Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
1
A STRUCTURAL SUPPORT SYSTEM AND A METHOD FOR PROVIDING A NODE
SECTION FOR USE IN A STRUCTURAL SUPPORT SYSTEM
Technical Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a structural support system, such as, but not
limited to; scaffolding, falsework, beams, bridges, staging, ski jumps and
slopes,
comprising vertical and horizontal poles, called herein verticals and
horizontals
respectively, connected at standard node points arranged spaced apart on the
vertical. Each node point comprises a locking device comprising a bottom cup,
rigidly
fixed to the vertical; a top cup rotatably and axially moveably on the
vertical; and
integral lugs fixed to the vertical for locking horizontals blade end to the
node point.
Background for the Invention
Structural support systems such as scaffolding and falsework are used in
several applications, to support and provide safe access related to
constructions and
maintenance of these. It is a temporary structure, which is assembled at
construction
site and dismantled upon completion. It is a modular system of metal
components,
where the components are reusable - assembled and dismantled from site to
site. In
conventional scaffolding, the components within the system usually comprise
poles
for vertical and horizontal purposes, where the vertical and horizontal poles
are
connected together with couplings usually pre-assembled at the vertical poles,
and
where the components are of metal, usually galvanized steel.
RinglockTM, AllroundTM, KwikstageTM and CUPLOKTM are well known
scaffolding systems.
The CUPLOKTM system is described in GB 1 463 867 and is consisting of a
bottom cup permanently and rigidly connected to a vertical pole at given
intervals
.. along the pole, with a loose and movable top cup above each bottom cup to
engage
a horizontal pole's end configuration for connecting the horizontal pole to
the vertical
pole by means of the bottom and top cups. Welding is used in order to lock
components such as bottom cup, wedges and mechanical stoppers of the system
permanently to the vertical pole and to make a permanent connection between
the
horizontal pole and the blade end configuration of the horizontal pole.
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
2
ON 105421757 discloses a bowl fastener connector for a bowl-holding
scaffold. The bowl fastener connector comprises a vertical rod, an upper bowl
fastener, a cross rod-limiting module, a lower bowl fastener and a cross rod
connector, wherein the upper bowl fastener, a limiting pin, the cross rod-
limiting
-- module and the lower bowl fastener are installed on the outer wall of the
vertical rod
from top to bottom in sequence. According to the bowl fastener connector, a
cross
rod is fixed through the upper bowl fastener and the lower bowl fastener,
installation
and detachment are both possible, the cross rod is clamped and fixed to the
upper
bowl fastener and the lower bowl fastener through the upper end and lower end
of
the cross rod connector respectively, and scaffold installation stability can
be
effectively guaranteed through a saw tooth groove formed in the bottom of the
cross
rod connector and a cross rod-limiting stand column arranged on the inner wall
of the
cross rod connector. The upper end and the lower end of the bowl fastener
connector are clamped and stressed, so that the stability of the scaffold is
not to be
-- affected i.e. if the bowl fastener connector rusts.
ON 200978854 relates to a detachable tightening connecting device
comprising a connector equipped on a pillar of a scaffold or a ceiling rack,
wherein
the outer side wall is equipped with an equipping structure, and a wedge
lining jacket
is equipped between the connector and the pillar, and a locating locking
device used
to prevent the generating of comparative movement between the wedge lining and
the pillar is equipped between the wedge lining jacket and the pillar. The
utility model
adopts a structure of adding the locating locking device between the pillar
and the
wedge lining, the connection between the wedge lining and the pillar can
realize that
the wedge lining and the pillar become a detachable structure through the
detachable locating locking device structure, avoiding deficits brought by the
glue
sticking or welding to connect the wedge lining and the pillar, and also
making the
detaching and equipping of the connecting device and the maintenance possible.
FR 2298720 discloses a junction piece consisting of a metal cup drilled with a
number of holes which are normal to the surface of the cup. The tubular struts
are
-- each fitted with a tapped plug insert. The outside of the cup may be
reinforced by a
ring which fits between the cup and the tubes. The tubes and cup are joined by
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
3
means of screws or bolts. Horizontal tubes are fixed in any direction by the
screw
holes and a central vertical tube by the fixing hole. Angular tubes may also
be fitted.
ON 102817890 discloses a fastener, which belongs to the technical field of
machinery. The fastener comprises two butt-jointed half ring-shaped bodies,
and is
characterized in that a stud pin and a stud pin hole matched with the stud pin
are
respectively formed on the two end surfaces of the half ring-shaped bodies;
the two
half ring-shaped bodies are clamped and in butt joint with each other by the
stud pin
and the stud pin hole; and reinforcing ribs are arranged on the inner side
walls of the
half ring-shaped bodies. The fastener may be assembled and disassembled, and
can be applied to connection of scaffolds or stud bodies.
ON 2003034788 discloses a flexible scaffold capable of being assembled and
detached. The scaffold is formed by a vertical rod, a cross rod, a plug pin
and a
locking plate and is characterized in that the vertical rod is provided with
the locking
plate which is provided with a lock hole; the plug pin is arranged in the lock
hole; the
cross rod is connected with the plug pin; a lock sleeve and a lock ring are
connected
into a whole to form into the locking plate; the lateral side of the locking
plate is
provided with a screw hole; one side of the upper end of the plug pin is
provided with
a connecting hole; the other side of the upper end of the plug pin is provided
with a
pushing block; the lower end of the plug pin is provided with a pin; the end
portion of
the pushing block is provided with an arc opening which is matched with the
vertical
rod; and an angle from 70 to 80 degrees is formed between an outer lateral
edge of
the pin and the horizontal direction of the lock hole.
ON 102704670 discloses a lower bowl-type coupler for a bowl-type coupler
scaffolding, which includes a bowl-type coupler body, wherein a sleeve is
arranged
on the bowl-type coupler body; a recess is arranged on a vertical upright;
both the
bowl-type coupler body and the sleeve are arranged on the vertical upright; a
protrusion is arranged on the inner wall of the sleeve, and extends to the
inside of
the recess to be tightly matched with the recess. The invention further
includes a
mounting method for the lower bowl-type coupler for the bowl-type coupler
scaffolding, which includes the following steps: firstly, the bowl-type
coupler body
and the sleeve are arranged on the vertical upright; and secondly, the sleeve
is
clamped through a clamping device, and a radial clamping force is exerted to
the
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
4
protrusion through the clamping device, so that the protrusion extends into
the
vertical upright, and the recess is formed on the vertical upright, the
protrusion
extends to the inside of the recess to be tightly matched with the recess, as
a result,
the lower bowl-type coupler is installed on the vertical upright. The lower
bowl-type
coupler for the bowl-type coupler scaffolding can be connected with the
vertical
upright.
