Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
METHOD, DEVICE, COMPUTER EQUIPMENT AND STORAGE MEDIUM FOR
VERIFYING INTER-SYSTEM DATA ADMISSION
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Technical Field
[0001] The present application relates to the field of inter-system data
admission, and more
particularly to a method of and a device, a computer equipment and a storage
medium for
verifying inter-system data admission.
Description of Related Art
[0002] The modes for inter-system data interaction are numerous and
complicated, and there
are also many such data formats as JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), XML
(eXtensible
Markup Language), for example; sorting, filtering and verifying of these data
bring about
relatively large workload, generate more and more judging branches and logical
operations,
cyclomatic complexity is still very high even after reconstruction and
disassembly, and all
these also bring about challenges to subsequent maintenance work.
[0003] The currently available inter-system data admission verification
patterns are usually
realized via hard coding, but such modes mainly exhibit the following
deficiencies: 1)
conditional branches become increasingly cumbersome in order to realize
complicated
business rules (combination relations, priority sequencing, etc., for
example); 2)
corresponding amendments should be made in various conditional branches when
it is
needed to readjust business rules, but it tends to engender problems out of
such
amendments, and maintenance thereof is inferior; 3) online issuance of
procedures is
needed to realize readjustment of business rules, but such readjustment mode
is long in
duration; 4) every time new system data is accessed, a set of rule codes
should be custom-
1
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
made therefor, and there would be much repetitive works in doing so, and
efficiency thereof
is low.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0004] In view of the deficiencies in the state of the art, the present
invention provides a method
of and a device, a computer equipment and a storage medium for verifying inter-
system
data admission, and embodiments of the present invention enable to enhance the
admission
verification efficiency of system data.
[0005] According to the first aspect of the present invention, a method of
verifying inter-system
data admission is provided, in one embodiment, the method is applied to a
system that is
accessed to a general verification framework, and the system is connected with
a plurality
of external systems; the method comprises:
[0006] converting system data to a java object when the system receives the
system data from
any of the external systems, wherein the java object includes one or more
target(s) to be
verified;
[0007] obtaining business ID of the system data, and obtaining a preconfigured
verification rule
to which each target to be verified as included in the java object corresponds
according to
the business ID;
[0008] in the case that the java object includes plural targets to be
verified, creating a multi-tree
according to the plural targets to be verified as included in the java object,
wherein the
multi-tree includes plural nodes, the plural nodes correspond to the plural
targets to be
verified on a one-to-one basis, and the multi-tree consists of at least one
parent node and a
child node to which each parent node corresponds; and
[0009] determining a value of a root node of the multi-tree according to the
verification rule to
which each target to be verified as included in the java object corresponds,
and determining
admission verification result of the system data according to the value of the
root node,
wherein the root node is a node with corresponding child node(s) and without
any
2
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
corresponding parent node in the multi-tree.
[0010] In one embodiment, the step of converting system data to a java object
includes:
[0011] determining a data format of the system data; and
[0012] using a converter that corresponds to the data format in plural preset
converters to
convert the system data to a java object.
[0013] In one embodiment, the step of obtaining a preconfigured verification
rule to which each
target to be verified as included in the java object corresponds according to
the business ID
includes:
[0014] enquiring a preconfigured rule configuration table according to the
business ID to obtain
a rule configuration list of the business ID; and
[0015] obtaining a verification rule to which each target to be verified as
included in the java
object corresponds from the rule configuration list.
[0016] In one embodiment, the step of creating a multi-tree according to the
plural targets to be
verified as included in the java object includes:
[0017] determining length of the system data, and employing a mode that
matches with the
length of the system data to create an initial multi-tree, wherein nodes
included in the initial
multi-tree correspond to the plural targets to be verified on a one-to-one
basis;
[0018] determining filling orders to which the nodes included in the initial
multi-tree
correspond according to a top-to-bottom traversing order; and
[0019] sequentially filling corresponding object instances in the nodes to
which the filling
orders correspond to obtain the multi-tree.
[0020] In one embodiment, the step of employing a mode that matches with the
length of the
system data to create an initial multi-tree includes:
[0021] employing a recursive algorithm to create the initial multi-tree if the
length of the system
data satisfies a preset condition; and
3
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
[0022] employing a stack operation to create the initial multi-tree if the
length of the system
data does not satisfy the preset condition.
[0023] In one embodiment, the step of determining a value of a root node of
the multi-tree
according to the verification rule to which each target to be verified as
included in the java
object corresponds includes:
[0024] determining all child nodes of the root node in the multi-tree, and
determining
calculation orders to which the child nodes of the root node correspond in a
bottom-to-top
traversing order;
[0025] sequentially determining targets to be verified to which the child
nodes of the root node
correspond according to the calculation orders, and verifying the child nodes
according to
verification rules to which the targets to be verified correspond to determine
values of the
nodes; and
[0026] determining the value of the root node according to the values of all
child nodes of the
root node.
[0027] In one embodiment, the method further comprises: in the case the java
object includes
one target to be verified, performing admission verification on the target to
be verified
according to the verification rule to which the target to be verified as
included in the java
object corresponds to determine admission verification result of the system
data.
