Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 1 -
TITLE
INFILL MATERIAL FOR SYNTHETIC TURFS AND SYNTHETIC
TURFS SO OBTAINED
DESCRIPTION
Field of the invention
The present invention relates to infill materials for
synthetic turfs and to synthetic turfs obtained by using
such infill materials.
The invention, furthermore, relates to a method for
making such synthetic turfs.
Description of the prior art
As known, a synthetic turf essentially consists of a
mat made of plastic material to which blades of synthetic
material, also called "bristles", are fixed in such a way
to form a synthetic turf. The blades made of synthetic
material are knitted to the mat by means of known processes
that allow to obtain a warp of blades, which are close to
each other according to the needs.
All around the blades made of synthetic material, an
infill material is distributed, also simply called
"infill". This is, usually, granular-shaped, and is
selected both according to the kind of sport to which the
synthetic turf is destined, for example soccer, hockey,
cricket, rugby, but also according to the weather
conditions that are more frequent where the synthetic turf
is installed.
CA 03099390 20-11-13,1
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 2 -
As well known, the infill material provides a draining
action by adjusting the drainage of rainwater or of
irrigation water, protects the mat assuring to the synthetic
turf a high duration, and especially gives to the turf
mechanical, physical and technological features typical of
the natural turf.
The most important features of an infill material are,
in particular, the elasticity of the ground for the user,
the rebound of the ball, the capacity of absorption of the
hits when falling down, tensile and torque resistance to
the force caused by the shoe, the resistance against the
compression, to the penetration of external bodies, as
well as the capacity of absorption and drainage of water
in case of meteorological and environmental events.
The drainage action of the synthetic turf is, usually,
carried out by a base portion, or "stabilizing infill",
essentially constituted of sand. Instead, the elasticity
of the synthetic turf is, usually, guaranteed by the
presence of granules of rubber that are concentrated in
the upper portion of the turf, or "performance infill". An
example of a similar infill material is disclosed in
US2002/081399.
However, the synthetic turfs of known type containing
rubber and sand have many drawbacks. Firstly, owing to the
compression caused by trampling, or by settling of the
drainage water percolation, eventually the layer of sand
tends to become compacted thus losing its drainage
properties. Therefore, in particular in case of abundant
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 3 -
rainfall, the synthetic turf is not able to drain away the
rain water and is subjected to flooding. This causes a
random and turbulent mixture of the infill material, in
particular at the upper layers of the same, that is,
therefore, shifted from the correct position within the
infill. In particular, the infill material, in the time,
provides zones where the material dragged by water
concentrates, and other zones, instead, completely, or
however impoverished of the same material. Therefore, the
synthetic turf loses its original structure and,
accordingly, the physical, mechanical and drainage
features that it had at the moment of laying.
Another drawback of the synthetic turfs of prior art
is strictly correlated with the presence of rubber. In
particular, the presence of rubber, both in the most
frequent case that it comes from waste materials, such as
ground spent tyres, but also in the case in which it is
rubber of first synthesis, mainly in the hotter seasons,
quickly accumulates heat and reaches temperatures above
55 C, with consequent troubles to the athletes if compared
to natural turf fields. For this reason, the synthetic
turf containing elastomeric materials must be periodically
irrigated in order to avoid as much as possible the above
mentioned overheating of the synthetic turf with
consequent consumption of time and waste of water.
Furthermore, the above disclosed irrigation and drainage
cycles of the infill tends, with the passing of time, to
compact the sand layer that, therefore, as above
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 4 -
explained, performs an even less effective drainage
action.
In addition to the above, the rubber, with the passing
of time, tends to crumble and, therefore, the resulting
fragments clog the empty spaces of the sand layer, thus,
highlighting the above mentioned drawback of reducing the
effectiveness of drainage at the stabilizing infill.
Summary of the invention
It is therefore an object of the present invention to
provide an infill material for synthetic turfs, which is
highly performance and that is able to solve the above
mentioned drawbacks of the infill materials of prior art.
It is, in particular, object of the present invention
to provide an infill material for synthetic turfs that is
able to maintain in the time the structure that it had at
the moment of laying.
It is, furthermore, an object of the present invention
to provide an infill material for synthetic turfs that is
able to perform an effective drainage of water.
These and other objects are achieved by an infill
material for synthetic turfs, according to the invention,
comprising:
- a stabilizing infill comprising a predetermined
quantity per unit surface area of vegetable material
of rachis of cereal ear not coated by a layer, or
film, of coating material, said predetermined quantity
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 5 -
per unit surface area being set between 2 kg/m2 and 15
kg/m2;
- a performance infill positioned above said
stabilizing infill and constituted of polymeric
material with elastomeric properties in granular form
in a predetermined quantity per unit surface area.
