Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
Method for sampling sea surface microlayer
Technical Field
The present invention relates to the technical field of sea surface microlayer
sampling, in particular to a method for sampling sea surface microlayer.
Background Technology
Sea surface microlayer is a thin layer between the atmosphere and the ocean
surface, with a thickness of about 30-200 pm. It has unique physical, chemical
and biological characteristics and can enrich a variety of substances. The
determination of various parameters in the sea surface microlayer is of
special
significance for calculation of substance flux, climate change prediction,
environmental condition prediction, marine organism monitoring and so on.
Relevant research has attracted attention in the field of marine sciences for
long.
High quality sampling is not only a prerequisite for the study of sea surface
microlayer, but also a difficulty in the study of sea surface microlayer.
At present, the sampling methods of sea surface microlayer mainly include
the screen method, the glass plate method and the rotation drum method. By
using
the screen method, a 16-mesh stainless steel wire screen is fixed in a 40 cm X
40
cm stainless steel frame. The screen surface contacts the water surface, and
then it
is lifted at a uniform speed. One corner of the screen is vertically placed on
the
mouth of the sampling bottle to let the water film flow into the sampling
bottle.
The thickness of the sea surface microlayer is about (200 10) p.m. The
screen
sampler is simple to make, easy to operate and can be suitable in bad sea
states,
but the sampling thickness is large, which is difficult to match the
requirements of
scientists. The glass plate method is to immerse a flat glass plate with
certain
specification vertically into the water surface, and then lift it vertically
from the
water at a certain speed. The seawater from sea surface microlayer with a
certain
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
thickness remains on the glass plate, and the residual seawater is scraped
into the
sampling bottle with a scraper. The general sampling thickness of the glass
plate
sampler is 40-100 1.1m. The sampling thickness of the glass plate sampler is
ideal,
and the sampling thickness can match the requirements. The rotation drum
method
is to coat the surface of the roller (diameter 46 cm, length 61cm) with
hydrophilic
glass fiber coating. The height of the roller contacting the water surface can
be
adjusted. The motor is connected with the reducer to adjust the speed of the
roller.
The roller moves slowly in the seawater to collect the water layer with a
thickness
of 50-100 gm. Finally, the seawater is scraped into the sample bottle with a
fixed
scraper. The sampling thickness of the rotation drum sampler is ideal, but it
cannot work under adverse sea states.
Existing patents, such as a Chinese patent with the publication date of
August 23, 2019 and the publication number of CN110160840A, has published a
glass plate sampler for collecting seawater from the sea surface microlayer
and
sampling method thereof. However, the sampling process requires manual
operation and the operation is complicated. In the sampling process, it is
difficult
to ensure a proper water inlet angle, water outlet angle and operation speed.
The
processes have poor stability, and it is difficult to ensure the sampling
quality.
The sampler has low degree of automation and low sampling efficiency, and is
not
suitable for working under adverse sea states.
Summary of invention
Aiming at solving the above-mentioned technical problems, the present
invention proposes a sea surface microlayer sampling method with a reasonable
sampling thickness, excellent sampling quality, a high degree of automation, a
high sampling efficiency and can adapt to certain adverse sea states.
2
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
In order to achieve the above purpose, the technical scheme adopted by the
present invention is:
A sampling method for sampling a sea surface microlayer, comprising the
following steps:
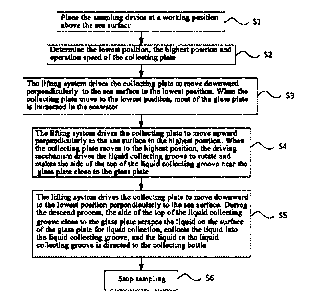
step Si: placing a sampling device at a working position above a sea
surface;
step S2: determining a lowest position, a highest position and an operation
speed of a collecting plate;
step S3: driving with a lifting system the collecting plate to move
downward perpendicularly to the sea surface to the lowest position; when the
collecting plate moves to the lowest position, a glass plate is immersed in
the
seawater;
step S4: driving with the lifting system the collecting plate to move upward
perpendicularly to the sea surface to the highest position; when the
collecting
plate moves to the highest position, a driving mechanism drives a liquid
collecting tank to rotate and draws a side of a top portion of the liquid
collecting
tank that is adjacent the glass plate into a position that is close to the
glass plate
relative to an original position of the side of the top portion of the liquid
collecting tank prior to rotation;
step S5: driving with the lifting system the collecting plate to move
downward to the lowest position perpendicularly to the sea surface; during
descending, the side of the top portion of the liquid collecting tank close to
the
glass plate scrapes liquid on a surface of the glass plate for liquid
collection,
collects the liquid into the liquid collecting tank, and directs the liquid in
the
liquid collecting tank to a collecting bottle; and
step S6: stopping sampling.
