Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03118465 2021-04-30
WO 2020/128827
PCT/IB2019/060914
1
DESCRIPTION
MACHINE FOR MAKING TUBULAR SEGMENTS OF THE TOBACCO
INDUSTRY
Technical field
This invention relates to a machine for making tubular segments of the
tobacco industry or of loose materials containing fibres, in particular
tubular
segments provided with a filling material, where the filling is obtained from
a material in the form of a web, preferably of paper. In the context of this
invention, the segments may form part of a traditional cigarette or a heat-
not-burn cigarette and, in particular, an unfiltered cigarette or a cigarette
of
the hand-made or roll-your-own or make-your-own type.
In effect, in cigarettes of this kind, a spacing element must be placed
between the element which burns or is heated to generate the aerosol and
the smoker's mouth so as to cool the smoke and, above all, to prevent the
tobacco from reaching the smoker's mouth. The term "tobacco" as used
herein, denotes any loose material containing fibres, whether of plant or
other origin.
Background art
A typical hand-made cigarette consists of a paper tube rolled around a
paper filling in the form of an insert or obtained using a piece of the
selfsame
paper.
In a manual method for making the tube, an outer sheet of paper material is
rolled into the shape of a tube and a filling insert is then placed inside the
outer tube to partly fill the cavity defined by the outer tube. The insert may
be made by manually folding another piece of paper material, in particular
to form a specific, three-dimensional element intended to partly fill the tube
and also capable of acting as a barrier preventing the passage of tobacco
fragments.
These cigarettes, made basically using ready-cut paper sheets, are very
convenient to make by hand but do not lend themselves to industrial
CA 03118465 2021-04-30
WO 2020/128827
PCT/IB2019/060914
2
production for evident reasons of incompatibility with the production
processes, in particular on account of the very low productivity attainable by
working separate sheets. Working on the inserts individually is, indeed,
highly time-consuming and, what is more, does not allow repeatability of the
quality of the result.
Aim of the invention
In this context, the basic technical purpose of this invention is to provide a
machine for making tubular segments of the tobacco industry to overcome
the above mentioned disadvantages of the prior art.
More specifically, the aim of this invention is to provide a machine for
making
tubular segments of the tobacco industry which allows making tubes
provided with at least one filling insert and which is characterized by the
high speeds and repeatability typical of an industrial process.
The technical purpose indicated and the aim specified are substantially
achieved by a machine for making tubular segments of the tobacco industry,
comprising the technical features described in one or more of the appended
claims 1 to 14.
This invention also has for an object a method for making tubular segments
of the tobacco industry, comprising the technical features described in one
or more of the appended claims 15 to 22.
Brief description of the drawings
The invention is described below with reference to the accompanying
drawings, which illustrate a non-limiting embodiment of it and in which:
- Figure 1 schematically represents a machine according to a first
embodiment of this invention;
- Figure lA is an enlarged view of a detail of the machine of Figure 1;
- Figure 2 schematically represents a machine according to a second
embodiment of this invention;
- Figure 3 shows a detail of the machine of Figure 1 or 2;
CA 03118465 2021-04-30
WO 2020/128827
PCT/IB2019/060914
3
- Figures 4 and 5 are cross sections of a portion of the machine of Figure
1
or 2 along two successive section planes;
- Figure 6 is a cross section of a tubular segment made with the machine of
Figure 2;
- Figure 6A shows an enlarged view of the segment of Figure 6;
- Figure 7 is a detail view showing a portion of the machine of Figure 1 or
2;
- Figure 8 schematically represents an operating step carried out in the
machine portion of Figure 7.
Detailed description of preferred embodiments of the invention
With reference to the accompanying drawings, the numeral 1 denotes in its
entirety a machine for making tubular segments of the tobacco industry
according to this invention.
In the context of this invention, the term "tubular segment of the tobacco
industry" is used to denote a tube-shaped segment usable as part of a
smoking article, specifically as a component of a smoking article such as a
traditional cigarette or a heat-not-burn cigarette and, more specifically, an
unfiltered cigarette or a cigarette of the hand-made or roll-your-own type.
