Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
SELF-PROPELLED CONVEYOR WITH PERPENDICULAR LATERAL
MOVEMENT
This disclosure relates to the field of self-propelled conveyors and in
particular self-
propelled conveyors with movement in an operating travel direction along a
conventional
path and perpendicular lateral movement at ninety degrees with respect to the
operating
travel direction along a lateral path.
BACKGROUND
Portable belt and auger conveyors are used in many industries for moving
granular
material. In the agricultural industry for example gains, oilseeds,
fertilizer, and the like
must often be transported from a harvesting implement, transferred to a
storage bin, and
then transferred from the bin to a transport vehicle again to be carried to
market, or to
seeding or fertilizer implements in the field.
These conveyors typically are mounted on a conveyor frame that is supported on
wheels
for movement in an operating travel direction. They have an input at a rear
lower end
and an output at an upper forward end. In a typical agricultural application
the conveyor
will be moved into a position where the input is located under the discharge
opening of a
transport vehicle and the output is oriented to discharge conveyed granular
material into
the top opening of a bin.
In one common type of conveyor the conveyor frame is mounted on two front
frame
wheels fixed to rotate in an operating travel direction. The frame is
configured to move
the upper output end of the conveyor up and down with respect to front frame
wheels,
and with respect to the lower input end that rests on the ground. The conveyor
is
balanced so most of the weight is on the front frame wheels, and the lower
rear end
17911377v1
CA 3028763 2019-01-02
resting on the ground is relatively light. Movement is accomplished by picking
up the
lower end and pushing and pulling the conveyor into the desired position.
As conveyors have become larger, various drive systems have been added, for
example
as disclosed in United States Patent Number 8,365,896 to Jesse. Jesse
discloses an un-
driven steerable wheel to support the lower end, and a pair of driven wheels
attached to a
front axle of the frame which are lowered into contact with the ground and
rotated to
move the conveyor.
Similarly United States Patent Number 4,650,058 to Vaughn discloses in one
embodiment a drive apparatus connected to drive the conventional front wheels
supporting the conveyor frame. United States Patent Number 4,714,149 to Tiede
discloses a conveyor mounted on what is essentially a small vehicle operative
to lift and
lower the upper and lower ends, and to steer and propel the conveyor into a
desired
position.
To improve maneuverability United States Patent Numbers 8,033,376 and
8,033,384 to
Toews et al. disclose front frame wheels that are steered by hydraulic
cylinders activated
from a towing tractor.
United States Patent Number 6,805,229 to Dekoning discloses an extendable
conveyor
which further facilitates positioning the conveyor input and the conveyor
output at the
desired locations.
Maneuverability is an important consideration since in a typical agricultural
harvesting
operation a farmer will have a plurality of bins at a location and the
conveyor must be
maneuvered with respect to each bin to both a bin loading position, where the
upper
output is oriented to discharge into the bin's top opening, and the lower
input is accessible
for receiving granular material from the discharge opening of a transport
vehicle, and a
17911377v1 2
CA 3028763 2019-01-02
bin unloading position where the lower input is oriented to receive material
from the
discharge opening of the bin, and the upper output is oriented to discharge
granular
material into a transport vehicle.
Similarly in a typical agricultural seeding operation, a farmer will have an
air seeder tank
=
with a plurality of compartments each of which must be filled with seeds or
fertilizers of
various kinds. A conveyor, commonly mounted to the air seeder tank cart, must
be
maneuvered in coordination with a transport vehicle to receive granular
material from the
transport vehicle while the upper input end is directed into the selected tank
compartment.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present disclosure provides a conveyor apparatus that overcomes problems
in the
prior art.
