Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
LUBRICATING OIL CONTAINING ALKYL PHOSPHONIC ACID
TECHNICAL FIELD
[001] This disclosure relates to lubricating oil additives and lubricating oil
compositions containing the same. More specifically, this disclosure describes
zinc-
free additives that impart anti-wear properties to lubricating oil
compositions.
BACKGROUND
[002] Zinc dialkyldithiophosphate (ZnDTP) has long been used as a wear
inhibitor in various lubricating fluids such as automotive engine oil. At
least one
drawback is that ZnDTP can decompose due to high temperature, oxidative
deterioration, or hydrolysis in the presence of water. The result of the
decomposition
is a sludge that decreases friction coefficient and/or clogs important moving
parts.
[003] When ZnDTP is used in automatic transmission fluids (ATE), the
decomposition products can accumulate in the pores of the paper material that
forms
the wet clutch, which can lead to clogging. Consequently, the cooling
performance
and durability of the clutch are significantly reduced.
[004] Thus, there exists a need for alternative zinc-free wear inhibitors that
can
be used in various lubricating fluids.
SUMMARY
[005] In one aspect, there is provided a lubricating oil composition
comprising:
a major amount of an oil of lubricating viscosity having a kinematic viscosity
at 100 C
in a range of about 1.5 to about 35 mm2/s; and an anti-wear mixture
comprising: one
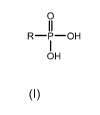
or more ashless dispersants and an alkyl phosphonic acid having a structure
given by
(I)I
R-T -OH
OH
1
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
wherein R is a C3-C20 hydrocarbyl group; initial pH of the anti-wear mixture
is between
5.0-9.5 as measured by ASTM D664; and wherein the lubricating oil composition
is free
of zinc.
[006] In another aspect, there is provided a lubricating oil composition
comprising: a major amount of an oil of lubricating viscosity having a
kinematic
viscosity at 100 C in a range of about 1.5 to about 35 mm2/s; and an anti-wear
mixture
comprising: one or more polyisobutenyl succinimide dispersants and an alkyl
phosphonic acid having a structure given by
(1)1
R-T-OH
OH
wherein R is a C3-C20 hydrocarbyl group; initial pH of the anti-wear mixture
is between
5.0 ¨ 9.5 as measured by ASTM D664; and wherein the lubricating oil
composition is
free of zinc.
[007] In yet another aspect, there is provided a method of reducing wear of a
transmission or gear comprising: lubricating the transmission or gear with a
lubricating
oil composition comprising: a major amount of an oil of lubricating viscosity
having a
kinematic viscosity at 100 C in a range of about 1.5 to about 35 mm2/s; and an
anti-
wear mixture comprising: one or more ashless dispersants and an alkyl
phosphonic
acid of the following formula:
(IDI
R-T-OH
OH
wherein R is a C3-C20 hydrocarbyl group; wherein the initial pH of the anti-
wear mixture
is between 5.0 ¨ 9.5 when measured by the ASTM D664 method; and wherein the
lubricating oil composition is free of zinc.
2
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023 PCT/IB2021/058338
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
Definitions
[008] The term "succinimide" is understood in the art to include many of the
amide, imide, and amidine species which may be formed by the reaction of a
succinic
anhydride with an amine. The predominant product, however, is a succinimide
and
this term has been generally accepted as meaning the product of a reaction of
an
alkenyl- or alkyl-substituted succinic acid or anhydride with an amine.
Alkenyl or alkyl
succinimides are disclosed in numerous references and are well known in the
art
Certain fundamental types of succinimides and related materials encompassed by
the
term of art "succinimide" are taught in US. Patent Nos. 2,992,708; 3,018,291;
3,024,237;
3,100,673; 3,219,666; 3,172,892; and 3,272,746.
[009] The term "hydrocarbyr refers to a chemical group or moiety derived
from hydrocarbons including saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Examples
of
hydrocarbyl groups include alkenyl, alkyl, polyalkenyl, polyalkyl, phenyl, and
the like.