The function of such a segment, when used in such a smoking article, is
one of filtering and/or cooling and/or flavouring and/or
conducting/dissipating heat and/or of aesthetic/characteristic appearance
(replicating the cross sectional shape of a specific brand).
Further, in the context of this invention, the tubular segment (labelled 100
in
the accompanying drawings) is defined by an outer tube 110 and at least
one insert 120 disposed therein to at least partly fill the duct inside the
outer
tube 110.
In an embodiment, the outer tube 110 and/or the insert 120 are made from
respective continuous webs of a paper material; material other than paper
may, however, also be used without departing from the inventive concept of
this invention. More specifically, for one or both of the continuous webs, a
different material might be used, selected from the following materials
CA 03118465 2021-04-30
WO 2020/128827
PCT/IB2019/060914
4
(individually or mixed together):
- materials derived from cellulose: for example cellulose acetate (tow);
- tobacco, reconstituted tobacco (recon) or other materials of plant
origin:
for example, wheat, maize, sugar cane, hemp, sugar beet, palm, pawpaw,
etc.
- polymeric plastic materials: for example, polylactic acid (PLA),
polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinylchloride (PVC),
polyethylene terephthalate (PET), etc.
- biodegradable or compostable materials, such as the following bio-
plastics: Mater-Bi, PHAs (polyhydroxyalkanoates)
- metals: for example aluminium, stainless steel...
These materials may also contain:
- plasticizers, solvents or humectants: for example, triacetin (glycerin
triacetate), TEC (triethyl citrate), PEG 400 (low molecular weight
polyethylene glycol);
- materials which in turn generate vapours, fumes or aerosols: for example,
water, glycerol, propylene glycol, etc.;
- natural or artificial flavours such as, for example, menthol, fruit
extracts,
sugars, liquorice, liqueur flavourings, cocoa, etc.;
- materials having a selective or adsorbent filtering effect: for example,
activated carbons, silica-gel, etc.;
- materials that facilitate joining the web components by gluing:
typically,
PVA, plant- or animal-derived glue, starches, alginates, fats, etc.
The above materials may be present simultaneously in the web of the tube
or of the insert or they may be chemically mixed or mechanically joined, for
example by rolling, pressing, moulding, compression, extrusion, coating,
impregnation, sintering, gluing, powder or granule or wire inclusion, etc.
The web can be made using methods similar to those used for preparing
paper or recon tobacco or plastic tapes (for example, pressing) or it might
also be a mesh, a textile or a non-woven web.
Figure 1 shows a first embodiment of the machine 1 according to the
CA 03118465 2021-04-30
WO 2020/128827
PCT/IB2019/060914
invention. In this embodiment of it, the machine 1 comprises first feed
means 10 for feeding a first continuous web and configured to make at least
a first continuous web 2 advance along a first feed path P1 and second feed
means 20 for feeding a second continuous web and configured to make a
5 second continuous web 3 advance along at least a respective second feed
path P2.
The webs 2, 3 may be made of paper or other materials, depending on the
type of tubular segment required.
Further, the webs 2, 3 are unwound from respective rolls 2a, 3a, preferably
motor-driven.
Preferably, the webs 2, 3, at least in a step of unwinding them from the
respective roll 2a, 3a are defined by a single layer.
The machine 1 also comprises a forming station 30, disposed on the first
feed path P1 and configured to fold and/or deform the first continuous web
2 in such a way as to obtain a continuous web with a shaped configuration.
In other words, the forming station 30 elastically and/or permanently
deforms the first web 2 so that the web changes from a flat configuration to
a three-dimensional configuration, in particular a laterally gathered
configuration, such as to make it suitable for insertion into, thus partly
filling,
a continuous tube following it.
