Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
1
1
f
DESCRIPTION
Title of Invention
INTERIOR BUILDING MATERIALS
Technical Field
[0001] The present invention relates to an
improvement in an interior building material including
a plate-like base material, such as a gypsum board, to
which a magnet does not attach inherently and
specifically relates to an interior building material
to be used for forming an interior wall and the like,
wherein: a functionality that a magnet, which is a
magnetic material, can be attached to a surface of the
interior building material has been imparted; and, in
addition to this functionality, favorable construction
efficiency such that the interior building material can
be easily cut with a cutter knife or the like has been
achieved.
Background Art
[0002] A gypsum board (also called a plaster board)
is a building material obtained by shaping a material
which uses gypsum as a main component into a plate and
wrapping the plate with a special paperboard, and is very
strong, has excellent fire resistance, and has high
levels of heat insulating properties and sound
insulating properties, so that gypsum boards are widely
used as interior building materials in making walls and
ceilings. The reason that the gypsum boards have been
widely used as interior building materials is also due
to the fact that, in addition to the above-described
excellent functionalities, the gypsum boards are
excellent in construction efficiency by which the gypsum
boards can be easily cut with a simple sharp cutting tool
such as a cutter knife even though the gypsum boards are
building materials made of an inorganic material.
[0003] However, to favorably display, for example,
a picture, a photograph, or the like on a wall face made
of a gypsum board, a special anchor developed for gypsum
boards needs to be used. In addition, there is a problem
that in the case where a usual screw, nail, or thumbtack,
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
2
or a special anchor for gypsum boards, which has been
forcibly used for a wall face made of a gypsum board,
is pulled out when it becomes unnecessary to use them,
a hole is left on a wall. The problem that a hole is left
on a wall after a screw, a nail, a thumbtack, or the like
is pulled out occurs similarly to other interior building
materials, not limited to the gypsum boards.
[0004] To solve this
problem, a stopper with a magnet,
which makes it unnecessary to make a hole in a wall and
is a substitute for a thumbtack is developed, and such
stoppers with a magnet are widely used for walls made
of steel or the like. In addition, a magnet sheet which
can be easily attached to walls made of steel or the like
and has an image, characters, or the like thereon, a
magnet sheet which can also be utilized as a white board,
and the like are known, and such magnet sheets are widely
used because they are freely attachable and detachable,
and a trace of detachment is not left on a wall.
[0005] However, these
products which employ a system
of attaching them to a wall with a magnet restrict wall
materials and cannot be used, for example, for generally
used wall faces made of a gypsum board. To use such
products, a sheet dedicated for attaching a magnet sheet
needs to be installed on a wall face, and therefore
another problem that the design property of a wall face
is impaired arises in addition to complication.
[0006] To solve the
above-described problems, there
is a proposal on a wall member in which a magnetic sheet
such as a steel sheet is pasted to a surface of a support
member such as a gypsum board, and wallpaper is
superimposed on the surface of the magnetic sheet (see
Patent Literature 1). In addition, a building material
in which a material such as a gypsum board and a metal
sheet are laminated and made into a composite, the
building material being developed in order to prevent
malfunction of electronic devices, has been known in
recent years, and there is a possibility that a magnet
can be attached to the surface of the building material
in some cases (see Patent Literature 2).
Citation List
Patent Literature
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
3
,
,
[ 0007 ] Patent Literature 1: Japanese Patent Laid-Open No.
2014-152596
Patent Literature 2: Japanese Patent Laid-Open No.
2008-87404
Summary of Invention
Technical Problem
[0008] However, according to studies conducted by
the present inventors, in the wall member described in
Patent Literature 1, the magnetic sheet such as a steel
sheet is pasted to almost the whole face of the support
member such as a gypsum board or pasted to the support
member over a large area even if the magnetic sheet is
pasted to only a portion of the support member, and
therefore the construction efficiency of the support
member is remarkably inferior. In addition, the
specific wall member described in Patent Literature 1
has constitution in which: a magnetic sheet such as a
steel sheet is pasted, with a double sided tape or an
adhesive, to the surface of a commercially available
gypsum board both surfaces of which are covered with
paper; and a paperboard is superposed on the magnetic
sheet, so that a part where a magnet can be attached to
a wall face is formed by construction work, and therefore,
the construction work is extremely complicated and the
constitution is such that the wall member cannot be used
for general purposes.
[0009] In addition, the previously described
building material developed in order to prevent
malfunction of electronic devices intends to impart
electromagnetic wave shielding properties, and
therefore most of the metal sheets that are described
to be usable are those of types to which a magnet does
not attach. Further, with respect to the structure of
the building material, many materials are laminated on
the metal sheet, and therefore the building material is
not constituted so that a magnet can attach to the surface
thereof.