[010] The terms 'oil--soluble' or 'oil-dispersible' as used herein do not
necessarily indicate that the compounds or additives are soluble, dissolvable,
miscible
or capable of being suspended in the oil in all proportions. These do mean,
however,
that they are, for instance, soluble or stably dispersible in oil to an extent
sufficient to
exert their intended effect in the environment in which the oil is employed.
Moreover,
the additional incorporation of other additives may also permit incorporation
of higher
levels of a particular additive, if desired.
[011] It is understood that when combinations, subsets, groups, etc. of
elements are disclosed (e.g., combinations of components in a composition, or
combinations of steps in a method), that while specific reference of each of
the various
individual and collective combinations and permutations of these elements may
not
be explicitly disclosed, each is specifically contemplated and described
herein.
[012] A dispersant is an essential lubricant additive, particularly in engine
oil
and automatic transmission fluid, for preventing sludge generation and
increasing
friction coefficient of wet clutch. However, dispersants can often reduce the
effects of
3
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
anti-wear agents (e.g., ZnDTP) and extreme pressure (EP) additives
particularly in sulfur
phosphorus (S-P) type gear oils and automatic transmission fluids.
[013] The present invention describes wear inhibitors (or anti-wear agents)
that can impart anti-wear properties to lubricating oil compositions. In some
embodiments, the present invention describes a wear inhibitor system
comprising a
succinimide and a phosphonic acid. The wear inhibitor system of the present
invention
is zinc-free (present in less than about 10 ppm) and therefore avoids at least
some of
the performance issues associated with conventional zinc anti-wear agents.
[014] The wear inhibitor system of the present invention may be added to any
compatible lubricating oil such as engine oil, hydraulic fluid, slide way
lubricant,
automatic transmission fluid (ATE), continuously variable transmission (CVT)
fluid,
battery electric vehicle (BEV), hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) transmission
fluid, and gear
oil.
Succinimide Dispersants
[015] The succinimide dispersant can be prepared by any known method such
as those described in, for example, U.S. Patent Publication No. 20180034635
and U.S.
Patent No. 7,091,306, which are hereby incorporated by reference.
[016] In accordance with the present invention, the succinimide is a
hydrocarbyl succinimide obtained as the product of a reaction of alkyl-
substituted
succinic anhydrides with a polyamine. In lubricating oil applications, the
succinic
anhydrides are typically substituted in alpha position by an alkyl chain such
as
polyisobutylene (PIBSA) or PIBSA-type moiety. However, any alkyl group
compatible
with the present invention may be contemplated.
[017] For lubricating oil application, polyalkylene polyamine is commonly used
as the polyamine. However, any polyamine compatible with the present invention
may
be contemplated.
[018] The polyamine can react with the alkyl-substituted succinic anhydride to
produce, according to their molar ratio, mono-succinimides, bis-succinimides,
tris-
succinimides or mixtures of thereof.
4
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
[019] In one embodiment, a hydrocarbyl bis-succinimide can be obtained by
reacting a hydrocarbyl-substituted succinic anhydride of structure II
N_.- -
0
0
Structure II
(wherein R is a hydrocaryl substituent is derived from a polyalkene group
having a
number average molecular weight of from about 500 to about 3000) with a
polyamine.
[020] In one embodiment, R is a hydrocarbyl substituent is derived from a
polyalkene group having a number average molecular weight of from about 1000
to
about 2500. In one embodiment, R is a polyisobutenyl substituent derived from
a
polyisobutene having a number average molecular weight of from about 500 to
about
3000 (such as from 850 to 1700). In another embodiment, R is a polyisobutenyl
substituent derived from a polyisobutene having a number average molecular
weight
of from about 1000 to about 2500.
[021] Suitable polyamines can have a straight- or branched-chain structure
and may be cyclic, acylic, or combinations thereof.
[022] In some embodiments, polyalkylene polyamines may be used to prepare
the bis-succinimide dispersants. Such polyallwlene polyamines will typically
contain
about 2 to about 12 nitrogen atoms and about 2 to 24 carbon atoms.