The current state of the art is reflected in use of tubes and fittings made in
steel. This makes the components of the structural support system in many
cases
unnecessary heavy. There is also a health, environment and safety (HES) aspect
due to weight of components and allowed lifting weight. Therefore, there is a
need
for reducing weight of components and increased system flexibility in order to
obtain
of a structural support system, which meets the HES requirements without
reducing
the capacity or integrity of the structural support system.
There is a need for a system wherein the vertical and the cups can be made
of aluminium or where the cups may also be made of a tougher and more solid
material, such as steel. It is also a need for a system that is simple to
assemble and
erect, and where the nodes are solid and strong, meeting the structural and
HES
criteria.
Summary of the Invention
In the following throughout the specification, when referring to structural
support system, this includes, but is not limited to, scaffolding, falsework,
beams,
bridges, staging, ski jumps and slopes and such, unless clearly specified
otherwise.
Moreover, in the following, the following terms mean:
The noun term "horizontal" refers to elongated tube elements intended to be
arranged in horizontal direction. In the industry of structural support
systems,
"elongated tubes", "horizontal ledger", "transom", "ledger", "runner" etc. are
also well-
known expressions.
The noun term "diagonal" refers to elongated tube elements intended to be
arranged diagonally in a structural support system.
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
The noun term "vertical" refers to the elongated tube element intended to be
arranged in vertical direction. Expressions like "standard upright",
"standards,
"posts", "poles" etc. are also known in the industry.
The present invention is in principle functioning as a CUPLOKTM system, but
5 .. with improved solutions for attaching its couplers or cups to a pole with
vertical
standing purposes. The key point of the present invention is the ability to
held and/or
permanently fix the bottom cup to the vertical without using welding or
components
which compromises the pole's inside hollow section, hence being compatible and
may be used interchangeably with the existing prior art CUPLOKTM system. The
present invention opens for the possibility of using materials for the
vertical and the
node section, which are either undesirable to weld, or non-weldable
altogether, but
possesses other desirable features such as for instance being lightweight
and/or
environmentally friendly. A lightweight structural support system will ease
both
transport and handling, will provide working capacity and reduce the
environmental
.. impact of transportation, in addition to open up new areas where the
structural
support system may be utilized.
The main object of the present invention is to provide new methods for joining
components of a structural support system together and being able to choose
materials for reduced weight of the structural support systems.
Another object of the present invention is to provide a backward compatibility
to existing CUPLOKTM systems.
Another object of the invention is to provide a bottom cup which may be
rigidly
fixed to the vertical in a removable and/or replaceable manner without
influencing the
integrity of the new joint or the vertical.
Another object of the invention is to provide a new system where the vertical,
the elements forming the joint and possibly also the horizontals may be made
of
aluminium without being dependent on welding operations.
Yet another object of the invention is to provide a cup assembly allowing
removal of a bottom cup for substitution with a new or a modified bottom cup
or a
cup with a different shape, adapted to a differently shaped ends of the
horizontals.
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
6
A still further object of the invention is to allow change of position of the
node
along the length of the vertical and/or the locking surface of the node,
adapted to a
differently shaped end of a horizontal.
Another object of the invention is to retain the full tensile strength of the
vertical and/or full working capacity, i.e. for example the aluminium tubular
sections,
and/or the node.
Yet a further object of the invention is to enable provision of a node and a
fixture to a vertical, for example being made up of two different material,
that cannot
easily be welded together and without being dependent on welding operations.
Yet another object of the invention is to provide a solution where a lower and
upper cup also may be used in connection with a traditional vertical made of
steel.
Another object of the invention is to provide a system wherein the bottom cup
may be made of aluminium and may being fixed to a vertical of steel or
aluminium in
a non-welded manner without reducing the bearing capacity.
Another object of the invention is to provide a solution where the fixing of
the
lower cup is not dependent on a rigid fixing to a vertical.
An object of the invention is to provide a new cup that is compatible to
existing
system.
The objects are achieved by a structural support system and method as
further defined by the independent claims, while embodiments, options and
variants
are defined by the dependent claims.
In a first aspect, the present invention relates to a structural support
system,
such as, but not limited to, a scaffolding or a falsework system comprising
verticals
and horizontals connected at node sections at the verticals, where each node
section comprises a locking device for joining horizontals and/or diagonals
with
bladed ends arranged at ends of the horizontals and the vertical, where the
locking
device is a cup pair comprising a bottom cup held at a positon on the
verticals and a
top cup moveably arranged on the verticals, where bladed ends of the
horizontals
and/or diagonals are configured to be locked by bottom cup part and top cup
part,
providing a rigid connection. Parts of the structural support system intended
to be
held at a position on the verticals are held by using at least one fastener
means and
corresponding hole(s) in the parts and the verticals, the fastener means being
rigidly
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
7
fixed by screwing a headed bolt into the vertical, providing a compressive
vertical
load in vertical and/or horizontal direction capacity of the lower cup via the
bolt.
According to an embodiment, the bottom cup may comprise a lower part
preferably of cylindrical form, an intermediate part, preferably inclined
upwardly and
outwardly, an upper part preferably of cylindrical form.
The bottom cup may further comprise at least one hole for fastening means
preferably at the circumference of the lower part or the bottom cup, the
diameter of
the hole being larger than the diameter of a part of the fastening means, e.g.
a bolt,
intended to be in contact with the bottom cup. Moreover, the hole(s) in the
bottom
cup may optimally may be without threads.
According to an option, the bottom cup further comprises at least one
drainage recess in the lower part of the bottom cup.
Moreover, the system may further comprise a bottom cup guard in order to
protect the bottom cup and the fastening means, e.g. the bolts, from
mechanical
impact and environmental elements causing material degradation.
According to another embodiment, the bottom cup guard comprises a lower
part, preferably of cylindrical form, and an upper part, preferably inclined
upwardly
and outwardly.
In an embodiment, the bottom cup guard further comprises at least one
drainage recess at least in the lower part of the bottom cup guard, and with
same
height as the drainage recess of the bottom cup.
In an embodiment, the bottom cup guard further comprises a flange at the free
end of the lower part of the bottom cup guard, pointing inwards the bottom cup
guard
having a diameter with a tolerance in order to approximately face the
vertical.
The parts of the structural support system may also be intended to be
permanently fixed to the verticals by using fastening means, being one or more
dowel pins, and corresponding hole(s) in the parts and the verticals, the
dowel pin(s)
being rigidly fixed using a bonding agent or by press fit.
