Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Docket No.: P9930CA00
DEVICE, SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR ALLOCATING RESOURCES FOR
VIDEO STREAMING
BACKGROUND
[00011 Videos are often provided to streaming systems by client devices for
streaming on-
demand by video streaming devices. However, allocation of resources for
streaming the
videos can be problematic. For example, planning for resources used to stream
the videos
must be made in a balanced manner, to balance expected demand for the videos
with actual
demand, such that bandwidths and/or resources allocated for streaming the
videos are
neither too high (e.g. which may lead to a waste of allocated bandwidth), nor
too low (e.g.
such that the streaming of the videos exceed an allocated bandwidth, which may
lead to
slow streaming of the videos and/or other videos).
1
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
BRIEF DESCRIPTIONS OF THE DRAWINGS
100021 For a better understanding of the various examples described herein and
to show
more clearly how they may be carried into effect, reference will now be made,
by way of
example only, to the accompanying drawings in which:
100031 FIG. 1 depicts a system for allocating resources for video streaming,
according to
non-limiting examples.
100041 FIG. 2 depicts a block diagram of a computing device for allocating
resources for
video streaming, according to non-limiting examples.
100051 FIG. 3 depicts a method for allocating resources for video streaming,
and according
to non-limiting examples.
100061 FIG. 4 depicts an example of a method for allocating resources for
video streaming
being implemented in components of the system of FIG. I, and according to non-
limiting
examples.
100071 FIG. 5 further depicts the example of the method for allocating
resources for video
streaming being implemented in components of the system of FIG. 1, and
according to
non-limiting examples.
100081 FIG. 6 further depicts the example of the method for allocating
resources for video
streaming being implemented in components of the system of FIG. 1, and
according to
non-limiting examples.
100091 FIG. 7 further depicts the example of the method for allocating
resources for video
streaming being implemented in components of the system of FIG. 1, and
according to
non-limiting examples.
100101 FIG. 8 further depicts the example of the method for allocating
resources for video
streaming being implemented in components of the system of FIG. 1, and
according to
non-limiting examples.
2
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
100111 Videos are often provided to streaming systems by client devices for
streaming on-
demand by video streaming devices. However, allocation of resources for
streaming the
videos can be problematic. For example, planning for resources used to stream
the videos
must be made in a balanced manner, to balance expected demand for the videos
with actual
demand, such that bandwidths and/or resources allocated for streaming the
videos are
neither too high (e.g. which may lead to a waste of allocated bandwidth), nor
too low (e.g.
such that the streaming of the videos exceed an allocated bandwidth, which may
lead to
slow streaming of the videos and/or other videos).
100121 The situation may be exacerbated by a client device providing a video,
which is
shorter in length than a reserved allocated resource. For example, an operator
of the client
device may reserve allocated resources for streaming of a 10 second video, but
provide
only a 7 second video; as such, while allocated resources for streaming of a
10 second
video may be reserved at the streaming system, actual allocated resources used
at the
streaming system may be for a 7 second video. A computing device managing
allocation
of resources at the streaming system, for example on behalf of the client
devices, for a
plurality of videos, which have respective actual allocated resources that are
less than
reserved allocated resources, may hence determine that reserving allocated
resources at the
streaming system, based on the allocated resources reserved by the client
device, results in
too many resources being allocated, which can lead to the aforementioned
issues. As such
the computing device may reserve allocated resources at the streaming system
based on the
actual allocated resources of the videos, however such allocation may be too
low.
100131 In particular, some streaming systems provide a plurality of discrete
selectable
allocated resources from which a computing device may select. For example, a
selectable
allocated resource, of the plurality of discrete selectable allocated
resources, may
correspond to an amount ofbandwidth reserved for streaming videos in a given
time period,
such as a month, and the like. As such, each of the plurality of discrete
selectable allocated
resources may comprise increasing discrete amounts of bandwidth that may be
selected by
the computing device for streaming the videos in a given time period.
3
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
100141 Hence, when reserving allocated resources at the streaming system, the
computing
device may select a first reserved aggregate allocated resources from a
plurality of discrete
selectable allocated resources available at the streaming system.
[00151 Thereafter, the videos may be streamed, for example on-demand, or
pushed, from
.. the streaming system to video streaming devices, such personal computers,
laptop
computers, mobile devices, video display devices, electronic billboards, video
kiosks, and
the like.
[00161 As the computing device may initially have no statistics on demand for
the videos,
the selected first reserved aggregate allocated resources may be too high or
too low.
However, the selected first reserved aggregate allocated resources may be
selected based
on an estimated demand for the videos, for example an estimated number of
streams of the
videos, using the actual allocated resources for videos, over the given time
period. In a
simple example, if a total length of all the videos provided by the client
devices is 26
minutes, and estimated number of streams of the videos is 100 streams per
month per video,
.. the selected first reserved aggregate allocated resources may be a value
that corresponds to
streaming of at least 2600 minutes of video per month (and may also be based
on other
factors, such as the resolution of the streaming of the videos, and the like),
with for
example, a factor to account for error, such as 10% (e.g. or 2860 minutes).
For example,
the selected first reserved aggregate allocated resources may be one of the
plurality of
discrete selectable allocated resources, which corresponds to 2860 minutes of
streaming
per month and/or one of the plurality of discrete selectable allocated
resources, which
corresponds to greater than 2860 minutes is greater than, and closest to, 2860
minutes of
streaming per month.
[00171 However, the selected first reserved aggregate allocated resources is
generally
selected to be less than the reserved allocated resources for the videos. For
example, if the
total length of all the videos is 26 minutes, but the client devices have
reserved 30 minutes,
in total, for the videos (e.g. an aggregate difference of 4 minutes), the
selected first reserved
aggregate allocated resources is generally selected to be less than the 3000
minutes (e.g.
minutes times 100 times per month) and/or less than 3000 minutes plus 10%
thereof
30 .. (e.g. 3300 minutes).
4
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
100181 Furthermore, while allocated resources are described in this example
with respect
to minutes of videos, such allocated resources may be provided as any suitable
parameter
including, but not limited, bits and/or bytes of data to be streamed, for
example for a given
time period.
.. 100191 As such, the computing device generally monitors used resources for
streaming the
videos to the video-playing devices from the streaming system; for example,
the computing
device may receive reports from the streaming system that indicate used
resources. In
general, the used resources exceeding the first reserved aggregate allocated
resources (e.g.
demand for the videos was higher than estimated) may result in problems with
videos being
streamed. In a worst case scenario, for example, the streaming system may stop
streaming
the videos once the used resources meet or exceed the first reserved aggregate
allocated
resources; however, even when the streaming system continues to stream the
videos, the
streaming system may apply additional restrictions and/or penalties for
streaming the
videos (e.g. streaming at slower speeds, increasing cost, and the like).
[00201 As such, the computing device may determine that the used resources are
within a
threshold value of the first reserved aggregate allocated resources (and/or is
higher than the
first reserved aggregate allocated resources), and, in response, select second
reserved
aggregate allocated resources, from the plurality of discrete selectable
allocated resources,
for streaming the videos to the video-playing devices. However, such a
selection of the
second reserved aggregate allocated resources is generally based on the
respective
differences between the reserved allocated resources and the actual allocated
resources for
the videos, such that, for example, the second reserved aggregate allocated
resources does
not exceed the reserved allocated resources of the videos (e.g. which may also
take into
account an estimated number of streams of the videos in a given time period
for the second
.. reserved aggregate allocated resources, and the like).
100211 Put another way, the selected second reserved aggregate allocated
resources may
be selected similar to the selected first reserved aggregate allocated
resources, but based
on a larger number of streams per month than initially estimated, but still
limited by the
reserved allocated resources and the actual allocated resources, and/or an
aggregate
difference therebetween.
5
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
100221 An aspect of the present specification provides a method comprising:
determining,
at a computing device, respective differences between reserved allocated
resources and
actual allocated resources for videos provided to a streaming system by client
devices;
selecting, via the computing device, at the streaming system, first reserved
aggregate
allocated resources, from a plurality of discrete selectable allocated
resources available at
the streaming system, the first reserved aggregate allocated resources
selected based on the
actual allocated resources for the videos, the first reserved aggregate
allocated resources
for streaming the videos to video-playing devices; monitoring, via the
computing device,
used resources for streaming the videos to the video-playing devices from the
streaming
system; and in response to determining, via the computing device, that the
used resources
are within a threshold value of the first reserved aggregate allocated
resources: selecting,
via the computing device, second reserved aggregate allocated resources, from
the plurality
of discrete selectable allocated resources, for streaming the videos to the
video-playing
devices, the second reserved aggregate allocated resources selected based on
the respective
differences between the reserved allocated resources and the actual allocated
resources for
the videos.
