Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
INSTANT DIGITAL ISSUANCE
CROSS-REFERENCES TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
100011 This application is a continuation-in-part of US Non-Provisional
Application No.
16/443,169, filed on June 17, 2019, and which in turn claims priority to U.S.
Provisional
Application No. 62/686,369, filed June 18, 2018, the entireties of which are
incorporated by
reference herein.
BACKGROUND
100021 Banks and other credit providers often issue cards for fund use to
users, making fast
payment quick and easy for users through the use of a credit or debit card. In
this way, users
must have the card physically available at the point of sale. However, to
issue a physical card
takes time and costs the issuer and/or user money to generate the card due to
labor, material, and
shipping costs and costs the issuer and/or user time to wait for generation
and shipping of the
card before the card can be used. With the advent of online sales and secure
mobile devices,
other strategies are needed and would be beneficial to both users and card
issuers to reduce the
time and costs associated with the existing physical card payment systems.
SUMMARY
100031 To address the issues associated with provisioning a physical payment
source, systems
and methods for providing instant digital issuance of a new payment source,
such as a credit
card, in a mobile or digital wallet of the user, are described herein. The
relevant provisioning
and encryption necessary to ensure, for the token service provider, the
validity of the payment
source from the issuer for the user is described herein.
100041 A system of one or more computers can be configured to perform
particular operations
or actions by virtue of having software, firmware, hardware, or a combination
of them installed
on the system that in operation causes or cause the system to perform the
actions. One or more
-1-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
computer programs can be configured to perform particular operations or
actions by virtue of
including instructions that, when executed by data processing apparatus, cause
the apparatus to
perform the actions. One general aspect includes receiving, at a gateway
encryption service of a
gateway system, from an issuer mobile application server, user information for
a user and
account information for a payment source of the user. The gateway encryption
service can
transmit the user information and the account information to a gateway lookup
service of the
gateway system. The gateway lookup service can receive, from an issuing host
platform, primary
account number data for the payment source. The gateway lookup service can
transmit the
primary account number data to the gateway encryption service. The gateway
encryption service
can encrypt the primary account number data to generate encrypted provision
data. The gateway
encryption service can transmit the encrypted provision data to the issuer
mobile application
server. The issuer mobile application server, having the encrypted provision
data, can allow the
user to utilize the digital payment source in a digital wallet without the
user having the physical
payment source. Other embodiments of this aspect include corresponding
computer systems,
apparatus, and computer programs recorded on one or more computer storage
devices, each
configured to perform the actions of the methods.
10005] Implementations may include one or more of the following features.
Optionally,
encrypting the primary account number data includes identifying an encryption
key and/or a
validation key from multiple encryption and/or validation keys using the
primary account
number data, and encrypting, using the encryption key, and/or signing, using
the validation key,
the primary account number data to generate the encrypted provision data.
Optionally, the
encryption key and/or the validation key identifies a token service provider.
100061 Optionally, encrypting the primary account number data further includes
identifying a
first set of encryption requirements for the mobile device pay wallet using
wallet data from the
mobile device pay wallet, and identifying a second set of encryption
requirements for the token
service provider. In such cases, encrypting the primary account number data
using the encryption
key includes complying with the first set of encryption requirements and
complying with the
second set of encryption requirements.
-2-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
[0007] Optionally, the gateway encryption service may receive the encryption
key and/or the
validation key and store the encryption key and/or the validation key in a
database with other
encryption and/or validation keys. In such cases, identifying the encryption
key and/or the
validation key includes identifying an associated issuer using the primary
account number data
and searching the database for the encryption key and/or the validation key
using the associated
issuer.
[0008] Optionally, the payment source is a credit card. Optionally, the user
information for the
user and the account information for the payment source of the user includes a
name of the user,
a digital wallet data of the user, and an issuer nonce. Optionally, the
primary account number
data includes a sixteen-digit primary account number of the payment source, an
address of the
user, and a nickname of the payment source.
[0009] Optionally, an issuer mobile application using a software development
kit receives a list
of accounts for the user, where the payment source is selected from the list
of accounts.
Optionally, the issuer mobile application using a software development kit
receives the
encrypted provision data. The software development kit can invoke a request to
provision the
payment source in the mobile device pay wallet of the user using the encrypted
provision data.
The software development kit can receive a result of the request to provision
the payment source
in the mobile device pay wallet. Optionally, receiving the result of the
request to provision the
payment source in the mobile device pay wallet includes receiving a token for
providing the
payment source in the mobile device pay wallet.
10010] Optionally, the gateway encryption service receives, from the issuer
mobile application
server, an issuer nonce indicating that the user was authenticated by the
issuer mobile application
server. Optionally, encrypting the primary account number data includes
encrypting the issuer
nonce along with the primary account number data. Optionally, The token
service provider
receives the encrypted primary account number data along with the issuer
nonce. The token
service provider may decrypt the encrypted primary account number data and the
issuer nonce
using an encryption key and validates the signature using a validation key. In
response to
-3-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
validating the signature, the token service provider may transmit the issuer
nonce to the issuer in
a provision request. The issuer may authorize the provision request and log
the issuer nonce.
Implementations of the described techniques may include hardware, a method or
process, or
computer software on a computer-accessible medium.
[00111 In accordance with some embodiments of the present disclosure, a non-
transitory
computer-readable medium having computer-readable instructions stored thereon
is disclosed.
The computer-readable instructions that when executed by at least one first
processor associated
with a gateway and at least one second processor associated with a software
development kit for
provisioning a payment source cause the at least one first processor and the
at least one second
processor to receive, by the gateway, a first request from an issuer
application on behalf of a
cardholder for a list of entities comprising merchants or pay wallets that are
eligible to receive
the payment source, send, by the gateway, the list of entities to the issuer
application for display
to the cardholder for selection of an entity from the list of entities;
receive, by the gateway, a
second request from the issuer application in response to sending the list of
entities to the issuer
application, such that the second request includes an asset identifier
associated with the selected
entity and user data associated with the cardholder, prepare and transmit, by
the gateway, a
response to the issuer application upon receiving the second request, such
that depending upon a
type of a token service provider or the selected entity, the response includes
(a) an encrypted
payload obtained by encrypting, by the gateway, at least the entity identifier
and the user data; or
(b) a receipt identifier; receive, by the software development kit, the
response from the issuer
application. The computer-readable instructions that when executed by at least
one first
processor associated with a gateway and at least one second processor
associated with a software
development kit for provisioning a payment source further cause the at least
one first processor
and the at least one second processor to redirect, by the software development
kit, from the issuer
application to an entity application associated with the selected entity, such
that the redirection
includes sending the encrypted payload or the receipt identifier to the entity
application to allow
the entity application to send the encrypted payload or the receipt identifier
to the token service
provider to request a new token for the payment source from the token service
provider, receive,
-4-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
by the software development kit, a result from the entity application
indicating whether the entity
application successfully received the new token from the token service
provider, and determine,
by the software development kit and based on the result, whether the request
for the provisioning
of the payment source is successful.
