Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 1 -
Tobacco constituent releasing components, methods of making
the components and articles comprising the components
Technical Field
The invention relates to tobacco constituent releasing components comprising
tobacco
particles in an agglomerated structure. The invention also relates to tobacco
industry
products including the tobacco constituent releasing components and to methods
of
manufacturing the tobacco constituent releasing components.
io Background
It is known to provide a source of tobacco constituents from which said
tobacco
constituents are released upon heating the source without combustion.
Drawbacks
associated with such sources can include, for example, inadequate control of
the release
of the tobacco constituents, and only a relatively small proportion of the
constituents
is being released during the normal use of the product.
Summary
According to a first aspect of the invention, a tobacco constituent releasing
component
is provided, comprising an agglomerated structure formed from a precursor
20 composition comprising tobacco particles, the release of the tobacco
constituents upon
heating the component without combustion being controlled by adjusting one or
more
of: (i) the surface area to volume ratio of the component; and (ii) the amount
of aerosol
forming agent(s) included.
25 In some embodiments, the one or more aerosol forming agent is included
in an amount
of from about 3% to about 30% by weight of the component, preferably in an
amount of
from about 15% to about 30% by weight of the component.
According to a second aspect of the invention, a tobacco constituent releasing
30 component is provided comprising an agglomerated structure formed from a
precursor
composition comprising tobacco particles and at least 10 % by weight of at
least one
aerosol forming agent, the tobacco constituent releasing component having one
or
more undulating or irregular surfaces and/or channels within the component,
and
wherein the tobacco within the component does not have a basic pH.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538
PCT/GB2020/050085
- 2 -
In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing component has one or
more
inner channels extending through the component.
In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing component has a cross-
sectional shape of a spoked wheel or a star.
In some embodiments, the agglomerated structure is formed by extrusion.
In some embodiments, the aerosol forming agent is one or more selected from
the
io group consisting of glycerol, propylene glycol and glyceryl triacetate.
In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing component is
impregnated
with one or more aerosol forming agents, and/or the tobacco particles are
impregnated
with the one or more aerosol forming agents.
In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing component comprises at
least
50% by weight tobacco particles.
In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing component comprises at
least
80% by weight a combination of tobacco particles and aerosol forming agent.
In some embodiments, the tobacco particles have an average diameter no greater
than
0.5 mm and preferably wherein the tobacco particles have an average particle
size
within the range of about 0.1 to about 0.4 mm.
In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing component has a
generally
rod-shaped external form.
In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing component has a
diameter of
from about 4 mm to about 10 mm, and preferably from about 5 mm to about 8 mm.
In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing component has a length
of
from about 5 mm to about 80 mm, and preferably from about 10 mm to about 25
mm.
In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing component does not have
a
basic pH and/or the precursor composition does not have a basic pH.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 3 -
In some embodiments, the precursor composition does not include a basic pH
adjusting agent.
.. In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing component further
comprises
one or more binders, preferably wherein the one or more binders are selected
from the
group consisting of: starches, polysaccharides, pectins, celluloses, cellulose
derivatives
such as carboxymethylcellulose, and alginates.
In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing component does not
comprise
a binder to assist agglomeration of the tobacco particles.
In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing component further
comprises
one or more flavour-modifying additive.
According to a third aspect of the invention, a process for preparing a
tobacco
constituent releasing component is provided, comprising forming an
agglomerated
structure from a precursor composition comprising tobacco particles, wherein a
desired
release of the tobacco constituents is provided upon heating the component
without
combustion by adjusting one or more of: (i) the surface area to volume ratio
of the
component; and (ii) the amount of aerosol forming agent(s) included.
In some embodiments, the process is for preparing a tobacco constituent
releasing
component according to the first aspect.
According to a fourth aspect of the invention, a process for preparing a
tobacco
constituent releasing component is provided, comprising forming by extrusion
an
agglomerated structure from a precursor composition comprising tobacco
particles and
at least 10 % by weight of at least one aerosol forming agent, the extruded
tobacco
constituent releasing component having one or more undulating or irregular
surfaces
and/or channels within the component, and wherein the process does not include
adjusting the pH of the tobacco within the component to a basic pH.
In some embodiments of the processes, the precursor composition is extruded to
form
the agglomerated structure.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 4 -
In some embodiments of the processes, the precursor composition is extruded
through
a die to provide one or more inner channels extending through the component.
In some embodiments of the processes, the precursor composition is extruded
through
.. a die to provide the component with a cross-sectional shape of a spoked
wheel or a star.
In some embodiments of the processes, the precursor composition is heated to a
temperature of from about 4.0 C to about 120 C.
In some embodiments of the processes, the precursor composition is cooled
during or
after extrusion, preferably wherein the precursor composition is cooled by
exposure to
a surface having a temperature of from about 5 C to about 15 C.
In some embodiments of the processes, the pH of the component and/or of the
/5 precursor composition is not adjusted to a basic pH.
In some embodiments of the processes, the precursor composition does not
include a
basic pH adjusting agent.
.. According to a fifth aspect of the invention, there is provided, in the
preparation of a
tobacco constituent releasing component having an agglomerated structure
formed
from a precursor composition comprising tobacco particles and one or more
aerosol
forming agents, the use of a step of selecting one or more of: (i) the surface
area to
volume ratio of the component; and (ii) the amount of aerosol forming agent(s)
included, to provide the tobacco constituent releasing component with a
desired release
of the tobacco constituents upon heating the component without combustion.
In some embodiments, the use is for preparing a tobacco constituent releasing
component according to the first aspect.
In some embodiments of the use, the surface area to volume ratio of the
component is
increased by forming the agglomerated structure to provide one or more inner
channels
extending through the component.
In some embodiments of the use, the component has a cross-sectional shape of a
spoked wheel or a star.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 5 -
In some embodiments of the use, the pH of the component and/or of the
precursor
composition is not adjusted to a basic pH.
In some embodiments of the use, the precursor composition does not include a
basic
pH adjusting agent.
According to a sixth aspect of the invention, a smoking article comprising a
filter and a
rod of smokeable material is provided, the filter comprising a tobacco
constituent
io releasing component according to the first aspect.
According to a seventh aspect of the invention, a filter or filter element for
a
combustible smoking article is provided, comprising a tobacco constituent
releasing
component, the tobacco constituent releasing component comprising an
agglomerated
/5 .. structure formed by extruding a precursor composition comprising tobacco
particles,
the tobacco constituent releasing component delivering flavour to mainstream
smoke
upon use of the smoking article, wherein the pH of the component and/or of the
precursor composition is not adjusted to a basic pH.
20 In some embodiments, the filter or filter element for a combustible
smoking article
comprises a tobacco constituent releasing component according to the first
aspect.
According to an eighth aspect of the invention, an apparatus for heating
smokeable
material without combustion to volatilise at least one component of the
smokeable
25 material is provided, the smokeable material comprising one or more
tobacco
constituent releasing components according to the first aspect.
In some embodiments, the apparatus further comprises liquid which is to be
heated to
form a vapour, optionally wherein the liquid does not comprise nicotine.
In some embodiments of the apparatus, the smokeable material is heated by the
vapour.