In the context of this invention, the term "shaped" referred to the first web
is
used to mean a three-dimensional configuration obtained by a process of
elastic or permanent deformation intended to give the web a transverse
cross section having a specific shape that is visible from the outside in the
final tubular segment. The shape is preferably modelled on a geometrical
figure or a symbol or a generic shape of varying complexity. By way of non-
limiting example, the shape may have a wavy configuration or it may be the
shape of a star or a leaf or a letter of the alphabet (for example, an "S" or
an omega) or of a logo (for example, a trademark) or a geometrical figure
(square, triangle, rectangle), or a heart or other shape. In the context of
this
invention, the specific shape does not constitute a limitation of the
invention
CA 03118465 2021-04-30
WO 2020/128827
PCT/IB2019/060914
6
but only one aspect of it, insofar as the continuous web is deformed to define
a specific, predetermined shape, in particular a shape that evokes a specific
image or sensation in the user.
The forming station is illustrated in detail in Figure 1A.
Advantageously, the forming station 30 is configured to operate steplessly,
thus deforming the first web 2 while the first web 2 advances steplessly.
This is preferably achieved thanks to the structure of the forming station 30,
which is configured to make the first web 2 pass uninterruptedly through a
forming gap whose transverse cross section is such as to give the first web
2 the above mentioned shaped configuration. Preferably, the forming gap is
defined by a slot extending along an open line ¨ that is to say, where the
ends of the line along which the forming gap extends are spaced and do not
coincide.
In an embodiment, the forming station 30 is configured to deform the first
web 2 at least partly elastically. More in detail, that means folding
longitudinal portions of the first web 2 relative to each other in such a way
as to allow "lateral compacting" or, more generally speaking, "transverse
compacting" of the first web 2, but reversibly, so that the first web 2 thus
shaped retains a certain elastic tendency to return laterally to its original
shape, causing it to adapt to the internal shape of the continuous tube it
will
next be inserted into.
In this embodiment, the forming gap extends along an open line which is at
least partly, and preferably entirely, defined by a succession of curved
stretches and in particular by a spline curve. The open line may also have
straight stretches ¨ for example, straight stretches alternated with curved
stretches or splines ¨ thereby compacting gently and gradually in order to
prevent or limit permanent deformations.
In addition or alternatively to deforming elastically, as just described, the
forming station 30 is configured to deform the first web 2 at least partly
permanently, in particular to fold the first web 2 about one or more
longitudinal fold lines. More in detail, that means permanently deforming
CA 03118465 2021-04-30
WO 2020/128827
PCT/IB2019/060914
7
certain specific zones of the first web 2, allowing lateral compacting to a
greater degree than in the case of purely elastic deformation, as well as
repeatedly folding superposed layers.
In this embodiment, the forming gap extends along an open line which has
one or more sharp corners defining respective longitudinal fold lines for
permanently folding the first web 2.
As mentioned above, the forming station 30 may produce lateral compacting
elastically or permanently, or a combination of the two, in particular with
elastically deformed zones alternated with permanent fold lines.
In a preferred embodiment, shown in Figure 3, the forming station 30
comprises a pair of rollers 31, 32 between which the first web 2 is made to
pass and which have respective matchingly shaped external features 31a,
32a (that is to say, whose profiles are shaped to match each other and are
thus geometrically compatible) defining the forming gap between them. In
other words, the rollers 31, 32, rotatable about parallel axes, have
respective peripheral profiles (Figure 3) which, in cross section relative to
a
plane passing through the respective axis, correspond to, and hence are
shaped to match, each other so as to define the forming gap of substantially
uniform width through which the first web 2 is shaped.
In the embodiment illustrated in Figure 1, a forming gap of the type
described above is also defined by a second forming element, hereinafter
called preforming element 33, disposed upstream of the forming rollers 31,
32 and configured to pre-shape the first web 2.
Looking in more detail, the preforming element 33 may be defined by a rigid
or monolithic element provided with a fixed forming gap by which the first
web 2 undergoes an initial deformation to give the first web 2 a configuration
that makes it easier for it to pass through the pair of rollers 31, 32.
In an embodiment not illustrated, the preforming element 33 may even be
sufficient to act as a single forming element, in place of the pair of rollers
31,32.
