Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
1
TITLE
CHASSIS ANCHORING SYSTEMS
CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
[0001] This application is a continuation-in-part application of U.S.
Nonprovisional Patent Application No. 16/168,957, filed October 24, 2018, and
U.S. Nonprovisional Patent Application No. 16/168,978, filed October 24, 2018,
each of which claims the benefit of U.S. Provisional Application No.
62/577,423,
filed October 26, 2017, U.S. Provisional Application No. 62/577,965, filed
October 27, 2017, U.S. Provisional Application No. 62/616,601, filed January
12,
2018 and U.S. Provisional Application No. 62/735,966, filed September 25,
2018; and this application claims the benefit of U.S. Provisional Application
No.
62/735,966, filed September 25, 2018 and the benefit of U.S. Provisional
Application No. 62/736,021, filed September 25, 2018.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the Invention
[0002] This invention relates to vehicle structural design.
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
2
Description of the Related Art
[0003] A variety of structural arrangements are currently utilized in
automotive
vehicles for fixing in position the power, suspension and payload-bearing
components relative to each other. Such structural arrangements, in some
contexts referred to as the vehicle's chassis, range from a ladder chassis
design,
in which components are by and large secured to robust metallic beams running
longitudinally and transversely underneath the vehicle, to a monocoque design,
where there is not any structure specifically tasked to secure load
components,
but instead the vehicle's skin performs that function.
[0004] A structural arrangement arguably intermediate between the ladder
chassis and the monocoque design is in the form of a tubular exoskeleton,
sometimes referred to as a space frame. The exoskeleton/space frame employs a
number of tubular members fastened to each other and arranged to form a three
dimensional skeleton-like structure that distributes compressive, bending and
torsional loads somewhat in the manner of a monocoque design, yet provides
multiple discrete regions for securing load components, in the manner of a
ladder
frame (although to a greater extent). The exoskeleton/space frame is often
employed for limited production vehicles, due to it high performance and
relative
ease of manufacture.
[0005] Vehicle components are generally attached to the tubular members of an
exoskeleton/space frame using chassis tabs. Chassis tabs generally are
metallic
pieces, cut from plate stock, sometimes bent to shape and/or drilled to accept
a
bolt, and then welded to the tubular members at discrete locations. However,
chassis tabs are labor-intensive to install, being subject to movement or
creep
during installation. Further, chassis tabs create localized areas of stress
and are
known to break, and are unsightly and potentially hazardous if left on the
tubular
member in the event a component is relocated to another position.
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
3
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0006] The present inventions provide chassis anchoring systems that are easy
to
install and strong, and which permit removal and relocation of vehicle
components without leaving behind vestigial protrusions as in the case of
chassis
tabs. The subject inventions are not subject to movement or creep during
installation, and do not induce localized stress areas in the manner of
chassis tabs.
In contrast therewith, the subject inventions can increase the strength in the
anchoring region, and, when used to secure vehicle components to tubular
structural members, distribute the force transferred to both sides of the
member.
Among other applications, the inventions described herein have utility in
securing
active components to a vehicle's chassis, such as shock absorbers, suspension
and
brake arms and linkages, door and compartment hinges and the like.
[0007] In one aspect, the present invention is directed to an anchor assembly
for
attachment to a tubular member having an exterior surface, where the assembly
comprises an anchor base and first and second opposed spaced-apart anchor
cheek members extending from the anchor base, and where the anchor cheek
members are adapted to secure a load-bearing vehicle component. The anchor
base comprises a load-bearing exterior skirt and a load-bearing interior skirt
circumscribed by the exterior skirt, where the exterior and interior skirts
are
dimensioned to be in contact with the exterior surface of the tubular member
when positioned against it; the exterior skirt has a first pair of spaced-
apart
opposed cut-outs, with each of the first pair of cut-outs having a shape that
generally conforms to a shape of the exterior surface of the tubular member;
and
the interior skirt has a second pair of spaced-apart opposed cut-outs, with
each of
the second pair of cut-outs having a shape that generally conforms to the
shape of
the exterior surface of the tubular member. The assembly further comprises a
boss having a first flanged end and a second end, where the boss is adapted to
be
positioned in first and second apertures in the exterior surface of the
tubular
member with the flanged end in contact with the first aperture and the second
end
accessible through the second aperture; and a fastener connected to the anchor
base and the second end to secure the anchor base to the boss.