Dowel pins are fixed on face to face permanently connections where dowel
pins are put into pre-machined holes in the verticals and in the opposite face
of
connecting part in combination with a bonding agent, such as glue.
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
8
The face-to-face dowel pin surfaces may be provided with bonding agents,
such as glue, in order to fully make a strong and firm connection.
The bottom cup may have machined recesses at the bottom end matching
dowel pins projecting out from the vertical and bonded by a bonding agent or
by
press fit in holes pre-machined around the vertical's periphery at the same
level as
described above, where the bottom cup is to be lowered and simultaneously
adjusted to mate the recesses with the dowel pins and being permanently
connected
to the dowel pins with a bonding agent and/or spot welds between dowel pins
and
bottom cup.
Alternatively, the bottom cups may be fixed using at least two wedges for the
bottom cup and by pushing the bottom cup onto the wedges in a permanently
connection is made and where the wedges are connected to the vertical using a
bonding agent and/or welds.
The bottom cup may comprise two identical but mirrored halves with pre-
machined holes for dowel pins in surfaces facing the two halves and in
surfaces
facing the verticals, where the bottom cup halves and the verticals are
connected as
described above.
The horizontal may comprise an elongated tube and a blade end with fins,
which fits with an engaging tube, where the engaging tube and blade end are
permanently connected to the elongated tube by applying glue to the connecting
surfaces, where the connecting surfaces are the inner surface of the elongated
tube
and the outer surface of the engaging tube.
The elongated tube, preferably semi-cylindrically shaped may be thread onto
the engaging tube, preferably semi-cylindrically shaped but might also be
conical
-- shaped, chamfered shaped or it might even be threaded for a threading
connection
between engaging tube and elongated tube.
The installed bottom cup may be covered with a bottom cup guard in order to
protect the bottom cup, dowel pins and bonding agent from mechanical impacts
and
environmental elements causing material degradation.
Material used in the bottom cup guard may be of a polymer, such as plastic or
rubber.
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
9
The horizontals may be supported with an extra support bracket in order to
transfer forces between horizontals and the verticals, where the support
bracket
comprises two identical but mirrored shaped steel or aluminium plates. These
plates
are placed together in order to be able to grip around the horizontals and the
verticals where the two plates are loosely connected with bolts, washers and
nuts to
be screwed together and tighten around the horizontals and verticals.
In a second aspect, the present invention relates to a method for mounting a
node section on a vertical for use in a structural support system, where each
node
section is a locking device for connecting horizontals and/or diagonals with
bladed
ends arranged at ends of the horizontals with verticals, where the locking
device is a
cup comprising a bottom cup of metal material, preferably aluminium or steel
held at
a predetermined position on the verticals and a top cup of metal material,
preferably
aluminium or steel moveably connected to the verticals. Forming the vertical
from
extruded aluminium tubes, forming one or more radially orientated holes in the
outer
surface of the vertical surface, the surface of each hole preferably being
threaded,
positioning the holes in the bottom cup with the holes in the vertical and
introducing a
fastener means of steel into each of the holes via the holes in the bottom
cup. A
bottom cup guard threaded onto the vertical may be raised towards the bottom
cup
until the free end of the lower part of the bottom cup guard aligns a free end
of the
lower part of the bottom cup, or until a surface of the flange of the bottom
cup guard
pointing in direction of the bottom cup is mating against the free end of the
lower part
of the bottom cup.
The method further providing the bottom cup guard being adjusted in position,
where drainage recesses in the bottom cup guard is being aligned with drainage
.. recesses in the bottom cup.
Alternatively, the surface of each hole is being treated with a bonding agent
and introducing a dowel pin of steel into each of the holes, lowering the
bottom cup
down onto the dowel pin(s) and welding the dowel pin(s) and the lower surface
of the
bottom cup together in a permanent fixture to the vertical using a bonding
agent.
The method may further provide the lower surface of the bottom cup with
downwardly open holes or recesses, positioned to be complimentary to the
position
of the dowel pin(s) and moving the bottom cup vertically downwards and
possibly
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
rotating the bottom cup so as to allow the dowel pin(s) to enter into
corresponding
hole(s) or recess(es) at the bottom surface of the bottom cup.
Structural support system, such as scaffolding or falsework, comprises
verticals and horizontals connected together with coupling agents at the
verticals
5 placed with intervals along the verticals. The coupling agents comprises
lower and
upper coupling parts, where the lower coupling part is being permanently
connected
and rigidly fixed to the vertical, and the upper coupling part is in a loose
and movable
connection with the vertical. The horizontals comprise elongated tubes with
flanged
ends at each end of the elongated tube fitting into the coupling parts. The
flanged
10 end is lifted into the lower coupling parts, the upper coupling parts
are being rotated
and in order to lock the upper coupling, a helical surface at the upper
coupling part is
wedged against a lug permanently connected to the vertical. Stoppers are
preferably
installed on the vertical in order to prevent the last upper coupling part to
fall off the
vertical.
A structural support system is traditionally predominated by welded steel
structures. Using light material, such as aluminium is of great interest in
order to gain
easier handling of elements without, or with reduced need for lifting
equipment. As a
result of being a non-welded structure, one can retain a full tensile strength
of the
aluminium tubular sections. The system of the present invention is a fully non-
welded
element, resulting in that the aluminium elements retains full working
capacities.
In one embodiment, the bottom cup is fixed to an aluminium vertical by using
bolts. The bolts do not fix the cup against the vertical tube in the
traditional sense,
but act as a support for the lower cup to rest on. The bolt is fixed
horizontally to the
vertical via the holes within the lower part of the bottom cup, providing
compressive
vertical load capacity of the lower cup via the bolt head as opposed to a
tightening of
the bolt between the lower cup and the vertical tube. Holes in the vertical is
predrilled
and preferably threaded. Since the bolt do not press or fix the bottom cup to
the
vertical, the bolt goes straight through the cup and the cup simply rests on
the bolt
head. Bolts are used as a vertical restraint as opposed to a clamping
function. The
bolts may come in varying sizes. Since the bottom cup rests on a head of the
bolt,
this is allowing a higher force to be applied through the head of the bolt and
back into
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
11
the vertical due to larger surface area between the bolt head and the surface
of the
vertical.
The bottom cup is designed to be compatible with current steel systems on
the market. The system of the present invention will provide all the same
connectivity
features as current system with the only difference being the vertical
capacity being
reduced due to the working tensile capacity of the aluminium vs. steel. The
system is
bi-directionally compatible with other similar systems.
The bottom cup is preferably formed out of a forged aluminium billet. By
forging the bottom cup, the material changes occurring through the forging
process
causing the tensile capacities of the cup to increase, providing an aluminium
product
with comparable tensile properties as steel.