In some embodiments of the apparatus, a means for heating the liquid to form a
vapour
is included, but a separate means for heating the smokeable material is not
included.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 6 -
Brief Description of the Drawings
Embodiments of the invention will now be described, by way of example only,
with
reference to accompanying drawings, in which:
Figure 1 is a flow chart showing key steps of a process according to
embodiments of the
present invention;
Figures 2a, 2b and 2c show examples of nozzle designs for forming extruded
agglomerates having inner channels, whilst Figures 2d and 2e show how such a
die may
be used to shape the extruded agglomerate;
Figure 3 shows a series of extruded agglomerates, showing different cross-
sectional
io geometries forming inner channels;
Figure 4a shows an example of a die used to produce granules by extrusion,
whilst
Figure 4h shows how such a die may be used to form the extruded agglomerates;
Figure 5 is a schematic representation of some extruded granules;
Figure 6 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a tobacco heating product for
heating
/5 smokeable material to volatilise at least one component of the smokeable
material
including a tobacco constituent releasing component;
Figure 7 is a schematic view of a Hybrid device for heating smokeable material
to
volatilise at least one component of the smokeable material including a
tobacco
constituent releasing component; and
20 Figure 8 is a schematic cross-sectional view of an example of a
cartridge containing
multiple tobacco constituent releasing components.
Figure 9 is a schematic side view of a combustible smoking article including a
filter
comprising multiple tobacco constituent releasing components;
Figure lo is a schematic side view of a combustible smoking article including
a filter
25 comprising a single tobacco constituent releasing component; and
Figure 11 is a schematic side view of a combustible smoking article including
a multi-
segment filter wherein one filter segment is a tobacco constituent releasing
component.
Detailed Description
30 The invention relates to tobacco constituent releasing components that
are formed
from tobacco particles. These components are able to release tobacco
constituents
including flavours and nicotine. They may also act as a carrier for other
materials that
are to be released. The tobacco constituent releasing components are suitable
for
incorporation into various tobacco industry products.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 7 -
At least some of the released constituents are directly derived from the
tobacco
particles used to form the components. In some embodiments, further materials
may
be added to the components for release. These further materials may, for
example, also
comprise tobacco constituents added to supplement those directly derived from
the
tobacco particles. Alternatively or in addition, the further materials added
to the
components for release may not be derived from tobacco. For example, the
components may also, in some embodiments, carry and release other flavours,
including those not derived from tobacco.
io Incorporated into a tobacco industry product, the tobacco constituent
releasing
component is able to modify the aerosol produced by said product during use.
The flow
of air or aerosol over and/or through the component, optionally with heating,
causes
the release of materials from the component. The released materials may, in
some
embodiments, include tobacco constituents such as flavours and aromas, as well
as
/5 other tobacco derived materials such as nicotine, and, where included in
the tobacco
constituent releasing component, materials that are not derived from tobacco
or are not
derived from the tobacco particles included in the components.
The released materials become entrained in the air or aerosol, modifying it.
In some
20 embodiments, the flavour, aroma or taste of the aerosol produced by the
tobacco
industry product is modified by the tobacco constituent releasing component.
In some
embodiments, the aerosol is enriched with natural tobacco flavours and aromas.
Additionally or alternatively, the aerosol is modified with non-tobacco
flavours as a
result of flavours or flavour sources being incorporated into the tobacco
constituent
25 releasing components. In further embodiments, the aerosol may be
modified by the
addition of nicotine. In yet further embodiments, the mouthfeel of the aerosol
may be
modified by materials, such as aerosol forming agents, released by the tobacco
component releasing components.
30 The tobacco constituent releasing components are agglomerated structures
formed
from a precursor composition comprising tobacco particles. This means that the
components are a mass or cluster formed by fusing or adhering multiple
particles to
one another. The constituent particles include tobacco particles. In some
embodiments, particles of other materials may also be included.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538
PCT/GB2020/050085
- 8 -
An important aspect of the invention is that the release of materials from the
tobacco
constituent releasing components may be controlled and adapted to the specific
requirements of the tobacco industry product into which it is to be
incorporated. In
particular, it is desirable to control the rate and extent of release. The
release of
materials is key for providing the desired flavour profile during use of the
tobacco
industry product, as well as the desired sensorial experience. In particular,
it may be
desirable to control how quickly the release occurs following commencement of
the use
of the product, the longevity of release and the consistency of release. It is
also
important to ensure that a significant proportion of the materials to be
released
/o contained in the tobacco constituent releasing component is actually
released during
the normal use of the tobacco industry product.
A tobacco constituent releasing component is provided, comprising an
agglomerated
structure formed from a precursor composition comprising tobacco particles,
the
/5 release of the tobacco constituents upon heating the component without
combustion
being controlled by adjusting one or more of: (i) the surface area to volume
ratio of the
component; and (ii) the amount of aerosol forming agent(s) included.
In order to improve release of the tobacco constituents and other materials
from the
20 component during use in a tobacco industry product (where the component
is heated
but not combusted), it is desirable for the component to have a high surface
area to
volume ratio. An increased surface area of the tobacco constituent releasing
component will increase the release of the tobacco constituents and other
materials.
The increased surface area to volume ratio means that more of the tobacco
constituents
25 and other materials will be situated closer to the surface of the
component, so that they
are heated and released more readily, and a greater proportion is released. As
used
herein, an increased surface area or an increased surface area to volume ratio
refers to
in a comparison with the surface area of a solid structure which is roughly
spheroid or
has a cylindrical rod shape or the same volume.
As described in greater detail below, the shape of the tobacco constituent
releasing
components may be selected to increase the surface area to volume ratio, for
example
by increasing the surface area by creating undulating or irregular surfaces or
by
creating channels within the components. It is desirable to reduce the
distance from
the surface of the component of the tobacco constituents and other materials
to be
released, so that as much of these materials may be released during use of the
tobacco
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 9 -
industry product, rather than remaining trapped within the agglomerated
structure.
Increased proximity of the tobacco constituents and other materials to the
surface of
the tobacco constituent releasing component will also mean that the materials
can be
released in a controlled manner as they will be more readily heated and
volatilise when
the component is heated.
The surface area of the tobacco constituent releasing component, and thus the
release
of the tobacco constituents and other materials, may also be increased by the
presence
of pores within the agglomerated structure. Such pores will reduce the density
of the
io agglomerated structure, enhancing thermal transfer throughout the
tobacco constituent
releasing component. In some embodiments, pores may be formed by including
porous
materials in the precursor composition. Selecting larger diameter tobacco
particles
and/or tobacco particles with a narrow particle size distribution can also
enhance the
formation of small gaps or pores within the agglomerated structure.
Alternatively or in
addition, pores may be formed in the agglomerated structure after the
agglomerated
structure has been made from the precursor composition, for example by
puncturing
the structure or by selectively removing part or parts of the agglomerated
structure.
Thus, a combination of the shape of the tobacco constituent releasing
component and
the porosity/density may be selected to control the surface area to volume
ratio and/ or
to control: (i) the heat transfer rate; (ii) the aerosol production rate;
(iii) the amount of
aerosol produced; and (iv) the extent of the release of the tobacco
constituents and
other materials.
The tobacco constituent releasing components according to the invention
include at
least one aerosol forming agent. It is known to use aerosol forming agents to
improve
the mouthfeel of aerosols. The amount of aerosol forming agent that is
included in
tobacco components or materials, such as those included in tobacco heating
products,
tends to be limited as the aerosol forming agents are generally in liquid form
and are
present on the surface of the tobacco material they are added to. As a result,
in practice
the inclusion of more than about 10% by weight of the aerosol forming agent
renders
the material difficult to handle and process.
