Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
AUTOMATIC DOOR SENSOR, AUTOMATIC DOOR SYSTEM,
AND METHOD OF CONTROLLING AUTOMATIC DOOR
SYSTEM
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0001] The present invention relates to an automatic door sensor, an
automatic
door system, and a method of controlling an automatic door system.
BACKGROUND
[0002] Automatic door sensors used for automatic doors are required to have
appropriate detection areas in order to ensure safety Various techniques for
setting a
detection area of an automatic door sensor have been proposed For example,
Japanese Patent Application Publication No. 2003-3750 describes a technique
for
improving the safety of a doorway by setting the detection area on the
doorway.
SUMMARY
[0003] A detection means (predetermined sensor or detection algorithm)
appropriate for a target detection area of the automatic door sensor has been
used for
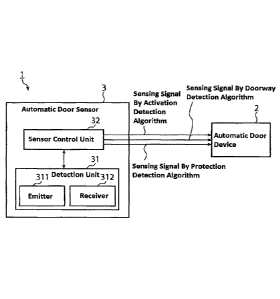
detection by the automatic door sensor. Specifically, for an automatic door
sensor that
performs detection in an activation area where a person approaching is
detected to
open the door, a detection means for opening the door while reducing the
frequency of
unnecessary opening and closing operations of the door has been used. Whereas
for
an automatic door sensor that performs detection in a protection area such as
a
doorway to protect a person approaching, a detection means for monitoring the
- 1 -
85488242
the person standing by the door and the like has been used.
[0004] However, when a single automatic door sensor detects both the
protection area
and the activation area, a part of the protection area must be used as the
activation area. In this
case, the detection means used to detect the protection area will be also used
to detect the
activation area. When the detection means for detecting the protection area is
used to detect
the activation area, false detections may easily occur due to effects of the
automatic door and
its installation environment, which results in a increased frequency of
unnecessary opening
and closing operations of the door.
10005] The invention has been made in consideration of the above drawback
and one
object of the invention is to provide an automatic door sensor that can
achieve both reduction
of frequency of unnecessary door opening and closing and improvement in safety
of the door.
The invention also provides an automatic door system, and a control method of
the automatic
door system thereof.
[0006] According to a first aspect of the invention, provided is an
automatic door sensor
that includes an activation detection means detecting a person or an object,
and a protection
detection means having a higher detection sensitivity for the person or the
object than the
activation detection means. The automatic door sensor has a special detection
area in which
detections by the activation detection means and the protection detection
means are
performed and the automatic door sensor is capable of outputting results of
the detections
individually, wherein the activation detection means detect the person or the
object based on a
sensing signal sensed from the special detection area, and the protection
detection means
detect the person or the object based on the sensing signal.
[0007] In the automatic door sensor, the automatic door sensor may further
have an
activation detection area in which detection is performed only by the
- 2 -
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-07-14
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
activation detection means, and the special detection area may be disposed
closer to a
door than the activation detection area.
[0008] The automatic door sensor may further include a doorway detection
means detecting a person or an object on a track of the door. The automatic
door
sensor may have a second special detection area in which detections by the
doorway
detection means and the protection detection means are performed and may
output
results of the detections individually or collectively.
[0009] In the automatic door sensor, the detection by the protection
detection
means in the second special detection area may be performed only when the door
is
in a fully-opened position.
[0010] The automatic door sensor may further include a fixed-wall side
detection means detecting a person or an object in the vicinity of a fixed
wall of the
door. The automatic door sensor may have a third special detection area in
which
detections by the fixed-wall side detection means and the protection detection
means
are performed and outputs results of the detections individually or
collectively.
[0011] In the automatic door sensor, in the detection by the protection
detection
means, a stationary object detection time, which is time from when a person or
an
object is detected to when the detected person or object is determined as a
stationary
object and excluded from a detection target, may be bnger than the stationary
object
detection time in the detection by the activation detection means.
[0012] According to a second aspect of the invention, provided is an
automatic
door system including a control means that drive-controls a door based on a
result of
detection of a person or an object in a detection area. In a special detection
area that is
- 3 -
85488242
a part of the detection area, the control means uses a result of detection by
an activation
detection means detecting a person or an object for drive control of the door
when the door is
in a closed position, and uses a result of detection by a protection detection
means having a
higher detection sensitivity for the person or the object than the activation
detection means for
the drive control of the door when the door is in a position other than the
closed position,
wherein the activation detection means detect the person or the object based
on a sensing
signal sensed from the special detection area, and the protection detection
means detect the
person or the object based on the sensing signal.
[0013] In the automatic door system, the detection area may further include
an
activation detection area in which detection perform only by the activation
detection means,
and the special detection area may be disposed closer to the door than the
activation detection
area.
[0014] The automatic door system may further include a doorway detection
means
detecting a person or an object on a track of the door. The detection area may
include a second
special detection area in which detections by the doorway detection means and
the protection
detection means are performed. In the second special detection area, the
control means may
use a result of detection by the protection detection means for drive control
of the door when
the door is in a fully opened position, and use a result of detection by the
doorway detection
means for the drive control of the door when the door is in a position other
than the fully-
opened position.
[0015] The automatic door system may further include a fixed-wall side
detection means
detecting a person or an object in the vicinity of a fixed wall of the door.
The detection area
may include a third special detection area in which detections by the fixed-
wall side detection
means and the protection detection means are performed. In the third special
detection area,
the control means may use a result of detection by the fixed-wall side
detection means for
- 4 -
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-07-14
85488242
drive control of the door when the door is moving to a fully-opened position,
and use a result
of detection by the protection detection means for the drive control of the
door except when
the door is moving to the fully-opened position.
100161 In the detection by the protection detection means in the automatic
door system,
a stationary object detection time, which is time from when a person or an
object is detected to
when the detected person or object is determined as a stationary object and
excluded from a
detection target, may be longer than the stationary object detection time in
the detection by
the activation detection means.
100171 In the detection by the protection detection means in the automatic
door sensor,
a stationary object detection time, which is time from when a person or an
object is detected to
when the detected person or object is determined as a stationary object and
excluded from a
detection target, may be longer than the stationary object detection time in
the detection by
the activation detection means.
100181 According to a third aspect of the invention, provided is
performing, a method of
controlling an automatic door system. The method includes, performing, in a
special detection
area that is a part of a detection area for detecting a person or an object,
detection by an
activation detection means that detects a person or an object is performed
when a door is in a
closed position, and using a result of the detection for drive control of the
door and,
performing, in the special detection area, detection by a protection detection
means that has a
higher detection sensitivity for the person or the object than the activation
detection means
when the door is in a position other than the closed position, and using a
result of the
detection for the drive control of the door, wherein the activation detection
means detect the
person or the object based on a sensing signal sensed from the special
detection area, and the
protection detection means detect the person or the object based on the
sensing signal.
- 5 -
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-07-14
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0019] According to the aspects of the invention, it is possible to achieve
both
the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the door
and the
improvement of the safety.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0020] Fig. 1 is a block diagram illustrating an automatic door system
according
to one embodiment.
Fig. 2 is a bird's-eye view showing a detection area of the automatic door
sensor according to the embodiment.
Fig. 3 is a flowchart for describing an operation of the automatic door sensor
according to the embodiment.
Fig. 4 is a flowchart for describing detection and a stationary object
detection
time control performed by the automatic door sensor according to the
embodiment.
Fig. 5 is an explanatory view for describing the detection and the stationary
object detection time control performed by the automatic door sensor according
to
the embodiment.
Fig. 6 is a block diagram illustrating an automatic door system according to a
first modification example.
Fig. 7 is a block diagram illustrating an automatic door system according to a
second modification example.
Fig. 8 is a block diagram illustrating an automatic door system according to a
third modification example.
Fig. 9a is a plan view showing a detection area of an automatic door sensor
according to a fourth modification example of the embodiment when doors are
fully
closed
- 6 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
Fig. 9b is a plan view showing a detection area of the automatic door sensor
according to the fourth modification example of the embodiment when the doors
are
fully opened.
Fig. 10a is a plan view showing a detection area of an automatic door sensor
according to a fifth modification example of the embodiment when the doors are
fully
closed
Fig. 10b is a plan view showing a detection area of the automatic door sensor
according to the fifth modification example of the embodiment when the doors
are
fully opened.
Fig. 11a is a plan view showing a detection area of an automatic door sensor
according to a sixth modification example of the embodiment when the doors are
fully
closed
Fig. llb is a plan view showing a detection area of the automatic door sensor
according to the sixth modification example of the embodiment when the doors
are
fully opened.
Fig. 12a is a plan view showing a detection area of an automatic door sensor
according to a seventh modification example of the embodiment when the doors
are
fully closed
Fig. 12b is a plan view showing a detection area of the automatic door sensor
according to the seventh modification example of the embodiment when the doors
are
fully opened.
Fig. 13a is a plan view showing a detection area of an automatic door sensor
according to an eighth modification example of the embodiment when something
is
caught by the doors.
Fig. 13b is a plan view showing a detection area of the automatic door sensor
- 7 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
according to the eighth modification example of the embodiment when a person
is
passing through the doors.
Fig. 14 is a block diagram illustrating an automatic door system according to
one embodiment.
Fig. 15 is a conceptual diagram showing a detection algorithm used in the
automatic door system according to the embodiment.
Fig. 16 is a flowchart illustrating switching of the detection algorithm
depending
on the status of the doors in an operation example of the automatic door
system
according to the embodiment.
Fig. 17 is a flowchart illustrating an activation detection control in the
operation
example of the automatic door system according to the embodiment.
Fig. 18 is a flowchart illustrating a protection detection control in the
operation
example of the automatic door system according to the embodiment.
Fig. 19 is a flowchart illustrating loading of control parameters in the
operation
example of the automatic door system according to the embodiment.
Fig. 20 is a flowchart illustrating a first mode control in the operation
example
of the automatic door system according to the embodiment.
Fig. 21 is a flowchart illustrating a second mode control in the operation
example of
the automatic door system according to the embodiment.
Fig. 22 is a flowchart illustrating a third mode control in the operation
example
of the automatic door system according to the embodiment.
Fig. 23 is a flowchart illustrating an exit invalid control in the operation
example
of the automatic door system according to the embodiment.
Fig. 24 is an explanatory diagram for describing the exit invalid control in
the
operation example of the automatic door system according to the embodiment.
- 8 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
Fig. 25 is a flowchart illustrating a traverse invalid control in the
operation
example of the automatic door system according to the embodiment.
Fig. 26 is an explanatory diagram for describing the traverse invalid control
in
the operation example of the automatic door system according to the
embodiment.
Fig. 27 is a flowchart illustrating a detection determination in the operation
example of the automatic door system according to the embodiment.
Fig. 28 is a block diagram illustrating an automatic door system according to
a
first modification example.
Fig. 29 is a block diagram illustrating an automatic door system according to
a
second modification example.
Fig. 30 is a block diagram illustrating an automatic door system according to
a
third modification example.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
[0021] An automatic door system according to an embodiment of the invention
will now be described with reference to the appended drawings. Embodiments
described below are each one example of an embodiment of the invention, and
the
invention is not intended to be construed as being limited thereto.
Furthermore, in the
drawings referred to in this embodiment, the same parts or parts having
similar
functions are denoted by the same or like reference characters, and duplicate
descriptions thereof are omitted Furthermore, for the sake of convenience of
description, a dimensional ratio of the drawings is possibly different from an
actual
dimensional ratio, and some elements of a configuration are possibly omitted
from the
drawings.
[0022] Fig. 1 illustrates an automatic door system 1 according to one
- 9 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
embodiment. Fig. 2 is a bird's-eye view showing a detection area 5 of an
automatic
door sensor 3 according to the embodiment. Referring to Fig. 1, the automatic
door
system 1 includes an automatic door device 2 and the door sensor 3. The
automatic
door system 1 operates to open a door 21 shown in Fig. 2 when the automatic
door
sensor 3 detects a person who is approaching and going to pass through the
door 21
(traffic).
[0023] Automatic Door Device 2
The automatic door device 2 includes a motor 22 (not shown) for opening and
closing the door 21 in an open-close direction dl shown in Fig. 2, and a door
control
unit 23 (not shown) that drive controls the motor based on a signal or
information
obtained from the automatic door sensor 3. In the example illustrated in Fig.
2, the
door 21 is a double-leaf sliding door that is drawn apart to be opened. The
type of the
door 21 is not limited to the example shown in Fig. 2. Any type of door may be
adopted
such as a single sliding door, a hinged door, a folding door, and a glide
door.
[0024] For example, the automatic door sensor 3 supplies a sensing signal
corresponding to detection of a person in an effective detection area, which
will be
described later, to the door control unit 23. In response to reception of the
sensing
signal, the door control unit 23 performs a control (hereinafter, also
referred to as an
open drive control) of driving the door 21 in the opening direction.
[0025] Automatic Door Sensor 3
As shown in Fig. 2, the automatic door sensor 3 is provided on a transom bar
24 at the middle position thereof, more specifically, above the boundary
between the
two leaves of the closed door 21 in order to detect a person approaching the
door 21.
The automatic door sensor 3 may be provided at a place other than the transom
bar
- 10 -
I g
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
24 such as a ceiling or on the lower surface of the transom bar 24.