Preferably, in step Si, the working position is 10-20 cm above the sea
surface.
3
Date Recue/Date Received 2023-07-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
Preferably, in the step 2, a height of the collecting plate is H; when the
collecting plate is in the lowest position, a vertical distance from a contact
position between the collecting plate and the side of the top portion of the
liquid
collecting tank near the glass plate to a bottom portion of the collecting
plate is
DI, 1 / 2H < D1 <H; and when the collecting plate is in the highest position,
the
vertical distance from the contact position between the collecting plate and
the
side of the top portion of the liquid collecting tank near the glass plate to
the top
portion of the collecting plate is D2, 1 / 2H < D2 < H.
Preferably, in the step S2, the operation speed includes a rising speed and
a falling speed of the collecting plate.
Preferably, the collecting plate rises at a uniform speed.
Preferably, in the step 5, the following steps are also included:
When the collecting plate moves to the lowest position, the driving
mechanism drives the liquid collecting tank to rotate, and makes the side of
the
top portion of the liquid collecting groove near the glass plate far away from
the
glass plate.
Preferably, between the step 5 and the step 6, the following steps are also
included:
Judging whether the collecting bottle is full; when the collecting bottle is
not full, returning to the step S4; and when the collecting bottle is full,
driving
with the lifting system the collecting plate to move upward perpendicularly to
the sea surface to the highest position, and executing the step S6.
Preferably, the driving mechanism comprises one or more electromagnets,
one or more magnets and one or more springs;
When the one or more electromagnets are powered on, the one or more
4
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
electromagnets generate magnetic attraction after being energized to make the
one or more magnets move towards the one or more electromagnets, and the one
or more magnets move to drive the liquid collector to rotate, then make the
side
of the top portion of the liquid collecting groove near the glass plate close
to the
glass plate tightly;
When the one or more electromagnets are powered off, the one or more
electromagnets lose magnetic force; the one or more magnets are pulled away
from the one or more electromagnets by a spring force; movement of the one or
more magnets drives the liquid collector to rotate, and makes a side of a top
portion of the liquid collecting groove near the glass plate far away from the
glass plate.
Preferably, the lifting system is a lead screw lifting system, and the lead
screw lifting system comprises at least one lead screw.
Preferably, a control cabin of the control system sends a signal to control
rotation of the at least one lead screw and drives the collecting plate to
move
downward along a track, the control cabin sends a signal to control reverse
rotation of the at least one lead screw and drive the collecting plate to move
upward along the track, and the control cabin controls turning on and turning
off
the electromagnets.
Compared with existing methods, the present invention has the following
beneficial effects:
The sampling method has reasonable sampling thickness, can match the
requirements of researchers with high degree of automation, high sampling
quality, excellent stability, and can match the requirements of working under
adverse sea states.
The sampling method for sea surface microlayer according to the present
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
invention completes sample collection by setting a lifting system and a
driving
mechanism. The method is simple and the operation speed is easy to control.
