Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 1 -
AN AEROSOL-FORMING SUBSTRATE
The present invention relates to an aerosol-forming substrate comprising
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose and one or more cellulose based strengthening
agents.
Aerosol-generating systems for delivering an aerosol to a user typically
comprise an
atomiser configured to generate an inhalable aerosol from an aerosol-forming
substrate.
Some known aerosol-generating systems comprise a thermal atomiser such as an
electric
heater or an inductive heating device. The thermal atomiser is configured to
heat and vaporise
the aerosol-forming substrate to generate an aerosol. Typical aerosol-forming
substrates for
use in aerosol-generating systems are nicotine formulations, which may be
liquid nicotine
formulations comprising an aerosol former such as glycerine and/or propylene
glycol.
It would be desirable to provide an aerosol-generating article having an
aerosol-
forming substrate that exhibits increased tensile strength.
It would also be desirable to provide an aerosol-generating article having an
aerosol-
forming substrate that exhibits a reduced tendency to melt and form a crust on
a part of the
aerosol-generating article or a part of the aerosol-generating system.
There is provided an aerosol-forming substrate for use in an aerosol-
generating
system. The aerosol-forming substrate may comprise one or more aerosol
formers. The
aerosol-forming substrate may comprise hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may comprise one or more cellulose based strengthening agents.
There is also provided an aerosol-forming substrate for use in an aerosol-
generating
system, the aerosol-forming substrate comprising: one or more aerosol formers;
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose; and one or more cellulose based strengthening
agents.
There is also provided an aerosol-generating article for use in an aerosol-
generating
system. The aerosol-generating article may comprise an aerosol-forming
substrate. The
aerosol-forming substrate may comprise one or more aerosol formers. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may comprise hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
comprise one or more cellulose based strengthening agents.
There is also provided an aerosol-generating article comprising: an aerosol-
forming
substrate comprising: one or more aerosol formers; hydroxypropylmethyl
cellulose; and one
or more cellulose based strengthening agents.
There is also provided an aerosol-generating system comprising: an aerosol-
generating device; and an aerosol-generating article. The aerosol-generating
article may
comprise an aerosol-forming substrate. The aerosol-forming substrate may
comprise one or
more aerosol formers. The aerosol-forming substrate may comprise
hydroxypropylmethyl
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 2 -
cellulose. The aerosol-forming substrate may comprise one or more cellulose
based
strengthening agents.
There is also provided an aerosol-generating system comprising: an aerosol-
generating device; and an aerosol-generating article comprising an aerosol-
forming substrate,
the aerosol-forming substrate comprising: one or more aerosol formers;
hydroxypropylmethyl
cellulose; and one or more cellulose based strengthening agents.
As used herein, the term "aerosol-generating article" refers to an article for
producing
an aerosol. An aerosol-generating article typically comprises an aerosol-
forming substrate that
is suitable and intended to be heated or combusted in order to release
volatile compounds
that can form an aerosol. A conventional cigarette is lit when a user applies
a flame to one
end of the cigarette and draws air through the other end. The localised heat
provided by the
flame and the oxygen in the air drawn through the cigarette causes the end of
the cigarette to
ignite, and the resulting combustion generates an inhalable smoke. By
contrast, in "heated
aerosol-generating articles", an aerosol is generated by heating an aerosol-
forming substrate
and not by combusting the aerosol-forming substrate. Known heated aerosol-
generating
articles include, for example, electrically heated aerosol-generating
articles.
As used herein, the term "aerosol-forming substrate" refers to a substrate
that is
capable of producing upon heating volatile compounds, which can form an
aerosol. The
aerosol generated from aerosol-forming substrate may be visible to the human
eye or invisible
and may include vapours (for example, fine particles of substances, which are
in a gaseous
state, that are ordinarily liquid or solid at room temperature) as well as
gases and liquid
droplets of condensed vapours.
An aerosol-forming substrate that includes a combination of
hydroxypropylmethyl
cellulose and a cellulose based strengthening agent may have a number of
advantages.
The inclusion of hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose in the aerosol-forming
substrate may
help in improving the manufacturing process of the aerosol-forming substrate.
For example,
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose may reduce the overall viscosity of the slurry
that is mixed when
making the aerosol-forming substrate. A lower viscosity slurry may flow more
easily compared
to conventional slurries, and a lower viscosity slurry is easier to mix,
transfer and handle during
the manufacturing process.
The inclusion of a cellulose based strengthening agent in the aerosol-forming
substrate
may increase the tensile strength of the aerosol-forming substrate. An aerosol-
forming
substrate with a higher tensile strength may be less likely to deteriorate or
break, for example
during transit or during the manufacturing process.
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 3 -
Despite the above mentioned advantages, the present inventors found that an
aerosol-
forming substrate containing hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose may have
insufficient tensile
strength. However, using a cellulose based strengthening agent to increase the
tensile
strength of the aerosol-forming substrate may overcome the reduction in
tensile strength
caused by the inclusion of hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose, whilst still
providing the above
mentioned processing advantages associated with hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content
of
greater than about 0.5 percent by weight. Advantageously, the present
inventors have found
that hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose may be an effective binder for an aerosol-
forming
substrate.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content
of
greater than about 1 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have
a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of greater than about 5 percent by
weight. The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of greater
than about 10
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose
content of greater than about 15 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of greater than about 20 percent by
weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content
of
less than about 50 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of less than about 45 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of less
than about 40
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose
content of less than about 35 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate
may have a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of less than about 30 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of less
than about 25
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose
content of less than about 20 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content
of
between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 50 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about
0.5 percent by
weight and about 45 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have
a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about 0.5 percent by weight
and about 40
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose
content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 35 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between
about 0.5
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 4 -
percent by weight and about 30 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about 0.5 percent by weight
and about
25 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
hydroxypropylmethyl
cellulose content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 20 percent
by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content
of
between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about 1
percent by
weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have
a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about 5 percent by weight and
about 40
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose
content of between about 10 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between
about 15
percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about 20 percent by weight
and about 40
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose
content of between about 25 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content
of
between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 45 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about 1
percent by
weight and about 45 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have
a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about 1 percent by weight and
about 40
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose
content of between about 5 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between
about 5
percent by weight and about 35 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about 10 percent by weight
and about 35
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose
content of between about 10 percent by weight and about 30 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between
about 15
percent by weight and about 30 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about 15 percent by weight
and about 25
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose
content of between about 20 percent by weight and about 25 percent by weight.
The hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose may be low viscosity hydroxypropylmethyl
cellulose. For example, the hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose may have a viscosity
of 0.05 Pa/s.
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 5 -
In some examples the hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose may have a viscosity of
0.015 Pa/s. In
some examples the hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose may have a viscosity of
between 0.015
Pa/s and 0.05 Pa/s.