The present disclosure provides a conveyor apparatus comprising a conveyor
frame
mounted on front and rear wheels for movement along the ground, and a conveyor
mounted on the conveyor frame such that an upper output end of the conveyor is
forward
of the front wheels and a lower input end of the conveyor is rearward of the
conveyor .
frame. A drive system is connected to rotate the front and rear wheels. The
front and
rear wheels are movable from a conventional orientation where rotational axes
of the
front and rear wheels arc substantially perpendicular to a longitudinal axis
of the
conveyor and the drive system rotates the front and rear wheels to move the
conveyor
frame along a conventional path, to a lateral orientation where the rotational
axes of the
front and rear wheels are substantially parallel to the longitudinal axis of
the conveyor
and the drive system rotates the front and rear wheels to move the conveyor
frame along
a lateral path.
17911377v1 3
CA 3028763 2019-01-02
The present disclosure provides a conveyor apparatus capable of moving in
forward and
rearward along a conventional path aligned with the longitudinal axis of the
conveyor, or
along a lateral path perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the conveyor.
Time spent
positioning the conveyor is significantly reduced.
DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
=
While the invention is claimed in the concluding portions hereof, preferred
embodiments
are provided in the accompanying detailed description which may be best
understood in
conjunction with the accompanying diagrams where like parts in each of the
several
diagrams are labeled with like numbers, and where:
Fig. 1 is a schematic top view of an embodiment of the conveyor apparatus of
the
present disclosure;
Fig. 2 is a schematic side view of the embodiment of Fig. 1;
Fig. 3 is a schematic top view of the conveyor frame of the embodiment of Fig.
1 with
front and rear wheels in the conventional orientation;
Fig. 4 is a schematic top view of the conveyor frame of the embodiment of Fig.
1 with = .
front and rear wheels in the lateral orientation;
Fig. 5 is a schematic cutaway view of the reversing valve of the embodiment of
Fig. 1;
Fig. 6 a schematic top view of the conveyor frame of an alternate embodiment
of the
conveyor apparatus of the present disclosure with front and rear wheels in the
conventional orientation;
17911377v1 4
CA 3028763 2019-01-02
Fig. 7 is a schematic top view of the conveyor frame of Fig. 6 with front and
rear
wheels in the lateral orientation;
Fig. 8 is a schematic top view of an alternate rear wheel assembly with dual
wheels;
Fig. 9 a schematic top view of the conveyor frame of a further alternate
embodiment of
the conveyor apparatus of the present disclosure with front and rear wheels in
the
conventional orientation;
Fig. 10 is a schematic top view of the conveyor frame of Fig. 9 with front and
rear
wheels in the lateral orientation;
Fig. 11 a schematic top view of the conveyor frame of another further
alternate
embodiment of the conveyor apparatus of the present disclosure with front and
rear
wheels in the conventional orientation;
Fig. 12 is a schematic top view of the coiweyor frame of Fig. 11 with front
and rear
wheels in the lateral orientation;
Fig. 13 is a schematic top view of the embodiment of Fig. 1 in position to
receive =
granular material from a transport vehicle and convey same into one of a line
of gain .
bins;
Fig. 14 is a schematic top view of the embodiment of Fig. 1 in position to
receive
granular material from a transport vehicle and convey same into compartments
of an
air seeder tank cart.
17911377v1 5
CA 3028763 2019-01-02
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE ILLUSTRATED EMBODIMENTS
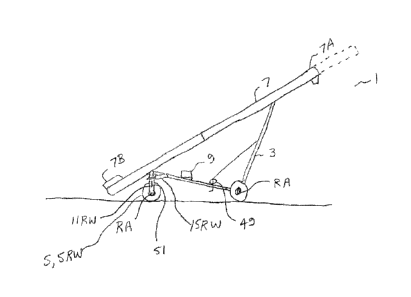
Figs. 1 ¨ 5 schematically illustrate an embodiment of a conveyor apparatus 1
of the
present disclosure. The apparatus 1 comprises a conveyor frame 3 mounted on
front and
rear wheels 5 for movement along the ground. A conveyor 7 is mounted on the
conveyor
frame 3 such that an upper output end 7A of the conveyor is forward of the
front wheels
5F and a lower input end 7B of the conveyor 7 is rearward of the conveyor
frame 3. The
frame 3 is configured to raise and lower the upper output and lower input ends
7A, 7B to
desired operating positions as is known in the art.