[0010] On the other hand, paints each obtained by
blending a magnetic substance such as an iron powder are
commercialized, and an interior building material such
as a gypsum board can be constructed so that a magnet
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
4
can attach thereto by providing a coating film on the
surface thereof. However, in this case, construction of
thick coating on the construction site needs to be carried
out, and therefore it is difficult to apply a paint
uniformly and there are various problems that the
construction requires a great deal of skill, the
construction site gets dirty, high incombustibility of
a gypsum board cannot be secured, etc. , so that such
paints cannot be used for general purposes, which is
similar to the technique described in Patent Literature
1.
[0011] To solve these problems, it is also considered
that a coating film layer containing a magnetic substance
is formed in advance by applying a paint containing a
magnetic substance blended therein on an interior
building material such as a gypsum board. However, in
this case, there is a practical problem that facilities
and a technique for coating the surface of the interior
building material uniformly with a paint, and facilities
and a technique for drying are required, making the scale
of the facilities large.
[0012] Accordingly, an object of the present
invention is to provide an interior building material
by which: in an interior building material which is
represented by a gypsum board and to which a magnet does
not attach, the surface of such an interior building
material can be modified so that a magnet can attach to
the surface by simple means that can be put into practical
use; a wall face and the like for which a stopper with
a magnet, which is a substitute for a thumbtack, and a
magnet sheet are usable can thereby be formed; and
favorable construction efficiency such that the interior
building material can be easily cut with a cutter knife
or the like has been achieved.
Solution to Problem
[0013] The above-described object is achieved by the
present invention described below. That is, the present
invention provides an interior building material
comprising a plurality of sheet-like magnetic materials
fixed to at least a portion of a surface or back surface
of a plate-like base material to which a magnet does not
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
attach, wherein adjacent magnetic materials are disposed
in such a way as to have a portion where the adjacent
magnetic materials are in contact with each other, or
adjacent magnetic materials are disposed through a gap
having a narrow portion.
[0014] Preferred embodiments of the interior
building material according to the present invention
include the followings.
The adjacent magnetic materials are disposed in
such a way as to be in contact with each other and the
plurality of sheet-like magnetic materials are fixed in
a state of being arranged without a gap; the narrow
portion of the gap is within a range of 0.05 to 5.0 mm;
the narrow portion of the gap is within a range of 0.10
to 1.0mm; the plurality of sheet-like magnetic materials
have the same shape, and the shape is any one of shapes
selected from the group consisting of a square, a
rectangle, a trapezoid, a triangle, a circle, and an
ellipse; four sides of the square, two sides of the
rectangle, at least one side of the trapezoid or the
triangle, a diameter of the circle, or at least one of
a major axis and a minor axis of the ellipse is 10 cm
to 35 cm; the gap is formed by only the narrow portion,
and the narrow portion is linear; at least one of the
plurality of sheet-like magnetic materials is a
sheet-like magnetic material having a through hole; at
least one of the plurality of sheet-like magnetic
materials has a chamfered portion at an outer
circumference thereof; when the interior building
material is stood in such a way as to be vertical, and
one sheet of A4 plain paper is held at a portion where
the sheet-like magnetic materials are disposed with one
disk-like magnet having a diameter of a magnet portion
of 17 mm(I) and having a force of attraction of 3.5 N to
an iron sheet having a thickness of 1 mm, the portion
where the sheet-like magnetic materials are disposed has
force of attraction by which the plain paper does not
fall; having a structure in which the base material is
a plate-like member made of gypsum, and, further, a paper
sheet is pasted on the plurality of disposed sheet-like
magnetic materials; the sheet-like magnetic materials
have a thickness of 0.1 to 1.0 mm; the sheet-like magnetic
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
6
materials have a thickness of 0.2 to 0.8 mm; any one of
the plurality of sheet-like magnetic materials is an iron
sheet or a steel sheet having rust-proofing performed
on both faces or one face thereof; having a thickness
of 9.5 to 10.0 mm; and having a thickness of 12.5 to 13.0
mm.
Advantageous Effects of Invention
[0015] According to
the present invention, a highly
convenient interior building material in which an
interior building material the surface of which cannot
be attached to a magnet, the interior building material
represented by a gypsum board, has been modified so that
the surface thereof can be attached to a magnet by simple
means that can be put into practical use is provided
although the highly convenient interior building
material has simple constitution. According to the
present invention, a highly convenient interior building
material wherein when plain paper or the like is held
on the surface of the interior building material with
a stopper with a magnet which is a substitute for a
thumbtack, a magnet sheet, or the like, which has been
used in various types and forms in a wide range of fields,
the interior building material exhibiting force of
attraction of the magnet which is sufficient for the
interior building material to be able to hold the plain
paper, and, further, a highly convenient wall face using
the highly convenient interior building material are
provided by adopting the above-described constitution.