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
4
[0008] In another aspect, the invention is directed to a two-position anchor
assembly for attachment to a tubular member having an exterior surface, where
the assembly comprises an anchor base and first and second opposed spaced-
apart anchor cheek members extending from the anchor base, and where the
anchor cheek members are adapted to secure a vehicle component. The anchor
base comprises a load-bearing exterior skirt and a load-bearing interior skirt
circumscribed by the exterior skirt, where the exterior and interior skirts
are
dimensioned to be in contact with the exterior surface of the tubular member
when positioned against it; the exterior skirt has first and second pairs of
spaced-
apart opposed cut-outs, with the first pair being approximately perpendicular
to
the second pair, and with each of the cut-outs of the first and second pairs
of cut-
outs having a shape that generally conforms to a shape of the exterior surface
of
the tubular member; and the interior skirt has third and fourth pairs of
spaced-
apart opposed cut-outs, with the third pair being approximately perpendicular
to
the fourth pair, and with each of the cut-outs of the third and fourth pairs
of cut-
outs having a shape that generally conforms to the shape of the exterior
surface of
the tubular member. The assembly further comprises a boss having a first
flanged end and a second end, where the boss is adapted to be positioned in
first
and second apertures in the exterior surface of the tubular member with the
flanged end in contact with the first aperture and the second end accessible
through the second aperture; and a fastener connected to the anchor base and
the
second end to secure the anchor base to the boss.
[0009] In yet another aspect, the invention is directed to a bearing anchor
assembly for attachment to a tubular member having an exterior surface,
comprising an anchor base and first and second opposed spaced-apart anchor
cheek plates extending from the anchor base, where the first and second anchor
cheek plates each includes portions that define an annular aperture and where
the
assembly additionally comprises a cylindrical shroud joining the portions of
the
first and second anchor cheek plates which define the first and second
apertures
to thereby define a recess, with the recess adapted to receive a bearing
assembly.
The assembly additionally incudes a boss having a first flanged end and a
second
end, where the boss is adapted to be positioned in first and second apertures
in
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
the exterior surface of the tubular member with the flanged end in contact
with
the first aperture and the second end accessible through the second aperture;
and
at least one fastener connected to the anchor base and the second end to
secure
the anchor base to the boss.
[0010] In a further aspect, the invention is directed to a load anchor
assembly for
attachment to a tubular member having an exterior surface, comprising an
anchor
base and first and second opposed spaced-apart anchor cheek plates extending
from the anchor base, where the anchor cheek plates are adapted to secure a
vehicle component; a boss having a first flanged end and a second end, the
boss
adapted to be positioned in first and second apertures in the exterior surface
of
the tubular member with the flanged end in contact with the first aperture and
the
second end accessible through the second aperture; and at least one fastener
connected to the anchor base and the second end to secure the anchor base to
the
boss.
[0011] In a still further aspect, the invention is directed to an anchor
assembly
for attachment to a tubular member having an exterior surface, the anchor
assembly comprising an anchor yoke having two opposed fastening mounts, each
defining an annular aperture, an accessory support strut joined to the anchor
yoke, an accessory mounting surface distal from the anchor yoke and joined to
the accessory support strut, a boss having a first flanged end and a second
end,
the boss adapted to be positioned in first and second apertures in the
exterior
surface of the tubular member with the flanged end in contact with the first
aperture and the second end accessible through the second aperture, and a
fastener passing through each of the annular apertures of the two opposed
fastening mounts and the boss to secure the anchor yoke to the boss.
[0012] These and other aspects of the present invention are described in the
drawings annexed hereto, and in the description of the preferred embodiments
and claims set forth below.
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
6
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
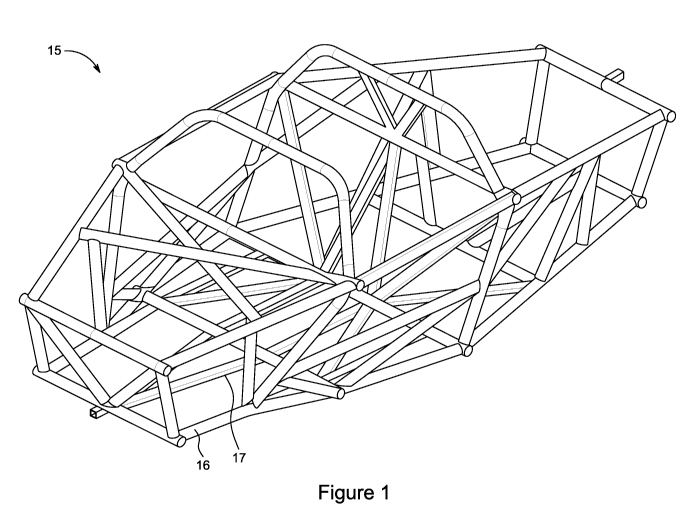
[0013] Figure 1 depicts an exoskeleton/space frame chassis in respect of which
the present invention can be employed.