Advantageously, the present inventors have found that using low viscosity
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose may provide benefits during the manufacturing
process. Use of
low viscosity hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose may result in a low viscosity
slurry being formed,
which is easier to mix and transfer during manufacturing and processing.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent
content of greater than about 0.5 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a cellulose based strengthening agent content of greater than about 1 percent
by weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent
content of greater
than about 5 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
cellulose based
strengthening agent content of greater than about 10 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of greater
than about 15
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based
strengthening
agent content of greater than about 20 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent
content of less than about 50 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate
may have a
cellulose based strengthening agent content of less than about 45 percent by
weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent
content of less
than about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
cellulose based
strengthening agent content of less than about 35 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of less than
about 30
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based
strengthening
agent content of less than about 25 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of less than about 20
percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent
content of
less than about 15 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent
content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 50 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of
between about
0.5 percent by weight and about 45 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of between about 0.5
percent by weight
and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
cellulose based
strengthening agent content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about
35 percent by
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 6 -
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening
agent
content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 30 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of
between about
0.5 percent by weight and about 25 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of between about 0.5
percent by weight
and about 20 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
cellulose based
strengthening agent content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about
15 percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening
agent
content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 10 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of
between about
0.5 percent by weight and about 5 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent
content of between about 1 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of
between about
5 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a cellulose based strengthening agent content of between about 10 percent by
weight and
about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose
based
strengthening agent content of between about 15 percent by weight and about 40
percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening
agent
content of between about 20 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of
between about
percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of between about 30 percent
by weight
and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
cellulose based
25 strengthening agent content of between about 35 percent by weight and
about 40 percent by
weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent
content of between about 1 percent by weight and about 35 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of
between about
5 percent by weight and about 35 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a cellulose based strengthening agent content of between about 5 percent by
weight and
about 30 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose
based
strengthening agent content of between about 10 percent by weight and about 30
percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening
agent
content of between about 10 percent by weight and about 25 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 7 -
forming substrate may have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of
between about
15 percent by weight and about 25 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a cellulose based strengthening agent content of between about 15 percent
by weight
and about 20 percent by weight.
The one or more cellulose based strengthening agents may comprise cellulose
fibres.
Advantageously, the present inventors have found that cellulose fibres may be
a cellulose
based strengthening agent that is particularly effective at increasing the
tensile strength of an
aerosol-forming substrate.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of greater
than
about 0.5 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
cellulose fibres
content of greater than about 1 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have a
cellulose fibres content of greater than about 5 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of greater than about 10 percent
by weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of greater than
about 15 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content
of greater than
about 20 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of less than
about
50 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose
fibres content of
less than about 45 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
cellulose
fibres content of less than about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a cellulose fibres content of less than about 35 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of less than about 30 percent by
weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of less than
about 25 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content
of less than
about 20 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose
fibres content
of less than about 15 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of between
about
0.5 percent by weight and about 50 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a cellulose fibres content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and
about 45 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content
of between
about 0.5 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming substrate
may have a cellulose fibres content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and
about 35
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres
content of
between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 30 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of between about 0.5 percent by
weight and
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 8 -
about 25 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose
fibres content
of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 20 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of between about 0.5 percent by
weight and
about 15 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose
fibres content
of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 10 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of between about 0.5 percent by
weight and
about 5 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of between
about 1
percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a cellulose fibres content of between about 5 percent by weight and about 40
percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of
between about
10 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a cellulose fibres content of between about 15 percent by weight and
about 40 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content
of between
about 20 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate
may have a cellulose fibres content of between about 25 percent by weight and
about 40
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres
content of
between about 30 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming
substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of between about 35 percent by
weight and
about 40 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of between
about 1
percent by weight and about 35 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a cellulose fibres content of between about 5 percent by weight and about 35
percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of
between about
5 percent by weight and about 30 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a cellulose fibres content of between about 10 percent by weight and about 30
percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content of
between about
10 percent by weight and about 25 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a cellulose fibres content of between about 15 percent by weight and
about 25 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose fibres content
of between
about 15 percent by weight and about 20 percent by weight.
The one or more cellulose based strengthening agents may comprise
microcrystalline
cellulose. Advantageously, the present inventors have found that
microcrystalline cellulose
may be a cellulose based strengthening agent that is particularly effective at
increasing the
tensile strength of an aerosol-forming substrate.
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 9 -
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of
greater
than about 0.5 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
microcrystalline
cellulose content of greater than about 1 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming substrate
may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of greater than about 5 percent
by weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of
greater than about
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline
cellulose
content of greater than about 15 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a microcrystalline cellulose content of greater than about 20 percent by
weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of
less
10
than about 50 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
microcrystalline
cellulose content of less than about 45 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a microcrystalline cellulose content of less than about 40 percent by
weight. The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of less than
about 35 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose
content of less
than about 30 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
microcrystalline
cellulose content of less than about 25 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a microcrystalline cellulose content of less than about 20 percent by
weight. The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of less than
about 15 percent
by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of
between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 50 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of between about 0.5
percent by
weight and about 45 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have
a
microcrystalline cellulose content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and
about 40
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline
cellulose
content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 35 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of between
about 0.5 percent
by weight and about 30 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may
have a
microcrystalline cellulose content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and
about 25
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline
cellulose
content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 20 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of between
about 0.5 percent
by weight and about 15 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may
have a
microcrystalline cellulose content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and
about 10
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 10 -
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline
cellulose
content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 5 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of
between about 1 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming
substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of between about 5
percent by weight
and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
microcrystalline
cellulose content of between about 10 percent by weight and about 40 percent
by weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of
between about 15
percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a microcrystalline cellulose content of between about 20 percent by weight and
about 40
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline
cellulose
content of between about 25 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of between
about 30 percent
by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may
have a
microcrystalline cellulose content of between about 35 percent by weight and
about 40 percent
by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of
between about 1 percent by weight and about 35 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming
substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of between about 5
percent by weight
and about 35 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
microcrystalline
cellulose content of between about 5 percent by weight and about 30 percent by
weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of
between about 10
percent by weight and about 30 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a microcrystalline cellulose content of between about 10 percent by weight and
about 25
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a microcrystalline
cellulose
content of between about 15 percent by weight and about 25 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a microcrystalline cellulose content of between
about 15 percent
by weight and about 20 percent by weight.