As discussed in detail in the following, the presence
of rachis of cereal ear in the stabilizing infill allows
to avoid the above mentioned drawbacks of synthetic turfs
of prior art. The material constituted of rachis of cereal
ear, preferably corn-cob of maize, has, in particular, the
property of absorbing high quantity of water "swelling",
and then of releasing, in the drier and hotter seasons,
the absorbed moisture in the surrounding environment.
Consequently, the rachis of cereal ear acts as a "lung"
for the synthetic turf, which incorporates it, because, as
anticipated above, it absorbs the water, or the moisture,
in excess, increasing its volume, and then gradually
reducing it by releasing the moisture, when the climatic
conditions return drier and the ambient temperature
increases. The rachis of cereal ear provides, in fact, a
high porosity and is subjected to alternating cycles of
expansion, and of compression, or in any case of reduction
of volume. Therefore, the whole infill material, and in
particular the performance infill, is subjected to a
decompacting action that allows to keep the infill
material tilled, and preserving substantially intact in
the time the physical properties of the infill. In
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 6 -
addition to the above, the material constituted of rachis
of cereal ear, in particular corn-cob, is able to absorb a
high quantity of moisture, for example during rain and
irrigation interventions, and, then, to release the above
mentioned moisture in the hotter seasons, thus obtaining a
thermal balance of the turf. In particular, corn-cob has a
water absorption capacity that is about 138%. Such
properties avoid excessive heating of the performance
infill, in particular of the above mentioned plastic
W material having elastomeric properties, during the hotter
seasons.
Other features of the invention are defined in the
dependent claims.
Advantageously, the stabilizing infill, furthermore,
comprises a predetermined quantity per unit surface area
of sand.
In particular, the stabilizing infill can provide a
mixture of a predetermined percentage by volume of said
vegetable material of rachis of cereal ear and a
predetermined percentage by volume of sand.
More in particular, the mixture of vegetable material
of rachis of cereal ear and sand has the following
composition:
- between 25% and 90% by volume of the above
mentioned material of rachis of cereal ear;
- between 10% and 75% by volume of sand.
In particular, the infill material can comprise a
predetermined quantity per unit surface area of the above
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 7 -
mentioned mixture, said predetermined quantity per unit
surface area being set between 2.5 kg /m2 and 15 kg/m2.
Preferably, the vegetable material constituted of
rachis of cereal ear is corn-cob, i.e. rachis of maize.
This solution is particularly advantageous because corn-
cob, i.e. the rachis of maize, has a size that is normally
higher than the size of the rachis of other cereals and
has, therefore, better physical properties, in particular
in terms of capacity of expanding and reducing in size,
with respect to the other cereals.
In an embodiment of the invention, the stabilizing
infill of the infill material can comprise:
- a first layer of sand;
- a second layer positioned on said first layer of
sand and constituted of the above mentioned vegetable
material of rachis of cereal ear.
In particular, the first layer can be constituted of a
predetermined quantity per unit surface area of sand, said
predetermined quantity being set between 10 kg/m2 and 25
kg/m2.
More in particular, the second layer can be
constituted of a predetermined quantity per unit surface
area of the above mentioned vegetable material of rachis
of cereal ear, said predetermined quantity per unit
surface area being set between 2 kg /m2 and 5 kg/m2.
Advantageously, the above mentioned plastic material
having elastomeric properties in granular form of the
performance infill is selected from the group consisting
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 8 -
of: styrene-butadiene rubber, or "SBR", a thermoplastic
material, an ethylene-propylene-diene monomer, or rubber
"EPDM", polyvinyl chloride, or "PVC", a synthetic organic
material, or a combination thereof.
In particular, the above mentioned synthetic organic
material is a mixture of a plastic material with
elastomeric properties, and an organic material of
vegetable origin, preferably selected from the group
comprised of coconut and cellulose.
Advantageously, the vegetable material constituted of
rachis of cereal ear, in particular corn-cob, has a
granulometry set between 0.3 mm and 5.0 mm.
In particular, with the term "sand" it is to be
understood a material having a mineralogical composition,
for example siliceous sand, sand of pumice, sand of
lapillus, zeolite, vermiculite, etc.
In another alternative embodiment of the invention,
the performance infill can be constituted of only
vegetable material of rachis of cereal ear in a
predetermined quantity per unit surface area set between 2
kg/m2 and 8 kg/m2.
Advantageously, the predetermined quantity per unit
surface area of polymeric material with elastomeric
properties in granular form, of the infill material, is
set between 8 kg /m2 and 18 kg/m2.
According to another aspect of the invention, a
synthetic turf comprises:
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 9 -
- a mat having a first face and a second face
opposite to the first face;
- a plurality of blades made of synthetic material
fixed to said mat, said plurality of blades made of
synthetic material protruding from said second face in
such a way to form a synthetic turf;
- an infill material, as above described, distributed
on said second face of said mat.
