Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 1
PCT/DE2019/000296
Title:
Disk-shaped tool and method for machining workpieces, cutting
device and use of a cutting, grinding and polishing disk to
produce a surface structure on a workpiece
Description:
The invention relates to a tool and a method for machining
workpieces as specified in the respective preambles of claims
1 and 6, in particular for the simultaneous multiple machining
of workpieces and a cutting device according to claim 10 and a
use according to claim 12.
To machine workpieces, cutting and separating processes are
carried out for example by means of rotating tools that are
used in stationary or mobile devices. DE 20 2016 102 268 U1 is
mentioned here as a possible embodiment of a cutting machine.
After cutting and separating processes have been carried out,
the resulting cut surfaces have surface characteristics
resulting from the cutting or separating process. Separating
and cutting tools are mainly designed for a high cutting
performance and, due to the correspondingly coarse cutting
edges, often produce cut surfaces with a high surface
roughness, burrs and material damage caused by the
temperatures. In many applications, the surface quality of a
cut surface resulting from a cutting or separating process
does not meet the requirements of the laboratories in which
the cut surface produced as a process result must be examined
more closely. In the industrial production as well, clean,
burr-free cut surfaces are required, for example, for a
further processing of cut workpieces, which should be as free
as possible from damage of any kind. It is usually still
necessary to further process the relevant cut surface, for
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 2
PCT/DE2019/000296
example, in a grinding or polishing process. Individual
influences during the specimen preparation are now almost
inevitable.
In the following description, the possible processing steps
for increasing the surface quality in an axial working
direction of a disk-shaped rotating tool are collectively
referred to as "grinding." The cutting and separating
processes in a radial working direction are referred to as
"cutting."
According to common methods, for example when insulated cables
are cut to length, cutting processes and grinding processes
are carried out with different tools in successive operations,
because cutting processes and grinding processes each place
different demands on the tool structure and the removal rate
of the executing tool. Special machine tools are usually used
for each process. Workpiece changes or manual grinding
processes occur.
During cutting processes that use rotating tools, the tool
plunges into the workpiece to be machined in a radial working
direction. It is desirable that the rotating cutting tools
have a small thickness so that the material removal necessary
for performing the separating cut is low.
In contrast to rotating cutting tools, rotating grinding tools
usually have a greater thickness in the axial direction. This
way, the axial forces occurring with the side surfaces of the
tool during grinding processes are absorbed and the largest
possible contact is achieved between tool and workpiece
surface during grinding processes in the radial working
direction. DE 696 11 764 T2 is mentioned here as an example
for the design of disk-shaped grinding tools.
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 3
PCT/DE2019/000296
The degree of wear on the tool is usually checked before
starting a cutting or grinding process. This check is often
purely visual, and the result is subjectively limited to the
impression of the examiner. If a tool now reaches its wear
limit during an ongoing machining process, the process must be
interrupted and restarted with a new tool. In addition to the
extra time required for the tool change, the tool change
performed during the machining process can lead to an uneven
work result. This is problematic when used for the preparation
of a specimen and a subsequent surface analysis on the
workpiece.
DE 10 2015 223 428 B4 proposes a disk-shaped cutting tool for
making gentle separating cuts, which is particularly suitable
for cutting composite materials with poor thermal
conductivity. By means of an exclusively radially acting main
cutting edge on the outer circumference of the disk-shaped
cutting tool, a cutting gap is produced, which is then widened
by means of convex secondary cutting edges which are arranged
adjacent to the main cutting edge and which act in a partly
radial and partly axial manner. The high temperatures that
arise when material is removed are distributed over a larger
region both in the tool and in the workpiece. Workpiece
material in the region of the cut surfaces that has undergone
temperature-related, material-damaging structural changes
during the production of the cutting gap is at least partially
removed during the subsequent widening of the cutting gap. In
the application, the invention disclosed in DE 10 2015 223 428
B4 achieves cut surfaces with less pronounced temperature
damage.
The material removal required to carry out a separating cut
with the tool disclosed in DE 10 2015 223 428 B4 is higher
than with a conventional cutting disk due to the special
geometry of the peripheral region of the disk. This conflicts
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 4
PCT/DE2019/000296
with a use for making efficient separating cuts in metallic
materials.
It should also be noted that the tool disclosed in DE 10 2015
223 428 B4 should not be used for surface grinding purposes in
an axial working direction.