[00121 In accordance with some other embodiments of the present disclosure, a
system is
disclosed. The system includes at least one memory having computer-readable
instructions
stored thereon and at least one first processor associated with a gateway and
at least one second
processor associated with a software development kit to provision a payment
source, such that
the at least one first processor and the at least one second processor
executes the computer-
readable instructions to receive, by the gateway, a first request from an
issuer application on
behalf of a cardholder for a list of entities comprising merchants or pay
wallets that are eligible
to receive the payment source; send, by the gateway, the list of entities to
the issuer application
for display to the cardholder for selection of an entity from the list of
entities, receive, by the
gateway, a second request from the issuer application in response to sending
the list of entities to
the issuer application, such that the second request comprises an asset
identifier associated with
the selected entity and user data associated with the cardholder; prepare and
transmit, by the
gateway, a response to the issuer application upon receiving the second
request, such that
depending upon a type of a token service provider or the selected entity, the
response comprises
(a) an encrypted payload obtained by encrypting, by the gateway, at least the
entity identifier and
the user data; or (b) a receipt identifier, receive, by the software
development kit, the response
from the issuer application, redirect, by the software development kit, from
the issuer application
to an entity application associated with the selected entity, such that the
redirection includes
sending the encrypted payload or the receipt identifier to the entity
application to allow the entity
application to send the encrypted payload or the receipt identifier to the
token service provider to
request a new token for the payment source from the token service provider,
receive, by the
software development kit, a result from the entity application indicating
whether the entity
application successfully received the new token from the token service
provider, and determine,
-5-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
by the software development kit and based on the result, whether the request
for the provisioning
of the payment source is successful.
10013] In accordance with some other embodiments of the present disclosure, a
method is
disclosed. The method includes receiving, by at least one first processor
associated with a
gateway and at least one second processor associated with a software
development kit for
provisioning a payment source and executing computer-readable instructions
stored on at least
one memory, a first request from an issuer application on behalf of a
cardholder for a list of
entities including merchants or pay wallets that are eligible for receiving
the payment source,
sending, by the gateway, the list of entities to the issuer application for
display to the cardholder
for selection of an entity from the list of entities, receiving, by the
gateway, a second request
from the issuer application in response to sending the list of entities to the
issuer application,
such that the second request comprises an asset identifier associated with the
selected entity and
user data associated with the cardholder, preparing and transmitting, by the
gateway, a response
to the issuer application upon receiving the second request, such that
depending upon a type of a
token service provider or the selected entity, the response comprises (a) an
encrypted payload
obtained by encrypting, by the gateway, at least the entity identifier and the
user data; or (b) a
receipt identifier, receiving, by the software development kit, the response
from the issuer
application, redirecting, by the software development kit, from the issuer
application to an entity
application associated with the selected entity, such that the redirection
includes sending the
encrypted payload or the receipt identifier to the entity application to allow
the entity application
to send the encrypted payload or the receipt identifier to the token service
provider to request a
new token for the payment source from the token service provider, receiving,
by the software
development kit, a result from the entity application indicating whether the
entity application
successfully received the new token from the token service provider, and
determining, by the
software development kit and based on the result, whether the request for the
provisioning of the
payment source is successful.
-6-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0(14] FIG. 1 illustrates a system for instant digital issuance of payment
sources
100151 FIG. 2 illustrates a swim diagram for instant digital issuance of
payment sources.
[0016] FIG. 3 illustrates a method for instant digital issuance of payment
sources.
[0017] FIG. 4 illustrates an exemplary computer system.
[0018] FIG. 5 illustrates an exemplary user interface for instant digital
issuance of payment
sources.
[0019] FIG. 6 illustrates an example block diagram of another push
provisioning system, in
accordance with some embodiments of the present disclosure.
[0020] FIG. 7 illustrates an example swimlane diagram for push provisioning a
payment source
to a merchant using a mobile or web issuer application, in accordance with
some embodiments of
the present disclosure.
[00211 FIG. 8 illustrates another example swimlane diagram for push
provisioning a payment
source to a merchant using a mobile or web issuer application, in accordance
with some
embodiments of the present disclosure.
[0022] FIGS. 9A-9E illustrate example interfaces of a client device for push
provisioning a
payment source to a merchant, in accordance with some embodiments of the
present disclosure.
[0023] FIG. 10 illustrates an example swimlane diagram for push provisioning a
payment source
to Apple Pay wallet using a web issuer application, in accordance with some
embodiments of
the present disclosure.
-7-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
[0024] FIG. 11 illustrates an example swimlane diagram for push provisioning a
payment source
to Google PayTM wallet using a web issuer application, in accordance with some
embodiments of
the present disclosure.
100251 FIG. 12 illustrates an example swimlane diagram for push provisioning a
payment source
to Samsung Pay wallet using a web issuer application, in accordance with some
embodiments
of the present disclosure.
[00261 FIGS. 13A-13E illustrate example interfaces of a client device for push
provisioning a
payment source to Apple Pay wallet, in accordance with some embodiments of
the present
disclosure.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
10027] Consumers paying for goods and services often use credit or debit cards
as a payment
method. However, payment using debit or credit cards for a user typically
involves obtaining the
account and then waiting for the card to arrive so that it can be used. For
the card issuer,
typically there are time and money costs involved in generating and shipping
the card, which
leaves the user unable to use the card to purchase goods and services until
the card arrives. Both
issuers and users (i.e., consumers) would benefit from the ability of an
issuer to instantly issue a
digital card to the user on a mobile device.
100281 Many users have secure mobile devices that are personally owned and
used. For
example, many users have a mobile cellular telephone and/or tablet. A mobile
device may
include a digital pay wallet. A pay wallet may be software on the mobile
device that allows a
user to link a payment source (e.g., credit or debit card) to the mobile
device so that the payment
source can be used to purchase goods and services without having a physical
card or check, for
example. Often near field communication is used between the point-of-sale
device and the
mobile device to securely provide the payment information from the mobile
device to the point-
of-sale device.
-8-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
100291 In some existing systems, the user of the mobile device typically uses
the physical card
information to set up the pay wallet with the payment source. For example, a
user can use a pay
wallet application on their mobile device and either take a picture of the
physical card or
manually enter the information from the physical card to add the card to their
pay wallet in this
manner. This type of provisioning of a card into a pay wallet is typically
termed pull
provisioning. The payment source information is "pulled" into the pay wallet.
The user is
limited, however, to waiting until the physical card arrives to provision the
card into the pay
wallet. Entering the physical card information, however, assures the pay
wallet provider, the
issuer, and the token service provider that the user is the owner of the
payment source. As such
the user can be authenticated for provisioning the payment source into the pay
wallet.
100301 Described herein are methods and systems for facilitating push
provisioning, which may
allow an issuer to provide a button in an issuer's mobile application for the
user to simply push
the button to request that the payment source be imported into the user's pay
wallet. In this way,
the payment source information is "pushed" into the pay wallet. Using push
provisioning, the
user need not enter any physical card information. However, the user must be
authenticated
properly to prove to each of the issuer, the pay wallet provider, and the
token service provider
that the user owns the payment method.