Gluing is a well-known method for joining metal parts together and opens up
the potential to use new materials or combination of different materials where
use of
traditionally joining methods is inconvenient. Using high strength material
such as
steel on load bearing or impact exposed parts and being able to choose lighter
materials, such as aluminium or fibre reinforced plastics, on joining parts,
may be of
great interest in relation to, for example, easier handling of the elements
without, or
with reduced need for lifting equipment. Gluing in combination with dowel
pins, or
local welding of high strength material, such as steel, gives a structural
reinforcement of the connection for load bearing components transferring and
distributing loads to connecting components.
In another embodiment, the bottom cup is rigidly fixed to the vertical by
means
of dowel pins of steel inserted and glued in pre-machined holes filled with
glue in the
vertical, preferably made of aluminium. A bottom cup of the coupling agent,
threaded
onto the vertical is provided with pre-machined recesses arranged on its lower
circumferential edge, matching the size and position of the configuration of
the dowel
pins, the bottom cup is then lowered down onto the matching dowel pins in the
vertical. Spot welding between the dowel pins and the recesses of the bottom
cup,
where both dowel pins and bottom cup are of the same weldable material,
preferably
steel, provide a firm, rigid and permanent connection of the bottom cup to the
vertical. Gluing the matching surfaces of the dowel pins and recesses in the
bottom
cup may be an alternative or addition to the welding.
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
12
Another way of joining the bottom cup together with the pole is with the use
of
wedges. The bottom cup wedges being of a high strength material such as steel,
are
distributed around the circumference of the pole, where the bottom cup is
being
fastened to the pole by wedges. The wedges are fixed to the pole using dowel
pins
with glue in holes of both the pole, as indicated above, and the wedges.
Additionally
extra glue may be added in the interfacing mating surfaces of the pole and the
wedge. Alternatively, or in addition, a welding seam between the lower end
surface
of the bottom cup and the wedge may be used. Other components, such as a wedge
lug for the top cup and mechanical stoppers, preferably being of a high
strength
material such as steel, which might be dowel pins, are also connected through
dowel
pins and gluing, or alternatively or additionally by welding.
In yet another embodiment of the bottom cup, the cup preferably being of a
high strength material such as steel, the cup comprises two cup halves with
holes for
dowel pins. The halves are joined together, embracing a pole with dowel pins
between the joining surfaces of the two halves and between the inner surfaces
of the
cups and the pole, and further fixed together either by welding or gluing of
the joining
surfaces. The inner surface of the bowl-shaped halves has curved faces
complementary to the side of the vertical with holes for dowel pins and with
corresponding holes for dowel pins on the vertical. When the halves are
brought
together around the vertical, dowel pins are also placed between the halves
and the
vertical before welding or gluing both the two halves together, but also the
welded or
glued cup formed by the two halves together with the vertical.
A structural support system of the present invention is a flexible system able
to take all kind of shapes, from right angled to complex curves. In heavy
constructions with scaffolding elements, extra support of the structure is
required.
The structural support system is able to also take poles arranged diagonally
as a
framework construction, alternatively or supplementary support brackets can be
used in the corners or junction points between verticals and horizontals. Such
support brackets easily grip and lock around the poles by loosening and
fastening of
bolts and nuts.
The present invention is backward compatible with the CUPLOKTM system,
since the bottom cups of the present invention are designed to fit existing
equipment
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
13
utilizing the CUPLOKTM system. This is beneficial for the customer being able
to
easily adapt their existing equipment and save potentially high investment
cost.
Brief Description of the Drawings
Embodiments of the present invention will now be described in further detail
by way of example only, with reference to the following diagrams wherein:
Figure 1 shows schematically a perspective of a locking system of prior art;
Figure 2 shows schematically and in perspective a section of a typical
scaffold
built up with embodiments according to the present invention;
Figure 3 shows schematically and in perspective a section of a heavy-duty
support structure, e.g. falsework, used for supporting heavy duty steel
girders or
beams for formwork, used for supporting formwork for construction of bridges,
or the
like;
Figure 4 shows schematically and in perspective a view of a bottom cup of
one embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 5 shows schematically and in perspective a view of a bottom cup guard
used to protect the bottom cup and fastening means from mechanical impacts and
environmental elements causing material degradation;
Figure 6a shows a vertical with preinstalled pairs of bottom cups and a top
cups arranged at different levels and spaced along the vertical. Figure 6b
shows a
detail A from figure 6a of the lower part of the vertical, showing one pair of
a bottom
cup and a top cup;
Figure 7a shows schematically an exploded view, while Figure 7b shows an
assembled view of an embodiment of an assembly of the bottom cup, the top cup,
as
well as the bottom cup guard of the present invention;
Figure 8a shows schematically and in perspective an exploded view of an
embodiment of the bottom cup of a node using the dowel fastening method
according to the present invention, while Figure 8b shows schematically and in
perspective an assembled view of the embodiment shown in Figure 8a;
Figure 9a shows schematically and in perspective an exploded view of
another embodiment of the bottom cup using the dowel fastening method, while
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
14
Figure 9b shows schematically and in perspective an assembled view of the
embodiment shown in Figure 9b;
Figure 10a shows schematically and in perspective an exploded view of yet
another embodiment of the bottom cup using the dowel pins and wedges according
to the invention, while Figure 10b shows schematically and in perspective an
assembled view of the embodiment shown in Figure 10a;
Figure 11a shows schematically and in perspective an exploded view of yet
another embodiment of the bottom cup of the present invention, where the
bottom
cup comprises two identical but mirrored halves joined together, while Figure
llb
shows schematically and in perspective an assembled view of the embodiment
shown in Figure 11a;
Figure 12a shows schematically and in perspective an exploded view of an
embodiment for fixing a lug used for locking the top cup of the coupling
system
against upwards movement to the vertical; while Figure 12b shows schematically
and in perspective the embodiment shown in Figure 12a, the unit being in an
assembled state;
Figure 13a shows schematically and in perspective an end of a horizontal and
its end configuration in an exploded view, while Figure 13b shows the
horizontal end
in an assembled state;
Figure 14 shows in perspective an assembled node on a vertical, with one
horizontal supported the support bracket, extending between the vertical below
a
node and a horizontal, the support bracket forming an angle with the
horizontal and
the vertical;
Figure 15a shows schematically and in perspective an embodiment of the
support bracket in an exploded state, while Figure 15b shows the embodiment
shown in Figure 15a in an assembled state; and
Figure 16a shows schematically and in perspective an exploded view of an
embodiment of the bottom cup according to the invention including a bottom cup
guard, while Figure 16b shows schematically and in perspective an assembled
view
of the embodiment shown in Figure 16a.