[0014] Figure 2A is a forward perspective view of a two position general
purpose anchor in accordance with the present invention.
[0015] Figure 2B is a top view of a two position general purpose anchor in
accordance with the present invention.
[0016] Figure 2C is a rearward perspective view of a two position general
purpose anchor in accordance with the present invention.
[0017] Figure 2D is a side view of a two position general purpose anchor in
accordance with the present invention.
[0018] Figure 2E is a front view of a two position general purpose anchor in
accordance with the present invention.
[0019] Figure 2F is a perspective sectional view of a two position general
purpose anchor in accordance with the present invention.
[0020] Figure 2G is a perspective view of a one position general purpose
anchor
in accordance with the present invention.
[0021] Figure 2H is a front sectional view of a one position general purpose
anchor in accordance with the present invention
[0022] Figure 3A is a perspective view of a bearing anchor in accordance with
the present invention.
[0023] Figure 3B is a front view of a bearing anchor in accordance with the
present invention.
[0024] Figure 3C is a side view of a bearing anchor in accordance with the
present invention.
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
7
[0025] Figure 3D is a front sectional view of a bearing anchor in accordance
with the present invention.
[0026] Figure 4A is a perspective view of a tangential load anchor in
accordance
with the present invention.
[0027] Figure 4B is a perspective sectional view of a tangential load anchor
in
accordance with the present invention.
[0028] Figure 4C is a front view of a tangential load anchor in accordance
with
the present invention.
[0029] Figure 4D is a side view of a tangential load anchor in accordance with
the present invention.
[0030] Figures 5A and 5B are perspective and front views of a boss in
accordance with the present invention.
[0031] Figure 6 shows a portion of a tubular member and the elements utilized
to
mount a general purpose anchor of the present invention to the tubular member.
[0032] Figure 7A is a perspective front view of an accessory anchor, including
a
boss and fastener assembly, and accessory mounting bolts.
[0033] Figure 7B is a side sectional view of an accessory anchor, when
sectioned into two equal halves in the manner shown in Figure 7D.
[0034] Figure 7C is a perspective sectional view of an accessory anchor,
including a boss and fastener assembly, accessory mounting bolts, and
sectioned
through an accessory mounting aperture.
[0035] Figure 7D is a perspective sectional view of an accessory anchor,
including a boss and fastener assembly, and an accessory mounting bolt.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
8
[0036] Figure 1 depicts the exoskeleton/space frame chassis 15 of a type in
which the chassis anchoring system described herein can be used. Chassis 15 is
characterized by a number of tubular members fastened to each other and
arranged to form a three dimensional skeleton-like structure. The tubular
members of chassis 15 are of two types: circular in cross section, as
exemplified
by tubular member 16, and rectangular, as exemplified by tubular member 17.
The present invention can be utilized with tubular members of either cross
section, or for that matter, any elongate or other vehicle component
sufficiently
robust to bear the loads transferred to it by the anchoring system described
herein.
[0037] The chassis anchoring system of the present invention includes a number
of discrete components that enable the transfer of loads from vehicle
components
to a vehicle chassis, such as the chassis depicted in Figure 1, at various
locations
on the chassis. There is particularly described below general purpose anchors
230 and 260, bearing anchor 250 and tangential load anchor 270. These anchors
are utilizable in connection with a wide variety of vehicle components, such
as to
secure suspension elements to an exoskeleton/space frame, as disclosed in U.S.
Provisional Patent Application No. 62/736,201, filed September 25, 2018,
entitled "Vehicle Suspension" and having the same inventors as the subject
application; the contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference into
the
present disclosure as if fully set forth herein, particularly including the
disclosure
relating to suspension components using anchoring systems to be secured to an
exoskeleton/space frame, as well as the associated anchoring systems. In
addition, the contents of U.S. Nonprovisional Patent Application No.