The most advantageous point of the present invention is
in that according to the present invention, there is
provided an interior building material which is a highly
convenient interior building material as described above,
and by which favorable construction efficiency such that
a cutter knife can be inserted between adjacent
sheet-like magnetic materials, and thereby the interior
building material can be easily cut into an appropriate
size has been achieved.
Brief Description of Drawings
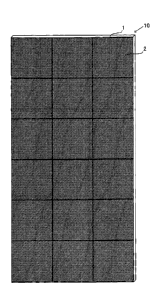
[0016][Figure 1] Figure 1 is a schematic diagram
illustrating an interior building material of Example
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
7
2 according to the present invention.
[Figure 2] Figure 2 is a schematic diagram illustrating
an interior building material of Example 1 according to
the present invention.
[Figure 3] Figure 3 is a schematic diagram illustrating
another example of the interior building material
according to the present invention.
[Figure 4] Figure 4 is a schematic diagram illustrating
another example of the interior building material
according to the present invention.
[Figure 5] Figure 5 is a schematic diagram illustrating
another example of the interior building material
according to the present invention.
[Figure 6] Figure 6 is a schematic diagram illustrating
another example of the interior building material
according to the present invention.
[Figure 7] Figure 7 is a schematic diagram illustrating
another example of the interior building material
according to the present invention.
[Figure 8] Figure 8 is a schematic diagram illustrating
another example of the interior building material
according to the present invention.
[Figure 9] Figure 9 is a schematic diagram illustrating
another example of the interior building material
according to the present invention.
[Figure 10] Figure 10 is a schematic diagram illustrating
another example of the interior building material
according to the present invention.
[Figure 11] Figure 11 is a schematic diagram illustrating
another example of the interior building material
according to the present invention.
[Figure 12] Figure 12 is a schematic diagram illustrating
another example of the interior building material
according to the present invention.
[Figure 13] Figure 13 is a schematic diagram describing
a method for measuring force of attraction of a magnet
to a 1-mm iron sheet, the magnet used in evaluating the
force of attraction of the interior building material
according to the present invention to the magnet.
Description of Embodiments
[0017] Hereinafter,
the present invention will be
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
8
described in detail giving preferred embodiments. The
present invention is not restricted by the following
embodiments, and various modifications and replacements
of the following embodiments can be added without
deviation from the scope of the present invention.
[0018] The present inventors have conducted diligent
studies in order to solve the previously described
problems of the conventional techniques to recognize
that any of the conventional techniques in which a
plate-like base material, such as a gypsum board, to which
a magnet does not attach is modified so that the surface
thereof can be attached to a magnet deteriorates the
construction efficiency and design property of the base
material and lacks the industrial applicability, and
this point is the biggest technical problem in the
conventional techniques. Studies have been conducted
based on such recognition to find that in the case where
constitution is made in such a way that a plurality of
sheet-like magnetic materials are disposed and fixed to
at least a portion of the surface or the back surface
of the base material so that the surface can be attached
to a magnet, an embodiment is made in such a way that
adjacent magnetic materials are made to be in contact
with each other and the plurality of sheet-like magnetic
materials are fixed in a state of being arranged without
a gap, or an embodiment is made in such a way that a
plurality of adjacent sheet-like magnetic materials are
disposed and fixed through a gap having at least a narrow
portion, and thereby an interior building material in
which the problems of the conventional techniques are
solved, which is highly convenient, and which is
excellent in construction efficiency can be made, and
thus the present inventors have reached the present
invention.
[0019] That is, the present inventors have found that
by fixing a plurality of sheet-like magnetic materials
in a state of being arranged without a gap, or by arranging
and fixing a plurality of sheet-like magnetic materials
through a gap having a narrow portion, the interior
building material according to the present invention is
in a state where the adjacent sheet-like magnetic
materials are cut and separated even in the state where
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
9
the sheet-like magnetic materials are arranged without
a gap, not to mention the case where the gap is provided,
so that a blade of a cutter knife can be easily inserted
between the sheet-like magnetic materials, and the
construction efficiency which is similar to that before
the modification can thereby be secured.
[0020] According to
studies conducted by the present
inventors, for example, even in the case where an interior
building material 10 is made by fixing on a gypsum board,
which is a plate-like base material shown by reference
sign lin Figure 1, a plurality of galvanized steel sheets,
which are sheet-like magnetic materials shown by
reference sign 2, in a state of being arranged without
a gap, surprisingly, a blade of a cutter knife can be
easily inserted between the adjacent magnetic materials
by bending the above-described interior building
material 10 a little so that the side on which the
plurality of galvanized steel sheets are fixed is made
convex, and as a result, the present inventors have found
that the interior building material having the
above-described constitution can be easily cut by a
cutter knife. In addition, in the case where an interior
building material 10 the constitution of which is such
that, as illustrated in Figure 2, adjacent sheet-like
magnetic materials 2 are arranged and fixed through a
gap having a narrow part shown by reference sign 3 is
made, a blade of a cutter knife or even a blade of a sharp
cutting tool the thickness of which is thicker than a
blade of a cutter knife can be easily inserted into this
gap, and the base material can be easily cut by this blade .