A drive system 9 is connected to rotate the front and rear wheels 5. The front
and rear
wheels 5 are movable from a conventional orientation shown in Figs. 1, 2, and
3, where
rotational axes RA of the front and rear wheels 5 are substantially
perpendicular to a
longitudinal axis LA of the conveyor 7 and the drive system 9 rotates the
front and rear
wheels 5 to move the conveyor frame 7 in forward and reverse directions along
a
conventional path CP, to a lateral orientation shown in Fig. 4 where the
rotational axes
RA of the front and rear wheels 5 are substantially parallel to the
longitudinal axis LA of
the conveyor 7 and the drive system 9 rotates the front and rear wheels 5 to
move the
conveyor frame 3 in rightward and leftward directions along a lateral path LP.
The right and left front wheels 5FR, 5FL are mounted on corresponding right
and left
front wheel assemblies 11FR, 11FL pivotally attached to corresponding right
and left
ends of a front axle 13 of the conveyor frame 3 about vertical pivot axes FPA.
A front
wheel actuator, illustrated as right and left front hydraulic cylinders 15FR,
15FL, is
connected to pivot the right and left front wheel assemblies 11FR, 11FL with
respect to
corresponding right and left ends of the front axle 13 of the conveyor frame 3
to move the
corresponding right and left front wheels 5FR, 5FL from the conventional
orientation of
Fig. 3 to the lateral orientation of Fig. 4
17911377v1 6
CA 3028763 2019-01-02
In the apparatus 1, the right and left front wheel assemblies 11FR, 11FL pivot
in the same
direction forward with respect to the front axle 13 to move the corresponding
right and
left front wheels from the conventional orientation to the lateral
orientation. It is
contemplated that both of the right and left front wheel assemblies 11FR, 11FL
could
.. also pivot rearward with respect to the front axle 13 to move the
corresponding right and
left front wheels from the conventional orientation to the lateral orientation
if preferred.
The drive system 9 rotates the right and left front wheels in the same first
rotational
direction RD as shown in Fig. 3 to move the conveyor frame 3 in a forward
direction
along the conventional path CP. However when the wheels 5 move to the lateral
orientation shown in Fig. 4 it can be seen that if the front left wheel 5FL is
rotated in
direction RD and the front right wheel is rotated in direction RD the wheels
will both roll
toward the center of the conveyor frame 3, and movement will not be possible.
The drive
system 9 is therefore arranged so that when the wheels 5 move to the lateral
orientation,
the drive system 9 rotates the right front wheel in the first rotational
direction RD and
rotates the left front wheel in an opposite second rotational direction RD' to
move the
conveyor frame 3 along the lateral path LP.
In the illustrated apparatus 1, the drive system 9 comprises a front right
hydraulic motor
17FR connected to drive the front right wheel 5FR and a front left hydraulic
motor 17FL
connected to drive the front left wheel 5FL. The drive system 9 here is
provided by a
hydraulic pump 9A driven by a motor 9B, and control valves 9C. The illustrated
drive
system 9 comprises a reversing valve 19 linked to the front left wheel
assembly 11FL and
to the corresponding front left hydraulic motor 17FL, such that when the front
left wheel
5FL on the front left wheel assembly 11FL moves from the conventional
orientation to
the lateral orientation, hydraulic fluid flow through the front left hydraulic
motor 17FL is
reversed.
17911377v1 7
CA 3028763 2019-01-02
Fig. 5 schematically illustrates the reversing valve 19 with hydraulic
conduits 27 from the
drive system 9 and hydraulic conduits 29 connected to the front left hydraulic
motor
17FL. In a conventional mode the reversing valve 19 directs pressurized
hydraulic fluid
out in direction A and the hydraulic fluid returns in direction B, while in a
lateral mode
the reversing valve 19 directs pressurized hydraulic fluid to the hydraulic
motor 17FL in
the opposite direction A' and the hydraulic fluid returns in direction B',
such that the front
left wheel 5FL rotates in the opposite direction.