10031] In existing systems, various different pay wallet providers and issuers
have differing
requirements for provisioning a payment source into a pay wallet. Because of
the complications
associated with tracking the various requirements of each pay wallet provider,
issuers are
reluctant to implement push provisioning in their issuer mobile applications.
Described herein is
a software development kit for including by an issuer in the issuer's mobile
application that
provides the interfaces for easily implementing push provisioning with any pay
wallet provider.
100321 Further, in existing systems, obtaining the primary account number
("PAN") data and
appropriately encrypting the information varies by token service provider,
making the issuer
even more reluctant and sometimes simply unable to implement push
provisioning. In addition
to the software development kit, the described solution provides a PAN gateway
lookup service
-9-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
and a PAN gateway encryption service with which the software development kit
can interface for
ensuring that the push provisioning works not only with any pay wallet but
with any token
service provider.
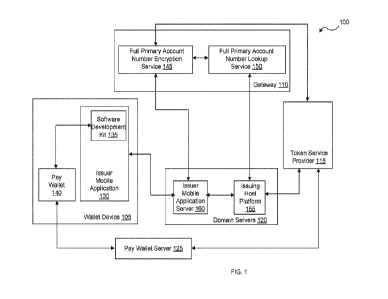
100331 FIG. 1 illustrates a system 100 for instant digital issuance of payment
sources. The
system 100 can include a wallet device 105, a gateway 110, a token service
provider 115,
domain servers 120, and a pay wallet server 125.
[0034] The wallet device 105 may be any suitable device that can support a
digital wallet. The
wallet device 105 may be computer system 400 as described with respect to FIG.
4. The wallet
device 105 may be, for example, a mobile cellular telephone, a tablet, a
personal digital assistant,
or the like. The wallet device 105 (also referred to herein as a user device
or a mobile device)
may include a pay wallet 140 and an issuer mobile application 130. While only
a single wallet
device 105 is depicted in FIG. 1, any number of wallet devices 105 may be
supported within
system 100.
(0035] The pay wallet 140 may be any suitable digital wallet. The pay wallet
140 may be
implemented as a software application installed and executed upon the wallet
device 105.
Currently digital wallets are available from multiple vendors including, for
example, Apple
Pay from Apple Inc., Google PayTM from Google LLC, and Samsung Pay from
Samsung.
[0036] The issuer mobile application 130 may be a software user interface
application provided
by the card issuer. The card issuer may be any suitable payment source (e.g.,
debit or credit
card) issuer. Example card issuers include, for example, JPMorgan Chase & Co,
Wells Fargo,
Bank of America Corporation, Capital One, and so forth. Each issuer may
provide an issuer
mobile application 130. The issuer mobile application 130 may be a software
application that is
installed on the wallet device 105 and allows the user to access the user's
account information
with the issuer.
[0037] The issuer mobile application 130 may incorporate a software
development kit 135. The
software development kit 135 may provide interfaces and methods for
interfacing with pay
-10-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
wallet 140 and domain servers 120 that facilitate push provisioning of a
payment source from the
issuer that provides issuer mobile application 130 into the pay wallet 140 for
use on the wallet
device 105.
100381 The token service provider 115 may provide a token service for digital
use of the
payment source. For example, when sending digital payment information, the
full account
information, such as the sixteen digit account number may not be sent to
protect the account
information. Rather, a token may be generated and assigned to the sixteen
digit account number.
The token service provider 115 may receive and validate the push provision
request with the
encrypted provision data and activation data. The token service provider 115
may authorize the
token and provide notification of the approval to the pay wallet server 125 as
well as the issuing
host platform 155. While only one token service provider 115 is depicted in
FIG. 1, any number
of token service providers 115 may be included in system 100. Token service
provider 115 may
be, for example First Data universal token service by First Data Corporation
or Visa token
service by Visa Inc. The token service provider 115 may be a service provided
on a computer
system (e.g., a server) such as computer system 400 of FIG. 4.
100391 The domain servers 120 may include the issue mobile application server
160 and the
issuing host platform 155. The domain servers 120 may be any suitable servers
the issuer of the
payment source provides and may be computer systems 400 of FIG. 4. The issuer
mobile
application server 160 may be a server managed by the issuer that the issuer
mobile application
130 interfaces with to obtain user account information for display in the user
interface of the
issuer mobile application 130 on the user's wallet device 105. The issuing
host platform 155
may be the host server managed by the issuer that stores and manages all user
account
information.
100401 The pay wallet server 125 may be any suitable server provided by the
pay wallet provider
(e.g., Google LLC for Google Pay, Samsung for Samsung Pay , and so forth),
such as for
example computer system 400 of FIG. 4. The pay wallet server 125 may interface
between the
token service provider 115 and the pay wallet 140 to provision the payment
source in the pay
-11-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
wallet 140. While a single pay wallet server 125 is depicted in FIG. 1, any
number of pay wallet
servers 125 may be included in system 100.
10041] The gateway 110 may include full PAN encryption service 145 and full
PAN lookup
service 150. The gateway may be one or more servers that are hosted on a
network (not shown)
for communication with the domain servers 120 and the token service provider
115. The
gateway 110 may be computer system 400 of FIG. 4. While a single gateway 110
is shown in
FIG. 1, any number of gateways 110 may be included. The full PAN encryption
service 145 and
the full PAN lookup service 150 provided by gateway 110 provide a many-to-many
gateway
service for encrypting PAN data. Each pay wallet server 125 has specific
encryption
requirements that differ. For example, Apple Pay has different encryption
requirements than
Samsung Pay . Further, each token service provider 115 has differing
encryption requirements.
For example, First Data universal token service has different encryption
requirements than Visa
token service. The combination of digital wallet (e.g., Apple Pay , Samsung
Pay , or the like)
and token service provider (e.g., Visa token service, First Data universal
token service, or the
like) each has a unique combination of encryption requirements that complicate
push
provisioning for an issuer to implement push provisioning in the issuer's
mobile application.
The gateway 110 with the full PAN encryption service 145 and the full PAN
lookup service 150
in combination with the software development kit 135 provide a technical
solution that simplifies
implementing push provisioning in the issuer's mobile application (issuer
mobile application
130).
[0042) The full PAN lookup service 150 and the full PAN encryption service 145
may be
software services installed upon the gateway 110 for providing their
respective services as
described in more detail herein.
100431 The full PAN lookup service 150 may provide lookup services of a user's
PAN from an
issuing host platform 155. The full PAN lookup service 150 may obtain the
information for a
user account including the full sixteen digit account number, a card nickname,
an associated
address of the user, credentials (e.g., user name of the user) from the issuer
mobile application
-12-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
130, and so forth. The full PAN lookup service 150 is optional. In some
embodiments, the
issuer may provide the full sixteen digit account number and all other
necessary information such
that the full PAN lookup service 150 is not used.