In this embodiment for carrying out the present invention,
which is illustrated in Figure 2, it is preferable to
design the shape and disposition of the plurality of
sheet-like magnetic materials 2 based on the recognition
that the gap having a narrow portion 3 and being formed
by disposing the plurality of sheet-like magnetic
materials 2 on the base material 1 is a portion to be
a position that is freely cut in the interior building
material according to the present invention. By
designing the shape and disposition of the plurality of
sheet-like magnetic materials 2 in this way, an interior
building material that is more excellent in construction
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
,
,
efficiency can be provided.
[0021] The gap having a narrow portion 3 in the
interior building material according to the present
invention may be appropriately designed as necessary
considering the above-described construction efficiency
of the interior building material. That is, the size of
the gap may have a width such that a blade of a sharp
cutting tool such as a cutter knife can be easily inserted
without an operation of, for example, bending the
interior building material as described above at the
narrow portion 3. As the specific size of the narrow
portion 3 in the case where the constitution in which
the gap is provided is adopted, the shortest distance
between adjacent magnetic materials (narrow portion 3)
may be approximately within a range of 0.05 to 5.0 mm
or may be narrower as narrow as approximately within a
range of 0.10 to 1.0 mm. In addition, the position where
the gap is provided may be arbitrarily determined
considering the convenience in cutting and using the
interior building material.
[0022] Usually, the size of an interior building
material is 3 shaku x 6 shaku, which is a standard shaku
size of panel plywood, in many cases. Therefore, in the
present invention, in the case where a plurality of
sheet-like magnetic materials are arranged according to
either of the above-described types of constitution, it
is preferable to adopt the constitution in which magnetic
materials are each disposed at a position where
construction work is easily done and the magnetic
materials can be cut at every desired, predetermined
intervals. In the case where the interior building
material is cut at a portion where adjacent magnetic
materials are in contact with each other or at a gap formed
by adjacent magnetic materials, it is preferable to adopt
the constitution in which the gaps are disposed at every
predetermined intervals in such a way that the width
thereof is in a range of, for example, 10 to 35 cm, more
specifically, a width of either 10 cm, 15 cm, or 30 cm.
[0023] Any of the conventional interior building
materials using a metal sheet uses a metal sheet having
a large area, and this has been a cause for deteriorating
the construction efficiency. In contrast, in the
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
11
present invention, an interior building material 10
having an embodiment in which, for example, a gypsum board
which is an interior building material of 3 shaku x 6
shaku is used as a base material 1, and sheet-like
magnetic materials 3 of about 30-cm square are orderly
arranged and fixed to the surface of the base material
1 in such a way as to be in contact with each other or
through a narrow gap, as illustrated in Figure 1 or Figure
2, is made. By constituting the interior building
material 10 in this way, the above-described
deterioration of the construction efficiency, which is
caused by using the above-described metal sheet having
a large area, is solved, and remarkable effects of the
present invention are obtained. It is to be noted that
Figure 1 and Figure 2 are schematic diagrams and
illustrates the contact portions and gaps with emphasis.
The same applies to the other figures.
[0024] By constituting the interior building
material 10, which is illustrated in Figure 1 or Figure
2, in the manner as described above, the interior building
material 10 according to the present invention has the
constitution in which the interior building material 10
can be cut by a cutter knife of the like at this portion
where a blade of a cutter knife can be easily inserted
between the adjacent sheet-like magnetic materials 2 and
is divided about every 30 cm. As a result, in the
interior building material according to the present
invention, by utilizing these divisions (contact
portions and gaps) where a blade of a cutter knife can
be easily inserted and cutting can be conducted, a gypsum
board which is a base material 1 can be easily cut in
a width (length) of, for example, 30 cm, 60 cm, 90 cm,
etc. using the magnetic materials as guides without using
a safety ruler or the like. In this way, the interior
building material product according to the present
invention can be used up without waste and therefore is
excellent in effective utilization of resources and in
economic efficiency. When sheet-like magnetic
materials of about 10-cm square or about 15-cm square,
not limited to those described above, are used, the
interior building material according to the present
invention is a useful product which can be easily cut
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
12
into a width (length) of 10 cm, 15 cm, 20 cm, 40 cm, 45
cm, 50 cm, 60 cm, 70 cm, 75 cm, 80 cm, etc.
[0025] The shape of a plurality of sheet-like
magnetic materials 2 that constitute the interior
building material 10 according to the present invention
is not limited to a square illustrated in Figure 1 and
Figure 2, but may be anyone of, for example, a rectangle
(see Figures 3 and 4), a trapezoid (not illustrated in
Figures), a circle (see Figure 5), an ellipse (not
illustrated in Figures), a triangle (see Figures 6 and
7), and the like. In the examples illustrated in Figures,
the shapes of a plurality of sheet-like magnetic
materials are the same, but in the present invention,
the shapes are not limited to these, and combinations
of the above-described geometrical figures may be used.