However, as discussed in greater detail below, embodiments of the present
invention
allow greater amounts of aerosol forming agent to be included. This provides
greater
flexibility in selecting the amount of aerosol forming agent and this may be
used to
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 10 -
control or adjust the release of tobacco constituents and other materials from
the
tobacco constituent releasing components. Release of the aerosol forming agent
in the
form of an aerosol as a result of the heating (but not combustion) of the
tobacco
constituent releasing component not only improves the properties of the
aerosol
generated by the tobacco industry product the component is incorporated into,
but also
enhances the release of tobacco constituents and other materials from the
component.
This is particularly the case where the tobacco and/or the agglomerated
structure is
impregnated with the aerosol forming agent.
io The amount of aerosol forming agent will also influence the rate at
which the aerosol is
generated.
The aerosol forming agent may be, for instance, a polyol aerosol generator or
a non-
polyol aerosol generator, preferably a non-polyol aerosol generator. It may be
a solid or
is liquid at room temperature, but preferably is a liquid at room
temperature. Suitable
polyols include sorbitol, glycerol, and glycols like propylene glycol or
triethylene glycol.
Suitable non-polyols include monohydric alcohols, high boiling point
hydrocarbons,
acids such as lactic acid, and esters such as diacetin, triacetin, triethyl
citrate or
isopropyl myristate. A combination of aerosol forming agents may be used, in
equal or
20 differing proportions. Glycerol, propylene glycol and glyceryl
triacetate (also known as
triacetin) are particularly preferred.
In this invention, the release of the tobacco constituents or other materials
is not
controlled by adjusting the pH of the tobacco and/or the precursor composition
or of
25 the tobacco constituent releasing component. Such pH adjustment can
change the
nature of the constituents and may be undesirable or unacceptable from a
regulatory
standpoint for some products in some jurisdictions.
Tobacco particles
30 The tobacco particles present in the precursor composition have a size
small enough to
ensure that multiple such particles can be agglomerated to form tobacco
constituent
releasing components having desired dimensions based upon their intended use.
Smaller tobacco particles have a greater surface area to volume ratio and they
may
therefore exhibit enhanced release of tobacco constituents compared to
particles of
35 larger sizes.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 11 -
In addition, the size of the tobacco particles (and of other particles in the
precursor
composition) will have an effect on the porosity and density of the
agglomerated
structures and tobacco constituent releasing components. Thus, the size of the
tobacco
particles may be selected to produce a more porous agglomerated structure,
which will
have an impact on the release of the tobacco constituents. Thus, the size of
the tobacco
particles is another factor that may be adjusted in order to influence the
release of
tobacco constituents.
The extrusion processes used to form the agglomerated structures can be
sensitive to
io the size of the particles within the composition being extruded.
Therefore, it may be
desirable for the particles in the precursor composition, including the
tobacco particles,
to have an average particle size of no greater than about 0.5 mm, or to have
an average
particle size of no greater than about 0.3 mm, when measured by sieving. In
some
embodiments, it may be desirable for the tobacco particles in the precursor
/5 composition to have an average particle size of no greater than about
0.5 mm, or to
have an average particle size of no greater than about 0.3 mm, when measured
by
sieving. In some embodiments, the average particle size is within the range of
about 0.1
to about 0.4 mm, or in the range of about 0.2 to about 0.3 mm. In some
embodiments,
at least about 90% of the particles of the precursor composition will have a
particle size
20 within the range of 0.1 to 0.5 mm. In some embodiments, at least about
90% of the
tobacco particles of the precursor composition will have a particle size
within the range
of 0.1 to 0.5 mm. In some embodiments, none of the particles in the precursor
composition have a particle size greater than 1 mm.
25 Tobacco particles for inclusion in the tobacco constituent releasing
components may be
formed by grinding, shredding, cutting or crushing tobacco material. Suitable
machinery to create such tobacco particles includes, for example, shredders,
cutters, or
mills, such as hammer mills, roller mills or other types of commercially
available
milling machinery.
Without wishing to be bound by any one particular theory, it is speculated
that the
chopping of the tobacco to form the tobacco particles enhances the release of
tobacco
constituents including volatile flavours and aromatic constituents, as well as
nicotine.
The increased surface area of the tobacco particles is also thought to aid
volatilisation.
The smaller tobacco particles also improve the homogeneity of agglomerated
structures
formed therefrom together with other components.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538
PCT/GB2020/050085
- 12 -
The tobacco material used to form the tobacco particles may be any type of
tobacco and
any part of the tobacco plant, including tobacco lamina, stem, stalk, ribs,
scraps and
shorts or mixtures of two or more thereof. Suitable tobacco materials include
the
following types: Virginia or flue-cured tobacco, Burley tobacco, Oriental
tobacco, or
blends of tobacco materials, optionally including those listed here. The
tobacco may be
expanded, such as dry-ice expanded tobacco (DIET), or processed by any other
means.
In some embodiments, the tobacco material may be reconstituted tobacco
material.
The tobacco may be pre-processed or unprocessed, and may be, for instance,
solid
io .. stems (SS); shredded dried stems (SDS); steam treated stems (STS); or
any
combination thereof. The tobacco material may be fermented, cured, uncured,
toasted,
or otherwise pre-treated.
Additional components of precursor composition
/5 In some embodiments, the precursor composition comprises a diluent. The
diluent
may be in solid or liquid form. In some embodiments, the diluent is inert or
substantially inert.
In some embodiments, the agglomerated structure formed from the precursor
20 composition may have an increased surface area by including in the
precursor
composition particles of an inert filler material. Suitable inert fillers may
be porous or
non-porous.
In some embodiments, the precursor composition does not include a binder or
binding
25 additive. In other embodiments, the precursor composition comprises a
binder or
binding additive. The binding additive may be selected to assist in the
formation of an
agglomerated structure by helping to adhere the tobacco particles to each
other and to
other components in the composition. Suitable binding additives include, for
example,
starches, polysaccharides, pectins, celluloses, cellulose derivatives such as
30 carboxymethylcellulose, and alginates.
In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing components may include
a
flavour-modifier, to modify the flavour provided by the tobacco particles or
to add
flavour. In some embodiments, the flavour-modifier may be included in the
precursor
35 composition. Alternatively or in addition, the flavour-modifier may be
added to or
applied to the agglomerated structure. Flavour-modifiers include, for example,
casing
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 13 -
materials, as well as "flavour" and "flavourant" materials which, where local
regulations
permit, may be used to create a desired taste or aroma in a product for adult
consumers. They may include extracts (e.g., licorice, hydrangea, Japanese
white bark
magnolia leaf, chamomile, fenugreek, clove, menthol, Japanese mint, aniseed,
cinnamon, herb, wintergreen, cherry, berry, peach, apple, Drambuie, bourbon,
scotch,
whiskey, spearmint, peppermint, lavender, cardamon, celery, cascarilla,
nutmeg,
sandalwood, bergamot, geranium, honey essence, rose oil, vanilla, lemon oil,
orange oil,
cassia, caraway, cognac, jasmine, ylang-ylang, sage, fennel, piment, ginger,
anise,
coriander, coffee, or a mint oil from any species of the genus Mentha),
flavour
enhancers, bitterness receptor site blockers, sensorial receptor site
activators or
stimulators, sugars and/or sugar substitutes (e.g., sucralose, acesulfame
potassium,
aspartame, saccharine, cyclamates, lactose, sucrose, glucose, fructose,
sorbitol, or
mannitol), and other additives such as charcoal, chlorophyll, minerals,
botanicals, or
breath freshening agents. They may be imitation, synthetic or natural
ingredients or
is blends thereof. They may be in any suitable form, for example, oil,
liquid, gel, wax or
powder.