Particularly
suitable polyallwlene polyamines include those having the formula:
H2N¨(R"NH)x¨H
wherein R' is a straight- or branched-chain alkylene group having 2 or 3
carbon atoms
and x is 1 to 9. Representative examples of suitable polyallwlene polyamines
include
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
diethylenetriamine (DETA), triethylenetetramine (TETA), tetraethylenepentamine
(TEPA), pentaethylene hexamine (PEHA), and heavier poly-allwlene-amines (HPA).
[023] In some embodiments, the polyamine may contain cyclic groups.
Specific examples include N, N'-bis-(2-aminoethyl)piperazine) (Bis AEP), N-[(2-
aminoethyl) 2-aminoethyl]piperazine) (PEEDA), 1-(2-aminoethyl)-4-[(2-
aminoethyl)amino]ethyl]-
piperazine) (AEPEEDA) and 142-[[2-[(2-aminoethyl)amino]ethyllaminolethyll-
piperazine) (PEDETA).
[024] Many of the polyamines suitable for use in the present invention are
commercially available and others may be prepared by methods which are well
known
in the art. For example, methods for preparing amines and their reactions are
detailed
in Sidgewick's "The Organic Chemistry of Nitrogen", Clarendon Press, Oxford,
1966;
Noller's "Chemistry of Organic Compounds", Saunders, Philadelphia, 2nd Ed.,
1957;
and Kirk-Othmer's "Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology", 2nd Ed., especially
Volume
2, pp. 99 116.
[025] Generally, the hydrocarbyl-substituted succinic anhydride is reacted
with
the polyamine at a temperature of about 130 C to 220 C (e.g., 140 C to 200 C,
145 C
to 175 C, etc.). The reaction can be carried out under an inert atmosphere,
such as
nitrogen or argon. Generally, a suitable molar charge of polyamine to
polyalkenyl-
substituted succinic anhydride is from about 0.35:1 to about 1:1 (e.g., 0.4:1
to 0.75:1).
As used herein, the "molar charge of polyamine to polyalkenyl-substituted
succinic
anhydride" means the ratio of the number of moles of polyamine to the number
of
succinic groups in the succinic anhydride reactant.
[026] One class of suitable hydrocarbyl succinimides may be represented by
the following structure:
6
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
0 0
1\
N -------------------------- R -- N -- R'
o 0
Structure III
wherein Rand R' are as described herein above and y is 1 to 11.
[027] In some embodiments, the succinimide dispersant may be post-treated
by a reactive boron compound or organic carbonate.
[028] Suitable boron compounds that can be used as a source of boron
include, for example, boric acid, a boric acid salt, a boric acid ester, and
the like.
Representative examples of a boric acid include orthoboric acid, metaboric
acid,
paraboric acid, and the like. Representative examples of a boric acid salt
include
ammonium borates, such as ammonium metaborate, ammonium tetraborate,
ammonium pentaborate, ammonium octaborate, and the like. Representative
examples of a boric acid ester include monomethyl borate, dimethyl borate,
trimethyl
borate, monoethyl borate, diethyl borate, triethyl borate, monopropyl borate,
dipropyl
borate, tripropyl borate, monobutyl borate, dibutyl borate, tributyl borate,
and the like.
[029] Suitable organic carbonates include, for example, cyclic carbonates such
as 1,3-dioxolan-2-one (ethylene carbonate); 4-methyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-
one(propylene
carbonate); 4-ethyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-one(butylene carbonate); 4-hydroxymethy1-
1,3-
dioxolan-2-one; 4,5-dimethy1-1,3-dioxolan-2-one; 4-ethyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-one;
4,4-
dimethy1-1,3-dioxolan-2-one; 4-methyl-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-one; 4,5-diethy1-
1,3-
dioxolan-2-one; 4,4-diethyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-one; 1,3-dioxan-2-one; 4,4-dimethy1-
1,3-
dioxan-2-one; 5,5-dimethy1-1,3-dioxan-2-one; 5,5-dihydroxymethy1-1,3-dioxan-2-
one; 5-methyl-1,3-dioxan-2-one; 4-methyl-1,3-dioxan-2-one; 5-hydroxy-1,3-
dioxan-
7
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
2-one; 5-hydroxymethy1-5-methyl-1,3-dioxan-2-one; 5,5-diethyl-1,3-dioxan-2-
one; 5-
methyl-5-propy1-1,3-dioxan-2-one; 4,6-dimethy1-1,3-dioxan-2-one; 4,4,6-
trimethyl-
1,3-dioxan-2-one and spiro[1,3-oxa-2-cyclohexanone-5,5'-1',3'-oxa-2'-
cyclohexanone]. Other suitable cyclic carbonates may be prepared from
saccharides
such as sorbitol, glucose, fructose, galactose and the like and from vicinal
diols
prepared from Ci to C30 olefins by methods known in the art.