A saw blade with geometrically defined, alternately set saw
teeth on its outer circumference, which is equipped with guide
elements on its side surfaces, is known from US 6632131B1.
According to the invention, the guide elements do not project
axially beyond the separating cut width. The guide elements
can therefore not have a grinding effect in the axial
direction, but are intended to remove splinters that were torn
out of the body of the workpiece by the cutting edges but
still adhere to the workpiece and protrude into the separating
cut.
WO 2011/029106A2 describes a wear indicator for rotating
material-removing cutting or grinding tools, which provides
information on the radial or axial wear of the tool via
depressions or elevations integrated into the tool.
Based on the prior art shown, the present invention
furthermore has the object of providing a tool or a machining
method that can be used on commercially available portable or
stationary cutting and grinding machines and with which it is
possible to efficiently cut a workpiece with a defined surface
characteristic by means of a cutting process. The machining
quality should be assured. It should be possible to reproduce
the produced surfaces in the same way over and over again.
Another object of the invention is to provide a tool which, if
possible, comprises a wear indicator that allows the tool user
to draw a conclusion as to whether the operation in question
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 5
PCT/DE2019/000296
can be fully carried out within the remaining utilization
capacity of the tool before the start of an operation.
The object of the invention is achieved by the subject matter
of the independent claims, including their respective
features.
Advantageous further developments of the invention are defined
in the respective subclaims.
The disk-shaped cutting tool according to the invention is
provided for the rotating cutting of a stationary clamped
workpiece elongated at least roughly along an axis of
rotation, with a radial advance with respect to this axis of
rotation at least roughly in the direction of the orthogonally
clamped workpiece. However, the cutting tool does not
exclusively have cutting edges in a radially outer
circumferential region of the cutting tool. At least one of
two opposing disk flanks is provided with at least one
grinding and/or polishing agent in a radially inner region
with respect to the circumferential region.
A disk-shaped tool according to the invention is
advantageously provided for use in commercially available
mobile or stationary cutting and grinding machines. A use in a
test laboratory for electrical cables has saved considerable
effort and improved the informative value of studies.
Following the idea of the invention further, a cutting device
according to the invention is suitable for a method for the
machining of test workpieces, namely by means of a disk-shaped
cutting tool. During an exclusively at least roughly radial
movement of the tool, the tool is separated, ground and/or
polished in succession, either simultaneously or directly
consecutively, particularly preferably during a single infeed
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 6
PCT/DE2019/000296
instruction from a machine control. According to a further
advantageous embodiment, a wear indicator shows a remaining
utilization capacity, in particular a remaining cutting volume
and/or a remaining utilization time. The display particularly
preferably reacts independently to mechanical wear of the tool
that exceeds a certain level, in particular in that a
different color appears or becomes recognizable.
In its design, the tool already takes into account loads that
impair the quality of the workpiece such as the temperature
and the tool fatigue.
The wear indicator now even provides information on the
process parameters to be selected such as the tool speed and
the feed speed.
The invention avoids a separate performance of the "cutting,"
"grinding" and, if necessary, "polishing" processes. Setup
work and thus machine and personnel costs are saved. Setup
work on machines that work with material-removing processes is
time-consuming and labor-intensive, since, for example, during
each changeover, all mounting surfaces for workpieces and
tools have to be cleaned of machining residue such as material
chips and cooling lubricants very thoroughly. Setup work on
machine tools usually results in the positions of the
workpiece to be machined and possibly also in the tool being
shifted from the machine's coordinate system and having to be
found again. Setup, spanning and programming work on machine
tools involve, especially concerning the uses according to the
invention in view, a certain potential for errors due to the
complex work processes.
If a workpiece needs to be reworked after a cutting process,
it must have a certain minimum size so that it can be fastened
with a clamping device for further processing. Especially with
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 7
PCT/DE2019/000296
very expensive materials or materials that are only available
to a limited extent, the need to maintain a minimum workpiece
size is associated with increased effort, such as a fastening
of the workpiece on a support.
In a particularly preferred embodiment, the tool according to
the invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-polishing
disk, comprises a disk-shaped base body, which preferably
consists of a composite material, that uses, for example, a
synthetic resin matrix similar to a cutting disk.