The one or more cellulose based strengthening agents may comprise cellulose
powder. Advantageously, the present inventors have found that cellulose powder
may be a
cellulose based strengthening agent that is particularly effective at
increasing the tensile
strength of an aerosol-forming substrate.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content of greater
than
about 0.5 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
cellulose powder
content of greater than about 1 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have a
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 11 -
cellulose powder content of greater than about 5 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a cellulose powder content of greater than about 10 percent
by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content of greater
than about 15
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder
content of
greater than about 20 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content of less than
about
50 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose
powder content of
less than about 45 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
cellulose
powder content of less than about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a cellulose powder content of less than about 35 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a cellulose powder content of less than about 30 percent by
weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content of less than
about 25 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content
of less than
about 20 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose
powder
content of less than about 15 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content of between
about
0.5 percent by weight and about 50 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a cellulose powder content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and
about 45 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content
of between
about 0.5 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming substrate
may have a cellulose powder content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and
about 35
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder
content of
between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 30 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a cellulose powder content of between about 0.5 percent by
weight and
about 25 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose
powder
content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 20 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content of between about 0.5
percent by
weight and about 15 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have
a cellulose
powder content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 10 percent by
weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content of between about
0.5 percent
by weight and about 5 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content of between
about
1 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a cellulose powder content of between about 5 percent by weight and about 40
percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content of
between about
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 12 -
percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a cellulose powder content of between about 15 percent by weight and
about 40 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content
of between
about 20 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate
5 may have a cellulose powder content of between about 25 percent by weight
and about 40
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder
content of
between about 30 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming
substrate may have a cellulose powder content of between about 35 percent by
weight and
about 40 percent by weight.
10 The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content of
between about
1 percent by weight and about 35 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a cellulose powder content of between about 5 percent by weight and about 35
percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content of
between about
5 percent by weight and about 30 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a cellulose powder content of between about 10 percent by weight and about 30
percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content of
between about
10 percent by weight and about 25 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a cellulose powder content of between about 15 percent by weight and
about 25 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a cellulose powder content
of between
about 15 percent by weight and about 20 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may comprise a carboxymethyl cellulose.
Advantageously, using a carboxymethyl cellulose may help to reduce crusting of
the aerosol-
forming substrate when used in an aerosol-generating article. In some
examples, use of a
carboxymethyl cellulose eliminates crusting. As explained below, crusting is
the formation of
a solid layer on a component of the aerosol-generating article. The present
inventors have
found that crusting may occur because a component of the aerosol-forming
substrate may
melt and then re-solidify around a component of the aerosol-generating
article. Crusting can
be a particular problem when an aerosol-forming substrate is used in an
aerosol-generating
article that contains a susceptor. If a crust is formed on the susceptor then
the crusted
susceptor becomes less effective at heating the aerosol-forming substrate,
which may lead to
reduced delivery of nicotine to a user and/or reduce formation of aerosol from
the aerosol-
forming substrate.
The carboxymethyl cellulose may comprise sodium carboxymethyl cellulose.
Advantageously, the present inventors have found that sodium carboxymethyl
cellulose is a
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 13 -
carboxymethyl cellulose that may be particularly effective at preventing the
above mentioned
problem of crusting.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxymethyl cellulose content of
greater
than about 0.5 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
carboxymethyl
cellulose content of greater than about 1 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming substrate
may have a carboxymethyl cellulose content of greater than about 5 percent by
weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxymethyl cellulose content of
greater than about
percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxymethyl cellulose content of
less
10 than about 20 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have
a carboxymethyl
cellulose content of less than about 15 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a carboxym ethyl cellulose content of less than about 10 percent by
weight. The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a carboxymethyl cellulose content of less than
about 8 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxymethyl cellulose
content of less
than about 5 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxymethyl cellulose content of
between
about 0.5 percent by weight and about 20 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming substrate
may have a carboxymethyl cellulose content of between about 0.5 percent by
weight and
about 15 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
carboxymethyl
cellulose content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 10 percent
by weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxymethyl cellulose content of
between about 0.5
percent by weight and about 8 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate
may have a
carboxymethyl cellulose content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and
about 5 percent
by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxymethyl cellulose content of
between
about 1 percent by weight and about 20 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a carboxymethyl cellulose content of between about 5 percent by weight
and about 20
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxymethyl
cellulose content
of between about 8 percent by weight and about 20 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a carboxymethyl cellulose content of between about 10
percent by weight
and about 20 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
carboxymethyl
cellulose content of between about 15 percent by weight and about 20 percent
by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxymethyl cellulose content of
between
about 1 percent by weight and about 15 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a carboxymethyl cellulose content of between about 1 percent by weight
and about 10
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 14 -
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxymethyl
cellulose content
of between about 5 percent by weight and about 10 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have a carboxym ethyl cellulose content of between about 5
percent by weight
and about 8 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may comprise nicotine.
The nicotine may comprise one or more nicotine salts. The one or more nicotine
salts
may be selected from the list consisting of nicotine lactate, nicotine
citrate, nicotine pyruvate,
nicotine bitartrate, nicotine benzoate, nicotine pectate, nicotine alginate,
and nicotine
salicylate.
The nicotine may comprise an extract of tobacco.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a nicotine content of greater than
about 0.5
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a nicotine content
of greater than
about 1 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a nicotine
content of
greater than about 2 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have
a nicotine
content of greater than about 3 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have a
nicotine content of greater than about 5 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming substrate may
have a nicotine content of greater than about 8 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a nicotine content of less than about
10
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a nicotine content
of less than
about 8 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a nicotine
content of less
than about 5 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
nicotine content of
less than about 3 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
nicotine
content of less than about 2 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate
may have a
nicotine content of less than about 1 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a nicotine content of between about 0.5
percent by weight and about 10 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a nicotine content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 8 percent
by weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a nicotine content of between about 0.5
percent by weight
and about 5 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
nicotine content of
between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 3 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming
substrate may have a nicotine content of between about 0.5 percent by weight
and about 2
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a nicotine content
of between
about 0.5 percent by weight and about 1 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a nicotine content of between about 1
percent
by weight and about 5 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may
have a nicotine
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 15 -
content of between about 2 percent by weight and about 5 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have a nicotine content of between about 3 percent by
weight and
about 5 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a nicotine content of between about 0.5
percent by weight and about 4 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate
may have a
nicotine content of between about 1 percent by weight and about 4 percent by
weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a nicotine content of between about 1
percent by weight
and about 3 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
nicotine content of
between about 1 percent by weight and about 2 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may comprise one or more carboxylic acids.
Advantageously, including one or more carboxylic acids in the aerosol-forming
substrate may
create a nicotine salt.