[0028] According to the second aspect of the present invention, a device for
verifying inter-
system data admission is provided, in one embodiment, the device comprises:
[0029] a converting module, for converting system data to a java object when
the system data
is received from any external system, wherein the java object includes one or
more target(s)
to be verified;
[0030] a verification rule obtaining module, for obtaining business ID of the
system data, and
obtaining a preconfigured verification rule to which each target to be
verified as included
in the java object corresponds according to the business ID;
4
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
[0031] a multi-tree creating module, for, in the case that the java object
includes plural targets
to be verified, creating a multi-tree according to the plural targets to be
verified as included
in the java object, wherein the multi-tree includes plural nodes, the plural
nodes correspond
to the plural targets to be verified on a one-to-one basis, and the multi-tree
consists of at
least one parent node and a child node to which each parent node corresponds;
and
[0032] a first verification result determining module, for determining a value
of a root node of
the multi-tree according to the verification rule to which each target to be
verified as
included in the java object corresponds, and determining admission
verification result of
the system data according to the value of the root node, wherein the root node
is a node
with corresponding child node(s) and without any corresponding parent node in
the multi-
tree.
[0033] According to the third aspect of the present invention, a computer
equipment is provided,
which comprises a memory, a processor and a computer program stored on the
memory
and executable on the processor, and the method steps according to anyone of
the
aforementioned embodiments are realized when the processor executes the
computer
program.
[0034] According to the fourth aspect of the present invention, further
provided is a computer-
readable storage medium storing thereon a computer program, and the method
steps
according to anyone of the aforementioned embodiments are realized when the
computer
program is executed by a processor.
[0035] In the embodiments of the present invention, when the system receives
system data
coming from any of external systems connected therewith, the system filters
the system
data, namely converts the system data to a java object that includes one or
more target(s)
to be verified, then obtains a business ID of the system data, obtains a
preconfigured
verification rule to which each target to be verified as included in the java
object
corresponds according to the business ID, in the case the java object includes
plural targets
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
to be verified, creates a multi-tree according to the plural targets to be
verified as included
in the java object, determines a value of a root node of the multi-tree
according to the
verification rule to which each target to be verified as included in the java
object
corresponds, and determines admission verification result of the system data
according to
the value of the root node. The general verification framework is capable of
providing the
system with a set of general admission verification functions, on the basis of
the framework
the system is enabled to filter and verify the received system data, and to
perform
independent configurations for admission verification rules with respect to
the data of
different external systems, whereby priority levels of configuration rules are
supported, and
such relations as Or, And can be combined, the mode of configurable
verification rules is
excellent in readability and easy in maintenance as compared with the
traditional hard
coding mode, and the admission verification efficiency of the system data is
markedly
enhanced.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
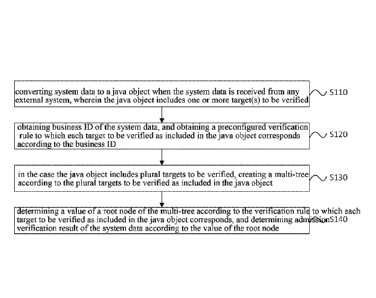
[0036] Fig. 1 is a flowchart schematically illustrating a method of verifying
inter-system data
admission in an embodiment;
[0037] Fig. 2 is a view illustrating the application environment of a method
of verifying inter-
system data admission in an embodiment;
[0038] Fig. 3 is a view schematically illustrating the functions of a general
verification
framework in an embodiment;
[0039] Fig. 4 is a flowchart schematically illustrating conversion of system
data to java object
in an embodiment;
[0040] Fig. 5 is a view schematically illustrating multi-tree object design in
an embodiment;
6
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
[0041] Fig. 6 is a view schematically illustrating a corresponding multi-tree
exemplified as a
mobile phone in an embodiment;
[0042] Fig. 7 is a block diagram illustrating the structure of a device for
verifying inter-system
data admission in an embodiment; and
[0043] Fig. 8 is a view illustrating the internal structure of a computer
equipment in an
embodiment.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
[0044] To make more lucid and clear the objectives, technical solutions and
advantages of the
present application, the present application is described in greater detail
below with
reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. As should be
understood, the
specific embodiments as described here are merely meant to explain the present
application,
rather than to restrict the present application.
[0045] The present invention provides a method of verifying inter-system data
admission. In
one embodiment, as shown in Fig. 1, the method comprises the following steps.
[0046] S110 - converting system data to a java object when the system data is
received from
any external system, wherein the java object includes one or more target(s) to
be verified.
[0047] In this embodiment, the application environment of the method of
verifying inter-system
data admission can be as shown in Fig. 2, in which it is required for system
10 (hereinafter
referred to as -the current system") to carry out data interaction with a
plurality of external
systems (the external systems are meant for systems other than the current
system), such
as external systems 21, 22 and 23. The current system and the various external
systems can
7
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
be respectively embodied as an independent server or a server cluster
consisting of a
plurality of servers. In addition, the current system and the various external
systems can
also be deployed in a single server. Specifically, it is possible to access
the general
verification framework in the current system by integrating the codes of the
general
verification framework in the current system and by introducing thereto
relevant
dependencies (such as dependent package of the rule engine). Moreover, as
shown in Fig.
