Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
METHODS OF TREATING PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS IN OBESE PATIENTS WITH
BREXP1PRAZOLE
BACKGROUND
[0001] Brexpiprazole, also called REXULTI , is an atypical antipsychotic used
for treating major
depressive disorder and schizophrenia. The mechanism of action of
brexpiprazole in the treatment
of major depressive disorder (MDD) and schizophrenia is unknown. However, the
efficacy of
brexpiprazole may result from partial agonist activity at serotonin 5-HT1A and
dopamine D2
receptors and antagonist activity at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors.
[0002] The brexpiprazole (REXULTIS) Food and Drug Administration (FDA) label
revised in
March 2020 reflects the state-of-the art regarding the appropriate dosing for
patients in need of
brexpiprazole, and provides instructions for a brexpiprazole starting dose,
recommended dose, and
maximum dose with a titration timeline based on a patient's clinical response
and tolerability. The
FDA label also provides instructions to administer half of the usual dose to
patients that are
CYP2D6 poor metabolizers.
[0003] An ideal dosage regimen for brexpiprazole enables psychiatric patients
to reach therapeutic
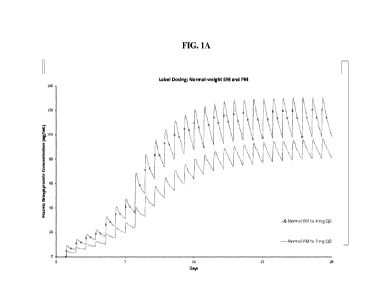
levels of brexpiprazole as quickly as possible while avoiding side effects
from brexpiprazole. One
serious side effect of administering too much brexpiprazole is akathisia, a
movement and mental
distress disorder which is a state of agitation, distress, and restlessness.
Akathisia rates in
brexpiprazole patients have been shown to be dose-dependent, and increase as
exposure to
brexpiprazole increases.
[0004] It is not presently recognized in the art that the dosing regimen for
brexpiprazole should be
adjusted based on the body weight or obesity status of the patient, despite
the fact that obesity and
schizophrenia or depression are often comorbid conditions. While the REXULTI
label, for
example, teaches that weight gain can be a side effect of treatment with
brexpiprazole, or that
being overweight is a risk factor for other side effects such as
hyperglycemia, the label does not
instruct any changes in dosing for obese or overweight patients compared to
normal weight
patients. Brexpiprazole dosing adjustments are only recommended based on the
indication treated,
hepatic or renal impairment status, drug interactions with CYP2D6 inhibitors,
or CYP3A4
inhibitors or inducers.
1
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0005] The inventors have discovered that the pharmacokinetics of
brexpiprazole are substantively
different in obese patients, requiring dosing changes when initiating
treatment with brexpiprazole
to achieve the same clinical response: effective treatment of schizophrenia
and major depressive
disorder. Prior to this invention, the standard of care left such obese
patients untreated or
undertreated, delaying resolution of their condition.
[0006] The invention addresses additional complexities and identifies modified
dosing regimens
that are critical to safely and effectively initiate treatment with
brexpiprazole. In various
embodiments the present invention is directed, inter cilia, to specific dose
adjustments that avoid
under-treatment but do not exceed known exposure levels which would expose
patients to serious
side effects. In various embodiments the present invention is directed, inter
alia, to specific dosing
regimens needed for different indications and for different CYP2D6 metabolizer
status.
Expected Dru2 Profile
[0007] The expected blood plasma brexpiprazole concentrations during the
initiation of
brexpiprazole treatment (days 1-28) for patients with schizophrenia and major
depressive disorder
(MDD) according to the brexpiprazole FDA label (revised in March 2020) are
shown in FIG. 1A
and FIG. 1B, respectively. Because there was no recognition in the art that
the dosing regimen
for initiating treatment with brexpiprazole should be adjusted based on the
obesity status of the
patient, obesity status was not expected to affect the blood plasma
concentration of brexpiprazole.
In other words, obese patients with schizophrenia or major depressive disorder
were expected to
have qualitatively similar blood plasma concentrations as normal weight
patients.
[0008] The present inventors are not aware of anything in the art which would
contradict the use
of the same brexpiprazole dosing regimen for obese and normal-weight patients
disclosed in the
FDA-approved label for brexpiprazole. It is acknowledged in the art that body
size and obesity can
have an effect on the pharmacokinetics of some drugs; however, the clinical
relevance of this effect
is highly dependent on the particular characteristics of that drug. For
example, Hanley et al., in
reviewing the effects of obesity on drug pharmacokinetics, found that
appropriate drug dosing
should be individualized to the particular drug at issue, and that the
distribution of a drug in obese
patients cannot be entirely predicted based on the physiochemical attributes
of the drug (e.g.,
2
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
lipophilicity, hydrophilicity) alone. (Hanley et al., Effect of Obesity on the
Pharmacokinetics of
Drugs in Humans, Clin. Pharmacokinet 2010, 49(2): 70-87.) The pharmacokinetic
studies leading
to the approval of brexpiprazole did not include patients with BlVII >35
kg/m2, and previous studies
have found that the effect of weight on the pharmacokinetics of brexpiprazole
was less than 20%
and was not a significant determinant in brexpiprazole pharmacokinetics. The
inventors are not
aware of any evidence in the prior art that suggests that there is any
clinically important effect of
obesity on brexpiprazole pharmacokinetics that would require any difference in
the brexpiprazole
dosing regimen between obese and normal-weight patients. Thus, at the time of
the present
application, the FDA-approved dosing instructions for obese and normal weight
patients are the
same. However, the present invention is based on the discovery that a
patient's body size
significantly affects the time it takes a patient to reach therapeutic levels
of brexpiprazole. See
FIG. 2A and FIG. 2B.
[0009] Without this new information, it was not appreciated in the art that,
using the instructions
for brexpiprazole dosing found in the existing FDA-approved labels for
brexpiprazole (at the time
of the present disclosure), obese patients do not reach therapeutic levels of
brexpiprazole as quickly
as normal weight patients upon initiating brexpiprazole treatment; or
alternatively stated, it has
been discovered that it takes significantly longer to reach therapeutic levels
of brexpiprazole in
obese patients compared to normal-weight patients using the FDA-approved
label's instructions.
[0010] The REXULT1 label teaches reducing the dose of brexpiprazole to half
of the usual
dosage if the patient is a CYP2D6 poor metabolizer (CYP2D6 PMs or simply
"PMs"). Similarly,
the present inventors have also found that the time required to reach
therapeutic levels of
brexpiprazole for obese patients who are also PMs, using the FDA-approved
brexpiprazole dosing
regimen (i.e., half of the recommended dose), is longer than for normal-weight
PMs.
[0011] Thus, prior to the present invention, for obese patient populations (as
described herein), the
patient's psychiatric disorders (e.g., schizophrenia and major depressive
disorder) were
unknowingly left undertreated because these patients did not reach therapeutic
concentrations in
a similar time as normal-weight patient. Such unintended undertreatment of
psychiatric disorders
is potentially quite serious, as complications of untreated psychiatric
disorders include suicide
attempts, anxiety, depression, alcohol or drug abuse, inability to work or
attend school, financial
problems, homelessness, social isolation, health and medical problems, being
victimized, and
aggressive behavior.
3
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
[0012] Thus, the development of the presently disclosed new dosage regimens
allow obese
patients to reach therapeutic levels of brexpiprazole as quickly as normal-
weight patients without
putting them at risk of akathisia.
[0013] The present disclosure provides an alternative dosing regimen for
treating a patient with a
psychiatric disorder, such as schizophrenia or major depressive disorder, with
brexpiprazole,
wherein the patient has one or more of the following characteristics: (i) a
BMI of at least about 35;
(ii) %IBW of at least about 150%; (iii) waist size greater than about 42
inches; (iv) A) body fat
greater than about 40%; (v) % android body fat greater than about 40%; (vi) %
gynoid body fat
greater than about 40%; (vii) total body fat greater than about 40 kg; or
(viii) CYP2D6 poor
metabolizer.
[0014] The present inventors have discovered that patients dosed according to
the brexpiprazole
FDA label dosage instructions that have any of the aforementioned
characteristics do not reach
therapeutic levels of brexpiprazole as quickly as non-obese CYP2D6 EM
patients. In particular,
patients that are obese (e.g., have one or more of the following
characteristics: (i) a BMI of at least
about 35 kg/m2; (ii) %IBW of at least about 150%; (iii) waist size greater
than about 42 inches;
(iv) % body fat greater than about 40%; (v) % android body fat greater than
about 40%; (vi) %
gynoid body fat greater than about 40%; (vii) total body fat greater than
about 40 kg) or obese (as
defined herein) CYP2D6 poor metabolizers (PM) take longer to reach the similar
therapeutic
concentrations of patients that are normal-weight CYP2D6 extensive
metabolizers (EM) (FIG. 2A
and FIG. 2B). The brexpiprazole dosage regimen recommended by the FDA label is
shown in
Table 1.
Table 1. Brexpiprazole Dosing According to FDA Label
Indication Starting Dose Recommended Dose Maximum Dose
Major depressive 0.5-1 mg/day 2 mg/day 3 mg/day
disorder (MDD)
Schizophrenia 1 mg/day 2-4 mg/day 4 mg/day
[0015] For adjunctive treatment for MDD, the FDA label recommends a starting
dose of
brexpiprazole of 0.5 mg, then titrating the starting dose of brexpiprazole up
to 1 mg (if starting at
0.5 mg) once daily, and then up to the recommended dosage of 2 mg once daily.
Alternatively, the
FDA label recommends using a starting dose of 1 mg once daily, then titrating
up to the
recommended dosage of 2 mg once daily. Dosage increases should occur at weekly
intervals based
on the patient's clinical response and tolerability. The maximum daily dosage
is 3 mg.
4
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
[0016] For treatment of schizophrenia, the label teaches starting with an
initial or starting dose of
1 mg of brexpiprazole administered once daily on each of the first 4 days of
treatment (days 1-4),
then administering 2 mg once daily on the next 3 days of treatment (day 5
through day 7), and then
administering 4 mg once daily on day 8 based on the patient's clinical
response and tolerability.
The maximum daily dosage is 4 mg.
[0017] The dosage for CYP2D6 poor metabolizers (patients classified as having
a CYP2D6
enzyme phenotype with little or no CYP2D6 activity compared to normal levels
of CYP2D6
activity) is half of the dose that would otherwise be administered if the
patent was not a CYP2D6
poor metabolizer.
[0018] Applicants have developed a modified brexpiprazole dosage regimen for
initiating
treatment with brexpiprazole that allows obese patients and/or obese CYP2D6 PM
(poor
metabolizer) patients to reach therapeutically effective concentrations at a
similar time compared
to normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients (extensive metabolizers; i.e., patients
classified as having
a CYP2D6 enzyme phenotype with normal levels of CYP2D6 activity) (FIGS. 3-9).
As Table D
of Example 2 reveals, one embodiment of the modified dosage regimen of the
present invention
provides double the total daily dose of brexpiprazole of the FDA label on days
1-7. As Table J in
Example 3 reveals, other embodiments of the modified dosage regimen provide
double the total
daily dose of brexpiprazole of the FDA label on days 1-14 or days 1-21.
[0019] The FDA label for brexpiprazole (REXULTI revised 3/2020) neither
recognizes that
obese CYP2D6 EM patients and/or obese CYP2D6 PM patients do not reach
therapeutic levels as
quickly as normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients, nor does it provide a dosage
regimen that corrects
this (hitherto unknown) problem. Instead, the label implicitly teaches that
obese CYP2D6 EM
should receive the same dose as normal-weight CYP2D6 EM, and explicitly
teaches that all
CYP2D6 PM patients (i.e., normal-weight and obese) should receive half of the
dose that CYP2D6
EM patients receive. However, Applicants have discovered that administering
the same dose to
obese CYP2D6 EM that normal-weight CYP2D6 EM receive, and half of the dose to
obese
CYP2D6 PM (as taught by the FDA label) causes obese CYP2D6 EM and obese CYP2D6
PM
patients to reach therapeutic brexpiprazole concentrations more slowly than
normal-weight
CYP2D6 EM patients. Administering brexpiprazole according to a modified dosage
regimen
provided herein enables obese and/or obese CYP2D6 PM patients to approach
therapeutic levels
of brexpiprazole as quickly as normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients (FIGS. 3-9).
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
[0020] In embodiments, the disclosure provides method of initiating treatment
of schizophrenia
with brexpiprazole in an obese patient who is not a CYP2D6 poor metabolizer,
comprising: (a)
administering 1 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on each of the first 4 days of
brexpiprazole treatment;
(b) administering 2 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on each of the next 3 days
following step (a);
and then (c) administering a recommended dose of brexpiprazole once daily
thereafter; wherein
the obese patient has one or more of the following characteristics: (i) BMI of
at least about 35; (ii)
%IBW of at least about 150%; (iii) waist size greater than about 42 inches;
(iv) % body fat greater
than about 40%; (v) % android body fat greater than about 40%; (vi) % gynoid
body fat greater
than about 40%; or (vii) total body fat greater than about 40 kg. In
embodiments, the recommended
dose of brexpiprazole is 2-4 mg/day. In embodiments, the recommended dose of
brexpiprazole is
2 mg/day. In embodiments, the recommended dose of brexpiprazole is 2.25
mg/day. In
embodiments, the recommended dose of brexpiprazole is 2.5 mg/day. In
embodiments, the
recommended dose of brexpiprazole is 2.75 mg/day. In embodiments, the
recommended dose of
brexpiprazole is 3 mg/day. In embodiments, the recommended dose of
brexpiprazole is 3.25
mg/day. In some embodiments, the recommended dose of brexpiprazole is 3.5
mg/day. In
embodiments, the recommended dose of brexpiprazole is 3.75 mg/day. In
embodiments, the
recommended dose of brexpiprazole is 4 mg/day.
[0021] In embodiments, the disclosure provides a method of initiating
treatment of schizophrenia
with brexpiprazole in an obese patient who is a CYP2D6 poor metabolizer,
comprising: (a)
administering 0.5 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on each of the first 4 days of
brexpiprazole
treatment; (b) administering 1 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on each of the
next 3 days following
step (a); and then (c) administering half of a recommended daily dose of
brexpiprazole once daily
thereafter; wherein the obese patient has one or more of the following
characteristics: (i) BlVII of
at least about 35; (ii) %IBW of at least about 150%; (iii) waist size greater
than about 42 inches;
(iv) % body fat greater than about 40%; (v) % android body fat greater than
about 40%; (vi) %
gynoid body fat greater than about 40%; or (vii) total body fat greater than
about 40 kg. In
embodiments, half of the recommended dose of brexpiprazole is 1-2 mg/day. In
embodiments,
half of the recommended dose of brexpiprazole is 1 mg/day. In embodiments,
half of the
recommended dose of brexpiprazole is 1.25 mg/day. In embodiments, half of the
recommended
dose of brexpiprazole is 1.5 mg/day. In embodiments, half of the recommended
dose of
6
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
brexpiprazole is 1.75 mg/day. In embodiments, half of the recommended dose of
brexpiprazole is
2 mg/day.
[0022] In embodiments, the disclosure provides a method of initiating
adjunctive treatment of
major depressive disorder with brexpiprazole in an obese patient who is not a
CYP2D6 poor
metabolizer, comprising: (a) administering either 0.5 or 1 mg brexpiprazole
twice daily on each of
the first 7 days of brexpiprazole treatment; (b) administering double the
individual brexpiprazole
dose of step (a) once daily on each of the next 7 days following step (a); and
then (c) administering
the recommended daily dose of brexpiprazole once daily thereafter; wherein the
obese patient has
one or more of the following characteristics: (i) BlV11 of at least about 35;
(ii) %IBW of at least
about 150%; (iii) waist size greater than about 42 inches; (iv) % body fat
greater than about 40%;
(v) % android body fat greater than about 40%; (vi) % gynoid body fat greater
than about 40%; or
(vii) total body fat greater than about 40 kg. In embodiments of the method of
initiating adjunctive
treatment of major depressive disorder with brexpiprazole, step (a) is
administering 0.5 mg
brexpiprazole twice daily for each of the first 7 days of brexpiprazole
treatment, and step (b) is
administering 1 mg brexpiprazole once daily for each of the next 7 days
following step (a). In
embodiments of the method of initiating treatment of major depressive disorder
with
brexpiprazole, step (a) is administering 1 mg brexpiprazole twice daily for
each of the first 7 days
of brexpiprazole treatment, and step (b) is administering 2 mg brexpiprazole
once daily for each
of the next 7 days following step (a). In embodiments, the recommended daily
dose of step (c) is
2-3 mg/day. In embodiments, the recommended daily dose of step (c) is 2
mg/day. In
embodiments, the recommended daily dose of step (c) is 2.25 mg/day. In
embodiments, the
recommended daily dose of step (c) is 2.5 mg/day. In embodiments, the
recommended daily dose
of step (c) is 2.75 mg/day. In embodiments, the recommended daily dose of step
(c) is 3 mg/day.