The one or more carboxylic acids comprise one or more of lactic acid and
levulinic
acid. Advantageously, the present inventors have found that lactic acid and
levulnic acid are
particularly good carboxylic acids for creating nicotine salts.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of greater
than
about 0.5 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
carboxylic acid
content of greater than about 1 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have a
carboxylic acid content of greater than about 2 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming
substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of greater than about 3 percent
by weight. The
aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of greater than
about 5 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of
greater than
about 8 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic
acid content
of greater than about 10 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may
have a
carboxylic acid content of greater than about 15 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of less than
about
20 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid
content of
less than about 15 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a
carboxylic
acid content of less than about 10 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a carboxylic acid content of less than about 8 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming substrate
may have a carboxylic acid content of less than about 5 percent by weight. The
aerosol-
forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of less than about 3
percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of less than
about 2 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of
less than
about 1 percent by weight.
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 16 -
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of between
about
0.5 percent by weight and about 20 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a carboxylic acid content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and
about 15 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of
between about
0.5 percent by weight and about 10 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have a carboxylic acid content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and
about 8 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of
between about
0.5 percent by weight and about 5 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a carboxylic acid content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 3
percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of
between about
0.5 percent by weight and about 2 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a carboxylic acid content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 1
percent by
weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of between
about 1
percent by weight and about 10 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a carboxylic acid content of between about 2 percent by weight and about 10
percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of
between about
3 percent by weight and about 10 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a carboxylic acid content of between about 5 percent by weight and about 10
percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of
between about
8 percent by weight and about 10 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of between
about 1
percent by weight and about 20 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a carboxylic acid content of between about 1 percent by weight and about 15
percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of
between about
1 percent by weight and about 10 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
a carboxylic acid content of between about 1 percent by weight and about 8
percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have a carboxylic acid content of between
about 2 percent
by weight and about 5 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may
have a carboxylic
acid content of between about 3 percent by weight and about 5 percent by
weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may include one or more aerosol formers.
Advantageously, including one or more aerosol formers in the aerosol-forming
substrate
improves the formation of aerosol.
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 17 -
The one or more aerosol formers may comprise glycerine. The one or more
aerosol
formers may comprise propylene glycol. The one or more aerosol formers may
include a
combination of glycerine and propylene glycol.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former content of greater
than
about 0.5 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol
former
content of greater than about 10 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
an aerosol former content of greater than about 20 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have an aerosol former content of greater than about 30 percent
by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former content of greater
than about 40
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former
content of
greater than about 50 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may
have an aerosol
former content of greater than about 60 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former content of less than
about
80 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former
content of
less than about 70 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have
an aerosol
former content of less than about 60 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former content of between
about
0.5 percent by weight and about BO percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have an aerosol former content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and
about 70 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former content of
between
about 0.5 percent by weight and about 60 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming substrate
may have an aerosol former content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and
about 50
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former
content of
between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight. The
aerosol-forming
substrate may have an aerosol former content of between about 0.5 percent by
weight and
about 30 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol
former
content of between about 0.5 percent by weight and about 20 percent by weight.
The aerosol-
forming substrate may have an aerosol former content of between about 0.5
percent by weight
and about 10 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former content of between
about
1 percent by weight and about 80 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may have
an aerosol former content of between about 10 percent by weight and about 80
percent by
weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former content of
between about
20 percent by weight and about 80 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have an aerosol former content of between about 30 percent by weight and about
80 percent
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 18 -
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former content of
between
about 40 percent by weight and about 80 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate
may have an aerosol former content of between about 50 percent by weight and
about 80
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former
content of
between about 60 percent by weight and about 80 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming
substrate may have an aerosol former content of between about 70 percent by
weight and
about 80 percent by weight.
The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former content of between
about
20 percent by weight and about 80 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate may
have an aerosol former content of between about 30 percent by weight and about
80 percent
by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former content of
between
about 30 percent by weight and about 70 percent by weight. The aerosol-forming
substrate
may have an aerosol former content of between about 40 percent by weight and
about 70
percent by weight. The aerosol-forming substrate may have an aerosol former
content of
between about 40 percent by weight and about 60 percent by weight. The aerosol-
forming
substrate may have an aerosol former content of between about 50 percent by
weight and
about 60 percent by weight.
The ratio of the weight percent hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content to the
weight
percent cellulose based strengthening agent content of the aerosol-forming
substrate may be
greater than or equal to about 1. The ratio of the weight percent
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose
content to the weight percent cellulose based strengthening agent content of
the aerosol-
forming substrate may be greater than or equal to about 1.25. The ratio of the
weight percent
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content to the weight percent cellulose based
strengthening
agent content of the aerosol-forming substrate may be greater than or equal to
about 1.5.
The ratio of the weight percent hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content to the
weight
percent cellulose based strengthening agent content of the aerosol-forming
substrate may be
less than or equal to about 1. The ratio of the weight percent
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose
content to the weight percent cellulose based strengthening agent content of
the aerosol-
forming substrate may be less than or equal to about 0.75. The ratio of the
weight percent
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content to the weight percent cellulose based
strengthening
agent content of the aerosol-forming substrate may be less than or equal to
about 0.5.
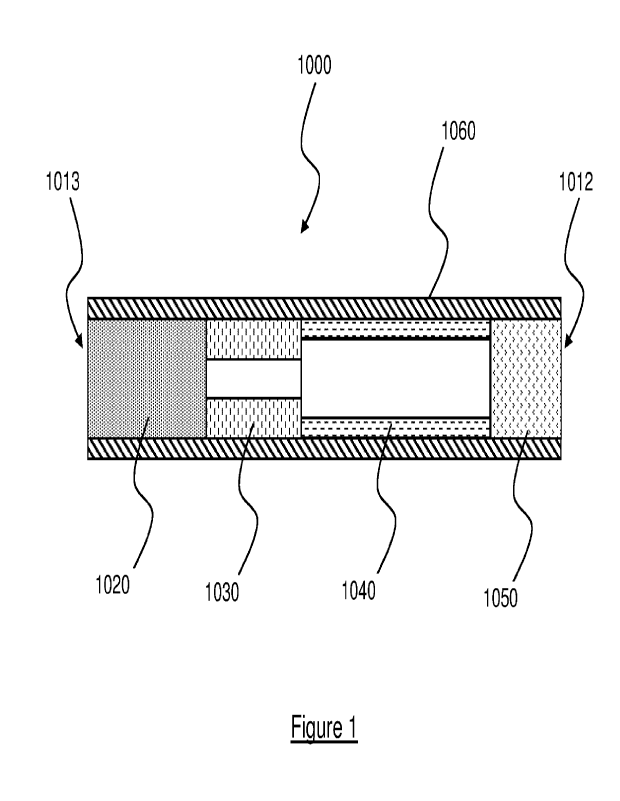
The aerosol-generating article may include the aerosol-forming substrate.
The aerosol-generating article may include a hollow cellulose acetate tube.