The tool according to the invention particularly preferably
comprises, in particular, a cutting-grinding-polishing disk,
at least one region with cutting edges acting in the radial
working direction and at least one grinding and polishing
region acting in the axial working direction. The cutting
edges that are used are preferably designed to be
geometrically indeterminate, for example, as a grained
abrasive. Furthermore, the tool according to the invention, in
particular a cutting-grinding-polishing disk, preferably has a
central bore in the axial direction for fastening in the usual
standardized tool holders of mobile and stationary cutting and
grinding machines.
The feed movement of the tool according to the invention, in
particular a cutting-grinding-polishing disk, in the radial
working direction for the performance of the separating cut
can, depending on the design of the machine technology used,
take place mechanically or manually.
The tool according to the invention, in particular a cutting-
grinding-polishing disk, is provided with grinding and
polishing agents on at least one disk flank. The grinding and
polishing agents are more finely grained or toothed or
designed for less material removal than the cutting agents in
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 8
PCT/DE2019/000296
order to be able to achieve the intended improvement of the
surface quality of the cut surfaces in the axial direction
while at the same time being able to achieve an efficient
separating machining in the radial direction.
The tool according to the invention ensures its usability due
to its combined geometric and kinematic properties and
therefore does not have any of the problems and limitations
described above. When the tool according to the invention
touches the workpiece with its outer circumference in a radial
infeed movement during the cutting process, several specific
and deliberately exploited factors lead to a defined
deflection of the disk in both axial directions without the
cutting tool itself moving axially in its center. This leads
to a widening of the cutting gap, which is for example 10% in
this explanation. The cutting gap is therefore 10% wider than
the radial outer geometry of the cutting tool would
traditionally dictate. In this 10% wider cutting gap, the
grinding/polishing layers applied to the disk sides take
effect and are therefore not relevant for the cutting process.
In any case, no effect is relevant in the radial direction,
and the separation process itself is not influenced at all.
The material thickness of the grinding/polishing layers is
precisely matched to the resulting widening of the cutting
gap. There is, therefore, no need for a wider cutting edge, in
the shadow of which the grinding/polishing elements can act
during the radial cutting process. Their relevance for the
functioning of the invention now lies in the axial action,
namely grinding/polishing.
This axial deflection of the disk, and thus the widening of
the cutting gap, is made possible by certain properties of the
disk. The combination of material properties and geometric
properties, such as the width of the disk, give the cutting
disk a certain flexibility. This flexibility makes it possible
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 9
PCT/DE2019/000296
for the process forces that occur during the cutting process
to lead to an axial deflection of the disk of up to
approximately 5% of the disk width in both directions. In
addition, the operating speed of the cutting disk has a value
that corresponds to a multiple of one of the natural
frequencies of the cutting disk. When in operation, the
cutting disk performs axial vibrations, the amplitude of which
is approximately up to 5% of the thickness of the disk. In
addition, the cutting disk is not flat, but has an impact of
up to approximately 10% of the width of the disk. This impact
additionally supports the widening of the cutting gap. The
impact of these effects can be increased with a
grinding/polishing layer that widens towards the center of the
disk. This utilization of geometric and kinematic properties
that lead to an axial deflection of the tool according to the
invention make it possible to dispense with a wide cutting
edge. A radial consumption of the tool according to the
invention is basically possible up to the tool holder of the
operating machine. This leads to a more efficient use of the
tool and allows for the use of wear-prone binding materials
for the abrasive grains responsible for the cutting process.
This allows for a precise and yet efficient cut. The described
axial deflection of the tool according to the invention also
leads to an infeed of the grinding/polishing layers applied to
the cutting disk sides in the axial direction to the cut
surfaces of the workpiece. This infeed ensures a clean
grinding/polishing of the cut surfaces, regardless of the
degree of wear on the grinding/polishing surfaces. No machine
control is required for the grinding/polishing process of the
cut surfaces, which allows for the axial infeed of the
grinding/polishing elements to the cut surfaces. The machine
only has to provide a radial feed.
A preferably provided thickening of the flanks of the disk-
shaped tool according to the invention towards the center has
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 10
PCT/DE2019/000296
a supporting effect with regard to the axial movement of the
grinding and polishing means towards the cut surfaces to be
processed. The thickening is preferably carried out in a
single or multiple gradation in order to hold the grinding and
polishing surfaces parallel to the cut surfaces of the
separating cut. The thickening can be realized in one or more
layers.
As a result of the feed movement in a radial working direction
when performing the separating cut, the tool according to the
invention plunges into the workpiece and, when the tool
according to the invention is plunged, it leads to a flat
contact of the grinding and polishing surfaces with at least
one cutting surface of the workpiece.