[0023] In embodiments, the disclosure provides a method of initiating
adjunctive treatment of
major depressive disorder with brexpiprazole in an obese patient who is a
CYP2D6 poor
metabolizer, comprising: (a) administering 0.5 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on
each of the first 7
days of brexpiprazole treatment; (b) administering 1 mg twice daily on each of
the next 7 days
following step (a); and then (c) administering half of the recommended daily
dose of brexpiprazole
once daily thereafter; wherein the obese patient has one or more of the
following characteristics:
(i) BlVII of at least about 35; (ii) %IBW of at least about 150%; (iii) waist
size greater than about
42 inches; (iv) % body fat greater than about 40%; (v) % android body fat
greater than about 40%;
7
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
(vi) % gynoid body fat greater than about 40%; or (vii) total body fat greater
than about 40 kg. In
embodiments, half of the recommended daily dose of step (c) is 1-1.5 mg/day.
In embodiments,
half of the recommended daily dose of step (c) is 1 mg/day. In embodiments,
half of the
recommended daily dose of step (c) is 1.25 mg/day. In embodiments, half of the
recommended
daily dose of step (c) is 1.5 mg/day. In embodiments, half of the recommended
daily dose of step
(c) is 1.75 mg/day. In embodiments, half of the recommended daily dose of step
(c) is 2 mg/day.
[0024] In embodiments, the disclosure provides method of initiating adjunctive
treatment of major
depressive disorder with brexpiprazole in an obese patient who is a CYP2D6
poor metabolizer,
comprising: (a) administering 0.25 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on each of the
first 7 days of
brexpiprazole treatment; (b) administering 0.5 twice daily on each of next 7
days following step
(a); (c) administering 1 mg daily twice on each of the next 7 days following
step (b); and then
(d) administering half of the recommended daily dose of brexpiprazole once
daily thereafter;
wherein the obese patient has one or more of the following characteristics:
(i) BMI of at least about
35; (ii) %IBW of at least about 150%; (iii) waist size greater than about 42
inches; (iv) % body fat
greater than about 40%; (v) % android body fat greater than about 40%; (vi) %
gynoid body fat
greater than about 40%; or (vii) total body fat greater than about 40 kg. In
some embodiments,
half of the recommended daily dose of step (c) is 1-1.5 mg/day. In some
embodiments, half of the
recommended daily dose of step (c) is 1 mg/day. In some embodiments, half of
the recommended
daily dose of step (c) is 1.25 mg/day. In some embodiments, half of the
recommended daily dose
of step (c) is 1.5 mg/day. In some embodiments, half of the recommended daily
dose of step (c)
is 1.75 mg/day. In some embodiments, half of the recommended daily dose of
step (c) is 2 mg/day.
[0025] Applicant also surprisingly discovered that normal-weight CYP2D6 PM
patients do not
reach therapeutic levels as quickly as normal-weight CYP2D6 EM (FIG. 1A and
FIG. 1B).
Administering brexpiprazole according to a modified dosage regimen provided
herein enables
normal-weight CYP2D6 PM patients to approach therapeutic levels of
brexpiprazole as quickly as
normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients (FIGS. 5, 11, and 12)
[0026] In embodiments, the disclosure provides a method of initiating
treatment of schizophrenia
with brexpiprazole in a normal-weight patient who is a CYP2D6 poor
metabolizer, comprising:
(a) administering 0.5 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on each of the first 4 days
of brexpiprazole
treatment; (b) administering 1 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on each of the
next 3 days following
step (a); and then (c) administering half of the recommended dose of
brexpiprazole once daily
8
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
thereafter, wherein the normal-weight patient has at least one of the
following characteristics: (i)
BMI less than about 35 kg/m2; (ii) % IBW less than about 150%; (iii) waist
size less than about 42
inches; (iv) % body fat less than about 40%; (v) % android body fat less than
about 40%; (vi) %
gynoid body fat less than about 40%; or (vii) total body fat less than about
40 kg. In embodiments,
half of the recommended dose of brexpiprazole is 1-2 mg/day. In embodiments,
half of the
recommended dose of brexpiprazole is 1 mg/day. In embodiments, half of the
recommended dose
of brexpiprazole is 1.25 mg/day. In embodiments, half of the recommended dose
of brexpiprazole
is 1.5 mg/day.
[0027] In embodiments, the disclosure provides a method of initiating
adjunctive treatment of
major depressive disorder with brexpiprazole in a normal-weight patient who is
not a CYP2D6
poor metabolizer, comprising: (a) administering either 0.25 or 0.5 mg
brexpiprazole twice daily
on each of the first 7 days of brexpiprazole treatment; (b) administering
double the individual
brexpiprazole dose of step (a) once daily on each of the next 7 days following
step (a); and then
(c) administering the recommended daily dose of brexpiprazole once daily
thereafter; wherein the
normal-weight patient has at least one of the following characteristics: (i)
BMI less than about 35
kg/m2; (ii) % IBW less than about 150%; (iii) waist size less than about 42
inches; (iv) % body fat
less than about 40%; (v) % android body fat less than about 40%; (vi) % gynoid
body fat less than
about 40%; or (vii) total body fat less than about 40 kg. In embodiments of
the method of initiating
adjunctive treatment of major depressive disorder with brexpiprazole, step (a)
is administering
0.25 mg brexpiprazole twice daily for each of the first 7 days of
brexpiprazole treatment, and step
(b) is administering 0.5 mg brexpiprazole once daily for each of the next 7
days following step (a).
In embodiments of the method of initiating treatment of major depressive
disorder with
brexpiprazole, step (a) is administering 0.5 mg brexpiprazole twice daily for
each of the first 7
days of brexpiprazole treatment, and step (b) is administering 1 mg
brexpiprazole once daily for
each of the next 7 days following step (a). In embodiments, half of the
recommended dose of
brexpiprazole is 1-1.5 mg/day. In embodiments, half of the recommended dose of
brexpiprazole
is 1 mg/day. In embodiments, half of the recommended dose of brexpiprazole is
1.25 mg/day. In
embodiments, half of the recommended dose of brexpiprazole is 1.5 mg/day.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
9
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
[0028] FIG. lA shows the plasma levels of brexpiprazole in normal-weight
CYP2D6 EM and
CYP2D6 PM patients with schizophrenia that are treated according to the
brexpiprazole FDA
label. While steady-state brexpiprazole plasma levels of CYP2D6 PM patients
are lower than
brexpiprazole plasma levels of CYP2D6 EM patients, these steady-state levels
are considered
therapeutically effective concentrations for CYP2D6 PM patients.
[0029] FIG. 1B shows the plasma levels of brexpiprazole in normal-weight
CYP2D6 EM and
CYP2D6 PM patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) that are treated
according to the
brexpiprazole FDA label, with a starting dose of 0.5 mg. While steady-state
brexpiprazole plasma
levels in CYP2D6 PM patients are lower than brexpiprazole plasma levels in
CYP2D6 EM
patients, these steady-state levels are considered therapeutically effective
concentrations for
CYP2D6 PM patients.
[0030] FIG. 2A shows the plasma levels of brexpiprazole in normal-weight
CYP2D6 EM, normal-
weight CYP2D6 PM, obese CYP2D6 EM, and obese CYP2D6 PM patients with
schizophrenia
that arc treated according to the brexpiprazole FDA label. Obese CYP2D6 EM and
obese CYP2D6
PM patients take longer to reach therapeutic concentrations of brexpiprazole
than normal-weight
CYP2D6 EM patients, and may not reach therapeutic concentrations at all in the
first 28 days of
brexpiprazole administration.
[0031] FIG. 2B shows the plasma levels of brexpiprazole in normal-weight
CYP2D6 EM, normal-
weight CYP2D6 PM, obese CYP2D6 EM, and obese CYP2D6 PM patients with MDD that
are
treated according to the brexpiprazole FDA label, with a starting dose of 0.5
mg. Obese CYP2D6
EM and obese CYP2D6 PM patients take longer to reach therapeutic
concentrations of
brexpiprazole than normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients, and may not reach
therapeutic
concentrations at all in the first 28 days of brexpiprazole administration.
[0032] FIG. 3 shows the plasma levels of brexpiprazole over time of obese
CYP2D6 EM
schizophrenia patients that are administered 1 mg brexpiprazole twice daily
for days 1-4 and 2 mg
BID for days 5-7 (Table 3. Modified Dosing Regimen 1). Obese CYP2D6 EM
patients treated
according to the disclosed modified dosage regimen reach therapeutic
concentrations that are
similar to normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients treated according to the
brexpiprazole FDA label.
[0033] FIG. 4 shows the plasma levels of brexpiprazole over time of obese
CYP2D6 PM
schizophrenia patients that are administered 0.5 mg brexpiprazole twice daily
on days 1-4, 1 mg
BID on days 5-7, and then are administered 2 mg brexpiprazole twice daily for
days 8-14 (Table
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
3. Modified Dosing Regimen 2). Obese CYP2D6 PM patients treated according to
the modified
dosage regimen reach therapeutic concentrations of brexpiprazole in a similar
time as normal-
weight CYP2D6 EM patients treated according to the brexpiprazole FDA label.
When
administered brexpiprazole according to the FDA label, obese CYP2D6 PM
patients do not reach
therapeutic concentrations in the first 28 days of administration.
[0034] FIG. 5 shows the plasma brexpiprazole concentration over time of normal-
weight
CYP2D6 PM schizophrenia patients that are administered brexpiprazole according
to the modified
dosage regimen of Table D.
[0035] FIG. 6 shows the plasma levels of brexpiprazole over time of obese
CYP2D6 EM major
depressive disorder patients that are administered 0.5 mg brexpiprazole twice
daily for the first
seven days (Table 4. Modified Dosing Regimen A). Obese CYP2D6 EM patients
treated according
to the disclosed modified dosage regimen reach therapeutic concentrations that
are similar to
normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients treated according to the brexpiprazole FDA
label.
[0036] FIG. 7 shows the plasma levels of brexpiprazole over time of obese
CYP2D6 EM major
depressive disorder patients that are administered 1 mg brexpiprazole twice
daily for the first seven
days (Table 4. Modified Dosing Regimen B). Obese CYP2D6 EM patients treated
according to
the modified dosage regimen reach therapeutic concentrations of brexpiprazole
in a similar time
as normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients treated according to the brexpiprazole FDA
label.
[0037] FIG. 8 shows the plasma levels of brexpiprazole over time of obese
CYP2D6 PM major
depressive disorder patients that are administered 0.25 mg brexpiprazole twice
daily for the first
seven days, 0.5 mg twice daily for days 8-15, and 1 mg twice daily for days 16-
21 (Table 4.
Modified Dosing Regimen C). Obese CYP2D6 PM patients treated according to the
disclosed
modified dosage regimen reach therapeutic concentrations that are similar to
normal-weight
CYP2D6 EM patients treated according to the brexpiprazole FDA label. When
administered
brexpiprazole according to the FDA label, obese CYP2D6 PM patients do not
reach therapeutic
concentrations in the first 28 days of administration.
[0038] FIG. 9 shows the plasma levels of brexpiprazole over time of obese
CYP2D6 PM major
depressive disorder patients that are administered 0.5 mg brexpiprazole twice
daily for the first 7
days, and 1 mg twice daily on days 8-14 (Table 4. Modified Dosing Regimen D).
Obese CYP2D6
PM patients treated according to the modified dosage regimen reach therapeutic
concentrations of
brexpiprazole in a similar time as normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients treated
according to the
11
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
brexpiprazole FDA label. When administered brexpiprazole according to the FDA
label, obese
CYP2D6 PM patients do not reach therapeutic concentrations in the first 28
days of administration.
[0039] FIG. 10 shows the plasma levels of brexpiprazole over time for an obese
CYP2D6 EM
when the patient is administered brexpiprazole (i) according to the
brexpiprazole FDA label; (ii)
BID for 7 days according to a modified dosing regimen of the disclosure; and
(iii) BID for 14 days.
When BID dosing exceeds the modified dosing of the disclosure, plasma levels
elevate
significantly above those of normal-weight CYP2D6 EM and present a risk of
serious side effects.
[0040] FIG. 11 shows the plasma levels of brexpiprazole over time of normal-
weight CYP2D6
PM major depressive disorder patients that are administered 0.25 mg
brexpiprazole twice daily for
the first 7 days (Table 4. Modified Dosing Regimen E), Normal-weight CYP2D6 PM
patients
treated according to the modified dosage regimen reach therapeutic
concentrations of
brexpiprazole in a similar time as normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients treated
according to the
brexpiprazole FDA label.
[0041] FIG. 12 shows the plasma levels of brexpiprazole over time of normal-
weight CYP2D6
PM major depressive disorder patients that are administered 0. 5 mg
brexpiprazole twice daily for
the first 7 days (Table 4. Modified Dosing Regimen F). Normal-weight CYP2D6 PM
patients
treated according to the modified dosage regimen reach therapeutic
concentrations of
brexpiprazole in a similar time as normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients treated
according to the
brexpiprazole FDA label.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
Definitions
[0042] Any reference to brexpiprazole herein also encompasses all of the
pharmaceutically
acceptable isomers (e.g., stereoisomers), solvates, hydrates, polymorphs,
salts, and prodrugs (e.g.,
esters and phosphates).
[0043] As used herein, "normal," "normal-weight," or other derivations or
variations thereof refers
to a non-obese state in a person who can have at least one of the following
characteristics: BMI
less than about 35 kg/m2, % IBW less than about 150%, waist size less than
about 42, % body fat
less than about 40%, % android body fat less than about 40%, % gynoid body fat
less than about
40%, and total body fat less than about 40 kg. Unless otherwise modified,
"normal metabolizer"
also means an extensive CYP2D6 metabolizer.
12
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
[0044] As used herein, the terms "reference dose", "reference daily dose",
"recommended dose",
or "usual dose" refer to the maintenance dosage of brexpiprazole, as indicated
on the manufacture's
FDA-approved label (e.g., the most recent FDA-approved label in effect as of
March, 2020). The
REXULTI label also refers to a "Starting Dose- and a "Maximum Dose- as
distinct from the
"Recommended Dose". While colloquially the term "recommended" or "usual" dose
could refer
to any dose taught in the REXULTI label, in this disclosure the term
"recommended dose" refers
more narrowly to doses recommended for maintenance treatment (including the
"maximum dose"
suitable for such treatment) of a normal weight, extensive CYP2D6 metabolizer
patients. Thus,
where the REXULTI label teaches administering 2 mg once daily up to a maximum
dose of 3
mg once daily for an MDD patient, such dose or dose range is a "recommended"
dose or dose
range. Where the REXULTIO label teaches reducing the "usual dosage by half"
for "Known
CYP2D6 Metabolizers", the recommended or usual dose as used herein is the dose
recommended" or "usual" for patients who are not CYP2D6 PMs.
[0045] It is common for a particular drug to be approved for multiple
different indications, and
each indication may have a different reference or recommended dose. For
example, the
recommended dose" listed in the March 2020 REXULTI label indicates that 2 to
3 mg once
daily is the "recommended dose" for MDD and 2 to 4 mg once daily is the
"recommended dose"
for schizophrenia.