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
Detailed Description of embodiment disclosed in the Drawings
The following description of the exemplary embodiments refers to the
accompanying drawings. The drawings illustrate exemplary embodiments of the
invention configured to be integrated in a structural support system such as a
5 scaffolding or a falsework system. The exemplary embodiments disclosed in
the
drawings should not be understood as a limitation to the scope of protection
of the
invention.
The same reference numbers in different drawings identify the same or similar
elements. The following detailed description does not limit the invention.
Instead, the
10 scope of the invention is defined by the appended claims.
Reference throughout the specification to "one embodiment" or "an
embodiment" means that a particular feature, structure or characteristic
described in
connection with an embodiment is included in at least one embodiment of the
subject
matter disclosed. Thus, the appearance of the phrases "in one embodiment" or
"in an
15 embodiment" in various places throughout the specification is not
necessarily
referring to the same embodiment. Further, the particular features,
structures, or
characteristics may be combined in any suitable manner in one or more
embodiments.
In general, the verticals are made of aluminium, and the elements forming the
node or the wedges or the lugs of the embodiments described below, i.e. top
and
bottom cup and the dowels may be made either of forged aluminium or steel,
unless
otherwise specifically defined. In this manner, if bottom cup is made of
steel, steel
dowel pins and bottom cup may be welded together, or the dowel pins used may
be
glued, or press fitted with corresponding elements. In addition, or as an
alternative,
interconnected surfaces may also be glued.
Figure 1 shows schematically a perspective of a prior art node section 120
used for locking horizontals or the like in a prior art scaffolding system.
The system is
made of steel. Only a single node section 120 is shown. It should be noted,
however
that each vertical 10, which is delivered in standard lengths, are provided
with node
sections 120 shown in Figure 1, preferably equally spaced apart in tube
longitudinal
direction. The system consists of a vertical 10 provided with a bottom cup 20,
welded
to the vertical 10. The bottom cup 20 defines an annular channel 21 (not shown
in
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
16
Figure 1) around it, such annular channel 21 being open at its upper end. The
lower
part 22 of the wall of the bottom cup 20 is inclined upwardly and outwardly
from the
vertical 10 and terminates in a short upper part 24 of cylindrical form.
The node section 120 also consist at its upper end of a top cup 30 which is
slidably and rotatably mounted on the vertical 10 and also defines an annular
channel (not shown in Figure 1) around it, the annular channel being open at
its
lower end, the wall of the top cup 30 having a cylindrical upper part which
fits loosely
around the vertical 10 and a downwardly inclined lower part. At one side, the
top cup
30 has a bulge 31, in which there is formed adjacent to the vertical 10, a
vertical slot
32. The top face of the top cup 30 may be inclined upwardly from either side
of the
bulge 31 or continuously for a full 360 from one side, thus forming a wedge-
shaped
surface.
The vertical 10 has on one side thereof a lug 12, which is of such size that
it
can pass through the vertical slot 32 in the bulge 31 of the top cup 30. Thus,
if the
top cup 30 is turned to bring the lug 12 into line with the vertical slot 32,
the top cup
30 can be moved up and down the vertical 10 past the lug 12.
A horizontal 40 is at each end provided with a blade end 41 provided with two
diametrically opposed fins 42 (not shown). The fins 42 on each end of the
horizontal
40 are pointing in the same direction. The end surface of the blade end 41 is
curved,
i.e. given a shape that is complimentary to the corresponding shape of the
vertical
10.
For assembling a vertical 10 and a horizontal 40, the top cup 30 is in a
position above the lug 12 on the vertical 10. A flanged coupling end (the
horizontal's
40 blade end 41) is brought into position with one fin 42 positioned inside
the open
ended annular channel 21 in the bottom cup 20, also bringing the horizontal 40
into a
position where it is perpendicular to the vertical 10. The top cup 30 is then
lowered
by bringing the vertical slot 32 in the top cup 30 in aligned position with
the lug 12,
whereupon the top cup 30 is lowered down past the lug 12 and around the upper
fin
42. In this position, the inclined upper surface of the top cup 30 is
positioned below
the lower end of the lug 12. In order to lock the position of the horizontal
40, the top
cup 30 is rotated in a clockwise direction. Due to the inclining surface of
the top cup
30, when the top cup 30 is rotated in this position, the top cup 30 will act
as a wedge
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
17
against the lug 12, forcing the top cup 30 in the downwards direction, thus
providing
a secure locking engagement between the top cup 30, the blade end 41 and the
vertical 10. In order to achieve rotational movement of the top cup 30, the
top cup 30
is fitted with top cup lugs 33, spaced apart around the top cup 30, said top
cup lugs
33 being intended to be hit by a hammer or a sledge in order to force the top
cup 30
into a locking engagement. It should be noted that the blade ends 41, which
are
made of steel, are welded to the end of the horizontal 40.
Figure 2 shows schematically and in perspective a view of a typical scaffold
built up with embodiments according to the present invention. The scaffold may
comprise of a number of verticals 10 arranged in spaced relation and
interconnected
by a number of horizontals 40. As indicated in the Figure 2, the verticals 10
and the
horizontals 40 are locked together by means of node sections 120. The node
sections 120 disclosed are of a type that shall be described in more detail
below. It
should be noted that the scaffold may also be provided with accessories, such
as
bracings with brace ledge ends, brackets, base jacks, all adapted to form an
integrated part of the node system described below. As indicated in Figure 2,
the
horizontals 40 are assembled in a node section 120, i.e. two horizontals 40
being
aligned arranged with an angle of 180 there between, while the third
horizontal 40 is
arranged orthogonally with the two aligned horizontals 40. It should be noted
that
other angles and another number of horizontals 40 adjoining in a node section
120
on a vertical 10 is also possible.
Figure 3 shows schematically, principally and in perspective a view of a
heavy-duty falsework support structure, for example usable for supporting
heavy
duty steel girders or beams for formwork, for example for supporting formwork
for
construction of bridges, or the like. As shown in Figure 3, the falsework is
made up of
nine verticals 10 and a large number of horizontals 40, adjoined to the
respective
verticals 10. Dependent on type and size of falsework and the structure to be
supported, the falsework may be made up of numerous verticals 10 and
horizontals
40. In this respect, a typical joint may be made up of four adjoining
horizontals 40,
forming an angle of 90 between each. Again, the built-up of each node section
120,
the method for fabricating the verticals and the method for assembling the
system
shall be described in further details below.