In a particularly preferred embodiment, the tool according to
the invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-polishing
disk, is provided with at least one channel along at least one
side flank for an improved removal of chips, broken-off
grinding material and/or cooling lubricant.
In a further preferred embodiment, the at least one grinding
and polishing region present on at least one disk flank is
designed without cooling channels.
In a preferred embodiment of the tool according to the
invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-polishing disk, it
is provided to have the grinding and polishing material become
finer towards the center of the disk in order to have
increasingly finer grinding and polishing agents come into
contact as the depth of the tool in the workpiece increases
and thus to achieve the highest possible surface quality in
one operation.
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 11
PCT/DE2019/000296
In a particularly preferred embodiment, the tool according to
the invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-polishing
disk, is equipped with an optical wear indicator for the at
least one grinding and polishing region. The at least one
grinding and polishing region is preferably made up of
multiple layers, as shown in Fig. 2 to 5, with the number of
layers increasing towards the center of the disk. The
individual layers are marked with individual color codes,
which indicate the wear in both the radial and the axial
direction. On the basis of the visible color codes, the
current degree of wear and thus also the remaining capacity of
the tool according to the invention, in particular a cutting-
grinding-polishing disk, can be reliably determined.
Another preferred embodiment provides for the wear indicator
to be designed in a single layer so that the wear of the
grinding layer on the side of the pane reveals the differently
colored support layer underneath, which is responsible for the
cutting, and thus visually indicates the wear. This single-
layer grinding layer on the side of the disk can also be
segmented towards the center of the disk on the basis of a
different grain size or simply in a different color. If the
radial wear then reaches such a specific segment, conclusions
can be drawn about the state of wear as well. Wear can thus be
visualized in the radial and the axial direction.
In further preferred embodiments, other configurations of the
wear indicator, for example using acoustic or electronic
signals, are conceivable as well.
The drawings show the following:
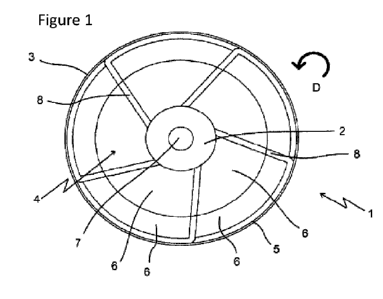
Fig. 1 - a side view of a disk flank with a view of the base
body, the cutting edge and the grinding and polishing elements
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 12
PCT/DE2019/000296
of a tool according to the invention, in particular a cutting-
grinding-polishing disk,
Fig. 2 - a side view of a disk flank showing the grinding
stages of a tool according to the invention, in particular a
cutting-grinding-polishing disk
Fig. 3 - a side view of a disk flank showing the layer
structure of a tool according to the invention, in particular
a cutting-grinding-polishing disk,
Fig. 4 - a front view of the outer circumferential region with
a representation of the cutting edge and the step-like
structure of the grinding and polishing components of a tool
according to the invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-
polishing disk,
and
Fig. 5 - an exploded drawing of a tool according to the
invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-polishing disk, in
a side view with a representation of the color code for
displaying the wear of the cutting, grinding and polishing
components
The invention is explained in detail below with reference to
the drawings listed above. Fig. 1 shows, in a side view, a
particularly preferred embodiment of a disk-shaped tool 1
according to the invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-
polishing disk. A base body 2, preferably formed from a
composite material, which, similar to a commercially available
cutting disk, already contains cutting agents of a defined
grain size and thus has geometrically undefined cutting edges
on an outer circumferential area 3, is clearly shown. A
fastening bore 7 is provided centrally in the axial direction
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 13
PCT/DE2019/000296
in the base body 2 for fastening the disk-shaped tool 1
according to the invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-
polishing disk, in the standardized tool holders of stationary
or mobile cutting and grinding machines.
In a particularly preferred embodiment, grinding and polishing
surfaces 6 are applied on one side of a disk flank 4 of the
base body 2. These grinding and polishing surfaces 6 make it
possible for the cutting surface of a workpiece to be reworked
simultaneously for the execution of the separating cut. The
separating cut is carried out in a radial working direction VR
shown in Fig. 2 and 4 by means of cutting edges 5 on the outer
circumferential region 3 of the disk-shaped tool 1, in
particular a cutting-grinding-polishing disk. The advance in a
radial working direction VR can take place manually or
mechanically, depending on the design of the cutting or
grinding machine used.