100441 The full PAN encryption service 145 may obtain the user account
information from the
full PAN lookup service 150 and prepare encrypted provision data used to
complete the push
provisioning as described in detail herein. The encrypted provision data is
encrypted and signed
by the full PAN encryption service 145. The encryption is completed using an
encryption key
provided to the full PAN encryption service 145 by the token service provider
115. Each token
service provider 115 provides an encryption key for encryption of user data.
In some
embodiments. The token service provider 115 provides a single encryption key
for all user
accounts that use the token service provider 115, and in some embodiments an
encryption key
unique to each issuer is provided. The encryption ensures that only the
destined token service
provider 115 or the destined pay wallet server 125 can decrypt the data. The
encryption
provision data is also signed by the full PAN encryption service 145 using a
validation key
established by the full PAN encryption service 145 and exchanged with the
token service
provider 115. The signature ensures the token service provider 115 can
validate the signature in
the provision request to ensure the chain of trust is complete as described in
more detail herein.
10045] FIG. 2 illustrates a swim diagram 200 of a method for instant digital
issuance of a
payment source using the components described with respect to FIG. 1. Along
the top of the
swim diagram 200, the components described with respect to FIG. 1 are shown
including the
wallet device 105, issuer mobile application 130, software development kit
135, pay wallet 140,
pay wallet server 125, issuer mobile application server 160, gateway 110, full
PAN encryption
service 145, full PAN lookup service 150, token service provider 115, and
issuing host platform
155.
100461 Beginning with the issuer mobile application 130, as arrow 202, the
issuer mobile
application 130 transmits user information entered by the user using the user
interface of the
-13-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
issuer mobile application 130. The user information is transmitted to the
issuer mobile
application server 160.
10047] The issuer mobile application server 160 may authenticate the user
using the user
information (e.g., a user name and password, biometric data, and so forth).
The issuer mobile
application server 160 may transmit a request, shown by arrow 204, to issuing
host platform 155
for a list of eligible accounts for the user. The eligible accounts may
include any user accounts
the issuer has recorded for the user. For example, a user may have one or more
checking or
savings accounts associated with one or more debit cards and/or one or more
credit cards from
the same issuer (e.g., Wells Fargo, Capital One, and so forth).
100481 The issuing host platform 155 may transmit the full PAN suffix data
(e.g., the last four
digits of the sixteen digit account number) for each eligible account for the
user to the issuer
mobile application server 160 as shown by arrow 206. The issuer mobile
application server 160
may transmit the full PAN suffix data to the issuer mobile application 130 as
shown by arrow
208. The issuer mobile application 130 may not maintain account information
for the user on the
wallet device 105, so all account information may be obtained from the issuer
mobile application
server 160 for display in the user interface of the issuer mobile application
130.
100491 Once the issuer mobile application 130 has obtained the full PAN suffix
data, the issuer
mobile application 130 can invoke methods provided by the software development
kit 135 as
shown by arrow 210. Arrow 212 indicates that the software development kit 135
may include a
method to query the pay wallet 140 for whether the full PAN suffix data
identifies an account
(i.e., payment source) that has previously been provisioned by the pay wallet
140. If the account
has previously been provisioned by the pay wallet 140, there is no need to
provision the account
again. However, if the account has not previously been provisioned by the pay
wallet 140, the
user may wish to use push provisioning to provision the pay source into the
pay wallet 140.
-14-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
100501 The pay wallet 140 may respond to the query, as shown by arrow 214,
with information
indicating whether the account associated with the full PAN suffix data for
each eligible account
has previously been provisioned.
100511 If at least one account has not previously been provisioned, the
software development kit
135 may invoke another method to request wallet data for push provisioning.
Wallet data may
include, for example, a wallet identifier (i.e., an identifier for pay wallet
140), a device identifier
(e.g., an Internet Protocol address for wallet device 105, a media access
control ("MAC")
address for wallet device 105, or any other suitable identifier for wallet
device 105), a binding
identifier or a digital signature that binds the user to the pay wallet 140, a
name of the wallet
device 105, the push provision request (used to prevent the request from being
replayed or
spoofed), a wallet certificate that contains a public key for encrypting PAN
data to be sent back
to the pay wallet server 125, and the like. For simplicity of explanation,
only a single account
provision is described, but multiple accounts from an issuer may be
provisioned into pay wallet
140 in parallel or serially. The software development kit 135 may request the
wallet data from
the pay wallet 140 as shown by arrow 216. The pay wallet 140 may request the
wallet data from
the pay wallet server 125 as shown by arrow 218. The pay wallet server 125 may
provide the
wallet data for the account to the pay wallet 140 as shown by arrow 220. The
pay wallet 140
may provide the wallet data to the software development kit as shown by arrow
222. The
software development kit 135 may provide the wallet data to the issuer mobile
application 130 as
shown by arrow 224. The issuer mobile application 130 may then display a
button within the
user interface of the issuer mobile application 130. The button, when pressed
by the user, may
invoke the push provisioning process for adding the account to the pay wallet
140.
100521 Arrow 226 may transmit the wallet data from the issuer mobile
application 130 to the
issuer mobile application server 160 when the user pushes the button within
the issuer mobile
application 130 to invoke the push provisioning process for adding the payment
source (i.e.,
eligible account for which the full PAN suffix data was obtained) to the pay
wallet 140.
-15-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
100531 The issuer mobile application server 160 may authenticate the user and
confirm the
authenticity of the received information. Once authenticated, the issuer
mobile application
server 160 may provide the account information (e.g., the user name, the full
PAN suffix data,
and so forth), the wallet data, and an issuer nonce to the Full PAN encryption
service 145 as
shown by arrow 228. The issuer nonce may be a randomly generated identifier
that indicates
that the user has been authenticated by the issuer mobile application server
160 (the user was
previously authenticated at arrow 202) and is used in the push provision
request for the
transaction beginning at arrow 228. Optionally, the PAN data including the
full sixteen digit
account number may have been provided to the full PAN encryption service 145
from the issuer
mobile application server 160 as well.
[0054] The full PAN encryption service 145 may determine whether a full PAN
lookup is
needed based on whether the full PAN encryption service 145 has the PAN data.
If the full PAN
encryption service 145 does not have the PAN data, the full PAN encryption
service 145 may
transmit the account information, the wallet data, and the issuer nonce to the
full PAN lookup
service 150 as shown by arrow 230.
[0055] The full PAN lookup service 150 may request the PAN data from the
issuing host
platform 155 as shown by arrow 232. The request may include the user
information, account
information, and/or credentials obtained from the issuer mobile application
server sent through
the full PAN encryption service. The issuing host platform 155 may search a
database or other
data source using the user information, account information, and/or
credentials to identify the
requested PAN data. The issuing host platform 155 may return the PAN data to
the full PAN
lookup service 150 as shown by arrow 234. The PAN data may include the full
sixteen digit
account number, the user's address, and/or the payment source (e.g., credit
card) nickname.