Figs. 3 and 4 schematically illustrate a wand 21 attached to the front right
wheel
assembly 11FL and a switch 23 extending from the reversing valve 19. As the
front left
wheel 5FL on the front left wheel assembly 11FL moves from the conventional
orientation shown in Fig. 3 to the lateral orientation shown in Fig. 4, the
wand 21
contacts the switch 23 and moves the valve body 25 to the lateral mode, and
when the
front left wheel 5FL on the front left wheel assembly 11FL moves back from the
lateral
orientation shown in Fig. 4 to the conventional orientation shown in Fig. 3,
the wand 21
again contacts the switch 23 and moves the valve body 25 to the conventional
mode.
Figs. 6 and 7 schematically illustrate an alternate embodiment of the conveyor
apparatus
101 of the present disclosure (the conveyor itself is not shown for clarity of
illustration)
where the right and left front wheels 10FR, 105FL attached to corresponding
right and
left front wheel assemblies 111FR, 111FL are pivoted by the hydraulic
cylinders 115FR,
115FL in opposite directions forward and rearward with respect to the front
axle 113
when moving from the conventional orientation shown in Fig. 6 to the lateral
orientation
shown in Fig. 7. In this apparatus 101 the drive system 109 rotates the right
and left front
wheels 10FR, I05FL in the same rotational direction RD to move the conveyor
frame
103 along both the conventional path CP and the lateral path LP. Hydraulic
condnits 127
carry pressurized hydraulic fluid directly to the front hydraulic motors
117FR, 117FL and
no reversing valve is required.
17911377v1 8
CA 3028763 2019-01-02
In the illustrated apparatus 1 a single rear wheel 5RW is mounted on a rear
wheel
assembly 11RW, and the rear wheel assembly 11RW is pivotally attached to a
rear
portion of the conveyor frame 3 about a substantially vertical pivot axis RPA
under a
lower portion of the conveyor 7. The drive system rotates the rear wheel 5RW
in the
same rotational direction RD to move the conveyor frame 7 along both the
conventional
path CP and the lateral path LP.
A rear wheel actuator, hydraulic cylinder 15RW, is connected to pivot the rear
wheel
assembly 11RW with respect to the conveyor frame 3 to move the rear wheel 5RW
from
the conventional orientation of Fig. 3 to the lateral orientation of Fig. 4.
Conveniently the
front wheel actuator, provided by hydraulic cylinders 15FR, 15FL, and the rear
wheel
actuator, provided by hydraulic cylinder 15RW, are linked such that the front
and rear
wheels 5 move between the conventional orientation and the lateral orientation
together.
This can be accomplished for example by directing hydraulic fluid into the
front and rear
hydraulic cylinders 15 at the same time, or by slaving the hydraulic cylinders
15 such that
hydraulic fluid flows from into the other as is known in the art.
=
In either the conventional or lateral orientation, the front and rear wheels 5
are rotated =
together in either direction by pressurized hydraulic fluid directed by
control valves 9C.
The apparatus 101 shown in Figs. 6 and 7 uses the same rear wheel arrangement.
The
control valves 9C can be configured to rotate the front and rear wheels 5 at
the same
speed to move the conveyor apparatus 1 directly along the lateral path LP, or
can be
operative to rotate the front and rear wheels 5 at a different speeds such
that the upper
output end 7A of the conveyor 7 moves faster or slower than the lower input
end 7B of
the conveyor such the apparatus 1 can be steered right or left along the
lateral path LP.
To facilitate some manual steering guidance the control valves 9C can also be
configured
to allow the rear wheel 5RW to rotate freely in either direction when the
front wheels
5FR, 5FL are rotated in either direction.