[attorney docket no. 128245.100321 entitled "Vehicle Suspension," having the
same inventors as the subject application and filed on the same date as the
subject
application, are hereby incorporated by reference as if fully set forth
herein,
particularly including the disclosure relating to suspension components using
anchoring systems to be secured to an exoskeleton/space frame, as well as the
associated anchoring systems, found for example at paragraphs 40-41, 43-56, 57
(sentences 1-3), 58-82 and 100-101, and in Figures 1A-13B. There is also
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
9
described below accessory anchor 360, which provides a further option for
securing vehicle components and accessories to a vehicle chassis.
General Purpose Anchor (Two Position) (230)
[0038] General purpose anchor 230, a forward perspective view of which is
shown in Figure 2A, includes a base 231 from which extends two spaced-apart
opposed cheek members 232 whose ends distal from base 231 are provided with
circular mounts 233. Mounts 233 are each provided with annular apertures 234,
which have a centerline 240, and through which a rod end joint or other
vehicle
component can be secured with a threaded bolt. An integral locking nut 235
(Figure 2B) is optionally provided on the exterior face of one of the mounts
233
to facilitate securing the threaded bolt to anchor 230.
[0039] Referring to Figure 2F, the base 231 of anchor 230 is provided with a
mounting aperture 236 through which a removable fastener 295 can be placed to
secure general purpose anchor 230 to for example a tubular member of an
exoskeleton/space frame chassis, preferably utilizing the Securing Elements
described further below. There is further provided an annular recess 237 in
base
231 to receive a head of fastener 295.
[0040] The shape of the portion or portions of base 231 contacting the tubular
member or other vehicle component against which anchor 230 is positioned (the
"contact elements") can be planar or curved. If the portion of the tubular
member
or other vehicle component to be in contact with base 231 is planar, then the
contact elements can be planar. If the portion of the tubular member or other
vehicle component to be in contact with base 231 is curved, then the contact
elements can be correspondingly curved.
[0041] In one embodiment of the present invention adapted for use with a
tubular member that is circular in cross section, base 231 has a load-bearing
exterior skirt 238 as shown in Figures 2C and 2F, which is to be placed in
contact
with a chassis tubular member. Exterior skirt 238 terminates with two pairs of
concavely shaped spaced-apart opposed arcuate cut-outs 241 and 242, each pair
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
perpendicular to the other and having a curvature that generally conforms to
the
outside diameter of the tubular member to which anchor 230 is secured. Base
231 also includes a load-bearing interior skirt 243, circumscribed by exterior
skirt
238, which terminates with two pairs of concavely shaped spaced-apart opposed
arcuate cut-outs 244 and 245, each pair perpendicular to the other and having
a
curvature that generally conforms to the outside diameter of the tubular
member
to which anchor 230 is secured. Skirts 238 and 243 preferably are dimensioned
to be in flush contact with the exterior surface of a tubular member when
anchor
230 is positioned against the tubular member. Exterior skirt 238 and interior
skirt
243 each has a thickness and construction to be able to bear compressive loads
which are primarily imposed upon it by fastener 295 and from other vehicle
components through mounts 233 and cheek members 232.
[0042] The provision of two pairs of cut-outs 241 and 242 on exterior skirt
238
and two pairs of cut-outs 244 and 245 on interior skirt 243 facilitates
positioning
anchor 230 in two different orientations: a first orientation where centerline
240
is generally parallel to the axis of the tubular member on which it is
mounted, and
a second orientation where centerline 240 is rotated approximately 90 from
the
first orientation to be generally perpendicular to the axis of the tubular
member
on which it is mounted. This permits orienting the mounts 233 and their
apertures 234 in accordance with the alignment of the fastening points of the
vehicle component at issue.
[0043] General purpose anchor 230 is useful for securing a wide variety of
components to a vehicle chassis, such as suspension components.
General Purpose Anchor (One Position) (260)
[0044] General purpose anchor 260, a forward perspective view of which is
shown in Figure 2G, is similar to general purpose anchor 230, except that
anchor
260 is designed to be used in one orientation only.
[0045] As shown in Figures 2G and 2H, general purpose anchor 260 includes a
base 261 from which extends two spaced-apart opposed cheek members 262
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
11
whose ends distal from base 261 are provided with circular mounts 263. Mounts
263 are each provided with annular apertures 264, which have a centerline 239,
and through which a rod end joint or other vehicle component can be secured
with a threaded bolt. An integral locking nut 265 is optionally provided on
the
exterior face of one of the mounts 263 to facilitate securing the threaded
bolt to
anchor 260.