10056] As shown by arrow 236, the PAN data may be transmitted from the full
PAN lookup
service 150 to the full PAN encryption service 145. The full PAN encryption
service may
encrypt the PAN data to create encrypted provision data. Optionally, the user
information,
account information, wallet data, issuer nonce, PAN data, user's address,
and/or card nickname
-16-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
may be included with the PAN data and encrypted. The full PAN encryption
service 145 may
encrypt the PAN data (including the user information, account information,
wallet data, issuer
nonce, PAN data, user's address, and/or card nickname) using an encryption key
and may
digitally sign the PAN data using a validation key. The encryption key and/or
the validation key
may be set with the token service provider information. In other words, the
encryption key
and/or the validation key may identify the token service provider. The
encryption key and/or the
validation key may be obtained from the issuer when the issuer registers with
the gateway 110,
which may optionally include registering with the full PAN encryption service
145 and/or the
full PAN lookup service 150. Optionally, the encryption key and/or the
validation key may be
established directly between the full PAN encryption service 114 and the token
service provider
115, and all provision requests for issuers that use that token service
provider 115 have data that
is encrypted with the encryption key and signed with the validation key for
that token service
provider 115.. Optionally, multiple issuers may utilize the same encryption
key and/or validation
key. When the full PAN encryption service 145 obtains an encryption and/or
validation key, the
encryption and/or validation key may be stored with other keys in a database
or other storage
location accessible to the full PAN encryption service 145. The full PAN
encryption service 145
may search the key database using, for example, the primary account number
data. As an
example, the first four digits of a sixteen digit account number may identify
an issuer, so the
database may be queried using the first four digits of the sixteen digit
account number from the
PAN data to identify the encryption key and/or validation key. As another
example, the issuer
may be identified based on the PAN data and the database may be queried using
the issuer for
the encryption key and/or validation key. Optionally, the PAN data encrypted
with the
encryption key may also be encrypted with the wallet certificate from the
wallet data. The wallet
certificate may include a public key used for encrypting the PAN data. The pay
wallet server
125 may have the corresponding private key for decryption that the pay wallet
server may use to
decrypt the PAN data as described below.
100571 In some embodiments, the validation key is unique to the issuer and the
token service
provider. In other embodiments, the token service provider permits the full
PAN encryption
-17-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
gateway to use the same validation key across multiple issuers processed by
that gateway
because the gateway performs mutual authentication with the issuer server, and
the token service
provider trusts the gateway's authentication of the issuer server. Using the
same validation key
across multiple issuers speeds up the implementation timeline for enabling
this gateway service
for a new issuer. The chain of trust generated by the process is sufficient to
ensure security. For
example, the chain of trust is that the issuer authorizes the user and sends
the request to the
encryption gateway. The encryption gateway has mutual authentication of the
issuer and signs
the request payload with a key trusted by the token service provider.
Accordingly, because the
request is encrypted with a trusted key by a trusted partner that in turn has
authenticated the
issuer, and the issuer has in turn authenticated the user, the token service
provider can be assured
that the user is validly requesting the provisioning of the payment source
into the user's digital
pay wallet.
100581 As discussed above with respect to gateway 110 of FIG. 1, the token
service provider 115
and the pay wallet server 125 may each have different encryption requirements.
Further, for any
given push provision request, any available digital wallet (i.e., pay wallet
server 125) and any
available token service provider (i.e., token service provider 115) may be
used so that any given
push provision request may require any combination of encryption requirements
that meet both
the selected token service provider encryption requirements and the digital
wallet encryption
requirements. The full PAN encryption service 145 may identify the set of
encryption
requirements for the token service provider identified by the encryption key.
The full PAN
encryption service 145 may also identify the set of encryption requirements
for the pay wallet
server 125 based on the wallet data included with the PAN data. The encryption
requirements
for all available token service providers 115 may be stored in a database
available to full PAN
encryption service 145. The encryption requirements for all available pay
wallet servers 125
may also be stored in a database available to full PAN encryption service 145.
Full PAN
encryption service 145 may identify each set of encryption requirements (i.e.,
the set of
encryption requirements for the token service provider and the set of
requirements for the pay
wallet server) and ensure the encryption of the PAN data complies with each
set of requirements.
-18-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
Example requirements may include the type of encryption algorithm (e.g.,
symmetric-key
algorithm, format-preserving algorithm, and so forth) that may be used, the
minimum length of
the encryption key (e.g., 128-bit key, 256-bit key, and so forth) that may be
used, and so forth.
10059] Once the full PAN encryption service 145 has generated the encrypted
provision data, the
full PAN encryption service 145 may transmit the encrypted provision data to
the issuer mobile
application server 160 as shown by arrow 238. The issuer mobile application
server 160 may
transmit the encrypted provision data to the issuer mobile application 130 as
shown by arrow
240. The issuer mobile application 130 may invoke an add card method that may
call methods
within the software development kit 135 as shown by arrow 242.
100601 The software development kit 135 may initiate a request to add the card
to the pay wallet
140 by transmitting the encrypted provision data to the pay wallet 140 as
shown by arrow 244.
The pay wallet may transmit the provision request to the pay wallet server 125
by transmitting
the encrypted provision data as shown by arrow 246. The pay wallet server 125
may transmit the
provision request and the encrypted provision data to the token service
provider 115 as shown by
arrow 248.
100611 The token service provider 115 may use the encryption key to decrypt
the encrypted
provision data and may use the validation key to authenticate the data as from
the encryption
gateway. The token service provider 115 may identify within the decrypted
provision data the
account information including the PAN data (e.g., the sixteen digit account
number), the user
information, the wallet data, and so forth, and use the identified information
to generate a token
to be used by the user within the pay wallet 140. The token service provider
115 may transmit a
provision authorization, including the token and the issuer nonce, to the
issuing host platform
155 as shown by arrow 250.
[0062] The issuing host platform 155 may store the token with the PAN data.
Optionally, the
issuer mobile application 130 may have previously sent the issuer nonce to the
issuing host
platform 155 (not depicted in FIG. 2). The issuing host platform 155 may check
the issuer nonce
-19-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
from the issuer mobile application 130 against the issuer nonce received at
250 to confirm that
the push provision request was authenticated by the issuer mobile application
server 160, thereby
validating the chain-of-trust. The issuing host platform may transmit an
acknowledgement to the
token service provider 115 as shown by arrow 252. The token service provider
may then
transmit a provision notification to the issuing host platform 155 as shown by
arrow 254, and the
issuing host platform 155 may transmit an acknowledgement to the token service
provider 115 as
shown by arrow 256. After these acknowledgements, the token service provider
115 and the
issuing host platform 155 both acknowledge the token and consider the account
provisioned into
the pay wallet 140.
[00631 The token service provider 115 then transmits the provision response
(e.g., successful
provisioning indicated by the token, which is also transmitted) to the pay
wallet server 125 as
shown by arrow 258. The pay wallet server 125 then stores the token with the
user information
and account information so that future requests to determine whether the add
button should be
included in the issuer mobile application will result in a negative response.
Further, the pay
wallet 140 will obtain the token from the pay wallet server 125 to allow the
user to use the
payment source (i.e., account associated with the token) from the pay wallet
140. The pay wallet
server 125 transmits the token to the pay wallet 140 as shown by arrow 260.