17911377v1 9
, =
CA 3028763 2019-01-02
Fig. 8 schematically illustrates an alternate dual rear wheel assembly 11RW
where first
and second rear wheels 5RWA', 5RWB' are mounted on the rear wheel assembly
11RW'
about a common rotational axis and the rear wheel assembly 11RW' pivots about
the
vertical pivot axis RPA.
While it is contemplated that the illustrated arrangement of a single rear
wheel will
provide sufficient stability for most applications, embodiments are described
below with
a rear axle and widely spaced rear wheels which provide improved stability and
may be
desired for some situations.
Figs. 9 and 10 schematically illustrate an alternate embodiment of the
conveyor apparatus
201 of the present disclosure (the conveyor itself is not shown for clarity of
illustration).
The front wheel and actuator arrangement is the same as in the apparatus 1
shown in
Figs. 3 and 4, however here the conveyor frame 203 comprises a rear axle 231
and right
and left rear wheels 205RWR, 205RWL are mounted on corresponding right and
left rear
wheel assemblies 211RWR, 211RWL pivotally attached to corresponding right and
left
ends of the rear axle 231 of the conveyor frame 203. A rear wheel actuator,
provided by
hydraulic cylinders 215RWR, 215RWL, is connected to pivot the right and left
rear
wheel assemblies 211RWR, 211RWL with respect to corresponding right and left
ends of
the rear axle 231 of the conveyor frame to move the corresponding right and
left rear
= wheels 205RWR, 205RWL from the conventional orientation shown in Fig. 9
to the
lateral orientation shown in Fig. 10.
In the apparatus 201 the right and left rear wheel assemblies 211RWR, 211RWL
pivot in
the same direction rearward with respect to the rear axle 231 to move the
corresponding
right and left rear wheels 205RWR, 205RWL from the conventional orientation of
Fig. 9
to the lateral orientation of Fig. 10. The drive system rotates the right and
left rear
wheels 205RWR, 205RWL in the same first rotational direction RD to move the
conveyor frame along the conventional path CP. To move the conveyor frame
along the
17911377v1 10
CA 3028763 2019-01-02
lateral path the drive system rotates the left rear wheel 205RWL in the first
rotational
direction RD, and rotates the right rear wheel 205RWR in an opposite second
rotational
direction RD' to move the conveyor frame 203 along the lateral path LP.
The drive system comprises a right rear hydraulic motor 217RWR connected to
drive the
right rear wheel 205RWR and a left rear hydraulic motor 217RWL connected to
drive the
left rear wheel 205RWL, and a reversing valve 219R linked to, in the
illustrated
apparatus 201, the right rear wheel assembly 211RWR and to the right rear
hydraulic
motor 217RWR, such that when the rear wheel on the selected rear wheel
assembly =
moves from the conventional orientation to the lateral orientation, hydraulic
fluid flow
through the corresponding right rear hydraulic motor 217RWR is reversed.
Thus the apparatus 201, a reversing valve is required on the front left wheel
assembly as
in the apparatus 1, and also on the right rear wheel assembly 211RWR. All
wheels roll in
rotational direction RD when in the conventional orientation of Fig. 9, while
the left front
and right rear wheels must roll in opposite direction RD when in the lateral
orientation in
order roll the same direction as the right front and left rear wheels.
Figs. 11 and 12 schematically illustrate an alternate embodiment of the
conveyor
apparatus 301 of the present disclosure (the conveyor itself is not shown for
clarity of
illustration). The front wheel and actuator arrangement is the same as in the
apparatus
101 shown in Figs. 6 and 7, however here the conveyor frame 303 comprises a
rear axle
331 and right and left rear wheels 305RWR, 305RWL are mounted on corresponding
right and left rear wheel assemblies 311RWR, 311RWL pivotally attached to
corresponding right and left ends of the rear axle 331 of the conveyor frame
303. = A rear
wheel actuator, provided by hydraulic cylinders 315RWR, 315RWL, is connected
to
pivot the right and left rear wheel assemblies 311RWR, 311RWL with respect to
corresponding right and left ends of the rear axle 331 of the conveyor frame
to move the
17911377v1 11
CA 3028763 2019-01-02
corresponding right and left rear wheels 305 RWR, 305RWL from the conventional
orientation shown in Fig. 11 to the lateral orientation shown in Fig. 12.