In a preferred embodiment, the rollers 31, 32 are, instead, structured and/or
CA 03118465 2021-04-30
WO 2020/128827
PCT/IB2019/060914
8
mounted in such a way as to be held together by a predetermined force
such as to compress the first web 2 passing between them. In this
configuration, therefore, the size of the forming gap between the rollers 31,
32 is defined by the thickness and compressibility of the first web 2. This
advantageously allows giving the rollers 31, 32 not only a function of forming
the first web 2 but also of entraining it, where at least one of the two
rollers
31, 32 is associated with respective motor means.
Downstream of each of the aforementioned feed means 10, 20 and of the
forming station 30, the machine 1 also comprises a tubular guide 40
configured to guide the first web 2 as it leaves the forming station 30 that
has given it the shaped configuration and so that it keeps the shaped
configuration as it proceeds from the forming station to a wrapping station
50 (described below).
In effect, the passage of the first web 2 through the tubular guide 40 in the
shaped configuration allows the first web 2 to keep its shape, contrasting its
tendency to return elastically to a laterally expanded configuration.
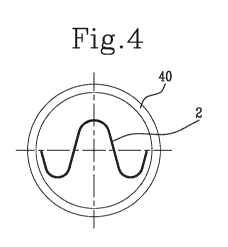
The tubular guide 40 is shown in detail in Figure 7.
Preferably, the tubular guide 40 has at least one stretch 41 whose
transverse cross section progressively decreases, gradually decreasing in
diameter, for example, so as to further compact the shaped first web 2
transversely before it reaches the wrapping station 50, so that the first web
2 that has already been shaped is given the required final transverse cross
section.
Figures 4 and 5 show cross sections of the tubular guide 40, respectively
upstream and downstream of the stretch 41 with the decreasing transverse
cross section, specifically at the cross sections Si and S2 of Figure 7.
In a preferred embodiment, the tubular guide 40 is made entirely in one
piece. It may, however, also be made up of a succession of parts connected
to each other to form a single rigid body.
As shown in Figure 8, the tubular guide 40 has an outlet end portion 42 with
an outlet opening 43 lying in an inclined plane not perpendicular to the feed
CA 03118465 2021-04-30
WO 2020/128827
PCT/IB2019/060914
9
direction of the shaped first web in such a way that the outlet opening 43
faces down.
In a further embodiment not illustrated, the tubular guide 40 may itself be a
forming element if the web 2 is not required to adopt a predetermined
shaped configuration and has to pass through the tubular guide 40 only.
Downstream of the forming station 30 and of the tubular guide 40, the
machine 1 also comprises the aforementioned wrapping station 50, where
the first feed path P1 and the second feed path P2 meet and where the
second web 3 is wrapped around the previously formed first web having the
shaped configuration, thus obtaining a continuous tube defined by an outer
covering enclosing within it the first web that has been shaped.
Looking in more detail, the wrapping station 50 is located at the end portion
42 of the tubular guide 40 from which the first web 2 comes out with the
shaped configuration and the second web 3 is at least partly wrapped
directly round the end portion 42 of the tubular guide 40. Wrapping is
accomplished by superposing opposite lateral edges of the second web 3
and gluing them to each other.
The wrapping station preferably also comprises a belt (not illustrated) for
guiding the second web 3 driven along a closed path and designed to act in
conjunction with fixed deflectors for guiding the second web 3 being
wrapped around the end portion 42 of the tubular guide 40.
As shown in Figure 8, the second web 3, during its initial wrapping
movement around the end portion 42 of the tubular guide 40, comes from
below and thus the aforementioned outlet opening 43 of the tubular guide
40 faces a central portion of the second web 3 being wrapped around the
end portion 42 itself. This advantageously allows exposing a portion of the
second web 3 and/or of the shaped first web 2 so that they can be glued to
each other to permanently join the shaped first web 2 to the second web 3.