100231 Another aspect of the present specification provides a device
comprising: a
communication interface configured to communicate with a streaming system;
and, a
controller configured to: determine respective differences between reserved
allocated
resources and actual allocated resources for videos provided to the streaming
system by
client devices; select, via the communication interface, at the streaming
system, first
reserved aggregate allocated resources, from a plurality of discrete
selectable allocated
resources available at the streaming system, the first reserved aggregate
allocated resources
selected based on the actual allocated resources for videos, the first
reserved aggregate
allocated resources for streaming the videos to video-playing devices;
monitor, via the
communication interface, used resources for streaming the videos to the video-
playing
devices from the streaming system; and in response to determining that the
used resources
are within a threshold value of the first reserved aggregate allocated
resources: select, via
the communication interface, second reserved aggregate allocated resources,
from the
plurality of discrete selectable allocated resources, for streaming the videos
to the video-
playing devices, the second reserved aggregate allocated resources selected
based on the
6
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
respective differences between the reserved allocated resources and the actual
allocated
resources for the videos.
f00241 A further aspect of the present specification provides a non-transitory
computer-
readable medium comprising instructions that, when executed by a processor,
causes the
processor to implement a method comprising: determining respective differences
between
reserved allocated resources and actual allocated resources for videos
provided to a
streaming system by client devices; selecting at the streaming system, first
reserved
aggregate allocated resources, from a plurality of discrete selectable
allocated resources
available at the streaming system, the first reserved aggregate allocated
resources selected
.. based on the actual allocated resources for the videos, the first reserved
aggregate allocated
resources for streaming the videos to video-playing devices; monitoring, used
resources
for streaming the videos to the video-playing devices from the streaming
system; and in
response to determining that the used resources are within a threshold value
of the first
reserved aggregate allocated resources: selecting second reserved aggregate
allocated
resources, from the plurality of discrete selectable allocated resources, for
streaming the
videos to the video-playing devices, the second reserved aggregate allocated
resources
selected based on the respective differences between the reserved allocated
resources and
the actual allocated resources for the videos.
f00011 Attention is next directed to FIG. 1, which depicts a system 100 for
allocating
resources for video streaming. The various components of the system 100 are in
communication via any suitable combination of wired and/or wireless
communication
links, and communication links between components of the system 100 are
depicted in
FIG. 1, and throughout the present specification, as double-ended arrows
between
respective components; the communication links may include any suitable
combination
.. of wireless and/or wired links and/or wireless and/or wired communication
networks, and
the like.
100251 As depicted, the system 100 comprises a computing device 101 for
allocating
resources for video streaming. For example, as depicted, the system 100
comprises a
streaming system 103 in communication with the computing device 101, an
integer number
"N" of client devices 105-1,...105-N, and an integer number "P" of video-
playing devices
107-1,...107-P.
7
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
100261 The client devices 105-I,... 105-N will be interchangeably referred to
hereafter,
collectively, as the client devices 105 and, generically, as a client device
105. This
numbering scheme will be used throughout the present specification. For
example, the
video-playing devices 107-1,...107-P will be interchangeably referred to
hereafter as the
video-playing devices 107 and/or as a video-playing device 107.
100271 While details of the computing device 101 are described in further
detail below with
respect to FIG. 2, the computing device 101 generally comprises any suitable
number of
servers, cloud computing devices, personal computers, laptop computers, and
the like, for
allocating resources for video streaming, for example at the streaming system
103, and
which may be performed on behalf of the client devices 105. Furtheiniore,
while not
depicted, the computing device 101 may comprise a client device 105 and/or the
computing
device 101 may comprise a video-playing device 107. Put another way, while the
devices
101, 105, 107 are depicted as being different from one another, in some
examples,
functionality of two or more of the devices 101, 105, 107 may be combined.
Indeed, in
some examples, a client device 105 may comprise a video-playing device 107,
and vice
versa.
100281 However, in a specific example, the computing device 101 is different
from the
streaming system 103, and in this specific example, the system 100 includes at
least one
client device 105 that is different from the computing device 101, and at
least one video-
playing device 107 from a client device 105. In such specific example, the
computing
device, the streaming system 103, at least one client device 105 and at least
one video
playing device 107 are all different from each other. Regardless, the
streaming system 103
is generally understood to host the videos 115, but is not otherwise tasked
with advertising
the videos 115; indeed entities and/or users associated with the client
devices 105 and the
video playing devices 107, the computing 101 is understood to be associated
with
managing the videos 115 (e.g. and not the streaming system 103). As such, the
computing
device 101 and the streaming system 103 are understood to be different from
television
streaming systems which advertise and provide television shows, movies, and
the like; for
example, such television streaming systems do not generally include client
devices which
reserve resources for videos, where reserved allocated resources and actual
allocated
resources for videos, provided to a streaming system by client devices, are
different.
8
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
100291 The streaming system 103 generally comprises any suitable number of
servers,
cloud computing devices, and the like, which may store and stream videos, as
described in
more detail below. The streaming system 103 may perform other functions, such
as hosting
websites, and the like, which may act as an interface between the streaming
system 103
and the computing device 101 and the client devices 105. For example, as
depicted, the
streaming system 103 comprises a site engine 109, which may be used to receive
and store
videos, for example at a memory 111 (e.g. which may include one or more
memories
provided in the form of one or more databases, and which may be internal
and/or external
to the streaming system 103). The streaming system 103 further comprises a
video
streaming engine 113 for providing videos 115-1...115-Q (e.g. as depicted, as
stored at the
memory 111) to the video-playing devices 107. The videos 115-1...115-Q are
referred to
hereafter as the videos 115 and/or a video 115. The streaming system 103 may
comprise
other engines to perform other functionality thereof', for example billing
engines, and the
like. In some examples, the functionality of the engines 109, 113 may be
combined into
one (or more engines).
100301 As used herein, the term "engine" refers to hardware (e.g., a
processor, such as a
central processing unit (CPU) an integrated circuit or other circuitry) or a
combination of
hardware and software (e.g., programming such as machine- or processor-
executable
instructions, commands, or code such as firmware, a device driver,
programming, object
code, etc. as stored on hardware). Hardware includes a hardware element with
no software
elements such as an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC), a Field
Programmable
Gate Array (FPGA), etc. A combination of hardware and software includes
software hosted
at hardware (e.g., a software module that is stored at a processor-readable
memory such as
random access memory (RAM), a hard-disk or solid-state drive, resistive
memory, or
optical media such as a digital versatile disc (DVD), and/or implemented or
interpreted by
a processor), or hardware and software hosted at hardware.
100311 In some examples, the streaming system 103 may comprise the computing
device
101 (e.g. as a component of the site engine 109, and the like).
100321 The client devices 105 may comprise any suitable device configured to
provide a
video 115 to the streaming system 103 for streaming. The client devices 105
may
communicate with the computing device 101 via the streaming system 103 (e.g.
via the site
9
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
engine 109) and/or the streaming system 103 may act as an interface between
the client
devices 105 and the computing device 101. The client devices 105 may comprise
personal
computers, laptop computers, mobile devices, and/or any other suitable type of
devices
including, but not limited to, servers, cloud computing devices, and the like.
In a particular
example, the client devices 105 may access a website at the streaming system
103 (e.g.
hosted by the site engine 109) via a respective local browser application
and/or engine
installed at the client devices 105, to provide and/or upload a video 115 to
the streaming
system 103 (e.g. for storage at the memory 111 and for streaming to the video-
playing
devices 107).
100331 For example, a client device 105 may upload a video 115 (or videos 115)
to the
streaming system 103 and/or a client entity may request that the entity
associated with the
computing device 101 generate and provide a respective video 115 (e.g. in
which case, the
computing device 101 may act as a proxy client device 105 on behalf of such a
client
entity).
[00341 In particular, when providing a video 115 and/or in conjunction with
providing a
video 115, a client device 105 may reserve allocated resources for the video
115, but actual
allocated resources for the video 115 may be less than reserves allocated
resources. In a
simple example, the computing device 101 (e.g. via a website provided via the
site engine
109) may prompt the client device 105 to select a length of a video 115 to be
uploaded, for
example from a plurality of fixed predetermined lengths, such as 5 seconds, 10
seconds,
15 seconds, 20 seconds, 25 seconds, and the like. The client device 105 may
select a
predetermined length, which is greater than, or equal to, a length of the
video 115, and
upload the video 115. While the selected predetermined length may be
associated with a
respective cost, it is understood that the selected predeteimined length is
generally used for
allocated streaming resource planning by the computing device 101.
Furthermore, as the
video 115 may be less than the selected predetermined length, the difference
between the
actual length and the selected predetermined length may be used by the
computing device
101 for allocated streaming resource planning, as described in more detail
below.