In the apparatus 301 the right and left rear wheel assemblies 311RWR, 311RWL
pivot in
opposite directions forward and rearward with respect to the rear axle 331
when moving
from the conventional orientation to the lateral orientation. In this
configuration the drive
system can rotate the right and left rear wheels 305RWR, 305RWL in the same
rotational
direction RD to move the conveyor frame 303 along both the conventional path
and the
lateral path. No reversing valve is needed.
=
Fig. 13 schematically illustrated the apparatus 1 in position to receive
granular material .
from a transport vehicle and convey the received granular material up and into
the open
top of a bin 35A. The conveyor apparatus 1 is shown in the lateral orientation
and when
the bin 35A is full the conveyor apparatus 1 can simply be moved along the
lateral path
LP to convey received granular material up and into the open top of a second
bin 35B.
Farm grain bins are typically arranged in a line as shown in Fig. 13, and the
apparatus 1
greatly simplifies the movement of the conveyor 7 from one bin to the next.
Similarly Fig. 14 schematically illustrates the apparatus 1 in a position to
transfer
granular material such as seed or fertilizer from one of a plurality of
transport
compartments 37 in a transport vehicle 39 into one of a plurality of seeder
compartments
41 in an air seeder tank cart 43. Again the conveyor apparatus 1 can be moved
along the =
lateral path PL to simplify loading from the transport compartments 37 into an
appropriate seeder compartment 41.
To further enhance the ease of precise positioning the conveyor apparatus 1,
the length of
the conveyor 7 between the upper output end 7A of the conveyor 7 and the lower
input
end 7B of the conveyor 7 can be made adjustable as indicated by the phantom
lines in
Figs. 1 and 2.
17911377v1 12
CA 3028763 2019-01-02
This feature allows the apparatus shown in Fig. 14 to transfer agricultural
products from
the same transport compartment 37 to either seeder compartment 41A or seeder
compartment 41B without moving the transport vehicle 39 or the tank cart 43.
By
increasing or decreasing the conveyor length and operating the front and rear
wheels at
different speeds the conveyor apparatus can be maneuvered from position P1 to
position
P2.
The apparatus 1 includes the conventional raising and lowering systems
required to move
.. the upper output end 7A up and down, provided by a winch 49, and to lower
the lower
input end 7B onto the ground and raise same above the ground, provided by a
jack 51
incorporated into the rear wheel assembly 11RW. By resting the lower input end
7B on
the ground, and allowing the rear wheel 5RW to rotate freely the conveyor 7
can be
moved in a windshield wiper fashion pivoting about the lower input end 7B.
Similarly since the discharge chutes 45 of the various transport compartments
37 on the
transport vehicle 39 will not typically be aligned with the fill openings 47
of the various
seeder compartments 41 the apparatus 1 can be extended or retracted and
steered to a
location suitable to transfer agricultural products from any one of the
transport
.. compartments to any one of the seeder compartments.
The present disclosure provides a conveyor apparatus 1, 101, 201, 301 capable
of moving
in forward and rearward along a conventional path CP aligned with the
longitudinal axis
LA of the conveyor, or along a lateral path LP perpendicular to the
longitudinal axis LA
of the conveyor.
The foregoing is considered as illustrative only of the principles of the
invention.
Further, since numerous changes and modifications will readily occur to those
skilled in
the art, it is not desired to limit the invention to the exact construction
and operation
17911377v1 13
CA 3028763 2019-01-02
shown and described, and accordingly, all such suitable changes or
modifications in
structure or operation which may be resorted to are intended to fall within
the scope of
the claimed invention.
17911377v1 14
CA 3028763 2019-01-02