In some embodiments, the pH of the tobacco of the tobacco constituent
releasing
components is not adjusted. In particular, in some embodiments, the component
does
not have a basic pH and/or the precursor composition does not have a basic pH.
Additionally or alternatively, the precursor composition preferably does not
include a
basic pH adjusting agent.
In some embodiments, water may be added to the precursor composition as a
processing aid. For example, the presence of water may help to dissolve
components of
the precursor composition, and/or it may assist with binding or improve
agglomeration.
Forming the agglomerated structures
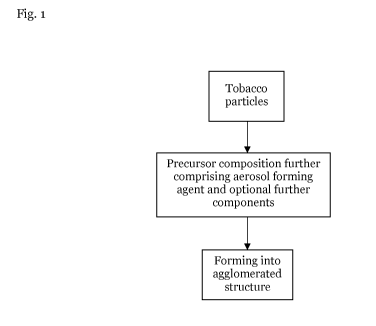
Figure 1 is a flow chart showing the key steps in the processes of the present
invention.
The tobacco starting material, which may be pre-treated or pre-processed, is
provided
in the form of particles having the desired particle size. The tobacco
precursor
composition is formed, comprising the tobacco particles, at least one aerosol
forming
agent and, in some embodiments, may include further additional components.
These
.. additional components may be in liquid form or in solid form. Additional
solid
components are preferably in particulate or powder form. In other embodiments,
the
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538
PCT/GB2020/050085
- 14 -
additional components may be introduced into the agglomerated structure
separate
from the tobacco precursor composition.
In some embodiments, water may be added to the precursor composition as a
processing aid. For example, the presence of water may help to dissolve
components of
the precursor composition, and/or it may assist with binding or improve
agglomeration.
Finally, the precursor composition is formed into an agglomerated structure,
i.e., a
io monolithic structure formed from multiple tobacco particles and the
other components
of the precursor composition. In some embodiments, the agglomerated structure
may
be formed from the precursor composition by a process including one or more
steps
selected from the group consisting of granulation and/or extrusion, and
optionally also
spheronisation.
Granulation of the precursor composition involves the binding or fusing
together of the
particles of the precursor composition to form larger, multi-particle entities
which are
referred to herein as agglomerated structures. The multi-particle entities
formed by
granulation are called granules and they may have various geometric shapes,
including,
for example, the general form of spheres, cylinders, and the like.
In one embodiment, the granulation step used is wet granulation. In wet
granulation,
granules are formed by the addition of a granulation liquid onto a powder bed.
Agitation in the system, along with the wetting of the components within the
precursor
composition, results in the aggregation of the particles to produce wet
granules. The
granulation liquid may be at least partially removed by drying to provide dry
granules.
The granulation liquid may be water-based or solvent-based. Suitable
granulation
liquids include, for example, water, glycerol, ethanol and isopropanol, either
alone or in
combination. In some embodiments, the granulation liquid comprises an aerosol
forming agent, such as glycerol or one of the other agents mentioned herein,
and/or a
binder or binding agent. In some embodiments, no water is added to the
precursor
composition to aid granulation.
In another embodiment, the granulation step used is dry granulation. In dry
granulation, granules are formed without using a granulation liquid. This type
of
process has the advantage that it does not expose the precursor composition to
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 15 -
moisture and so there is no requirement to expose the granules to heat in
order to dry
them. Forming granules by dry granulation involves compacting and densifying
the
precursor composition, usually under high pressure.
Extrusion of the precursor composition involves the feeding of the precursor
composition through an orifice to produce an extruded agglomerate. The
process,
which applies pressure to the precursor composition combined with shear
forces,
results in agglomerated structures.
io Extrusion may be performed using one of the main classes of extruders:
screw, sieve
and basket, roll, and ram extruders. Forming the tobacco constituent releasing
components by extrusion has the advantage that this processing combines
mixing,
conditioning, homogenizing and moulding of the precursor composition.
In some embodiments, during extrusion the free-flowing precursor composition
is
exposed to elevated pressure and temperature and is forced though an orifice,
such as a
shaping die, to form an extruded agglomerate. In some embodiments, the
extruded
agglomerate has an elongated form and/or it may be cut into segments of a
desired
length as it exits the orifice. A rod-like extruded agglomerate may
subsequently be cut
into segments of desired length.
In some embodiments, the precursor composition comprising tobacco particles is
exposed to temperatures from about 4.0 C to about i5o C, or from about 80 C to
about
130 C within the extruder. The composition may be exposed to pressures ranging
from
about 2 bar to about loo bar, or from about 5 bar to about 60 bar, depending
on the
design of the die being used.
In some embodiments, due to the relatively high density of the extruded
agglomerate
and the relatively open surface of the tobacco particles within it, the
tobacco constituent
releasing components formed from the extruded agglomerate exhibit good heat
transfer
and mass transfer, which has a positive impact on the release of tobacco
constituents,
such as flavours and nicotine.
In some embodiments, the extrusion may be a generally dry process, with the
precursor
composition being a substantially dry material that includes tobacco
particles, as well
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 16 -
as optionally other particulate materials including, for example, base,
diluent, solid
flavour modifiers, etc.
In some embodiments, liquids may be added to the precursor composition during
the
extrusion process. For example, water may be added to the precursor
composition, for
example as a processing aid to assist dissolution or solubilisation of
components of the
composition, or to aid binding or agglomeration. Alternatively or
additionally, a
wetting agent may be added to the precursor composition.
In some embodiments, the liquid may be an aerosol forming agent such as
glycerol or
others discussed herein. When liquid is added to the precursor composition in
this
manner, the liquid is applied not only on the surface, but, as a result of the
extruder
pressure combined with the intensive mixing by high shear forces, the extruded
agglomerate becomes impregnated with the liquid. Where the liquid is an
aerosol
/5 forming agent, this can result in a high availability of the aerosol
forming agent in the
agglomerated product to enhance evaporation of flavour components from the
tobacco
particles and other components of the agglomerated structure, enhancing
release of
tobacco constituents from the resultant extruded tobacco constituent releasing
components.
In some embodiments, in view of the impregnation of the extruded agglomerate
with
the aerosol forming agent, greater volumes of this agent can be incorporated
into the
tobacco constituent releasing component than if the aerosol forming agent were
simply
being applied to the surface of the precursor composition or of the extruded
agglomerate. In some embodiments, the amount of aerosol forming agent
incorporated
into the tobacco constituent releasing component may be at least about 3% by
weight,
at least about 4%, 5%, 6%, 7%, 8%, 9%, 10%, 11%, 12%, 13%, 14%, 15%, 16%, 17%,
18%,
19% by weight, or at least about 20% by weight. In some embodiments, the
amount of
aerosol forming agent incorporated into the tobacco constituent releasing
component
may be up to about 15%, up to about 16%, 17%, 18%, 19%, 20%, 21%, 22%, 23%,
24%,
25%, 26%, 27%, 28%, 29% by weight or up to about 30% by weight.