100351 The video-playing devices 107 may comprise personal computers, laptop
computers, mobile devices, video display devices, video kiosks, and/or any
suitable device
to which a video 115 may be streamed. Such streaming may occur on demand, for
example
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
via a video-playing device 107 accessing a website (e.g. via a respective
local browser
applications and/or engine installed at the video-playing devices 107
accessing the site
engine 109) to select a video and/or videos for streaming and which, once
selected, are
streamed to a video-playing device 107 via the video streaming engine 113. In
yet further
examples, a video-playing device 107 may include a mobile device (e.g. a smart-
phone,
and the like) using a locally installed application (e.g. an "app") to request
and receive
videos streamed thereto from the streaming system 103, for example on-demand.
100361 In yet further examples, a video-playing device 107 may comprise a
video display
device, and the like, such as a device, which includes a display screen
installed in a public
space, and which may include, but is not limited to, electronic billboards
installed in
outdoor spaces, video kiosks installed in indoor public spaces, and the like.
However, such
electronic billboards, video kiosks and the like may be installed in any
suitable space,
indoor or outdoor, public or not private, and the like. In some of these
examples, the
streaming system 103 may be configured to stream videos 115 provided by the
client
devices 105 to such a video-playing device 107 via pushing (e.g. rather than
on demand)
for example in a loop. Such video display devices may be operated by the same
entity
operating the computing device 101, and/or another entity.
100371 Hence, streaming of the videos 115 may occur on-demand and/or via
pushing.
Furthermore, while streaming of the videos 115 has been described with respect
to specific
types of the video-playing device 107 requesting the videos 115 on-demand
(e.g. pulling),
or receiving the videos 115 via pushing, pushing or pulling of the videos 115
may occur at
any suitable type of video-playing device 107. For examples, videos 115 may be
pushed to
a personal computer, laptop computer, mobile device, and the like, upon such a
device
accessing a website via a browser and/or opening an app. Similarly, videos 115
may be
requested by a video display device, which includes an electronic billboard, a
video kiosk,
and the like.
100381 As depicted the system 100 includes a number "N" of the client devices
105, a
number "P" of video-playing devices 107, and a number "Q" of the videos 115.
The
number "N" of the client devices 105 may comprise any suitable number of the
client
devices 105, and furthermore the number "N" of the client devices 105 may vary
with time.
For example, it is generally understood that the computing device 101
generally manages
11
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
streaming of the videos 115 and specifically manages allocation of resources
for streaming
of the videos 115 at the streaming system 103. Furthermore, the computing
device 101 may
be operated by, and/or associated with, an entity that is providing a service
to entities
operating the client devices 105 and/or associated with the client devices
105. For example,
the computing device 101 may be providing a service to the client devices 105
that targets
streaming of the videos 115 to certain regions (e.g. geographic regions) based
on location
of the video-playing devices 107, such that viewers of the video-playing
devices 107 may
view content of the videos 115 based on region. For example, the videos 115
may include
content that is particular to a given region, whether due to pre-determined
licensing
agreements, specific content in the videos 115, and the like; for example, a
particular video
115 may include content pertaining to a store, a restaurant, a tourist
attraction, and the like,
located in a given region, and a client entity associated with a client device
105 may engage
the entity associated with the computing device 101 to stream the particular
video 115 to
video-playing devices 107 in the given region. Such regional targeting of
video-playing
devices 107 may occur by associating videos 115 with regions at the memory 111
(e.g.
during an upload thereto) and the streaming system 103 determining a region in
which a
video-playing device 107 is located via an associated network address, and the
like.
100391 As such, the number "N" of the client devices 105 may vary with time,
based on
numbers of client entities that engage, or disengage, the entity associated
with the
computing device 101 to provide respective videos 115.
100401 Similarly, the number "Q" of the videos 115 may vary with time, based
on numbers
videos 115 provided by the client devices 105. In some examples, the number
"Q" of the
videos 115 may be the same as the number "N" of the client devices 105 (e.g.
each of the
client devices 105 may provide a respective video 115). However, in other
examples, the
number "Q" of the videos 115 may be larger than the number "N" of the client
devices 105
(e.g. one or more of the client devices 105 may provide more than one
respective video
115). In yet further examples, the number "Q" of the videos 115 may be less
than the
number "N" of the client devices 105 (e.g. one or more of the client devices
105 may
engage the entity associated with the computing device 101 but may not have
yet provided
a respective video 115). Regardless, the number "Q" of the videos 115 may be
any suitable
number.
12
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
100411 Similarly, the number "P" of the video-playing devices 107 may vary
with time, for
example as the video-playing devices 107 access a website and/or execute an
application
for receiving the videos 115 and/or as the video-playing devices 107 come on-
line and/or
go off-line. Regardless, the number "P" of the video-playing devices 107 may
be any
suitable number.
100421 As depicted, the streaming system 103 may generally include a plurality
of discrete
selectable allocated resources 117-1 ....117-R (e.g. selectable allocated
resources 117) from
which the computing device 101 may select. Each of the discrete selectable
allocated
resources 117 may correspond to a specific amount of streaming resources that
may be
reserved for streaming the videos 115, and each of the selectable allocated
resources 117
may be different from others of the selectable allocated resources 117. For
example, the
discrete selectable allocated resources 117 may comprise lowest discrete
selectable
allocated resources 117, which is less than next discrete selectable allocated
resources 117,
which is less than yet next discrete selectable allocated resources 117, and
so on. As
depicted, for example, there are an integer number "R" of selectable allocated
resources
117 from which the computing device 101 may select, and the number "R" of
selectable
allocated resources 117 may be any suitable number of selectable allocated
resources 117,
depending on offerings that the streaming system 103 may make available to
computing
devices of entities using the streaming system 103 for streaming respective
videos 115.
Values of the selectable allocated resources 117 are understood to be stored
at a memory
of the streaming system 103 (e.g. which may include, but is not limited to,
the memory 111
and/or another memory) and accessed and/or provided to the computing device
101, for
example upon request, and the like. Furthermore, the discrete selectable
allocated resources
117 may be provided per a given time period; for example, a value of a
discrete selectable
allocated resources 117 may comprise a number of bits and/or bytes and/or
minutes per
month reserved for streaming videos.
100431 For example, the streaming system 103 may provide the plurality of
discrete
selectable allocated resources 117, as a plurality of "packages" from which
the computing
device 101 may select to reserve associated streaming resources for streaming
the videos
115 per month and/or any other suitable time period. Such packages may also
include
provisions for resolution of streaming of the videos 115, and the like. As
will be described
13
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
in more detail below, the computing device 101 generally initially selects one
of the
discrete selectable allocated resources 117, for example as a first reserved
aggregate
allocated resources, for a first given time period, which is generally based
the actual
allocated resources for the videos 115.
100441 Depending on a "package" (e.g. one of the discrete selectable allocated
resources
117) selected by the computing device 101, as well as packages (e.g. discrete
selectable
allocated resource 117) selected by other entities, which are also using the
streaming
system 103 to stream videos, the streaming system 103 may negotiate use of
network
resources for performing streaming of all videos of all such entities (e.g.
including the
videos 115), for example by a network provider.
100451 However, when used resources for streaming the videos 115 exceed the
discrete
selectable allocated resources 117 selected by the computing device 101 as
first reserved
aggregate allocated resources, streaming of other videos (e.g. of other
entities, which are
also using the streaming system 103 to stream videos) may be impacted. As
such, the
streaming system 103 may respond in a manner that stops streaming of the
videos 115
and/or reduces quality and/or resolution thereof and/or increases a cost to
the computing
device 101 for streaming the videos 115.
100461 As such, the computing device 101 is generally configured to select
another of the
discrete selectable allocated resources 117, as second reserved aggregate
allocated
resources for a second given time period, based on monitoring the used
resources for
streaming the videos 1 15, and differences between the reserved allocated
resources and the
actual allocated resources for the videos 115, as described in more detail
below, for
example via a resource allocation engine 119.
100471 Details of the computing device 101 are now described with respect to
FIG. 2.
100481 The computing device 101, can comprise any suitable computing device,
including
but not limited to one or more personal computers, laptops, servers, cloud
computing
devices, and the like. In some examples, where the computing device 101 may be
used to
generate videos 115 as a proxy client device 105, the computing device 101
include one or
more of a graphics processing unit (GPU), a graphics processing device, a
graphics
processing engine, a video processing device, and the like.
14
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
100491 As depicted, the computing device 101 generally comprises: a controller
220; a
memory 222 storing one or more applications 223, and a communication interface
224
(interchangeably referred to hereafter as the interface 224). While the memory
222 is
depicted as internal to the computing device 101, the memory 222 may be
external to the
computing device 101 and the controller 220 may have access to the memory 222
via the
interface 224.