3, the framework provides such functions as data adapter, rule analysis and
business
verification, it is possible to create a model, namely a rule configuration
table, by brushing
the script or through other modes, thereafter to define relevant message data
for business
scenarios existing between the current system and the various external systems
to be
connected therewith, and to configure corresponding verification rules for the
various
business scenarios in the rule configuration table.
[0048] In this embodiment, before the current system receives system data from
any external
system, the method further comprises: creating a rule configuration table;
assigning a
unique business ID to each business scenario existing between the current
system and the
any external system to be connected therewith, and defining corresponding
system data for
each business ID, wherein each system data includes one or more pieces of
information to
be verified; and configuring a corresponding rule verification list for each
business scenario
to which the any external system corresponds in the rule configuration table.
[0049] Since the logics of the various accessed external systems in the
traditional scheme are
all independent, logic multiplexing cannot be realized, so when a new external
system is to
be accessed to the current system, it is required to customize and develop a
corresponding
logic for the data of the newly accessed external system, in which a workload
of 10
persons/days is needed by coarse estimation. In this embodiment, once the
current system
is accessed to the general verification framework, when a new external system
is to be
accessed, it is merely necessary to configure corresponding verification rules
for the
various business scenarios of the new external system before use can be
started, whereby
8
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
great amount of branch customization and development is reduced, extensibility
of the
current system is markedly enhanced, and there is no need for the operating
personnel (such
as the developing personnel) to dedicatedly develop corresponding verification
logics for
the new external system, as it suffices to sort out specific rules and make
corresponding
configurations for the business scenarios of the new external system, and
thusly the
workload will be reduced to 2-3 persons/days, and workload of the operating
personnel is
greatly reduced.
[0050] Moreover, the method further comprises: when the current system is to
be connected
with a new external system, assigning a unique business ID to each business
scenario
existing between the current system and the new external system, and defining
corresponding system data for each business ID, wherein each system data
includes one or
more pieces of information to be verified; and configuring a corresponding
rule verification
list for each business scenario in the rule configuration table, wherein each
rule verification
list includes verification rules corresponding to each piece of information to
be verified as
included in the system data to which the business ID corresponds.
[0051] Specifically, with respect to data rule change of an already accessed
external system,
dynamic readjustment is impossible in the traditional solution because logics
are all present
in the codes, only issuance operation can be made directed to versions, and
the time
duration therefor ranges from half a month to more than one month
(specifically dependent
upon the period of a version); when the framework is used, since the framework
logic is
universal and only the verification rules of specific configurations are
different, there is no
need for issuance when verification rules are changed, as it is possible to
directly amend
the verification rules within the range supported by this framework (most
logic judgments
are supported), the newest rule will be directly used after such amendment to
perform data
verification, whereby real-time validation is achieved. In addition, since
configurations of
verification rules are precisely matched in all cases, insofar as the
configuration is correct,
there would be no such case as misjudgment during verification.
9
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
[0052] Exemplarily, configuration information of a rule configuration table
created in an
MySQL database can be as shown in the following Table 1:
[0053] Table 1:
Field Names Types Notes
id int primary key
biz type char(8) Business ID,
differentiating
scenarios
filter node varchar(32) node value
parent node varchar(32) parent node value, root =
-1
rule object varchar(128) node category
rule object type char(8) node category types, such
as
Object, List, Map etc.
biz rule varchar(1024) node expression field
string
value
desc varchar(128) rule description
[0054] Exemplarily, mobile phones should be selected in a certain business
scenario, the
selection requirements are that the brand of the mobile phones should be
"huawei", prices
of the mobile phones should be "between 2000 to 6000 RMB Yuan", display sizes
of the
mobile phones should be "greater than 6.56 inches or with resolutions more
than 1080p",
and material of the phone displays should be "AMOLED". These selection
requirements
can be written in an expression, as: brand = "huawei" && prices >=
2000&&prices <=
6000 && ((display sizes > 6.56 inches 0 display resolutions > 1080p) &&
material =
"AMOLED". When message data is defined, such objects as phone (indicative of
mobile
phones) and display (indicative of phone displays) can be defined. The rule
configuration
list configured for this business scenario can be as shown in the following
Table 2:
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
[0055] Table 2:
filter node parent no rule object biz-rule Desc
de
phone -1 phone phone.brand= brand should be
huawei,
"huawei" prices are between
2000
&& to 6000, display
phone.price >=2000 requirement refers to
&& phone.price child nodes
<=6000
&& phone.Display
phoneDisp phone di splay (display.size>6.5611di display sizes
greater
lay splay.resolution>108 than 6.56 inches
or with
Op)&& resolutions more than
display.material= 1080p, material must
be
"AMOLED" AMOLED
[0056] After the current system has received system data from any external
system (the system
data means such data as message data sent from anyone of external systems
connected with
the current system), it converts the system data to a java object that
includes one or more
target(s) to be verified.