[0046] As used herein "therapeutic concentration" refers to the steady state
pharmacokinetic
profile of brexpiprazole based on the pharmacokinetic studies supporting FDA
approval of
brexpiprazole as measured in normal-weight patients. As shown in FIG. 14 and
FIG. 1B, normal-
weight patients treated with brexpiprazole achieve steady state
pharmacokinetics after the
initiation phase of treatment, typically around days 14-21 of treatment
according to FIG. lA and
FIG. 1B. Because the blood plasma levels in FIG. 14 and FIG. 1B represent
averages from all
patients, some deviation from the average steady state pharmacokinetic profile
in a particular
patient or patient population is expected and is acceptable in the art. The
modified dosing regimens
of the present disclosure bring the blood plasma concentrations of
brexpiprazole in obese patients
and obese CYP2D6 PM patients within appropriate degrees of variation of the
average steady
state pharmacokinetic profile of normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients shown in
FIG. lA and FIG.
1B. This enables obese patients or obese CYP2D6 PM patients to reach
therapeutic concentrations
of brexpiprazole at a similar time as normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients,
allowing for better
13
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
clinical response. It is not necessary for the pharmacokinetic profile of the
modified dosing
regimens disclosed herein to overlap exactly with the pharmacokinetic profile
of brexpiprazole
based on the pharmacokinetic studies supporting FDA approval.
[0047] As used herein "BID" refers to twice daily administration.
[0048] As used herein "QD" refers to once daily administration.
Brexpiprazole
[0049] Brexpiprazole is an atypical antipsychotic, available as REXULTIO, to
be used as an
adjunctive therapy to antidepressants for the treatment of major depressive
disorder and as a
treatment for schizophrenia. The FDA label of REXULTI (Otsuka and Lundbeck,
revised
03/2020) is incorporated by reference herein in its entirety. Brexpiprazole is
7- {4-[4-(1-
B enzothiophen-4-yl)p iperazin- 1 -yl]butoxy quinolin-2(11/)-one. The
empirical formula is
C25H27N302S and its molecular weight is 433.57.
[0050] The chemical structure of brexpiprazole is
N N
N
[0051] The FDA label provides the following dosage instructions for adjunctive
treatment for
major depressive disorder: The starting dosage for brexpiprazole (REXULTIg) as
adjunctive
treatment is 0.5 mg or 1 mg once daily, taken orally with or without food.
Titrate to 1 mg once
daily, then up to the recommended dosage of 2 mg once daily. Dosage increases
should occur at
weekly intervals based on the patient's clinical response and tolerability.
The maximum
recommended daily dosage is 3 mg. Periodically reassess to determine the
continued need and
appropriate dosage for treatment.
[0052] The FDA label provides the following dosage instructions for
schizophrenia: The starting
dosage for brexpiprazole (REXULTIO) is 1 mg once daily on Days 1 to 4, taken
orally with or
without food. The recommended brexpiprazole (REXULTI8) dosage is 2 mg to 4 mg
once daily.
14
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
Titrate to 2 mg once daily on Day 5 through Day 7, then to 4 mg on Day 8 based
on the patient's
clinical response and tolerability. The maximum daily dosage is 4 mg.
[0053] The FDA label provides dosage modifications for CYP2D6 Poor
Metabolizers and for
concomitant use with CYP Inhibitors or Inducers: Dosage adjustments are
recommended in
patients who are known cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6 poor metabolizers and in
patients taking
concomitant CYP3A4 inhibitors or CYP2D6 inhibitors or strong CYP3A4 inducers
(see Table 2).
If the coadministered drug is discontinued, adjust the REXULTI dosage to its
original level. If the
coadministered CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued, reduce the REXULTI dosage to
the original
level over 1 to 2 weeks.
Table 2
Factors Adjusted Brexpiprazole
(REXULTIO)
Dosage
CYP2D6 Poor Metabolizers
CYP2D6 poor metabolizers Administer half of the usual
dose.
Known CYP2D6 poor metabolizers taking Administer a quarter of the
usual dose.
strong/moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors
Patients taking CYP2D6 Inhibitors and/or CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Strong CYP2D6 inhibitors (paroxetine, Administer half of the usual
dose.
fluoxetine)
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors Administer half of the usual
dose.
Strong/moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors with Administer a quarter of the
usual dose.
strong/moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors
Patients taking CYP3A4 Inducers
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers Double usual dose over 1 to 2
weeks
[0054] Applicant found that the brexpiprazole (REXULTIg) dosage instructions
for initiating
treatment with brexpiprazole do not provide therapeutically effective levels
of brexpiprazole for
patients that are obese or obese CYP2D6 PM as quickly as for normal-weight
CYP2D6 EMs.
Dosage Regimens
[0055] The various dosing methods of the present invention, as described
herein, comprise
initiating treatment by administering an elevated daily dose of brexpiprazole
for one or more
defined time periods, then at an appropriate time (as described herein),
administering the FDA-
recommended dose appropriate for the indication (e.g., schizophrenia or major
depressive
disorder). The initial, elevated daily dose is administered in the form of
multiple daily doses, as a
single elevated dose would result in sharp "peaks" in the plasma level that
could cause serious side
effects such as akathisia. The multiple daily brexpiprazole doses administered
at the initiation of
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
brexpiprazole treatment according to various embodiments of the present
invention are typically
administered in the form of two equal daily doses, that when combined provided
a daily dose of
brexpiprazole that is higher than the starting dose of brexpiprazole described
in the REXULTI
label. Typically, the multiple daily brexpiprazole doses administered at the
initiation of
brexpiprazole treatment provide a daily dose that is double the starting dose
of brexpiprazole
described in the REXULTI label. However, in view of the discovery described
herein, the initial
dose of brexpiprazole according to the present invention could comprise
unequal doses, and/or
could be administered in more than two (e.g., three or four) daily doses.
Alternatively, instead of
administering multiple daily doses at the initiation of brexpiprazole
treatment, the starting doses
described herein (e.g. double the starting dose of brexpiprazole described in
the REXULTI label)
may be administered once daily in a sustained or extended release formulation.
Such a formulation
can release brexpiprazole over the course of a day in a manner that is similar
to twice (or more)
daily administration of brexpiprazole. The guiding principle for initiating
administration of
brexpiprazole according to the methods disclosed herein is to increase the
daily dose of
brexpiprazole for a defined period such that obese CYP2D6 EM or obese CYP2D6
PM patients
reach therapeutic plasma levels of brexpiprazole more quickly than would be
obtained for such
patients using the dosing regimens provided in FDA-approved brexpiprazole
labels prior to the
present invention. Further, the use of multiple daily doses (e.g., BID dosing)
to provide such
elevated daily doses of brexpiprazole (e.g., elevated relative to the daily
"Starting Dose" and/or
"Recommended Dose" provided in REXULTI labels published prior to the present
invention)
are designed to ensure that no single dose elevates the brexpiprazole plasma
levels of such patients
to levels which would increase the risk of serious side effects such as
akathisia. The limited
duration of such multiple dosing prior to reverting to the recommended or
usual maintenance dose
of brexpiprazole is also designed to prevent elevated plasma levels of
brexpiprazole that could
increase the risk of serious side effects such as akathisia. FIG. 10 shows the
effect of BID dosing
in an obese schizophrenia patient during the first 14 days of treatment. After
7 days of BID dosing,
the plasma levels of brexpiprazole begin to elevate above the blood plasma
levels that would occur
in normal-weight patients treated according to the FDA label, and the
increased exposure becomes
more pronounced and potentially more dangerous each day of BID treatment
through day 14. This
results in blood plasma concentrations that present an unacceptable risk of
serious side effects.
16
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
[0056] The skilled artisan understands that in various embodiments, the
magnitude and/or number
of initial doses of brexpiprazole can be varied, along with the duration of
the initial dosing period,
such that the obese patients (EM and PM) according to the present invention
reach therapeutic
plasma levels of brexpiprazole more rapidly than they would if using the
dosing regimens provided
in FDA-approved brexpiprazole labels prior to the present invention, without
increasing the risk
of serious side effects.
[0057] The skilled artisan understands that the REXULTI label (March 2020)
contains
provisions for dose adjustments in the case of concomitant use with a strong
CYP2D6 or strong
CYP3 A4 inhibitor (e.g., administer half of the dose), or concomitant use with
a strong CYP2D6
and strong CYP3A4 inhibitor (e.g., administer a quarter of the dose). These
dose adjustments are
applied to any relevant recommended dose or patient population.
[0058] In some embodiments, the modified dosage regimens described herein
provide
therapeutically effective levels of brexpiprazole for certain patient
populations (e.g., for patients
that are obese or are obese CYP2D6 poor metabolizers).
[0059] In some embodiments, the modified dosage regimens of the present
invention provide a
starting dose. As used herein, a "starting dose" is the lowest dose of
brexpiprazole that is
administered when initiating treatment with brexpiprazole. In some
embodiments, the starting dose
is administered on day 1 of brexpiprazole treatment. In some embodiments, the
starting dose is
administered on days 1-4 of brexpiprazole treatment. In some embodiments, the
starting dose is
administered on days 1-7 of brexpiprazole treatment. In some embodiments, the
starting dose of
the modified brexpiprazole dosage regimens of the present invention is double
that of the starting
dose instructed by the brexpiprazole (REXULTIg) FDA label (03/2020). In some
embodiments,
the starting dose of the modified brexpiprazole dosage regimen is triple that
instructed by the
brexpiprazole (REXULTIS) FDA label (03/2020). In some embodiments, the
starting dose on
days 1-4 of the modified brexpiprazole dosage regimen is double that of the
starting dose instructed
by the brexpiprazole (REXULTIR) FDA label (03/2020) for days 1-4. In some
embodiments, the
starting dose on days 1-7 of the modified brexpiprazole dosage regimen is
double that of the
starting dose instructed by the brexpiprazole (REXULTIV) FDA label (03/2020)
for days 1-7. In
some embodiments, the dose administered on days 8-14 or days 8-21 of the
modified brexpiprazole
dosage regimen is double that of the dose instructed by the brexpiprazole
(REXULTI8) FDA label
(03/2020) for days 8-14 or days 8-21. As used herein, phrases such as "days 1-
4", "days 5-7",
17
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
"days 1-7" and the like refer to days after first initiating the
administration of brexpiprazole. That
is, "day 1" is the first day brexpiprazole is administered to the patient upon
initiating treatment,
day 7 is the seventh day of brexpiprazole treatment, etc. Initiating
brexpiprazole treatment can
refer to the first administration to a brexpiprazole-naive patient who has
never been administered
brexpiprazole, or to a patient who may have been administered brexpiprazole in
the past, but has
ceased treatment with brexpiprazole for a period sufficient to require re-
introduction of
brexpiprazole with a lower starting dose of brexpiprazole before increasing to
the recommended
dose.
[0060] In some embodiments, a patient is administered a starting dose of about
0.25 mg to about
3 mg of brexpiprazole, for example, about 0.25, about 0.5 mg, about 0.75 mg,
about 1 mg, about
1.25 mg, about 1.5 mg, about 1.75 mg, about 2 mg, about 2.25 mg, about 2.5 mg,
about 2.75 mg,
or about 3 mg of brexpiprazole. In some embodiments, a patient is administered
a total daily dose
of 0.5 mg brexpiprazole on days 1-4 or days 1-7 (depending on the patient's
condition). In some
embodiments, a patient is administered a total daily dose of 1 mg
brexpiprazole on days 1-4 or
days 1-7 (depending on the patient's condition). In some embodiments, a
patient is administered a
total daily dose of 1.5 mg brexpiprazole on days 1-4 or days 1-7 (depending on
the patient's
condition). In some embodiments, a patient is administered a total daily dose
of 2 mg brexpiprazole
on days 1-4 or days 1-7 (depending on the patient's condition).
[0061] In various embodiments, any of the starting doses described herein are
administered as two
equal doses, twice per day (BID) for a defined period of time, e.g., for 1, 2,
3, 4, 5, 6, or 7 days, or
any combination or range thereof. In some embodiments, a patient is
administered 0.25 mg
brexpiprazole twice daily on days 1-7. In some embodiments, a patient is
administered 0.5 mg
brexpiprazole twice daily brexpiprazole on days 1-4 or days 1-7 (depending on
the patient's
condition). In some embodiments, a patient is administered 0.75 mg
brexpiprazole twice daily
brexpiprazole on days 1-4 or days 1-7 (depending on the patient's condition).
In some
embodiments, a patient is administered 1 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on days
1-4 or days 1-7
(depending on the patient's condition).
[0062] In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased from the
starting dose. In
some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased every 2-3 days, every
3-4 days, every
4-5 days, or every 6-7 days. In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is
increased every
week, every two weeks, every three weeks, or every month. In some embodiments,
on day 5 of
18
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
brexpiprazole administration, the dose of brexpiprazole is double that of the
dose provided on the
FDA label for day 5. In some embodiments, on day 8 of brexpiprazole
administration, the dose of
brexpiprazole is double that of the dose provided on the FDA label for day 8.
In some
embodiments, on day 15 of brexpiprazole administration, the dose of
brexpiprazole is double that
of the dose provided on the FDA label for day 15.
[0063] In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased from the
starting dose by an
amount ranging from about 0.25 mg to about 2 mg, for example, about 0.25 mg,
about 0.5 mg,
about 1 mg, about 1.5 mg, or about 2 mg, including all values and ranges in
between. In some
embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased by an amount ranging from
about 0.25 mg to
about 6 mg, for example, about 0.5 mg, about 1 mg, about 1.5 mg, about 2 mg,
about 2.5 mg, about
3 mg, about 3.5 mg, about 4 mg, about 4.5 mg, about 5 mg, about 5.5 mg, or
about 6 mg, every 2-
3 days, every 3-4 days, every 4-5 days, or every 6-7 days, including all
values and ranges
therebetween. In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased by
an amount ranging
from about 0.5 mg to about 6 mg, for example, about 0.5 mg, about 1 mg, about
1.5 mg, about 2
mg, about 2.5 mg, about 3 mg, about 3.5 mg, about 4 mg, about 4.5 mg, about 5
mg, about 5.5 mg,
or about 6 mg, every week, every two weeks, every three weeks, or every month,
including all
values and ranges therebetween. In some embodiments, on day 5 of brexpiprazole
administration,
the dose of brexpiprazole is doubled from the starting dose. In some
embodiments, on day 8 of
brexpiprazole administration, the dose of brexpiprazole is doubled from the
starting dose.
Schizophrenia
[0064] In some embodiments, an obese CYP2D6 EM patient or obese CYP2D6 PM
patient is
administered a starting dose of 1 mg or 2 mg brexpiprazole as a total daily
dose on days 1-4,
according to the modified dosing regimens disclosed herein. In some
embodiments, an obese
CYP2D6 EM patient or obese CYP2D6 PM patient is administered a starting dose
of 0.5 mg or 1
mg brexpiprazole, twice daily, on days 1-4, according to the modified dosing
regimens disclosed
herein.
[0065] In some embodiments, on day 5, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased
from the starting
dose. In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased on day 5 and
maintained for
the duration of brexpiprazole use. In some embodiments, the dose of
brexpiprazole is increased on
day 5, and the increased dose is administered from days 5-7. In some
embodiments, the total daily
19
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
dose administered on days 5-7 is 2-4 mg (2 mg, 2.5 mg, 3 mg, 3.5 mg, or 4 mg,
inclusive of all
values and ranges therebetween). In some embodiments, the dose administered on
days 5-7 is 1-2
mg (e.g., 1 mg, 1.5 mg, or 2 mg, inclusive of all values and ranges
therebetween) brexpiprazole
twice daily.
[0066] In some embodiments, the patient resumes administration of the
recommended daily dose
starting on day 8. In some embodiments, an obese CYP2D6 EM patient or obese
CYP2D6 PM
patient is administered 2-4 mg (2 mg, 2.5 mg, 3 mg, 3.5 mg, or 4 mg, inclusive
of all values and
ranges therebetween) on day 8.
[0067] In some embodiments, on day 8, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased
from the starting
dose. In some embodiments, on day 8, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased
from the dose
administered on days 5-7. In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is
increased on day 8,
from the starting dose or from the dose administered on days 5-7. In some
embodiments, the dose
of brexpiprazole is increased on day 8 and maintained for the duration of
brexpiprazole use. In
some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased on day 8, from the
starting dose or from
the dose administered on days 5-7, wherein the increase is maintained for days
8-14 of
brexpiprazole use. In some embodiments, the dose administered on days 8-14 is
1-4 mg (1 mg, 1.5
mg, 2 mg, 2.5 mg, 3 mg, 3.5 mg, or 4 mg, inclusive of all values and ranges
therebetween) as a
total daily dose. In some embodiments, the dose administered on days 8-14 is 1-
2 mg (e.g., 1 mg,
1.5 mg, or 2 mg, inclusive of all values and ranges therebetween)
brexpiprazole twice daily.