100501 In general, while not depicted in FIG. 2, the resource allocation
engine 119 may
generally comprise a combination of the controller 220 and the memory 222
storing the
application 223, and the interface 224.
100511 Each of the one or more applications 223 may be similar, but for a
different mode
of the computing device 101; for example, in one mode, the computing device
101 may
allocate resources, as described herein, while in another mode a machine
learning
algorithm may be trained to implement functionality as describe herein. For
simplicity, the
one or more applications 223 will be interchangeably referred to hereafter as
the application
223.
100521 While not depicted, the computing device 101 may include other suitable
components, including, but not limited to, a display screen, an input device
and the like, to
enable an administrator to interact with the computing device 101; however,
such an
administrator may alternatively interact with the computing device 101
remotely via the
interface 224.
100531 The interface 224 comprises any suitable wired or wireless
communication
interface configured to communicate with the streaming system 103 (and/or the
client
devices 105). The interface 224 may communicate in a wired and/or wireless
manner as
desired including, but not limited using cables, Internet-based communication
links,
WiFiTM communication links, wide area networks, personal area networks, local
area
networks, and the like.
100541 The controller 220 can comprise a processor and/or a plurality of
processors,
including but not limited to one or more central processors (CPUs) and/or one
or more
graphics processing units (GPUs) and/or one or more processing units; either
way, the
controller 220 comprises a hardware element and/or a hardware processor. In
some
implementations, the controller 220 can comprise an ASIC (application-specific
integrated
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
circuit) and/or an FPGA (field-programmable gate array) specifically
configured for
allocating resources for video streaming. Hence, the computing device 101 may
preferably
not be a generic computing device, but a device specifically configured to
implement
specific functionality for allocating resources for video streaming. For
example, the
computing device 101 and/or the controller 220 can specifically comprise a
computer
executable engine, such as the resource allocation engine 119, configured to
implement
functionality for allocating resources for video streaming.
100551 The memory 222 can comprise a non-volatile storage unit (e.g. Erasable
Electronic
Programmable Read Only Memory ("EEPROM"), Flash Memory) and a volatile storage
unit (e.g. random-access memory ("RAM")). Programming instructions that
implement the
functional teachings of the computing device 101 as described herein are
typically
maintained, persistently, in the memory 222 and used by the controller 220,
which makes
appropriate utilization of volatile storage during the execution of such
programming
instructions. Those skilled in the art recognize that the memory 222 is an
example of
computer readable media that can store programming instructions executable on
the
controller 220. Furthermore, the memory 222 is also an example of a memory
unit and/or
memory module and/or a non-volatile memory.
100561 In particular, the memory 222 stores the application 223 that, when
processed by
the controller 220, enables the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101
to:
.. determine respective differences between reserved allocated resources and
actual allocated
resources for videos provided to a streaming system by client devices; select,
at the
streaming system, first reserved aggregate allocated resources, from a
plurality of discrete
selectable allocated resources available at the streaming system, the first
reserved
aggregate allocated resources selected based on the actual allocated resources
for videos,
the first reserved aggregate allocated resources for streaming the videos to
video-playing
devices; monitor used resources for streaming the videos to the video-playing
devices from
the streaming system; and in response to determining that the used resources
are within a
threshold value of the first reserved aggregate allocated resources: select
second reserved
aggregate allocated resources, from the plurality of discrete selectable
allocated resources,
for streaming the videos to the video-playing devices, the second reserved
aggregate
16
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
allocated resources selected based on the respective differences between the
reserved
allocated resources and the actual allocated resources for the videos.
100571 The application 223, and/or the resource allocation engine 119, may
include
numerical algorithms configured to implement the functionality as described
above
and/or to generate estimates of respective resources to be used to stream the
videos 115,
from the streaming system 103, in respective time periods, for example to
assist in
selecting the first reserved aggregate resources and the second reserved
aggregate
resources.
100581 Alternatively, and/or in addition to numerical algorithms, the
application 223,
and/or the resource allocation engine 119, may include machine learning models
and/or
algorithms, and the like, which have been trained to implement the
functionality as
described above and/or trained to generate estimates of respective resources
to be used to
stream the videos 115, from the streaming system 103, in respective time
periods, for
example to assist in selecting the first reserved aggregate resources and the
second
reserved aggregate resources, and/or any other suitable functionality of the
computing
device 101. The one or more machine learning models and/or algorithms of the
application 223 may include, but are not limited to: a deep-learning based
algorithm; a
neural network; a generalized linear regression algorithm; a random forest
algorithm; a
support vector machine algorithm; a gradient boosting regression algorithm; a
decision
tree algorithm; a generalized additive model; evolutionary programming
algorithms;
Bayesian inference algorithms, reinforcement learning algorithms, and the
like. Any
suitable machine learning algorithm and/or deep learning algorithm and/or
neural
network is within the scope of present examples.
100591 Furtheimore, in examples where the application 223 includes machine
learning
models and/or algorithms, and the like, the application 223 may include a
machine
learning training module, and the like, in which the computing device 101
receives input
corresponding resources used at the streaming system 103 to stream the videos
115 (e.g.
in a given time period), as well as any other suitable parameters (e.g.
numbers of the
videos 115, types of the video-playing devices 107, regions into which the
videos 115 are
streamed, and the like).
17
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
100601 While details of the streaming system 103, and the devices 105, 107 are
not
depicted, the streaming system 103, and the devices 105, 107 may have
structure similar
to the computing device 101, but adapted for their respective functionality
and/or
including various respective components for implementing such functionality.
For
example, the client devices 105 and the video-playing devices 107 may
generally include
display screens and input devices, and the like.
100611 Attention is now directed to FIG. 3, which depicts a flowchart of a
method 300 for
allocating resources for video streaming according to non-limiting examples.
The
operations of the method 300 may correspond to machine readable instructions
that are
executed by the computing device 101, and specifically the controller 220 of
the computing
device 101. In the illustrated example, the instructions represented by the
blocks of FIG. 3
are stored at the memory 222 for example, as the application 223. The method
300 of FIG.
3 is one way in which the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101
and/or the system
100 may be configured. Furthermore, the following discussion of the method 300
of FIG.
.. 4 will lead to a further understanding of the system 100, and its various
components
100621 The method 300 of FIG. 3 need not be performed in the exact sequence as
shown
and likewise various blocks may be performed in parallel rather than in
sequence.
Accordingly, the elements of method 300 are referred to herein as "blocks"
rather than
"steps." The method 300 of FIG. 3 may be implemented on variations of the
system 100,
as well.
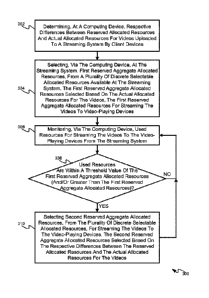
[00631 At a block 302, the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101
determines
respective differences between reserved allocated resources and actual
allocated resources
for the videos 115 provided to the streaming system 103 by the client devices
105.
[00641 For example, as described above, a client device 105 may provide a
video 115 to
the streaming system 103 and the computing device 101 may determine that the
client
device 105 selects reserved allocated resources for the video 115; for
example, the client
device 105 may select a given length and/or size of a video, from a plurality
of available
given lengths and/or given sizes, but the video 115 provided may be less than
a selected
given length and/or given size, thereby causing the computing device 101 to
store, at a
memory (e.g. the memory 222 or another suitable memory), the selected given
length
and/or given size and the actual length and/or given size, and detei ______
mine the difference
18
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
therebetween, which is also stored at the memory. For simplicity, storage of
such various
items by the computing device 101 will be described with respect to the memory
222,
however it is understood that the computing device 101 may store such items
(e.g. values
for the reserved allocated resources, actual allocated resources and a
difference
therebetween) at any suitable memory.
100651 Regardless, when storing such items, the computing device 101 causes
the memory
222 (and the like) to undergo a tangible physical change. Indeed, storage of
any items at
the memory 222 (and the like), as described herein, causes the memory 222 to
undergo a
tangible physical change.
100661 As mentioned above, reserved allocated resources for a video 115 may
comprise a
reserved length of the video 115, and actual allocated resources for the video
115 may
comprise an actual length of the video 115. Hence, a difference therebetween
may
correspond to a difference in the reserved length and the actual length.
However, while the
reserved and actual allocated resources has heretofore been described with
respect to length
of videos 115, the reserved and actual allocated resources may be in any
suitable format
including, but not limited to, a size of the video 115 (e.g. as indicated by
numbers of bits
and/or bytes of a video 115), with a difference therebetween in a similar
and/or same
format.
100671 Put another way, each of the reserved allocated resources (e.g. for the
videos 115)
may be selected from a plurality of discrete reserved allocated resources
(e.g. the above
described plurality of available given lengths, and the like).