[0057] Further, in one embodiment, the step of converting system data to a
java object includes
determining a data format of the system data, and using a converter that
corresponds to the
data format in plural preset converters to convert the system data to a java
object. The java
object includes one or more target(s) to be verified, for instance, such
targets as "phone",
"phone.brand", "phone.price", "phoneDisplay", "display.size",
display.resolution" and
"di splay.material".
11
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
[0058] Specifically, as shown in Fig. 4, the current system can select a
corresponding adapter
(namely converter) in combination with variously typed Java object conversion
APIs
(Application Programming Interfaces) according to the formats (such as json,
xml, map,
etc.) of incoming parameter objects (namely system data) to uniformly convert
the
incoming parameter objects into Java objects.
[0059] S120 - obtaining business ID of the system data, and obtaining a
preconfigured
verification rule to which each target to be verified as included in the java
object
corresponds according to the business ID.
[0060] In this embodiment, each business scenario corresponds to a unique
business ID, and
the system can obtain the business ID to which the system data corresponds to
thereby
obtain a preconfigured verification rule to which each target to be verified
corresponds
according to the business ID.
[0061] In one embodiment, the step of obtaining a preconfigured verification
rule to which each
target to be verified as included in the java object corresponds according to
the business ID
includes:
[0062] enquiring a preconfigured rule configuration table according to the
business ID to obtain
a rule configuration list of the business ID; and
[0063] obtaining a verification rule to which each target to be verified as
included in the java
object corresponds from the rule configuration list.
[0064] Specifically, the business ID is a field in the rule configuration
table, and different
business IDs correspond to respective records, without interfering one
another. Accordingly,
the system can base on the business ID to enquire and obtain from the rule
configuration
table the record, namely rule configuration list (such as the one shown in
Table 2), to which
this business ID corresponds, and can thereafter obtain the verification rule
(alternatively
referred to as "expression") to which each target to be verified corresponds
from the rule
12
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
configuration list.
[0065] For instance, the verification rule of "phone" obtainable from the rule
configuration list
shown in Table 2 is phone.brand
"huawei"&&phone.price>=2000&&phone.price<=6000&&phoneDisplay,
the
verification rule of "phone.brand" is phone.brand = "huawei", the verification
rule of
"phone.price" is phone.price>=2000, and the verification rule of
"phoneDisplay" is
(display.size>511display.resolution>1080p)&&display.materia1=-AMOLED".
[0066] S130 - in the case that the java object includes plural targets to be
verified, creating a
multi-tree according to the plural targets to be verified as included in the
java object. The
multi-tree includes plural nodes, the plural nodes correspond to the plural
targets to be
verified on a one-to-one basis, and the multi-tree consists of at least one
parent node and a
child node to which each parent node corresponds.
[0067] In this embodiment, if the java object includes only one target to be
verified, then the
current system can directly base on the verification rule to which the target
to be verified
as included in the java object corresponds to perform admission verification
on the target
to be verified to determine the admission verification result of the system
data. For instance,
in another business scenario in which mobile phones are selected, it is only
required that
the brand of the mobile phones is "huawei", then the corresponding
verification rule can
be phone.brand = "huawei", so it is merely required to obtain the information
corresponding to the one target to be detected as phone.brand in the system
data and to
judge whether the information is "huawei", if yes, it will be determined that
the admission
verification result of the system data is succeeded verification, to the
contrary, if the
information is not "huawei", but "xiaomi" for example, it will be determined
that the
admission verification result of the system data is failed verification.
Further, if the java
object includes plural (two, three, seven, for example) targets to be
verified, it is then
required to create a multi-tree according to the plural targets to be verified
as included in
13
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
the java object, and to thereafter analyze the multi-tree so as to verify the
various targets to
be verified.
[0068] In one embodiment, the step of creating a multi-tree according to the
plural targets to be
verified as included in the java object includes:
[0069] determining length of the system data, and employing a mode that
matches with the
length of the system data to create an initial multi-tree, wherein nodes
included in the initial
multi-tree correspond to the plural targets to be verified on a one-to-one
basis;
[0070] determining filling orders to which the nodes included in the initial
multi-tree
correspond according to a top-to-bottom traversing order; and
[0071] sequentially filling corresponding object instances in the nodes to
which the filling
orders correspond to obtain the multi-tree.
[0072] In this embodiment, the object design of the multi-tree can be
exemplarily as shown in
Fig. 5, in which the three members, filterCode, parentCode and children, would
constitute
a tree (taking the aforementioned example of selecting mobile phones, a mobile
phone as
the object, such internal objects as its brand, price, and display included in
the mobile phone,
and such internal objects as size, resolution and material as included in the
display as the
object together constitute a tree) (filterCode stands for the current node id,
parentCode
stands for the parent code id of filterCode, and children stand for the child
codes of the
current node), while the other members are all related to verification rules,
one node on the
tree represents one verification rule, instance data of the targets to be
verified and the
verification rules are preserved, and results obtained via expression engine
(for calculating
the values to which the various nodes in the tree correspond) verification are
also preserved.