[0068] In some embodiments, the patient resumes administration of the
recommended daily dose
starting on day 15. In some embodiments, an obese CYP2D6 FM patient or obese
CYP2D6 PM
patient is administered 2-4 mg (2 mg, 2.5 mg, 3 mg, 3.5 mg, or 4 mg, inclusive
of all values and
ranges therebetween) on day 15.
[0069] In some embodiments, a dose of about 0.5 mg to about 1 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered twice daily on days 1-4, a dose of about 1 mg to about 2 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered twice daily on days 5-7, and about 2 mg to about 4 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered once daily or twice daily starting on day 8. In some embodiments,
a dose of about
0.5 mg to about 1 mg of brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 1-4,
a dose of about 1
mg to about 2 mg of brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 5-7,
about 2 mg to about 4
mg of brexpiprazole is administered once daily or twice on days 8-15, and
about 2-4 mg
brexpiprazole is administered once daily starting on day 15. In some
embodiments, a dose of about
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
0.5 mg brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 1-4, a dose of about
1 mg of
brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 5-7, about 2 mg of
brexpiprazole is administered
twice daily on days 8-15, and about 1-2 mg brexpiprazole is administered once
daily starting on
day 15. In some embodiments, a dose of about 1 mg brexpiprazole is
administered twice daily on
days 1-4, a dose of about 2 mg of brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on
days 5-7, about 2-
4 mg of brexpiprazole is administered once daily starting on day 8-15. In some
embodiments, a
dose of about 0.5 mg brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 1-4, a
dose of about 1 mg
of brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 5-7, about 1-2 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered once daily starting on day 8. In some embodiments, a dose of
about 1 mg
brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 1-4, a dose of about 2 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered twice daily on days 5-7, about 2-4 mg of brexpiprazole is once
daily starting on day
8.
[0070] In some embodiments, a total daily dose of about 1 mg to about 2 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered on days 1-4, a total daily dose of about 2 mg to about 4 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered on days 5-7, and a total daily dose of between about 2-4 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered starting on day 8.
[0071] In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased from the
starting dose on day
and maintained for days 5-7, and then decreased to the recommended daily dose
on day 8 for the
duration of brexpiprazole use. In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole
is increased from
the starting dose on day 5 and maintained for days 5-7, then increased again
on day 8 and
maintained from days 8-14, and decreased to the recommended daily dose on day
15 for the
duration of brexpiprazole use. In some embodiments, the dose administered on
day 15 is 1 mg, 2
mg, 3 mg, or 4 mg.
[0072] In some embodiments, the patient with schizophrenia is an obese patient
who is not a
CYP2D6 poor metabolizer (in other words, the patient is an obese CYP2D6 EM
patient), and the
method comprises: (a) administering 1 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on each of
the first 4 days of
brexpiprazole treatment; (b) administering 2 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on
each of the next 3
days following step (a); and then (c) administering a recommended dose of
brexpiprazole (2-4
mg/day) once daily thereafter. In some embodiments, the patient with
schizophrenia is an obese
patient who is a CYP2D6 poor metabolizer, and the method comprises: (a)
administering 0.5 mg
brexpiprazole twice daily on each of the first 4 days of brexpiprazole
treatment; (b) administering
21
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
1 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on each of the next 3 days following step (a);
and then (c)
administering half of a recommended daily dose of brexpiprazole (e.g., 1-2
mg/day) once daily
thereafter.
[0073] In some embodiments, a patient with schizophrenia is treated with a
modified dosage
regimen as found in Table 3. The dosage found in Table 3 is the total daily
dose of brexpiprazole.
In some embodiments, the total daily dose is divided into two doses, for
example, a patient that is
administered a total daily dose of 4 mg brexpiprazole may be administered a
first dose of 2 mg
brexpiprazole and a second dose of 2 mg brexpiprazole.
Table 3. Dosing Regimens for Schizophrenia
Dosage Days 1-4 Days 5-7 Days 8-14 Days 15+ Weight
CYP2D6
Regimen
Status
FDA 1 mg (QD) 2 mg (QD) 2-4 mg 2-4 mg All EM
Label (QD) (QD)
FDA 0.5 mg 1 mg (QD) 1-2 mg 1-2 mg All PM
Label (QD) (QD) (QD)
Modified 2 mg (1 mg 4 mg (2 mg 2-4 mg 2-4 mg Obese EM
Dosing BID) BID) (QD) (QD)
Regimen
1
Modified 1 mg (0.5 2 mg (1 mg 2-4 mg (1-2 1-2 mg Obese PM
Dosing mg BID) BID) mg BID) (QD)
Regimen
2
Modified 1 mg (0.5 2 mg (1 mg 1-2 mg 1-2 mg Non-obese PM
Dosing mg BID) BID) (QD) (QD)
Regimen
3
22
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
Adjunctive Treatment ofMajor Depressive Disorder
[0074] In some embodiments, an obese CYP2D6 EM patient or obese CYP2D6 PM
patient is
administered, as a starting daily dose, a total daily dose of 0.5 mg, 1 mg or
2 mg brexpiprazole on
days 1-7, according to the modified dosing regimens disclosed herein. In some
embodiments, an
obese patient or obese CYP2D6 PM patient is administered a starting dose of
0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, or
1 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on days 1-7, according to the modified dosing
regimens disclosed
herein
[0075] In some embodiments, on day 8, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased
from the starting
dose. In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased on day 8 and
maintained for
the duration of brexpiprazole use. In some embodiments, the dose of
brexpiprazole is increased on
day 8, and the increased dose is administered from days 8-14. In some
embodiments, the patient
resumes administration of the recommended daily dose starting on day 8 or
starting on day 15. In
some embodiments, the total daily dose of brexpiprazole administered on days 8-
14 is 1-4 mg
(e.g., 1 mg, 1.5 mg, 2 mg, 2.5 mg, 3 mg, 3.5 mg, or 4 mg, inclusive of all
values and ranges
therebetween). In some embodiments, 0.5-2 mg (0.5 mg, 1 mg, 1.5 mg, or 2 mg,
inclusive of all
values and ranges therebetween) is administered twice daily on days 8-14.
[0076] In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased on day 15,
from the dose
administered on days 8-14 of brexpiprazole use. In some embodiments, the dose
of brexpiprazole
is increased on day 15 from the dose administered on days 8-14 and maintained
for the duration
of brexpiprazole use. In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is
increased on day 15 from
the dose administered on days 8-14, and the dose is administered on days 15-21
of brexpiprazole
treatment. In some embodiments, the total daily dose of brexpiprazole
administered on days 15-
21 is 1-6 mg (e.g., 1 mg, 1.5 mg, 2 mg, 2.5 mg, 3 mg, 3.5 mg, 4 mg, 4.5 mg, 5
mg, 5.5 mg, or 6
mg, inclusive of all values and ranges therebetween). In some embodiments, 0.5-
3 mg (0.5 mg, 1
mg, 1.5 mg, 2 mg, 2.5 mg, or 3 mg, inclusive of all values and ranges
therebetween) is administered
twice daily on days 8-14.
[0077] In some embodiments, patients resume administration of the recommended
daily dose
starting on day 22.
[0078] In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased on day 8
from the starting
dose. In some embodiments, the dose administered on day 8 is double the
starting dose
administered on day 1. In some embodiments, the starting dose of brexpiprazole
is 0.25 mg, 0.5
23
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
mg, 1 mg, or 2 mg. In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole administered
on days 8-14 is
0.5 mg, 1 mg, or 2 mg.
[0079] In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased from the
starting dose on day
8 and maintained for days 8-14, increased again on day 14 and maintained from
days 14-21, and
decreased to the recommended daily dose on day 22 for the duration of
brexpiprazole use. In some
embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole administered on starting on day 22 is 1
mg, 1.5 mg, 2 mg,
or 3 mg.
[0080] In some embodiments, the dose of brexpiprazole is increased from the
starting dose on day
8 and maintained for days 8-14, and then decreased to the recommended daily
dose on day 15 for
the duration of brexpiprazole use. In some embodiments, the dose of
brexpiprazole administered
on starting on day 15 is 1 mg, 1.5 mg, 2 mg, or 3 mg.
[0081] In some embodiments, a patient is administered a starting dose of 2 mg
on days 1-7, a total
daily dose of 4 mg on days 8-14, a total daily dose of 2-3 mg starting on day
15 and for the duration
of brexpiprazole use.
[0082] In some embodiments, a total daily dose of about 0.5 mg to about 2 mg
of brexpiprazole is
administered on days 1-7, a total daily dose of about 1 mg to about 4 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered on days 8-14, and a total daily dose of between about 1-6 of
brexpiprazole is
administered starting on day 15. In some embodiments, a total daily dose of
about 0.5 mg to about
1 mg of brexpiprazole is administered on days 1-7, a total daily dose of about
1 mg to about 2 mg
of brexpiprazole is administered on days 8-14, and a total daily dose of about
2-3 mg of
brexpiprazole is administered starting on day 15. In some embodiments, a total
daily dose of about
0.5 mg of brexpiprazole is administered on days 1-7, a total daily dose of
about 1 mg of
brexpiprazole is administered on days 8-14, a total daily dose of about 2 mg
is administered on
days 14-21, and a total daily dose of 2-3 mg is administered starting on day
22 and for the duration
of treatment. In some embodiments, a total daily dose of about 1 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered on days 1-7, a total daily dose of about 1 mg of brexpiprazole is
administered on days
8-14, a total daily dose of between about 2 mg is administered on days 14-21,
and a total daily
dose of 2-3 mg is administered starting on day 22 and for the duration of
treatment. In some
embodiments, a total daily dose of about 0.5 mg of brexpiprazole is
administered on days 1-7, a
total daily dose of about 1 mg of brexpiprazole is administered on days 8-14,
a total daily dose of
24
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
about 1-1.5 mg is administered on days 14-21, and a total daily dose of 1-1.5
mg is administered
starting on day 22 and for the duration of treatment.
[0083] In some embodiments, a dose of about 0.25 mg to about 1 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered twice daily on days 1-7, a dose of about 0.5 mg to about 4 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered on days 8-14, and about 1 mg to about 3 mg of brexpiprazole is
administered starting
on day 15. In some embodiments, a dose of about 0.25 mg to about 1 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered twice daily on days 1-7, a dose of about 0.5 mg to about 2 mg of
brexpiprazole is
administered twice daily on days 8-14, about 1 mg to about 3 mg of
brexpiprazole is administered
once daily starting on day 15. In some embodiments, a dose of about 0.25 mg to
about 1 mg of
brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 1-7, a dose of about 0.5 mg
to about 1 mg of
brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 8-14, a dose of about 1 mg
to about 2 mg of
brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 14-21, and dose of about 1
mg to about 1.5 mg
is administered starting on day 22.
[0084] In some embodiments, about 0.5 or 1 mg brexpiprazole is administered
twice daily on days
1-7 days, and then an increased dose of about 1 mg to about 2 mg of
brexpiprazole is administered
twice daily on days 8-14, and then from about 1 mg to about 3 mg brexpiprazole
is administered
once daily starting on day 15. In some embodiments, about 0.5 mg brexpiprazole
is administered
twice daily on days 1-7, about 1 mg of brexpiprazole is administered twice
daily on days 8-14, and
then about 2 mg to about 3 mg is administered once daily starting on day 15.
In some embodiments,
about 1 mg brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 1-7, about 2 mg
of brexpiprazole is
administered once daily on days 8-14, and then about 2 mg to about 3 mg is
administered once
daily starting on day 15.
[0085] In some embodiments, about 0.25 or 0.5 mg brexpiprazole is administered
twice daily on
days 1-7 of brexpiprazole treatment, an increased dose of 0.5 mg or about 1 mg
brexpiprazole is
administered twice daily on days 8-14, an increased dose of 1-1.5 mg
brexpiprazole is administered
twice daily on days 15-21, and a dose from about 1 mg to about 1.5 mg is
administered starting on
day 22. In some embodiments, about 0.25 mg brexpiprazole is administered twice
daily on days
1-7 of brexpiprazole treatment, about 0.5 mg brexpiprazole is administered
twice daily on days 8-
14, about 1 mg brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 15-21, and
about 1-1.5 mg
brexpiprazole is administered once daily starting on day 22. In some
embodiments, about 0.5 mg
brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 1-7 of brexpiprazole
treatment, about 1 mg
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
brexpiprazole is administered twice daily on days 8-14, about 1-1.5 mg
brexpiprazole is
administered twice daily on days 15-21, and about 1-1.5 mg brexpiprazole is
administered once
daily starting on day 22.
[0086] In some embodiments, the patient with MDD in an obese patient who is
not a CYP2D6
poor metabolizer (in other words, the patient is an obese CYP2D6 EM patient),
and the method
comprises: (a) administering either 0.5 or 1 mg brexpiprazole twice daily on
each of the first 7
days of brexpiprazole treatment; (b) administering double the individual
brexpiprazole dose of step
(a) once daily on each of the next 7 days following step (a); and then (c)
administering the
recommended daily dose of brexpiprazole (e.g., 2-3 mg/day) once daily
thereafter. In some
embodiments, the patient with MDD is an obese patient who is a CYP2D6 poor
metabolizer (i.e.,
an obese CYP2D6 PM), and the method comprises: (a) administering 0.5 mg
brexpiprazole twice
daily on each of the first 7 days of brexpiprazole treatment; (b)
administering 1 mg twice daily on
each of the next 7 days following step (a); and then (c) administering half of
the recommended
daily dose of brexpiprazole (1-1.5 mg/day) once daily thereafter. In some
embodiments, the
patient with MDD is an obese patient who is a CYP2D6 poor metabolizer (i.e.,
an obese CYP2D6
PM), and the method comprises (a) administering 0.25 mg brexpiprazole twice
daily on each of
the first 7 days of brexpiprazole treatment; (b) administering 0.5 twice daily
on each of next 7 days
following step (a); (c) administering 1 mg daily twice on each of the next 7
days following step
(b); and then (d) administering half of the recommended daily dose of
brexpiprazole (1-1.5
mg/day) once daily thereafter;
[0087] In some embodiments, an obese CYP2D6 EM or obese CYP2D6 PM patient with
MDD is
treated with a modified dosage regimen as found in Table 4. The dosage found
in Table 4 is the
total daily dose of brexpiprazole. Where indicated, the total daily dose is
divided into two doses.
Table 4. Dosing Regimens for 11/DD
Dosage Days 1-7 Days 8-14 Days 15+ Weight
CYP2D6
Regimen
Status
FDA Label 0.5 mg (QD) 1 mg (QD) 2-3 mg (QD) All EM
FDA Label 1 mg (QD) 2 mg (QD) 2-3 mg (QD) All EM
FDA Label 0.25 mg (QD) 0.5 mg (QD) 1-1.5 mg All PM
(QD)
26
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
Dosage Days 1-7 Days 8-14 Days 15+ Weight
CYP2D6
Regimen
Status
FDA Label 0.5 mg (QD) 1 mg (QD) 1-1.5 mg All PM
(QD)
Modified 0.5 mg (BID) 1 mg (QD) 2-3 mg (QD) Obese EM
Dosing
Regimen A
Modified 1 mg (BID) 2 mg (QD) 2-3 mg (QD) Obese EM
Dosing
Regimen B
Modified 0.25 mg (BID) 0.5 mg (BID) 1 mg (BID to Obese PM
Dosing 21 days)
Regimen C
1-1 5 mg
(QD starting
on day 22)
Modified 0.5 mg (BID) 1 mg (BID) 1-1.5 mg Obese PM
Dosing (QD)
Regimen D
Modified 0.25 mg (BID) 1 mg (QD) 1-1.5 mg Normal- PM
Dosing (QD) weight
Regimen E
Modified 0.5 mg (BID) 1 mg (QD) 1-1.5 mg Normal- PM
Dosing (QD) weight
Regimen F
Patient Populations
[0088] Applicants have found that certain classes of patients, i.e., obese
patients and/or poor
hepatic enzyme metabolizers (e.g., CYP2D6 PM), treated with brexpiprazole
according to the
instructions within the brexpiprazole FDA label (revised 3/2020), have
substantially lower plasma
levels of brexpiprazole when initiating treatment with brexpiprazole, exhibit
a substantially longer
27
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
elimination half-lives (t1/2) of brexpiprazole compared to those exhibited in
"normal" patients,
and have lower Cain values than those exhibited in "normal" patients. "Normal"
patients are
patients who do not exhibit the specific physiological characteristics
described herein such as BMI
of at least about 35 kg/m2, % IBW of at least about 150%, waist size greater
than about 42 inches,
% body fat greater than about 40 %, % android body fat greater than about 40%,
% gynoid body
fat greater than about 40%, total body fat greater than about 40 kg,
optionally in combination with
impaired hepatic metabolizing enzyme function, e.g., intermediate or poor
CYP2D6 metabolizers.
