Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
SHOCK-ABSORBING HELMET
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to protective headgear, and more particularly to
a shock-absorbing
helmet.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Helmets are used by athletes in many sports as well as by people in other
applications to protect
the head of the wearer from injuries and, in particular, from injuries caused
by concussive
impacts. The helmets protect the brain by reducing impact loading and
accelerations experienced
by the wearer's head. Particularly, in sports such as, for example, hockey,
football, cycling, ski
racing, and motor racing, significant concussive impacts can be encountered
and with the
increasing awareness of the significant injuries that are caused by concussive
impacts there is an
increasing need for a helmet design that is capable of substantially reducing
the risk of injury
when experiencing concussive impacts.
Shock reducing helmet designs and materials employed, intended to protect a
wearers head from
shock-based injuries and concussions, are well known in the art. Materials and
the geometry of
Page 1
Date recue / Date received 2021-11-02
the various components of a helmet can be adjusted to mitigate the concussive
impact
experienced by the wearer's head.
Unfortunately, present-day helmet designs and materials employed require
substantial quantities
of shock absorbing material in order to provide sufficient protection. The
employment of large
quantities of shock absorbing material results in large helmets having a
considerable weight,
substantially impeding the wearer's movements when practicing a sport such as,
for example,
hockey, football, cycling, and racing.
It is desirable to provide a shock-absorbing helmet that substantially reduces
concussive impacts
on a wearer's head.
It is also desirable to provide a shock-absorbing helmet that substantially
reduces concussive
impacts on a wearer's head and does not impede the wearer's movements.
It is also desirable to provide a shock-absorbing helmet that is compact in
size and light weight.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
Accordingly, one object of the present invention is to provide a shock-
absorbing helmet that
substantially reduces concussive impacts on a wearer's head.
Page 2
Date recue / Date received 2021-11-02
Another object of the present invention is to provide a shock-absorbing helmet
that substantially
reduces concussive impacts on a wearer's head and does not impede the wearer's
movements.
Another object of the present invention is to provide a shock-absorbing helmet
that is compact in
size and light weight.
According to one aspect of the present invention, there is provided a shock-
absorbing helmet.
The shock-absorbing helmet comprises an exterior shell. An interior shell is
joined with the
exterior shell along respective circumferential edges. The interior shell is
adapted to fit a
wearer's head. A non-Newtonian medium is disposed between the interior shell
and the exterior
shell.
According to the aspect of the present invention, there is provided a shock-
absorbing helmet. The
shock-absorbing helmet comprises an exterior shell. An interior shell is
joined with the exterior
shell along respective circumferential edges. The interior shell is adapted to
fit a wearer's head.
A non-Newtonian medium is disposed between the interior shell and the exterior
shell. The non-
Newtonian medium is a shear thinning non-Newtonian foam or a shear thinning
non-Newtonian
liquid. At least one of opposite surfaces of the exterior shell and the
interior shell comprises
means for enlarging a surface area thereof. The opposite surfaces are in
contact with the non-
Newtonian medium.
According to the aspect of the present invention, there is provided a shock-
absorbing helmet. The
shock-absorbing helmet comprises an exterior shell. An interior shell is
joined with the exterior
Page 3
Date recue / Date received 2021-11-02
shell along respective circumferential edges. The interior shell is adapted to
fit a wearer's head.
A non-Newtonian medium is disposed between the interior shell and the exterior
shell. The non-
Newtonian medium is a shear thinning non-Newtonian foam or a shear thinning
non-Newtonian
liquid. Opposite surfaces of the exterior shell and the interior shell
comprise bubbles for
enlarging a surface area thereof. The opposite surfaces are in contact with
the non-Newtonian
medium. Shape, size, and placement of the bubbles may vary depending on design
preferences.
According to the aspect of the present invention, there is provided a shock-
absorbing helmet. The
shock-absorbing helmet comprises an exterior shell. An interior shell is
joined with the exterior
shell along respective circumferential edges. The interior shell is adapted to
fit a wearer's head.
A non-Newtonian medium is disposed between the interior shell and the exterior
shell. The non-
Newtonian medium is a shear thinning non-Newtonian foam or a shear thinning
non-Newtonian
liquid. Opposite surfaces of the exterior shell and the interior shell
comprise ridges extending
therefrom for enlarging a surface area thereof. The opposite surfaces are in
contact with the non-
Newtonian medium.
The advantage of the present invention is that it provides a shock-absorbing
helmet that
substantially reduces concussive impacts on a wearer's head.
A further advantage of the present invention is that it provides a shock-
absorbing helmet that
substantially reduces concussive impacts on a wearer's head and does not
impede the wearer's
movements.
Page 4
Date recue / Date received 2021-11-02
A further advantage of the present invention is that it provides a shock-
absorbing helmet that is
compact in size and light weight.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
A preferred embodiment of the present invention is described below with
reference to the
accompanying drawings, in which:
Figures 1 and 2 are simplified block diagrams illustrating in a side view and
a cross-
sectional view, respectively, a shock-absorbing helmet according to a
preferred
embodiment of the invention;
Figures 3 to 8 are simplified block diagram illustrating in a cross-sectional
detail different
implementations of means for enlarging a surface area of the exterior shell
and the
interior shell of the shock-absorbing helmet according to the preferred
embodiment of the
invention;
Figure 9 is a simplified block diagram illustrating von Mises stress
transmissibility of a
prototype design of the shock-absorbing helmet according to the preferred
embodiment
of the invention; and,
Page 5
Date recue / Date received 2021-11-02
Figure 10 is a simplified block diagram illustrating in a cross-sectional
detail another
implementation of means for enlarging a surface area of the exterior shell and
the interior
shell of the shock-absorbing helmet according to the preferred embodiment of
the
invention.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
Unless defined otherwise, all technical and scientific terms used herein have
the same meaning
as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which the
invention belongs.