For example, in interior finishing, it is preferable to
appropriately select the shapes and disposition of the
magnetic materials to use the magnetic materials so that
a portion where the base material is greatly exposed
exists in a region surrounded and formed by a plurality
of adjacent sheet-like magnetic materials when
considering that a case where through holes need to be
provided in the interior building material occurs.
[0026] In addition, the interior building material
according to the present invention includes a
plurality of sheet-like magnetic materials 2 disposed
over the whole face of the base material 1 in the examples
given in Figure 1 to Figure 10. It is preferable that
the magnetic materials 2 be disposed in 90% or more, more
preferably 95% of the area of the surface or back surface
of the base material 1. However, the magnetic materials
2 are not necessarily disposed in this manner. For
example, as illustrated in Figure 11 and Figure 12, the
magnetic materials 2 may be disposed in a range where
the convenience is considered to be improved when the
surface of the interior building material can be attached
to a magnet. Further, as illustrated in Figure 8 to
Figure 10, it is also a preferred embodiment of the
present invention that the constitution in which a
plurality of sheet-like magnetic materials 2 are
disposed in only the portion where there is a high
possibility that the building material which is the base
CA 03055065 2019-039
13
material 1 can be cut and used is adopted considering
the construction efficiency, and a sheet-like magnetic
material 2 having a large area is disposed in a portion
where there is no possibility that the building material
is cut and used.
[0027] An important thing in the present invention
is, rather than the range where a plurality of sheet-like
magnetic materials are arranged, to adopt the
constitution in which a state where a plurality of
sheet-like magnetic materials are arranged is made, so
that a blade of a cutter knife or the like can be easily
inserted between the adjacent magnetic materials as
necessary in construction work and the base material can
be cut along the outer circumferences of the sheet-like
magnetic materials (that is, sheet-like magnetic
materials are not cut). That is, as a result of adopting
such constitution, an interior building material can be
made into a size as needed freely, and easily and without
waste, and therefore it can be achieved to provide a
product which can make the surface of a formed wall, in
forming an interior wall, highly convenient in such a
way that a magnet can attach thereto, and which is
excellent in convenience /construction
efficiency/economic efficiency by which the
construction efficiency is not impaired, and the amount
of left-over materials produced can be reduced.
[0028] More preferred embodiments of the interior
building material being the object of the present
invention and having the constitution in which a blade
of a cutter knife or the like can be easily inserted
between adjacent magnetic materials include an
embodiment using a building material in which a chamfered
portion is provided at the outer edge (outer
circumference) of at least one of a plurality of
sheet-like magnetic materials 2, or, if necessary, of
all the plurality of sheet-like magnetic materials 2.
When such an embodiment is adopted, even in an interior
building material having the constitution particularly
as illustrated in Figure 1 in which adjacent magnetic
materials are disposed on the base material 1 in such
a way as to be in contact with each other, and a plurality
of sheet-like magnetic materials 2 are fixed in a state
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
14
of being arranged without a gap, a blade of a cutter knife
or the like can be inserted more easily between adjacent
sheet-like magnetic materials. In addition, when the
chamfered portion is provided at the outer edge (outer
circumference) of the magnetic materials 2, a blade of
a cutter knife or the like can be easily inserted between
the adjacent magnetic materials even in the state where
a sheet-like material such as wallpaper is pasted to the
surface of the interior building material according to
the present invention, so that the interior building
material according to the present invention is easily
cut.
[0029] The method for fixing a plurality of
sheet-like magnetic materials that constitute the
interior building material according to the present
invention on the base material may any of conventionally
known methods. For example, the magnetic materials may
be pasted to the base material with an adhesive or stopped
to the base material with a double-sided tape. The
adhesive is not particularly limited, and, for example,
organic adhesives such as vinyl acetate-based adhesives
and epoxy-based adhesives and inorganic adhesives such
as alkali metal silicates may be used.
[0030] Examples of the sheet-like magnetic material
that constitutes the interior building material
according to the present invention include an iron sheet
or a steel sheet. The steel sheet may be a
surface-treated steel sheet on which a surface treatment
has been performed. The surface treatment on the
surface-treated steel sheet may be any of surface
treatments that can make a state where a magnet attaches
to the surface of the building material when the interior
building material according to the present invention is
constituted. Examples of the steel sheet include steel
sheets plated with a monometal (monometal-plated steel
sheets) suchasazinc-plated steel sheet and steel sheets
plated with alloy (alloy-plated steel sheets) such as
hot-dip 55% aluminum-zinc alloy steel sheet
(Galvalume(R)). In Examples, which will be described
later, cases where galvanized steel sheets, as a
representative example of the steel sheets are disposed
are shown, but, as a matter of course, the steel sheet
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
is not limited thereto.