Initiating brexpiprazole treatment according to the methods of the disclosure
raises the plasma
levels of brexpiprazole more quickly to therapeutic levels, and thus increases
the C.A. values of
brexpiprazole more rapidly to the therapeutic levels obtained by normal
patients dosed according
to the regimen described in the FDA-approved labels for brexpiprazole
published prior to the
present invention (e.g., the REXULTI label dated March 2020).
[0089] In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are used to treat a
patient that is obese.
In some embodiments, an obese patient has various characteristics of body fat
status (BFS). The
term "body fat status," "body fat characteristics," "obese status," "obese
characteristics," "body
habitus," or other derivations or variations thereof refer to at least seven
characteristics (BMI,
%IBW, waist size, % body fat, % android fat, % gynoid fat, and total body fat)
as described herein.
In some embodiments, an obese patient can be classified using one or more of
the aforementioned
BFS. In some embodiments, obese patients exhibit one or more of the following
characteristics:
BMI of at least about 35 kg/m2, %IBW of at least about 150%, waist size
greater than about 42
inches, % body fat greater than about 40%, % android body fat greater than
about 40%, % gynoid
body fat greater than about 40%, total body fat greater than about 40 kg.
[0090] In some embodiments, the class of patients treated by the methods of
the present disclosure
have a body mass index (BMI; expressed in units of kg/m' unless otherwise
specified) of at least
about 25, at least about 26, at least about 27, at least about 28, at least
about 29, at least about 30,
at least about 31, at least about 32, at least about 33, at least about 34, at
least about 35, at least
about 36, at least about 37, at least about 38, at least about 39, at least
about 40, at least about 41,
at least about 42, at least about 43, at least about 44, at least about 45, at
least about 46, at least
about 47, at least about 48, at least about 49, at least about 50, at least
about 51, at least about 52,
at least about 53, at least about 54, at least about 55, at least about 56, at
least about 57, at least
about 58, at least about 59, at least about 60, at least about 61, at least
about 62, at least about 63,
28
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
at least about 64, at least about 65, at least about 66, at least about 67, at
least about 68, at least
about 69, at least about 70, at least about 71, at least about 72, at least
about 73, at least about 74,
at least about 75, at least about 76, at least about 77, at least about 78, at
least about 79, at least
about 80, at least about 81, at least about 82, at least about 83, at least
about 84, at least about 85,
at least about 86, at least about 87, at least about 88, at least about 89, at
least about 90, at least
about 91, at least about 92, at least about 93, at least about 94, at least
about 95, at least about 96,
at least about 97, at least about 98, at least about 99, at least about 100,
at least about 101, at least
about 102, at least about 103, at least about 104, at least about 105, at
least about 106, at least about
107, at least about 108, at least about 109, at least about 110, at least
about 111, at least about 112,
at least about 113, at least about 114, at least about 115, at least about
116, at least about 117, at
least about 118, at least about 119, at least about 120, at least about 121,
at least about 122, at least
about 123, at least about 124, at least about 125, at least about 126, at
least about 127, at least about
128, at least about 129, at least about 130, at least about 131, at least
about 132, at least about 133,
at least about 134, at least about 135, at least about 136, at least about
137, at least about 138, at
least about 139, at least about 140, at least about 141, at least about 142,
at least about 143, at least
about 144, at least about 145, at least about 146, at least about 147, at
least about 148, at least about
149, at least about 150, at least about 151, at least about 152, at least
about 153, at least about 154,
at least about 155, at least about 156, at least about 157, at least about
158, at least about 159, at
least about 160, at least about 161, at least about 162, at least about 163,
at least about 164, at least
about 165, at least about 166, at least about 167, at least about 168, at
least about 169, at least about
170, at least about 171, at least about 172, at least about 173, at least
about 174, at least about 175,
at least about 176, at least about 177, at least about 178, at least about
179, at least about 180, at
least about 181, at least about 182, at least about 183, at least about 184,
at least about 185, at least
about 186, at least about 187, at least about 188, at least about 189, at
least about 190, at least about
191, at least about 192, at least about 193, at least about 194, at least
about 195, at least about 195,
at least about 196, at least about 197, at least about 198, at least about
199, at least about 200, at
least about 201, at least about 202, at least about 203, at least about 204,
at least about 205, at least
about 206, at least about 207, at least about 208, at least about 209, or at
least about 210, inclusive
of all ranges and subranges therebetween, and any BlVII described herein. In
one embodiment, the
patient has a body mass index (B1VII) of at least about 35. In another
embodiment, the patient has
29
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
a body mass index (B1V11) of at least about 40. In another embodiment, the
patient has a body mass
index (B1VII) of at least 50.
[0091] In some embodiments, a patient treated according to the methods of the
present invention
has a BlVIE of at least about 25 to at least about 29.9, at least about 25.5
to at least about 29, at least
about 26 to at least about 28.5, at least about 26.5 to at least about 28, or
at least about 27 to at
least about 27.5, inclusive of all ranges and subranges therebetween, and can
be termed overweight
or pre-obese. In some embodiments, a patient with a BlVII of at least about 30
to at least about
34.9, at least about 30.5 to at least about 34, at least about 31 to at least
about 33.5, at least about
31.5 to at least about 33, or at least about 32 to at least about 32.5,
inclusive of all ranges and
subranges therebetween can be considered obese. In some embodiments, a patient
with a BlVII of
at least about 35 to at least about 39.9, at least about 35.5 to at least
about 39, at least about 36 to
at least about 38.5, at least about 36.5 to at least about 38, or at least
about 37 to at least about 37.5,
inclusive of all ranges and subranges therebetween, and any BME described
herein, can be
considered obese. In other embodiments, a patient treated by the methods of
the present disclosure
has a BMI of at least about 35 or more, 40 or more, 50 or more, 60 or more, 70
or more, 80 or
more, 90 or more, 100 or more, 110 or more, 120 or more, 130 or more, 140 or
more, 150 or more,
160 or more, 170 or more, 180 or more, 190 or more, 200 or more, or 210 or
more, inclusive of all
ranges and subranges therebetween.
[0092] In some embodiments, the patient treated according to the methods of
the present
disclosure is a child or an adolescent with a BMI of at least about the 85th
percentile to at least
about 95th percentile, at least about the 86th percentile to at least about
94th percentile, at least
about the 87th percentile to at least about 93th percentile, at least about
the 88th percentile to at
least about 92th percentile, at least about the 89th percentile to at least
about 90th percentile,
inclusive of all ranges and subranges therebetween, can be considered
overweight or pre-obese.
In some embodiments, the patient is a patient with a BMI of at least about the
95th percentile, at
least about 96th percentile, at least about the 97th percentile, at least
about 98th percentile, at least
about 99th percentile, or at least about 100th percentile, inclusive of all
ranges and subranges
therebetween, and any BlVIE percentile described herein, and can be considered
obese. In one
embodiment, the patient is about 5 to about 19 years old or about 7 to about
18 years old.
[0093] In some embodiments, the patient treated according to the methods of
the present
disclosure is a female patient in the first trimester through third trimester
of a pregnancy and has a
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
BMI of at least 25 to at least about 29.9, at least about 25.5 to at least
about 29, at least about 26
to at least about 28.5, at least about 26.5 to at least about 28, or at least
about 27 to at least about
27.5, inclusive of all ranges and subranges therebetween, and can be
considered overweight or pre-
obese. In some embodiments, the patient is a female patient in the first
trimester through third
trimester of a pregnancy and has a BMI of at least about 30 to at least about
34.9, at least about
30.5 to at least about 34, at least about 31 to at least about 33.5, at least
about 31.5 to at least about
33, or at least about 32 to at least about 32.5, inclusive of all ranges and
subranges therebetween,
and can be considered obese. In some embodiments, the patent treated according
to the methods
of the present invention is a female patient in the first trimester through
third trimester of a
pregnancy and has a BlVII of at least about 35 to at least about 39.9, at
least about 35.5 to at least
about 39, at least about 36 to at least about 38.5, at least about 36.5 to at
least about 38, at least
about 37 to at least about 37.5, inclusive of all ranges and subranges
therebetween, and can be
considered severely obese.
[0094] In some embodiments, methods of calculating BMI may include, but are
not limited to
body weight in kilogram / (height in meters)2, body weight in pounds / (height
in inches)2] x 703,
and the like.
[0095] In some embodiments, the patient treated according to the methods of
the present
disclosure can alternatively be described as having a % ideal body weight
(%IBW) of at least about
110%, at least about 111%, at least about 112%, at least about 113%, at least
about 114%, at least
about 115%, at least about 116%, at least about 117%, at least about 118%, at
least about 119%,
at least about 120%, at least about 121%, at least about 122%, at least about
123%, at least about
124%, at least about 125%, at least about 126%, at least about 127%, at least
about 128%, at least
about 129%, at least about 130%, at least about 131%, at least about 132%, at
least about 133%,
at least about 134%, at least about 135%, at least about 136%, at least about
137%, at least about
138%, at least about 139%, at least about 140%, at least about 141%, at least
about 142%, at least
about 143%, at least about 144%, at least about 145%, at least about 146%, at
least about 147%,
at least about 148%, at least about 149%, at least about 150%, at least about
151%, at least about
152%, at least about 153%, at least about 154%, at least about 155%, at least
about 156%, at least
about 157%, at least about 158%, at least about 159%, at least about 160%, at
least about 161%,
at least about 162%, at least about 163%, at least about 164%, at least about
165%, at least about
166%, at least about 167%, at least about 168%, at least about 169%, at least
about 170%, at least
31
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
about 171%, at least about 172%, at least about 173%, at least about 174%, at
least about 175%,
at least about 176%, at least about 177%, at least about 178%, at least about
179%, at least about
180%, at least about 181%, at least about 182%, at least about 183%, at least
about 184%, at least
about 185%, at least about 186%, at least about 187%, at least about 188%, at
least about 189%,
at least about 190%, at least about 191%, at least about 192%, at least about
193%, at least about
194%, at least about 195%, at least about 196%, at least about 197%, at least
about 198%, at least
about 199%, at least about 200%, at least about 201%, at least about 202%, at
least about 203%,
at least about 204%, at least about 205%, at least about 206%, at least about
207%, at least about
208%, at least about 209%, at least about 210%, at least about 211%, at least
about 212%, at least
about 213%, at least about 214%, at least about 215%, at least about 216%, at
least about 217%,
at least about 218%, at least about 219%, at least about 220%, at least about
221%, at least about
222%, at least about 223%, at least about 224%, at least about 225%, at least
about 226%, at least
about 227%, at least about 228%, at least about 229%, at least about 230%, at
least about 231%,
at least about 232%, at least about 233%, at least about 234%, at least about
235%, at least about
236%, at least about 237%, at least about 238%, at least about 239%, at least
about 240%, at least
about 241%, at least about 242%, at least about 243%, at least about 244%, at
least about 245%,
at least about 246%, at least about 247%, at least about 248%, at least about
249%, at least about
250%, at least about 251%, at least about 252%, at least about 253%, at least
about 254%, at least
about 255%, at least about 256%, at least about 257%, at least about 258%, at
least about 259%,
at least about 260%, at least about 261%, at least about 262%, at least about
263%, at least about
264%, at least about 265%, at least about 266%, at least about 267%, at least
about 268%, at least
about 269%, at least about 270%, at least about 271%, at least about 272%, at
least about 273%,
at least about 274%, at least about 275%, at least about 276%, at least about
277%, at least about
278%, at least about 279%, or at least about 280%, inclusive of all ranges and
subranges
therebetween, and any % ideal body weight described herein. In one embodiment,
the patient has
% ideal body weight (IBW) of at least about 150%. In one embodiment, the
patient has % ideal
body weight (IBW) of at least about 250%. In other embodiment, the patient has
% IBW of at
least 150% and can be considered obese.
[0096] In some embodiments, the patient treated according to the present
disclosure can
alternatively be described as having a waist size or waist circumference
greater than about 32,
greater than about 33, greater than about 34, greater than about 35 inches,
greater than about 36,
32
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
greater than about 37, greater than about 38, greater than about 39, greater
than about 40, greater
than about 41, greater than about 42, greater than about 43, greater than
about 44, greater than
about 45, greater than about 46, greater than about 47, greater than about 48,
greater than about
49, greater than about 50, greater than about 51, greater than about 52,
greater than about 53,
greater than about 54, greater than about 55, greater than about 56, greater
than about 57, greater
than about 58, greater than about 59, greater than about 60 inches, greater
than about 61 inches,
greater than about 62 inches, greater than about 63 inches, greater than about
64 inches, greater
than about 65 inches, inclusive of all ranges and subranges therebetween, and
any waist size or
circumference described herein. In one embodiment, a patient having a waist
size or waist
circumference of about 42 inches can be considered obese. In another
embodiment, the patient
has waist size or waist circumference greater than about 48 inches. In other
embodiment, the
patient has waist or waist circumference of at least 42 inches.
[0097] In some embodiments, a patient treated according to the methods of the
present disclosure
has a % body fat greater than about 20%, greater than about 21%, greater than
about 22%, greater
than about 23%, greater than about 24%, greater than about 25%, greater than
about 26%, greater
than about 27%, greater than about 28%, greater than about 29%, greater than
about 30%, greater
than about 31%, greater than about 32%, greater than about 33%, greater than
about 34%, greater
than about 35%, greater than about 36%, greater than about 37%, greater than
about 38%, greater
than about 39%, greater than about 40%, greater than about 41%, greater than
about 42%, greater
than about 43%, greater than about 44%, greater than about 45%, greater than
about 46%, greater
than about 47%, greater than about 48%, greater than about 49%, or greater
than about 50%,
inclusive of all ranges and subranges therebetween, and any % body fat
described herein. In one
embodiment, the patient has a % body fat greater than about 40%. In one
embodiment, the patient
has a % body fat of at least about 50%. In another embodiment, a patient
having a % body fat
greater than about 40% can be considered obese. In some embodiments, methods
of calculating
% body fat can include, but are not limited to total body fat expressed as a
percentage of total body
weight. Other standards for obesity can be used. For example, the American
Council on Exercise
suggests that an "average" percentage of body fat for women is about 25-31%,
and for men, about
18-24%, and for obese women, about 32% and higher, and obese men, about 25%
and higher.
[0098] In some embodiments, a patient treated according to the methods of the
present disclosure
has a % android body fat greater than about 30%, greater than about 31%,
greater than about 32%,
33
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
greater than about 33%, greater than about 34%, greater than about 35%,
greater than about 36%,
greater than about 37%, greater than about 38%, greater than about 39%,
greater than about 40%,
greater than about 41%, greater than about 42%, greater than about 43%,
greater than about 44%,
greater than about 45%, greater than about 46%, greater than about 47%,
greater than about 48%,
greater than about 49%, greater than about 50%, greater than about 51%,
greater than about 52%,
greater than about 53%, greater than about 54%, greater than about 55%,
greater than about 56%,
greater than about 57%, greater than about 58%, greater than about 59%,
greater than about 60%,
greater than about 61%, greater than about 62%, greater than about 63%,
greater than about 64%,
greater than about 65%, greater than about 66%, greater than about 67%,
greater than about 68%,
greater than about 69%, greater than about 70%, greater than about 71%,
greater than about 72%,
greater than about 73%, greater than about 74%, greater than about 75%,
greater than about 76%,
greater than about 77%, greater than about 78%, greater than about 79%, or
greater than about
80%, inclusive of all ranges and subranges therebetween, and any % android
body fat described
herein. In one embodiment, a patient having a % android body fat greater than
about 40% can be
considered obese. In one embodiment, a patient having a % android body fat
greater than about
50% can be considered obese.