Although any methods and materials similar or equivalent to those described
herein can be used
in the practice or testing of the present invention, the preferred methods and
materials are now
described.
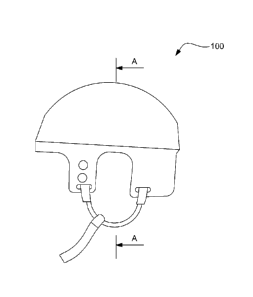
Referring to Figures 1 to 10 a shock-absorbing helmet 100 according to a
preferred embodiment
of the invention is provided. As illustrated in Figures 1 and 2, the shock-
absorbing helmet 100
comprises two shells, an exterior shell 102 and an interior shell 104. The
interior shell 104 is
joined with the exterior shell 102 along respective circumferential edges,
thus forming an
enclosure therebetween. The interior shell 104 is adapted to fit a wearer's
head. A non-
Newtonian medium 106 is disposed inside the enclosure between the interior
shell 104 and the
exterior shell 102, as illustrated in the detail in Figures 3 to 8 and 10.
Page 6
Date recue / Date received 2021-11-02
In shock absorption it is desirable to use materials that will deform
substantially for absorbing
energy. Shock absorbing materials are divided into Newtonian and non-Newtonian
materials
depending on their strain response to shear deformation. A Newtonian material
has a linear
response while non-Newtonian materials do not. Two non-Newtonian responses are
possible ¨
shear thickening and shear thinning. For shock absorption a shear thinning
material is employed.
The shock-absorbing helmet 100 comprises a shear thinning non-Newtonian medium
106
sandwiched between the exterior shell 102 and the interior shell 104. The
exterior shell 102 and
the interior shell 104 are made of a substantially stiff and lightweight
material such as, for
example, a PolyCarbonate (PC) material. Preferably, at least one of opposite
surfaces of the
exterior shell 102 and the interior shell 104, which are in contact with the
non-Newtonian
medium 106, comprises means for enlarging a surface area thereof. Further
preferably, both
surfaces comprise means for enlarging a surface area thereof such as, for
example, bubbled
shaped protrusions extending therefrom.
Due to its shear thinning non-Newtonian qualities the medium 106 stiffens when
exposed to
impact forces. With the protrusions increasing the surface area exposed to the
non-Newtonian
medium 106 the impact forces through the helmet 100 are further diffused, thus
substantially
reducing the impact forces experienced on the inside surface of the helmet 100
in contact with
the wearer's head. The non-Newtonian medium 106 may be provided as a non-
Newtonian fluid
or as a non-Newtonian foam such as, for example, commercially available D30
non-Newtonian
foam.
Page 7
Date recue / Date received 2021-11-02
The interior shell 104 is shaped and sized to fit a wearer's head, either in a
custom size or in one
of a number of predetermined sizes that are adaptable for use by multiple
wearers. Optionally,
the inside of the interior shell 104 may be fitted with one or more layers of
foam 108 such as, for
example, commercially available Low Density PolyEthylene (LDPE) foam, to
increase comfort
and/or to improve hold of the helmet 100 in an appropriate position on the
wearer's head. Further
optionally, a steel shell 110 is disposed onto the outward facing surface of
the exterior shell 102
to provide further protection in high impact situations experienced, for
example, in motor racing.
Depending on design preferences protrusions of various sizes and shapes may be
employed,
examples of which will be described hereinbelow. Figure 3 illustrates a
section of the helmet 100
with the protrusions being provided as bubbles having sphere type shape. The
bubbles of the
exterior shell 102 and the bubbles of the interior shell 104 are placed such
that a bubble of the
exterior shell 102 is placed opposite a bubble of the interior shell 104. The
block arrow in Figure
3 indicates the direction of the impact forces. In Figure 4 the size of the
bubbles is changed
compared to Figure 3.
The bubbles of the exterior shell 102 and the bubbles of the interior shell
104 may be placed such
that a bubble of the exterior shell 102 faces a space between bubbles of the
interior shell 104, as
illustrated in Figure 5.
Furthermore, the bubbles may have different shapes such as an ellipsoid type
shape, as illustrated
in Figure 6, or an elongated shape, as illustrated in Figure 7.
Page 8
Date recue / Date received 2021-11-02
A sample test was conducted using a prototype design of the shock-absorbing
helmet 100 having
a 20 mm x 5 mm bubble configuration as illustrated in Figure 8. In a
computerized drop
simulation, the von Mises stress was monitored at six different nodes of the
exterior shell 102
and at six nodes of the interior shell 104. Calculated drop test values at
each node are averaged
and graphed ¨ the difference between the exterior shell 102 and interior shell
104 responses
shown in Figure 9 indicate the force transmitted stability of the shells,
including the
demonstration that stress transmitted stability remained reasonably constant
and low for the
interior shell 104 measurements, even when extreme force was exerted onto the
exterior shell
102. The prototype design substantially reduced the stress transmitted
therethrough, thus
substantially reducing the forces acting on the wearer's head.
Referring to Figure 10, depending on design preferences, the protrusions may
also be provided as
ridges extending from the exterior shell 102 and the interior shell 104 which
may be, for
example, straight or curved, oriented parallel and/or perpendicular to each
other.
The present invention has been described herein with regard to preferred
embodiments.
However, it will be obvious to persons skilled in the art that a number of
variations and
modifications can be made without departing from the scope of the invention as
described
herein.
Page 9
Date recue / Date received 2021-11-02