The aerosol-generating article may include a spacer element.
The aerosol-generating article may include a mouthpiece filter.
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 19 -
The aerosol-forming substrate, the hollow cellulose acetate tube, the spacer
element
and the mouthpiece filter may be arranged sequentially. The aerosol-forming
substrate, the
hollow cellulose acetate tube, the spacer element and the mouthpiece filter
may be arranged
in a coaxial alignment.
The aerosol-generating article may include a cigarette paper.
The aerosol-forming substrate, the hollow cellulose acetate tube, the spacer
element
and the mouthpiece filter may be assembled by a cigarette paper.
The aerosol-generating article may have a mouth-end and a distal end 1013. In
use, a
user may insert the mouth-end into his or her mouth.
The aerosol-generating article may be suitable for use with an electrically-
operated
aerosol-generating device comprising a heater for heating the aerosol-
generating substrate.
The aerosol-forming substrate may be provided in the form of a plug.
The aerosol-generating article may comprise a susceptor.
The susceptor may be a plurality of susceptor particles which may be deposited
on or
embedded within the aerosol-forming substrate. The susceptor particles may be
immobilized
by the aerosol-forming substrate and remain at an initial position. The
susceptor particles may
be homogeneously distributed in the aerosol- forming substrate. Due to the
particulate nature
of the susceptor, heat may be produced according to the distribution of the
particles in the
aerosol-forming substrate. Alternatively, the susceptor may be in the form of
one or more
sheets, strips, shreds or rods that may be placed next to or embedded in the
aerosol-forming
substrate. The aerosol-forming substrate may comprise one or more susceptor
strips.
The aerosol-generating device may comprise a housing defining a device cavity
configured to receive at least a portion of the aerosol-generating article.
The aerosol-generating device may comprise an atomiser configured to generate
an
aerosol from the aerosol-forming substrate.
The atomiser may be a thermal atomiser.
As used herein, the term "thermal atomiser" describes an atomiser that is
configured
to heat the aerosol-forming substrate to generate an aerosol.
The aerosol-generating device may comprise any suitable type of thermal
atomiser.
For example, the thermal atomiser may comprise a heater. The thermal atomiser
may
comprise an electric heater. In one example, the thermal atomiser may comprise
an electric
heater comprising a heating element. The heating element may be a resistive
heating element.
In one example, the heating element may comprise a heater blade or pin adapted
to be
inserted into the aerosol-forming substrate so that the aerosol-forming
substrate is heated
from its inside. In another example, the heating element may partially or
completely surround
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 20 -
the aerosol-forming substrate and heat the aerosol-forming substrate
circumferentially from
its outside.
In another example, the thermal atomiser may comprise an inductive heating
device.
Inductive heating devices typically comprise an induction source that is
configured to be
coupled to a susceptor, which may be provided externally to the aerosol-
forming substrate or
internally within the aerosol-forming substrate. The induction source
generates an alternating
electromagnetic field that induces magnetization or eddy currents in the
susceptor. The
susceptor may be heated as a result of hysteresis losses or induced eddy
currents which heat
the susceptor through ohmic or resistive heating.
The aerosol-generating device may include a susceptor. The susceptor may be as
described above in relation to the aerosol-generating article.
An aerosol-generating device comprising an inductive heating device may be
configured to receive an aerosol-generating article having the aerosol-forming
substrate and
a susceptor in thermal proximity to the aerosol-forming substrate. Typically,
the susceptor is
in direct contact with the aerosol-forming substrate and heat is transferred
from the susceptor
to the aerosol-forming substrate primarily by conduction.
Examples of electrically operated aerosol-generating systems having inductive
heating
devices and aerosol-generating articles having susceptors are described in WO-
Al -95/27411
and WO-Al -2015/177255.
The aerosol-generating device may comprise a battery and control electronics.
There is further provided an aerosol-generating system comprising an aerosol-
forming
substrate according to the invention and an atomiser configured to generate an
aerosol from
the aerosol-forming substrate.
The atomiser may be a thermal atomiser.
The aerosol-generating system may comprise any suitable type of thermal
atomiser.
For example, the thermal atomiser may comprise a heater. The thermal atomiser
may
comprise an electric heater. In one example, the thermal atomiser may comprise
an electric
heater comprising a heating element. The heating element may be a resistive
heating element.
In one example, the heating element may comprise a heater blade or pin adapted
to be
inserted into the aerosol-forming substrate so that the aerosol-forming
substrate is heated
from its inside. In another example, the heating element may partially or
completely surround
the aerosol-forming substrate and heat the aerosol-forming substrate
circumferentially from
its outside.
In another example, the thermal atomiser may comprise an inductive heating
device.
Inductive heating devices typically comprise an induction source that is
configured to be
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 21 -
coupled to a susceptor, which may be provided externally to the aerosol-
forming substrate or
internally within the aerosol-forming substrate. The induction source
generates an alternating
electromagnetic field that induces magnetization or eddy currents in the
susceptor. The
susceptor may be heated as a result of hysteresis losses or induced eddy
currents which heat
the susceptor through ohmic or resistive heating.
The aerosol-generating system may include a susceptor. The susceptor may be as
described above in relation to the aerosol-generating article.
An aerosol-generating system comprising an inductive heating device may be
configured to receive an aerosol-generating article having the aerosol-forming
substrate and
a susceptor in thermal proximity to the aerosol-forming substrate. Typically,
the susceptor is
in direct contact with the aerosol-forming substrate and heat is transferred
from the susceptor
to the aerosol-forming substrate primarily by conduction.
Examples of electrically operated aerosol-generating systems having inductive
heating
devices and aerosol-generating articles having susceptors are described in WO-
Al -95/27411
and WO-Al -2015/177255.
The aerosol-generating system may comprise a battery and control electronics.
For the avoidance of doubt, features described above in relation to the
aerosol-forming
substrate may also relate, where appropriate, to the aerosol-generating
article, the aerosol-
generating device, and the aerosol-generating system. Similarly, features
described above in
relation to the aerosol-generating article may also relate, where appropriate,
to the aerosol-
generating device and to the aerosol-generating system, and vice versa.
It will be appreciated that any features described herein in relation to one
embodiment
of an aerosol-forming substrate, an aerosol-generating article, an aerosol-
generating device,
or an aerosol-generating system may also be applicable to other embodiments of
aerosol-
forming substrates, an aerosol-generating articles, an aerosol-generating
devices, or aerosol-
generating systems according to this disclosure. A feature described in
relation to one
embodiment may be equally applicable to another embodiment in accordance with
this
disclosure. It will also be appreciated that an aerosol generator according to
this disclosure
may be provided in an aerosol-generating device without a cartridge.
Accordingly, any of the
features described herein with relation to a cartridge may be equally
applicable to an aerosol-
generating device.