100681 Indeed, the videos 115 may also be limited, by the computing device
101, and/or
the site engine 109, to a given highest resolution (e.g. 720p and/or any other
suitable
resolution) and/or a converted to a given resolution, to prevent a client
device 105 from
selecting, for example, a given length of a video, but uploading a very high
resolution video
115 (e.g. 8K), which would increase later usage of streaming resources. Such a
limitation
of resolution may also occur due to a package selected by the computing device
101 at the
streaming system 103 that limits videos to be streamed to a given resolution.
Such limits
on resolution, and the like, may also be incorporated into the reserved
allocated resources
and actual allocated resources (e.g. selected lengths and actual lengths of
videos 115 may
be for a given resolution and/or smaller than such a given resolution).
19
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
100691 Furthermore, when a video 115 is provided (e.g. uploaded to the site
engine 109),
the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101 (and/or the site engine
109) may check
the actual allocated resources of the video 115 against the reserved allocated
resources to
ensure that that the actual allocated resources of the video 115 does not
exceed the reserved
allocated resources. For example, when a client device 105 selects reserved
allocated
resources corresponding to 10 seconds for a video 115, the controller 220
and/or the
computing device 101 (and/or the site engine 109) checks the length of the
video 115 to
ensure the video 115 does not exceed 10 seconds. Similar checks on resolution
of the video
115 may also occur. When the actual allocated resources of the video 115 is
greater than
the reserved allocated resources, the controller 220 and/or the computing
device 101
(and/or the site engine 109) may instruct a client device 105 to again select
reserved
allocated resources that is greater than, or equal to, the actual allocated
resources of the
video 115, and/or upload another video 115 that is less then, or equal to,
initially selected
reserved allocated resources.
[00701 Regardless, it is understood that actual allocated resources of a video
115 are
limited by the computing device 101 to being less than reserved (e.g.
selected) allocated
resources.
100711 It is yet further understood that the controller 220 and/or the
computing device 101
determines a difference between reserved allocated resources and actual
allocated
resources for all the videos 115, and that the reserved allocated resources
may be different
for two or more of the videos 115, and furthermore the difference between
reserved
allocated resources and actual allocated resources may be may be different for
two or more
of the videos 115. Put another way, different videos 115 where 10 seconds may
be reserved
therefor may be of different lengths (e.g. videos 115 of 6 seconds, 7 seconds,
7.8 seconds,
etc. may be provided, and/or any length up to 10 seconds).
100721 At the block 302, the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101
may further
determine a total of the differences between the reserved allocated resources
and the actual
allocated resources for the videos 115. At the block 302, the controller 220
and/or the
computing device 101 may further determine a total of the reserved allocated
resources and
a total of the actual allocated resources.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
[0073] At a block 304, the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101
selects, at the
streaming system 103, first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117, from
the plurality
of discrete selectable allocated resources 117 available at the streaming
system 103, the
first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 selected based on the actual
allocated
resources for the videos 115, the first reserved aggregate allocated resources
117 for
streaming the videos 115 to video-playing devices 107, for example in a first
time period.
[0074] For example, the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101 may
determine an
aggregate length and/or size (e.g. in bits, bytes, and the like) of the actual
allocated
resources for the videos 115, and estimate a number of streams per given time
period of
the videos 115. Such an estimate may initially be based on numbers of known
video-
playing devices 107 to which the videos 115 may be pushed; for example,
entities operating
video display devices and/or electronic billboard and/or video kiosks may
cooperate with
the entity operating the computing device 101 to arrange for streaming of the
videos 115
to the video display devices (e.g. and which may be based on regional
locations of the
.. video display devices), and/or the entity operating the computing device
101 may operate
such video display devices. Such an estimate may be alternatively be based on
a number
of times an application for receiving the videos 115 (e.g. which may be
provided by the
entity operating the computing device 101) has been downloaded to mobile
devices, and
the like. Such an estimate may be alternatively be based on a number of times
a website
for receiving the videos 115 has been accessed, and the like. However, such an
estimate
may be based on any suitable combination of such factors and/or other factors
and/or
provided via a machine learning algorithm, and the like.
100751 With an estimate of resources to be used to stream the videos 115 for a
given time
period (e.g. the first given time period for first reserved aggregate
allocated resources 117),
the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101 selects, at the streaming
system 103,
first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117, from the plurality of
discrete selectable
allocated resources 117 based on the actual allocated resources for the videos
115. For
example, an estimate of a number of times that the videos 115 may be streamed
may be
multiplied by the total of the actual allocated resources for the videos 115,
and a closest
.. one of the discrete selectable allocated resources 117, that is also
greater than the total of
21
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
the actual allocated resources for the videos 115, may be selected, by the
controller 220
and/or the computing device 101, as the first reserved aggregate allocated
resources 117.
100761 The selection of the first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117
may further be
based on a factor to account for error and/or variation in the estimates, such
as 10%, and/or
any other suitable factor (e.g. 5%, 15%, etc.), which may be predetermined and
provisioned
at the computing device 101 (e.g. in the application 223) by an administrator
of the
computing device 101, and/or dynamically determined using machine learning
algorithms,
and the like. For example, the estimate of a number of times that the videos
115 may be
streamed, multiplied by the total of the actual allocated resources for the
videos 115, may
.. be fin-ther increased by the factor.
100771 In yet further examples, a plurality of estimates of a number of
respective times that
respective videos 115 may be streamed may be determined on a regional basis,
based on
locations of the video-playing devices 107 as described above, and the
selection of the first
reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 may be based on a total of such
regional
.. estimates. For example, actual allocated resources for the videos 115 for a
first region may
be multiplied by a first estimate of streams to video-playing devices 107
associated with
the first region, and added to actual allocated resources for the videos 115
for a second
region multiplied by a second estimate of streams to video-playing devices 107
associated
with the second region; such estimates may occur for any suitable number of
regions.
.. [00781 It is yet further understood that selection of the first reserved
aggregate allocated
resources 117 may be selected for a first given time period, for example a
month, and the
like.
100791 Furthermore, the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101 may
store an
indication of the first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117, for
example at the
.. memory 222.
100801 Thereafter, the videos 115 may be available for streaming from the
streaming
system 103, via the video streaming engine 113, and the streaming system 103
provides
the videos 115 to the video-playing devices 107, as described above.
100811 At a block 306, the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101
monitors used
resources for streaming the videos 115 to the video-playing devices 107 from
the streaming
system 103. For example, the streaming system 103 may provide data, reports,
messages,
22
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
and the like, to the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101,
indicative of the
resources used by the streaming system 103 to stream the videos 115. Such
data, and the
like, may indicate a number of minutes and/or bits and/or bytes of the videos
115 streamed
in a given time period, which may be the same as, or less than the first given
time period
for which the first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 were selected.
For example,
the streaming system 103 may provide such data periodically, for example, on
an hourly
basis, a weekly basis, a monthly basis and/or according to any other suitable
time period
and/or periodicity. Such data may further indicate regional streaming of the
videos 115
and/or respective numbers of times individual videos 115 were streamed, and/or
to which
regions. Such data may alternatively be requested by the computing device 101.
100821 Furthermore, the data, and the like, may be provided as any suitable
combination
of parameters, which indicate resources used to stream the videos 115
including, but not
limited to, an amount of bandwidth used to stream the videos 115, seconds
and/or minutes
streamed, an amount of bits and/or bytes streamed, and the like. Furthermore,
the data may
be provided in any suitable format including, but not limited to, in a message
(e.g. an email,
and the like), a report, a databased and/or tabular format, and the like.
100831 In some examples, the streaming system 103 may provide such data to the
controller
220 and/or the computing device 101 upon request by the controller 220 and/or
the
computing device 101.
100841 Regardless, the data enables the controller 220 and/or the computing
device 101 to
determine actual used resources for streaming the videos 115, which may be
compared to
the selected first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117.
f00851 At a block 308, the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101
determines
whether the used resources are within a threshold value of the first reserved
aggregate
allocated resource 117. Such a determination may occur within a given time
before an end
of the first time period associated with the selected first reserved aggregate
allocated
resources 117 (e.g. to ensure that if the used resources are within a
threshold value of the
first reserved aggregate allocated resource 117, reserved aggregate allocated
resources 117
are selected before a next time period commences, as described hereafter).
100861 Such a threshold value may comprise any suitable threshold value, such
as 10% of
the first reserved aggregate allocated resource 117, and/or any other suitable
threshold
23
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
value (e.g. 5%, 15%, etc.), which may be predetermined and provisioned at the
computing
device 101 (e.g. in the application 223) by an administrator of the computing
device 101,
and/or dynamically determined using machine learning algorithms, and the like.