The
system includes a collecting plate, and has high automation, high sampling
efficiency and ideal sampling thickness. It can match the requirements of
scientists, adapt to the adverse sampling environment, and the sampling is
authentic and reliable;
Set the side of the top portion of the liquid collecting groove near the
glass plate close to the glass plate. During falling of the collecting plate,
use the
liquid collecting groove to scrape the liquid on the surface of the glass
plate. At
the same time, during the falling process of the collecting plate, the
collecting
plate penetrates into the seawater to continue sample collection, so that
sampling
of the collecting plate and scraping of the liquid collecting groove can be
carried
out simultaneously, which can simplify the operation steps and have high
sampling efficiency;
Set the working position 10-20cm above the sea surface, so that the
sampling device is close to the sea surface as much as possible, and because
there is an outer case for protection, the waves will not hit the sampling
device,
waves contaminating the seawater sample can be avoided;
By limiting the lowest position and the highest position of the collecting
plate, the liquid collecting groove can be close to the glass plate when
rotating
during the working process of the collecting plate, so as to prevent the
position
of the collecting plate from being too high and too low, affecting the
relative
position of the collecting plate and the liquid collecting groove, and further
affecting smooth completion of the collecting work;
Set the collection plate to rise at a uniform speed, which can conduct the
collection work smoothly, make a thickness difference between the collected
6
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
seawater samples small, and can collect the seawater sample matching sampling
standards;
The driving mechanism includes electromagnets, magnets and springs.
The electromagnets are configured to generate magnetic force when energized
and lose magnetic force when powered off. The magnets are controlled to
further
control the contact relationship between the liquid collecting groove and the
glass plate, which can better control the liquid collecting groove for liquid
sample scraping. It has simple structures and involves easy operations;
The lifting system adopts the lead screw lifting system, and the control
cabin is configured control the lifting system and the driving mechanism, so
that
lifting of the collecting plate and rotation of the liquid collecting groove
can be
done automatically, with a high degree of automation and is easy to control.
Brief description of drawings
In order to more clearly explain embodiments of the present invention or
the technical solutions in the prior art, the following will briefly introduce
the
attached figures which are necessary to be used in the description of the
embodiments or the state of art. It is obvious that the attached figures in
the
following description show only some embodiments of the present invention. For
those of ordinary skill in the art, other figures can be obtained according to
these
figures without paying creative labor.
Figure 1 is a flowchart diagram showing an embodiment of the method for
sampling sea surface microlayer disclosed by the present invention;
Figure 2 is a flowchart diagram showing an embodiment of the method for
sampling sea surface microlayer disclosed by the present invention;
Figure 3 is an internal assembly drawing of an embodiment of the device
for sampling sea surface microlayer disclosed by the invention;
7
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
Figure 4 is a structural diagram showing another embodiment of the
device for sampling sea surface microlayer disclosed by the present invention;
Figure 5 is a structural diagram of the collecting plate disclosed by the
present invention;
Figure 6 is an internal structural diagram of the outer case disclosed by
the invention;
Figure 7 is an internal front view of the outer case disclosed by the
present invention;
Figure 8 is a structural diagram of the liquid collector disclosed by the
present invention;
Figure 9 is an upward view showing another embodiment of the liquid
collector disclosed by the present invention.
In the above figures, 1, outer case; 2, lifting ring; 3, collecting plate; 4,
control cabin; 5, liquid collector; 6, collecting bottle; 7, lead screw; 8,
track; 9,
extension hole of the collecting plate; 10, electromagnet; 11, limit groove of
liquid collector; 12, glass plate frame; 13, glass plate; 14, magnet; 15,
spring; 16,
liquid collecting groove; and 17, outlet hole.
Detailed embodiments
Next, the present invention will be described in detail through an
exemplary embodiment. However, it should be understood that without further
description, the elements, structures and features in one embodiment can also
be
usefully combined with other embodiments.
In the description of the invention, it should be noted that the orientation
or position relationship indicated by the terms "inside", "outside", "up",
"down",
"front", "back", "left", "right" and so on is based on the position
relationship
shown in the attached figures, only for convenience of describing the present
8
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
invention and simplifying the description, rather than indicating or implying
that
the device or element must have a specific orientation, or be constructed and
operated in a specific orientation. Therefore, it cannot be understood as a
limitation of the present invention. In addition, the terms "first", "second"
and
"third" are used only for descriptive purposes and cannot be understood as
indicating or implying relative importance.