The invention is defined in the claims. However, below there is provided a non-
exhaustive list of non-limiting examples. Any one or more of the features of
these examples
may be combined with any one or more features of another example, embodiment,
or aspect
described herein.
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 22 -
EX1. An aerosol-forming substrate for use in an aerosol-generating system, the
aerosol-forming substrate comprising:
one or more aerosol formers;
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose; and
one or more cellulose based strengthening agents.
EX2. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX1, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of greater than
about 0.5
percent by weight.
EX3. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX2, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about
0.5 percent
by weight and about 50 percent by weight.
EX4. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX3, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about
10 percent
by weight and about 40 percent by weight.
EX5. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX4, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about
15 percent
by weight and about 30 percent by weight.
EX6. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX5, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose content of between about
20 percent
by weight and about 25 percent by weight.
EX7. An aerosol-forming substrate according to any one of examples EX1 to EX6,
wherein the aerosol-forming substrate has a cellulose based strengthening
agent content of
greater than about 0.5 percent by weight.
EX8. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX7, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose based strengthening agent content of between
about 0.5
percent by weight and about 50 percent by weight.
EX9. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX8, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose based strengthening agent content of between
about 0.5
percent by weight and about 40 percent by weight.
EX10. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX9, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose based strengthening agent content of between
about 5
percent by weight and about 30 percent by weight.
EX1 1. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX10, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose based strengthening agent content of between
about 10
percent by weight and about 20 percent by weight.
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 23 -
EX1 2. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX1 1, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose based strengthening agent content of between
about 15
percent by weight and about 20 percent by weight.
EX13. An aerosol-forming substrate according to one of examples EX1 to EX12,
wherein the one or more cellulose based strengthening agents comprises
cellulose fibres.
EX14. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX13, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose fibres content of greater than about 0.5
percent by weight.
EX15. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX14, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose fibres content of between about 0.5 percent
by weight and
about 50 percent by weight.
EX1 6. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX15, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose fibres content of between about 0.5 percent
by weight and
about 40 percent by weight.
EX1 7. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX16, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose fibres content of between about 5 percent by
weight and
about 30 percent by weight.
EX1 8. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX17, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose fibres content of between about 10 percent
by weight and
about 20 percent by weight.
EX1 9. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX18, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose fibres content of between about 15 percent
by weight and
about 20 percent by weight.
EX20. An aerosol-forming substrate according one of examples EX1 to EX19,
wherein
the one or more cellulose based strengthening agents comprises
microcrystalline cellulose.
EX21. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX20, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a microcrystalline cellulose content of greater than
about 0.5 percent
by weight.
EX22. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX21, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a microcrystalline cellulose content of between about
0.5 percent by
weight and about 50 percent by weight.
EX23. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX22, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a microcrystalline cellulose content of between about
0.5 percent by
weight and about 40 percent by weight.
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 24 -
EX24. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX23, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a microcrystalline cellulose content of between about 5
percent by
weight and about 30 percent by weight.
EX25. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX18, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a microcrystalline cellulose content of between about 10
percent by
weight and about 20 percent by weight.
EX26. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX24, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a microcrystalline cellulose content of between about 15
percent by
weight and about 20 percent by weight.
EX27. An aerosol-forming substrate according to any one of examples EX1 to
EX26,
wherein the one or more cellulose based strengthening agents comprises
cellulose powder.
EX28. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX27, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose powder content of greater than about 0.5
percent by weight.
EX29. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX28, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose powder content of between about 0.5 percent
by weight and
about 50 percent by weight.
EX30. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX29, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose powder content of between about 0.5 percent
by weight and
about 40 percent by weight.
EX31. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX30, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose powder content of between about 5 percent by
weight and
about 30 percent by weight.
EX32. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX31, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose powder content of between about 10 percent
by weight and
about 20 percent by weight.
EX33. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX32, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a cellulose powder content of between about 15 percent
by weight and
about 20 percent by weight.
EX34. An aerosol-forming substrate according to any one of examples EX1 to
EX33,
wherein the aerosol-forming substrate comprises a carboxymethyl cellulose.
EX35. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX34, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a carboxymethyl cellulose content of greater than about
0.5 percent by
weight.
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 25 -
EX36. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX35, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a carboxymethyl cellulose content of between about 0.5
percent by
weight and about 20 percent by weight.
EX37. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX36, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a carboxymethyl cellulose content of between about 0.5
percent by
weight and about 15 percent by weight.
EX38. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX37, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a carboxymethyl cellulose content of between about 5
percent by weight
and about 10 percent by weight.
EX39. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX38, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a carboxymethyl cellulose content of between about 5
percent by weight
and about 7 percent by weight.
EX40. An aerosol-forming substrate according to any one of examples EX28 to
EX39,
wherein the carboxymethyl cellulose comprises sodium carboxymethyl cellulose.
EX41. An aerosol-forming substrate according to any one of examples EX1 to
EX40,
wherein the aerosol-forming substrate comprises nicotine.
EX42. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX41, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a nicotine content of greater than about 0.5 percent by
weight.
EX43. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX42, wherein the
aerosol-
forming substrate has a nicotine content of between about 0.5 percent by
weight and about 5
percent by weight.
EX44. An aerosol-forming substrate according to any one of examples EX1 to
EX43,
wherein the aerosol-forming substrate comprises one or more carboxylic acids.
EX45. An aerosol-forming substrate according to example EX44, wherein the one
or
more carboxylic acids comprise one or more of lactic acid and levulinic acid.
EX46. An aerosol-generating article comprising the aerosol-forming substrate
of any
one of examples EX1 to EX45.
EX42. An aerosol-generating system comprising:
an aerosol-generating device; and
an aerosol-generating article comprising according to example EX46.
Specific embodiments will be further described, by way of example only, with
reference
to the accompanying drawings in which:
Figure 1 illustrates an example of an aerosol-generating article containing
the aerosol-
forming substrate as described herein; and
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 26 -
Figure 2 illustrates an example of an aerosol-generating system comprising an
aerosol-generating device and the aerosol-generating article shown in Figure
1.
Aerosol-generating systems for delivering an aerosol to a user typically
comprise an
atomiser configured to generate an inhalable aerosol from an aerosol-forming
substrate.
Some known aerosol-generating systems comprise a thermal atomiser such as an
electric
heater or an inductive heating device. The thermal atomiser is configured to
heat and vaporise
the aerosol-forming substrate to generate an aerosol. Typical aerosol-forming
substrates for
use in aerosol-generating systems are nicotine formulations, which may be
liquid nicotine
formulations comprising an aerosol former such as glycerine and/or propylene
glycol.