[00871 In some examples, the threshold value may be based on an intet _____
mediate
determination of the used resources (e.g. which may be determined from
periodic receipt
of the used resources at the computing device 101, prior to an end of the
first given time
period for which the first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 were
selected. In
particular, the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101 may determine a
rate of
change of the used resources and adjust the threshold value accordingly. For
example,
initially a threshold value of 10% may be selected, and, as a rate of change
of the used
resources increases or decreases, the threshold value may be increased or
decreased from
10%.
[00881 In general, the threshold value is used to determine whether or not to
select another
of the plurality of discrete selectable allocated resources 117, which is
greater than the first
reserved aggregate allocated resources 117, for a next given time period. When
the used
resources are not within the threshold value of the first reserved aggregate
allocated
resources 117, in some examples, the first reserved aggregate allocated
resources 117 may
be maintained for a next time period (e.g. a next month). However, when the
used resources
are not the threshold value of the first reserved aggregate allocated
resources 117, a second
reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 may be selected from the plurality
of discrete
selectable allocated resources 117.
100891 Hence, when a rate of change of the used resources is increasing, the
threshold value
may be increased to sooner change the selection of the plurality of discrete
selectable
allocated resources 117; however, when the rate of change of the used
resources is
decreasing, the threshold value may be decreased to later change the selection
of the
plurality of discrete selectable allocated resources 117.
100901 At the block 308, the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101
may further
determine whether, or not, the used resources are greater than the first
reserved aggregate
allocated resources 117, which may automatically trigger selection of second
reserved
aggregate allocated resources 117 (e.g. greater than the first reserved
aggregate allocated
resources 117) for a next time period (e.g. a next month).
24
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
100911 In response to determining, at the block 308, that the used resources
are within a
threshold value of the first reserved aggregate allocated resources (e.g. a
"YES" decision
at the block 308), at a block 310 the controller 220 and/or the computing
device 101 selects
second reserved aggregate allocated resources 117, from the plurality of
discrete selectable
allocated resources 117, for streaming the videos 115 to the video-playing
devices 107. In
general, the second reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 may be selected
based on
the respective differences between the reserved allocated resources and the
actual allocated
resources for the videos 115 as described above. Such a selection of second
reserved
aggregate allocated resources 117 may also occur when the used resources are
greater than
the first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 (e.g. which also leads to
a "YES"
decision at the block 308).
100921 In particular, the second reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 is
selected to
be greater than the used resources. However, the second reserved aggregate
allocated
resources 117 is further selected to be greater than total actual allocated
resources for the
videos 115 (e.g. multiplied by an updated estimate for streaming the videos
115), further
taking into account the respective differences between the reserved allocated
resources and
the actual allocated resources for the videos 115 and, in particular, the
total differences
between the reserved allocated resources and the actual allocated resources
for the videos
115.
100931 For example, the second reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 may
be
selected to be greater than total actual allocated resources for the videos
115 (e.g. multiplied
by an updated estimate for streaming the videos 115), but less than total
reserved allocated
resources for the videos 115 (e.g. multiplied by the updated estimate for
streaming the
videos 115).
100941 The updated estimates referred to above may be for a next time period,
and/or a
second time period for which the second reserved aggregate allocated resources
117 is
selected (e.g. the second time period following the first time period for
which the first
reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 was selected), and may be based on
demand for
the videos 115 in the first time period and/or historical demand for the
videos 115, which
may be represented by the aforementioned used resources.
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
100951 Hence, in general, the first reserved aggregate resources 117 and the
second
reserved aggregate resources 117 may be further selected based on respective
estimates of
respective resources to be used to stream the videos 115, from the streaming
system 103,
in respective time periods.
[0096] Furtheimore, in general, the first reserved aggregate allocated
resources 117 are
selected for a first time period, and the second reserved aggregate allocated
resources 117
are selected for a second time period following the first time period. The
time periods may,
however, be any suitable length. For example, the controller 220 and/or the
computing
device 101 may determine that the used resources are not within the threshold
value of the
first reserved aggregate allocated resources (e.g. a "NO" decision at the
block 308) for
consecutives months such that the first reserved aggregate allocated resources
117 does not
change for such consecutive months. However, in a last of such consecutive
months, the
controller 220 and/or the computing device 101 may detennine that the used
resources are
within the threshold value of the first reserved aggregate allocated resources
117 (e.g. a
"YES" decision at the block 308) for consecutives months such that the second
reserved
aggregate allocated resources 117 is selected for a next month following the
consecutive
months. Put another way, the respective time periods associated with first and
second
reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 may be any suitable time periods.
f00971 In general, the total of the respective differences (e.g. multiplied by
an updated
estimate for streaming the videos 115) between the reserved allocated
resources and the
actual allocated resources for the videos 115 may added to the total actual
allocated
resources for the videos 115 (e.g. multiplied by the updated estimate for
streaming the
videos 115) and the second reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 may be
selected to
be greater than total actual allocated resources for the videos 115 (e.g.
multiplied by an
updated estimate for streaming the videos 115) but less than the total actual
allocated
resources for the videos 115 with the total respective differences added
thereto (e.g. both
multiplied by an updated estimate for streaming the videos 115).
100981 Hence, the respective differences may be used to cap selection of the
second
reserved aggregate allocated resources 117.
100991 For example, the total actual allocated resources for the videos 115
with the total
respective differences added thereto, may be determined to represent a demand
for the
26
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
videos 115 (e.g. by the video-playing devices 107), which is "too high" such
that the
streaming service 103 may not effectively stream the videos 115 and/or at
which (and/or
above which), the computing device 101 (and/or an entity operating the
computing device
101) may not be able to effectively manage streaming of the videos 115. In
particular, while
the video streaming engine 113 may be dynamically scaled to meet demand for
the videos
115, the streaming service 103 may penalize streaming of the videos 115 based
on the
demand, as described above, leading to lower quality streaming, higher costs
to the
computing device 101, and the like. The total actual allocated resources for
the videos 115
with the total respective differences added thereto may represent a demand
above which
quality of the streaming decreasing, and/or some associated cost, is
unacceptable for the
computing device 101. While the term "unacceptable" is understood to be a
relative term,
the total actual allocated resources for the videos 115 with the total
respective differences
added thereto is further understood to represent an unambiguous representation
of such
unacceptability, and the like.
[00100] In yet further examples, the total actual allocated resources for the
videos 115 with
the total respective differences added thereto may be adjusted to a capped
amount and/or
capped to capped allocated resources (e.g. which may be based on a
predetermined capping
factor, such as 10% less than the total actual allocated resources for the
videos 115 with
the total respective differences added thereto and/or any other suitable
value). Such a
capped amount (and/or capped allocated resources) may also represent an amount
above
which demand for the videos 115 may be determined to be unacceptable, with the
total
respective differences added thereto, and adjusted by the predetermined
capping factor, is
understood to represent an unambiguous representation of such unacceptability.
[00101] In yet further examples, the capped allocated resources may be set to
the total
actual allocated resources for the videos 115 with the total respective
differences added
thereto (e.g. the predetermined capping factor may be set to "0").
1001021 It is hence understood that the first reserved aggregate resources 117
is also less
than the capped amount.
1001031 Put another way, the method 300 may further comprise the controller
220 and/or
.. the computing device 101 determining capped allocated resources, and the
first reserved
aggregate resources 1] 7 and the second reserved aggregate resources 117 are
selected to
27
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
be less than the capped allocated resources, the capped allocated resources
determined from
the actual allocated resources and the respective differences between the
reserved allocated
resources and the actual allocated resources, adjusted by a predetermined
capping factor.
[00104] Regardless, when the second reserved aggregate resources 117 are
selected, the
videos 115 remain available for streaming from the streaming system 103, via
the video
streaming engine 113, and the streaming system 103 provides the videos 115 to
the video-
playing devices 107, as described above. Indeed, selection of the second
reserved aggregate
resources 117, in place of the second reserved aggregate resources 117, may
occur without
interruption of streaming of the videos 115.
.. [00105] Returning briefly to the block 308, in response to determining that
the used
resources are not within a threshold value of the first reserved aggregate
allocated resources
but are not greater than the first reserved aggregate allocated resources,
(e.g. a "NO"
decision at the block 308), at a block 310, the controller 220 and/or the
computing device
101 continues to monitor the used resources at the block 306. Alternatively,
and/or
periodically, the controller 220 and/or the computing device 101 may again
implement the
blocks 302, 304, etc. in the event a number of the videos 115 change and/or
changes occur
to the respective differences between reserved allocated resources and actual
allocated
resources for the videos 115, for example to again select a reserved aggregate
allocated
resources 117, from the plurality of discrete selectable allocated resources
117 at the block
.. 306.