[0046] Referring to Figure 2G and 2H, the base 261 of anchor 260 is provided
with a mounting aperture 266 through which a removable fastener 295 can be
placed to secure general purpose anchor 260 to for example a tubular member of
an exoskeleton/space frame chassis, preferably utilizing the Securing Elements
described further below. There is further provided an annular recess 267 in
base
261 to receive a head of fastener 295.
[0047] The shape of the contact elements of base 261 can be planar or curved.
If
the portion of the tubular member or other vehicle component to be in contact
with base 261 is planar, then the contact elements can be planar. If the
portion of
the tubular member or other vehicle component to be in contact with base 261
is
curved, then the contact elements can be correspondingly curved.
[0048] In one embodiment of the present invention adapted for use with a
tubular member that is circular in cross section, base 261 has a load-bearing
exterior skirt 268 as shown in Figure 2H, which is to be placed in contact
with a
chassis tubular member. Exterior skirt 268 terminates with one pair of
concavely
shaped spaced-apart opposed arcuate cut-outs 246 and 247, each having a
curvature that generally conforms to the outside diameter of the tubular
member
to which anchor 260 is secured. Base 261 also includes a load-bearing interior
skirt 269, circumscribed by exterior skirt 268, which terminates with one pair
of
concavely shaped spaced-apart opposed arcuate cut-outs 248 and 249, each
having a curvature that generally conforms to the outside diameter of the
tubular
member to which anchor 260 is secured. Skirts 268 and 269 preferably are
dimensioned to be in flush contact with the exterior surface of a tubular
member
when anchor 260 is positioned against the tubular member. Exterior skill 268
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
12
and interior skirt 269 each has a thickness and construction to be able to
bear
compressive loads which are primarily imposed upon it by fastener 295 and from
other vehicle components through mounts 263 and cheek members 262.
[0049] As illustrated, the distance between centerline 239 and the contact
elements of base 261 (of anchor 260) are greater than between centerline 240
and
the contact elements of base 231 (of anchor 230). Thus general purpose anchor
260 provides more clearance above the tubular member on which it is mounted
than general purpose anchor 230. In general, the clearance distance of the
anchors of the present invention above the chassis component on which they are
mounted is a matter of design choice depending on, for example, the shape and
size of the component mounted to the anchor, and the magnitude and direction
of
the force vector that is to be borne. Also in the embodiment of general
purpose
anchor 260 shown, the centerline 239 of circular mounts 263 is generally
perpendicular to the axis of the tubular member on which anchor 260 is
mounted.
However, it is also possible to orient arcuate cut-outs 246 ¨ 249 so that
centerline
239 is generally parallel to the axis of the tubular member on which anchor
260 is
mounted, in accordance with design preference.
[0050] General purpose anchor 260 is useful for securing a wide variety of
components to a vehicle chassis, such as shock absorbers or other suspension
components.
Bearing Anchor (250)
[0051] Bearing anchor 250, a perspective view of which is shown in Figure 3A,
includes a base 251 from which extends two opposed spaced-apart crescent-
shaped cheek plates 252, which are each provided with an annular aperture 254.
The apertures 254 are joined by a cylindrical shroud 255 to define a closed
through-recess 256, having a centerline 257, dimensioned so that a vehicle
component, particularly a friction-reducing roller or ball bearing assembly,
can be
press-fitted or otherwise secured therein. Referring to Figures 3A and 3D, the
base 251 of bearing anchor 250 is provided with two spaced-apart mounting
apertures 258 into which removable fasteners 295 can be placed to secure
general
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
13
purpose anchor 260 to for example a tubular member of an exoskeleton/space
frame chassis, preferably utilizing the Securing Elements described further
below.
[0052] The shape of the contact elements of base 251 can be planar or curved.
If
the portion of the tubular member or other vehicle component to be in contact
with base 251 is planar, then the contact elements can be planar. If the
portion
of the tubular member or other vehicle component to be in contact with base
251
is curved, then the contact elements can be correspondingly curved.
[0053] In one embodiment of the present invention adapted for use with a
tubular member that is circular in cross section, base 251 includes a concave
load-bearing channel 259 having a curvature that generally conforms to the
outside diameter of the chassis tubular member to which anchor 250 is secured.
In the event that the width of shroud 255 (when measured along centerline 257)
need not be as wide as the distance across channel 259, one of cheek plates
252
(denominated 252A in Figure 3C) can be curved toward the other of cheek plates
220 (denominated 252B in Figure 3C) as the distance from base 210 increases.
Alternatively, both cheek plates 252 can be curved toward each other as the
distance from base 210 increases, in accordance with design preference.