The pay wallet 140
transmits the token and/or a success or failure message indicating whether the
payment source
was successfully provisioned or not to the software development kit 135 as
shown by arrow 262.
The software development kit 135 transmits the token and/or the success or
failure message to
the issuer mobile application 130 as shown by arrow 264. The issuer mobile
application 130
then optionally displays a notification to the user that the account was
successfully provisioned
into the pay wallet 140 or indicates a failure if the provisioning was
unsuccessful.
100641 FIG. 3 illustrates a method 300 for instant digital issuance of a
payment source. The
method may be performed by the gateway 110 as described with respect to FIG.
1. The method
300 begins at block 305 with the gateway encryption service (e.g., full PAN
encryption service
145 of FIG. 1) receiving user information for a user and account information
for a payment
source of the user from an issuer mobile application server (e.g., issuer
mobile application server
-20-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
160). Optionally, the user information and account information is transmitted
to the gateway
encryption service in response to a user requesting push provisioning of the
account into a pay
wallet from the issuer's mobile application.
100651 At block 310, the gateway encryption service may transmit the user
information and the
account information to a gateway lookup service (e.g., full PAN lookup service
150 of FIG. 1).
The account information may include a PAN suffix (e.g., the last four digits
of the sixteen digit
account number), the user's name, the user's credentials (e.g., a username and
password,
biometric data including a fingerprint or iris scan, and/or so forth), wallet
data for the pay wallet
into which the user wishes to provision the account, an issuer nonce, and so
forth.
100661 At block 315, the gateway lookup service may receive PAN data for the
payment source
from an issuing host platform. The gateway lookup service may have transmitted
the PAN
suffix, the user's name, the user's credentials, the wallet data, and/or the
issuer nonce to the
issuing host platform requesting the PAN data. The PAN data may include the
sixteen digit
account number, the user's address, and/or a nickname the user may have
assigned to the
account.
100671 At block 320, the gateway lookup service may provide the PAN data to
the gateway
encryption service. At block 325, the gateway encryption service may encrypt
the PAN data to
generate encrypted provision data. The gateway encryption service may use an
encryption key
to encrypt the data and a validation key to sign the data. The encryption key
and validation key
may be set with a specific token service provider for the issuer that the
issuer may have provided
to the gateway encryption service. In some embodiments, the encryption key and
the validation
key used for a token service provider is used for all issuers that use that
token service provider.
The gateway encryption service may user the encryption key to encrypt the PAN
data.
Optionally, the gateway encryption service may combine the PAN data, the
user's credentials,
the PAN suffix, the user's name, the wallet data, and/or the issuer nonce
before encrypting with
the encryption key. The gateway encryption service also signs the data with
the validation key.
Optionally, the gateway encryption service may further encrypt the encrypted
data with the
-21-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
wallet certificate. The encrypted provision data is any or all of the above
described data that was
combined and encrypted with the encryption key and/or the wallet certificate.
10068] At block 330, the gateway encryption service may transmit the encrypted
provision data
to the issuer mobile application server, which can be used to finalize the
push provisioning
process as described in detail with respect to FIG. 2.
100691 FIG. 4 illustrates an embodiment of a computer system 400. A computer
system 400 as
illustrated in FIG. 4 may be incorporated into devices such as a personal
computer, server
computer, mobile device (e.g., smartphone, smart watch, tablet, and the like),
point of service
("POS") terminal, and the like. FIG. 4 provides a schematic illustration of
one embodiment of a
computer system 400 that can perform some or all of the steps of the methods
provided by
various embodiments. It should be noted that FIG. 4 is meant only to provide a
generalized
illustration of various components, any or all of which may be utilized as
appropriate. FIG. 4,
therefore, broadly illustrates how individual system elements may be
implemented in a relatively
separated or relatively more integrated manner.
100701 The computer system 400 is shown comprising hardware elements that can
be electrically
coupled via a bus 405, or may otherwise be in communication, as appropriate.
The hardware
elements may include one or more processors 410, including without limitation
one or more
general-purpose processors and/or one or more special-purpose processors such
as digital signal
processing chips, graphics acceleration processors, and/or the like; one or
more input devices
415, which can include without limitation a mouse, a keyboard, a camera, a
remote control,
and/or the like; and one or more output devices 420, which can include without
limitation a
display device, a printer, and/or the like.
[00711 The computer system 400 may further include and/or be in communication
with one or
more non-transitory storage devices 425, which can comprise, without
limitation, local and/or
network accessible storage, and/or can include, without limitation, a disk
drive, a drive array, an
optical storage device, a solid-state storage device, such as a random access
memory ("RAM"),
-22-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
and/or a read-only memory ("ROM"), which can be programmable, flash-
updateable, and/or the
like. Such storage devices may be configured to implement any appropriate data
stores,
including without limitation, various file systems, database structures,
and/or the like.
100721 The computer system 400 might also include a communications subsystem
430, which
can include without limitation a modem, a network card (wireless or wired), an
infrared
communication device, a wireless communication device, and/or a chipset such
as a Bluetooth
device, an 802.11 device, a Wi-Fi device, a WiMax device, cellular
communication facilities,
etc., and/or the like. The communications subsystem 430 may include one or
more input and/or
output communication interfaces to permit data to be exchanged with a network
such as the
network described below to name one example, other computer systems,
television, and/or any
other devices described herein. Depending on the desired functionality and/or
other
implementation concerns, a portable electronic device or similar device may
communicate
transaction and/or other information via the communications subsystem 430. In
other
embodiments, a portable electronic device, may be incorporated into the
computer system 400
(e.g., an electronic device), as an input device 415. In many embodiments, the
computer system
400 will further comprise a working memory 435, which can include a RAM or ROM
device, as
described above.
10073] The computer system 400 also can include software elements, shown as
being currently
located within the working memory 435, including an operating system 440,
device drivers,
executable libraries, and/or other code, such as one or more application
programs 445, which
may comprise computer programs provided by various embodiments, and/or may be
designed to
implement methods, and/or configure systems, provided by other embodiments, as
described
herein. Merely by way of example, one or more procedures described with
respect to the
methods discussed above, such as those described in relation to FIG. 6, might
be implemented as
code and/or instructions executable by a computer and/or a processor within a
computer; in an
aspect, then, such code and/or instructions can be used to configure and/or
adapt a general
purpose computer or other device to perform one or more operations in
accordance with the
described methods.
-23-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
[0074] A set of these instructions and/or code might be stored on a non-
transitory computer-
readable storage medium, such as the storage device(s) 425 described above. In
some cases, the
storage medium might be incorporated within a computer system, such as
computer system 400.
In other embodiments, the storage medium might be separate from a computer
system (e.g., a
removable medium), such as a compact disc, and/or provided in an installation
package, such
that the storage medium can be used to program, configure, and/or adapt a
general purpose
computer with the instructions/code stored thereon. These instructions might
take the form of
executable code, which is executable by the computer system 400 and/or might
take the form of
source and/or installable code, which, upon compilation and/or installation on
the computer
system 400 (e.g., using any of a variety of generally available compilers,
installation programs,
compression/decompression utilities, etc.), then takes the form of executable
code.