In other words, at least the shaped first web 2 or the second web 3 have to
interact with a gluing device 60 along their path in order to spread a layer
of
glue on at least one of the two webs 2 or 3 so as to join the two webs 2 and
CA 03118465 2021-04-30
WO 2020/128827
PCT/IB2019/060914
3 to each other.
In a possible embodiment, the end portion 42 of the tubular guide 40 may
have the shape of a truncated cone or otherwise tapered in the direction of
the continuous tube being formed.
5 In particular, the gluing device 60, configured to apply an adhesive
substance ¨ for example, vinyl glue or PVA or hot-melt glue ¨ on the shaped
first web or on the second web 3, may be disposed in proximity to the
wrapping station 50, and, more specifically, near the outlet opening 43. The
gluing device 60 preferably comprises one or more spray nozzles, not
10 illustrated, configured to direct a jet of glue on the shaped first
web or on the
second web 3.
In embodiments not illustrated, the gluing device may be disposed at a
different position: for example, on the first and/or the second feed path P1,
P2.
Located downstream of the wrapping station 50 there is a cutting station 70
for dividing the continuous tube into a succession of tubular segments 100.
The cutting station 70 may comprise a rotary blade of customary type as
used, for example, to cut continuous cigarette or filter rods, and provided
with a rotary drum fitted with one or more radial, preferably adjustable
blades.
Figure 2 shows a second embodiment of the machine 1 according to the
invention. The machine 1 of this embodiment differs from that of Figure 1 in
that it comprises, on the second feed path P2, upstream of the wrapping
station 50, a folding device 80 operating on the second web 3 to fold the
second web 3 about two parallel, longitudinal fold lines to give the second
web 3 a three-layer structure.
In this situation, the outer tube 110 thus made is visible in the view of
Figure
6 and in the enlarged view of Figure 6A, showing the splicing zone where
the opposite lateral edges of the second, three-layer web 3 are joined.
More generally, the folding device 80 disposed on the second feed path P2
may be configured to fold the second web 3 one or more times about one
CA 03118465 2021-04-30
WO 2020/128827
PCT/IB2019/060914
11
or more parallel, longitudinal fold lines to give the second web 3 a
multilayer
structure. Folding in this way is carried out continuously by one or more
fixed
deflectors having respective folding edges disposed at the respective
longitudinal fold line. In order to facilitate folding the second web about
the
longitudinal fold lines, a scoring device (not illustrated) may be provided on
the second feed path P2, upstream of the folding device 80, to make one or
more longitudinal lines of weakness that will constitute the fold lines in the
folding device 80.
This invention is susceptible of modifications without departing from the
inventive concept. By way of an example, in the case of a multilayer outer
tube, for example with at least two at least partly superposed webs, two or
more second webs from respective rolls (or from a single roll cut lengthways
to form two webs) and wrapped in such a way as to present respective
splicing zones angularly spaced about the axis of the final tubular segment
can be used instead of a single second web folded about one or more
longitudinal, parallel fold lines.
Furthermore, on the first feed path, there may be an applicator device for
applying on the first web as the first web advances and/or after it is formed
an additional substance such as a flavouring or a substance suitable for
increasing the conductive and/or heat dissipative properties of the first web.
According to a further optional possibility, a creasing and/or scoring device
may be provided on the first feed path to make one or more lines of
weakness (either continuous or with cyclic interruptions) on the first web to
facilitate its subsequent deformation in the forming station. Alternatively,
the
first web might have these creases and/or scored cuts already made on it
when it is unwound from the respective roll.
Moreover, according to this invention, the guide 40 might coincide totally or
at least partly with the wrapping station 50, where the outer surface of the
guide 40 allows wrapping the second web 3.
The present invention achieves the preset aims, overcoming the
disadvantages of the prior art.
CA 03118465 2021-04-30
WO 2020/128827
PCT/IB2019/060914
12
In effect, the invention provides a machine that is configured to implement
an industrial method for making tubular segments provided with at least one
filling insert, where the segments can be made from respective continuous
webs, allowing high productivity and a high level of quality and
repeatability.