[0031] The sheet-
like magnetic material to be used
in the present invention may be a sheet-like magnetic
material having one through hole or a plurality of through
holes (not illustrated in Figures) . By constituting the
sheet-like magnetic material in this way, a nail or a
screw can be driven to this through hole during or after
the construction work for the interior building material
according to the present invention, and therefore the
construction efficiency, convenience, and design
property of the interior building material according to
the present invention can be more improved. More
specifically, for example, when the through hole is
provided in the sheet-like magnetic material in the case
of stopping the interior building material according to
the present invention, in which the sheet-like magnetic
materials are fixed to a base material face, the interior
building material according to the present invention can
be simply stopped with a screw or the like using a
general-purpose electric tool by utilizing this through
hole, and a surface state after stopping the interior
building material according to the present invention is
made flat and favorable. In contrast, in the case where
a through hole is not provided in the sheet-like magnetic
material, when an attempt of stopping the interior
building material according to the present invention
with a screw or the like using a general-purpose electric
tool is made, a bulge occurs on the surface of the magnetic
material (protrusion occurs on the side of the surface)
to no small extent although it depends on the thickness
of the magnetic material, and therefore there is a risk
that when the surface of the magnetic material is finished
with wallpaper or the like, a problem occurs to the
appearance, and the design property is impaired. From
these points, it is preferable that one through hole or
a plurality of through holes be provided in advance in
the sheet-like magnetic materials to be used in the
present invention.
[0032] Accordingly,
it is preferable that the size
of the through hole be, for example, the size of about
10 to about 20 mm 4), in which the screw head or the nail
head can fall. The position where the through hole is
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
16
provided and the number of through holes are not
particularly limited and may be appropriately determined
considering improvements in the construction efficiency,
improvements in the convenience, and improvements in the
design property each obtained by providing a through hole
or through holes in the interior building material
according to the present invention. In addition, the
through hole portions into which a screw head or a nail
head falls can be treated to be flat by treating through
hole portions using a pate material containing a magnetic
material, and a resin or the like.
[0033] In addition, examples of preferred
embodiments of the interior building material according
to the present invention include an embodiment having
constitution in which, on the surface side of a plurality
of sheet-like magnetic materials such as iron sheets
disposed on one face of the base material, a sheet of
paper or the like is further pasted. By constituting the
interior building material according to the present
invention in this way, painting can be performed without
performing a primer treatment, and, in addition, wall
paper can be pasted with a usual paste for wallpaper.
The material of the sheet to be used above is not limited
to paper and may be any material. Examples of the
preferred material include materials on which paste for
wallpaper is easily spread or materials by which a surface
property enabling a paint to be directly applied are
obtained.
[0034] The thickness of the sheet-like magnetic
material such as an iron sheet is not particularly limited
as long as, for example, force of attraction by which
one or more sheets of A4 printing paper can be held with
one commercially available stopper with a magnet (so
called magnet), which is a substitute for a thumbtack,
is obtained. According to studies conducted by the
present inventors, it is preferable that the thickness
be specifically 0.1 mm or more, more preferably 0.2 mm
or more. In addition, the thickness of the sheet-like
magnetic material, such as an iron sheet, that
constitutes the interior building material according to
the present invention may be thick, but even when the
thickness exceeds 1 mm, resultant force of attraction
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
17
is not so large, and when thick magnetic materials are
used, the interior building material is heavy although
it depends on the range of disposing the sheet-like
magneti c materi al s , so that it is concerned that the heavy
interior building material is a cause for deteriorating
the construction efficiency and the workability. In
addition, when the thickness is too thick, material costs
increase unnecessarily, which is uneconomical, and
therefore it is preferable to make the thickness 1 mm
or less. When the desired force of attraction is such
an extent that a sheet of A4 paper is fixed with one magnet,
use of a sheet-like magnetic material having a thickness
of about 5mm is enough. According to studies conducted
by the present inventors, it is preferable that the
sheet-like magnetic material have a thickness of about
0.8 mm in the case of considering that a heavy, small
shelf is installed with a commercially available stopper
with a magnet, the stopper having realized strong force
of attraction.