[0099] In some embodiments, a patient treated according to the methods of the
present disclosure
has a % android body fat of at least about 30%, at least about 31%, at least
about 32%, at least
about 33%, at least about 34%, at least about 35%, at least about 36%, at
least about 37%, at least
about 38%, at least about 39%, at least about 40%, at least about 41%, at
least about 42%, at least
about 43%, at least about 44%, at least about 45%, at least about 46%, at
least about 47%, at least
about 48%, at least about 49%, at least about 50%, at least about 51%, at
least about 52%, at least
about 53%, at least about 54%, at least about 55%, at least about 56%, at
least about 57%, at least
about 58%, at least about 59%, at least about 60%, at least about 61%, at
least about 62%, at least
about 63%, at least about 64%, at least about 65%, at least about 66%, at
least about 67%, at least
about 68%, at least about 69%, at least about 70%, at least about 71%, at
least about 72%, at least
about 73%, at least about 74%, at least about 75%, at least about 76%, at
least about 77%, at least
about 78%, at least about 79%, or at least about 80%, inclusive of all ranges
and subranges
therebetween, and % android body fat described herein. In one embodiment, the
patient has %
android body fat of at least about 50%.
34
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
[00100] In some embodiments, a patient treated according to the
methods of the present
disclosure has a % gynoid body fat greater than about 30%, greater than about
31%, greater than
about 32%, greater than about 33%, greater than about 34%, greater than about
35%, greater than
about 36%, greater than about 37%, greater than about 38%, greater than about
39%, greater than
about 40%, greater than about 41%, greater than about 42%, greater than about
43%, greater than
about 44%, greater than about 45%, greater than about 46%, greater than about
47%, greater than
about 48%, greater than about 49%, greater than about 50%, greater than about
51%, greater than
about 52%, greater than about 53%, greater than about 54%, greater than about
55%, greater than
about 56%, greater than about 57%, greater than about 58%, greater than about
59%, greater than
about 60%, greater than about 61%, greater than about 62%, greater than about
63%, greater than
about 64%, greater than about 65%, greater than about 66%, greater than about
67%, greater than
about 68%, greater than about 69%, greater than about 70%, greater than about
71%, greater than
about 72%, greater than about 73%, greater than about 74%, greater than about
75%, greater than
about 76%, greater than about 77%, greater than about 78%, greater than about
79%, or greater
than about 80%, inclusive of all ranges and subranges therebetween, and any %
gynoid body fat
described herein. In one embodiment, a patient having a % gynoid body fat
greater than about
40% can be considered obese. In one embodiment, a patient having a % gynoid
body fat greater
than about 50% can be considered obese.
[00101] In some embodiments, a patient treated according to the
methods of the present
disclosure has a total body fat content greater than about 30 kg, greater than
about 31 kg, greater
than about 32 kg, greater than about 33 kg, greater than about 34 kg, greater
than about 35 kg,
greater than about 36 kg, greater than about 37 kg, greater than about 38 kg,
greater than about 39
kg, greater than about 40 kg, greater than about 41 kg, greater than about 42
kg, greater than about
43 kg, greater than about 44 kg, greater than about 45 kg, greater than about
46 kg, greater than
about 47 kg, greater than about 48 kg, greater than about 49 kg, greater than
about 50 kg, greater
than about 51 kg, greater than about 52 kg, greater than about 53 kg, greater
than about 54 kg,
greater than about 55 kg, greater than about 56 kg, greater than about 57 kg,
greater than about 58
kg, greater than about 59 kg, greater than about 60 kg, greater than about 61
kg, greater than about
62 kg, greater than about 63 kg, greater than about 64 kg, greater than about
65 kg, greater than
about 66 kg, greater than about 67 kg, greater than about 68 kg, greater than
about 69 kg, greater
than about 70 kg, greater than about 71 kg, greater than about 72 kg, greater
than about 73 kg,
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
greater than about 74 kg, greater than about 75 kg, greater than about 76 kg,
greater than about 77
kg, greater than about 78 kg, greater than about 79 kg, greater than about 80
kg, greater than about
81 kg, greater than about 82 kg, greater than about 83 kg, greater than about
84 kg, greater than
about 85 kg, greater than about 86 kg, greater than about 87 kg, greater than
about 88 kg, greater
than about 89 kg, greater than about 90 kg, greater than about 91 kg, greater
than about 92 kg,
greater than about 93 kg, greater than about 94 kg, greater than about 95 kg,
greater than about 96
kg, greater than about 97kg, greater than about 98 kg, greater than about 99
kg, greater than about
100 kg, at least 101 kg, at least 102 kg, at least 103 kg, at least 104 kg, at
least 105 kg, at least 106
kg, at least 107 kg, at least 108 kg, at least 109 kg, or at least 110 kg,
inclusive of all ranges and
subranges therebetween, and any total body fat described herein. In one
embodiment, a patient
having total body fat greater than about 40 kg can be considered obese. In one
embodiment, a
patient having total body fat greater than about 50 kg can be considered
obese.
[00102] In other embodiments, obesity status of patients treated
with the methods of the
present disclosure can be measured by waist-to-hip ratio. In other
embodiments, obesity status of
patients can be measured by skinfold thickness. In other embodiments, obesity
status of patients
can be measured by bioelectric impedance. In other embodiments, obesity status
of patients can
be measured by underwater weighing or densitometry. In other embodiments, the
obesity status
of patients can be measured by air-displacement plethysmography. In other
embodiments, obesity
status of patients can be measured by dilution method or hydrometry. In other
embodiments, the
obesity status of patients can be measured by dual energy X-ray
absorptiometry. In other
embodiments, the obesity status of patients can be measured by computerized
tomography and
magnetic resonance imaging. In some embodiments, the obesity status can be
defined by, but is
not limited to adopting the clinical standards, conventional standards, and/or
the standards
published by the World Health Organization and Center of Disease Control (both
of which are
herein incorporated by reference in their entireties for all purposes) when
using the methods
described herein. For example, the WHO defines an obese person as a person
with a BMI of 30 or
more, an overweight person is one with a BMI equal to or more than 25 (to less
than 30). Similarly,
the CDC defines normal as a BMI of 18.5 to less than 25, 25.0 to less than 30
as overweight, and
30.0 or higher as obese. The CDC further subdivides obesity into 3 classes:
Class 1, a BMI of 30
to less than 35; Class 2, a BlVII of 35 to less than 40; and Class 3, as a BMI
of 40 or higher. The
CDC sometimes refers to Class 3 obesity as "extreme" or "severe" obesity.
36
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
[00103] As used herein, the term "about" refers to an amount
somewhat more or less than
the stated parameter value, for example plus or minus five or ten percent of
the object that "about"
modifies, or as one of skill in the art would recognize from the context
(e.g., approximately 50%
of the interval between values). The term "about- also includes the value
referenced. For example,
a BMI of about 40 includes 40, as well as values somewhat below or above 40.
[00104] In some embodiments, the patient treated by the methods
of the present disclosure
can be characterized by two or more of the physiological characteristics
described herein. For
example the patient can have a BMI of at least about 35 and can have a % IBW
of at least 150%.
In some embodiments, the patient can have a BMI of at least about 35 and can
have a waist size
greater than about 42 inches. In some embodiments, the patient can have a BMI
of at least about
35 and can have a % body fat greater than about 40%. In some embodiments, the
patient can have
a BMI of at least about 35 and can have a % android body fat greater than
about 40%. In some
embodiments, the patient can have a BMI of at least about 35 and can have a %
gynoid body fat
greater than about 40%. In some embodiments, the patient can have a BMI of at
least about 35
and can have total body fat greater than about 40 kg. In various other
embodiments, the patient
can have any combination of two or more of any of the specific physiological
parameters described
herein.
[00105] In some embodiments, the patient can have three or more
of the physiological
parameters described herein, for example a BMI of at least about 35, a % IBW
of at least 150%,
and waist size greater than about 42 inches. In some embodiments, the patient
can have a BMI of
at least about 35, a % IBW of at least 150%, and a % body fat greater than
about 40%. In some
embodiments, the patient can have a BMI of at least about 35, a % IBW of at
least 150%, and a %
android body fat greater than about 40%. In some embodiments, the patient can
have a BMI of at
least about 35, a % IBW of at least 150%, and a % gynoid body fat greater than
about 40%. In
some embodiments, the patient can have a BMI of at least about 35, a % IBW of
at least 150%,
and total body fat greater than about 40 kg. In various other embodiments, the
patient can have
any combination of three or more of any of the specific physiological
parameters described herein.
[00106] In some embodiments, the patient can have four or more of
the physiological
parameters described herein, for example the patient can have a BMI of at
least about 35, a % IBW
of at least 150%, waist size greater than about 42 inches, and a % body fat
greater than about 40%.
In some embodiments, the patient can have a BMI of at least about 35, a % IBW
of at least 150%,
37
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
waist size greater than about 42 inches, and a % android body fat greater than
about 40%. In some
embodiments, the patient can have a BMI of at least about 35, a % IBW of at
least 150%, waist
size greater than about 42 inches, and a % gynoid body fat greater than about
40%. In some
embodiments, the patient can have a BMI of at least about 35, a % IBW of at
least 150%, a waist
size greater than about 42 inches, and total body fat greater than about 43
kg. In some
embodiments, the patient can have a BMI of at least about 35, a % IBW of at
least 150%, a waist
size greater than about 42 inches, a % body fat greater than about 40%, and a
% android body fat
greater than about 40%. In some embodiments, the patient can have a BMI of at
least about 35, a
% IBW of at least 150%, a waist size greater than about 42 inches, a % body
fat greater than about
40%, and a % gynoid body fat greater than about 40%. In some embodiments, the
patient can have
a BMI of at least about 35, a % IBW of at least 150%, a waist size greater
than about 42 inches, a
% body fat greater than about 40%, and total body fat greater than about 40
kg. In some
embodiments, the patient can have a BMI of at least about 35, a % IBW of at
least 150%, a waist
size greater than about 42 inches, a % body fat greater than about 40%, a %
android body fat
greater than about 40%, in % gynoid body fat greater than about 40%, and total
body fat greater
than about 40 kg. In one embodiment, the patient who has a BMI of at least
about 35, in % IBW
of at least 150%, a waist size greater than about 42 inches, and a % body fat
greater than about
40%, a % android body fat greater than about 40%, a % gynoid body fat greater
than about 40%,
and total body fat greater than about 40 kg. In various other embodiments, the
patient can have
any combination of any or all of the specific physiological parameters
described herein.
[00107] In some embodiments, the patient can have a waist size
greater than about 42
inches, a % body fat greater than about 40%, and a % android body fat greater
than about 40%. In
some embodiments, the patient can have a waist size greater than about 42
inches, a % body fat
greater than about 40%, and a % gynoid body fat greater than about 40%. In
some embodiments,
the patient can have a waist size greater than about 42 inches, a % body fat
greater than about 40%,
and total body fat greater than about 40 kg.
[00108] In some embodiments, the patient can have a % body fat
greater than about 40%, a
% android body fat greater than about 40%, and a % gynoid body fat greater
than about 40%. In
some embodiments, the patient can have a % body fat greater than about 40%, a
% android body
fat greater than about 40%, and total body fat greater than about 40 kg. In
some embodiments, the
patient can have a % body fat greater than about 40%, a % gynoid body fat
greater than about 40%,
38
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
and total body fat greater than about 40 kg. In some embodiments, a % android
body fat greater
than about 40%, and a % gynoid body fat greater than about 40%, and total body
fat greater than
about 43 kg. In some embodiments, the patient can have any combinations of
obesity
characteristics described herein.
[00109] In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are
used to treat a normal-
weight patient. As used herein, a normal-weight patient has a BMI between
about 18 kg/m2 and
25 kg/m2. In some embodiments, normal-weight patients do not exhibit one or
more of the
following characteristics: BMI of at least about 35 kg/m2, %IBW of at least
about 150%, waist
size greater than about 42 inches, % body fat greater than about 40%, %
android body fat greater
than about 40%, % gynoid body fat greater than about 40%, total body fat
greater than about 40
kg.
[00110] In some embodiments, the patient treated by the methods
of the present disclosure
can be an adult human. In other embodiments, the patient can be a male human.
In still other
embodiments, the patient can be a female human.
[00111] In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are
utilized to treat patients
with various hepatic enzyme statuses. Brexpiprazole is metabolized primarily
through oxidation
via P450 isozymes such as CYP2D6. Alternatively, brexpiprazole is metabolized
through
oxidation via P450 isozymes such as CYP3A4/5, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2A6, CYP2C8,
or
CYP2B6. Each individual may have different activity levels of the P450
isozymes to metabolize
brexpiprazole. Categorizations of metabolizers may include, but are not
limited to allelic
heterogeneity in the P450 isozyme genes. For instance, the CYP2D6 gene can
have allelic
heterogeneity and its functionality (i.e., associated enzyme activity) can be
categorized as full
functionality, decreased functionality, and non-functionality. Further, CYP2D6
genotype can be
categorized based on its metabolic status by using the -gene dose" method and
can have the
following scoring scale: (1) alleles with full functionality: a value of 1,
(2) alleles with reduced
functionality: a value of 0.5, and (3) alleles with no functionality: a value
of 0. Alternatively, in
some embodiments, the CYP2D6 genotype can be tested by using targeted variant
analysis. In
some embodiments, the CYP2D6 genotype can be tested by using sequence analysis
of select
exons.
[00112] The "normal" or typical patient has 2 normally
functioning CYP2D6 alleles, and
has full "normal- CYP2D6 enzyme functionality or activity and is referred to
as an "extensive
39
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
CYP2D6 metabolizer." Patients with one non-functional CYP2D6 allele and one
normally
functioning allele have reduced CYP2D6 enzyme function and are termed
"intermediate CYP2D6
metabolizers." Patients with 2 non-functional CYP2D6 alleles have little or no
CYP2D6
functionality or activity and are termed "poor CYP2D6 metabolizers- or
alternatively "CYP2D6
poor metabolizers (PM)."
[00113] As used herein, the term "extensive CYP2D6 metabolizer"
refers to a person who
may have a gene dose score for the CYP2D6 allele of 1.5 or 2 and may have
superior capabilities
for metabolizing brexpiprazole compared to his or her counterpart who is
assigned as "intermediate
CYP2D6 metabolizer" or "poor CYP2D6 metabolizer." As used herein, the term
"intermediate
CYP2D6 metabolizer" refers to a person who may have a gene dose score for the
CYP2D6 allele
of 0.5 to 1 and may have superior capabilities for metabolizing brexpiprazole
compared to his or
her counterpart who is assigned as -poor CYP2D6 metabolizer." As used herein,
the term -poor
CYP2D6 metabolizer" refers to a person who may have a gene dose score for the
CYP2D6 allele
of 0 and may have the least capabilities for metabolizing brexpiprazole
compared to his or her
counterpart who is assigned as an "intermediate metabolizer" or an "extensive
metabolizer." In
some embodiments, other suitable or conventional standards of categorizing
CYP2D6
metabolizers may be used.
[00114] In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are
used to treat a CYP2D6
poor metabolizer. In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are used
to treat a CYP2D6
extensive metabolizer. In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are
used to treat a
CYP2D6 intermediate metabolizer.
[00115] In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are
used to treat a patient that
is an intermediate CYP2D6 metabolizer and has at least one of the obesity
characteristics described
herein. In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are used to treat a
patient that is a
poor CYP2D6 metabolizer and has at least one of the obesity characteristics
described herein. In
some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are used to treat a patient
that is an extensive
CYP2D6 metabolizer and has at least one of the obesity characteristics
described herein.
[00116] In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are
utilized to treat a patient
that is a normal weight and is an intermediate CYP2D6 metabolizer. In some
embodiments, the
methods of the disclosure are utilized to treat a patient that is a normal
weight and is a poor
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
CYP2D6 metabolizer. In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are
utilized to treat a
patient that is a normal weight and is an extensive CYP2D6 metabolizer.