When the value of the root node of the tree is calculated, while a parent node
that contains
child nodes should be performed with rule verification, it must be ensured
that all child
nodes have been calculated to completion (as should be particularly noted, in
the case of
short circuit, the result can be directly obtained to return beforehand), to
this end, each node
in the tree correspondingly possesses the member of ruleExecuteFlag as shown
in Fig. 5,
14
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
this member being employed to characterize whether the node corresponding
thereto has
been verified.
[0073] Further, the recursive mode is usually employed to create the initial
multi-tree, but the
use of recursion to create the initial multi-tree engenders additional
overhead in the
invoking and returning of the method, and invoking too deep into the hierarchy
might most
probably cause OOM (Out0fMemory), therefore, when the system creates the
initial multi-
tree in this embodiment, the length of the system data is based on to select
the recursive
mode or the mode of stack operation to create the initial multi-tree, to
thereby avoid the
aforementioned problem, for instance, a recursive algorithm is employed to
create the
initial multi-tree if the length of the system data satisfies a preset
condition (for instance,
the length reaches a preset threshold), and a stack operation is employed to
create the initial
multi-tree if the length of the system data does not satisfy the preset
condition. The preset
condition is adjustable according to practical operational circumstances to
achieve
optimum performance.
[0074] After the initial multi-tree has been created, the current system then
sequentially fills
corresponding object instances in the nodes in the initial multi-tree
according to a top-to-
bottom order. The process can specifically be to hierarchically traverse the
initial multi-
tree, starting from the root node to find all child nodes, and subsequently to
invoke the
getter method of the parent node object instance via reflection mechanism to
hence obtain
child node object instances, until the bottom is reached. Further, the method
can be cached
here via map to reduce performance overhead, storage can be done by using
ConcurrentHashMap (a type of concurrent hash mapping table), and the form of
storage is
key-value, in which key is a member variable name of the category, and value
is a Method
object of the getter method corresponding to the variable name; when the child
node object
instances are needed, they are first extracted from Map, if there is none in
Map, a reflection
tool is used to invoke Java to reflect APIs to obtain a Method object, and the
Method object
as obtained is cached in Map.
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
[0075] S140 - determining a value of a root node of the multi-tree according
to the verification
rule to which each target to be verified as included in the java object
corresponds, and
determining admission verification result of the system data according to the
value of the
root node. The root node is a node with corresponding child nodes and without
any
corresponding parent node in the multi-tree.
[0076] In this embodiment, the step for the current system to determine a
value of a root node
of the multi-tree according to the verification rule to which each target to
be verified as
included in the java object corresponds can include: determining all child
nodes of the root
node in the multi-tree, and determining calculation orders to which the child
nodes of the
root node correspond in a bottom-to-top traversing order; sequentially
determining targets
to be verified to which the child nodes of the root node correspond according
to the
calculation orders, and verifying the child nodes according to verification
rules to which
the targets to be verified correspond to determine values of the nodes; and
determining the
value of the root node according to the values of all child nodes of the root
node.
Specifically, while calculating the value of the root node, the current system
employs a
bottom-to-top order to calculate expressions layer by layer starting from the
child nodes,
and the result on the parent node expression is replaced to finally converge
to the root node.
During the process of calculation, if any unsolved sub-problem is encountered,
this sub-
problem is firstly solved, once this sub-problem has been solved, the solution
of this sub-
problem is then directly used ¨ the process is recurred to finally arrive at
the value of the
root node.
[0077] For instance, in an example, the multi-tree generated in the
aforementioned business
scenario of selecting mobile phones can be as shown in Fig. 6, in which the
top layer "phone"
of the tree is the root node of the tree, and the child nodes to which the
root node
corresponds are the three nodes "brand", "price" and "display" located at the
second layer
of the tree, of which the node "display" is not only a child node of "phone"
but also a parent
16
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
node itself (namely a node having corresponding child nodes), whose
corresponding child
nodes are the three nodes "size", "resolution" and "material" located at the
bottom layer of
the tree. The verification rules (also referred to as "expressions") to which
the various nodes
of the tree correspond can also be known from Fig. 6, for instance, the
expression of the
node "phone" is "brand&&price&&display", and the expression of the node
"brand" is
"phone.brand = "huawei'". With respect to nodes not serving as parent nodes in
the tree,
such as the two nodes "brand" and "price", after having calculated their
corresponding
values, the current system replaces the values corresponding to their names in
the root node
expression as true or false, for instance, if it is calculated that the value
of "brand" is true,
then "brand" in the expression "brand&&price&&display" of the root node
"phone" is
replaced with true; after the values of other child nodes, namely "price" or
"display", have
been calculated, the above operation is also performed; after all child nodes
to which the
root node corresponds have been calculated to completion, attributes of the
root node are
entirely replaced, for instance, the three child nodes "brand", "price" and
"display" are all
replaced with true or false, thusly, the final result can be reached by
calculating the root
node expression. As should be noted, since the node "display" not only serves
as the child
node of the root node but also serves as the parent node of some other nodes
(such as the
three nodes "size", "resolution" and "material") at the same time, the
calculation thereof
should be firstly directed to the values of all its corresponding child nodes
before its
corresponding value can be calculated, while its calculation mode is identical
to the
aforementioned calculation mode of the root node.