[0026] As shown in Fig. 1, the automatic door sensor 3 includes a
detection unit
31 and a sensor control unit 32. The detection unit 31 and the sensor control
unit 32
are an example of a detection unit. The sensor control unit 32 is connected to
the
detection unit 31 and the automatic door device 2. The sensor control unit 32
includes
hardware such as a CPU, a ROM, and a RAM. Software may be used to realize at
least a
part of the sensor control unit 32. The detection unit 31 includes an emitter
311 and a
receiver 312.
[0027] The sensor control unit 32 has an effective detection area.
As shown in
Fig. 2, the effective detection area is set in at least a part of a detection
area 5 that is an
area detectable by the automatic door sensor 3 for detection of a person
approaching
the door 21. Fig. 2 shows the relative position of the detection area 5 on a
floor surface
6.
[0028] The emitter 311 includes an optical lens (not shown) for
emitting light
and a plurality of light emitting elements (not shown). The emitter 311
irradiates, that
is, emits near infrared light in a pulse form to the detection area 5 from
each of the
plurality of light emitting elements. The receiver 312 includes an optical
lens (not
shown) for receiving light and a plurality of light receiving elements (not
shown)
optically corresponding to the plurality of light emitting elements of the
emitter 311.
The receiver 312 receives the near infrared light that is irradiated onto the
detection
area 5 from each of the plurality of light emitting elements in the emitter
311 by the
corresponding light receiving elements, and senses the amount of the near
infrared
light received by each light receiving element. The receiver 312 outputs the
sensed
amount of the light to the sensor control unit 32 as a sensing signal having a
signal
- 11-
1 =
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
value corresponding to the amount of light received. Alternatively, the
emitter 311 and
the receiver 312 may emit and receive light other than the near infrared
light.
Furthermore, the emitter 311 and the receiver 312 may use another type of
optical
system instead of the optical lenses for light emitting and receiving, and an
optical lens
may not necessarily be used.
[00291 In the example of Fig. 2, the detection area 5 includes a
plurality of small
detection areas 51 arranged at intervals in the open-close direction dl of the
door 21
and the front-back direction d2 orthogonal to the open-close direction 21 at
the front
of the double-leaf sliding door 21. Specifically, there are a total of 72
small detection
areas 51, which is calculated as six columns x 12, as shown in Fig. 2.
[0030] Each small detection area 51 corresponds to an irradiation
spot of near-
infrared light that is emitted from the corresponding one of the plurality of
light
emitting elements in the emitter 311 and is respectively received by the
corresponding one of the plurality of light receiving elements in the receiver
312.
[0031] The effective detection area in the example of Fig. 2
includes at least one
small detection area 51 among the plurality of small detection areas 51. In
the example
of Fig. 2, each small detection area 51 has a circular shape. In this case,
the diameter
of the small detection area 51 at the floor surface 6 may have, for example,
any value
between 10 cm and 30 cm. The small detection area 51 may have a shape other
than a
circular shape such as an elliptical shape, a rectangular shape, and a
polygonal shape.
[0032] How to determine which small detection area 51 among the
plurality of
small detection areas 51 is to be set as the effective detection area is not
particularly
limited. For example, the effective detection area may be predetermined before
the
- 12 -
=
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
start of use of the automatic door system 1. Further, the effective detection
area may
be variable depending on the door position or the like.
[0033] The sensor control unit 32 causes all the light emitting
elements in the
emitter 311 to emit near infrared light toward the corresponding small
detection
areas 51. The sensor control unit 32 subsequently causes all the light
receiving
elements in the receiver 312 to receive reflected light of the near infrared
light from
the corresponding small detection areas 51. Then, the sensor control unit 32
selects a
sensing signal of the effective detection area from among the sensing signals
of the
small detection areas 51 supplied from the receiver 312.
[0034] Based on the selected sensing signal of the effective
detection area, the
sensor control unit 32 detects a person or an object in accordance with an
activation
detection algorithm and a protection detection algorithm which will be
described later.
In the detection of a person or object approaching, the sensor control unit 32
stores,
for example, a signal value (that is, the amount of light received) of the
sensing signal
of the effective detection area immediately after power on of the automatic
door
sensor 3 as a reference value. The sensor control unit 32 may detect a person
or
object based on a change of the signal value relative to the reference value.
When a
person or object situated in the effective detection area is detected, the
sensor control
unit 32 outputs a sensing signal to the automatic door device 2. In this way,
the
detection result in the effective detection area is used for a drive control
to open the
door 21.
[0035] In particular, the sensor control unit 32 detects a person
or object
situated in a special detection area 51A, which will be described later, using
two types
of detection algorithms, that are, the activation detection algorithm and the
protection
- 13 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
detection algorithm. Note that there may be more than one activation detection
algorithm, and more than one protection detection algorithm. By providing two
or
more detection algorithms, it is possible to select an appropriate detection
algorithm
depending on the installation environment of the automatic door sensor 3 and
the
conditions of the person or object.
[0036] The sensor control unit 32 may cause only the light emitting
element(s)
corresponding to the effective detection area to emit the near infrared light,
instead of
causing all the light emitting elements in the emitter 311 to emit the near
infrared
light. In this case, all the small detection areas 51 to which the near
infrared light is
irradiated become the effective detection area. By causing only the light
emitting
element(s) corresponding to the effective detection area to emit the near
infrared
light, it is possible to reduce power consumption. In addition, it is also
possible to
extend the life of the light emitting elements.
[0037] Detection Algorithms Applied to Detection Area 5
As shown in Fig. 2, the sensor control unit 32 has the special detection area
51A as a part of the plurality of small detection areas 51 constituting the
detection
area 5. Regardless of the open/close state of the door 21, detection is
performed in the
special detection area 51A in accordance with the activation detection
algorithm for
detecting a person or object and the protection detection algorithm having the
detection sensitivity for the person or the object higher than the activation
detection
algorithm. The detection results obtained through these detection algorithms
are
individually output and used for the drive control of the door 21. That is,
detections for
the same special detection area 51A are performed using the activation
detection
algorithm and the protection detection algorithm. Thus, the detection areas to
which
- 14-
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
the activation detection algorithm and the protection detection algorithm are
performed coincide with each other. Unlike a case where the activation
detection
algorithm and the protection detection algorithm each have an independent
detection
area and the two algorithms are independently performed for the detection area
by
physically different sensors, it is not necessary to align the detection area
to which the
activation detection algorithm is applied with the detection area to which the
protection detection algorithm is applied.
[0038] The
activation detection algorithm is, for example, a detection algorithm
for detecting a person or object approaching and opening (that is, activating)
the door
21. The activation detection algorithm focuses on reducing the malfunction of
the door
21 due to false detection of the automatic door sensor 3 stemming from
influences of
the structure of the automatic door system 1 and the installation environment
of the
automatic door system 1. The activation detection algorithm uses a process in
which
the sensitivity of the automatic door sensor 3 is relatively low.
Specifically, as a
reference value or algorithm for determining that a person or object is
present from
the signal value (physical value) detected by the automatic door sensor 3, the
activation detection algorithm uses one that is relatively insensitive so that
it less
frequently determines that the person or object is present. As such an
algorithm,
there are one that prevents false detection due to snowfall, and one that
prevents false
detection due to an insect flying around the automatic door sensor 3. The
activation
detection algorithm is suitable for reducing unnecessary opening and closing
operations of the door 21. In the embodiment, an activation detection means
includes
the detection unit 31 and the sensor control unit 32 that executes the
activation
detection algorithm.
- 15 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0039] The protection detection algorithm is a detection algorithm focusing
on
detecting, for example, a person stopping near the door 21 or an object
present in the
vicinity of the door 21 in order to protect the person or object from
collision with the
door 21, for example, to prevent the person or object from being caught in the
closing
door 21. The protection detection algorithm uses a process in which the
sensitivity of
the automatic door sensor 3 is relatively high. Specifically, as a reference
value or
algorithm for determining that a person or object is present from a signal
value
(physical value) detected by the automatic door sensor 3, the protection
detection
algorithm uses one that is relatively sensitive so that it tends to easily
determine that
the person or object is present. The protection detection algorithm is
suitible for
safety improvement. In the embodiment, a protection detection means includes
the
detection unit 31 and the sensor control unit 32 that executes the protection
detection
algorithm.
[0040] The activation detection algorithm and the protection detection
algorithm are stored in the sensor control unit 32 that performs detection of
an
person approaching.
[0041] The door control unit 23 opens or closes the door 21 based on an
activation detection algorithm sensing signal corresponding a result of a
detection
performed in accordance with the activation detection algorithm and a
protection
detection algorithm sensing signal corresponding to a result of a detection
performed
in accordance with the protection detection algorithm. In the closing
operation of the
door 21, when a person approaching is detected in accordance with the
protection
detection algorithm, the door control unit 23 may cause the door 21 to be
opened, stop
the closing operation of the door 21, or cause the door 21 to be closed at a
low speed.
- 16 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0042] In the special detection area 51A, it is possible to use, for the
driving
control of the door 21, a result of detection performed in accordance with the
activation detection algorithm in which the sensitivity of the automatic door
sensor 3
is set relatively lower than that of the protection detection algorithm. Here,
the
activation detection algorithm uses, as the reference value or algorithm for
determining that a person or object is present from a signal value (physical
value)
detected by the automatic door sensor 3, one that is insensitive relative to
the
protection detection algorithm so that it less frequently determines that the
person or
object is present.
[0043] Further, in the special detection area 51A, it is also possible to
use, for
the driving control of the door 21, a result of detection performed in
accordance with
the protection detection algorithm in which the sensitivity of the automatic
door
sensor 3 is set relatively higher than that of the activation detection
algorithm. Here,
the protection detection algorithm uses, as the reference (threshoki value) or
algorithm for determining that a person or object is present from a signal
value
(physical value) detected by the automatic door sensor 3, one that is
relatively more
sensitive than the activation detection algorithm so that it tends to easily
determine
that the person or object is present.
[0044] As described above, in the special detection area 51A, since the
automatic door device (door control unit 23) operates based on the detection
results in
accordance with both the activation detection algorithm and the protection
detection
algorithm, reduction of unnecessary opening and closing operations of the door
21
and the improvement of safety can be achieved at the same time. The special
detection area 51A is an example of a special detection area.
- 17 -
A
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0045] The standard requires that the detection area to which the
protection
detection algorithm is applied be situated within 200 mm from the door 21.
Thus, the
special detection area 51A is set as a small detection area 51A situated at
the second
and third rows of the small detection areas counting from the row closest to
the door
21 as shown in Fig. 2. When the small detection area 51A situated at the
second and
third rows is set as the special detection area 51A, the standard can be
satisfied, and
the safety in the vicinity of the door 21 can be further improved. The number
of rows
of the small detection areas that are set as the special detection area 51A
can be
changed depending on the size of each small detection area 51.
[0046] Further, as shown in Fig. 2, the sensor control unit 32 may
further has a
small detection area 51B that is different from the special detection area 51A
and set
in the area of the plurality of small detection areas 51. Only a detection in
accordance
with the activation detection algorithm is performed in the small detection
area 51B.
Alternatively detections in accordance with both the activation detection
algorithm
and the protection detection algorithm may be performed in the activation
detection
area 51B, and only a result of the detection in accordance with the activation
detection
algorithm may be used for the drive control of the door 21 regardless of the
position of
the door 21. The special detection area 51A may be disposed closer to the door
21
than the activation detection area 51B. In the example of Fig. Z, the
activation
detection area 51B is the small detection area 51B situated at the fourth to
sixth
columns. By setting the activation detection area 51B at a position distant
from the
door 21 where chances of false detection caused by a person standing, stopped
walking or the like are small, it is possible to effectively reduce false
detections in the
detection area 5 away from the door 21.
- 18 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0047] In the small detection area 51C at the first row may be an area
where
detection in accordance with only the activation detection algorithm is
performed
when the door 21 is closed, whereas when the door 21 is open, the area is
invalidated
in order to prevent false detections such as detecting the door 21 as a person
approaching and the like. Here, "invalid" or "invalidated" encompass meaning
that the
sensing signal is not treated as a valid signal even if the detection is
properly
performed, and meaning that the detection operation is stopped so that the
detection
is not performed (the same applies hereinafter).
[0048] Further, the sensor control unit 32 may further has a protection
detection area where detection in accordance with only the protection
detection
algorithm is performed as another small detection area 51 other than the
special
detection area 51A and the activation detection area 51B among the plurality
of small
detection areas 51. For example, the small detection area 51C at the first row
may be
used as the protection detection area. Even when the small detection area 51C
at the
first row is set as the protection detection area, in order to prevent false
detections as
the sensor detects the door 21 as a person approaching and the like, small
detection
area(s) 51 corresponding to the positions where the door 21 is situated may be
invalidated while the door 21 is moving. Alternatively the sensitivity of the
detection
for such a small detection area(s) may be lowered than the activation
detection area
51B (so that the false detection due to the door 21 is unlikely occurred).
This detection
algorithm in the embodiment is herein referred to as a doorway detection
algorithm.
In this case, the special detection area 51C serves as a second special
detection area,
and the detection unit 31 and the sensor control unit 32 executing the doorway
detection algorithm serve as a doorway detection means. In the case where the
small
detection area 51C at the first row is used as the protection detection area,
the special
- 19 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
detection area 51A is disposed between the activation detection area 51B and
the
protection detection area 51C. In this case, according to the switching of the
detection
algorithm applied to the special detection area 51A, it is possible to expand
the small
detection area(s) 51 where the detection by the activation detection algorithm
is
performed or the small detection area(s) 51 where the detection by the
protection
detection algorithm is performed In this way, it is possible to achieve both
the
reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the door 21 and
the
improvement of the safety more effectively.