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
18
Figure 4 shows schematically and in perspective a view of a bottom cup 20 of
one embodiment of the present invention. The bottom cup is made of metal
material,
preferably of aluminium, but may also be made of steel. A lower part 22 of the
wall of
the bottom cup 20 preferably forms a lower part 22 of a cylindrical form. An
intermediate part 23 of the bottom cup 20 is preferably inclined upwardly and
outwardly, while an upper part 24 of the bottom cup 20 preferably forms an
upper
part 24 of cylindrical form. Cut-outs in lower end of the bottom cup 20 are
drainage
recesses 26 for draining purposes, preventing accumulation of water, ice, etc.
in the
bottom cup 20. In order to fix the bottom cup 20 to a vertical 10 (not shown),
at least
one hole 25 for fastening means 50 (not shown), preferably at the lower part
22 of
the bottom cup 20, are furnished at the bottom cup 20. Corresponding hole(s)
11 is
furnished at the vertical 10. The holes 11 at the vertical are preferably
susceptible to
receive threaded fastening means 50.
Figure 5 shows schematically and in perspective a view of a bottom cup guard
110 used to protect the bottom cup 20 (not shown) and fastening means 50 (not
shown) from mechanical impacts and environmental elements causing material
degradation. A lower part 111 of the bottom cup guard 110 forms a lower part
111 of
preferably a cylindrical form. An upper part 112 of the bottom cup guard 110
forms
an upper part 112 preferably inclined upwardly and outwardly. A free end of
the
lower part 111 of the bottom cup guard 110 preferably has a flange 113
orthogonal
to the cylindrical form of the lower part 111 directed towards an axial axes
of the
bottom cup guard 110, having a diameter with a tolerance in order to
approximately
face the outer surface of the vertical 10 (not shown). Further the bottom cup
guard
110 may be furnished with cut-outs in the lower end of the bottom cup guard
110
being drainage recesses 114 corresponding the recesses 26 of the bottom cup 20
(not shown). The recesses 114 of the bottom cup guard 110, also serving as
draining
purposes as those recesses 26 of the bottom cup 20 (not shown), preventing
accumulation of water, ice etc. in the bottom cup 20 (not shown). The bottom
cup
guard 110 can be of for example a polymer, such as plastic or rubber. The
bottom
cup guard 110 can also serve as a marketing object, sporting for instance
company
logo or product name, and/or being in bright colour. The bottom cup guard 110
is
made up of a single unit and may be applied an adhesive and attached to the
bottom
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
19
cup 20, thus providing permanent joining of the bottom cup guard 110 and the
bottom cup 20.
Figure 6a shows a vertical 10 with preinstalled pairs of bottom cups 20 and a
top cups 30 arranged at different levels and spaced along the vertical 10,
ready to be
installed in a falsework, scaffold or the like and ready to receive bladed
ends of
horizontals 40 comprising in a falsework, scaffold or the like. The top cup 30
is made
of metal material, preferably aluminium. The vertical 10 shows six pairs of
bottom
cups 20 and top cups 30, there may be fewer and there may be more, but each
vertical 10 shall preferably comprise at least one pair of one bottom cup 20
and one
top cup 30. At each end of the vertical 10 there are bolts going straight
through the
vertical with an accompanying nuts. These bolts and nuts are for connection to
internal spigots used when stacking one vertical 10 on top of another when the
structural support system moves vertically/grows upwards. Figure 6b shows a
detail
A from figure 6a of the lower part of the vertical 10, showing one pair of a
bottom cup
20 and a top cup 30. A bottom cup guard 110 (not shown) may also be
preinstalled
below each pair of bottom cups 20 and top cups 30 arranged at the vertical 10.
A lug
12 is shown on the vertical 10 arranged above a pair of bottom cups 20 and top
cups
30. An inclined helical surface 34 at the upper part of the top cup 30. In
order to lock
the horizontal 40 (not shown), the top cup 30 is rotated in order for top cup
30 to
slide it's helical surface 34 towards the lug 12 forcing the top cup 30 in an
downward
direction. The lug 12 and the helical surface 34 acting as a wedge, providing
a
secure locking engagement.
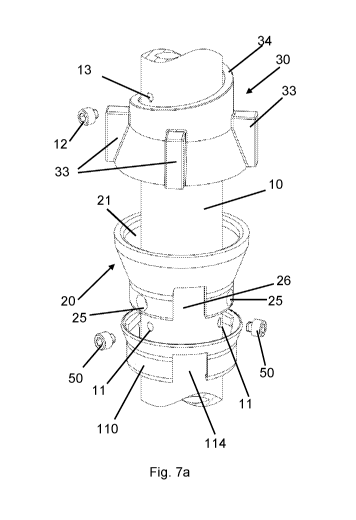
Figure 7a shows schematically an exploded view, while Figure 7b shows an
assembled view of an assembly of the bottom cup 20 and the top cup 30 of the
present invention. At its upper end, the bottom cup 20 is configured to form
an
annular channel 21 around the vertical 10 when assembled and fixed to the
vertical
10. The annular channel 21 is formed by the room between the vertical 10 and
surface facing inwards and towards the vertical 10 of the intermediate part 23
and
the upper part 24 of the bottom cup 20 as described above in the description
of
Figure 4. In Figure 7a is shown holes 11 in the vertical 10, there should be
at least
one hole 11, preferably two holes 11, and more preferably three holes 11.
These
holes 11 in the vertical 10 corresponds to the at least one hole 25 of the
bottom cup
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
20. When the bottom cup 20 is lowered or raised in order for the at least one
hole 25
in the bottom cup 20 to be at the level of the at least one hole 11 in the
vertical 10,
the bottom cup 20 should be adjusted to align the axis of the at least one
hole 25 in
the bottom cup 20 with the axis of the at least one hole in the vertical 10.
Thus, when
5 at least two holes 25 in the bottom cup 20, those holes should be
distributed around
it's circumferences with the same distribution/angle as the at least two holes
11 in
the vertical 10 distributed around it's circumferences, the at least two holes
11 being
in a common plane approximately orthogonal to a longitudinal axis of the
vertical 10.
When the holes 11, 25 in the vertical 10 and the bottom cup 20 respectively,
are
10 aligned, at least one fastening means 50 may be threaded through the at
least one
hole 11, 25 of the vertical 10 and the bottom cup 20. The fastening means 50
may
preferably be a cap-head socket bolt, but may also be any other suitable
threaded or
unthreaded bolts, with or without heads, or even pins or wedges. The fasting
means
50 not fixing the bottom cup 20 to the vertical 10, rather serving as support
for the
15 bottom cup 20 to rest on. The fixing of the at least one bolt 50 to the
vertical 10 via
the holes 25 in the bottom cup 20 provides a compressive vertical load
capacity of
the lower cup via the fastening means as opposed to a tightening of the
fastening
means between the bottom cup 20 and the vertical 10.