In some embodiments, the one or more aerosol forming agent is included in an
amount
of from about 3% to about 30% by weight of the component, preferably in an
amount of
from about 15% to about 30% by weight of the component.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 17 -
The extruded agglomerate will be shaped by the orifice or die through which it
is forced.
In some embodiments, the extruded agglomerate is cut into pieces of desired
length.
The pieces formed in this way may be used as tobacco constituent releasing
components or they may undergo further processing.
In some embodiments, the orifice or die is shaped to provide a solid strand of
extruded
agglomerate. For example, the extruded agglomerate may have the form of a
solid
cylindrical rod. Alternatively, the extruded agglomerate may have different
cross-
sectional shapes, including oval, polygonal (such as triangular, square,
etc.), and stars.
In some embodiments, the extruded composition is formed into a desired shape
selected to enhance or promote the release of flavour, for example by
providing a form
having a large surface area per unit volume. This large surface area may be
provided on
the outer surface of the extruded agglomerate, for example by selecting cross-
sectional
is shapes with large perimeter. Alternatively or in addition, the large
surface area may be
provided through the creation of channels within the extruded agglomerate.
In some embodiments, the orifice or die is shaped to provide an extruded
agglomerate
with inner channels. These inner channels provide further surface area and can
enhance tobacco constituent release.
Examples of some nozzle or die designs are shown in Figures 2a, 2b and 2c.
These
nozzles or dies have orifices 21 through which the extruded composition is
forced to
produce an extruded agglomerate with a cartwheel-like spoked structure. These
nozzles or dies are used in an extruder, as shown in Figures 2d and 2e, in
which the
direction of the flow of the material being extruded is indicated by the arrow
A.
Figure 3 is an image of a series of extruded agglomerates, showing different
cross-
sectional geometries including inner channels. Some of these extruded
agglomerates
have been made using the nozzle designs of Figures 2a, 2b and 2c.
Tobacco constituent releasing components formed from such shaped extruded
agglomerate sections have an inner channel structure which has advantageous
adjustable strand ventilation properties and a significantly enlarged inner
surface
leading to improved heat and mass transfer. As a result, such components
exhibit
better, more uniform release of flavour by evaporation. Furthermore, the
structure
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 18 -
with inner channels exhibits significantly improved strength in both the
radial and axial
directions, which is beneficial for the further processing of the extruded
agglomerate,
for example when it is cut into segments.
In some embodiments, the diameter of the tobacco constituent releasing
component is
from about 4 mm to about 10 mm, or the diameter may be from about 5 mm to
about 8
mm.
In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing component is a
cylindrical
io tobacco segment. In some embodiments the cylinder has a diameter of from
about 5
mm to about 8 mm and a length of from about 5 mm to about 80 mm, from about 15
mm to about 50 mm, or from about 20 mm to about 30 mm.
By means of various nozzle designs and/or different process parameters within
the
extruder, including the temperature, pressure and shear forces, extruded
agglomerates
with different physical properties may be prepared, including different heat
transfer
properties, draft resistance, and capable of producing different aerosols
and/or of
modifying aerosols being drawn through the extruded agglomerate.
The make up of the precursor composition can also play a very significant role
in
determining the physical and mechanical properties of the extruded material
and, as a
consequence, of the tobacco constituent releasing components.
In some embodiments, the extruded agglomerate is shaped upon discharge from
the
extruder. In some embodiments, the extruded agglomerate is cut to an initial
length,
for example, 1 metre, and allowed to cool before then being cut into sections
of the
desired length to provide tobacco constituent releasing components of the
desired
dimensions.
In some embodiments, the extruded agglomerate may be cooled just before or
just as it
leaves the extruder. In some embodiments, the cooling is intensive and
involves
exposing the extruded agglomerate, which will be at an elevated temperature,
for
example from about 30 C to about 100 C, or from about 40 C to about 70 C, to a
cooling means that will reduce the temperature to within a range of from about
0 C to
about 25 C, or from 5 C to about 15 C. This rapid cooling of the extruded
agglomerate
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538
PCT/GB2020/050085
- 19 -
may enhance the internal and external stability of the extruded agglomerate.
In some
embodiments, it is the die that is cooled to achieve this effect.
In some embodiments, it may be desirable to control the temperature of the
precursor
composition during extrusion, including before feeding the composition through
the
die. This is especially the case where the precursor composition includes
temperature
sensitive components, such as aerosol forming agents such as glycerol. Thus,
in some
embodiments, extrusion of the precursor composition includes reducing the
temperature of the precursor composition before it reaches the die. Such
cooling of the
/o precursor composition may result in the formation of an extruded
agglomerate with
beneficial properties, or may improve the strand-shaping process, for example
where
channels are to be formed within the extruded agglomerate strand.
In some embodiments, the precursor composition may be granulated prior to
/5 .. extrusion. Where the precursor composition includes multiple different
types of
particles, this granulation step can enhance homogenisation within the
extruded
agglomerate. The granulated precursor composition may be fed into an extruder
to
form the tobacco constituent releasing components.
20 Granulation of the precursor composition involves the binding or fusing
together of the
particles of the precursor composition to form larger, multi-particle entities
which are
agglomerated structures. The multi-particle entities formed by granulation are
called
granules and they may have various geometric shapes, including, for example,
the
general form of spheres, cylinders, and the like.
In one embodiment, the granulation step used is wet granulation. In wet
granulation,
granules are formed by the addition of a granulation liquid onto a powder bed.
Agitation in the system, along with the wetting of the components within the
precursor
composition, results in the aggregation of the particles to produce wet
granules. The
.. granulation liquid may be at least partially removed by drying to provide
dry granules.
The granulation liquid may be water-based or solvent-based. Suitable
granulation
liquids include, for example, water, ethanol and isopropanol, either alone or
in
combination. In some embodiments, the granulation liquid comprises an aerosol
forming agent, such as glycerol.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538
PCT/GB2020/050085
-20 -
In another embodiment, the granulation step used is dry granulation. In dry
granulation, granules are formed without using a granulation liquid. This type
of
process has the advantage that it does not expose the precursor composition to
moisture and so there is no requirement to expose the granules to heat in
order to dry
them. Forming granules by dry granulation involves compacting and densifying
the
precursor composition, usually under high pressure.
In some embodiments, spheronisation is used to further process extruded
segments.
These segments are typically cylindrically-shaped and are cut or broken into
uniform
/o lengths following extrusion. They are then gradually transformed into
spherical shapes
by spheronisation. This shaping occurs as a result of plastic deformation and
spheronisation can lead to spherical agglomerated structures, often with a
nearly
uniform diameter.
/5 Incorporation into a product
A tobacco industry product refers to any item made in, or sold by the tobacco
industry,
typically including a) cigarettes, cigarillos, cigars, tobacco for pipes or
for roll-your-own
cigarettes, (whether based on tobacco, tobacco derivatives, expanded tobacco,
reconstituted tobacco or tobacco substitutes); b) non-smoking products
incorporating
20 tobacco, tobacco derivatives, expanded tobacco, reconstituted tobacco or
tobacco
substitutes such as snuff, snus, hard tobacco, and heat-not-burn (HnB)
products; and
c) other nicotine-delivery systems such as inhalers, aerosol generation
devices
including e-cigarettes, lozenges and gum. This list is not intended to be
exclusive, but
merely illustrates a range of products which are made and sold in the tobacco
industry.