[0049] In the
detection in accordance with the protection detection algorithm, a
stationary object detection time, which is time from when a person or object
is
detected to when the detected person or object is determined as a stationary
object
(that is, the background) and excluded from the detection target, may be
longer than
the stationary object detection time in the detection in accordance with the
activation
detection algorithm. A specific example of the stationary object detection
time is not
particularly limited. For example, the stationary object detection time in the
activation
detection algorithm may be 5 seconds, and the stationary object detection time
in the
protection detection algorithm may be 30 seconds. By making the stationary
object
detection time in the protection detection algorithm longer than the
stationary object
detection time in the activation detection algorithm, it becomes possible to
detect a
person standing by the door for a long time. In this way, the safety is
improved.
Whereas when the stationary object detection time in the activation detection
algorithm is made shorter than the stationary object detection time in the
protection
detection algorithm, influence of disturbance can be reduced so that
unnecessary
opening and closing operations of the door 21 can be prevented.
- 20 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0050] Further, the sensor control unit 32 may have an exit-side detection
area
(hereinafter also referred to as an exit-side activation detection area) where
detection
in accordance with only the activation detection algorithm is performed and
another
exit-side detection area (hereinafter also referred to as an exit-side
protection
detection area) where detection in accordance with only the protection
detection
algorithm is performed. In this case, the sensor control unit 32 may perform
an exit
invalid control that invalidates the exit detection area when nothing is
detected in the
protection detection area on the exit side. By performing the exit invalid
control, it is
possible to reducing the time length when the door 21 is opened while
preventing the
safety deterioration.
[0051] Further, the sensor control unit 32 may performs a traverse invalid
control that invalidates the activation detection area 51B when it is detected
that a
person or object is moving only in a direction along the door 21 in the
activation
detection area 51B. The "direction along the door 21" may be the opening-
closing
direction dl shown in Fig. 2 or a direction having an angle with the opening-
closing
direction dl smaller than a threshold (that is, a direction almost same as the
opening-
closing direction dl). By performing the traverse invalid control, it is
possible to more
effectively prevent the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the door
21 and
to prevent the safety deterioration.
[0052] The activation detection algorithm and the protection detection
algorithm are not limited to one type each, and two or more types may be
provided.
When multiple types of the protection detection algorithm are used, such
protection
detection algorithms may be switched depending on the door position, the state
of the
door control, the control state of the sensor and the like. Alternatively two
or more
- 21 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
protection detection algorithms may be concurrently executed and then
necessary
one at the time may be selected from among them.
[0053] Operation Examples
An operation example of the automatic door system 1 will now be described.
Fig. 3 is a flowchart illustrating operation of the automatic door sensor 3 in
the
operation example of the automatic door system according to the embodiment.
The
process shown in the flowchart of Fig. 3 may be repeatedly carried out as
necessary
[0054] Referring to Fig. 3, parameters necessary for processing of the
stationary object detection time and the like are loaded, and an initial
setting is
performed (step Si). Physical information about the detection area 5 obtained
by the
detection unit 31 is then acquired (step 52). The activation detection
algorithm is
applied to the acquired physical information, and a detection process to
determine
whether there is a person approaching or the like is performed (step S3).
Furthermore, the protection detection algorithm is applied to the acquired
physical
information, and a detection process to determine whether there is a person
approaching or the like is performed (step S4). Moreover, the doorway
detection
algorithm is applied to the acquired physical information, and a detection
process to
determine whether there is a person approaching or the like is performed (step
S5).
Next, sensing signals (contact signals) or detection information (data
communication)
based on the result of the detection process by the activation detection
algorithm and
the result of the detection process by the protection detection algorithm are
individually outputted to the automatic door device 2 (step S6).
[0055] In particular, in the special detection area 51A, both the
activation
detection algorithm and the protection detection algorithm are applied to the
same
- 22 -
, .
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
physical information, and a detection process is performed to determine
whether
there is a person approaching or the like.
[0056] The detection process (step S5) to which the doorway
detection
algorithm has been applied may be omitted as necessary.
[0057] Detection and Background Update Control
Next, a detection control commonly performed in each algorithm by the sensor
control unit 32 and a background update control after the stationary object
detection
time has elapsed will be described with reference to the flowchart of Fig. 4.
The
process shown in the fbwchart of Fig. 4 may be repeatedly carried out as
necessary.
[0058] In the detection control and the background update control
the sensor
control unit 32 first calculates an increase-side threshold value and a
decrease-side
threshold value of the amount of light received based on a value of the amount
of light
received stored in advance (an background value that is referenced for
determination) and a sensitivity parameter(s) loaded in the initial setting at
step Si.
The threshold values are determined with reference to the stored value of the
amount
of light received in order to determine that a person is detected (step 5221).
[0059] Fig. 5 is an explanatory diagram for describing the
detection and
background update controls in the operation example of the automatic door
system 1
according to the embodiment. Fig. 5 shows the relations between the amount of
light
received indicated by the sensing signal of the small detection area 51, the
stored
value of the light received amount, the sensitivity parameter, the increase-
side
threshold, the decrease-side threshold, and the state of the detection flag.
As shown in
Fig. 5, the sensitivity parameter indicates how much the amount of light
received
- 23 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
should be increased or decreased from the stored value of the amount of light
received (the reference value) to be determined that an object is detected The
stored
value of the amount of light received (the reference value) may be acquired at
a
predetermined time such as immediately after power-on of the automatic door
system 1. Thus, the smaller the sensitivity parameter, the higher the
sensitivity.
[0060] In the example of Fig. 5, the increase-side threshold is obtained by
adding
the sensitivity parameter to the stored value of the amount of light received.
When the
sensed amount of light received changes within the stationary object detection
time
frame, which will be described later, and the sensed amount of light received
is equal
to or greater than the increase-side threshold, the sensor control unit 32
turns on the
detection flag which means that a person the like is detected. In the example
of Fig. 5,
the decrease-side threshold is obtained by subtracting the sensitivity
parameter from
the stored value of the amount of light received. When the sensed amount of
light
received changes within the stationary object detection time frame which will
be
described later and the sensed amount of light received is equal to or less
than the
decrease-side threshold, the sensor control unit 32 turns on the detection
flag which
means that a person the like is detected. Whereas when the sensed amount of
light
received is larger than the decrease-side threshold and smaller than the
increase-side
threshold, the sensor control unit 32 turns off the detection flag which means
that a
person or the like is not detected, in other words, a not-detected state. The
detection
flag is set, for example, in a storage of the automatic door device 2.
[0061] As shown in Fig. 4, after calculating the increase-side threshold
and the
decrease-side threshold, the sensor control unit 32 determines whether the
amount of
light received indicated by the sensing signal is equal to or greater than the
increase-
- 24 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
side threshold or equal to or less than the decrease-side threshold. (Step
S222).
[0062] When the amount of light received is not equal to or greater than
the
increase-side threshold or not equal to or less than the decrease-side
threshold (step
S222: N), the sensor control unit 32 turns off the detection flag (step S223).
[0063] Whereas when the amount of light received is equal to or greater
than
the increase-side threshold or equal to or less than the decrease-side
threshold (step
S222: Y), the sensor control unit 32 determines whether the amount of light
indicated
by the sensing signal remains the same for the stationary object detection
time or
longer that has been loaded in step S212 in Fig. 7 (step S224).
[0064] When the amount of light received has changed within the stationary
object detection time (the time frame in which the background is not updated
and
stays the same) (step S224: N), the sensor control unit 32 turns on the
detection flag
(step S225). Whereas when there is no change in the amount of light received
during
the stationary object detection time or longer (step S224: Y), the sensor
control unit
32 turns off the detection flag (step S226). After turning off the detection
flag, the
sensor control unit 32 updates the stored value of the amount of light
received to the
current value of the amount of light received (step S227).
[0065] Exit Invalid Control
The sensor control unit 32 may perform the exit invalid control in the
activation detection algorithm but does not perform it in the protection
detection
algorithm. The exit invalid control will be now described. In the exit invalid
control, the
sensor control unit 32 first determines whether the detection flag is on. When
the
detection flag is not on, the sensor control unit 32 ends the exit invalid
control while
- 25 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
the detection flag remains turned off.
[0066] Whereas when the detection flag is on, the sensor control unit 32
determines whether a protection detection area 52A on the exit side, which is
set
among a plurality of small detection areas 52 on the exit side of the door 21
(the
opposite side of the door 21), has become the not-detected state, based on the
sensing
signal of the protection detection area 52A.
[0067] When the protection detection area 52A on the exit side is in the
not-
detected state, the sensor control unit 32 turns off the detection flag.
Whereas when
the protection detection area 52A on the exit side is not in the not-detected
state, the
sensor control unit 32 ends the exit invalid control while the detection flag
remains
turned on.
[0068] Traverse Invalid Control
The sensor control unit 32 may perform the traverse invalid control in the
activation detection algorithm but does not perform it in the protection
detection
algorithm. The traverse invalid control will be now described. In the traverse
invalid
control, the sensor control unit 32 first determines whether the detection
flag is on.
When the detection flag is not on, the sensor control unit 32 ends the
traverse invalid
control while the detection flag remains turned off.
[0069] Whereas when the detection flag is on, the sensor control unit 32
determines whether a person is moving only in the traverse direction in front
of the
door 21 (in other words, the direction along the door 21) based on a movement
vector
of the person obtained from a change in the small detection areas 51 in the
detected
state.
- 26 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0070] When the person moves only in the traverse direction in front of the
door 21, the sensor control unit 32 turns off the detection flag. Whereas when
the
person is not moving in the traverse direction in front of the door 21, the
sensor
control unit 32 ends the traverse invalid control while the detection flag
remains
turned on.
[0071] In the detection determination, the sensor control unit 32 checks
whether the detection flag is on. When the detection flag is not on, the
sensor control
unit 32 determines that a person approaching, an object and the like is not
detected.
Whereas when the detection flag is on, the sensor control unit 32 determines
that a
person approaching, an object and the is detected. The determination results
are
individually output to the automatic door device 2 (step S6).
[0072] As described above, the detection processes in accordance with the
algorithms are performed. The execution order of the algorithms may be
changed. Also,
one or more of the detection algorithms may be omitted. In the above-described
example, the sensing signal by the activation detection algorithm and the
sensing
signal by the doorway detection algorithm are outputted through different
contacts or
different flags in data communication packets. However, the invention is not
limited to
this. Alternatively, they may be outputted through the same contact or the
same flag in
data communication packets. When they are outputted through the same contact
or
the same flag in the data communication packets, it is possible to reduce the
number of
wirings required
[0073] In the embodiment, both detection in accordance with the activation
detection algorithm and detection in accordance with the protection detection
algorithm are performed in the special detection area 51A. According to the
- 27 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
= .
embodiment, it is possible to achieve both the reduction of the unnecessary
opening
and closing operations of the door and the improvement of the safety.
[0074] Since sensing is performed in the identical special
detection area 51A
using the activation detection algorithm and the protection detection
algorithm, unlike
a case where the activation detection algorithm and the protection detection
algorithm
each have an independent detection area and the two algorithms are
independently
performed for the detection area by physically different sensors, it is not
necessary to
align the detection area to which the activation detection algorithm is
applied with the
detection area to which the protection detection algorithm is applied.
[0075]First Modification Example
A description is given of a first modification example in which a detection
area 51D
(third special detection area) is provided in the vicinity of a fixed wall
located on the
trailing edge side of the door 21 when the door 21 is fully closed, and a
detection in
accordance with only a fixed-wall side detection algorithm is performed in the
detection area 51D to detect a person approaching and the like. The detection
area
51D is provided on the side where the door 21 is situated when opened in the
vicinity
of the fixed wall in order to monitor that a person approaching and the like
does not
contact the trailing edge of the door 21 when the door 21 is opening. The
width of the
area is at least as large as the width of the door 21 or larger and the length
of the area
(the dimension in the direction perpendicular to the fixed wall) is at least
as large as
the thickness of the door 21 or larger. Fig. 6 is a block diagram illustrating
the
automatic door system 1 according to the first modification example of the
embodiment. As shown in Fig. 6, the automatic door sensor 3 of the first
modification
example is provided with the sensor control unit 32 capable of executing a
fixed-wall
- 28 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
side detection algorithm in addition to the above-described detection
algorithms. The
fixed-wall side detection algorithm is executed only when the door 21 is
operated to be
opened (including fully closed state). The fixed-wall side detection algorithm
may be
executed at any stage as long as it is before step S6 and after step S2 in the
flowchart
of Fig 3. In the above-described configuration, it is possible to improve the
safety in
the area around the trailing edge of the door 21. In this embodiment, the
detection
unit 31 and the sensor control unit 32 that executes the fixed-wall side
detection
algorithm serve as a fixed-wall side detection means. To execute the fixed-
wall side
detection algorithm, setting of the detection flag is performed in advance in
the same
manner as the example of the detection and background update control described
above and therefore the description will be omitted
[0076] Alternatively the fixed-wall side detection algorithm may be
executed all
the time. Further, the width of the detection area 51D may be dynamically
changed
depending on the position of the door 21. Furthermore, in the case where the
door 21
is configured to be stored in the door case, the detection area 51D may be
provided
around the opening of the door case in order to monitor a person approaching
to
prevent his/her finger or the like from being caught by the door. The
execution order
of the algorithms may be changed
[0077] Further, one or more of the detection algorithms may be omitted In
the
above-described example, the sensing signal by the activation detection
algorithm, and
the sensing signal by the fixed-wall side detection algorithm are outputted
through the
same contact or the same flag in data communication packets. However, the
invention
is not limited to this. Alternatively, they may be outputted through different
contacts
or different flags in data communication packets. Moreover, the sensing signal
by the
- 29 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
fixed-wall side detection algorithm may be output through the same contact or
same
flag in the data communication packets as the sensing signal by the protection
detection algorithm.