[0078] Further, if it is needed to reduce unnecessary node calculations when
the values of the
nodes are calculated, a short-circuit switch can be employed to perform logic
judgment of
the layer when a certain node has been calculated and starts to be replaced
for parent node,
for instance, truell(x), then x needs not be calculated, and the entire
expression is replaced
with true; vice versa, false&&(x) is of the same principle. For instance, the
expression of
the -display" node in Fig. 6 is -
display.sizelldisplay.resolution&&display.rnaterial", as
regards -display.sizelldisplay.resolution" in this expression, if
"display.size" (or
17
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
"display.resolution") is true, then there will be no need to judge
"display.resolution" before
-display.sizelldisplay.resolution" can be directly replaced with true.
[0079] Based on the same inventive conception, the present invention further
provides a device
for verifying inter-system data admission. In one embodiment, as shown in Fig.
7, the
device for verifying inter-system data admission comprises the following
modules:
[0080] a converting module 110, for converting system data to a java object
when the system
data is received from any external system, wherein the java object includes
one or more
target(s) to be verified;
[0081] a verification rule obtaining module 120, for obtaining business ID of
the system data,
and obtaining a preconfigured verification rule to which each target to be
verified as
included in the java object corresponds according to the business ID;
[0082] a multi-tree creating module 130, for, in the case the java object
includes plural targets
to be verified, creating a multi-tree according to the plural targets to be
verified as included
in the java object, wherein the multi-tree includes plural nodes, the plural
nodes correspond
to the plural targets to be verified on a one-to-one basis, and the multi-tree
consists of at
least one parent node and a child node to which each parent node corresponds;
and
[0083] a first verification result determining module 140, for determining a
value of a root node
of the multi-tree according to the verification rule to which each target to
be verified as
included in the java object corresponds, and determining admission
verification result of
the system data according to the value of the root node, wherein the root node
is a node
with corresponding child node(s) and without any corresponding parent node in
the multi-
tree.
[0084] In one embodiment, the converting module includes:
[0085] a format determining sub-module, for determining a data format of the
system data; and
[0086] a converting sub-module, for using a converter that corresponds to the
data format in
plural preset converters to convert the system data to a java object.
18
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
[0087] In one embodiment, the verification rule obtaining module includes:
[0088] an enquiring sub-module, for enquiring a preconfigured rule
configuration table
according to the business ID to obtain a rule configuration list of the
business ID; and
[0089] a verification rule obtaining sub-module, for obtaining a verification
rule to which each
target to be verified as included in the java object corresponds from the rule
configuration
list.
[0090] In one embodiment, the multi-tree creating module includes:
[0091] an initial tree creating sub-module, for determining length of the
system data, and
employing a mode that matches with the length of the system data to create an
initial multi-
tree, wherein nodes included in the initial multi-tree correspond to the
plural targets to be
verified on a one-to-one basis;
[0092] a filling order determining sub-module, for determining filling orders
to which the nodes
included in the initial multi-tree correspond according to a top-to-bottom
traversing order;
and
[0093] a filling sub-module, for sequentially filling corresponding object
instances in the nodes
to which the filling orders correspond to obtain the multi-tree.
[0094] In one embodiment, the initial tree creating sub-module is further
employed for
employing a recursive algorithm to create the initial multi-tree if the length
of the system
data satisfies a preset condition, and employing a stack operation to create
the initial multi-
tree if the length of the system data does not satisfy the preset condition.
[0095] In one embodiment, the first verification result determining module
includes:
[0096] a calculation order determining sub-module, for determining all child
nodes of the root
node in the multi-tree, and determining calculation orders to which the child
nodes of the
root node correspond in a bottom-to-top traversing order;
[0097] a child node value determining sub-module, for sequentially determining
targets to be
verified to which the child nodes of the root node correspond according to the
calculation
19
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
orders, and verifying the child nodes according to verification rules to which
the targets to
be verified correspond to determine values of the nodes; and
[0098] a root node value determining sub-module, for determining the value of
the root node
according to the values of all child nodes of the root node.
[0099] In one embodiment, the device further comprises a first verification
result determining
module that is employed for, in the case the java object includes one target
to be verified,
performing admission verification on the target to be verified according to
the verification
rule to which the target to be verified as included in the java object
corresponds to
determine admission verification result of the system data.
[0100] Specific definitions relevant to the device for verifying inter-system
data admission may
be inferred from the aforementioned definitions to the method of verifying
inter-system
data admission, while no repetition is made in this context. The various
modules in the
aforementioned device for verifying inter-system data admission can be wholly
or partly
realized via software, hardware, and a combination of software with hardware.
The various
modules can be embedded in the form of hardware in a processor in a computer
equipment
or independent of any computer equipment, and can also be stored in the form
of software
in a memory in a computer equipment, so as to facilitate the processor to
invoke and
perform operations corresponding to the aforementioned various modules.