[0075] It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that substantial
variations may be made in
accordance with specific requirements. For example, customized hardware might
also be used,
and/or particular elements might be implemented in hardware, software
including portable
software, such as applets, etc., or both. Further, connection to other
computing devices such as
network input/output devices may be employed.
[0076] As mentioned above, in one aspect, some embodiments may employ a
computer system
such as the computer system 400 to perform methods in accordance with various
embodiments
of the technology. According to a set of embodiments, some or all of the
procedures of such
methods are performed by the computer system 400 in response to processor 410
executing one
or more sequences of one or more instructions, which might be incorporated
into the operating
system 440 and/or other code, such as an application program 445, contained in
the working
memory 435. Such instructions may be read into the working memory 435 from
another
computer-readable medium, such as one or more of the storage device(s) 425.
Merely by way of
example, execution of the sequences of instructions contained in the working
memory 435 might
cause the processor(s) 410 to perform one or more procedures of the methods
described herein.
Additionally or alternatively, portions of the methods described herein may be
executed through
specialized hardware.
-24-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
100771 The terms "machine-readable medium" and "computer-readable medium," as
used
herein, refer to any medium that participates in providing data that causes a
machine to operate
in a specific fashion. In an embodiment implemented using the computer system
400, various
computer-readable media might be involved in providing instructions/code to
processor(s) 410
for execution and/or might be used to store and/or carry such
instructions/code. In many
implementations, a computer-readable medium is a physical and/or tangible
storage medium.
Such a medium may take the form of a non-volatile media or volatile media. Non-
volatile media
include, for example, optical and/or magnetic disks, such as the storage
device(s) 425. Volatile
media include, without limitation, dynamic memory, such as the working memory
435.
[00781 Common forms of physical and/or tangible computer-readable media
include, for
example, a floppy disk, a flexible disk, hard disk, magnetic tape, or any
other magnetic medium,
a CD-ROM, any other optical medium, punchcards, papertape, any other physical
medium with
patterns of holes, a RAM, a PROM, EPROM, a FLASH-EPROM, any other memory chip
or
cartridge, or any other medium from which a computer can read instructions
and/or code.
100791 Various forms of computer-readable media may be involved in carrying
one or more
sequences of one or more instructions to the processor(s) 410 for execution.
Merely by way of
example, the instructions may initially be carried on a magnetic disk and/or
optical disc of a
remote computer. A remote computer might load the instructions into its
dynamic memory and
send the instructions as signals over a transmission medium to be received
and/or executed by
the computer system 400.
10080] The communications subsystem 430 and/or components thereof generally
will receive
signals, and the bus 405 then might carry the signals and/or the data,
instructions, etc. carried by
the signals to the working memory 435, from which the processor(s) 410
retrieves and executes
the instructions. The instructions received by the working memory 435 may
optionally be stored
on a non-transitory storage device 425 either before or after execution by the
processor(s) 410.
-25-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
[0081] FIG. 5 illustrates an exemplary mobile device 500 (e.g., wallet device
105) which is
displaying a user interface of the issuer mobile application (e.g., issuer
mobile application 130).
The user interface may be for a card issuer, which may be displayed in a
banner 505, in this case
"Your Bank" is the issuer. The card nickname ("My Card") and the PAN suffix
data ("8712") is
displayed as shown at 515. A balance 520, credit line 525, and available
credit 530, for example,
may be shown in the user interface. A collapsible link 535 for recent
transaction may be
available. Further, a collapsible link 540 for adding an account to a pay
wallet may be available.
Once the collapsible link 540 is selected, the button 545 for push
provisioning the account,
which has an associated nickname of "My Card" and a PAN suffix of 8712, into
Pay Wallet 1.
The button 545 may be provided as a result of the actions described in the
swim diagram 200
associated with arrows 202, 204, 206, 208, 210, 212, 214, 216, 218, 220, 22,
and 224. If the user
selects the button 545 to initiate the push provisioning process, the actions
described in swim
diagram 200 beginning with arrow 226 may ensue to successfully complete the
push
provisioning process and make the account with PAN suffix 8712 available for
use on the mobile
device 500 within Pay Wallet 1.
[0082] Turning to FIG. 6, another example push provisioning system 600 is
shown, in
accordance with some embodiments of the present disclosure. Similar to the
system 100 of FIG.
1, the push provisioning system 600 includes a client device 602 (e.g., the
wallet device 105) in
communication with a token service provider 604 via a gateway 606 and an
issuer application
server 608. The client device 602 may be any suitable device that a user
(e.g., cardholder) may
use to make a payment. For example, in some embodiments, the client device 602
may include a
mobile cellular telephone, a tablet, a personal digital assistant, a laptop, a
wearable device (e.g.,
smart watch, etc.), or the like. The client device 602 may be the computer
system 400 as
described above with respect to FIG. 4. In some embodiments, the client device
602 may be
configured to access a pay wallet application 610 (e.g., similar to the pay
wallet 140) and a
merchant application 612.
[0083] In some embodiments, either or both of the pay wallet application 610
and the merchant
application 612 may be a mobile application (e.g., software application) that
is installed, and
-26-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
designed to run, on the client device 602. In other embodiments, either or
both of the pay wallet
application 610 and the merchant application 612 may be a web application
(e.g., software
application) that is configured to run on a web server and may be configured
for access via a web
browser. For example, in some embodiments, the user (e.g., cardholder) may
open a web
browser on the client device 602 and enter a web address (e.g., Uniform
Resource Locator)
associated with the pay wallet to access the pay wallet application 610 of
that pay wallet.
Similarly, in some embodiments, the user (e.g., cardholder) may open a web
browser on the
client device 602 and enter a web address (e.g., Uniform Resource Locator)
associated with a
merchant to access the merchant application 612 of that merchant. In some
embodiments, the
client device 602 may be configured to access a web application (whether the
pay wallet
application 610 or the merchant application 612) via the client device 602 and
also have a mobile
application ((whether the pay wallet application or the merchant application)
installed on the
client device.
100841 While only a single pay wallet application (e.g., the pay wallet
application 610) and a
single merchant application (e.g., the merchant application 612) is shown on
the client device
602, in other embodiments, the client device may have multiple pay wallet
applications (e.g., one
pay wallet application for each type of pay wallet) and multiple merchant
applications (e.g., one
merchant application for each merchant). Further, in some embodiments, the pay
wallet
application 610 may correspond to any suitable digital wallet. Example digital
wallets may
include, for example, Apple Pay from Apple Inc., Google PayTM from Google
LLC, and
Samsung Pay from Samsung. In other embodiments, the pay wallet application
610 may
correspond to other or additional digital wallets. Similarly, the merchant
application 612 may
correspond to any merchant (e.g., card-on-file merchants, click-to-pay
merchants, etc.) that
allows online transactions, or in other words, allows buying and/or selling
products and/or
services using the client device 602.