[0078] According to the first modification example, it is also possible to
achieve
both the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the
door and
the improvement of the safety In the first modification example, since sensing
is
performed in the identical special detection area 51A using the activation
detection
algorithm and the protection detection algorithm, unlike a case where the
activation
detection algorithm and the protection detection algorithm each have an
independent
detection area and the two algorithms are independently performed for the
detection
area by physically different sensors, it is not necessary to align the
detection area to
which the activation detection algorithm is applied with the detection area to
which
the protection detection algorithm is applied Further, according to the first
modification example, it is also possible to improve the safety in the area
around the
fixed wall (the area around the trailing edge of the door 21).
[0079] Second Modification Example
A description is given of a second modification example in which detection
based on a captured image is performed. Fig. 7 is a block diagram illustrating
the
automatic door system 1 according to the second modification example of the
embodiment. As shown in Fig. 7, the automatic door sensor 3 of the second
modification example includes an image capturing unit 313 as an example of the
detection unit instead of the emitter 311 and the receiver 312. The image
capturing
unit 313 is, for example, a CCD or CMOS camera having sensitivity in the
visible light
range. The image capturing unit 313 may be an infrared camera having
sensitivity in
- 30 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
the infrared range.
[0080] The image capturing unit 313 captures an image of the detection area
5,
and outputs a sensing signal indicating the captured image of the detection
area 5 to
the sensor control unit 32. The sensor control unit 32 detects a person
approaching or
the like based on the sensing signal supplied from the image capturing unit
313, and
outputs a sensing signal of the person and the like to the automatic door
device 2.
[0081] In the second modification example, a high precision image is
captured
by the image capturing unit 313 and a person approaching and the like can be
detected with high accuracy based on the high precision image. Therefore it is
possible to achieve both the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing
operations of the door and the improvement of the safety. Also in the second
modification example, since sensing is performed in the identical special
detection
area 51A using the activation detection algorithm and the protection detection
algorithm, unlike a case where the activation detection algorithm and the
protection
detection algorithm each have an independent detection area and the two
algorithms
are independently performed for the detection area by physically different
sensors, it
is not necessary to align the detection area to which the activation detection
algorithm
is applied with the detection area to which the protection detection algorithm
is
applied
[0082] Third Modification Example
A description is given of a third modification example in which detection
utilizing the Doppler effect of a radio wave is performed Fig. 8 is a block
diagram
illustrating the automatic door system 1 according to the third modification
example
of the embodiment. As shown in Fig. 8, the automatic door sensor 3 of the
third
- 31 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
modification example includes a radio transceiver unit 314. The radio
transceiver unit
314 transmits a radio wave to the detection area 5 and detects an interference
wave
between a transmitted radio wave and a reflected wave reflected by a person
approaching or the like in the detection area 5. The radio transceiver unit
314 then
supplies a sensing signal that indicates the interference wave to the sensor
control
unit 32. The sensor control unit 32 performs detection of a person approaching
and
the like based on the sensing signal supplied from the radio transceiver unit
314, and
outputs a sensing signal about the person approaching and the like to the
automatic
door device 2.
[0083] According to the third modification example, it is also possible to
achieve
both the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the
door and
the improvement of the safety Also in the third modification example, since
sensing is
performed in the identical special detection area 51A using the activation
detection
algorithm and the protection detection algorithm, unlike a case where the
activation
detection algorithm and the protection detection algorithm each have an
independent
detection area and the two algorithms are independently performed for the
detection
area by physically different sensors, it is not necessary to align the
detection area to
which the activation detection algorithm is applied with the detection area to
which
the protection detection algorithm is applied
[0084] Fourth Modification Example
A more specific application example of the special detection area and the
activation detection area to a double-leaf sliding door will be described Fig.
9a is a plan
view showing a detection area of the double-leaf sliding door when the door is
fully
closed as the detection area of the automatic door sensor according to the
fourth
- 32 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
modification example. Fig. 9b is a plan view showing a detection area of the
double-leaf
sliding door when the door is fully opened as the detection area of the
automatic door
sensor according to the fourth modification example.
[0085] As shown in Fig. 9A, the sensor control unit 32 (see Fig. 1 and the
like)
has the special detection area 51A that has been described above with
reference to Fig.
2 in front of the fully opened double-leaf sliding door 21 (shown on the lower
side of
the door in Fig. 9a). Further, the sensor control unit 32 has the activation
detection
area 51B that has been described with reference to Fig. 2 at a position
further from
the front of the fully closed door 21 than the special detection area 51A.
Further, the
sensor control unit 32 has the second special detection area 51C that has been
described with reference to Fig. 2 on a track of the double-leaf sliding door
21, that is,
on the doorway. In addition, the sensor control unit 32 has the third special
detection
area 51D that has been described in the first modification, in front of the
fixed wall
211 and the second special detection area 51C.
[0086] In the fourth modification example, when the door is fully closed,
the
sensor control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with the doorway
detection
algorithm and the fixed-wall side detection algorithm in the second special
detection
area 51C shown in Fig. 9a. In this case, the sensor control unit 32 may
collectively
output the detection results by the doorway detection algorithm and the fixed-
wall side
detection algorithm. Further, the sensor control unit 32 performs detection in
accordance with the fixed-wall side detection algorithm in the third special
detection
area 51D shown in Fig. 9a. Moreover, the sensor control unit 32 performs
detection in
accordance with the activation detection algorithm in the special detection
area 51A
and the activation detection area 51B shown in Fig. 9a.
- 33 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0087] Whereas when the door is fully opened, the sensor control unit 32
performs detection in accordance with the doorway detection algorithm and a
closing
protection detection algorithm in the second special detection area 51C shown
in Fig.
9b. In this case, the sensor control unit 32 may collectively output the
detection results
by the doorway detection algorithm and the closing protection detection
algorithm.
Here, the closing protection detection algorithm is one mode of the protection
detection algorithm for detecting a person or object standing in the opened
space
between the door panels 21 when the door 21 is closing in order to protect the
person
or object from collision with the door 21 such as the person is caught by the
closing
door 21. Moreover, the sensor control unit 32 performs detection in accordance
with
the activation detection algorithm in the special detection area 51D and the
activation
detection area 5113 shown in Fig. 9b. The sensor control unit 32 performs
detection in
accordance with the activation detection algorithm and the closing protection
detection algorithm in the special detection area 51A shown in Fig. 9b.
[0088] According to the fourth modification example, it is possible to
achieve
both the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the
double-
leaf sliding door and the improvement of the safety Moreover, it is possible
to improve
the safety in the area around the fixed wall (the area around the trailing
edge of the
door 21). Also in the fourth modification example, since sensing is performed
in the
identical special detection area 51A using the activation detection algorithm
and the
protection detection algorithm, unlike a case where the activation detection
algorithm
and the protection detection algorithm each have an independent detection area
and
the two algorithms are independently performed for the detection area by
physically
different sensors, it is not necessary to align the detection area to which
the activation
detection algorithm is applied with the detection area to which the protection
- 34-
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
detection algorithm is applied
[0089] Fifth Modification Example
A more specific application example of the special detection area and the
activation detection area to a folding door will be described Fig. 10a is a
plan view
showing a detection area of the folding door when the door is fully closed as
the
detection area of the automatic door sensor according to a fifth modification
example.
Fig. 10b is a plan view showing a detection area of the folding door when the
door is
fully opened as the detection area of the automatic door sensor according to
the fifth
modification example.
[0090] As shown in Fig. 10a, the sensor control unit 32 (see Fig. 1 and the
like)
has two special detection area 51C that have a substantially fan-like shape
and
situated on a track of each leaf of the folding door 21 pivotally supported by
left and
right side walls 212. In addition, the sensor control unit 32 has the special
detection
area 51A between the two second special detection areas 51 in front of the
door 21.
Further, the sensor control unit 32 has the activation detection area 51B at a
position
further from the door 21 than the special detection area 51A.
[0091] In the fifth modification example, when the door is fully closed,
the
sensor control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with the doorway
detection
algorithm and the opening protection detection algorithm in the second special
detection areas 51C shown in Fig. 10a. The sensor control unit 32 performs
detection
in accordance with the activation detection algorithm and the opening
protection
detection algorithm in the special detection area 51A shown in Fig. 10a. Here,
the
opening protection detection algorithm is one mode of the protection detection
algorithm for detecting a person or object entering in the space between the
door 21
- 35 -
, CA 03052257 2019-07-31
,
and the fixed wall when the door 21 is opening in order to protect the person
or
object from collision with the door 21 such as the person is caught by the
opening
door 21. Moreover, the sensor control unit 32 performs detection in accordance
with
the activation detection algorithm in the activation detection area 51B shown
in Fig.
10a.
[0092] Whereas when the door is fully opened, the sensor control
unit 32
performs detection in accordance with the doorway detection algorithm and a
cbsing
protection detection algorithm in the second special detection area 51C shown
in Fig.
lob. The sensor control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with the
activation
detection algorithm and the cbsing protection detection algorithm in the
special
detection area 51A shown in Fig. 10b. Moreover, the sensor control unit 32
performs
detection in accordance with the activation detection algorithm in the
activation
detection area 51B shown in Fig. 10b.
[0093] According to the fifth modification example, it is also
possible to achieve
both the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the
folding
door and the improvement of the safety. Also in the fifth modification
example, since
sensing is performed in the identical special detection area 51A using the
activation
detection algorithm and the protection detection algorithm, unlike a case
where the
activation detection algorithm and the protection detection algorithm each
have an
independent detection area and the two algorithms are independently performed
for
the detection area by physically different sensors, it is not necessary to
align the
detection area to which the activation detection algorithm is applied with the
detection
area to which the protection detection algorithm is applied
[0094] Sixth Modification Example
- 36 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
A more specific application example of the special detection area and the
activation detection area to a glide door, more commonly known as a balanced
door
will be described. Fig. ha is a plan view showing a detection area of the
glide door
when the door is fully closed as the detection area of the automatic door
sensor
according to a sixth modification example. Fig. 11b is a plan view showing a
detection
area of the glide door when the door is fully opened as the detection area of
the
automatic door sensor according to the sixth modification example.
[0095] As shown in
Fig. 11a, the sensor control unit 32 (see Fig. 1 and the like)
has two special detection areas 51C-1, 51C-2 situated on a track of each leaf
of the
glide door 21. In the example of Fig. 11a, when the door is opened, the door
is moved
such that a leading edge 21a protrudes rearward (upward in Fig. 11a) and a
wailing
edge 21b protrudes forward (downward in Fig. 11a) with reference to the fully
closed
position of the door 21. Therefore, the second special detection areas 51C,
51C-1 and
51C-2 include the second special detection area 51C situated on the fully
closed
position of the door 21, the second special detection area 51C-1 situated on
the front
side of the door, and the second special detection area 51C-2 situated on the
rear side
of the door. In addition, the sensor control unit 32 has a front-side special
detection
area 51A-1 between the two second special detection areas 51C-1 on the front
side of
the door 21. Further, the sensor control unit 32 has a front-side activation
detection
area 51B-1 at a position further from the door 21 than the front-side special
detection
area 51A-1 toward the front side. Moreover, the sensor control unit 32 has a
rear-side
special detection area 51A-2 on the rear of the two rear-side second special
detection
areas 51C-2. Further, the sensor control unit 32 has a rear-side activation
detection
area 51B-2 at a position further from the door 21 than the rear-side special
detection
area 51A-2 toward the rear side.
- 37 -
, CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0096] In the sixth modification example, when the door is fully
closed, the
sensor control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with the doorway
detection
algorithm and the opening protection detection algorithm in the second special
detection areas 51C, 51C-1, and 51C-2 shown in Fig. 11a. The sensor control
unit 32
performs detection in accordance with the activation detection algorithm and
the
opening protection detection algorithm in the special detection areas 51A-1
and 51A-
2 shown in Fig. 11a. Moreover, the sensor control unit 32 performs detection
in
accordance with the activation detection algorithm in the activation detection
areas
51B-1 and 51B-2 shown in Fig. 11a.
[0097] Whereas when the door is fully opened, the sensor control
unit 32
performs detection in accordance with the doorway detection algorithm and the
closing protection detection algorithm in the second special detection areas
51C, 51C-
1, and 51C-2 shown in Fig. 11b. The sensor control unit 32 performs detection
in
accordance with the activation detection algorithm and the closing protection
detection algorithm in the special detection areas 51A-1 and 51A-2 shown in
Fig. 11b.
Moreover, the sensor control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with the
activation detection algorithm in the activation detection areas 51B-1 and 51B-
2
shown in Fig. 11b.