[0101] In one embodiment, a computer equipment is provided, and its internal
structure can be
as shown in Fig. 8. The computer equipment comprises a processor, a memory, a
network
interface and a database connected to each other via a system bus. The
processor of the
computer equipment is employed to provide computing and controlling
capabilities. The
memory of the computer equipment includes a nonvolatile storage medium, and an
internal
memory. The nonvolatile storage medium stores therein an operating system, a
computer
program and a database. The internal memory provides environment for the
running of the
operating system and the computer program in the nonvolatile storage medium.
The
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
database of the computer equipment is used to store such data as the rule
configuration
table. The network interface of the computer equipment is employed to connect
to an
external terminal via network for communication. The computer program realizes
a method
of verifying inter-system data admission when it is executed by a processor.
[0102] As understandable to persons skilled in the art, the structure
illustrated in Fig. 8 is merely
a block diagram of partial structure relevant to the solution of the present
application, and
does not constitute any restriction to the computer equipment on which the
solution of the
present application is applied, as the specific computer equipment may
comprise
component parts that are more than or less than those illustrated in Fig. 8,
or may combine
certain component parts, or may have different layout of component parts.
[0103] In one embodiment, a computer equipment is provided, which comprises a
memory, a
processor and a computer program stored on the memory and operable on the
processor,
and the following steps are realized when the processor executes the computer
program:
[0104] converting system data to a java object when the system data is
received from any
external system, wherein the java object includes one or more target(s) to be
verified;
obtaining business ID of the system data, and obtaining a preconfigured
verification rule
to which each target to be verified as included in the java object corresponds
according to
the business ID; in the case the java object includes plural targets to be
verified, creating a
multi-tree according to the plural targets to be verified as included in the
java object,
wherein the multi-tree includes plural nodes, the plural nodes correspond to
the plural
targets to be verified on a one-to-one basis, and the multi-tree consists of
at least one parent
node and a child node to which each parent node corresponds; and determining a
value of
a root node of the multi-tree according to the verification rule to which each
target to be
verified as included in the java object corresponds, and determining admission
verification
result of the system data according to the value of the root node, wherein the
root node is
a node with corresponding child node(s) and without any corresponding parent
node in the
multi-tree.
21
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
[0105] In one embodiment, when the processor executes the computer program to
realize the
step of converting system data to a java object, the following steps are
further realized:
[0106] determining a data format of the system data; and using a converter
that corresponds to
the data format in plural preset converters to convert the system data to a
java object.
[0107] In one embodiment, when the processor executes the computer program to
realize the
step of obtaining a preconfigured verification rule to which each target to be
verified as
included in the java object corresponds according to the business ID, the
following steps
are further realized:
[0108] enquiring a preconfigured rule configuration table according to the
business ID to obtain
a rule configuration list of the business ID; and obtaining a verification
rule to which each
target to be verified as included in the java object corresponds from the rule
configuration
list.
[0109] In one embodiment, when the processor executes the computer program to
realize the
step of creating a multi-tree according to the plural targets to be verified
as included in the
java object, the following steps are further realized:
[0110] determining length of the system data, and employing a mode that
matches with the
length of the system data to create an initial multi-tree, wherein nodes
included in the initial
multi-tree correspond to the plural targets to be verified on a one-to-one
basis; determining
filling orders to which the nodes included in the initial multi-tree
correspond according to
a top-to-bottom traversing order; and sequentially filling corresponding
object instances in
the nodes to which the filling orders correspond to obtain the multi-tree.
[0111] In one embodiment, when the processor executes the computer program to
realize the
step of employing a mode that matches with the length of the system data to
create an initial
multi-tree, the following steps are further realized:
[0112] employing a recursive algorithm to create the initial multi-tree if the
length of the system
22
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
data satisfies a preset condition; and employing a stack operation to create
the initial multi-
tree if the length of the system data does not satisfy the preset condition.
[0113] In one embodiment, when the processor executes the computer program to
realize the
step of determining a value of a root node of the multi-tree according to the
verification
rule to which each target to be verified as included in the java object
corresponds, the
followings steps are further realized:
[0114] determining all child nodes of the root node in the multi-tree, and
determining
calculation orders to which the child nodes of the root node correspond in a
bottom-to-top
traversing order; sequentially determining targets to be verified to which the
child nodes of
the root node correspond according to the calculation orders, and verifying
the child nodes
according to verification rules to which the targets to be verified correspond
to determine
values of the nodes; and determining the value of the root node according to
the values of
all child nodes of the root node.
[0115] In one embodiment, when the processor executes the computer program,
the following
step is further realized: in the case the java object includes one target to
be verified,
performing admission verification on the target to be verified according to
the verification
rule to which the target to be verified as included in the java object
corresponds to
determine admission verification result of the system data.
[0116] In one embodiment, further provided is a computer-readable storage
medium storing
thereon a computer program, and the following steps are realized when the
computer
program is executed by a processor: converting system data to a java object
when the
system data is received from any external system, wherein the java object
includes one or
more target(s) to be verified; obtaining business ID of the system data, and
obtaining a
preconfigured verification rule to which each target to be verified as
included in the java
object corresponds according to the business ID; in the case the java object
includes plural
targets to be verified, creating a multi-tree according to the plural targets
to be verified as
23
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
included in the java object, wherein the multi-tree includes plural nodes, the
plural nodes
correspond to the plural targets to be verified on a one-to-one basis, and the
multi-tree
consists of at least one parent node and a child node to which each parent
node corresponds;
and determining a value of a root node of the multi-tree according to the
verification rule
to which each target to be verified as included in the java object
corresponds, and
determining admission verification result of the system data according to the
value of the
root node, wherein the root node is a node with corresponding child node(s)
and without
any corresponding parent node in the multi-tree.