[0054] Bearing anchor 250 is useful for securing within through-recess 256 a
roller or ball bearing assembly which receives a rotating shaft, as found for
example with a bell crank, lever arm or other rotationally supported
suspension
linkage.
Tangential Load Anchor (270)
[0055] Tangential load anchor 270, as shown in the perspective views of
Figures
4A and 4B, includes abase 271 from which extends two spaced-apart opposed
generally triangular cheek plates 272, shown for example in Figures 4C and 4D.
The ends of plates 272 distal from base 271 are each provided with annular
apertures 274, which have a centerline 277, and through which a rod end joint
or
other vehicle component can be secured with a threaded bolt. An integral
locking
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
14
nut 273 is optionally provided on the exterior face of one of the cheek plates
272
to facilitate securing the threaded bolt to anchor 270. Referring to Figures
4A
and 4B, the base 271 of tangential load anchor 270 is provided with two spaced-
apart mounting apertures 278 into which removable fasteners 295 can be placed
to secure general purpose anchor 270 to for example a tubular member of an
exoskeleton/space frame chassis, preferably utilizing the Securing Elements
described further below.
[0056] The shape of the contact elements of base 271 can be planar or curved.
If
the portion of the tubular member or other vehicle component to be in contact
with base 271 is planar, then the contact elements can be planar. If the
portion of
the tubular member or other vehicle component to be in contact with base 271
is
curved, then the contact elements can be correspondingly curved.
[0057] In one embodiment of the present invention adapted for use with a
tubular member that is circular in cross section, base 271 includes a concave
load-bearing channel 279 having a curvature, as shown for example in Figure
4D,
which generally conforms to the outside diameter of the chassis tubular member
to which anchor 270 is secured.
[0058] Tangential load anchor 270 is useful for securing a component that
generates force largely parallel to the tubular member to which load anchor
300 is
secured, such as shock absorbers or other suspension components.
Securing Elements
[0059] The elements used to secure any of anchors 230, 250, 260, 270 and 360
(described below) to the tubular member of a vehicle chassis are described
below
with respect to general purpose anchor 230, although the description equally
applies to anchors 250, 260, 270 and 360 as well.
[0060] To secure general purpose anchor 230 to exemplary tubular member 16, a
portion of which is shown in Figure 6, two opposed circular tube apertures
281,
282 are formed in tubular member 16. Apertures 281, 282 are generally
orthogonal to the axial centerline 283 of member 16, as shown in Figure 6
(Angle
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
A is approximately 900), and are located along a diameter B (Figure 6) of
tubular
member 16.
[0061] Figures 5A and 5B depict an anchor securing element, boss 290, which is
a cylindrical member inserted through apertures 281, 282 shown in Figure 6.
Boss 290 has a shaft 291 that terminates in a flanged end 292. The length and
diameter of boss 290 can be varied in accordance with the particular
application
for which it is used. As a general design rule, the length of shaft 291 should
be
approximately the same as, or greater than, the outside diameter of tubular
member 16, such that it extends through tubular member 16 when inserted
through apertures 281, 282 and the flanged end 292 is positioned against the
outer surface of tubular member 16. Preferably, countersinks 253 (see, e.g.,
Figure 2F, 2H, 3D, 4A) are provided so that anchors 230, 250, 260 and 270 can
sit flush against the surface of tubular member 16 in the event the end of
shaft
291 distal from flanged end 292 protrudes beyond the surface of tubular member
16 when boss 290 is inserted through apertures 281, 282.
[0062] The end of boss 290 distal from flanged end 292, stepped end 293,
preferably has a reduced diameter as compared to the diameter of shaft 291
between flanged end 292 and stepped end 293. The diameter of tube aperture
281 preferably is smaller than the diameter of tube aperture 282. Further, it
is
preferred that the diameter of shaft 291 between flanged end 292 and stepped
end
293 be greater than the diameter of tube aperture 281 and slightly less than
the
diameter of tube aperture 282, and it is preferred that the diameter of
stepped end
293 be slightly less than the diameter of tube aperture 281.
[0063] In accordance with the foregoing design preferences, boss 290 is self-
aligning; i.e., boss 290 can be inserted into apertures 281, 282 from one
direction
only, and only up to the point where flanged end 292 comes into contact with
the
surface of tubular member 16. Therefore, utilizing a self-aligning anchor
securing element, which in the preferred embodiment is boss 290 with the
design
features disclosed herein, facilitates component assembly and provides a
measure
of quality control during component assembly.