[00106] In some examples, the used resources, for example determined at the
block 306,
may be less than the first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 and also
less than that
a given one of the of the plurality of discrete selectable allocated resources
117, that is also
less than the first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117. Put another
way, in some
examples, the resources used to stream the videos 115 may have been
overestimated during
selection of the first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117, such that
the used
resources are not only less than the first reserved aggregate allocated
resources 117, but are
also lower than another one of the plurality of discrete selectable allocated
resources 117
that is less than the first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117. In
these examples, the
.. method 300 may further comprise, the controller 220 and/or the computing
device 101: in
response to determining that the used resources are below a given one of the
plurality of
28
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
discrete selectable allocated resources 117, the given one of the plurality of
discrete
selectable allocated resources 117 below the first reserved aggregate
allocated resources
117: selecting the given one of the plurality of discrete selectable allocated
resources 117
for streaming the videos 115 to the video-playing devices 107. In other words,
a given one
of the plurality of discrete selectable allocated resources 117 is selected
that is greater than,
but closest to, the used resources and/or an estimate of the resources to be
used in a next
time period as deteimined from then used resources.
[00107] In yet further examples, one or more of the first reserved aggregate
allocated
resources 117 and the second reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 and
the used
resources may exceed the capped allocated resources described above. In these
examples,
as the capped allocated resources may represent an amount above which demand
for the
videos 115 may be determined to be unacceptable, the controller 220 and/or the
computing
device 101 may communicate with the client devices 105 to negotiate changes to
one or
more of the reserved allocated resources and the actual allocated resources,
for example to
negotiate streaming of lower quality versions of the videos 115 (e.g. to lower
actual
allocated resources), negotiate different lengths of the videos, negotiate an
updated cost for
streaming the videos 115 (e.g. based on increased demand), and the like. In
these examples,
the method 300 may further comprise, the controller 220 and/or the computing
device 101:
in response to determining that one or more of the first reserved aggregate
allocated
resources 117, the second reserved aggregate allocated resources 117 and the
used
resources exceeds capped allocated resources: communicating with the client
devices 105
to negotiate changes to one or more of the reserved allocated resources and
the actual
allocated resources. Once the negotiation of the changes occurs, the
controller 220 and/or
the computing device 101 may select one of the plurality of discrete
selectable allocated
resources 117 in accordance with the negotiated changes.
[00108] The method 300 is next described with respect to FIG. 4, FIG. 5, FIG.
6 FIG. 7
and FIG. 8, which depict the computing device 101 and/or the system 100 and/or
portions
of the system 100, with like components having like numbers. When the
computing device
101 and/or a portion of the system 100 is depicted in FIG. 4, FIG. 5, FIG. 6
FIG. 7 and
FIG. 8, it is understood that the remaining components of the system 100 are
also present.
Furthermore, while not always depicted, the example depicted in FIG. 4, FIG.
5, FIG. 6
29
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
FIG. 7 and FIG. 8 may be at least partially implemented by the resource
allocation engine
119.
[00109] Attention is next directed to FIG. 4, which depicts the computing
device 101
determining (e.g. at the block 302 of the method 300) respective differences
between
reserved allocated resources and actual allocated resources for eight videos
115 provided
to the streaming system 103 by the client devices 105. For simplicity and/or
clarity, such a
determination is represented graphically (e.g. with reserved allocated
resources represented
as arrows, and actual allocated resources and differences therebetween
represented as
boxes, with horizonal lengths thereof representing a size of allocated
resources and/or a
length and/or size of the videos 115, and the like), however the determination
may
generally be performed numerically.
f001101 While the eight videos 115 are not depicted, it is understood that:
four of the videos
115 have reserved allocated resources 415-1, corresponding to a first length
(e.g. of the
an-ow indicating the reserved allocated resources 415-1), and selected from a
plurality of
discrete reserved allocated resources as described above; and another four of
the videos
115 have reserved allocated resources 415-2, corresponding to a second length
(e.g. of the
arrow indicating the reserved allocated resources 415-2) greater than the
first length, and
selected from the plurality of discrete reserved allocated resources as
described above. For
example, the arrow representing the reserved allocated resources 415-2 is
longer than the
arrow representing the reserved allocated resources 415-1.
[00111] As mentioned above, the reserved allocated resources 415-1, 415-2
(e.g. reserved
allocated resources 415) are depicted as arrows with a horizontal length
thereof
representing a size and/or length of the respective videos 115. Hence, for
example, the
reserved allocated resources 415-1 may represent 10 seconds, and the like,
reserved for
four videos 115 (e.g. a reserved length), and the reserved allocated resources
415-2 may
represent 20 seconds, and the like, reserved for the other four videos 115.
However, as
described, the videos 115 may be less than the respective reserved allocated
resources 415
and/or less than the respective reserved lengths.
1001121 Under each of the reserved allocated resources 415 are four boxes that
correspond
to the eight example videos 115 (four for the respective reserved allocated
resources 415-
1 and another four for the respective reserved allocated resources 415-2). A
"white" portion
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
of each box under the reserved allocated resources 415 corresponds to
respective actual
allocated resources 416-1, 416-2, 416-3, 416-4, 416-5, 416-6, 416-7, 416-8
(e.g. actual
allocated resources 416) of the eight videos 115, with a total horizontal
length of each box
being the same length as respective reserved allocated resources 415, and a
respective
horizontal length of actual allocated resources 416 corresponding to the
actual size (e.g.
length) of the respective videos 115. Hence, a "shaded" portion of each box,
extending past
the actual allocated resources 416, corresponds to a respective difference 417-
1, 417-2,
417-3, 417-4, 417-5,417-6, 417-7, 417-8 (e.g. the differences 417 and/or a
difference 417)
between the reserved allocated resources 415 and the actual allocated
resources 416.
[00113] In particular, the actual allocated resources 416-1, 416-2, 416-3, 416-
4 and the
respective differences 417-1, 417-2, 417-3, 417-4 are for four videos 115,
which have a
reserved allocated resource 415-1 (e.g. of 10 seconds, and the like); and the
actual allocated
resources 416-5, 416-6, 416-7, 416-8 and the respective difference 417-5, 417-
6, 417-7,
417-8 are for four videos 115, which have a reserved allocated resource 415-2
(e.g. of 20
seconds, and the like).
1001141 Also depicted in FIG. 4, the computing device 101 determines total
reserved
allocated resources 425 (e.g. a sum of the total lengths of the actual
allocated resources 416
and the differences 417, and/or four times the length of the reserved
allocated resources
415-1 plus four times the length of the reserved allocated resources 415-2).
[00115] Similarly, the computing device 101 determines total actual allocated
resources
426 (e.g. a sum of the actual allocated resources 416) and total differences
427 (e.g. a sum
of the differences 417). As graphically depicted, the length of the total
actual allocated
resources 426 corresponds to a sum of the lengths of the actual allocated
resources 416,
and the length of the total differences 427 corresponds to a sum of the
lengths of the
differences 417.
[00116] Attention is next directed to FIG. 5, which depicts the computing
device 101
selecting (e.g. at the block 304 of the method 300) first reserved aggregate
allocated
resources 117-1, from a plurality of discrete selectable allocated resources
117, available
at the streaming system 103. As depicted, the plurality of discrete selectable
allocated
resources 117 comprises four discrete selectable allocated resources 117-0,
117-1, 117-2,
117-3, depicted graphically, with a respective length thereof indicating a
respective size
31
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
thereof. Numbering of the plurality of discrete selectable allocated resources
117 begins at
"0" to illustrate that while reserved aggregate allocated resources 117-1 may
be selected,
as described hereafter, one or more of the plurality of discrete selectable
allocated resources
117 may be less than the first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117-1.
100117] As depicted, the four discrete selectable allocated resources 117 are
depicted as
aligned at a left end to show the relative sized thereof at respective right
ends, and also
relative to the total actual allocated resources 426 with, and without the
total differences
427 added thereto (e.g. which are depicted laid out linearly with a left end
thereof aligned
with the left ends of the four discrete selectable allocated resources 117).
[00118] Furthermore, the total actual allocated resources 426 and the total
differences 427
have been multiplied by an estimated number of streams of the respective eight
videos 115
in a given time period. For example, the computing device 101 may initially
estimate only
two streams per month for the respective eight videos 115. While such an
estimate is
understood to be small compared to actual estimates of numbers of streams
(e.g. when the
.. system 100 is deployed in the field, the number of streams may be in the
hundreds to
thousands or higher), the estimate of two streams per month for the respective
eight videos
115 is merely provided as an example to easily illustrate implementation of
the method
300.
[00119] Hence, continuing with the example estimate of two streams per month,
the total
actual allocated resources 426 and the total differences 427 are graphically
depicted twice
(e.g. and shown end-to-end) such that the length of twice the total actual
allocated resources
426 represents an estimate of the resources to be used by the streaming system
103 to
stream the videos 115 in a given time period. The lengths of the four discrete
selectable
allocated resources 117, relative to twice the total actual allocated
resources 426, with twice
the total differences 427 added thereto, is emphasized via dotted lines
extending from the
discrete selectable allocated resources 117.