Some aerosol-forming substrates have a low tensile strength. This means that
such
aerosol-forming substrates may break apart or deteriorate before the aerosol-
generating
article is used by a user, which is undesirable. Some aerosol-forming
substrates have a
tendency to melt, which may result in a crust forming on a part of the aerosol-
generating article.
A crust being formed on a part of the aerosol-generating article may reduce
the level of nicotine
that is delivered to a user. A crust being formed on a part of the aerosol-
generating article may
reduce the volume of aerosol that is generated by the aerosol-generating
system.
For example, as discussed above, in an aerosol-generating system that includes
an
inductive heating device, the aerosol-generating article may include a
susceptor that can be
heated by an induction source. The heat from the susceptor then transfers to
the aerosol-
forming substrate. Components of the aerosol-forming substrate may then
vaporise to
produce an aerosol. However, if the susceptor becomes coated in an aerosol-
forming
substrate crust then the crust may reduce heat transfer from the heated
susceptor to the
aerosol-forming substrate. The reduction in heat transfer from the heated
susceptor to the
aerosol-forming substrate may reduce the level of nicotine delivered to a
user. The reduction
in heat transfer from the heated susceptor to the aerosol-forming substrate
may reduce the
volume of aerosol that is generated by the aerosol-generating system.
It is therefore desirable to provide an aerosol-forming substrate that has an
increased
tensile strength. It is also desirable to provide an aerosol-forming substrate
that has a reduced
tendency to melt, which may lower the effect of crusting of the aerosol-
forming substrate on a
component of an aerosol-generating article.
Figure 1 illustrates an example of an aerosol-generating article 1000
containing an
aerosol-forming substrate as described herein.
In the example of Figure 1, the aerosol-generating article 1000 includes four
elements:
the aerosol-forming substrate 1020, a hollow cellulose acetate tube 1030, a
spacer element
1040, and a mouthpiece filter 1050. The four elements 1020, 1030, 1040, 1050
are arranged
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 27 -
sequentially and in a coaxial alignment. The four elements 1020, 1030, 1040,
1050 are
assembled by a cigarette paper 1060 to form the aerosol-generating article
1000.
In the example of Figure 1, the aerosol-generating article 1000 has a mouth-
end 1012
and a distal end 1013. A user may insert the mouth-end 1012 into his or her
mouth during use.
The distal end 101 3 is located at the opposite end of the aerosol-generating
article 1000 to
the mouth end 1012. The example of an aerosol-generating article 1000
illustrated in Figure
1 is particularly suitable for use with an electrically-operated aerosol-
generating device
comprising a heater for heating the aerosol-generating substrate.
In one example, when assembled, the aerosol-generating article 1000 is about
45
millimetres in length and has an outer diameter of about 7.2 millimetres and
an inner diameter
of about 6.9 millimetres.
In the example of Figure 1, the aerosol-forming substrate 1020 is provided in
the form
of a plug made by crimping a sheet of aerosol-forming substrate. A number of
examples of
aerosol-forming substrate 1020 are shown in Table 1 below. The sheet is
gathered, crimped
and wrapped in a filter paper (not shown) to form the plug.
An aerosol-generating article 1000 as illustrated in Figure 1 is designed to
engage with
an aerosol-generating device in order to be consumed. Such an aerosol-
generating device
includes means for heating the aerosol-forming substrate 1020 to a sufficient
temperature to
form an aerosol. Typically, the aerosol-generating device may comprise a
heating element
that surrounds the aerosol-generating article 1000 adjacent to the aerosol-
forming substrate
1020, or a heating element that is inserted into the aerosol-forming substrate
1020.
Once engaged with an aerosol-generating device, a user draws on the mouth-end
1012 of the smoking article 1000 and the aerosol-forming substrate 1020 is
heated to a
temperature of about 375 degrees Celsius. At this temperature, volatile
compounds are
evolved from the aerosol-forming substrate 1020. These compounds condense to
form an
aerosol. The aerosol is drawn through the filter 1050 and into the user's
mouth.
Figure 2 illustrates a portion of an electrically-operated aerosol-generating
system
2000. The aerosol-generating system utilises a heating blade 2100 to heat an
aerosol-
generating substrate 1020 of an aerosol-generating article 1000. In the
example of Figure 2,
the heating blade 2100 is mounted within an aerosol article receiving chamber
of an
electrically-operated aerosol-generating device 2010. The aerosol-generating
device 2010
defines a plurality of air holes 2050 for allowing air to flow to the aerosol-
generating article
1000. Air flow is indicated by the arrows in Figure 2. The aerosol-generating
device 2010
comprises a power supply and electronics, which are not illustrated in Figure
2. The aerosol-
generating article 1000 of Figure 2 is as described in relation to Figure 1.
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 28 -
Examples
Example formulations of an aerosol-forming substrate according to the
invention
(Examples A, B, C, D and E) are prepared having the compositions shown in
Table 1.
Example A
Hydroxypropylmethyl Cellulose (% by weight)
22.39 12.50 26.67 26.67 23.71
Cellulose Fibres (% by weight) 16.79 31.25 6.67
6.67 0
Microcrystalline Cellulose (% by weight) 0 0 0 6.67
0
Cellulose Powder ( /0 by weight) 0 0 0 0
17.79
Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose (% by weight) 5.60 6.25 0 0
5.93
Agar (`)/0 by weight) 0 0 6.67
6.67 0
Nicotine (% by weight) 1A0 0 0 0
1A8
Glycerine ( /0 by weight)
50.37 50.00 60.00 53.33 47.43
Lactic Acid (% by weight) 3.45 0 0 0
3.66
Table 1
The aerosol-forming substrates of Examples A, B, C, D and E are prepared by:
(1) mixing the components together with water using heat and agitation to form
a slurry;
(2) casting a layer of the slurry onto a plane surface to form a film having a
thickness
of about 210 micro metres;
(3) leaving the film on the plane surface to solidify; and
(3) drying the film by heating the film to about 140 degrees Celsius for about
8 minutes.
The aerosol-forming substrates obtained after drying are solid. In other
words, the
aerosol-forming substrates each have a stable size and shape and do not flow.
The term
"stable" is used herein to indicate that the aerosol-forming substrates
substantially maintain
their shape and mass when exposed to a variety of environmental conditions. As
such,
aerosol-forming substrates substantially do not release or absorb water when
exposed to
standard temperature and pressure while varying the relative humidity from
about 10 percent
to about 60 percent.
This is particularly advantageous as it ensures that aerosol-forming
substrates in
accordance with the present invention do not release a liquid phase during
storage or
transportation, for example, from the manufacturing facility to a point of
sale.
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 29 -
In use in an aerosol-generating device, as described above, the aerosol-
forming
substrates of Examples A, B, C, D and E are heated to a temperature of between
about 375
degrees Celsius. The nicotine and glycerine contained in the film evaporate.