Alkyl Phosphonic Acid
[030] Alkyl phosphonic acid may be described as a hydrocarbyl substituted
derivative of a phosphonic acid. Phosphonic acids including alkyl phosphonic
acids
are generally insoluble in base oil due to their diacid structure. This has
limited the
use of phosphonic acids in lubricating oils.
[031] Mixing alkyl phosphonic acids with a basic compound such as the
succinimide dispersant of the present invention neutralizes the alkyl
phosphonic acid
which in turn enhances the oil solubility of the mixture including the alkyl
phosphonic
acid and/or the alkyl phosphonate.
[032] In accordance with the present invention, the alkyl phosphonic acid is a
monoallwlphosphonic acid that can be described by the following formula:
(131
R-7-0H
OH
Structure IV
wherein R is a C3-C20 hydrocarbyl group. R may be saturated or unsaturated. R
may
be linear, branched, or cyclic. In some embodiments, R is aliphatic. In some
embodiments, R is aromatic. R may be an alkyl, aryl, or alkaryl group. In some
embodiments, R may include a heteroatom. In some embodiments, R may include an
ether or thioether moiety.
8
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
[033] The phosphonic acid may be obtained by any known compatible
method. For example, phosphonic acid may be obtained via oxidation of
phosphinic
acid. Another synthetic pathway involves hydrolysis of dially1 phosphonate to
phosphonic acid under acidic conditions. A more detailed discussion can be
found in
Bei!stein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 2186-2213, which is hereby incorporated by
reference.
[034] Suitable examples of compatible alkyl phosphonic acids include butyl
phosphonic acid, octyl phosphonic acid, decyl phosphonic acid, octadecyl
phosphonic
acid, and the like.
[035] In some embodiments, the alkyl phosphonic acid may be pre-mixed with
the succinimide dispersant prior to blending with the base oil. The initial pH
of such a
mixture is between about 5.0 to about 9.5 as measured by ASTM D664. In other
embodiments, no pre-mixing is required.
Lubricating Oil
[036] When employed as lubricant additives, the succinimide is usually present
in the lubricating oil composition in concentrations ranging from about 0.001
to about
20 wt. % (including, but not limited to, 0.01 to 5 wt. %, 0.2 to 4 wt. %, 0.5
to 3 wt. %, 1
to 2 wt. %, and so forth), based on the total weight of the lubricating oil
composition.
[037] The phosphonic acid may be present in concentrations ranging from
about 0.001 to about 20 wt. % (including, but not limited to, 0.01 to 5 wt. %,
0.02 to 4
wt. %, 0.05 to 3 wt. %, 0.1 to 2 wt. %, and so forth), based on the total
weight of the
lubricating oil composition.
[038] Oils used as the base oil will be selected or blended depending on the
desired end use and the additives in the finished oil to give the desired
grade of engine
oil, e.g. a lubricating oil composition having an Society of Automotive
Engineers (SAE)
Viscosity Grade of OW, OW-8, OW-16, OW-20, OW-30, OW-40, OW-50, OW-60, 5W, 5W-
20, 5W-30, 5W-40, 5W-50, 5W-60, 10W, 10W-20, 10W-30, 10W-40, 10W-50, 15W,
15W-20, 15W-30, or 15W-40.
[039] The oil of lubricating viscosity (sometimes referred to as "base stock"
or
"base oil") is the primary liquid constituent of a lubricant, into which
additives and
9
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
possibly other oils are blended, for example to produce a final lubricant (or
lubricant
composition). A base oil, which is useful for making concentrates as well as
for making
lubricating oil compositions therefrom, may be selected from natural
(vegetable,
animal or mineral) and synthetic lubricating oils and mixtures thereof.