One or more of the tobacco constituent releasing components disclosed herein
may be
incorporated into an aerosol provision device. As used herein, an aerosol
provision
device includes vapour devices such as e-cigarettes, devices for heating
smokeable
material such as tobacco heating devices and Hybrid devices.
As used herein, the apparatus for heating smokeable material to volatilise at
least one
component of the smokeable material includes so-called "heat not burn"
products or
tobacco heating devices or products, which release compounds by heating, but
not
burning, smokeable material.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 21 -
Hybrid devices are devices in which a liquid, such as a nicotine-containing
liquid or a
nicotine-free liquid, is heated to form an aerosol and this aerosol is then
drawn through
a smokeable material, such as a tobacco segment, picking up tobacco flavours
or
wherein a separate aerosol is formed by heating a smokeable material. In some
embodiments, the device includes a means for heating the smokeable material
directly,
in addition to, or as an alternative to, the heating of the smokeable material
by the
aerosol formed by heating the liquid to form an aerosol.
The tobacco constituent releasing component may be positioned within an
apparatus or
/o device so that the tobacco constituents that are released become
entrained in an aerosol
generated by the apparatus or device upon use, modifying the properties of the
aerosol,
for example by imparting tobacco constituents, including tobacco flavour, to
that
aerosol. Additionally or alternatively, the tobacco constituent releasing
component
may itself generate an aerosol during use, said aerosol including the released
tobacco
/5 constituents.
In some embodiments, an apparatus or device may be provided with a filter
having
tobacco constituent releasing component located within said filter. This may
be in
addition to or instead of the apparatus or device including other tobacco
constituent
20 releasing components.
In some embodiments the filter or filter element may comprise a filter
material which
has a filtering effect. Suitable filter material may include, for example, tow
comprising
or consisting of cellulose acetate, polylactic acid, and/or other suitable
polymers, or the
25 filter or filter element may comprise a hard material such as plastic
with holes.
In some embodiments where multiple tobacco constituent releasing components
are
incorporated into a filter, this may be in a "Dalmatian" style filter section,
where the
tobacco constituent releasing components are dispersed throughout a fibrous
filter plug
30 material. Alternatively, the tobacco constituent releasing components
may be located
in a cavity within the filter. The cavity may, for example, be a cavity
section positioned
between two (or more) adjacent filter plugs or the cavity may be a pocket
defined within
a filter plug. In such embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing
components may
be small in size, for example in the form of granules.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 22 -
In other embodiments, a larger, single tobacco constituent releasing component
is
incorporated into a filter. For example, a single tobacco constituent
releasing
component may be embedded in a fibrous filter plug material.
Alternatively, the tobacco constituent releasing component may be incorporated
into a
multi-segment filter, the tobacco constituent releasing component itself
making up one
of the filter segments. In such embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing
component may have any shape or size, but it may be advantageous for the
component
to a have a cylindrical shape and the dimensions similar to or compatible with
those of
io the filter segments. In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent
releasing
component may be surrounded by filter material such as a layer of fibrous
filter tow, to
form a filter segment. In other embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing
component may have the dimensions of a filter plug and it may be incorporated
into a
filter with one or more adjacent filter plugs. Alternatively, a tobacco
constituent
/5 releasing component may be included in a cavity section positioned
between two (or
more) adjacent filter plugs.
In some embodiments the tobacco constituent releasing component itself may be
the
filter element in the aerosol provision device, it being capable of filtering
condensates
20 and other particulate matter in the aerosol, before the aerosol is
inhaled by the user.
According to some embodiments, one or more tobacco constituent releasing
components are included in an aerosol provision device or apparatus for
heating
smokeable material to volatilise at least one component of the smokeable
material in
25 which a tobacco segment is heated but not combusted (i.e., a tobacco
heating product
or so-called Heat-not-Burn product). In some of these products, the tobacco
segment is
heated to generate an aerosol.
One option is to incorporate the one or more tobacco constituent releasing
components
30 in the filter of such products. In some embodiments, multiple tobacco
constituent
releasing components are incorporated into the filter of a tobacco heating
product. In
other embodiments, a single tobacco constituent releasing component is
incorporated
into the filter of a tobacco heating product.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538
PCT/GB2020/050085
- 23 -
Another option is to incorporate one or more tobacco constituent releasing
components
in the tobacco segment of such products. In some embodiments, one or more
tobacco
constituent releasing components may be incorporated into tobacco material to
form
the tobacco segment. For example, the one or more tobacco constituent
releasing
components may be dispersed within the tobacco material, such as cut tobacco
or
reconstituted tobacco, to contribute to the flavour imparted by the tobacco.
In other
embodiments, the tobacco included in the tobacco segment of the tobacco
heating
product consists or consists essentially of one or more tobacco constituent
releasing
components. In one embodiment, the tobacco segment heated by the tobacco
heating
/o product consists of or consists essentially of one or more tobacco
constituent releasing
component. The tobacco constituent releasing component may be heated directly.
Where the tobacco segment is multiple tobacco constituent releasing
components,
these may be held in a container or cartridge. At least portions of the
container or
cartridge may be permeable to air, to allow air to flow over or through the
tobacco
is .. constituent releasing components.
Figure 6 shows a cross-sectional view of an example of a tobacco heating
product for
heating a smokeable material. The apparatus ii has a heating chamber 14 which
in use
contains the smokeable material to be heated and volatilised. In this
embodiment, the
20 smokeable material is in the form of a monolithic tobacco constituent
releasing
component 13. The smokeable material could however be multiple tobacco
constituent
releasing components held in the heating chamber or provided in a cartridge
like the
one illustrated in Figure 8.
25 The apparatus ii of Figure 6 further has an electronics/power chamber 16
which may,
for example, contain electrical control circuitry and/or a power source (not
shown).
The electrical control circuitry may include a controller, such as a
microprocessor
arrangement, configured and arranged to control the heating of the smokeable
material
via a heating element (not shown). The electrical control circuitry may in use
receive a
30 signal from for example a puff-actuated sensor which is sensitive to for
example
changes in pressure or changes in rate of air flow that occur upon initiation
of a draw
on the apparatus 11 by a user. The electrical control circuitry can then
operate so as to
cause heating of the smokeable material "on demand". Various arrangements for
a
puff-actuated sensor are available, including for example a thermistor, an
electro-
mechanical device, a mechanical device, an optical device, an opto-mechanical
device
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 24 -
and a micro electro mechanical systems (MEMS) based sensor. As an alternative,
the
apparatus may have a manually operable switch for a user to initiate a puff.
The heating chamber 14 is contained within the housing 12. There may be a
support
and/or insulating means (not shown) positioned between the heating chamber 14
and
the housing 12, for example to assist in heat-insulating the housing 12 from
the heating
chamber 14, so that the housing 12 does not become hot or at least too hot to
touch
during use.
io The housing 12 includes an inlet 15 through which air is drawn into the
apparatus. The
housing 12 also includes an outlet 17 at a mouthpiece 18 of the apparatus 11.
Air is
drawn into the apparatus 11 through the inlet 15, travels through the
apparatus picking
up tobacco constituents released by the tobacco constituent releasing
component 13,
and the resulting aerosol generated by the apparatus 11 leaves the apparatus
11 through
is the outlet 19 and is inhaled by the user.