[0098] According to the sixth modification example, it is also
possible to achieve
both the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the
glide
door and the improvement of the safety. Similarly to the special detection
area 51A-1,
since sensing is performed in the identical special detection area 51A-2 using
the
activation detection algorithm and the protection detection algorithm, unlike
a case
where the activation detection algorithm and the protection detection
algorithm each
- 38 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
=
have an independent detection area and the two algorithms are independently
performed for the detection area by physically different sensors, it is not
necessary to
align the detection area to which the activation detection algorithm is
applied with the
detection area to which the protection detection algorithm is applied.
[0099] Seventh Modification Example
A more specific application example of the special detection area and the
activation detection area to a hinged door will be described Fig. 12a is a
plan view
showing a detection area of the hinged door when the door is fully closed as
the
detection area of the automatic door sensor according to the seventh
modification
example. Fig. 12b is a plan view showing a detection area of the hinged door
when the
door is fully opened as the detection area of the automatic door sensor
according to
the seventh modification example.
[0100] As shown in Fig. 12a, the sensor control unit 32 (see Fig. 1
and the like)
has the two special detection area 51C that have a substantially fan-like
shape and
situated on a track of each leaf of the hinged door 21 pivotally supported by
left and
right side walls 212. In addition, the sensor control unit 32 has the special
detection
area 51A between the two second special detection areas 51 in front of the
door 21.
Further, the sensor control unit 32 has the activation detection area 51B at a
position
further from the door 21 than the special detection area 51A.
[0101] In the seventh modification example, when the door is fully
closed, the
sensor control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with the doorway
detection
algorithm and the opening protection detection algorithm in the second special
detection areas 51C shown in Fig. 12a. The sensor control unit 32 performs
detection
in accordance with the activation detection algorithm and the opening
protection
- 39 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
detection algorithm in the special detection area 51A shown in Fig. 12a.
Moreover, the
sensor control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with the activation
detection
algorithm in the activation detection area 51B shown in Fig. 12A.
[0102] Whereas when the door is fully opened, the sensor control unit 32
performs detection in accordance with the doorway detection algorithm and a
cbsing
protection detection algorithm in the second special detection area 51C shown
in Fig.
12b. The sensor control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with the
activation
detection algorithm and the closing protection detection algorithm in the
special
detection area 51A shown in Fig. 12b. Moreover, the sensor control unit 32
performs
detection in accordance with the activation detection algorithm in the
activation
detection area 51B shown in Fig. 12b.
[0103] According to the seventh modification example, it is also possible
to
achieve both the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing operations
of the
hinged door and the improvement of the safety Also in the seventh modification
example, since sensing is performed in the identical special detection area
51A using
the activation detection algorithm and the protection detection algorithm,
unlike a
case where the activation detection algorithm and the protection detection
algorithm
each have an independent detection area and the two algorithms are
independently
performed for the detection area by physically different sensors, it is not
necessary to
align the detection area to which the activation detection algorithm is
applied with the
detection area to which the protection detection algorithm is applied.
[0104] Eighth Modification Example
A more specific application example of the special detection area and the
activation detection area to a rotating door will be described. Fig. 13a is a
plan view
- 40 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
showing a detection area of the rotating door when the door is closed as the
detection
area of the automatic door sensor according to the eighth modification
example. Fig.
13b is a plan view showing a detection area of the rotating door when the door
is
opened to allow a person to enter or exit as the detection area of the
automatic door
sensor according to the eighth modification example.
[0105] As shown in Fig. 13a, the sensor control unit 32 (see Fig. 1 and the
like)
has the second special detection area 51C on a track of the rotating door 21
that
revolves inside a cylindrical casing 212 provided with an entrance and exit
212a. In
addition, the sensor control unit 32 has the special detection area 51A
outside the
entrance and exit 212a adjacent to the second special detection area 51C.
Further, the
sensor control unit 32 has the activation detection area 51B at a position
further on
the outer side from the door 21 than the special detection area 51A.
[0106] In the eighth modification example, when the door is closed, the
sensor
control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with the doorway detection
algorithm and a door catching protection detection algorithm in the second
special
detection area 51C shown in Fig. 13a. Here, the door catching protection
detection
algorithm is one mode of the protection detection algorithm for detecting a
person or
object entering in the rotating door 21 in order to protect the person or
object from
collision with the door 21 such as the person is caught by the rotating door
21. The
sensor control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with the activation
detection
algorithm and the door catching protection detection algorithm in the special
detection area 51A shown in Fig. 13a. Moreover, the sensor control unit 32
performs
detection in accordance with the activation detection algorithm in the
activation
detection area 51B shown in Fig. 13a.
-41 -
= CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0107] Whereas when a person is about to walking through the door, the
sensor
control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with the doorway detection
algorithm and in the second special detection area 51C shown in Fig. 13b.
Moreover,
the sensor control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with the
activation
detection algorithm in the special detection area 51A and the activation
detection area
51B shown in Fig. 13b.
[0108] According to the eighth modification example, it is also
possible to
achieve both the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing operations
of the
rotating door and the improvement of the safety. Also in the eighth
modification
example, since sensing is performed in the identical special detection area
51A using
the activation detection algorithm and the protection detection algorithm,
unlike a
case where the activation detection algorithm and the protection detection
algorithm
each have an independent detection area and the two algorithms are
independently
performed for the detection area by physically different sensors, it is not
necessary to
align the detection area to which the activation detection algorithm is
applied with the
detection area to which the protection detection algorithm is applied.
[0109] The automatic door sensor 3 may use an ultrasonic wave or a
distance
measurement sensor instead of the infrared light, the image and the radio wave
described above.
[0110] Aspects of the invention are not limited to the individual
embodiments
described above. For example, instead of using the activation detection
algorithm as
the activation detection means and the protection detection algorithm as the
protection detection means, an activation sensor device and a protection
sensor device
that are physically separate but have overlapping detection areas may be used.
In this
- 42 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
,
case, the activation sensor device has a person or object detection function
equivalent
to the activation detection algorithm, and is, for example, a far-infrared
sensor device.
The protection sensor device has a person or object detection function
equivalent to
the protection detection algorithm, and is, for example, a near-infrared
sensor device.
The activation sensor device may be a radio wave type sensor device, and the
protection sensor device may be a near infrared type sensor device.
[0111] An automatic door system according to an embodiment of the
invention
will now be described with reference to the appended drawings. Embodiments
described below are each one example of an embodiment of the invention, and
the
invention is not intended to be construed as being limited thereto.
Furthermore, in the
drawings referred to in this embodiment, the same parts or parts having
similar
functions are denoted by the same or like reference characters, and duplicate
descriptions thereof are omitted Furthermore, for the sake of convenience of
description, a dimensional ratio of the drawings is possibly different from an
actual
dimensional ratio, and some elements of a configuration are possibly omitted
from the
drawings.
[0112] Fig. 14 illustrates the automatic door system 1 according to one
embodiment. Fig. 2 referred above is a bird's-eye view of the automatic door
system 1
according to the embodiment. Referring to Fig. 14, the automatic door system 1
includes the automatic door device 2 and the door sensor 3. In the automatic
door
system 1, the automatic door sensor 3 detects a person who try to pass through
the
door 21 shown in Fig. 2 and causes the door 21 to be opened to let the person
walk
therethrough in accordance with a detection result of the automatic door
sensor 3.
[0113] Automatic Door Device 2
- 43 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
The automatic door device 2 includes the door 21, the motor 22, and the door
control unit 23 which is an example of the door control means. The motor 22 is
supplied with power from a power supply (not shown) to generate a rotational
force
used to automatically open and close the door 21. The rotational force of the
motor 22
is transmitted to the door 21 as a translational force in the opening-closing
direction
dl shown in Fig. 2 via power transmission members such as a pulley and a
timing belt
(not shown). In the example illustrated in Fig. 2, the door 21 is a double-
leaf sliding
door that is drawn apart to be opened The type of the door 21 is not limited
to the
example shown in Fig. 2. Any type of door may be adopted such as a single
sliding door,
a hinged door, a folding door, and a glide door.
[0114] The door control unit 23 is connected to the motor 22 and the
automatic
door sensor 3. The door control unit 23 performs a drive control of the motor
22 by
controlling power supply based on signals or information acquired from the
automatic door sensor 3 and the motor 22. By performing the drive control of
the
motor 22, the door control unit 23 controls driving for operation of the door
21. The
drive control of the motor 22 is at least one or a combination of two or more
of
application/non-application of driving of the motor 22, a drive speed, a drive
torque,
and a rotation direction.
[0115] For example, the automatic door sensor 3 supplies an open signal
corresponding to detection of a person or object in an effective detection
area, which
will be described later, to the door control unit 23. In response to reception
of the
open signal, the door control unit 23 performs a control (hereinafter, also
referred to
as an open drive control) of driving the door 21 in the opening direction.
[0116] Automatic Door Sensor 3
-44-
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
As shown in Fig. 2, the automatic door sensor 3 is provided on the transom bar
24 at the middle position thereof, more specifically, above the boundary
between the
two leaves of the closed door 21 in order to detect a person and the like
approaching
the door 21. The automatic door sensor 3 may be provided at a place other than
the
transom bar 24 such as a ceiling.
[0117] As shown in Fig. 14, the automatic door sensor 3 includes the
detection
unit 31 and the sensor control unit 32. The detection unit 31 and the sensor
control
unit 32 are an example of the detection unit. The sensor control unit 32 is
connected
to the detection unit 31 and the door control unit 23. The sensor control unit
32
includes hardware such as a CPU, a ROM, and a RAM. Software may be used to
realize
at least a part of the sensor control unit 32. The detection unit 31 includes
the emitter
311 and the receiver 312.
[0118] The sensor control unit 32 has an effective detection area. As shown
in
Fig. 2, the effective detection area is set in at least a part of a detection
area 5 that is an
area of the floor detectable by the automatic door sensor 3 for detection of a
person
and the like approaching the door 21.
[0119] The emitter 311 includes a plurality of light emitting elements (not
shown). The emitter 311 irradiates or emits near infrared light in a pulse
form to the
detection area 5 from each of the plurality of light emitting elements. The
receiver 312
includes a plurality of light receiving elements (not shown) optically
corresponding to
the plurality of light emitting elements of the emitter 311. The receiver 312
receives
the near infrared light that is irradiated onto the detection area 5 from each
of the
plurality of light emitting elements in the emitter 311 by the corresponding
light
receiving elements, and senses the amount of the near infrared light received
by each
- 45 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
light receiving element. The receiver 312 outputs the sensed amount of the
light to the
sensor control unit 32 as a sensing signal having a signal value corresponding
to the
amount of light received. Alternatively, the emitter 311 and the receiver 312
may emit
and receive light other than the near infrared light.
[0120] In the example of Fig. 2, the detection area 5 includes a plurality
of small
detection areas 51 arranged at intervals in the open-close direction dl of the
door 21
and the front-back direction d2 orthogonal to the open-close direction 21 at
the front
of the double-leaf sliding door 21. Specifically, there are a total of 72
small detection
areas 51, which is cakulated as six columns x 12, as shown in Fig. 2.
[0121] Each small detection area 51 corresponds to an irradiation spot of
near-
infrared light that is emitted from the corresponding one of the plurality of
light
emitting elements in the emitter 311 and is respectively received by the
corresponding one of the plurality of light receiving elements in the receiver
312.
[0122] The effective detection area in the example of Fig. 2 includes at
least one
small detection area 51 among the plurality of small detection areas 51. In
the example
of Fig. 2, each small detection area 51 has a circular shape. In this case,
the diameter
of the small detection area 51 at the floor surface 6 may have, for example,
any value
between 10 cm and 30 cm. The small detection area 51 may have a shape other
than a
circular shape such as an elliptical shape, a rectangular shape, and a
polygonal shape.
[0123] How to determine which small detection area 51 among the plurality
of
small detection areas 51 is to be set as the effective detection area is not
particularly
limited For example, the effective detection area may be predetermined before
the
start of use of the automatic door system 1. Further, the effective detection
area may
-46 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
be variable depending on the door position or the like.
[0124] The sensor control unit 32 causes all the light emitting elements in
the
emitter 311 to emit near infrared light toward the corresponding small
detection
areas 51. The sensor control unit 32 subsequently causes all the light
receiving
elements in the receiver 312 to receive reflected light of the near infrared
light from
the corresponding small detection areas 51. Then, the sensor control unit 32
selects a
sensing signal of the effective detection area from among the sensing signals
of the
small detection areas 51 supplied from the receiver 312.
[0125] Based on the selected sensing signal of the effective detection
area, the
sensor control unit 32 detects a person and the like in accordance with an
activation
detection algorithm or a protection detection algorithm which will be
described later.
In the detection of a person or object approaching, the sensor control unit 32
stores,
for example, a signal value (that is, the amount of light received) of the
sensing signal
of the effective detection area immediately after power on of the automatic
door
system 1 as a reference value. The sensor control unit 32 may detect a person
or
object based on a variation of the signal value relative to the reference
value. When a
person situated in the effective detection area is detected, the sensor
control unit 32
outputs the open signal to the automatic door control unit 23. In this way,
the
detection result in the effective detection area is used for a drive control
to open the
door 21.