[040] Definitions for the base stocks and base oils in this disclosure are the
same as those found in American Petroleum Institute (API) Publication 1509
Annex E
("API Base Oil Interchangeability Guidelines for Passenger Car Motor Oils and
Diesel
Engine Oils," December 2016). Group I base stocks contain less than 90%
saturates
and/or greater than 0.03% sulfur and have a viscosity index greater than or
equal to
80 and less than 120 using the test methods specified in Table E-1. Group II
base stocks
contain greater than or equal to 90% saturates and less than or equal to 0.03%
sulfur
and have a viscosity index greater than or equal to 80 and less than 120 using
the test
methods specified in Table E-1. Group III base stocks contain greater than or
equal to
90% saturates and less than or equal to 0.03% sulfur and have a viscosity
index greater
than or equal to 120 using the test methods specified in Table E-1. Group IV
base
stocks are polyalphaolefins (PAO). Group V base stocks include all other base
stocks
not included in Group I, II, Ill, or IV.
[041] Natural oils include animal oils, vegetable oils (e.g., castor oil and
lard
oil), and mineral oils. Animal and vegetable oils possessing favorable thermal
oxidative
stability can be used. Of the natural oils, mineral oils are preferred.
Mineral oils vary
widely as to their crude source, for example, as to whether they are
paraffinic,
naphthenic, or mixed paraffinic-naphthenic. Oils derived from coal or shale
are also
useful. Natural oils vary also as to the method used for their production and
purification, for example, their distillation range and whether they are
straight run or
cracked, hydrorefined, or solvent extracted.
[042] Synthetic oils include hydrocarbon oil. Hydrocarbon oils include oils
such
as polymerized and interpolymerized olefins (e.g., polybutylenes,
polypropylenes,
propylene isobutylene copolymers, ethylene-olefin copolymers, and ethylene-
alphaolefin copolymers). Polyalphaolefin (PAO) oil base stocks are commonly
used
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
synthetic hydrocarbon oil. By way of example, PAOs derived from C8 to C14
olefins, e.g.,
C8, C10, C12, C14 olefins or mixtures thereof, may be utilized.
[043] Other useful fluids for use as base oils include non-conventional or
unconventional base stocks that have been processed, preferably catalytically,
or
synthesized to provide high performance characteristics.
[044] Non-conventional or unconventional base stocks/base oils include one
or more of a mixture of base stock(s) derived from one or more Gas-to-Liquids
(GTL)
materials, as well as isomerate/isodewaxate base stock(s) derived from natural
wax or
waxy feeds, mineral and or non-mineral oil waxy feed stocks such as slack
waxes,
natural waxes, and waxy stocks such as gas oils, waxy fuels hydrocracker
bottoms, waxy
raffinate, hydrocrackate, thermal crackates, or other mineral, mineral oil, or
even non-
petroleum oil derived waxy materials such as waxy materials received from coal
liquefaction or shale oil, and mixtures of such base stocks. Other base oils
include Coal
to liquid (CTL) products and alkyl-naphthalene.
[045] Base oils for use in the lubricating oil compositions of present
disclosure
are any of the variety of oils corresponding to API Group I, Group II, Group
Ill, Group
IV, and Group V oils, and mixtures thereof, preferably API Group II, Group
III, Group IV,
and Group V oils, and mixtures thereof, more preferably the Group III to Group
V base
oils due to their exceptional volatility, stability, viscometric and
cleanliness features.
[046] Typically, the base oil will have a kinematic viscosity at 100 C (ASTM
D445) in a range of 1.5 to 35 mm2/s (e.g., 1.5 to 25 mm2/s, 2.0 to 20 mm2/s,
or 2.0 to
15 mm2/s).