According to some embodiments, one or more tobacco constituent releasing
components are included in a so-called Hybrid product for heating smokeable
material
to volatilise at least one component of a smokeable material. In some of these
20 products, the tobacco segment is heated to generate an aerosol, in
addition to the
heating of a liquid, such as a nicotine-containing liquid or a nicotine-free
liquid, which
is heated by a heat source to form an aerosol or vapour. In some Hybrid
products, the
aerosol or vapour formed from the liquid is drawn over or through the tobacco
segment, picking up tobacco flavours. In other embodiments, the aerosol or
vapour
25 formed from the liquid is not drawn over or through the tobacco segment.
In Hybrid products that include a filter, one option is to incorporate the
tobacco
constituent releasing components in the filter of such products, in a similar
manner to
that described for tobacco heating products. In some embodiments, multiple
tobacco
30 constituent releasing components are incorporated into the filter of a
Hybrid product.
In other embodiments, a single tobacco constituent releasing component is
incorporated into the filter of a Hybrid product.
Where the smoking article is a so-called Hybrid product another option is to
35 incorporate the tobacco constituent releasing components in the tobacco
segment of
such products. In some embodiments, one or more tobacco constituent releasing
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538
PCT/GB2020/050085
- 25 -
components may be incorporated into tobacco material to form the tobacco
segment.
For example, the one or more tobacco constituent releasing components may be
dispersed within the tobacco material, such as cut tobacco or reconstituted
tobacco, to
contribute to the flavour imparted by the tobacco. In other embodiments, the
tobacco
included in the tobacco segment of the Hybrid product consists of one or more
tobacco
constituent releasing components. In one embodiment, the tobacco segment in
the
Hybrid product consists of or consists essentially of one or more tobacco
constituent
releasing components.
io Figure 7 shows a cross-sectional view of an example of a Hybrid product
for heating a
smokeable material and a liquid. The apparatus 21 has a housing 22 containing
a
chamber 24 which in use contains the smokeable material to be heated and
volatilised.
In this embodiment, the smokeable material is in the form of a monolithic
tobacco
constituent releasing component 23. The smokeable material could however be
/5 multiple tobacco constituent releasing components held in the chamber or
provided in
a cartridge like the one illustrated in Figure 8. The housing 22 also contains
a liquid
reservoir 25 containing a liquid 26 to be heated to form a vapour.
The apparatus 21 further has an electronics/power chamber 27 which may, for
20 example, contain electrical control circuitry and/or a power source (not
shown). The
electrical control circuitry may include a controller, such as a
microprocessor
arrangement, configured and arranged to control the heating of the smokeable
material
and of the liquid 26 via one or more heating elements (not shown). The
electrical
control circuitry may allow the apparatus 21 to be puff-actuated, so as to
cause heating
25 of the smokeable material "on demand". As an alternative, the apparatus
22 may have
a manually operable switch for a user to initiate a puff.
The housing 22 also includes an inlet 28 through which air is drawn into the
apparatus. The housing 22 also includes an outlet 29 at a mouthpiece 30 of the
30 apparatus 21. Air is drawn into the apparatus 21 through the inlet 28,
travels through
the apparatus picking up the vapour created by heating the liquid 26 in the
liquid
reservoir 25, and tobacco constituents released by the tobacco constituent
releasing
component 23, and the resulting aerosol generated by the apparatus 21 leaves
the
apparatus 21 through the outlet 29 and is inhaled by the user.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 26 -
The Hybrid device 21 shown schematically in Figure 7 represents just one
possible
configuration of such an apparatus. The relative positions of the liquid
reservoir 25
and the smokeable material chamber 24 can be changed, as can the path of the
air
flowing through the apparatus.
In one embodiment, the liquid reservoir is positioned upstream of the
smokeable
material to be volatilised. Alternatively, the liquid reservoir may be
positioned
downstream of the smokeable material to be volatilised. In a yet further
arrangement,
the two sources of aerosol in the apparatus may be arranged side-by-side, etc.
In some embodiments, the vapour produced by heating the liquid in the liquid
reservoir
flows over or through the smokeable material comprising or consisting of one
or more
tobacco constituent releasing components. In some embodiments, the elevated
temperature of the vapour causes the tobacco constituents to be released.
Alternatively
/5 or in addition, the smokeable material may be separately heated by a
heating means.
In some embodiments, a Hybrid device is provided in which the vapour created
by
heating a liquid heats the smokeable material in order to volatilise at least
one
component of the smokeable material. In some embodiments, the liquid is a
nicotine-
free liquid. In other embodiments, the liquid contains nicotine. Where the
smokeable
material is heated by the vapour to volatilise at least one component of the
smokeable
material, in certain embodiments the device does not include a separate means
for
heating the smokeable material. The smokeable material may comprise or consist
of at
least one tobacco constituent releasing component.
In other embodiments, the vapour produced by heating the liquid in the liquid
reservoir does not flows over or through the smokeable material comprising or
consisting of one or more tobacco constituent releasing components. Rather,
this
vapour and the aerosol generated by heating the smokeable material only mix
after they
are both formed.
The tobacco heating products and Hybrid products described herein may, in some
embodiments, include tobacco segments in the form of containers or cartridges
containing one or more tobacco constituent releasing components. These
containers or
cartridges may be removable. They may replace both the chamber holding the
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 27 -
smokeable material and the smokeable material in the apparatus described above
with
reference to Figures 6 and 7, and in the alternative embodiments discussed.
Referring to Figure 8, a tobacco segment cartridge 31 is shown, comprising a
housing
32 defining a cavity within which are held one or more tobacco constituent
releasing
components according to the invention (not shown). The housing 32 may, for
example
be made from moulded plastic or the like. In order to allow air drawn through
the
device to pass into the cartridge 31 and over or through the one or more
tobacco
constituent releasing components and then out of the cartridge 31, ventilation
holes 33
io are provided in the housing 32 of the cartridge 31. In some embodiments,
the
cartridge 31 may further comprise heating means that is heatable by a suitable
means
in order to heat the one or more tobacco constituent releasing components held
therein.
In some embodiments, one or more tobacco constituent releasing components are
incorporated into a filter or a filter element for inclusion in a combustible
smoking
article.
As used herein, the term "combustible smoking article" includes smokeable
products
such as cigarettes, cigars and cigarillos whether based on tobacco, tobacco
derivatives,
expanded tobacco, reconstituted tobacco or tobacco substitutes. The
combustible
smoking articles include a rod of smokeable material and a filter comprising
at least
one filter element.
As used herein, the term "combustible smoking article" does not include Heat-
not-Burn
(HnB) products, or other nicotine delivery products such as aerosol generation
devices
including e-cigarettes or Hybrid products.
The tobacco constituent releasing component may be positioned within the
filter or
within a filter element making up the filter of the combustible smoking
article, so that
the released tobacco constituents become entrained in an aerosol generated by
the
smoking article upon use, modifying the properties of the aerosol, for example
by
imparting tobacco constituents, including tobacco flavour, to that aerosol.
Filters and filter elements for use in combustible smoking articles include
filter
material to remove certain smoke constituents from the mainstream smoke drawn
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 28 -
through the smoking article during use. The filter material is gathered
together to form
a rod which is cut to form individual filter segments. The filter for a
smoking article
may be made of one segment of filter rod, or may be made from multiple filter
elements, with or without a cavity or spaces between them. A widely used
filter material
is a continuous tow of filamentary cellulose acetate plasticised with
triacetin. Other
filter materials can comprise at least one material selected from polyvinyl
alcohol
(PVOH), polylactic acid (PLA), poly(c-caprolactone)(PCL), poly(1-4 butanediol
succinate)(PBS), poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)(PBAT), starch based
materials, paper, aliphatic polyester materials and polysaccharide polymers in
the form
io of sheets or fibres.