Figure 1, a method for sampling sea surface microlayer includes the
following steps:
Step Si: placing the sampling device at the working position above the
sea surface.
Specifically, the sampling device is lifted to the working position above
the sea surface through a suspender or a folding arm of a ship or other tools.
The
working position is determined according to the working condition, making the
sampling device as close to the sea surface as possible, and ensuring that the
sea
waves will not hit the sampling device during the working process to prevent
the
sea waves from polluting the liquid sample. The working position is 10-20 cm
above the sea surface.
Step S2: determining a lowest position, a highest position and an
operation speed of the collecting plate.
Specifically, the lowest position and the highest position of the collecting
plate are determined according to the relative position of the collecting
plate and
the liquid collecting groove. The height of the collecting plate is H. When
the
collecting plate is in the lowest position, the vertical distance from the
contact
position between the collecting plate and a side of a top portion of the
liquid
collecting groove near the glass plate to a bottom portion of the collecting
plate
is D1, 1 / 2H < D1 < H. When the sampling plate is in the highest position,
the
9
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
vertical distance from the contact position between the collecting plate and
the
side of the top portion of the liquid collecting groove near the glass plate
to the
top portion of the collection plate is D2, 1 / 2H < D2 < H. The operation
speed of
the collecting plate is determined according to the thickness to be sampled
and
the actual sea state. The operation speed is controlled through a control
cabin.
The operation speed includes the falling speed and the rising speed of the
collecting plate. When the collecting plate rises at a uniform speed, sampling
can
be done better.
Step S3: the lifting system drives the collecting plate to move downward
perpendicularly to the sea surface to the lowest position. When the collecting
plate moves to the lowest position, most of the collecting plate is immersed
in
the sea water.
Specifically, the lifting system is a lead screw lifting system. The lead
screw lifting system includes at least one lead screw. A track is arranged on
the
outer case of the sampling device. The control cabin of the control system
sends
a signal to control rotation of the lead screw and drive the liquid collecting
plate
to move downward along the track to the lowest position. The collecting plate
extends from the extension hole of the collecting plate at the bottom portion
of
the outer case and inserts vertically into the seawater. When the collecting
plate
reaches the lowest position, most of the collecting is immersed in the
seawater.
When the collecting plate is vertically inserted into the seawater, sampling
can
be done better.
Step S4: the lifting system drives the collecting plate to move upward
perpendicularly to the sea surface to the highest position. When the
collecting
plate moves to the highest position, the driving mechanism drives the liquid
collecting groove to rotate and make the side of the top portion of the liquid
to
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
collecting groove near the glass plate close to the glass plate;
Specifically, the control cabin sends a signal to control the at least one
lead screw to rotate reversely to drive the collecting plate to move upward
along
the track to the highest position. The collecting plate is pulled off from the
sea
water vertically at a uniform speed, which can better collect samples with
thickness matching requirements. The driving mechanism includes
electromagnets, magnets and springs. When the collecting plate moves to the
highest position, the control cabin controls the electromagnets to be
energized.
After the electromagnets are powered on, they generate magnetic force, and the
magnets move towards the electromagnets. The magnets move to drive the liquid
collector to rotate, making the side of the top portion of the liquid
collecting
groove near the glass plate to be close to the glass plate.