[047] The present lubricating oil compositions may also contain conventional
lubricant additives for imparting auxiliary functions to give a finished
lubricating oil
composition in which these additives are dispersed or dissolved. For example,
the
lubricating oil compositions can be blended with antioxidants, ashless
dispersants,
anti-wear agents, detergents such as metal detergents, rust inhibitors,
dehazing
agents, demulsifying agents, friction modifiers, metal deactivating agents,
pour point
depressants, viscosity modifiers, antifoaming agents, co-solvents, package
11
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
compatibilizers, corrosion-inhibitors, dyes, extreme pressure agents and the
like and
mixtures thereof. A variety of the additives are known and commercially
available.
These additives, or their analogous compounds, can be employed for the
preparation
of the lubricating oil compositions of the invention by the usual blending
procedures.
[048] Each of the foregoing additives, when used, is used at a functionally
effective amount to impart the desired properties to the lubricant. Thus, for
example,
if an additive is an ashless dispersant, a functionally effective amount of
this ashless
dispersant would be an amount sufficient to impart the desired dispersancy
characteristics to the lubricant. Generally, the concentration of each of
these additives,
when used, may range, unless otherwise specified, from about 0.001 to about 20
wt.
%, such as about 0.01 to about 10 wt. %.
[049] The following non-limiting examples are illustrative of the present
invention.
EXAMPLES
[050] Lubricating oil samples (i.e., examples and comparative examples) were
evaluated for anti-wear performance. Each sample includes succinimide
dispersant, a
phosphorus additive (optional in some comparative examples), other lubricating
oil
additives (friction modifiers, ashless anti-wear additives, antioxidants,
metal
deactivators, seal swell additives, foam inhibitors, and viscosity modifiers),
and base
oil.
Succinimide Dispersant
[051] Borated Succinimide 1 is a boron-modified polyisobutenyl succinimide
with a polyisobutylene number average molecular weight of 950 (N: 1.95 wt%; B:
0.63
wt%).
[052] Borated Succinimide 2 is a boron-modified polyisobutenyl succinimide
with a polyisobutylene number average molecular weight of 1,300 (N: 1.88 wt%;
B: 0.36
wt%).
12
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
[053] Succinimide 1 is a polyisobutenyl succinimide with a polyisobutylene
number average molecular weight of 950 (N: 2.15 wt%).
[054] Succinimide 2 is a polyisobutenyl succinimide with a polyisobutylene
number average molecular weight of 950 (N: 2.0 wt%).
[055] Succinimide 3 is a low molecular weight alkenyl succinimide (N: 4.6
wt%).
Phosphorus Additive
[056] Phosphorus additive is a phosphorus-containing compound.
[057] Monoallylphosphonic acid includes butyl phosphonic acid (P: 22.4 wt%),
octyl phosphonic acid (P: 15.7 wt%), and octadecyl phosphonic acid (P: 9.3
wt%).
[058] Phosphorus compound 1 is inorganic phosphoric acid H3PO4 (P: 27.0
wt%).
[059] Phosphorus compound 2 is 2-ethylhexyl phosphate ester (P: 11.1 wt%).
[060] Phosphorus compound 3 is 3-bis(2-
methylpropoxy)phosphinothioylthio-2-methyl-propanoic acid, commercially
available
from BASF under the trade name lrgalube 0 353 (P: 9.3 wt%).
[061] Phosphorus compound 4 is trilauryl trithiophosphite (P: 4.9 wt%)
[062] Phosphorus compound 5 is a mixture of C12, C14, and C18 phosphate
ester (P: 8.3 wt%).
[063] Phosphorus compound 6 is isotridecyl phosphate ester (P: 8.2 wt%).
[064] Phosphorus compound 7 is dimethyl octadecyl phosphonate (P: 8.6 wt%)
[065] The examples and comparative examples were prepared from the above-
mentioned additives in the ratios described in Table 1 and Table 2. The
initial pH of
the mixture of succinimide dispersant (A) and phosphorus additive (B) was
measured
by ASTM D664 method and reported in Table 1.
Wear Test
[066] The anti-wear performance of each lubricating oil compositions was
determined using the 4 ball wear scar test (ASTM D4172) at 1200 rpm and 1800
rpm,
oil temperature of 80 C, and load of 392N for 60 min. After testing, the test
balls were
removed and the wear scars were measured. The wear scar diameters are reported
in
13
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
mm in Table 1 and Table 2. A smaller wear scar diameter indicates better anti-
wear
performance.