According to a further aspect of the invention, a
method for making a synthetic turf comprises the steps of:
- disposing a mat to which a plurality of blades made
of synthetic material is fixed, said mat providing a
first face and a second face opposite to the first
face, said plurality of blades made of synthetic
material protruding from said second face;
- distributing on said second face of said mat an
infill material, thus obtaining a synthetic turf, said
infill material comprising:
- a stabilizing infill comprising a predetermined
quantity per unit surface area of vegetable
material of rachis of cereal ear not coated with a
film, or layer, of coating material, said
predetermined quantity per unit surface area being
set between 2 kg /m2 and 15 kg/m2;
- a performance infill positioned above the above
mentioned stabilizing infill and constituted of
polymeric material with elastomeric properties in
a predetermined quantity per unit surface area.
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 10 -
In an alternative embodiment, the blades made of
synthetic material can comprise smooth blades, or wavy
blades, or smooth blades alternating to wavy blades.
In particular, the mat can provide a plurality of
holes arranged to put in communication said first face and
said second face, in such a way to allow the water to flow
under the mat.
According to another aspect of the invention, a
stabilizing infill for infill materials for synthetic
turfs comprises:
- between 10% and 75% by volume of sand;
- between 25% and 90% by volume of vegetable material
of rachis of cereal ear.
Brief description of the drawings
The invention will now be shown with the following
description of its exemplary embodiments, exemplifying but
not limitative, with reference to the attached drawings in
which:
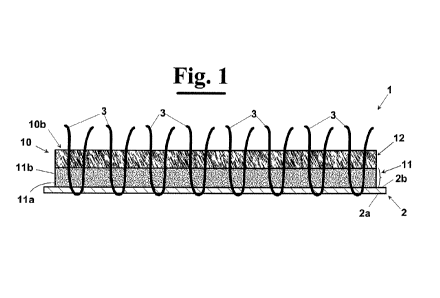
- Fig. 1 diagrammatically shows a cross sectional view
of a possible exemplary embodiment of a synthetic turf
obtained by using the infill material, according to the
invention;
- Fig. 2 diagrammatically shows a cross sectional
view of an alternative embodiment of synthetic turf of
figure 1;
- Fig. 3 diagrammatically shows a cross sectional view
of a possible alternative embodiment of synthetic turf
of figure 1;
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 11 -
- Fig. 4 diagrammatically shows a front elevational
perspective view provided with a portion removed of a
possible embodiment of a sack containing a mixture,
according to the invention, that can be used for making
the stabilizing infill;
- Fig. 5 diagrammatically shows an enlargement of the
mixture contained within the sack of figure 4 in order
to highlight some characteristics.
Detailed description of some exemplary embodiments of
the invention
With reference to figure 1, a synthetic turf 1,
according to the invention, comprises a mat 2, which
provides a face 2a, which, in use, is arranged adjacent to
the surface to be coated, and a face 2b opposite to face
2a. The synthetic turf 1 comprises, furthermore, a
plurality of blades, or bristles, 3 made of synthetic
material that are fixed to mat 2, for example by means of
gluing, or stitching. Above the face 2b of mat 2 is,
furthermore, present an infill material 10 arranged all
around the blades 3 made of synthetic material.
The infill material 10 provides a lower portion, or
stabilizing infill 11, and an upper portion, or
performance infill 12 positioned above the stabilizing
infill 11. In all the embodiments shown in the figures,
and disclosed in detail in the following, the performance
infill 12 is essentially constituted of a plastic material
having elastomeric properties, preferably selected between
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 12 -
styrene-butadiene rubber, or "SBR", a thermoplastic
material, an ethylene-propylene-diene monomer, or "EPDM"
rubber, polyvinyl chloride, or "PVC", a synthetic organic
material, or a combination thereof.
In particular, the above mentioned synthetic organic
material can be a mixture of a plastic material having
elastomeric properties, and of an organic material of
vegetable origin, preferably selected between coconut and
cellulose, or a combination thereof. The above mentioned
mixture is appropriately extruded in order to obtain
granules of the above mentioned synthetic organic
material.
More in particular, the above mentioned plastic
material having elastomeric properties in granular form
can be of black colour, or of a different colour, or can
provide a mixture of two, or more colours.
According to the present invention, the stabilizing
infill 11, comprises a vegetable material of rachis of
cereal ear not coated of a film, or layer, of coating
material, in a predetermined quantity per unit surface
area. In particular, the above mentioned predetermined
quantity per unit surface area of the above mentioned
vegetable material of rachis of cereal ear is set between
2 kg /m2 and 15 kg/m2, in function of the height of the
synthetic grass. In a possible embodiment the cereal can
be maize and, therefore, the rachis of cereal ear is
"corn-cob".