Step S5: the lifting system drives the collecting plate to move downward
to the lowest position perpendicularly to the sea surface. During descending,
the
side of the top portion of the liquid collecting groove close to the glass
plate
scrapes liquid on a surface of the glass plate for liquid collection, collects
the
liquid into the liquid collecting groove, and the liquid in the liquid
collecting
groove is directed to the collecting bottle;
Specifically, the control cabin of the control system sends a signal to
control rotation of the at least one lead screw to drive the collecting plate
to
move downward to the lowest position. The collecting plate extends from the
extension hole of the collecting plate at the bottom portion of the outer case
and
is vertically inserted into the seawater. During descending, the side at the
top
portion of the liquid collecting groove to the glass plate scrapes the liquid
on the
surface of the glass plate for liquid collection. The liquid is collected into
the
liquid collecting groove. A liquid outlet hole is set on the liquid collecting
11
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
groove. The collected liquid in the liquid collecting groove flows into the
collection bottle through the liquid outlet hole. When the collection plate
reaches
the lowest position, most of the collecting plate is immersed in seawater;
Step S6: stop sampling.
Specifically, the control cabin controls the sampling device to stop
sampling, and the control cabin controls the collecting plate and the liquid
collecting groove to return to the state before work.
Figure 2, in the step S5, the steps below are also included:
When the collecting plate moves to the lowest position, the driving
mechanism drives the liquid collecting groove to rotate, and makes the side of
the top portion of the liquid collecting groove near the glass plate far away
from
the glass plate.
Specifically, the control cabin controls the electromagnets to power off,
the electromagnets lose their magnetic force, the magnets are pulled away from
the electromagnets by a spring force, and the magnets move to drive the liquid
collector to rotate, so that the side of the top portion of the liquid
collecting
groove close to the glass plate is far away from the glass plate.
Between the step 5 and the step 6, the following steps are also included:
Judge whether the collecting bottle is full. When the collecting bottle is
not full, return to step S4. When the collecting bottle is full, the lifting
system
drives the collecting plate to move upward perpendicularly to the sea surface
to
the highest position, and then execute the step S6.
Fig. 3-9, the sea surface microlayer sampling device which the present
invention can realize the method for sampling sea surface microlayer includes
an
outer case 1, a sampling system, a lifting system, a liquid collecting system,
a
control system and a suspension system.
12
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
The outer case is a box structure, which is used to protect the sampling
system and the liquid collection system from wave pollution.
The sampling system includes a collecting plate 3, which is arranged in
the outer case 1. The collection plate 3 includes a glass frame 12 and a glass
plate 13. The glass plate 13 is fixed on the glass frame 12, and the glass
frame 12
wraps edges of the glass plate 13 to protect the glass plate 13.
The lifting system is fixed on the outer case 1, and the collecting plate 3
is arranged on the lifting system through the glass frame 12. The operation of
the
lifting system can drive the collecting plate 3 to move up and down. A
collecting
plate extension hole 9, which is a rectangular through-hole, is set in the
bottom
plate of the outer case 1. A maximum width and a maximum thickness of the
collecting plate 3 are less than a length and a width of the collecting plate
extension hole 9, which is convenient for the collecting plate 3 to move
outside
the outer case 1 through the collecting plate extension hole 9 for sample
collection.
The lifting system is a lead screw lifting system. The lead screw lifting
system includes a lead screw 7. The lead screw 7 is fixed in a groove at an
inner
wall of the outer case 1. The lead screw 7 is set along a longitudinal
direction of
the outer case 1. The inner wall of the outer case 1 is fixed with the track
8. The
track 8 is set along the longitudinal direction of the outer case 1. The glass
frame
12 is set on the lead screw 7 and leans against the track 8. The motor works
to
drive the lead screw 7 to rotate, and rotation of the lead screw 7 drives the
collecting plate to move up and down along the track 8. Setting the track 8 on
the
outer case 1 can limit movement directions of the collecting plate 3.
Controlling
forward and reverse rotation of the motor can control the rotation direction
of the
lead screw 7, and further control rise and fall of the collecting plate 3.
13
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
The liquid collecting system is arranged on the outer case 1. The liquid
collecting system includes a driving mechanism, a liquid collector 5 and a
collecting bottle 6. Two liquid collector limit grooves 11 are set on the
outer case
1, which are symmetrically arranged on the outer case 1. The liquid collector
5 is
arranged in the liquid collector limit groove 11 and can rotate relatively to
the
outer case 1 in the liquid collector limit groove 11. The liquid collecting
groove
16, which is arranged in the outer case 1, is set on the liquid collector tank
5.