[0126] Further, the sensor control unit 32 acquires a position signal
indicating
the position of the door 21 from the motor 22. Based on the acquired position
signal,
the sensor control unit 32 switches between the detection algorithm applied to
a
special detection area 51A which will be described later between the
activation
- 47-
= CA 03052257 2019-07-31
detection algorithm and the protection detection algorithm. A specific example
of the
position signal is not particularly limited as long as the position of the
door 21 is
detectible with the signal. For example, the position signal is generated
based on the
phase of a Hall element of the motor 22. The position signal may be a signal
based on
a rotary encoder that detects the revolution of the motor 22 or based on a
linear
encoder that detects the open and close positions of the door 21. Furthermore,
the
position signal may be acquired from the door control unit instead of directly
acquiring from the motor 22.
[0127] The sensor control unit 32 may cause only the light emitting
element(s)
corresponding to the effective detection area to emit the near infrared light,
instead of
causing all the light emitting elements in the emitter 311 to emit the near
infrared
light. In this case, all the small detection areas 51 to which the near
infrared light is
irradiated become the effective detection area. By causing only the light
emitting
element(s) corresponding to the effective detection area to emit the near
infrared
light, it is possible to reduce power consumption. In ackiition, it is also
possible to
extend the life of the light emitting elements.
[0128] Alternatively, the effective detection area may be set in the
door control
unit 23, and the door control unit 23 may function as the detection means. In
this case,
the sensor control unit 32 may output the sensing signals of all the small
detection
areas 51 supplied from the light receiving unit 312 to the door control unit
23. The
door control unit 23 may perform detection of a person approaching and the
like in
accordance with the activation detection algorithm or the protection detection
algorithm, which will be described later, based on the sensing signal of the
effective
detection area(s) predetermined in advance among the sensing signals of all
the small
-48-
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
detection areas 51 supplied from the sensor control unit 32.
[0129] Detection Algorithms Applied to Detection Area 5
As shown in Fig. 2, the sensor control unit 32 has the special detection area
51A (special detection area) as a part of the plurality of small detection
areas 51
forming the detection area 5. When the door 21 is in the closed position,
detection in
accordance with the activation detection algorithm is performed in the special
detection area 51A to detect a person or an object, and the detection result
by the
activation detection algorithm is used for the drive control of the door 21.
Moreover,
when the door 21 is in a position other than the closed position, detection in
accordance with the protection detection algorithm in which the detection
sensitivity
for a person or an object is higher than the activation detection algorithm is
performed in the special detection area 51A, and the detection result by the
protection
detection algorithm is used for the drive control of the door 21 instead of
the detection
result by the activation detection algorithm.
[0130] The activation detection algorithm is, for example, a detection
algorithm
for detecting a person or object approaching and opening (that is, activating)
the door
21. The activation detection algorithm focuses on reducing the malfunction of
the door
21 due to false detection of the automatic rigoor sensor 3 stemming from
influences of
the structure of the automatic door system 1 and the installation environment
of the
automatic door system 1. The activation detection algorithm uses a process in
which
the sensitivity of the automatic door sensor 3 is relatively low.
Specifically, as a
reference value or algorithm for determining that a person or object is
present from
the signal value (physical value) detected by the automatic door sensor 3, the
activation detection algorithm uses one that is relatively insensitive so that
it less
-49 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
frequently determines that the person or object is present. As such an
algorithm,
there are one that prevents false detection due to snowfall, and one that
prevents false
detection due to an insect flying around the automatic door sensor 3. The
activation
detection algorithm is suitable for reducing unnecessary opening and closing
operations of the door 21. In the embodiment, an activation detection means
includes
the detection unit 31 and the sensor control unit 32 that executes the
activation
detection algorithm.
[0131] The protection detection algorithm is a detection algorithm focusing
on
detecting, for example, a person stopping near the door 21 or an object
present in the
vicinity of the door 21 in order to protect the person or object from
collision with the
door 21, for example, to prevent the person or object from being caught in the
closing
door 21. The protection detection algorithm uses a process in which the
sensitivity of
the automatic door sensor 3 is relatively high. Specifically, as a reference
value or
algorithm for determining that a person or object is present from a signal
value
(physical value) detected by the automatic door sensor 3, the protection
detection
algorithm uses one that is relatively sensitive so that it tends to easily
determine that
the person or object is present. The protection detection algorithm is
suitable for
safety improvement. In the embodiment, the protection detection means includes
the
detection unit 31 and the sensor control unit 32 that executes the protection
detection
algorithm.
[0132] The activation detection algorithm and the protection detection
algorithm are stored in the sensor control unit 32 that performs detection of
an
person approaching.
[0133] The sensor control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with at
- 50 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
,
least one of the activation detection algorithm and the protection detection
algorithm
in the special detection area 51A, and the detection result in accordance with
the
activation detection algorithm or the protection detection algorithm selected
depending on the open or closed state of the door 21 is used for the drive
control of
the door 21.
[0134] More specifically, when the door 21 is in the closed
position, the sensor
control unit 32 performs detection in accordance with only the activation
detection
algorithm in the special detection area 51A set in the effective detection
area. Whereas
when the door 21 is in a position other than the closed position, the
detection method
may be switched to detection in accordance with only the protection detection
algorithm in the same special detection area 51A.
[0135] In this case, when the door 21 is in the closed position,
the sensor
control unit 32 supplies the open signal to the door control unit 23 based on
the result
of detection performed in the special detection area 51A in accordance with
the
activation detection algorithm. The door control unit 23 drives and controls
the door
21 based on the detection result performed in accordance with the activation
detection algorithm. When the door 21 is in the closed position, the sensor
control unit
32 supplies the open signal to the door control unit 23 based on the result of
detection
performed in the special detection area 51A in accordance with the protection
detection algorithm. The door control unit 23 drives and controls the door 21
based on
the result of detection performed in accordance with the protection detection
algorithm. For example, when the door 21 performs the closing operation from
the
fully opened state and the protection detection algorithm detects a person
approaching in the special detection area 51A, the sensor control unit 32
outputs the
- 51 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
open signal to the closing door 21 to prevent the person from being caught by
the
door 21. Alternatively, when the door 21 performs the closing operation and
the
protection detection algorithm detects a person approaching in the special
detection
area 51A, the sensor control unit 32 may stop supplying a close signal (in
other words,
stops the closing operation of the door 21) to prevent the person from being
caught
by the door 21.
[0136] Alternatively, when the door 21 is in the closed position, the
sensor
control unit 32 may perform detections in accordance with both the activation
and
protection detection algorithms in the special detection area 51A set in the
effective
detection area, and may then output only the result of the detection in
accordance
with the activation detection algorithm to the door control unit 23. The door
control
unit 23 performs the drive control of the door 21 based on this result of the
detection.
When the door 21 is in a position other than the closed position, the sensor
control
unit 32 may perform detections in accordance with both the activation and
protection
detection algorithms in the same special detection area 51A as the detection
area
when the door 211s in the closed position, and may then output only the result
of the
detection in accordance with the protection detection algorithm to the door
control
unit 23. The door control unit 23 performs the drive control of the door 21
based on
this result of the detection.
[0137] When detection of a person approaching is performed by the door
control unit 23, the activation detection algorithm and the protection
detection
algorithm may be stored in the door control unit 23. In this case, when the
door 21 is
in the closed position, the door control unit 23 performs detection in the
special
detection area 51A set in the effective detection area in accordance with the
activation
- 52 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
detection algorithm to detect a person approaching and the like, and performs
the
drive control to open the door 21 based on the result of the detection of the
person
and the like. Moreover, when the door 21 is in a position other than the
closed
position, the sensor control unit 32 performs detection in the special
detection area
51A set in the effective detection area in accordance with the protection
detection
algorithm to detect a person and the like, and performs the drive control to
open the
door 21 based on the result of the detection of the person and the like.
[0138] By providing the special detection area 51A, when the door 21 is
closed,
the result of the detection in accordance with the activation detection
algorithm in
which the sensitivity of the sensor 3 is reduced may be used for the drive
control of
the door 21, whereas when the door 21 is opened, the result of the detection
in
accordance with the protection detection algorithm in which the sensitivity of
the
sensor 3 is increased may be used for the drive control of the door 21. In
this way, it is
possible to achieve both the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing
operations of the door 21 and the improvement of the safety.
[0139] The standard requires that the detection area to which the
protection
detection algorithm is applied be situated within 200 mm from the door 21.
Thus, the
special detection area 51A is set as a small detection area 51A situated at
the second
and third rows of the small detection areas counting from the row closest to
the door
21 as shown in Fig. 2. When the small detection area 51A situated at the
second and
third rows is set as the special detection area 51A, the standard can be
satisfied, and
the safety in the vicinity of the door 21 can be further improved. The number
of rows
of the small detection areas that are set as the special detection area 51A
can be
changed depending on the size of each small detection area 51.
- 53 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0140] Further, as shown in Fig. 2, the sensor control unit 32 may further
has a
small detection area 51B that is different from the special detection area 51A
and set
in the area of the plurality of small detection areas 51. Only a detection in
accordance
with the activation detection algorithm is performed in the small detection
area 51B.
The activation detection area 51B may be an area where detections in
accordance with
both the activation detection algorithm and the protection detection algorithm
may be
performed, and only the result of the detection in accordance with the
activation
detection algorithm may be used for the drive control of the door 21. The
special
detection area 51A may be disposed closer to the door 21 than the activation
detection
area 51B. In the example of Fig. 2, the activation detection area 51B is the
small
detection area 51B situated at the fourth to sixth columns. By setting the
activation
detection area 51B at a position distant from the door 21 where chances of
false
detection caused by a person standing, stopped walking or the like are small,
it is
possible to effectively reduce false detections in the detection area 5 away
from the
door 21.
[0141] In the small detection area 51C at the first row may be an area
where
detection in accordance with only the activation detection algorithm is
performed
when the door 5 is in the closed position, whereas when the door 5 is open,
the area is
invalidated in order to prevent false detections such as detecting the door 5
as a person
approaching. Here, "invalid" or "invalidated" encompass meaning that the
sensing
signal is not treated as a valid signal even if the detection is properly
performed, and
meaning that the detection operation is stopped so that the detection is not
performed (the same applies hereinafter).
[0142] Further, the sensor control unit 32 may further has a protection
- 54-
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
detection area where detection in accordance with only the protection
detection
algorithm is performed as another small detection area 51 other than the
special
detection area 51A and the activation detection area 51B among the plurality
of small
detection areas 51. For example, the small detection area 51C at the first row
may be
used as the protection detection area. Even when the small detection area 51C
at the
first row is set as the protection detection area, in order to prevent false
detections as
the sensor detects the door 21 as a person approaching and the like, small
detection
area(s) 51 corresponding to the positions where the door 21 is situated may be
invalidated while the door 21 is moving. Alternatively the sensitivity of the
detection
for such a small detection area(s) may be lowered than the activation
detection area
51B (so that the false detection due to the door 21 is unlikely occurred).
This detection
algorithm in the embodiment is herein referred to as a doorway detection
algorithm.
In this case, the special detection area 51C serves as the second special
detection area,
and the detection unit 31 and the sensor control unit 32 executing the doorway
detection algorithm serve as the doorway detection means. In the case where
the
small detection area 51C at the first row is used as the protection detection
area, the
special detection area 51A is disposed between the activation detection area
51B and
the protection detection area 51C. In this case, according to the switching of
the
detection algorithm applied to the special detection area 51A, it is possible
to expand
the small detection area(s) 51 where the detection by the activation detection
algorithm is performed or the small detection area(s) 51 where the detection
by the
protection detection algorithm is performed In this way, it is possible to
achieve both
the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the door 21
and
the improvement of the safety more effectively.
[0143] Fig. 15 is a
conceptual diagram showing the detection algorithm used in
- 55 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
the automatic door system 1 according to the embodiment. As shown in Fig. 15,
in the
detection in accordance with the protection detection algorithm, the
stationary object
detection time, which is time from when a person or object is detected to when
the
detected person or object is determined as the stationary object (that is, the
background) and excluded from the detection target, may be longer than the
stationary
object detection time in the detection in accordance with the activation
detection
algorithm. A specific example of the stationary object detection time is not
particularly
limited. For example, the stationary object detection time in the activation
detection
algorithm may be five seconds, and the stationary object detection time in the
protection detection algorithm may be 30 seconds. By making the stationary
object
detection time in the protection detection algorithm longer than the
stationary object
detection time in the activation detection algorithm, it becomes possible to
detect a
person standing by the door for a long time when the door 21 is opened In this
way,
the safety is improved Moreover, since the influence of a disturbance can be
suppressed when the door 21 is closed, it is possible to prevent unnecessary
opening
and closing operations of the door 21.
[0144] As shown in Fig. 15, the activation detection algorithm is an
algorithm
using a temporal filter known in the field of signal processing, and may have
a first
mode for detecting a person or an object. In this case, the protection
detection
algorithm does not have the first mode. The first mode is a mode in which the
sensitivity of the automatic door sensor 3 is reduced in the time base. Since
the
activation detection algorithm has the first mode and the protection detection
algorithm does not have the first mode, the safety deterioration and the
unnecessary
opening and closing operations of the door 21 can be prevented under the
situation
where there is a fluctuation in time.
- 56 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0145] As shown in Fig. 15, the activation detection algorithm may be an
algorithm using a spatial filter known in the field of signal processing, and
may have a
second mode for detecting a person or an object. In this case, the protection
detection
algorithm does not have the second mode. The second mode is a mode in which
the
sensitivity of the automatic door sensor 3 is reduced in the space base. Since
the
activation detection algorithm has the second mode and the protection
detection
algorithm does not have the second mode, the safety deterioration and the
unnecessary opening and closing operations of the door 21 can be prevented
under
the situation where there is a fluctuation in space.