In a first particularly preferred embodiment, channels 8 for
removing chips or coolant from the cutting, grinding and
polishing region are clearly shown. In a particularly
preferred embodiment of the disk-shaped tool 1 according to
the invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-polishing
disk, the channels 8 run along the disk flank 4 in the radial
direction towards the outer circumferential region 3. The
channels 8 are preferably inclined against the direction of
rotation D in order to avoid or at least reduce a clogging of
the channels 8 during a movement in the radial advance
direction VR.
In a particularly preferred second embodiment, although not
shown here, the disk-shaped tool 1 according to the invention,
in particular a cutting-grinding-polishing disk, is designed
without channels 8.
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 14
PCT/DE2019/000296
In further particularly preferred embodiments, although not
shown here, the disk-shaped tool 1 according to the invention,
in particular a cutting-grinding-polishing disk, is designed
with single-layer grinding/polishing elements, with and
without channels.
Fig. 2 shows, in a side view of a disk flank 4, the
representation of the grinding stages of a disk-shaped tool 1
according to the invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-
polishing disk. The disk-shaped tool 1 according to the
invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-polishing disk, is
provided with grinding and polishing agents on at least one
disk flank 4. The grinding and polishing agents are finer
grained or toothed or designed for less material removal than
the cutting edges 5 in order to be able to achieve the
intended improvement in the surface quality of the cut
surfaces.
In order to bring the grinding and polishing surfaces 6 of the
disk-shaped tool 1 according to the invention, in particular a
cutting-grinding-polishing disk, as shown in Fig. 1, into
engagement in an axial working direction VA shown in Fig. 4, a
thickening of the at least one flank 4 of the disk-shaped tool
provided for engagement, which preferably achieved by means of
process-related vibrations of the tool 1, has a supporting
effect in the embodiment shown. The thickening is preferably
realized in a single or multiple gradation 40 in order to hold
the grinding and polishing surfaces 6 parallel to the cut
surfaces of the separating cut. The movement in an axial
working direction is amplified by vibrations of the disk-
shaped tool 1, in particular a cutting-grinding-polishing
disk, which are typical for the process, in an axial
direction.
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 15
PCT/DE2019/000296
Graduations 40 which delimit the surface of a first grinding
and polishing stage 10 and the surface of a second grinding
and polishing stage 11 can be seen. In a particularly
preferred embodiment of the disk-shaped tool 1 according to
the invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-polishing
disk, the grain size or toothing of the cutting edges 5 is
coarser than the grain size or the toothing of the surfaces of
the grinding and polishing stages 10, 11. The grain size or
toothing of the surface of the second grinding and polishing
stage 11 is particularly preferably finer than the grain size
or toothing of the surface of the first grinding and polishing
stage 10.
In the course of a separating cut in a radial feed direction,
the surface of the first grinding and polishing stage 10 first
comes into engagement with at least one cutting surface of the
separating cut and reworks the at least one separating cut
surface. By continuing the disk-shaped tool 1, in particular a
separating-grinding-polishing disk, in a radial working
direction VR, the surface of the second grinding and polishing
stage 11 also comes into engagement and completes the grinding
and polishing process of the at least one surface of the
separating cut to the desired surface quality.
In addition to the shaded areas of the first and second
grinding and polishing stage, Fig. 2 shows the dotted surfaces
12 of the channels 8 that are not initially engaged in a
grinding and polishing process and the exposed region of the
base body 2 that is shown as a white region.
Further preferred embodiments of the disk-shaped tool 1
according to the invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-
polishing disk, can be designed with a higher or even a lower
number of different grinding and polishing stages.
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 16
PCT/DE2019/000296
Fig. 3 shows, in a side view of a disk flank 4, a
representation of the layer structure of a particularly
preferred embodiment of the disk-shaped tool 1 according to
the invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-polishing
disk.
In the particularly preferred embodiment shown, a total of 3
layers of grinding and polishing agent 20, 21, 22 are applied
to a base body 2 in an abrasive paper-like form by gluing.
Alternative embodiments of disk-shaped tools 1 according to
the invention, in particular cutting-grinding-polishing disks,
in which the structure of the grinding and polishing agent
layers 20, 21, 22 is realized by means of a different method,
for example by spraying, are conceivable as well.