The liquid collecting groove 16 is arranged on one side of the collecting
plate 3.
The liquid collecting tank 16 is arranged along a horizontal direction of the
collecting plate 3, and the driving mechanism works to drive the liquid
collector
to rotate relatively to the outer case 1. When collecting samples, the lifting
system drives the collecting plate 3 to extend into the seawater, and then
pull it
out from the seawater and moves to the highest position. At this time, the
liquid
collecting groove 16 does not contact the collecting plate 3. The driving
mechanism drives the liquid collector 5 to rotate to make the side of the top
portion of the liquid collecting groove 16 near the glass plate 13 close to
the
glass plate 13. The lifting system drives the glass plate 13 to descend, and
the
side of the top portion of the liquid collecting groove 16 near the glass
plate 13
scrapes the liquid on the surface of the glass plate 13 for liquid collection.
The
liquid is collected into the liquid collecting groove 16. When the collecting
plate
3 penetrates vertically into the seawater and then is drawn out from the
seawater
at a uniform speed, higher quality sample can be done. The collecting bottle 6
is
arranged on the out case 1. The liquid outlet hole 17 is set in the collecting
tank
16 to discharge the liquid collected by the collecting tank 16. The liquid
outlet
hole 17 can be arranged at a bottom portion of the collecting tank 16. The
liquid
sample in the collecting tank 16 flows into the collecting bottle through the
14
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
liquid outlet hole 17, and the liquid outlet hole 17 is connected with the
collecting bottle 6 through at least one water tube. A depth of the collecting
tank
16 decreases from the liquid outlet hole 17 to the direction away from the
liquid
outlet hole 17, making the liquid outlet hole the lowest point of the liquid
collecting groove 16, and facilitating rapid flow of seawater samples into the
collecting bottle 6.
The driving mechanism comprises magnets 14, springs 15 and
electromagnets 10. The magnets 14 are fixed on the liquid collector 5. The
electromagnets 10 are fixed on the inner wall of the outer case 1 and
correspond
to the magnets 14. One end of the magnets 14 away from the electromagnets are
fixedly connected with one end of the springs 15.The other end of the springs
15
are fixed on the inner wall of the outer case 1 opposite to the inner wall of
the
outer case 10. The springs 15 are detachably connected with the outer case 1
and
the magnets 14 to facilitate the spring replacement. The springs 15 can also
be
hung on the outer case 1 and the magnets 14. When the electromagnets are
powered on, the electromagnets 10 generate magnetic force, the magnets 14
move towards the electromagnets 10, and the magnets 14 move to drive the
liquid
collector 5 to rotate, making the side of the top portion of the liquid
collector 16
near the glass plate 13 close to the glass plate 13. When the electromagnets
10
are powered off, the electromagnets 10 lose their magnetic force, the magnets
14
are pulled away from the electromagnets 10 by the elastic force of the springs
15,
and the magnets 14 move to drive the liquid collector 5 to rotate, keep the
side of
the top portion of the liquid collecting tank 16 close to the glass plate 13
away
from the glass plate 13, making the side of the top portion of the liquid
collecting tank 16 near the glass plate not contact with the glass plate 13,
and
preventing the glass plate 13 from generating resistance during the rise of
the
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
glass plate 13. There are at least one electromagnet 10, at least one magnet
14
and at least one spring 15, which can be two. The two electromagnets 10 are
symmetrically arranged on both sides of the collecting plate 3, and the two
magnets 14 are symmetrically arranged on both ends of the liquid collector 5.
The two springs 15 are symmetrically arranged on both sides of the collecting
plate 3.