[0146] Moreover, as shown in Fig. 15, the activation detection algorithm
may
have a third mode in which a condition to be determined that a person or
object is
detected is that a change is equal to or greater than a threshold set higher
than a
predetermined threshold for detecting the person or object. In this case, the
protection detection algorithm does not have the third mode. The third mode is
a mode
in which the originally set value of the detection sensitivity of the
automatic door
sensor 3 is uniformly reduced Since the activation detection algorithm has the
third
mode and the protection detection algorithm does not have the third mode, it
is
possible to prevent the safety deterioration and the unnecessary opening and
closing
operations of the door 21 due to the fluctuation in the position of the door
sensor 3
attached to the door 21 caused by the movement of the door 21.
[0147] Further, the sensor control unit 32 may have an exit-side detection
area
(hereinafter also referred to as an exit-side activation detection area) where
detection
in accordance with only the activation detection algorithm is performed and
another
exit-side detection area (hereinafter also referred to as an exit-side
protection
- 57 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
detection area) where detection in accordance with only the protection
detection
algorithm is performed In this case, the sensor control unit 32 may perform
the exit
invalid control that invalidates the exit detection area when the protection
detection
area on the exit side becomes undetected state. By performing the exit invalid
control,
it is possible to reducing the time length when the door 21 is opened while
preventing
the safety deterioration.
[0148] Further, the sensor control unit 32 may performs the traverse
invalid
control that invalidates the activation detection area 51B when it is detected
that a
person or object is moving only in a direction along the door 21 in the
activation
detection area 51B. The "direction along the door 21" may be the opening-
closing
direction dl shown in Fig. 2 or a direction having an angle with the opening-
closing
direction dl smaller than a threshold (that is, a direction almost same as the
opening-
closing direction dl). By performing the traverse invalid control, it is
possible to more
effectively prevent the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the door
21 and
to prevent the safety deterioration.
[0149] The activation detection algorithm and the protection detection
algorithm are not limited to one type each, and two or more types may be
provided
When multiple types of the protection detection algorithm are used, such
protection
detection algorithms may be switched depending on the door position, the state
of the
door control the control state of the sensor and the like. Alternatively two
or more
protection detection algorithms may be concurrently executed and then
necessary
one at the time may be selected from among them.
[0150] Further, the sensor control unit 32 may switch the algorithm from
the
activation detection algorithm to the protection detection algorithm at the
timing
- 58 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
when the door 21 begins to open, at the when the door 21 is fully opened, or
at any
timing between the door 21 begins to open and is fully opened
[0151] Operation Example
An operation example of the automatic door system 1 will now be described
Fig. 16 is a flowchart illustrating switching of the detection algorithm
depending on the
status of the door in the operation example of the automatic door system 1
according
to the embodiment. The process shown in the flowchart of Fig. 16 may be
repeatedly
carried out as necessary
[0152] As shown in Fig. 16, first, the sensor control unit 32 determines a
door
status whether the door 21 is opened or closed based on the position signal
supplied
from the motor 22 (step Si). When the door is in the fully closed state, the
sensor
control unit 32 executes an activation detection control, which is an example
of
detection in accordance with the activation detection algorithm, in the
special
detection area 51A (step S2A). When the door is in opening motion, the sensor
control
unit 32 executes a protection detection control in the special detection area
51A (step
S2B). In the activation detection area 51B, the activation detection control
is always
executed
[0153] Whereas when the door 21 is in the fully open state, the sensor
control
unit 32 executes the protection detection control, which is an example of
detection in
accordance with the protection detection algorithm, in the special detection
area 51A
(step S2C). When the door 21 is in closing motion, the sensor control unit 32
also
executes the protection detection control in the special detection area 51A
(step S2D).
In the protection detection area, the protection detection control is always
executed
- 59 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0154] Fig. 17 is a flowchart illustrating the activation detection control
in the
operation example of the automatic door system 1 according to the embodiment.
Fig.
18 is a flowchart illustrating the protection detection control in the
operation example
of the automatic door system 1 according to the embodiment. The processes
shown in
the flowcharts of Figs. 17 and 18 may be repeatedly carried out as necessary.
[0155] Activation Detection Control: SA2, S2B
When the activation detection control is executed (step S2A, step S2B), the
sensor control unit 32 first loads control parameters described in the
activation
detection algorithm (step S21) as shown in Fig. 17. Fig. 19 is a flowchart
illustrating
loading of the control parameters in the operation example of the automatic
door
system 1 according to the embodiment. The process shown in the flowchart of
Fig. 19
may be repeatedly carried out as necessary
[0156] Loading of Control Parameters: S21
In the loading of the control parameters (step S21), as shown in Fig. 19, the
sensor control unit 32 first loads a setting value of the sensitivity
parameter (step
S211). The setting value of the sensitivity parameter in the activation
detection
algorithm is equal to or less than the setting value of the sensitivity
parameter in the
protection detection algorithm.
[0157] After the setting value of the sensitivity parameter is loaded, the
sensor
control unit 32 loads a setting value of the stationary object detection time
(step S212).
The setting value of the stationary object detection time in the activation
detection
algorithm is shorter than the setting value of the stationary object detection
time in
the protection detection algorithm.
- 60 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0158] After the setting value of the stationary object detection time is
loaded,
the sensor control unit 32 loads a setting value of the time filter (step
S213). The
setting value of the time filter is a parameter related to presence or absence
of the
first mode. When the activation detection algorithm has the first mode and the
protection detection algorithm does not have the first mode, the setting value
of the
time filter in the activation detection algorithm is greater than the setting
value of the
time filter in the protection detection algorithm.
[0159] After the setting value of the time filter is loaded, the sensor
control unit
32 loads a setting value of the spatial filter (step S214). The setting value
of the spatial
filter is a parameter related to the presence or absence of the second mode.
The
setting value of the spatial filter in the activation detection algorithm
having the
second mode is greater than the setting value of the spatial filter in the
protection
detection algorithm that does not have the second mode.
[0160] After the setting value of the spatial filter is loaded, the sensor
control
unit 32 loads a setting value of a variation threshold (step S215). The
variation
threshold is a parameter related to the presence or absence of the third mode,
and
indicates a threshold of the variation in the amount of light received for
determining
that a person approaching is detected When the activation detection algorithm
has
the third mode and the protection detection algorithm does not have the third
mode,
the setting value of the variation threshold in the activation detection
algorithm is
higher than the setting value of the variation threshold in the protection
detection
algorithm.
[0161] Detection and Background Update Control: S22
As shown in Fig. 17, after the control parameters are loaded, the sensor
control
- 61 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
unit 32 performs the detection control and the background update control (step
S22).
Fig. 4 referred above is also a flowchart showing the detection and background
update
controls in the operation example of the automatic door system 1 according to
the
embodiment. The process shown in the flowchart of Fig. 4 may be repeatedly
carried
out as necessary.
[0162] In the detection control and the background update control, the
sensor
control unit 32 first calculates the increase-side threshoki value and the
decrease-side
threshold value of the amount of light received based on the stored value of
the
amount of light received and the sensitivity parameter loaded at step S211 in
Fig. 19.
The threshold values are determined with reference to the stored value of the
amount
of light received in order to determine that a person is detected (step S221).
[0163] Fig. 5 referred above is an explanatory diagram for describing the
detection and background update controls in the operation example of the
automatic
door system 1 according to the embodiment. The process shown in the flowchart
of
Fig. 5 may be repeatedly carried out as necessary. Fig. 5 shows the relations
between
the amount of light received indicated by the sensing signal of the small
detection
area 51, the stored value of the light received amount, the sensitivity
parameter, the
increase-side threshold, the decrease-side threshold, and the state of the
detection flag.
As shown in Fig. 5, the sensitivity parameter indicates how much the amount of
light
received should be increased or decreased from the stored value of the amount
of
light received (the reference value) to be determined that an object is
detected. The
stored value of the amount of light received (the reference value) may be
acquired at
a predetermined time such as immediately after power-on of the automatic door
system 1.
- 62 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
[0164] In the example of Fig. 5, the increase-side threshold is obtained by
adding
the sensitivity parameter to the stored value of the amount of light received.
When the
sensed amount of light received changes within the stationary object detection
time
frame, which will be described later, and the sensed amount of light received
is equal
to or greater than the increase-side threshold, the sensor control unit 32
turns on the
detection flag which means that a person the like is detected. In the example
of Fig. 5,
the decrease-side threshold is obtained by subtracting the sensitivity
parameter from
the stored value of the amount of light received. When the sensed amount of
light
received changes within the stationary object detection time frame which will
be
described later and the sensed amount of light received is equal to or less
than the
decrease-side threshold, the sensor control unit 32 turns on the detection
flag which
means that a person the like is detected. Whereas when the sensed amount of
light
received is larger than the decrease-side threshold and smaller than the
increase-side
threshold, the sensor control unit 32 turns off the detection flag which means
that a
person or the like is not detected, in other words, a not-detected state. The
detection
flag is set, for example, in a storage of the door control unit 23.
[0165] As shown in Fig. 4, after calculating the increase-side threshold
and the
decrease-side threshold, the sensor control unit 32 determines whether the
amount of
light received indicated by the sensing signal is equal to or greater than the
increase-
side threshold or equal to or less than the decrease-side threshold. (Step
S222).
[0166] When the amount of light received is not equal to or greater than
the
increase-side threshold or not equal to or less than the decrease-side
threshold (step
S222: N), the sensor control unit 32 turns off the detection flag (step S223).
[0167] Whereas when the amount of light received is equal to or greater
than
- 63 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
the increase-side threshold or equal to or less than the decrease-side
threshold (step
S222: Y), the sensor control unit 32 determines whether the amount of light
indicated
by the sensing signal remains the same for the stationary object detection
time or
longer that has been loaded in step S212 in Fig. 19 (step S224).
[0168] When the amount of light received has changed within the stationary
object detection time (step S224: N), the sensor control unit 32 turns on the
detection
flag (step S225).
[0169] Whereas when there is no change in the amount of light received
during
the stationary object detection time or longer (step S224: Y), the sensor
control unit
32 turns off the detection flag (step S226).
[0170] After turning off the detection flag, the sensor control unit 32
updates the
stored value of the amount of light received to the current value of the
amount of light
received (step S227).
[0171] First Mode Control: S23
As shown in Fig. 17, after the detection and background update controls are
performed, the sensor control unit 32 performs the first mode control (step
S23). Fig.
20 is a flowchart illustrating the first mode control in the operation example
of the
automatic door system 1 according to the embodiment. The process shown in the
flowchart of Fig. 20 may be repeatedly carried out as necessary
[0172] In the first mode control, the sensor control unit 32 first
determines
whether the detection flag is on (step S231) as shown in Fig. 20.
[0173] When the detection flag is not on (step S 231: N), the sensor
control unit
- 64-
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
32 ends the first mode control while the detection flag remains turned off.
[0174] Whereas when the detection flag is on (step S231: Y), the sensor
control
unit 32 determines whether the first mode control setting is enabled or
disabled based
on, for example, the description of the activation detection algorithm (step
S232).
[0175] When the first mode control setting is disabled (step S232: N), the
sensor
control unit 32 ends the first mode control while the detection flag remains
turned on.
[0176] Whereas when the first mode control setting is enabled (step S232:
Y),
the sensor control unit 32 determines whether the detection status remains the
same
even when the time filter is applied to the sensing signal (step S233).
[0177] When the detection status is not maintained after the time filter is
applied to the sensing signal (step S233: N), the sensor control unit 32 turns
off the
detection flag (step S234).
[0178] Whereas when the detection status remains the same even after the
time
filter is applied to the sensing signal (step S233: Y), the sensor control
unit 32 ends
the first mode control while the detection flag is turned on.
[0179] Second Mode Control: S24
As shown in Fig. 17, after the first mode control is performed, the sensor
control unit 32 performs the second mode control (step S24). Fig. 21 is a
flowchart
illustrating the second mode control in the operation example of the automatic
door
system 1 according to the embodiment. The process shown in the flowchart of
Fig. 21
may be repeatedly carried out as necessary.
[0180] In the second mode control, the sensor control unit 32 first
determines
- 65 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
whether the detection flag is on (step 5241) as shown in Fig. 21.
[0181] When the detection flag is not on (step S 241: N), the sensor
control unit
32 ends the second mode control while the detection flag remains turned off.
[0182] Whereas when the detection flag is on (step S241: Y), the sensor
control
unit 32 determines whether the second mode control setting is enabled or
disabled
based on, for example, the description of the activation detection algorithm
(step
S242).
[0183] When the second mode control setting is disabled (step S242: N), the
sensor control unit 32 ends the second mode control while the detection flag
remains
turned on.
[0184] Whereas when the second mode control setting is enabled (step S242:
Y),
the sensor control unit 32 determines whether the detection status remains the
same
even when the spatial filter is applied to the sensing signal (step S243).
[0185] When the detection status is not maintained after the spatial filter
is
applied to the sensing signal (step S243: N), the sensor control unit 32 turns
off the
detection flag (step S244).
[0186] Whereas when the detection status remains the same even after the
spatial filter is applied to the sensing signal (step S243: Y), the sensor
control unit 32
ends the second mode control while the detection flag is turned on.