A bottom cup guard 110 position on the vertical below the bottom cup 20 will
20 be raised towards the bottom cup 20 until the free end of the lower part
111 of the
bottom cup guard 110 aligns a free end of the lower part 22 of the bottom cup
20, or
until an surface of the flange 113 of the bottom cup guard 110 pointing in
direction of
the bottom cup 20 is mating against the free end of the lower part 22 of the
bottom
cup 20. The recesses drainage 114 of the bottom cup guard 110 being positioned
to
align with the drainage recesses 26 of the bottom cup 20 and thereby the
draining
purposes, preventing accumulation of water, ice, etc. in the bottom cup 20
being
fulfilled and protecting the bottom cup 20 and fastening means 50 from
mechanical
impacts and environmental elements causing material degradation.
The top cup 30 is arranged above the bottom cup 20, the vertical 10 being in
an upraised vertical position. A lug 12, preferably a cap-head socket bolt,
but may
also be any other suitable threaded or unthreaded bolts, with or without head,
or
even pins or wedges being arranged in a hole 13, threaded or unthreaded, in
the
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
21
vertical 10 preventing the top cup 30 for further movement upwards the
vertical 10.
When the bottom cup 20 is installed and the top cup 30 is installed and at
it's
uppermost position, preventing any further movement by means of the lug 12,
the
bottom cup 20 and top cup 30 is now ready to receive the bladed ends 41 of the
horizontals 40 (not shown) comprising in the falsework, scaffold or the like.
When the
lower part of the bladed ends 41 of the horizontals 40 (not shown) is received
by the
bottom cup 20, the top cup 30 will thereafter be lowered towards the bottom
cup 20
and rotated onto the upper part of the blade end 41, by rotating the top cup
30
comprising a helical surface 34 at its upper part against the lug 12, and
thereby
locking the horizontals 20 to the vertical 10 in a firm locking, but
releasable,
engagement. In order to achieve the rotational movement of the top cup 30, the
top
cup 30 is fitted with top cup lugs 33, spaced apart around the top cup 30,
said top
cup lugs 33 being intended to be hit by a hammer or a sledge in order to force
the
top cup 30 into the locking engagement.
Figure 8a shows schematically an exploded view while Figure 8b shows an
assembled view of another embodiment of the bottom cup 20 made of steel, fixed
to
the vertical 10. At its upper end, the bottom cup 20 is configured to form an
annular
channel 21 around the vertical 10 when assembled and fixed to the vertical 10
in
aluminium. The annular channel 21 is open at its upper end. The lower part 22
of the
wall of the bottom cup 20 is inclined upwardly and outwardly, while the upper
part 24
of the bottom cup 20 forms an upper part 24 of steel with a cylindrical form.
In order to fix the bottom cup 20 to the vertical 10, holes 11 for fastening
means 50, are pre-machined in the vertical 10 around its periphery at the same
level,
into which fastening means 50, preferably dowel pins of steel are fixed,
protruding
radially out of the vertical 10. The holes 11 in the verticals 10 are
preferably pre-
glued in order to permanently fix the dowel pins 50 to the vertical 10. The
dowel pins
50 are evenly positioned around the entire circumference of the vertical 10,
positioned at the same level. At its lower end surface, the bottom cup 20 is
provided
with a corresponding number of machined recesses 28 in bottom cup 20 to match
the number of dowel pins 50 arranged around the circumference of the vertical
10.
It should be noted that the bottom cup 20 may be machined as a single,
integrated unit, thread on to the vertical 10 for appropriate fixing, or the
bottom cup
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
22
20 may be machined or formed as separate units and subsequently assembled
around the vertical. The latter way of assembling will be described below.
When lowering bottom cup 20 down onto the dowel pins 50, the orientation of
the bottom cup 20 is adjusted so as to enable recesses 28 in bottom cup 20 on
the
lower surface of the bottom cup 20 to rest on the corresponding dowel pins 50.
If the
vertical 10 is in an upright position, the bottom cup 20 is now resting on the
dowel
pins 50. The bottom cup 20 is permanently connected to the dowel pins 50, and
thereby to the vertical 10, preferably through spot welds between bottom cup
20 and
each dowel pin 50 and/or by applying glue to either dowel pins 50 and/or the
machined recesses 28 in bottom cup 20, thus gluing the bottom cup 20 to the
dowel
pins 50. Cutouts in lower end of bottom cup 20 are drainage recesses 26 for
draining
purposes, preventing accumulation of water or ice in the bottom cup 20.
Figure 9a and 9b shows yet another embodiment of the bottom cup 20 of the
view shown in Figure 8, the only major difference being the height of the
cylindrical
part 15 of the bottom cup 20.
Figure 10a shows schematically an exploded view of yet another embodiment
of the present invention, while Figure 10b shows an assembled view of the same
embodiment of a bottom cup 20 according to the present invention. Apart for
the
differences described below, the shape, configuration, and function of the
bottom
cup 20 disclosed correspond to the shape, configuration and functions
disclosed
above in relation to Figure 8 and 9. According to this embodiment, upwards and
inwards inclined wedges 70 are used for locking the bottom cup 20 to the
vertical 10.
Holes 11 for dowel pins 50 are pre-machined in the vertical 10 around its
periphery,
in which dowel pins 50 are placed and fixed, protruding out from the outer
surface of
the vertical 10. The holes 11 in the vertical 10 are preferably pre-glued, in
order to
permanently fix the dowel pins 50 to the vertical 10. Glue is applied to the
dowel pins
50 protruding out of the outer surface of the vertical 10 and the wedges 70
provided
with corresponding machined holes (not shown) to match the dowel pins 50,
fixing
the wedges 70 to the dowel pins 50 for a permanent fixture on the vertical 10.
Correspondingly, the inner surface at the lower end of the bottom cup 20 is
provided
with complementary shaped recesses (not shown), configured to receive the
wedges
70 and securing the correct position of the bottom cup 20 on the vertical 10.
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
23
Alternatively, or supplementary, the mating surfaces of the wedges 7028
against the
vertical 10 might be applied with glue. The bottom cup 20 thereafter slides
down onto
to the wedges 70 for a stiff and firm connection. After the bottom cup 20 is
placed
onto the wedges 70, welding may be applied between the bottom cup 20 and the
wedges 70 in order to insure a fixed connection.