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
16
[0064] It is preferred that boss 290 be welded in place to tubular member 16,
at
flanged end 292 and at stepped end 293, to permanently fix it in place.
Alternatively, boss 290 can be left unsecured to tubular member 16, relying on
flanged end 292 to maintain it in proper position until the anchor/boss
assembly
is secured into place.
[0065] In an alternative embodiment of boss 290, flanged end 292 and stepped
end 293 are omitted, such that shaft 291 of boss 290 is of generally uniform
diameter along its length. In conjunction with this alternative embodiment,
apertures 281, 282 can have the same diameter, sized to received shaft 291.
Boss
290 in this alternative embodiment can then be inserted into tubular member 16
through either of apertures 281, 282. Given the omission of flanged end 292 in
this embodiment, it is preferable to permanently fix boss 290 in place, as by
welds at one or both of apertures 281, 282.
[0066] Boss 290 also has a bore 294 for receiving a removable fastener 295,
such as a threaded bolt. Bore 294 can be threaded or smooth. If bore 294 is
threaded, fastener 295 should be correspondingly threaded to permit fastener
295
to be secured tightly to boss 290. If bore 294 is smooth, fastener 295 should
be
of a length larger than the outside diameter of tube 16, such that when
inserted in
bore 294, the portion of fastener 295 protruding beyond tube 16 can be
secured,
such as by threading the protruding portion and securing it with a
corresponding
nut.
[0067] After boss 290 is placed in position in apertures 281, 282, general
purpose anchor 230 is positioned in place against tube member 16, with
mounting
aperture 236 superposed in the preferred embodiment over tube aperture 281. As
shown in Figure 6, fastener 295 is then inserted through mounting aperture 236
of
general purpose anchor 230 and tube aperture 281. Fastener 295 is thereafter
fixed in position relative to the structure of tubular member 16; thus if bore
294 is
threaded, fastener 295 is tightened to firmly secure general purpose anchor
230
in place. In the event the component to which anchor 230 is secured is to be
relocated or eliminated, the fastener 295 is simply removed from bore 294 as
by
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
17
unthreading, and anchor 230 is removed, leaving no significantly protruding
remnants.
[0068] The fastening and removal of anchors 250, 260, 270 and 360 to a tubular
member is accomplished in the same manner, except that in the case of anchors
250 and 270 two bosses 290 and two fasteners 295 are positioned in tube
apertures 281, 282.
Accessory Anchor (360)
[0069] Accessory anchor 360, shown in Figures 7A-7D, differs from anchors
230, 250, 260 and 270 in that anchor 360 is secured to two opposing sides of a
tubular member.
[0070] Referring to Figure 7A, accessory anchor 360 includes a support yoke
361 having two opposed fastening mounts 363, mounts 363 each defining an
annular mounting aperture 364. The distance between fastening mounts 363
preferably is slightly greater than the cross-sectional width of the tubular
member
to which anchor 360 will be fastened, so as to provide a removable yet snug
fit
between the tubular member and accessory anchor 360. Anchor 360 is to be
fastened to a tubular member received in support yoke 361 and can be secured
using apertures 364 and a removable fastener 295, preferably utilizing the
Securing Elements described above. In that connection, a boss 290 and a
fastener
295 are illustrated in their proper positions in Figures 7A, 7C and 7D. An
integral lock nut 365 is optionally provided to which fastener 295 can be
secured.
[0071] Support yoke 361 is joined to a support strut 369, which has two
opposed
generally planar anchor faces 364, each approximately parallel to the other.
Support strut 369 is joined to an accessory mounting surface 366 distal from
support yoke 361, as shown for example in Figure 7A. Accessory mounting
surface 366 defines two accessory mounting apertures 367 (e.g., Figures 7C and
7D), which are shown in the figures provided with accessory mounting bolts 368
for illustrative purposes.
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
18
[0072] Where accessory anchor 360 is for use with a tubular member having a
circular cross section, such as tubular member 16 shown in Figure 7B, support
yoke 361 preferably has a generally ring-shaped configuration, the inside
diameter of which preferably is slightly greater than the outer diameter of
tubular
member 16 so as to provide a removable yet snug fit between accessory anchor
360 and tubular member 16.
[0073] The contact surfaces of support yoke 361 define support surface 362.