[0035] Considering
various situations that occur in
the case where an inner wall face is formed, it is
preferable that the interior building material according
to the present invention be an interior building material
that can exhibit the force of attraction at least to such
an extent that a sheet of A4 paper can be held with one
magnet as described previously. More specifically, it
is desired that when the interior building material is
stood in such a way as to be vertical, and one sheet of
A4 plain paper is held at the portion where the sheet-like
magnetic materials are disposed with one disk-like
magnet having a diameter of a magnet portion of 17 mml)
and having a force of attraction of 3.5N to an iron sheet
having a thickness of 1 mm, the portion where the
sheet-like magnetic materials that constitute the
interior building material according to the present
invention are disposed has force of attraction by which
the plain paper does not fall. That the attraction force
of the disk-like magnet having a diameter of 17 mm (1) used
in the above-described test to the iron sheet having a
thickness of 1 mm is 3.5 N is measured in the manner as
illustrated in Figure 13. That is, a magnet 5 with a hook,
the magnet having a diameter of 17 mm(1), is placed on an
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
18
iron sheet 3 having a thickness of 1 mm, and the magnet
is pulled over with the hook by hand under a condition
of a testing speed of 3mm/sec to read the maximum strength
using Autograph (not illustrated in Figures).
[0036] Most common interior wall materials (base
materials) include gypsum boards. In addition, among
them, the gypsum boards which are most often used as an
interior wall material are gypsum boards having a
thickness of 9.5 to 10.0 mm or 12.5 to 13.0 mm.
Accordingly, it is suitable that the thickness of the
interior building material according to the present
invention, in which a plurality of sheet-like magnetic
materials, such as iron sheets, are arranged and fixed
through a particular gap, is 9.5 to 10.0 mm or 12.5 to
13.0 mm because finishing work can be conducted without
causing unevenness between a surrounding wall and the
interior building material.
[0037] Accordingly, it is preferable to use gypsum
boards as the base material that constitutes the interior
building material according to the present invention.
The gypsum boards include, not limited to
general-purpose boards, waterproof boards in which
waterproof properties are improved, fire-resistant
gypsum boards in which fire resistance performance is
reinforced more, and the like. Besides, the base
materials that constitute the interior building material
include boards made of rock wool, boards using a glass
fiber, and the like. According to studies conducted by
the present inventors, in the interior building material
according to the present invention of any embodiments
in which a plurality of sheet-like magnetic materials
are disposed on one face of a gypsum board in a state
where adjacent magnetic materials are in contact with
each other without a gap, or in which adjacent magnetic
materials are disposed through a gap, the gypsum board
which is a base material can be easily cut by easily
inserting a blade of a cutter knife or the like between
adjacent magnetic materials and making a cut into the
base paper on the surface of the gypsum board under the
magnetic materials. Therefore, by using an existing
gypsum board as the base material, a product in which
the convenience is highly enhanced can be realized
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
19
,
without deteriorating high construction efficiency
which the gypsum board has.
Examples
[0038] Hereinafter, the present invention will be
described further specifically giving Examples.
However, the present invention is not limited to these
Examples.
[0039][Example 1]
In an interior building material of the present
Example, a plate-like member made of gypsum (gypsum
board) and having a thickness of 12.5 mm, a length of
1820 mm, and a width of 901 mm was used as a base material.
In addition, 18 sheets of 30-cm square galvanized steel
sheets each having a thickness of 0.5 mm were prepared
as sheet-like magnetic materials. Subsequently, as
illustrated in Figure 2, on the surface of the gypsum
board, which is the base material 1, the 18 sheets of
galvanized steel sheets 2 were disposed so that adjacent
galvanized steel sheets were arranged orderly with 3
sheets in a horizontal direction x 6 sheets in a vertical
direction through a predetermined gap. Specifically,
the galvanized steel sheets were disposed over the whole
face of the base material by disposing the 3 sheets in
the horizontal direction each through a gap formed by
a linear narrow portion 3 having a width of 0.5 mm and
disposing the 6 sheets in the vertical direction each
through a gap formed by a linear narrow portion 3 having
a width of 0.4 mm, and thus the interior building material
of the present Example was obtained. A vinyl
acetate-based adhesive was used as the means for fixing
the galvanized steel sheets. It is to be noted that the
gaps in Figure 2 are illustrated to be larger than the
actual size with emphasis in order to be easily
understood.
[0040] The obtained plate-like interior building
material 10 was observed visually and by means of touch
to find that the appearance on the face of the side where
the galvanized steel sheets were arranged to be disposed
gave an impression which is similar to those of
conventional gypsum boards because the gap between
adjacent galvanized steel sheets were extremely narrow,
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
and, in addition, the feeling of touching by hand was
flat including the feeling of touching by hand on the
face of the side where the galvanized steel sheets were
disposed, which is similar to the feeling of touching
by hand for conventional gypsum boards.
[0041] In addition, the force of attraction by a
magnet to the face of the side where the galvanized steel
sheets were arranged to be disposed was checked by the
following method. That is, the interior building
material was stood in such a way as to be vertical, and
sheets of A4 paper each having a thickness of 0.09 mm
and a mass of 64 g/m2 were held at the face of the
galvanized steel sheet side with one magnet having a
diameter of a magnet portion of 17=4) and having a force
of attraction of 3.5 N to an iron sheet having a thickness
of 1 mm. As a result, 5 sheets of paper can be held without
a fall.