The dotted regions identify a single layer 30 of a first
grinding layer 20 applied to the base body 2.
The regions alternating with solid and dashed lines identify
two-layer layers 31 of a first grinding layer 20 and a second
grinding layer 21 applied to the base body 2.
The regions shaded with continuous lines identify three-layer
layers 32, consisting of three grinding layers 20, 21, 22.
The increase in the thickness of the grinding and polishing
agent layers from a single layer 30 and a two-layer layer 31
to a three-layer layer 32, with the layers being aligned
parallel to the radial feed direction VR, leads to the
recognizable gradations 40.
The use of the disk will lead to a degradation of the grinding
layers 20, 21, 22. The removal of the layer lying on the
outside in the radial direction, starting at the outer
circumferential region 3, reveals the respective layer
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 17
PCT/DE2019/000296
underneath, so that, both in the axial and in the radial
working direction, the desired sequence of grinding stages one
and two 10, 11, is preserved until the disk-shaped tool 1
according to the invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-
polishing disk, is worn.
Fig. 4 shows a front view, not to scale, of the outer
circumferential region 3 with the cutting edges 5 (not shown),
a base body 2 with the structure of the grinding and polishing
layers 20, 21, 22 of a disk-shaped tool 1 according to the
invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-polishing disk.
The one-layer layers 30, two-layer layers 31 and three-layer
layers 32 of the grinding and polishing agent structure are
clearly shown. The layers 30, 31, 32 are clearly separated
from one another by gradations 40.
The radial feed direction VR and the axial feed direction VA
are illustrated by arrows.
Fig. 5 shows an exploded view of a disk-shaped tool 1
according to the invention, in particular a cutting-grinding-
polishing disk, in a side view of a particularly preferred
embodiment with an optical wear indicator, in particular for
the cutting, grinding and polishing components. The grinding
and polishing agent layers are formed by differently colored
segments. The segments are arranged one above the other and
next to one another on a base body 2 in the axial direction of
the base body 2 in such a way that progressive wear can be
recognized and the remaining useful life can be determined by
using the recognizable color codes 41, 42, 43, 44.
In a particularly preferred embodiment, the grinding and
polishing elements with a color code one 41 form the grinding
and polishing agent layer closest to the base body of the
surfaces of the grinding and polishing stage two 11 described
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 18
PCT/DE2019/000296
in more detail in Fig. 2. The grinding and polishing elements
with the color code one 41 are applied to the base body 2 in
such a way that gaps between the elements promote the
formation of channels 8 in the above grinding and polishing
agent layers 20, 21, 22. In the axial direction of the base
body 2, elements with a color code two 42 and a color code
three 43 are arranged successively on the grinding and
polishing elements with the color code one 41. The progressive
wear of the surfaces of the grinding and polishing stage two
11 can thus be read from the color code one 41, the color code
two 42 and the color code three 43. If the color code one 41
becomes visible, the surfaces of the grinding and polishing
stage two are approaching the wear limit.
A color code four 44 is provided to evaluate the surfaces of
the grinding and polishing stage one 10. If, for example, due
to the radial wear of a base body 2 made of composite
material, the usable surface of grinding stage one decreases,
this decrease can be recognized and assessed by using the
color code four 44. A wear of the surfaces of grinding step
one 10 in an axial direction is recognized by the fact that
instead of the color code four 44, the color of the base body
2 can be seen.
In a particularly preferred embodiment of the disk-shaped tool
1 according to the invention, in particular a cutting-
grinding-polishing disk, the dimensions of the cutting,
grinding, and polishing elements are matched in such a way
that they can be replaced as simultaneously as possible.
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12
CA 03119695 2021-05-12
WO 2020/098852 19
PCT/DE2019/000296
List of reference signs:
1 Disk-shaped tool, especially a cutting-grinding-polishing
disk
2 Base body
3 Outer peripheral region
4 Disk flank
Cutting edge
6 Grinding and polishing surface
7 Fastening opening, especially bore
8 Channel
Surface grinding and polishing stage one
11 Surface grinding and polishing stage two
12 Surface channel
First grinding and polishing agent layer
21 Second grinding and polishing agent layer
22 Third grinding and polishing agent layer
One-layer layer
31 Two-layer layer
32 Three-layer layer
Gradation
41 Color code one
42 Color code two
43 Color code three
44 Color code four
VR Radial feed direction
VA Axial feed direction
D Direction of rotation
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-05-12