The nicotine and
glycerine condense to form an inhalable aerosol. The aerosol can then be
inhaled by a user.
The aerosol-forming substrates shrink slightly and their volumes are reduced.
However, the
film remains solid and maintains its film form. The aerosol-forming substrates
appear to harden
slightly and to take on a darker, brownish colour.
The aerosol-forming substrate of Example A includes a combination of
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose and a cellulose based strengthening agent. In
Example A, the
cellulose based strengthening agent is cellulose fibres. The aerosol-forming
substrate of
Example A also includes sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, nicotine, glycerine
and a carboxylic
acid. In Example A, the carboxylic acid is lactic acid.
The aerosol-forming substrate of Example B includes a combination of
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose and a cellulose based strengthening agent. In
Example B, the
cellulose based strengthening agent is cellulose fibres. The aerosol-forming
substrate of
Example B contains more cellulose fibres than the aerosol-forming substrate of
Example A.
The aerosol-forming substrate of Example B also includes sodium carboxymethyl
cellulose
and glycerine.
The aerosol-forming substrate of Example C includes a combination of
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose and a cellulose based strengthening agent. In
Example C, the
cellulose based strengthening agent is cellulose fibres. The aerosol-forming
substrate of
Example C contains fewer cellulose fibres than the aerosol-forming substrate
of Example A.
The aerosol-forming substrate of Example C includes agar rather than sodium
carboxymethyl
cellulose. The aerosol-forming substrate of Example C also includes glycerine.
The aerosol-forming substrate of Example D includes a combination of
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose and two cellulose based strengthening agents. In
Example D,
the cellulose based strengthening agents are cellulose fibres and
microcrystalline cellulose.
The aerosol-forming substrate of Example D contains fewer cellulose fibres
than the aerosol-
forming substrate of Example A. The aerosol-forming substrate of Example D
includes agar
rather than sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. The aerosol-forming substrate of
Example D also
includes glycerine.
The aerosol-forming substrate of Example E includes a combination of
hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose and a cellulose based strengthening agent. In
Example E, the
cellulose based strengthening agent is cellulose powder. The aerosol-forming
substrate of
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157 PCT/EP2021/077782
- 30 -
Example E also includes sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, nicotine, glycerine
and a carboxylic
acid. In Example E, the carboxylic acid is lactic acid.
The effect of the components of the above Examples A, B, C and D, including
the effect
of the cellulose based strengthening agents, will now be shown by comparison
to an example
of a comparative aerosol-forming substrate. The comparative aerosol-forming
substrate
includes 25.53 percent by weight hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose, 6.38 percent
by weight agar,
and 63.81 percent by weight glycerine.
Table 2 shows a comparison of tensile strength between the five example
formulations
of the aerosol-forming substrate (Examples A, B, C and D), and the comparative
example.
The tensile strength of the example formulations and the comparative
formulation is
measured by using the conventional method of stretching a given size of a test
specimen of
each formulation at a constant rate of elongation until it ruptures. A tensile
strength testing
instrument is attached to the test specimen, which provides a measure of the
fracture force
when the formulation ruptures. The tensile strength of a test specimen is
derived from the
fracture force at rupture divided by the width of the specimen.
Comparative
Example A B C D
Example
Tensile Strength (N/m) 421 677 1580 830
1199
Table 2
As shown in Table 2, the aerosol-forming substrate of Example A provides an
increase
in tensile strength of 256 N/m compared to the comparative example. This is a
61% increase
in tensile strength.
The aerosol-forming substrate of Example B provides an increase in tensile
strength
of 1159 N/m compared to the comparative example. This is a 275% increase in
tensile
strength.
The aerosol-forming substrate of Example C provides an increase in tensile
strength
of 409 N/m compared to the comparative example. This is a 97% increase in
tensile strength.
The aerosol-forming substrate of Example D provides an increase in tensile
strength
of 778 N/m compared to the comparative example. This is a 185% increase in
tensile strength.
Accordingly, the aerosol-forming substrates of Examples A, B, C and D all show
large
increases in tensile strength compared to the comparative example. The present
inventors
have found that this increase in the tensile strength of the aerosol-forming
substrate may
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5
WO 2022/074157
PCT/EP2021/077782
- 31 -
provide a number of advantages, particularly relating to the subsequent
processing steps of
manufacturing an aerosol-generating article that contains the aerosol-forming
substrate.
For example, after an aerosol-forming substrate is made, it is typically
rolled onto a
bobbin. An increase in the tensile strength of the aerosol-forming substrate
may reduce
breakage of the aerosol-forming substrate due to tension when it is
transferred to the bobbin.
The subsequent manufacturing step usually involves unwinding the aerosol-
forming
substrate from the bobbin, and then crimping the aerosol-forming substrate
using crimping
rollers. An increase in the tensile strength of the aerosol-forming substrate
may reduce
breakage during the crimping process.
Reduced breakage of the aerosol-forming substrate during subsequent processing
steps may reduce wastage of aerosol-forming substrate during the process of
manufacturing
an aerosol-generating article containing the aerosol-forming substrate. In
addition, if the
aerosol-forming substrate breaks during the processing steps then there may be
loss of
manufacturing time and so increased tensile strength of the aerosol-forming
substrate may
improve manufacturing time.
Although the aerosol-forming substrates of Examples C and D exhibit a high
increase
in tensile strength, Examples C and D may cause crusting on a part of an
aerosol-generating
article containing the aerosol-forming substrate because they contain agar.
The present
inventors believe that the agar melts when it is heated (for example by an
aerosol-generating
device). The melted agar can form agglomerate and form around the part of the
aerosol-
generating article. After the aerosol-generating article stops being heated,
the melted agar
may then cool and solidify as a crust. This is particularly a problem with an
aerosol-generating
article containing a susceptor because it has been found that crusting on the
susceptor
reduces heat transfer from the susceptor to the aerosol-forming substrate,
which may reduce
the level of nicotine and the volume of aerosol delivered to a user.
The aerosol-forming substrates of Examples A and B do not contain agar.
Instead, the
aerosol-forming substrates of Examples A and B contain sodium carboxymethyl
cellulose. The
present inventors have found that an aerosol-forming substrate containing a
carboxymethyl
cellulose instead of agar has reduced crusting. Indeed, in some examples, the
present
inventors have found that using a carboxymethyl cellulose instead of agar may
completely
eliminate the problem of crusting. Reducing and eliminating crusting,
particularly crusting on
a susceptor, may lead to an increased level of nicotine being delivered to a
user, and an
increased volume of aerosol being generated from the aerosol-forming
substrate.
CA 03195031 2023- 4- 5