[0042] A blade of a cutter knife can be easily
inserted into a gap portion formed by the linear narrow
portion 3 having a width of 0.5 mm or having a width of
0.4 mm, the linear narrow portion 3 formed by adjacent
galvanized steel sheets in the interior building
material obtained above, and it was thereby ascertained
that the interior building material can be easily cut.
As a result, the interior building material cut without
using a tape measure can be easily cut into members each
having a width (length) of 30 cm or having a width (length)
of 60 cm, etc.
[0043][Example 2]
In an interior building material of the present
Example, a plate-like member made of gypsum (gypsum
board) and having a thickness of 12.5 mm, a length of
1800 mm, and a width of 900 mm was used as abase material
1. Subsequently, the plate-like interior building
material of the present Example was obtained in the same
manner as in Example 1 except that adjacent galvanized
steel sheets were disposed in a state of being in contact
with each other using 18 sheets of 30-cm square galvanized
steel sheets which are the same as those used in Example
1, and the sheet-like magnetic materials were fixed in
a state of being arranged with 3 sheets in the horizontal
direction x 6 sheets in the vertical direction without
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
21
a gap on the surface of the base material 1 as illustrated
in Figure 1. As a result, a building material in which
the appearance gave an impression which is similar to
those of conventional gypsum boards, and, in addition,
the feeling of touching by hand was flat including the
feeling of touching by hand on the face of the side where
the galvanized steel sheets were disposed, which is
similar to the feeling of touching by hand for
conventional gypsum boards was obtained, which was the
same as in Example 1. With respect to the force of
attraction by a magnet to the face of the side where the
galvanized steel sheets were arranged to be disposed,
sheets of A4 paper can be held with the magnet, which
was the same as in the case of Example 1.
[0044] A blade of a cutter knife can be easily
inserted at a portion where adjacent galvanized steel
sheets are in contact with each other by protruding the
interior building material obtained above on the side
where the galvanized steel sheets were arranged, and as
a result, the plate-like member made of gypsum, which
is a base material, can be easily cut. In addition, the
interior building material cut without a tape measure
can be easily cut into members each having a width
(length) of 30 cm or having a width (length) of 60 cm,
etc.
[0045][Example 3]
In an interior building material of the present
Example, a plate-like member made of gypsum and
satisfying the size of a gypsum board defined in JIS
Standard, the plate-like member having a thickness of
12.5 mm, a length of 1820 mm, and a width of 910 mm, was
used as a base material 1. In addition, 18 sheets of
30.3-cm square galvanized steel sheets each having a
thickness of 0.5 mm were prepared as sheet-like magnetic
materials. Subsequently, as illustrated in Figure 2,
the 18 sheets of galvanized steel sheets were disposed
so that adjacent steel sheets were arranged orderly with
3 sheets in a horizontal direction x 6 sheets in a vertical
direction through a predetermined gap. Specifically,
the galvanized steel sheets were disposed over the whole
face of the base material 1 by disposing the 3 sheets
in the horizontal direction each through a gap formed
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
22 =
,
by a linear narrow portion 3 having a width of 0.5 mm
and disposing the 6 sheets in the vertical direction each
through a gap formed by a linear narrow portion 3 having
a width of 0.4 mm, and thus the interior building material
of the present Example was obtained.
[0046]
The plate-like interior building material obtained
above was observed visually and by means of touch to find
that the appearance on the face of the side where the
galvanized steel sheets were arranged to be disposed gave
an impression which is similar to those of conventional
gypsum boards because the gap between adjacent
galvanized steel sheets were extremely narrow, which was
the same as in the building material of Example 1, and,
in addition, the feeling of touching by hand was flat
including the feeling of touching by hand on the face
of the side where the galvanized steel sheets were
disposed, which is similar to the feeling of touching
by hand for conventional gypsum boards. The force of
attraction to the face of the side where the galvanized
steel sheets were arranged to be disposed was checked
using the magnet having particular force of attraction
to find that 5 sheets of A4 paper can be held with the
magnet, which was the same as in the case of Example 1.
[0047] A blade of a cutter knife can be easily
inserted into a gap portion formed by the linear narrow
portion 3 having a width of 0.5 mm or having a width of
0.4 mm, the linear narrow portion 3 formed by adjacent
galvanized steel sheets in the interior building
material obtained above, and it was thereby ascertained
that the interior building material can be easily cut.
As a result, the interior building material cut without
using a tape measure can be easily cut into members each
having a width (length) of 30 cm or having a width (length)
of 60 cm, etc.
Reference Signs List
[0048]1: Base material
2: Sheet-like magnetic material
3: Narrow portion of gap
4: Iron sheet
5: Magnet with hook, having force of attraction of 3.5 N
CA 03055065 2019-08-29
23
,
10: Interior building material