Support surface 362 has a width (measured in the axial direction of the
tubular
member) that is sufficient to resist any anticipated bending loads on
accessory
anchor 360. Support surface 362 can be shaped so that support strut 369 either
is
orthogonally disposed relative to the surface of the tubular member to which
anchor 360 is fastened, or is inclined at a select non-orthogonal angle
relative to
that tubular member surface. For example, as shown in Figure 7B, support
surface 362 is oriented so that support strut 369 is inclined at an angle ai
relative
to the surface of tubular member 16, where angle al is less than 90 degrees.
[0074] Although shown in the figures to be planar (see for example Figures 7A
and 7D), accessory mounting surface 366 optionally can be curved or shaped as
desired to accommodate the particular accessory to which it is to be fastened.
For
similar reasons, mounting surface 366 can be inclined relative to support
strut
369 in one or two directions. Thus as shown in Figures 7B and 7D, mounting
surface 366 is inclined at an angle a2 relative to support strut 369. Angle al
can
be approximately equal to angle a2, or can differ from angle a2, in accordance
with usage considerations. In the embodiment shown, angle al is approximately
equal to angle a2.
[0075] Accessory anchor 360 is useful for securing a wide variety of vehicle
components and accessories to a tubular member, such as vehicle radiators.
[0076] Although boss 290 is utilized herein to fasten anchors 230, 250, 260,
270
and 360 to a tubular member, boss 290 can also be utilized to fasten vehicle
components directly to an appropriate member of an automotive chassis without
utilization of anchors 230, 250, 260, 270 or 360, as the situation may admit.
In
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
19
particular, boss 290 and associated supporting elements can be utilized to
secure
gearbox hanger plates directly to an exoskeleton/space frame chassis, which
gearbox hanger plates facilitate the mounting of a gearbox to the chassis, and
which are disclosed in U.S. Provisional Application No. 62/577,965 entitled
"Invertible Reversible Multi-Application Gearbox," filed Oct. 27, 2017, and in
U.S. Patent Application No. 16/168,957, filed Oct. 24, 2018, entitled
"Invertible
Reversible Multi-Application Gearbox," each having the same inventors as the
subject application. Similarly, boss 290 and associated supporting elements
also
can be utilized to secure gearbox hangers directly to an exoskeleton/space
frame
chassis, which gearbox hangers facilitate the mounting of a gearbox to the
chassis
and which are disclosed in U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 62/616,601
entitled "Gearbox Mounting System," filed January 12, 2018, and in U.S. Patent
Application No. 16/168,978, filed Oct. 24, 2018, entitled "Gearbox Mounting
System," each having the same inventors as the subject application.
[0077] The contents of U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 62/577,965
entitled "Invertible Reversible Multi-Application Gearbox," filed Oct. 27,
2017
and having the same inventors as the subject application, are hereby
incorporated by reference as if fully set forth herein, particularly the
disclosure
relating to gearbox hanger plates using bosses and associated supporting
elements
to secure them to an exoskeleton/space frame chassis. Also, the contents of
U.S.
Nonprovisional Patent Application No. 16/168,957, entitled "Invertible
Reversible Multi-Application Gearbox," filed Oct. 24, 2018 and having the same
inventors as the subject application, are hereby incorporated by reference as
if
fully set forth herein, particularly including the disclosure relating to boss
design
and the design of gearbox hanger plates that are secured to an
exoskeleton/space
frame chassis using bosses and associated supporting elements, found for
example at paragraph 51 and Figure 2A. Further, the contents of U.S.
Provisional
Patent Application No. 62/616,601 entitled "Gearbox Mounting System," filed
January 12, 2018 and having the same inventors as the subject application, are
hereby incorporated by reference as if fully set forth herein, particularly
the
disclosure relating to the design of gearbox hangers that can be secured to an
exoskeleton/space frame chassis using bosses and associated supporting
CA 03114358 2021-03-25
WO 2020/068693
PCT/US2019/052479
elements. In addition, the contents of U.S. Nonprovisional Patent Application
No. 16/168,978, entitled "Gearbox Mounting System," filed Oct. 24, 2018 and
having the same inventors as the subject application, are hereby incorporated
by
reference as if fully set forth herein, particularly including the disclosure
relating
to boss design and the design of gearbox hangers that can be secured to an
exoskeleton/space frame chassis using bosses and associated supporting
elements, found for example at paragraphs 25-53, 54 (sentences 1-2) and in
Figures 1-2A and 2C-5D.
[0078] The foregoing detailed description is for illustration only and is not
to be
deemed as limiting the inventions, which are defined in the appended claims.