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 13 -
In particular, the vegetable material of rachis of
cereal ear is not coated with a film of coating material
in order to be able to absorb and to release moisture and,
therefore, to alternate the above mentioned cycles of
increasing and of reduction of volume that, as above
disclosed, are fundamental in order to avoid an excessive
heating of the material of which the performance infill is
constituted.
In the embodiment of figure 1, the stabilizing infill
W 11 provides a single layer constituted only of vegetable
material of rachis of cereal ear. In this case, a
distribution step is advantageously provides of a
predetermined quantity per unit surface area of the
stabilizing infill set between 2 kg /m2 and 8 kg/m2 on the
above mentioned mat 2. In this way, thanks to its above
mentioned properties, in particular the capacity of
increase its volume in presence of water and of decreasing
its volume with drier climatic conditions, the material of
rachis of cereal ear carries out an auto-decompacting
action that allows to keep the stabilizing infill tilled,
and of preserving substantially intact in the time, the
physical features, in particular the drainage capacity.
In the embodiment of the invention of figure 2, the
stabilizing infill 11 provides, instead, a lower layer ha
.. of sand, above of which is positioned a layer llb of the
above mentioned material of rachis of cereal ear,
preferably corn-cob. As can be easily understood, the
above mentioned predetermined quantity per unit surface
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 14 -
area of sand of the stabilizing infill will be mainly
concentrated, in this case, in the first layer, i.e. in
the lower layer 11a, whilst the above mentioned
predetermined quantity per unit surface area of vegetable
material constituted of rachis of cereal ear will be
mainly concentrated in the second layer, i.e. the upper
layer 11b. In this case, the material of rachis of cereal
ear prevents the sand layer 11a and, therefore, the whole
stabilizing infill 11 and, therefore, the synthetic turf,
from being compacted.
More precisely, the first layer 11a is constituted of
a predetermined quantity per unit surface area of sand set
between 10 kg /m2 and 25 kg/m2. The second layer is,
instead, constituted of a predetermined quantity per unit
surface area of the above mentioned vegetable material of
rachis of cereal ear set between 2 kg /m2 and 5 kg/m2.
In the alternative embodiment of figure 3, instead,
the infill material 10 provides for the stabilizing infill
11 a single layer constituted, in this case, of a mixture
of sand and the above mentioned material of vegetable
constituted of rachis of cereal ear. In particular, the
above mentioned mixture of vegetable material of rachis of
cereal ear and sand is constituted for a percentage by
volume set between 25% and 90% of material of rachis of
cereal ear, and for a percentage by volume set between 10%
and 75% of sand.
More in detail, the predetermined quantity per unit
surface area of the mixture of vegetable material of
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 15 -
rachis of cereal ear and sand is set between 2.5 kg/m2 and
15 kg/m2.
The combined use of sand and vegetable material of
rachis of cereal ear allows to obtain a highly draining
synthetic turf and, thanks to the properties of the
vegetable material of rachis of cereal ear, to avoid that
the sand, which is present in the stabilizing infill, can
be compacted and, therefore, that the synthetic turf
following to the irrigation, or to the rain, can flood. In
other words, the presence of vegetable material of rachis
of cereal ear guarantees that, in the time, the
effectiveness of the drainage action of the sand layer is
maintained.
With reference to figures 1 to 3, at the end of the
distribution of infill material, the blades, or bristles,
3 of synthetic material provide an upper portion
protruding of a determined height from the upper surface
10b of the infill material, for example protruding of
about 2-10 cm.
Furthermore, as shown in detail in figure 3, the mat,
or support, 2 can provide drainage holes 4, having sizes
such that they allow the outflow of the percolated water
obtained by the drainage action of the stabilizing infill
11. In figure 4 a sack 100 is shown, by way of example,
containing a predetermined quantity of a mixture 20 of
sand and vegetable material of rachis of cereal ear in the
above disclosed percentage by volumes. As shown in detail
in figure 5, the mixture 20 is substantially "homogeneous"
CA 03099390 2020-11-04
WO 2019/215768
PCT/IT2018/000067
- 16 -
in the sense that the granules of the two components, that
is to say of sand and of vegetable material of rachis of
cereal ear, are dispersed one in the other such that it is
not easily visible to the naked eye. The mixture 20 can be
used, in particular, for obtaining the embodiment of
infill material 10 of the synthetic turf of figure 3.
The foregoing description exemplary embodiments of
the invention will so fully reveal the invention
according to the conceptual point of view, so that
others, by applying current knowledge, will be able to
modify and/or adapt for various applications such
embodiment without further research and without parting
from the invention, and, accordingly, it is therefore to
be understood that such adaptations and modifications
will have to be considered as equivalent to the specific
embodiments. The means and the materials to realize the
different functions described herein could have a
different nature without, for this reason, departing
from the field of the invention. It is to be understood
that the phraseology or terminology that is employed
herein is for the purpose of description and not of
limitation.