[00117] In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are
utilized to treat a patient
that has a BMI greater than 25 kg/m2 but less than 35 kg/m2 and is an
intermediate CYP2D6
metabolizer. In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are utilized
to treat a patient that
has a BMI greater than 25 kg/m2 but less than 35 kg/m2 and is a poor CYP2D6
metabolizer. In
some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are utilized to treat a
patient that has a BMI
greater than 25 kg/m2 but less than 35 kg/m2 and is an extensive CYP2D6
metabolizer.
[00118] In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are
used to treat a patient with
a disease selected from major depressive disorder, schizophrenia, post-
traumatic stress disorder,
bipolar disorder, bipolar depression, acute mania, agitation associated with
Alzheimer's disease,
borderline personality disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder,
autism, conduct disorder,
oppositional defiant disorder, and combinations thereof.
[00119] In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure are
used to treat a patient with
major depressive disorder. In some embodiments, the methods of the disclosure
are used as an
adjunctive therapy to treat a patient with major depressive disorder. In some
embodiments, the
methods of the disclosure are used to treat a patient with schizophrenia.
[00120] As used herein, "normal," "normal-weight," "reference,"
or other derivations or
variations thereof refers to a non-obese state in a person who can have at
least one of the following
characteristics: BMI less than about 35 kg/m2, % IBW less than about 150%,
waist size less than
about 42, % body fat less than about 40%, % android body fat less than about
40%, % gynoid body
fat less than about 40%, and total body fat less than about 40 kg. Unless
otherwise modified
normal metabolizer" also means an extensive CYP2D6 metabolizer.
Pharmacokinetics
[00121] In some embodiments, after administering between about
0.5 mg and about 8 mg
(e.g., 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1.0 mg, 2.0 mg, 2.5 mg, 3.0 mg, 3.5 mg, 4.0 mg, 5.0
mg, 6.0 mg, 7.5 mg,
8 mg) of brexpiprazole, the obese CYP2D6 PM or obese CYP2D6 EM patient
treating according
to the modified dosing regimens disclosed herein have a minimum observed
plasma drug
concentration (Gain) between about 30 ng/mL and about 120 ng/mL. In some
embodiments, the
Gain is between about 30 ng/mL and about 60 ng/mL nine days after
administration of the day 1
dose of brexpiprazole. In some embodiments, the Crnin is between about 60
ng/mL and about 95
41
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
ng/mL 16 days after administration of the day 1 dose of brexpiprazole. In some
embodiments, the
Cnnn is at least about 40.4 ng/mL. In some embodiments, the Cram is at least
about 90.9 ng/mL. In
some embodiments, the Cnun is at least about 10.1 ng/mL. In some embodiments,
the Cmin is at
least about 40.4 ng/mL on day 14 of brexpiprazole administration. In some
embodiments, the Cmin
is at least about 90.9 ng/mL on day 14 of brexpiprazole administration. In
some embodiments, the
Calm is at least about 10.1 ng/mL on day 14 of brexpiprazole administration.
In some embodiments,
the Cnun is about 30 ng/mL, about 35 ng/mL, about 40 ng/mL, about 45 ng/mL,
about 50 ng/mL,
about 55 ng/mL, about 60 ng/mL, about 65 mg/mL, about 70 ng/mL, about 75
ng/mL, about 80
ng/mL, about 85 ng/mL, about 90 ng/mL, about 95 ng/mL, about 100 ng/mL, about
105 ng/mL,
about 110 ng/mL, about 115 ng/mL, about 120 ng/mL, about 125 ng/mL, or about
130 ng/mL,
including all ranges and values in between. In some embodiments, the Calm is
between 80 % and
125 % of any of the aforementioned values or ranges between the aforementioned
values.
[00122] In some embodiments, the time to reach Cmin is reduced
after dosage of
brexpiprazole according to a modified dosage regimen described herein as
compared to dosage
according to the brexpiprazole (REXULTIS) FDA label dated 3/2020. Example 2
shows that the
time to reach therapeutic concentrations of brexpiprazole using the modified
dosage regimen is
reduced in the patient populations described herein as compared to the time to
reach Cmin using
the brexpiprazole (REXULTIe) FDA Label. In some embodiments, the time to reach
Cmin
according to a modified dosage regimen is reduced by between about 1 day and
about 35 days, for
example, at least about 1 day, 2 days, 3 days, 4 days, 5 days, 6 days, 7 days,
8 days, 9 days, 10
days, 11 days, 12 days, 13 days, 14 days, 15 days, 16 days, 17 days, 18 days,
19 days, 2 days, 21
days, 22 days, 23 days, 24 days, 25 days, 26 days, 27 days, 28 days, 29 days,
30 days, 31 days, 32
days, 33 days, 34 days, or at least about 35 days, including all values and
ranges there between as
compared to dosage according to the brexpiprazole (REXULTIR) FDA label.
[00123] In some embodiments, after administering between about
0.5 mg and about 8 mg
(e.g., 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1.0 mg, 2.0 mg, 2.5 mg, 3.0 mg, 3.5 mg, 4.0 mg, 5.0
mg, 6.0 mg, 7.5 mg,
8 mg) of brexpiprazole, the obese CYP2D6 PM patient or obese CYP2D6 EM patient
has a
maximum observed plasma drug concentration (Cmax) between about 50 ng/mL and
about 150
ng/mL. In some embodiments, the Cmax is between about 50 ng/mL and about 100
ng/mL nine
days after administration of the day 1 dose of brexpiprazole. In some
embodiments, the Cmax is
between about 80 ng/mL and about 150 ng/mL 16 days after administration of the
day 1 dose of
42
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
brexpiprazole. In some embodiments, the Cmax is about 50 ng/mL, about 55
ng/mL, about 60
ng/mL, about 65 mg/mL, about 70 ng/mL, about 75 ng/mL, about 80 ng/mL, about
85 ng/mL,
about 90 ng/mL, about 95 ng/mL, about 100 ng/mL, about 105 ng/mL, about 110
ng/mL, about
115 ng/mL, about 120 ng/mL, about 125 ng/mL, about 130 ng/mL, about 135 ng/mL,
about 140
ng/mL, about 145 ng/mL, or about 150 ng/mL including all ranges and values in
between. In some
embodiments, the Cinax is between 80 % and 125 % of any of the aforementioned
values or ranges
between the aforementioned values.
[00124] In some embodiments, after administering between about
0.25 mg and about 8 mg
(e.g., 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1.0 mg, 2.0 mg, 2.5 mg, 3.0 mg, 3.5 mg, 4.0 mg, 5.0
mg, 6.0 mg, 7.5 mg,
8 mg,) of brexpiprazole, the obese CYP2D6 PM or obese CYP2D6 EM patient has an
area under
the concentration time curve from day 0 to day 9 (AUC9) between 1000 ng*hr/ mL
and 2000
ng*hr/ mL. In some embodiments, after administering between about 0.5 mg and
about 10 mg, the
patient has an AUC9 of between 1500 ng*hr/ mL and 2000 ng*hr/ mL. In some
embodiments, the
AUC9 is about 1000 ng*hr/ mL, about 1100 ng*hr/ mL, about 1200 ng*hr/ mL,
about 1300 ng*hr/
mL, about 1400 ng*hr/ mL, about 1500 ng*hr/ mL, about 1600 ng*hr/ mL, about
1700 ng*hr/ mL,
about 1800 ng*hr/ mL, about 1900 ng*hr/ mL, or about 2000 ng*hr/ mL, including
all ranges and
values in between. In some embodiments, the AUC9 is between 80 % and 125 % of
the
aforementioned values.
[00125] In some embodiments, after administering between about
0.25 mg and about 8 mg
(e.g., 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1.0 mg, 2.0 mg, 2.5 mg, 3.0 mg, 3.5 mg, 4.0 mg, 5.0
mg, 6.0 mg, 7.5 mg,
8 mg) of brexpiprazole, the obese CYP2D6 PM patient or obese CYP2D6 EM patient
patient has
an area under the concentration time curve from day 0 to day 16 (AUC16)
between 1800 ng*hr/
mL and 2600 ng*hr/ mL. In some embodiments, after administering between about
0.5 mg and
about 10 mg, the patient has an AUC16 between 2000 ng*hr/ mL and 2600 ng*hr/
mL. In some
embodiments, after administering between about 0.5 mg and about 10 mg, the
patient has an
AUC16 between 2000 ng*hr/ mL and 2300 ng*hr/ mL. In some embodiments, the
AUC16 is about
about 1800 ng*hr/ mL, about 1900 ng*hr/ mL, about 2000 ng*hr/ mL, about 2100
ng*hr/ mL,
about 2200 ng*hr/ mL, about 2300 ng*hr/ mL, about 2400 ng*hr/ mL, about 2500
ng*hr/ mL, or
about 2600 ng*hr/ mL, including all ranges and values in between. In some
embodiments, the
AUC16 is between 80 % and 125 % of the aforementioned values.
43
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
[00126] All documents or patents cited herein are incorporated by
reference in their
entireties for all purposes.
[00127] The following examples are offered by way of illustration
and not by way of
limitation.
EXAMPLE 1. BREXP1PRAZOLE PHARMACOKINETICS IN OBESE AND OBESE
CYP2D6 PM
[00128] Brexpiprazole is an atypical antipsychotic indicated to treat
schizophrenia and for use as
an adjunctive therapy to antidepressants for the treatment of major depressive
disorder.
Brexpiprazole is known to have a drug-drug interaction with CYP2D6 inhibitors,
and dose
reductions are recommended for patients that are cytochrome P450 CYP2D6 poor
metabolizers
(PM) or patients taking concomitant CYP2D6 inhibitors. CYP2D6 EM patients
metabolize
brexpiprazole normally, whereas CYP2D6 PM patients are believed to eliminate
brexpiprazole
more slowly. The FDA label of brexpiprazole (REXULTIM advises that these
patient populations
take half of the usual dose of brexpiprazole. Table A shows the recommended
dosing schedule of
brexpiprazole for treating schizophrenia in patients that are CYP2D6 PM and
CYP2D6 extensive
metabolizers (EM). The brexpiprazole FDA label does not contain
recommendations for
brexpiprazole dosage according to body size. Therefore, obese patients (as
described herein) are
treated according to the same dosing schedule as EM or PM (depending on their
CYP2D6
metabolizer status)
Table A. Brexpiprazole Dosing for Schizophrenia According to FDA Label
CYP2D6 Days 1-4 Days 5-7 Days 8+
EM 1 mg QD 2 mg QD 2-4 mg QD
PM 0.5 mg QD 1 mg QD 1-2 mg QD
PBPK Modeling of Patients Dosed with Brexpiprazole According to the FDA Label
[00129] Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling was used to
estimate the
pharmacokinetic parameters of brexpiprazole of the following schizophrenia
patient populations
after administering brexpiprazole according to the FDA label (REXULTIS label
dated March
2020): obese (BMI > 35 kg/m2), normal weight (BMI = 18 kg/m2 ¨ 25 kg/m2),
CYP2D6 poor
metabolizer (PM), and CYP2D6 extensive metabolizer (EM). Although the PBPK
modeling was
44
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
based on the dosing regimen for schizophrenia according to the FDA label
(REXULTIR, 3/2020),
pharmacokinetic parameters are dose-dependent and expected to be similar in
MDD.
[00130] In order to simulate brexpiprazole under various conditions, a whole-
body PBPK model
was constructed to capture the drug's kinetics in major tissues. Model tissue
compartments
included adipose, bone, brain, large intestine, small intestine, heart,
kidney, liver, lung, muscle,
spleen, stomach, and skin tissues, as well as venous and arterial blood
compartments. In order to
accurately capture first-pass clearance effects on the drug, the model also
included correct
representation of the gastrointestinal tract organs and the liver.
Additionally, a peripheral sampling
site compartment was used to represent the PK-sampled venous blood
concentration as it was
found to more accurately capture referenced plasma concentrations. Drug
distribution into each
tissue compartment was modeled assuming perfusion-limited kinetics, with
partitioning into tissue
described by a partition coefficient (Kp) estimated using methods described by
Poulin and Theil
(2002). Brexpiprazole-specific biochemical parameters such as the log of
octanol:water partition
coefficient (logP), negative log acid dissociation constant (pKa), fraction
unbound in the plasma
(fup), blood:plasma concentration ratio (BP), and clearance were obtained from
literature;
additional physiochemical properties used to calculate Kps were obtained via
DrugBank.
Absorption was modeled assuming simple first-order absorption, and clearance
of brexpiprazole
was assumed to occur entirely in the liver (-1% renal clearance). Based on the
literature it was
assumed that 46.7% of brexpiprazole clearance is due to CYP3A4, with the
remaining clearance
due to CYP2D6 (43.3%) and other routes (10%). The impact of CYP2D6 PM status
is known to
decrease baseline clearance by ¨30%, which was reflected in the reduced
baseline clearance
parameters due to CYP2D6 in PM simulations. Simulations were carried out in a
virtual population
of 500 normal-weight and 500 obese individuals with age- and sex-specific
physiological
parameters (i.e. tissue flows and volumes) sampled from the National Health
and Nutrition
Examination Survey (NHANES) dataset.
[00131] Model parameters were calibrated and subsequently qualified by
digitizing PK data from
available literature and comparing predicted vs. observed AUCo-., Cmax, and
time to Cmax (Tmax)
under various dose strengths, dosing scenarios (i.e., single dose vs. multiple
dose), and routes of
administration (i.e., intravenous or oral formulations). Calibration and
qualification simulations
were carried out using a single typical individual (male, age=30 years,
weight=73 kg, and
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
height=1.76 m). All comparisons yielded a geometric mean fold error less than
or equal to 2, and
thus were considered accurate for these purposes.
[00132] The Applicant's model was validated and shown to accurately predict
observed and
literature pharmacokinetic parameters as shown in Tables B and C, below.
Table B. Model Validation
AUG trw.himl 1 Cmax Inpfrni 1 Tmax 1111
Reference Route Dose (rngl Observed Predicted
GMFE Observed Predicted GMFE Observed Predicted (MFE Calibration
NDA Studyl IV 0.25 172 175 1.02 4.73 5.07 1.07 1 1
1.0 Yes
PO 2 1690 1350 1.25 22.10 19.5 1.13 6 4
1.5 Yes
PO 0.2 123 135 1.10 2.62 1.95 1.35 2 4 2.0
No
PO 0.5 287 337 1.17 6.64 4.87 1.36 4 4 1.0
No
P(..) 1 636 6/9 1.06 11./0 9./4 1.20 6 4 1.5
No
NDA Study2 PO 2 2160 1350 1.60 24.60 19.50 1.27 4
4 1.0 No
PO 4 2760 2700 2.00 47.20 38.90 1.21 6 4
1.5 No
PO 6 5230 4050 1.29 71.10 58.40 1.22 6 4
1.5 No
PO 8 7920 5400 1.47 79.20 77.90 1.02 6 4
1.5 No
GMFE = geometric mean fold error
Calibration: Data used to optimize and/or refine PK parameters in the final
model
References are from N DA 205422 Clinical Pharmacology and Riopharmaceutics
Review, p.26 and 23
Table C. Comparison to Literature CYP2D6 PM PK Values
Brexpiprazole Model Comparisons
AUC AUC G MR % Expected G MR
Cohort Dose Normal Obese Expected Normal Obese Normal
Obese
CYP2D6 EM 4 mg 2703 2779 1.0 1.00 1.00
100% 100%
CYP2D6 PM 4 mg 4289 4397 1.5 1.59 1.58
106% 105%
CYP2D6 PM 2 mg 2134 2093 0.75 0.79 0.75
105% 100%
"Expected" values are based on population PK analysis in N DA 205422 Clinical
Pharmacology and Biopharmaceutics Review
[00133] The modeling data showed that patients that are obese and obese CYP2D6
PM take
significantly longer to reach therapeutic plasma levels of brexpiprazole when
initiating
brexpiprazole treatment (Table D, and FIG. 2A). This is based, at least in
part, on Applicant's
surprising discovery that the half-life of brexpiprazole is dependent on both
body size and
CYP2D6 metabolizer status. Normal-weight CYP2D6 EM exhibit a lower mean half-
life than
patients that are obese and/or CYP2D6 PM (Table D).