The control system includes a control cabin 4, which is electrically
connected with the lifting system. The control cabin 4 sends a signal to
control
the operation of the lifting system. The control cabin can control forward and
reverse rotation of the motor which drives the lead screw 7 to rotate, control
the
rotation direction of the lead screw and further control rise and fall of the
collecting plate 3. The control cabin 4 can control the lowest position and
the
highest position of the operation of the collecting plate. It can also
intelligently
determine a rising speed and a falling speed of the collecting plate according
to
the actual sea state, so as to collect seawater samples from sea surface
microlayer with a certain thickness. The control cabin 4 is electrically
connected
with the electromagnets 10, and the control cabin can control the power on and
power off of the electromagnets 10.
The suspension system includes a lifting ring 2, which is arranged on the
top of the outer case 1 and fixedly connected with the outer case 1. The sea
surface microlayer sampling device is connected with the external lifting
devices
such as suspenders and folding arms through the lifting ring 2 of the
suspension
system, facilitating to suspend the sea surface layer sampling device to a
working position 10-20 cm above the sea surface for sampling. The working
position is determined according to the sea state, so that the sampling device
can
be as close to the sea surface as possible and also avoids the samples
polluted by
16
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
sea waves during the sampling process.
The outer case material can be 316L stainless steel, and the glass frame,
the collecting bottle and the liquid collector can be made of non-stick and
strong
moisture resistance polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon, PTEF).
The working principles of the sea surface microlayer sampling device are:
The sampling device is lifted to the working position 10-20 cm above the
sea surface by the suspension mechanism for sampling;
The control cabin 4 sends a signal to drive the lead screw 7 to rotate. The
lead screw 7 drives the collecting plate to move downward along the track 8 to
the lowest position. The collecting plate 3 extends from the collecting plate
hole
9 under the outer case and penetrates vertically into the seawater. When the
collecting plate 3 moves to the lowest position, most of the collecting plate
3 is
immersed in the seawater;
The control cabin 4 sends a signal to drive the lead screw 7 to rotate in the
reverse direction. The lead screw 7 drives the collecting plate 3 to move
upward
along the track 8 to the highest position, and the collecting plate is pulled
out
vertically from the seawater. When the collecting plate moves to the highest
position, the control cabin 4 energizes the electromagnets 10. After the
electromagnets 10 are powered on, they generate magnetic force to attract the
magnets 14 of the liquid collector 5 and drive the liquid collector to rotate,
making the side of the liquid collecting groove 16 near the glass plate close
to
the glass plate;
The control cabin 4 sends a signal to drive the lead screw 7 to rotate, and
the lead screw 7 drives the collecting plate to move downward to the lowest
position along the track 8. During descending, the seawater on the glass plate
is
scraped into the liquid collecting groove of the liquid collector by the side
of the
17
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26
CA 03162937 2022-05-26
top portion of the liquid collecting groove 16 near the glass plate 13, and
the
liquid collecting groove is guided into the collection bottle 6 through the
liquid
outlet hole 17 and the tube. When the collecting plate moves to the lowest
position, the control cabin 4 cuts off the power to the electromagnets 10, and
the
electromagnets lose their magnetic force. The liquid collector is pulled by
the
spring 15 to make the liquid collecting groove near the glass plate away from
the
glass plate;
Judge whether the collecting bottle is full. When the collecting bottle is
not full, the control cabin 4 sends a signal to drive the lead screw 7 to
rotate
reversely and drive the collecting plate 3 to move upward to the highest
position.
Repeat the previous operation process for liquid sample collection. If the
collecting bottle is full, the control cabin 4 sends a signal to drive the
lead screw
7 to rotate reversely and drive the collecting plate 3 to move upward to the
highest position, and then stop collection.
The above-mentioned description shows only some preferred
embodiments of the present invention and is not a limitation of the present
invention. Any one skilled in the art may change or modify the above-mentioned
disclosed technical solutions to be equivalent embodiments by making
equivalent
replacement and apply the same in other fields, but any simple modification,
equivalent changes and modifications to the above-mentioned embodiment
according to the technical essence of the present invention without departing
from the technical scheme of the present invention still belong to the
protection
scope of the technical scheme of the present invention.
18
Date Recue/Date Received 2022-05-26