Figure 11a shows schematically an exploded view of a yet another
embodiment of the bottom cup of the present invention, while Figure llb shows
an
assembled view of the same embodiment of the bottom cup 20 according to the
present invention. The bottom cup 20 comprises two identical, but mirrored,
bottom
cup halves 27, 27'. Dowel pins 60 are used to connect both the two bottom cup
halves 27, 27' together, and dowel pins 50 are at the same time connecting the
two
bottom cup halves 27, 27' together with the vertical 10. Pre-machined holes 29
in the
mating surfaces of the two bottom cup halves 27, 27'and pre-machined holes 11
in
the mating surfaces of the two bottom cup halves 27, 27' and the vertical 10
is
applied with glue before dowel pins 29, 50 are inserted protruding out of the
vertical
10 and one half 27, 27' of the bottom cup 20. Glue is filled in the remaining
holes 11,
29. The bottom cup halves 27, 27' are then joined together with each other and
at
the same time with the vertical 10 for a permanent connection.
Figure 8-10 shows cups in one piece, it is not restricted to be manufactured
in
one piece; it might in all embodiments as shown in figure 8-10 be manufactured
in
two pieces, joined together as described in figure 11, with or without dowel
pins in
combination with gluing and/or welding on joining surfaces, prior to being
thread onto
the vertical.
Figure 12a shows schematically an exploded view of an embodiment of a lug
12 for locking of the top cup 30 of the present invention, while Figure 12b
shows the
unit in an assembled state. Holes 13 are pre-machined in the vertical 10 in
which
dowel pins 130 are placed protruding out of the vertical 10, the holes 13 are
preferably pre-glued, in order to permanently fix the dowel pins 130 to the
vertical 10.
Glue is applied to the dowel pins 130 and the face of lug 12, which shall be
mated
with the vertical 10, before the lug 12, with pre-machined holes to match the
dowel
pins 130 in the vertical 10, is placed onto the dowel pins 130 for a permanent
connection. Stoppers 100, which might be dowel pins, shown at the top of the
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
24
vertical 10 are mechanical stoppers preventing loose objects, such as the top
cup
30, from falling off. The stoppers 100 are placed in pre-machined holes in the
vertical
filled with glue.
Figure 13a and 13b shows an exploded and assembled view of an
5 embodiment of the end piece of a horizontal 40 with an end piece on each
end of an
elongated tube 80 of the horizontal 40. The long elongated tube 80 of the
horizontal
40 being of a light material, such as aluminium, is to be permanently
connected to a
connecting end piece comprising a blade end 41 with an engaging tube 81, being
of
a stronger material such as steel.
10 The blade end 41 of the end piece fits the shape of the vertical 10, the
bottom
cup 20 and top cup 30. The end piece's engaging tube 81 has a shape to fit
within
the elongated tube 80 of the horizontal 40. The outer surface of the engaging
tube
81 of the connecting end piece being applied with glue before being treaded
into the
elongated tube 80 of the horizontal 40 for a permanent connection. The
engaging
tube 81 is preferably of a semi-cylindrical shape, but it might also take a
conical
shape, chamfered shape or it might be threaded for a threaded connection
between
engaging tube 81 and elongated tube 80.
Figure 14 shows schematically an embodiment of an assembly of the coupling
system of the present invention. Showing two horizontals 40, only end part
shown, to
be connected to the vertical 10 through first lowering one side of the blade
end 41
into the preinstalled, permanent bottom cup 20 as described in Figure 7, 8, 9,
10 and
11. A top cup 30 is thereafter lowered and rotated onto the other side of the
blade
end 41, by rotating the top cup 30 comprising a helical upper part against the
lug 12
described in Figure 12, and thereby locking the horizontals 40 to the vertical
10 in a
firm but releasable connection. A support bracket 90 may be assembled between
the
vertical 10 and horizontal 40 in order to aid the transfer of loads between
the
horizontal 40 and the vertical 10 creating a stronger and more rigid
connection
between the horizontal 40 and the vertical 10. The support bracket 90 is
configured
to be securely fixed to the vertical 10 below the node section 120 and the
horizontal
40 at a distance from the node section 120, thereby forming a strut or a
brace. The
support bracket 90 will be described in further details below, referring to
Figure 15a
and 15b.
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
Figure 15a and 15b shows an exploded and assembled view of an
embodiment of the support bracket 90 mentioned in Figure 14 comprising two
identical but mirrored support bracket plates 91, 91', being shaped steel or
aluminium plates, able to grip around both the horizontal 40 and the vertical
10. The
5 two support bracket plates 91, 91' are loosely connected with bolts 93,
washers 95
and nuts 96 before assembled in order to be fastened together and tightened
around
the horizontal 40 and the vertical 10. The bolts 93, which may be carriage
bolts used
with corresponding squared holes 94 in the support bracket plates 91, 91' in
order to
keep the bolts 933 in place while screwing the nuts 96 and tightening the
parts
10 together or loosening the parts, thereby eliminating the need of an
extra holding-on
tool while tightening of loosening of the parts.
Figure 16a and 16b shows an exploded and assembled view of an
embodiment of a bottom cup guard 110 used to protect the bottom cup 20, dowel
pins 50 and joining adhesive from mechanical impacts and environmental
elements
15 causing material degradation. The bottom cup guard 110 can be for
instance of a
polymer material such as plastic or rubber. The bottom cup guard 110 can also
serve
as a marketing object, sporting for instance company logo or product name,
and/or
being in bright colour. The bottom cup guard 110 is made up of a single unit
and is
applied an adhesive and attached to the bottom cup 20, thus providing
permanent
20 joining of the bottom cup guard 110 and the bottom cup 20.
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
26
Table 1
Vertical
11 Holes in the vertical
12 Lug on vertical
13 Hole for lug on vertical
Bottom cup
21 Annual channel
22 Lower part of the wall of the bottom cup
23 Intermediate part of the wall of the bottom cup
24 Upper part of the wall of the bottom cup
Hole in bottom cup
26 Drainage recess in bottom cup
27, 27' Bottom cup halves
28 Machined recesses in bottom cup
29 Holes in the mating surfaces of the bottom cup
halves
Top cup
31 Top cup bulge
32 Vertical slot
33 Top cup lug
34 Helical surface
Horizontal
41 Blade end
42 Fins
Fastening means
Dowel pins for bottom cup halves
Wedges
Elongate tube
81 Inner tube
Support bracket
91, 91' Support bracket plate
92, 92' Clamping portion
93 Bolt
94 Squared hole
Washer
CA 03094450 2020-09-18
WO 2019/182457
PCT/N02019/050060
27
96 Nut
100 Stopper
110 Bottom cup guard
111 Lower part of the bottom cup guard
112 Upper part of the bottom cup guard
113 Flange of the bottom cup guard
114 Drainage recess in bottom cup guard
120 Node section
130 Dowel pins for lugs in vertical