Table 1
Comp. Comp. Comp. Comp. Comp. Comp. Comp. Comp.
ex. 1 ex. 2 ex. 3 ex. 4 ex. 5 ex.6 ex. 7 ex. 8
(A) Dispeisants
.. .. ... ..
:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.::
Borated 1.24 1.24 1.24 1.24 1.24 1.24 1.24
1.24
succinimide 1
(950)
Succinimide 1 0.74 0.74 0.74 0.74 0.74 0.74 0.74
0.74
(XC180000144)
(B) Phosphorus
additives
Butyl
phosphonic
acid
Octyl
phosphonic
acid
Octadecyl
phosphonic
acid
P. compound 0.08
1
P. compound 0.18
2
P. compound 0.22
3
P. compound 0.41
4
P. compound 0.25
P. compound 0.25
6
P. compound 0.24
7
Initial pH of 10.0 7.7 6.7 8.3 9.6 6.6 6.6 7.9
A+ B mixture
Phosphorus 0 216 200 205 201 208 206 205
content from B
(PPrn)
Other 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
additives
Base oil Balance Balance Balance Balance Balance Balance Balance Balance
Wear and
Deposit test
14
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
Wear scar
diameter @ 0.48 0.48 0.53 0.51 0.45 0.49 0.49 -- 0.42
1200rpm (km)
Wear scar
diameter @ 0.54 0.61 0.64 0.56 0.53 0.62 0.63 0.54
1800rpm (km)
Table 1 cont.
Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 Example 4
(A) Dispersants
Borated succinimide 1(950) 1.24 1.24 1.24 1.24
Succinimide 1 (XC180000144) 0.74 0.74 0.74 0.74
(B) Phosphorus additives
Butyl phosphonic acid 0.09
Octyl phosphonic acid 0.13 0.30
Octadecyl phosphonic acid 0.22
P. compound 1
P. compound 2
P. compound 3
P. compound 4
P. compound 5
P. compound 6
P. compound 7
Initial pH of A+B mixture 7.6 7.5 6.9 7.2
Phosphorus content from B (ppm) 202 204 471 204
Other additives 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
Base oil Balance Balance Balance
Balance
Wear and Deposit test
Wear scar diameter @ 1200rpm (iim) 0.44 0.38 0.33 0.33
Wear scar diameter @ 1800rpm (iim) 0.49 0.38 0.34 0.36
[067] Comparative examples 1-8 which contain succinimide but do not contain
alkyl phosphonic acid showed poor anti-wear performance. By contrast,
inventive
examples 1-4 which contain succinimide and C4-C18 alkyl phosphonic acids
showed
superior anti-wear performance.
[068] The anti-wear property of alkyl phosphonic acid was also evaluated with
different succinimide mixtures. Table 2 below shows the 4-ball wear scar
results for
comparative examples 9-10 and inventive examples 5-6.
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023 PCT/IB2021/058338
Table 2
Comp. Example Comp. Example
ex. 9 5 ex. 10 6
(A) Dispersants
Borated succinimide 1(950) 1.24 1.24
Borated succinimide 2 1.20 1.20
(1300)
Succinimide 2(11001) 0.80 0.80
Succinimide 3 (CP4809) 0.35 0.35
(B) Phosphorus additives
Octyl phosphonic acid 0.13 0.13
Initial pH of A+B mixture 9.9 7.2 10.5 7.9
Phosphorus content from B 0 204 0 204
(loPm)
Other additives 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
Base oil Balance Balance Balance Balance
Wear and Deposit test:
Wear scar diameter @
0.48 0.41 0.78 0.41
1200rpm (iim)
Wear scar diameter @
0.57 0.44 0.64 0.49
1800rpm (iim)
[069] Inventive examples 5 and 6 which contain octyl phosphonic acid in
addition to succinimide, exhibited superior performance compared to
comparative
examples 9-10, further demonstrating the antiwear capabilities of alkyl
phosphonic
acids.