The filter can have a cylindrical shape and generally have a length and an
overall
circumference to suit the type of combustible smoking articles they are to be
used in.
Smoking articles such as cigarettes and their formats are often named
according to the
is cigarette length: "regular" (typically in the range 68-75 mm, e.g. from
about 68 mm to
about 72 mm), "short" or "mini" (68 mm or less), "king-size" (typically in the
range 75-
91 mm, e.g. from about 79 mm to about 88 mm), "long" or "super-king"
(typically in the
range 91-105 mm, e.g. from about 94 mm to about 101 mm) and "ultra-long"
(typically
in the range from about no mm to about 1211111-11).
They are also named according to the cigarette circumference: "regular" (about
23-25
mm), "wide" (greater than 25 mm), "slim" (about 22-23 mm), "demi-slim" (about
19-22
mm), "super-slim" (about 16-19 mm), and "micro-slim" (less than about 16 mm).
Accordingly, a cigarette in a king-size, super-slim format will, for example,
have a
length of about 83 mm and a circumference of about 17 mm. Cigarettes in the
regular,
king-size format have a circumference of from 23 to 25 mm and an overall
length of
from 75 to 91 mm.
Each format may be produced with filters of different lengths, smaller filters
being
.. generally used in formats of smaller lengths and circumferences. Typically
the filter
length will be from 15 mm, associated with short, regular formats, to 30 mm,
associated
with ultra-long super-slim formats. The tipping paper will have a greater
length than
the filter, for example from 3 to 10 mm longer.
Positioned within the filter of a combustible smoking article, the tobacco
constituent
releasing components of this invention are not exposed to significant
temperature
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538 PCT/GB2020/050085
- 29 -
increases during use of the smoking article. That said, the temperature within
the filter
of a conventional cigarette does gradually increase during use. In a
conventional
combustible smoking article, such as a cigarette, and under normal smoking
conditions, such as the ISO smoking regime, the smoking may involve 8-9 puffs
and the
first 5-6 puffs are accompanied by only slight increases in temperature during
the puffs.
For example, the first puffs may be accompanied by a temporary increase in
temperature of in the region of 1-5 C, with the temperature remaining between
20 and
30 C, and in some cases, between 23 and 26 C. During the final few puffs of a
conventional combustible smoking article, such as a cigarette, the temperature
starts to
io increase more during the puffs, with peaks starting to exceed 30 C, and
exceeding 60 C
for the penultimate and last puffs.
This temperature change may be used to trigger or assist the release of
materials from
the tobacco constituent releasing component during use of the smoking article.
For
.. example, the rise in temperature may help to volatilise remaining
components which
have not been released during the first few puffs. Alternatively or in
addition, materials
may be included in the tobacco constituent releasing component specifically to
be
released or to enhance release of tobacco constituents at these elevated
temperatures.
According to some embodiments, multiple tobacco constituent releasing
components
are incorporated into the filter element for a combustible smoking article. In
other
embodiments, a single tobacco constituent releasing component is incorporated
into
the filter element.
Where multiple tobacco constituent releasing components are incorporated into
a filter,
this may be in a "Dalmatian" style filter section, where the tobacco
constituent releasing
components are dispersed throughout a fibrous filter plug material.
Such an arrangement is shown in Figure 9. Referring to Figure 9, a smoking
article 21
comprises a filter 22 and a cylindrical rod of smokeable material 23, such as
tobacco,
aligned with the filter 22 such that one end of the smokeable material rod 23
abuts the
end of the filter 22. The filter 22 is wrapped in a plug wrap (not shown) and
the
smokeable material rod 23 is joined to the filter 22 by tipping paper in a
conventional
manner. The filter 22 is substantially cylindrical and comprises filter
material 24
throughout which are dispersed tobacco constituent releasing components 25.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538
PCT/GB2020/050085
- 30 -
Alternatively, the tobacco constituent releasing components may be located in
a cavity
within the filter. The cavity may, for example, be a cavity section positioned
between
two (or more) adjacent filter plugs or the cavity may be a pocket defined
within a filter
plug. In such embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing components may be
small in size, for example in the form of granules.
In other embodiments, larger, monolithic tobacco constituent releasing
components
are incorporated into a filter. For example, a single tobacco constituent
releasing
component may be embedded in a fibrous filter plug material.
Such an arrangement is shown in Figure 10, which shows a smoking article 21
comprising a filter 22 and a cylindrical rod of smokeable material 23, wherein
the filter
22 comprises a tobacco constituent releasing component 26 which is surrounded
by
filter material 24.
Alternatively, the tobacco constituent releasing component may be incorporated
into a
multi-segment filter, the tobacco constituent releasing component itself
making up one
of the filter segments. In such embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing
component may have any shape or size, but it may be advantageous for the
component
to a have a cylindrical shape and the dimensions similar to or compatible with
those of
the filter segments. In some embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing
component may be surrounded by filter material such as a layer of fibrous
filter tow, to
form a filter segment. In other embodiments, the tobacco constituent releasing
component may have the dimensions of a filter plug and it may be incorporated
into a
filter with one or more adjacent filter plugs. Alternatively, a tobacco
constituent
releasing component may be included in a cavity section positioned between two
(or
more) adjacent filter plugs.
Referring to Figure 11, a smoking article 21 comprises a filter 22 and a
cylindrical rod
.. of smokeable material 23, wherein the filter 22 is made up of multiple
filter segments.
There is a filter segment 27 positioned at the mouth end of the filter and a
filter
segment 28 positioned at the tobacco rod end of the filter. Positioned between
these
filter segments, which comprise filter material 24, is a tobacco constituent
releasing
component 26.
CA 03126746 2021-07-14
WO 2020/148538
PCT/GB2020/050085
- 31 -
The filters and filter elements of the present invention may, in some
embodiments,
further comprise additives. For example, the additive may be particles of
adsorbent
material, including, for example, activated carbon, an ion exchange resin,
such as
CR20, zeolite, silica gel, meerschaum, aluminium oxide (activated or not),
carbonaceous resin, magnesium silicate, including Sepiolite
(Mg4Si6015(OH)2.6H20)
and combinations thereof.
Where the smoking article filter comprises an adsorbent, in some embodiments
the
tobacco constituent releasing component is positioned downstream of the
adsorbent.
In order to address various issues and advance the art, the entirety of this
disclosure
shows by way of illustration various embodiments in which the claimed
invention(s)
may be practiced and provide for superior tobacco constituent releasing
components
and tobacco industry products including the same. The advantages and features
of the
/5 disclosure are of a representative sample of embodiments only, and are
not exhaustive
and/or exclusive. They are presented only to assist in understanding and teach
the
claimed features. It is to be understood that advantages, embodiments,
examples,
functions, features, structures, and/or other aspects of the disclosure are
not to be
considered limitations on the disclosure as defined by the claims or
limitations on
equivalents to the claims, and that other embodiments may be utilised and
modifications may be made without departing from the scope and/or spirit of
the
disclosure. Various embodiments may suitably comprise, consist of, or consist
essentially of, various combinations of the disclosed elements, components,
features,
parts, steps, means, etc. In addition, the disclosure includes other
inventions not
presently claimed, but which may be claimed in future.