Table D. Half-Life of Brexpiprazole in Different Patient Populations
46
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
Weight CYP2D6 Mean half-life
(SD), hours
Normal EM 68.6 (45.0)
Obese EM 192 (130)
Normal PM 107 (71.3)
Obese PM 297 (207)
[00134] Additionally, obese and obese CYP2D6 PM patients take longer to reach
steady state
plasma levels and therapeutic concentrations compared to normal weight CYP2D6
EM when
dosed using the instructions on the FDA label (Table E where EC50, EC80, and
EC90 correspond
to the plasma concentration at with 50%, 80%, or 90% of the population is
expected to respond to
treatment, respectively). Consequently, these patients take significantly
longer to be treated than
previously known, and some patients may not actually reach therapeutic
brexpiprazole
concentrations. Thus, obese and CYP2D6 PM schizophrenia patients dosed
according to the FDA
label (e.g., REXULTI label dated March 2020) are not effectively treated.
Ineffective
schizophrenia treatment results in severe complications, including suicide
attempts, anxiety,
depression, alcohol or drug abuse, inability to work or attend school,
financial problems,
homelessness, social isolation, health and medical problems, being victimized,
and aggressive
behavior.
Table E. Pharmacokinetics Based on Current FDA Label
Days to Reach Pharmacokinetic
Endpoints
Weight CYP2D6 EC50 EC80 Steady State
Normal EM 3 9 21
Obese EM 6 11 37
Normal PM 5 10 24
Obese PM 7 15 46
EXAMPLE 2. SCHIZOPHRENIA
PBPK Modeling of Schizophrenia Patients Treated with Higher Doses According to
Modified
Methods
[00135] A modified dosing regimen was developed so that obese and CYP2D6 PM
patients reach
therapeutic levels earlier (Table F). The modified dosage regimen for obese
CYP2D6 EM and
47
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
normal-weight CYP2D6 PM comprises doubling the total daily dose of
brexpiprazole for days 1-
7 of the dosage regimen. On day 8, patients returned to administering the
recommended dose once
daily. The modified dosage regimen for obese CYP2D6 PM comprises doubling the
total daily
dose of brexpiprazole for days 1-14 of the dosage regimen. On day 15, patients
returned to
administering the recommended dose once daily. In contrast to the modified
dosage regimen for
obese CYP2D6 PM described herein which doubles the total daily brexpiprazole
dosage for days
1-14, the brexpiprazole FDA label recommends decreasing the total daily
brexpiprazole dosage by
one-half in these patients.
Table F. Modified Schizophrenia Dosing Regimens
Weight CYP2D6 Days 1-4 Days 5-7 Days 8-14 Days
15+
All (Label) EM 1 mg QD (1 2 mg QD (2 4 mg QD (4 4 mg QD
(4
mg total daily mg total daily mg total daily mg total
dose) dose) dose) daily
dose)
Obese EM 1 mg BID (2 2 mg BID (4 4 mg QD (4 4 mg
QD (4
(Modified mg total daily mg total daily mg total
daily mg total
Dosing dose) dose) dose) daily
dose)
Regimen 1)
All (Label) PM 0.5 mg QD 1 mg QD (1 2 mg QD (2 2 mg QD
(2
(0.5 mg total mg total daily mg total daily mg total
daily dose) dose) dose) daily
dose)
Obese PM 0.5 mg BID 1 mg BID (2 2 mg BID (4 2 mg
QD (2
(Modified (1 mg total mg total daily mg total daily
mg total
Dosing daily dose) dose) dose) daily
dose)
Regimen 2)
Non-Obese PM 0.5 mg BID 1 mg BID (2 1-2 mg (QD) 1-2 mg
(Modified (1 mg total mg total daily (QD)
Dosing daily dose) dose)
Regimen 3)
48
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
[00136] PBPK modeling shows that the pharmacokinetic parameters of obese
CYP2D6 PM and
obese CYP2D6 EM schizophrenia patients treated with the modified dosage
regimen of Table F
approach those of normal-weight CYP2D6 EM (Table I).
[00137] FIG. 3 shows that obese CYP2D6 EM schizophrenia patients that are
treated according
to Modified Dosing Regimen 1 have plasma brexpiprazole concentrations that are
similar to
normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients. Obese CYP2D6 EM patients that are
administered twice the
starting and recommended daily doses for the first 7 days reach therapeutic
concentrations three
days faster than obese CYP2D6 EM patients that are administered brexpiprazole
according to the
FDA label (Table H).
[00138] FIG. 4 shows that obese CYP2D6 PM schizophrenia patients that are
treated according
to Modified Dosing Regimen 2 reach therapeutic concentration in a similar time
to normal-weight
CYP2D6 EM patients. Obese CYP2D6 PM schizophrenia patients that are
administered
brexpiprazole at twice the starting and recommended daily doses for the first
14 days reach
therapeutic brexpiprazole concentrations five days faster than once daily
dosing (Table H).
[00139] FIG. 5 shows that normal-weight CYP2D6 PM schizophrenia patients that
are
administered brexpiprazole according to Modified Dosing Regimen 3 reach
therapeutic
concentrations three days faster than once daily dosing.
[00140] Table G shows that the modified dosage regimen of Table F decreases
the time required
for schizophrenia patients that are CYP2D6 PM and/or obese to reach
therapeutic concentrations.
The modified dosage regimen brings the time required for obese CYP2D6 PM,
normal-weight
CYP2D6 PM, and obese CYP2D6 EM patients to reach therapeutic concentrations
closer to that
of normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients.
[00141] Table I shows a comparison between the area under the curve, maximal
plasma
concentration (Cmax), and minimal plasma concentration (Cmin) between
schizophrenia patients
dosed according to the FDA label and schizophrenia patients dosed according to
the modified
dosage regimen. The AUC, Cmax, and Cmin for obese CYP2D6 PM, obese CYP2D6 EM,
and
normal-weight CYP2D6 PM patients approach those of normal-weight CYP2D6 EM
patients after
treatment with the modified dosing regimen.
Table G. Days to Reach Pharmacokinetic Endpoints using Modified Brexpiprazole
Dosing
Regimens of Table F
49
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
Weight CYP2D6 Days of EC50 EC80 Steady
BID State
dosing
Normal EM 0 3 9 21
Obese EM 7 3 8 33
Normal PM 7 3 7 21
Obese PM 14 5 10 17
Table H. Days Reduced to Reach Pharmacokinetic Endpoints After Dosing
According to
Modified Dosing Regimen of Table F
Weight CYP2D6 EC50 EC80 Steady
State
Obese EM 3 3 -4
Obese PM 2 5 -29
Table I. Pharmacokinetic Parameters
Label Dosing Modified Dosing
Normal Normal Obese Obese Normal Obese Obese
EM PM EM PM PM EM PM
Day 9 AUC 1763 1073 1063 611 1554 1526
1166
(rig *
hr/mL)
Cmax 88.2 51.8 63.7 34.7 73.4 83.3
58.1
(ng/mL)
Cmin 51.9 33.2 30.0 17.3 54.4 50.2
36.5
(ng/mL)
Label Dosing Modified Dosing
Normal Normal Obese Obese Normal Obese Obese
EM PM EM PM PM EM EM
Day 16 AUC 2600 1908 1967 1229 2008 2189
2147
(ng *
hr/mL)
Cmax 128.8 88.4 104.1 61.2 94.0 113.7
100.2
(ng/mL)
Cmin 91.8 70.3 69.9 44.4 74.8 79.6
84.0
(ng/mL)
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
EXAMPLE 3. MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER (1VIDD)
PBPK Modeling of MDD Patients Treated with Higher Doses According to Modified
Methods
[00142] A modified dosing regimen was developed so that obese and CYP2D6 PM
patients reach
therapeutic levels earlier (Table I). For obese CYP2D6 EM, the modified dosage
regimen
comprises doubling the total daily dose of brexpiprazole for days 1-7 of the
dosage regimen on the
brexpiprazole label. On day 8, the patients are treated with the recommended
dose once daily
according to the brexpiprazole label. For obese CYP2D6 PM, the modified dosage
regimen
comprises doubling the total daily dose of brexpiprazole for days 1-14 or 1-21
(depending on the
starting dose) of the dosage regimen. Thereafter (on day 15 or 22, depending
on the starting dose),
the patients are treated with the recommended dose once daily according to the
brexpiprazole label.
In contrast to these modified dosage regimens for obese CYP2D6 PM (which
doubles the total
daily brexpiprazole dosage), the FDA label recommends decreasing the total
daily brexpiprazole
dosage by one-half in these patients.
Table J. Modified 1VMD Dosing Regimens
Weight CYP2D6 Days 1-7 Days 8-14 Days 15-21 Days
21+
All (FDA EM 0.5 mg QD 1 mg QD (1 2 mg QD (2 2-3 mg QD
Label) (0.5 mg total mg total daily mg total
daily (2-3 mg
daily dose) dose) dose) total
daily
dose)
All EM 1.0 mg QD 2 mg QD (2 2-3 mg QD 2-3 mg QD
(1.0 mg total mg total daily (2-3 mg total (2-3 mg
(FDA Label)
daily dose) dose) daily dose)
total daily
dose)
All (FDA PM 0.25 mg QD 0.5 mg QD 1.0 mg QD 1-1.5 mg
Label) (0.25 mg total (0.5 mg total (1.0 mg
total QD (1-1.5
daily dose) daily dose) daily dose)
mg total
daily dose)
51
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
Weight CYP2D6 Days 1-7 Days 8-14 Days 15-21 Days
21+
All PM 0.5 mg QD 1 mg QD (1 1-1.5 mg QD 1-1.5 mg
(0.5 mg total mg total daily (2 mg total QD (1-1.5
(FDA Label)
daily dose) dose) daily dose) mg
total
daily dose)
Obese EM 0.5 mg BID 1 mg QD (1 2 mg QD (2 2-3 mg
QD
(Modified (1 mg total mg total daily mg total daily
(2-3 mg
Dosing daily dose) dose) dose) total
daily
Regimen A) dose)
Obese EM 1 mg BID (2 2 mg QD (2 2-3 mg QD (2 2-3
mg QD
(Modified mg total daily mg total daily mg total
daily (2-3 mg
Dosing dose) dose) dose) total
daily
Regimen B) dose)
Obese PM 0.25 mg BID 0.5 mg BID 1 mg BID (2 1 mg
QD
(Modified (0.5 mg total (1 mg total mg total daily
Dosing daily dose) daily dose) dose)
Regimen C)
Obese PM 0.5 mg BID 1 mg BID (2 1 mg QD 1 mg
QD
(Modified (1 mg total mg total daily
Dosing daily dose) dose)
Regimen D)
Normal PM 0.25 mg BID 0.5 mg QD 1 mg QD 1-
1.5 mg
(Modified (0.5 mg total QD
Dosing daily dose)
Regimen E)
Normal PM 0.5 mg BID 1 mg QD 1-1.5 mg QD 1-1.5
mg
(Modified (1 mg total QD
Dosing daily dose)
Regimen F)
52
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
[00143] PBPK modeling shows that the pharmacokinetic parameters of obese
CYP2D6 PM and
obese CYP2D6 EM schizophrenia patients treated with the modified dosage
regimen of Table J
approach those of normal-weight CYP2D6 EM (Table K and Table L).
[00144] FIG. 6 shows the blood plasma profiles for obese CYP2D6 EM patients
with MDD that
are treated according to Modified Dosing Regimen A, and FIG. 7 shows blood
plasma profiles for
obese patient that are treated according to Modified Dosing Regimen B. In both
FIG. 6 and FIG.
7, starting on day 8, the recommended dose was administered once daily.
[00145] FIG. 6 shows that obese CYP2D6 EM MDD patients that are treated
according to the
Modified Dosing Regimen A (BID for the first 7 days and return to the
recommended dose
thereafter) have plasma brexpiprazole concentrations that are similar to
normal-weight CYP2D6
EM patients.
[00146] FIG. 7 shows that obese CYP2D6 EM MDD patients that are treated
according to the
Modified Dosing Regimen B (BID for the first 7 days and return to the
recommended dose
thereafter) have plasma brexpiprazole concentrations that are similar to
normal-weight CYP2D6
EM patients.
[00147] FIG. 8 shows the blood plasma profiles for obese CYP2D6 PM patients
with MDD that
are treated according to Modified Dosing Regimen C, and FIG. 9 shows blood
plasma profiles for
obese patients that are treated according to Modified Dosing Regimen D. In
FIG. 8, starting on
day 22, half of the recommended dose was administered once daily. In FIG. 9,
starting on day 15,
half of the recommended dose was administered once daily.
[00148] FIG. 8 shows that obese CYP2D6 PM MDD patients that are treated
according to
Modified Dosing Regimen C (BID for the first 21 days and return to half the
recommended dose
thereafter) reach therapeutic concentrations in a similar time to normal-
weight CYP2D6 EM
patients.
[00149] FIG. 9 shows that obese CYP2D6 EM MDD patients that are treated
according to the
Modified Dosing Regimen D (BID for the first 14 days and return to half the
recommended dose
thereafter) have plasma brexpiprazole concentrations that are similar to
normal-weight CYP2D6
EM patients.
[00150] FIG. 11 and FIG. 12 shows that normal-weight CYP2D6 PM MDD patients
that are
administered brexpiprazole according to Modified Dosing Regimen E and Modified
Dosing
53
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
Regimen F, respectively, reach therapeutic brexpiprazole concentration in a
similar time to
normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients.
[00151] Table K shows a comparison between the area under the curve, maximal
plasma
concentration (Cmax), and minimal plasma concentration (Cmin) between MDD
patients dosed
according to the FDA label and MDD patients dosed according to Modified Dosing
Regimens A
(starting dose of 0.5 mg BID) and C (starting dose of 0.25 mg BID). The AUC,
Cmax, and Cmin
for obese CYP2D6 PM, obese CYP2D6 EM, and normal-weight CYP2D6 PM patients
approach
those of normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients after treatment with the modified
dosing regimen.
Table K. Pharmacokinetic Parameters Modified Dosing Regimen with Starting
Doses of 0.5
mg BID (Obese CYP2D6 EM) or 0.25 mg BID (Obese CYP2D6 PM)
Label Dosing Modified Dosing
Normal Normal Obese Obese Normal Obese Obese
EM PM EM PM PM EM PM
Day 21 AUC 1271 924 965 938 938 1011
1209
(ng *
hr/mL)
Cmax 63.3 43.1 51.4 30.6 44.0 53.3
54.8
(ng/mL)
Cmin 44.5 33.8 34.2 22.2 34.5 36.0
45.9
(ng/mL)
Day 30 AUC 1368 1052 1227 840 1057 1246
1160
(ng *
hr/mL)
Cmax 66.6 48.5 62.5 40.4 48.8 63.2
54.0
(ng/mL)
Cmin 49.0 39.7 45.4 32.0 39.9 6.0
45.6
(ng/mL)
[00152] Table L shows a comparison between the area under the curve, maximal
plasma
concentration (Cmax), and minimal plasma concentration (Gain) between MDD
patients dosed
according to the FDA label and MDD patients dosed according to Modified Dosing
Regimens B
(starting dose of 1 mg BID) and D (starting dose of 0. 5 mg BID). The AUC,
Cmax, and Cmin for
54
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2
WO 2022/146462
PCT/US2021/016329
obese CYP2D6 PM, obese CYP2D6 EM, and normal-weight CYP2D6 PM patients
approach those
of normal-weight CYP2D6 EM patients after treatment with the modified dosing
regimen.
Table L. Pharmacokinetic Parameters Modified Dosing Regimen with Starting
Doses of 1
mg BID (Obese CYP2D6 EM) or 0.5 mg BID (Obese CYP2D6 PM)
Label Dosing Modified Dosing
Normal Normal Obese Obese Normal Obese Obese
EM PM EM PM PM EM PM
Day 21 AUC 1361 1031 1178 776 1066 1253
1121
(ng *
hr/mL)
Cmax 66.4 47.7 59.9 37.7 49.2 63.5
52.2
(ng/mL)
Cmin 48.7 38.8 43.1 29.3 40.3 46.5
44.2
(ng/mL)
Day 30 AUC 1375 1081 1304 935 1088 1332
1112
(ng *
hr/mL)
Cmax 66.9 49.5 65.9 44.1 49.7 67.2
52.4
(ng/mL)
Cmin 49.3 40.9 48.7 35.9 41.0 50.5
43.4
(ng/mL)
CA 03201123 2023- 6-2