[0187] Third Mode Control: S25
As shown in Fig. 17, after the second mode control is performed, the sensor
control unit 32 performs the third mode control (step S25). Fig. 22 is a
flowchart
- 66 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
illustrating the third mode control in the operation example of the automatic
door
system 1 according to the embodiment. The process shown in the flowchart of
Fig. 22
may be repeatedly carried out as necessary.
[0188] In the third mode control, the sensor control unit 32 first
determines
whether the detection flag is on (step S251) as shown in Fig. 22.
[0189] When the detection flag is not on (step S 251: N), the sensor
control unit
32 ends the third mode control while the detection flag remains turned off.
[0190] Whereas when the detection flag is on (step 5251: Y), the sensor
control
unit 32 determines whether the third mode control setting is enabled or
disabled
based on, for example, the description of the activation detection algorithm
(step
S252).
[0191] When the third mode control setting is disabled (step S252: N), the
sensor control unit 32 ends the third mode control while the detection flag
remains
turned on.
[0192] Whereas when the third mode control setting is enabled (step S252:
Y),
the sensor control unit 32 determines whether a variation of the amount of
received
light indicated by the sensing signal is equal to or more than the variation
threshold
loaded in step S215 of Fig. 19 (step S253).
[0193] When the amount of change in the amount of received light indicated
by
the sensing signal is less than the baded variation threshold (step S253: N),
the sensor
control unit 32 turns off the detection flag (step S254).
[0194] Whereas when the amount of change in the amount of received light
- 67 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
indicated by the sensing signal is equal to or more than the loaded variation
threshold
(step S253: Y), the sensor control unit 32 end the third mode control while
the
detection flag is turned off.
[0195] Exit Invalid Control: S26
As shown in Fig. 17, after the third mode control is performed, the sensor
control unit 32 performs the exit invalid control (step S26). Fig. 23 is a
flowchart
illustrating the exit invalid control in the operation example of the
automatic door
system 1 according to the embodiment. The process shown in the flowchart of
Fig. 23
may be repeatedly carried out as necessary.
[0196] In the exit invalid control, the sensor control unit 32 first
determines
whether the detection flag is on (step S261) as shown in Fig. 23.
[0197] When the detection flag is not on (step S 261: N), the sensor
control unit
32 ends the exit invalid control while the detection flag remains turned off.
[0198] Whereas when the detection flag is on (step S261: Y), the sensor
control
unit 32 determines whether the exit invalid control setting is enabled or
disabled
based on, for example, the description of the activation detection algorithm
(step
S262).
[0199] When the exit invalid control setting is disabled (step S262: N),
the
sensor control unit 32 ends the exit invalid control while the detection flag
remains
turned on.
[0200] Fig. 24 is an explanatory diagram for describing the exit invalid
control
in the operation example of the automatic door system 1 according to the
- 68 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
embodiment. When the exit invalid control setting is enabled (step S262 in
Fig. 23: Y),
among the small detection areas 52 on the exit side of the door 21, it is
determined
whether the protection detection area 52A on the exit side is in the
undetected state
based on the sensing signal from the protection detection area 52A, (step
S263) as
shown in Fig. 24. Fig. 24 shows a state in which a person moves from the
protection
detection area 52A on the exit side in the direction away from the door 21(the
direction of arrow in Fig. 24) after the person passed through the opening of
the door
21. In the example of Fig. 24, the protection detection area 52A on the exit
side is in
the undetected state.
[0201] When the protection detection area 52A on the exit side is in the
undetected state (step S263:Y), the sensor control unit 32 turns off the
detection flag
(step S264).
[0202] Whereas when the protection detection area 52A on the exit side is
not
in the undetected state (step S263: N), the sensor control unit 32 ends the
exit invalid
control while the detection flag remains turned on.
[0203] Traverse Invalid Control: S27
As shown in Fig. 17, after the exit invalid control is performed, the sensor
control unit 32 performs the traverse invalid control (step S27). Fig. 25 is a
flowchart
illustrating the traverse invalid control in the operation example of the
automatic door
system 1 according to the embodiment. The process shown in the flowchart of
Fig. 25
may be repeatedly carried out as necessary
[0204] In the traverse invalid control, the sensor control unit 32 first
determines
whether the detection flag is on (step 5271) as shown in Fig. 25.
- 69 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
,
[0205] When the detection flag is not on (step S 271: N), the
sensor control unit
32 ends the traverse invalid control while the detection flag remains turned
off.
[0206] Whereas when the detection flag is on (step S271: Y), the
sensor control
unit 32 determines whether the traverse invalid control setting is enabled or
disabled
based on, for example, the description of the activation detection algorithm
(step
S272).
[0207] When the traverse invalid control setting is disabled
(step S272: N), the
sensor control unit 32 ends the traverse invalid control while the detection
flag
remains turned on.
[0208] Fig. 26 is an explanatory diagram for describing the
traverse invalid
control in the operation example of the automatic door system 1 according to
the
embodiment. When the traverse invalid control is enabled (step S272: Y), the
sensor
control unit 32 determines whether a person is moving only in the traverse
direction
in front of the door 21 (in other words, the direction abng the door 21) as
indicated by
the arrow in Fig. 26 based on a movement vector of the person acquired from a
change in the small detection areas 51 in the detected state (step S273).
[0209] When the person moves only in the traverse direction in
front of the
door 21 (step S273: Y), the sensor control unit 32 turns off the detection
flag (step
S274).
[0210] Whereas when the person is not moving in the traverse
direction in
front of the door 21 (step S273: N), the sensor control unit 32 ends the
traverse
invalid control while the detection flag remains turned on.
- 70 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
,
[0211] Detection Determination: S28
As shown in Fig. 17, after the traverse invalid control is performed, the
sensor
control unit 32 performs the detection determination (step S28). Fig. 27 is a
flowchart
illustrating the detection determination in the operation example of the
automatic door
system 1 according to the embodiment. The process shown in the flowchart of
Fig. 27
may be repeatedly carried out as necessary.
[0212] In the detection determination, the sensor control unit 32 first
determines whether the detection flag is on (step S281) as shown in Fig. 27.
[0213] When the detection flag is not on (step S281: N), the sensor
control unit
32 determines that a person approaching is not detected (step S282).
[0214] Whereas when the detection flag is on (step S281: Y), the sensor
control
unit 32 determines that a person approaching is detected (step S283).
[0215] As described above, the activation detection control (SA2, S2B)
is
performed. In the activation detection control, the order of execution of
steps S22 to
S27 in FIG. 17 may be switched or changed. Also, one or more of the steps may
be
omitted
[0216] Protection Detection Control: S2C, S2D
When the protection detection control is performed (Step S2C, Step S2D), the
sensor control unit 32 performs the steps shown in Fig. 18. Unlike the
activation
detection control of Fig. 17, the first mode control (step S23), the second
mode control
(step S24), the third mode control (step S25), the exit invalid control (step
S26), and
the traverse invalid control (step S27) are not executed in the protection
detection
control of Fig. 18. However, depending on the relation between the extent of
the safety
- 71 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
to be secured and the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing
operations,
any combination of the first mode control, the second mode control, the third
mode
control, the exit invalid control, and the traverse invalid control may be
performed in
the protection detection control Further, the sensor control unit 32 may
select which
type of the protection detection algorithm is to be used depending on whether
the
door state determined in step Si of Fig. 16 is the fully opened state or in
closing
motion. That is, the sensor control unit 32 may change the protection
detection
algorithm used for detection depending on the door position.
[0217] According to the above-described embodiment, in the same special
detection area 51A, detection in accordance with the activation detection
algorithm is
performed when the door 21 is in the closed position, and detection in
accordance
with the protection detection algorithm when the door 21 is in a position
other than
the closed position. As a result, when the door 21 is in the closed position,
it is possible
to prevent the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the door 21
caused by
erroneous detection in accordance with the protection detection algorithm.
Moreover,
when the door 21 is a position other than the closed position, it is possible
to prevent
deterioration of the safety in the vicinity of the door 21 due to failures of
detection in
accordance with the activation detection algorithm. Therefore, according to
the
aspects of the embodiment, it is possible to achieve both the reduction of the
unnecessary opening and closing operations of the door and the improvement of
the
safety
[0218] First Modification Example
A description is given of a first modification example in which detection
based
on a captured image is performed Fig. 28 is a block diagram illustrating the
automatic
- 72 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
door system 1 according to the first modification example of the embodiment.
As
shown in Fig. 28, the automatic door sensor 3 of the first modification
example
includes the image capturing unit 313 as an example of the detection unit
instead of
the emitter 311 and the receiver 312. The image capturing unit 313 is, for
example, a
CCD or CMOS camera having sensitivity in the visible light range. The image
capturing
unit 313 may be an infrared camera having sensitivity in the infrared range.
[0219] The image capturing unit 313 captures an image of the detection area
5,
and outputs a sensing signal indicating the captured image of the detection
area 5 to
the sensor control unit 32. The sensor control unit 32 detects a person
approaching or
the like based on the sensing signal supplied from the image capturing unit
313, and
supplies the open signal to the automatic cbor control 23 in response to the
detection
of the person. Alternatively, it is also possible in the first modification
that the door
control unit 23 performs the detection of a person.
[0220] Also in the first modification example, for the same special
detection area
51A, the sensor control unit 32 uses a result of detection in accordance with
the
activation detection algorithm for the drive control of the door 21 when the
door 21 is
in the closed position, and switches from the result of the detection in
accordance with
the protection detection algorithm to a result of detection in accordance with
the
activation detection algorithm for the drive control of the door 21 when the
door 21 is
in a position other than the closed position. In this way, it is possible to
achieve both
the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the door
and the
improvement of the safety. In addition, since a person approaching and the
like can be
detected with high accuracy based on a captured image in the first
modification
example, it is possible to achieve both the reduction of the unnecessary
opening and
- 73 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
closing operations of the door and the improvement of the safety.
[0221] Second Modification Example
A description is given of a second modification example in which detection
based on the Doppler effect of a radio wave is performed. Fig. 29 is a block
diagram
illustrating the automatic door system 1 according to the second modification
example
of the embodiment. As shown in Fig. 29, the automatic door sensor 3 of the
second
modification example includes the radio transceiver unit 314 as an example of
the
detection unit. The radio transceiver unit 314 transmits a radio wave to the
detection
area 5 and detects an interference wave between a transmitted radio wave and a
reflected wave reflected by a person approaching or the like in the detection
area 5.
The radio transceiver unit 34 then supplies a sensing signal that indicates
the
interference wave to the sensor control unit 32. The sensor control unit 32
detects a
person approaching based on the sensing signal supplied from the radio
transceiver
unit 34, and supplies the open signal to the automatic door control 23 in
response to
the detection of the person and the like. Alternatively, it is also possible
in the second
modification that the door control unit 23 performs the detection of a person.
[0222] Also in the second modification example, for the same special
detection
area 51A, the sensor control unit 32 uses a result of detection in accordance
with the
activation detection algorithm for the drive control of the door 21 when the
door 21 is
in the closed position, and switches from the result of the detection in
accordance with
the protection detection algorithm to a result of detection in accordance with
the
activation detection algorithm for the drive control of the door 21 when the
door 21 is
in a position other than the closed position. In this way, it is possible to
achieve both
the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the door
and the
- 74-
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
,
improvement of the safety
[0223] The automatic door sensor 3 may use an ultrasonic wave or
a distance
measurement sensor instead of the infrared light, the image and the radio wave
described above.
[0224] Third Modification Example
Next, a third modification example will now be described. Fig. 30 is a block
diagram illustrating the automatic door system 1 according to the third
modification
example of the embodiment. As shown in Fig. 30, the automatic door sensor 3 of
the
third modified example supplies, to the door control unit 23, a result of
detection in
accordance with the activation detection algorithm and a result of detection
in
accordance the protection detection algorithm as sensing signals. The door
control
unit 23 that has received the two types of sensing signal determines which
detection
result is used for the control or neither of the detection results is not used
depending
on the position of the door 21 and other conditions. For example, when it is
determined that a person or an object does not exist from the result of
detection in
accordance with the activation detection algorithm but it is determined that a
person
exists from the result of detection in accordance with the protection
detection
algorithm, the door 21 can be closed at a lower speed than normal
[0225] Also in the third modification example, for the same
special detection
area 51A, the door control unit 32 uses a result of detection in accordance
with the
activation detection algorithm for the drive control of the door 21 when the
door 21 is
in the closed position, and switches from the result of the detection in
accordance with
the protection detection algorithm to a result of detection in accordance with
the
activation detection algorithm for the drive control of the door 21 when the
door 21 is
- 75 -
CA 03052257 2019-07-31
in a position other than the closed position. In this way, it is possible to
achieve both
the reduction of the unnecessary opening and closing operations of the door
and the
improvement of the safety.
[0226] Aspects of the invention are not limited to the individual
embodiments
described above. For example, instead of using the activation detection
algorithm and
the protection detection algorithm, an activation sensor and a protection
sensor that
are physically separate but have overlapping detection areas may be used. In
this case,
the activation sensor has a person or object detection function equivalent to
the
activation detection algorithm, and, the protection sensor has a person or
object
detection function equivalent to the protection detection algorithm.
[0227] Aspects of the present invention are not limited to the foregoing
individual embodiments and embrace various modifications conceivable by those
skilled in the art. Advantageous effects of the present invention are also not
limited to
those described above. That is, various additions, changes, and partial
deletions are
possible in a range of not departing from the conceptual ideas and spirit of
the present
invention derived from contents defined in the claims and equivalents thereof.
- 76 -