Volume Resistivity
[070] The electrical insulating ability of the lubricating oil compositions
was
determined in accordance with JIS C2101-1999-24. The volume resistivity values
of
several examples were measured at an applied voltage of 250 V and reported in
units
of acm in Table 3. A volume resistivity of greater than 1 x 108 Q= cm at 80 C
is
preferred for adequate insulating properties in transmission fluids.
Table 3
Example Example Example Example Example Example
1 2 3 4 5 6
Volume R
16
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
Volume Resistivity @ 40 C (0=
4.2 x 109 1.4 x 109 3.3 x 109 3.3 x 109 5.6 x 109 1.1 x 109
cm)
Volume Resistivity @ 80 C (0=
1.2 x 109 0.4 x 109 1.1 x 109 1.0 x 109 1.4 x 109 0.3 x
109
cm)
[071] All documents described herein are incorporated by reference herein,
including any priority documents and/or testing procedures to the extent they
are not
inconsistent with this text. As is apparent from the foregoing general
description and
the specific embodiments, while forms of the present disclosure have been
illustrated
and described, various modifications can be made without departing from the
spirit
and scope of the present disclosure. Accordingly, it is not intended that the
present
disclosure be limited thereby.
[072] For the sake of brevity, only certain ranges are explicitly disclosed
herein.
However, ranges from any lower limit may be combined with any upper limit to
recite
a range not explicitly recited, as well as, ranges from any lower limit may be
combined
with any other lower limit to recite a range not explicitly recited, in the
same way,
ranges from any upper limit may be combined with any other upper limit to
recite a
range not explicitly recited. Additionally, within a range includes every
point or
individual value between its end points even though not explicitly recited.
Thus, every
point or individual value may serve as its own lower or upper limit combined
with any
other point or individual value or any other lower or upper limit, to recite a
range not
explicitly recited.
[073] Likewise, the term "comprising" is considered synonymous with the term
"including." Likewise, whenever a composition, an element or a group of
elements is
preceded with the transitional phrase "comprising," it is understood that we
also
contemplate the same composition or group of elements with transitional
phrases
"consisting essentially of," "consisting of," "selected from the group of
consisting of,"
or "is" preceding the recitation of the composition, element, or elements and
vice
versa.
[074] The terms "a" and the as used herein are understood to encompass the
plural as well as the singular.
17
CA 03193618 2023-03-01
WO 2022/054023
PCT/IB2021/058338
[075] Various terms have been defined above. To the extent a term used in a
claim is not defined above, it should be given the broadest definition persons
in the
pertinent art have given that term as reflected in at least one printed
publication or
issued patent. Furthermore, all patents, test procedures, and other documents
cited in
this application are fully incorporated by reference to the extent such
disclosure is not
inconsistent with this application and for all jurisdictions in which such
incorporation
is permitted.
[076] The foregoing description of the disclosure illustrates and describes
the
present disclosure. Additionally, the disclosure shows and describes only the
preferred
embodiments but, as mentioned above, it is to be understood that the
disclosure is
capable of use in various other combinations, modifications, and environments
and is
capable of changes or modifications within the scope of the concept as
expressed
herein, commensurate with the above teachings and/or the skill or knowledge of
the
relevant art. While the foregoing is directed to embodiments of the present
disclosure,
other and further embodiments of the disclosure may be devised without
departing
from the basic scope thereof, and the scope thereof is determined by the
claims that
follow.
[077] It is understood that when combinations, subsets, groups, etc. of
elements are disclosed (e.g., combinations of components in a composition, or
combinations of steps in a method), that while specific reference of each of
the various
individual and collective combinations and permutations of these elements may
not
be explicitly disclosed, each is specifically contemplated and described
herein.
[078] The embodiments described hereinabove are further intended to explain
best modes known of practicing it and to enable others skilled in the art to
utilize the
disclosure in such, or other, embodiments and with the various modifications
required
by the particular applications or uses. Accordingly, the description is not
intended to
limit it to the form disclosed herein. Also, it is intended that the appended
claims be
construed to include alternative embodiments.
18