1001201 As depicted, twice the total actual allocated resources 426 is greater
than the
discrete selectable allocated resources 117-0, but less than the discrete
selectable allocated
resources 117-1. As such, the computing device 101 selects the first reserved
aggregate
allocated resources 117-1 (e.g. represented by "Selected" on the first
reserved aggregate
allocated resources 117-1).
32
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
1001211 Hence, the first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117-1 is
selected based on
the actual allocated resources 416 for the videos 115.
[00122] While the four discrete selectable allocated resources 117 are
depicted graphically
at the computing device 101, it is understood that values for the four
discrete selectable
.. allocated resources 117 may be retrieved from the streaming system 103 by
the computing
device and numerically compared to the actual allocated resources 416 (e.g.
multiplied by
an estimate of numbers of streams per month, and the like, to compare to the
total actual
allocated resources 426).
[00123] Regardless, as depicted in FIG. 6, the computing device 101 may
transmit a
communication 601 to the streaming system 103 indicating a selection of the
first reserved
aggregate allocated resources 117-1. Thereafter, as also depicted in FIG. 6,
the streaming
system 103 may stream the videos 115 to the video-playing devices 107.
Continuing with
the example of FIG. 4 and FIG. 5, in the example depicted in FIG. 6, it is
understood that
there may be eight (e.g. Q=8) videos 115 and four (e.g. R=4) discrete
selectable allocated
.. resources 117.
1001241 As also depicted in FIG. 6, the streaming system 103 transmits and/or
provides an
indication 603 of used resources to the computing device 101, as described
above. In
particular, as depicted, by receiving the indication 603, the computing device
101 monitors
(e.g. at the block 306 of the method 300) the used resources for streaming the
videos 115
.. to the video-playing devices 107. For example, the indication 603 of the
used resources
may represent a number of seconds of the streamed videos 115 in a given time
period, a
number of streamed bits and/or bytes, and the like.
100125] Attention is next directed to FIG. 7, which depicts the computing
device 101
comparing a value of the used resources 701 to the first reserved aggregate
allocated
resources 117-1 (e.g. a value of the used resources 701 determined via the
indication 603).
As in FIG. 4 and FIG. 5 the used resources 701 are depicted graphically,
relative to the first
reserved aggregate allocated resources 117-1, with their left ends aligned. A
threshold
value 703 is depicted as a shaded box extending rightwards from the left end
of the first
reserved aggregate allocated resources 117-1.
1001261 As also seen in FIG. 7, a length of the used resources 701 within the
region of the
threshold value 703 and hence, the computing device 101 determines (e.g. a
"YES"
33
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
decision at the block 308 of the method 300), that the used resources 701 are
within the
threshold value 703 of the first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117-1.
1001271 With respect to FIG. 8, as the computing device 101 that the used
resources 701
are within the threshold value 703 of the first reserved aggregate allocated
resources 117-
1, the computing device 101 selects (e.g. at the block 310 of the method 300)
second
reserved aggregate allocated resources 117-2, from the plurality of discrete
selectable
allocated resources 117, for streaming the videos 115 to the video-playing
devices 107.
1001281 As depicted, computing device 101 selects the second reserved
aggregate allocated
resources 117-2 based on the respective differences 417 and, in particular the
total
differences 427. For example, as in FIG. 4, the computing device 101 compares
the total
actual allocated resources 426 (e.g. again using an estimate of two streams
per month, but
which may be adjusted based on the used resources 701) with the plurality of
discrete
selectable allocated resources 117, but now taking into account the total
differences 427.
1001291 As depicted, the total differences 427, added to the total actual
allocated resources
426 are larger than the second discrete selectable allocated resources 117-2,
but less than
the third discrete selectable allocated resources 117-3. However, the third
discrete
selectable allocated resources 117-3 may represented allocated resources that
are too high
as they exceed the total differences 427, added to the total actual allocated
resources 426.
Hence, rather than select the third discrete selectable allocated resources
117-3, the
computing device 101 selects the second discrete selectable allocated
resources 117-2 as
the second reserved aggregate allocated resources 117-2 to be used for the
next time period.
1001301 Also depicted in FIG. 8 is a capped allocated resources 801, as
described above,
which is less than the second discrete selectable allocated resources 117-2
(but greater than
the first discrete selectable allocated resources 117-1); as such, the
computing device 101
may alternatively select the second discrete selectable allocated resources
117-2 as the
second reserved aggregate allocated resources 117-2 to be used for the next
time period on
the basis of the capped allocated resources 801.
1001311 Regardless, upon selection of the second reserved aggregate allocated
resources
117-2, the computing device 101 communicates with the streaming system 103,
similar to
.. as depicted in FIG. 6, to control streaming of the videos 115 according to
the second
reserved aggregate allocated resources 117-2. Such selection has a tangible
physical effect
34
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
in the system 100, as such a selection may generally prevent the streaming
system 103
from reducing resolution of the videos 115, increasing cost for streaming of
the videos 115
(e.g. other than any increased cost for selection of the second reserved
aggregate allocated
resources 117-2 vs. the first reserved aggregate allocated resources 117-1),
and the like.
1001321 Hence, in general, provided herein is a device, system and method for
allocating
resources for video streaming, which may be used to select reserved aggregate
allocated
resources for streaming to prevent reduction in quality of streaming of videos
by a
streaming system, and the like.
[001331 As should be apparent from the present specification, the
functionality of
computing devices described herein are sufficiently complex as to require
their
implementation on such computing devices and/or computing systems, and cannot,
as a
practical matter, be performed in the human mind. In particular, computing
devices
described herein are understood to include electronic components, which
provide speed,
accuracy and complexity management that are not obtainable by human mental
steps, in
addition to the inherently digital nature of such operations. For example, a
human mind
cannot interface directly with computer memory, digital storage, and the like.
Similarly, a
human mind cannot transmit and/or receive electronic messages, electronically
encoded
video, electronically encoded audio, etc., among other features and functions
set forth
herein.
f001341 In this specification, elements may be described as "configured to"
perform one
or more functions or "configured for" such functions. In general, an element
that is
configured to perform or configured for performing a function is enabled to
perform the
function, or is suitable for performing the function, or is adapted to perform
the function,
or is operable to perform the function, or is otherwise capable of performing
the function.
[00135] It is understood that for the purpose of this specification, language
of "at least one
of X, Y, and Z" and "one or more of X, Y and Z" can be construed as X only, Y
only, Z
only, or any combination of two or more items X, Y, and Z (e.g., XYZ, XY, YZ,
XZ, and
the like). Similar logic can be applied for two or more items in any
occurrence of "at least
one..." and "one or more..." language.
[00136] The tent's "about", "substantially", "essentially", "approximately",
and the like,
are defined as being "close to", for example as understood by persons of skill
in the art. In
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30
Docket No.: P9930CA00
some examples, the terms are understood to be "within 10%," in other examples,
"within
5%", in yet further examples, "within 1%", and in yet further examples "within
0.5%".
[00137] Persons skilled in the art will appreciate that in some examples, the
functionality
of devices and/or methods and/or processes described herein can be implemented
using
.. pre-programmed hardware or firmware elements (e.g., application specific
integrated
circuits (AS1Cs), electrically erasable programmable read-only memories
(EEPROMs),
etc.), or other related components. In other examples, the functionality of
the devices and/or
methods and/or processes described herein can be achieved using a computing
apparatus
that has access to a code memory (not shown), which stores computer-readable
program
code for operation of the computing apparatus. The computer-readable program
code could
be stored on a computer readable storage medium, which is fixed, tangible and
readable
directly by these components, (e.g., removable diskette, CD-ROM, ROM, fixed
disk, USB
drive). Furthermore, it is appreciated that the computer-readable program can
be stored as
a computer program product comprising a computer usable medium. Further, a
persistent
storage device can comprise the computer readable program code. It is yet
fiirther
appreciated that the computer-readable program code and/or computer usable
medium can
comprise a non-transitory computer-readable program code and/or non-transitory
computer usable medium. Alternatively, the computer-readable program code
could be
stored remotely but transmittable to these components via a modem or other
interface
device connected to a network (including, without limitation, the Internet)
over a
transmission medium. The transmission medium can be either a non-mobile medium
(e.g.,
optical and/or digital and/or analog communications lines) or a mobile medium
(e.g.,
microwave, infrared, free-space optical or other transmission schemes) or a
combination
thereof.
.. [00138] Persons skilled in the art will appreciate that there are yet more
alternative
examples and modifications possible, and that the above examples are only
illustrations of
one or more examples. The scope, therefore, is only to be limited by the
claims appended
hereto.
36
Date Recue/Date Received 2020-09-30