[0117] In one embodiment, when the computer program is executed by a processor
to realize
the step of converting system data to a java object, the following steps are
further realized:
[0118] determining a data format of the system data; and using a converter
that corresponds to
the data format in plural preset converters to convert the system data to a
java object.
[0119] In one embodiment, when the computer program is executed by a processor
to realize
the step of obtaining a preconfigured verification rule to which each target
to be verified as
included in the java object corresponds according to the business ID, the
following steps
are further realized:
[0120] enquiring a preconfigured rule configuration table according to the
business ID to obtain
a rule configuration list of the business ID; and obtaining a verification
rule to which each
target to be verified as included in the java object corresponds from the rule
configuration
list.
[0121] In one embodiment, when the computer program is executed by a processor
to realize
the step of creating a multi-tree according to the plural targets to be
verified as included in
the java object, the following steps are further realized:
[0122] determining length of the system data, and employing a mode that
matches with the
length of the system data to create an initial multi-tree, wherein nodes
included in the initial
multi-tree correspond to the plural targets to be verified on a one-to-one
basis; determining
24
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
filling orders to which the nodes included in the initial multi-tree
correspond according to
a top-to-bottom traversing order; and sequentially filling corresponding
object instances in
the nodes to which the filling orders correspond to obtain the multi-tree.
[0123] In one embodiment, when the computer program is executed by a processor
to realize
the step of employing a mode that matches with the length of the system data
to create an
initial multi-tree, the following steps are further realized:
[0124] employing a recursive algorithm to create the initial multi-tree if the
length of the system
data satisfies a preset condition; and employing a stack operation to create
the initial multi-
tree if the length of the system data does not satisfy the preset condition.
[0125] In one embodiment, when the computer program is executed by a processor
to realize
the step of determining a value of a root node of the multi-tree according to
the verification
rule to which each target to be verified as included in the java object
corresponds, the
followings steps are further realized:
[0126] determining all child nodes of the root node in the multi-tree, and
determining
calculation orders to which the child nodes of the root node correspond in a
bottom-to-top
traversing order; sequentially determining targets to be verified to which the
child nodes of
the root node correspond according to the calculation orders, and verifying
the child nodes
according to verification rules to which the targets to be verified correspond
to determine
values of the nodes; and determining the value of the root node according to
the values of
all child nodes of the root node.
[0127] In one embodiment, when the computer program is executed by a
processor, the
following step is further realized: in the case the java object includes one
target to be
verified, performing admission verification on the target to be verified
according to the
verification rule to which the target to be verified as included in the java
object corresponds
to determine admission verification result of the system data.
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
[0128] As comprehensible to persons ordinarily skilled in the art, the entire
or partial flows in
the methods according to the aforementioned embodiments can be completed via a
computer program instructing relevant hardware, the computer program can be
stored in a
nonvolatile computer-readable storage medium, and the computer program can
include the
flows as embodied in the aforementioned various methods when executed. Any
reference
to the memory, storage, database or other media used in the various
embodiments provided
by the present application can all include nonvolatile and/or volatile
memory/memories.
The nonvolatile memory can include a read-only memory (ROM), a programmable
ROM
(PROM), an electrically programmable ROM (EPROM), an electrically erasable and
programmable ROM (EEPROM) or a flash memory. The volatile memory can include a
random-access memory (RAM) or an external cache memory. To serve as
explanation
rather than restriction, the RAM is obtainable in many forms, such as static
RAM (SRAM),
dynamic RAM (DRAM), synchronous DRAM (SDRAM), dual data rate SDRAM
(DDRSDRAM), enhanced SDRAM (ESDRAM), synchronous link (Synchlink) DRAM
(SLDRAM), memory bus (Rambus) direct RAM (RDRAM), direct Rambus dynamic
RAM (DRDRAM), and Rambus dynamic RAM (RDRAM), etc.
[0129] Technical features of the aforementioned embodiments are randomly
combinable, while
all possible combinations of the technical features in the aforementioned
embodiments are
not exhausted for the sake of brevity, but all these should be considered to
fall within the
scope recorded in the Description as long as such combinations of the
technical features
are not mutually contradictory.
[0130] The foregoing embodiments are merely directed to several modes of
execution of the
present application, and their descriptions are relatively specific and
detailed, but they
should not be hence misunderstood as restrictions to the inventive patent
scope. As should
be pointed out, persons with ordinary skill in the art may further make
various
modifications and improvements without departing from the conception of the
present
application, and all these should pertain to the protection scope of the
present application.
26
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12
Accordingly, the patent protection scope of the present application shall be
based on the
attached Claims.
27
Date Recue/Date Received 2021-11-12