lower area 31b may be optional
or
angular cut or similar. Critical component support is now seen; by providing
multiple
points of contact for a conduit in close proximity to a component 30 it is
evident that not
only the conduits are supported better but now the components as well can be
protected from damages which could occur.
48
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
[154] Figure 72 described and illustrate the top single support or any upper
ridge 33L,
33R, 33M or higher plateau 11c of Figure 1a. This main embodiment lme of this
figure
is illustrated to show an example in plan view for a push hole 5e which is a
dedicated
intentional area within a main embodiment lme for the attachment of push pins
5d of
Figure lb or similar throughout this disclosure.
[155] Figure 73 is described with illustration of the bottom of a single
support or any
upper ridge 33L, 33R, 33M or higher plateau 11c of Figure la. The bottom of
main
embodiment lme may be solid or as illustrated now formed with a hollow area
lhb
where description is given with illustration that push holes 5e of Figure 72
intentionally
do not extend entirely though the main embodiment lme, this option is provided
to allow
for conduit and cover ejection or release when required due to extreme
pressure which
could occur by structural fatigue or similar. The push pins 5d as described
throughout
this disclosure are fitted by friction or pressure into the push holes 5e also
described
throughout this disclosure do not grip to the underside of a support or upper
ridge
however small drainage holes inside the bottom of the push holes 5e may be
present
and extend completely through the main embodiment lme.
[156] Figure 74 described and illustrate the top of any single support or
upper ridge
33L, 33R, 33M within this disclosure or higher plateau 11c of Figure la. This
figure
illustrates a recessed area 5ra which may be used to fit a nut or washer or
combination
of these or similar hardware into the upper ridge topside allowing the
completed action
of tightening to be flush with the topside of an upper ridge. This recessed
area 5ra may
have the center inner portion 1ci removed or void not formed as part of the
main
embodiment lme to allow passage of threaded rod 35 or similar of Figure 53
though the
main embodiment lme to the underside of an upper ridge.
[157] Figure 75 is a description of the bottom of a single support or any
upper ridge
33L, 33R, 33M or higher plateau 11c of Figure la. It can be noticed with
illustration and
description now that the center inner portion lci passes or extends completely
though to
49
CA 3020618 2018-10-12
main embodiment lme. Now on the underside of the upper ridge another recessed
area
5ra appears for the purpose of nut and washer placement as described in Figure
74.
This now described recessed area 5ra may also be molded to mimic the shape of
a nut
or bolt head or similar allowing a nut to be held in place without the use of
tools for the
purpose of installation. This recessed area 5ra may additionally serve as a
grip area for
push pins 5d; this can be accomplished when the push pins 5d are flared out at
the
bottom as illustrated in Figure 76.
[158] Figure 76 is described now similar to the push pins 5d of Figure la and
Figure 73
with noted or described differences where push pin 5d has flared ends 5fe
which are
inserted into or through center inner portion lci of Figure 75. The push pins
5d deflect
inward as the flared ends press against the walls of center inner portion 1ci
compressing the push pin 5d and flared ends 5fe at relief opening 1ro. Once
the action
of insertion is complete and the flared ends 5fe reach the recessed area 5ra
illustrated
in Figure 75 the compressed push pin 5d and flared ends 5fe resume there
original
shape as center inner portion 1ci wall pressure is removed. The flared ends
now larger
than the circumference of the center inner portion 1ci grip the underside of
an upper
ridge holding in place cover plate 5a. The distance of travel through a main
embodiment
for the push pin 5d or other attachment hardware is dependent upon the
thickness of a
main embodiment which may be less than the outer vertical distance from base
to
height as the inner areas of main embodiments may be made hollow or void of
materials when so desired at the time of manufacturing as illustrated and
described as
hollow block lhb of Figures 73 and Figure 75. This hollow block lhb is not
intended to
defeat the functions of recessed area 5ra and allowance is made for recessed
area 5ra
no mater the thickness of the main embodiment.
CA 3020618 2018-10-12