100851 The client device 602 may also be configured to access an issuer
application 614. In
some embodiments, the issuer application 614 may be a mobile application
(e.g., software
application) that is installed, and designed to run on, the client device 602.
In other
-27-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
embodiments, the issuer application 614 may be a web application that is run
on a web server
and may be accessed using a web browser on the client device 602. For example,
in some
embodiments, the user (e.g., cardholder) may open a web browser on the client
device 602 and
enter a web address (e.g., Uniform Resource Locator) associated with the
issuer to access the
issuer application 614 of that issuer. The issuer application 614 may be
associated with an issuer
of a payment source (also referred to herein as a payment instrument). For
example, in some
embodiments, the issuer application 614 may be associated with issuers such as
JPMorgan Chase
& Co, Wells Fargo, Bank of America Corporation, Capital One, etc. In other
embodiments, the
issuer application 614 may be associated with other or additional issuers. In
some embodiments,
the payment source may be any suitable payment mechanism. For example, in some
embodiments, the payment source may be a debit card, a credit card, etc. Using
the issuer
application 614, the user (e.g., cardholder) may view account details, payment
details, user
profile details, advertisements, rewards, etc., and any other service or
information that the issuer
makes available to the user via the issuer application. In some embodiments,
the user may also
use the issuer application 614 to push provision a payment source issued by
the issuer of the
issuer application to a merchant or pay wallet.
100861 The issuer application 614 may incorporate a software development kit
616. The
software development kit 616 may include software tools and programs to
provide interfaces and
methods for facilitating the push provisioning operations to a pay wallet or
to a merchant. In
some embodiments, the software development kit 616 may be embedded into the
issuer
application 614 and may be configured for use both via a mobile application
implementation of
the issuer application or via a web application implementation of the issuer
application. The
software development kit 616 may be configured to hide the complexity of the
push provisioning
operation from the user. For example and as explained in greater detail below,
in some
embodiments, different token service providers (e.g., the token service
provider 604), different
merchants, and/or different pay wallets may have varying communication
protocols (e.g., may
require different messaging formats) and/or require different types of
messages (e.g., different
types of API calls) for performing the same or similar functions. In some
embodiments, the
-28-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
operations for push provisioning to a merchant may be different from the
operations for push
provisioning to a pay wallet, which in turn may vary based upon the type of
merchant or pay
wallet, as well as whether the push provisioning is occurring through a mobile
application or a
web application. The software development kit 616 may be configured to hide
all of this
complexity from the user. From the user's standpoint, the software development
kit 616
provides a set of simple interfaces that guide the user through the push
provisioning process.
[0087] The software development kit 616 may be configured to interface with
the pay wallet
application 610 and the merchant application 612. For example, and as
discussed below, the
software development kit 616 may be configured to redirect the user between
the issuer
application 614 and the pay wallet application 610 if the user is push
provisioning to a pay wallet
or between the issuer application and the merchant application 612 if the user
is push
provisioning to a merchant. Although not shown, the software development kit
616 may include,
or be associated with, computer-readable instructions that may be executed by
a processor (e.g.,
a processor of the user device 602). In some embodiments, the computer-
readable instructions
may be located on the user device 602, while in other embodiments, the
computer-readable
instructions may be located remote (e.g., on a cloud) from the user device and
accessible by the
user device.
10088] The token service provider 604 (e.g., similar to the token service
provider 115) may
provide a token service for digital use of the payment source. For example,
when sending digital
payment information, the full account information, such as the sixteen digit
account or card
number may not be sent to protect the account information. Rather, the token
service provider
604 may generate a token and associate that token with the payment source. The
token service
provider 604 may receive and validate the push provision request by issuing a
token for a
payment source to a pay wallet or to a merchant. The token service provider
604 may be any of
a variety of token service providers. For example, in some embodiments, the
token service
provider 604 may be a MasterCard Digital Enablement Service ("MDES") token
service
provider. In other embodiments, the token service provider 604 may be a Visa
Token Service
("VTS") token service provider. In yet other embodiments, the token service
provider 604 may
-29-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
be a First Data Universal Token Service token service provider. In other
embodiments, the token
service provider 604 may be any other type of a token service provider.
10089] The token service provider 604 may be configured for communication with
a merchant
server 618, a pay wallet server 620, and an issuing host platform 622. The
token service
provider 604 may receive a push provisioning request from the merchant server
618 or the pay
wallet server 620. In response, the token service provider 604 may determine
that the push
provisioning request is a valid request and generate a token (e.g., a payment
token) for a payment
source selected by the user (e.g., cardholder). The token service provider 604
may return the
generated token to the merchant server 618 or the pay wallet server 620 that
made the push
provisioning request. In some embodiments, the token service provider 604 may
also provide a
notification of approval (and/or the generated token) to the issuing host
platform 622. Although
not shown, the token service provider 604 may include, or be associated with
computer-readable
instructions that may be executed by a processor.
100901 The merchant server 618 (also referred to as a commerce server) may be
associated with
the merchant application 612. The merchant server 618 may be configured to
handle
transactions occurring via the merchant application 612. For example, in some
embodiments, the
merchant server 618 may be configured to establish a secure channel of
communication between
the user and the issuer of the payment source that the user is using to make a
payment for a
transaction (e.g., purchase) using the merchant application 612. Thus, the
merchant server 618
may be configured to implement an electronic commerce protocol. In some
embodiments, the
merchant server 618 may be located remote from the merchant application 612.
The merchant
server 618 may include, or be associated with, computer-readable instructions
that may be
executed by a processor associated with the merchant server. The merchant
server 618 may
receive a push provisioning request to push provision a payment source to the
merchant
associated with the merchant server, and correspond with the token service
provider 604 and/or
the gateway 606 to receive a token for the payment source.
-30-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
100911 The pay wallet server 620 (similar to the pay wallet server 125) may be
associated with
the pay wallet application 610. The pay wallet server 620 may be configured to
handle
transactions occurring via the pay wallet application 610. For example, in
some embodiments,
the pay wallet server 620 may be configured to establish a secure channel of
communication
between the user and the issuer of the payment source that the user is using
to a make payment
for a transaction (e.g., purchase) using the pay wallet application 610. Thus,
the pay wallet
server 620 may be configured to implement an electronic commerce protocol. In
some
embodiments, the pay wallet server 620 may be located remote from the pay
wallet application
610. The pay wallet server 620 may include, or be associated with, computer-
readable
instructions that may be executed by a processor associated with the pay
wallet server. The pay
wallet server 620 may receive a push provisioning request to push provision a
payment source to
the pay wallet associated with the pay wallet server, and correspond with the
token service
provider 604 and/or the gateway 606 to receive a token for the payment source.
100921 The issuing host platform 622 may be associated with the issuer
providing the issuer
application 614. The issuing host platform 622 (similar to the issuing host
platform 155) may be
configured to store and/or manage user account information. Although the
issuing host platform
622 is shown separate from the issuer application server 608, in some
embodiments, the issuing
host platform and the issuer application server may be combined together into
a single system
(e.g., the domain servers 120). The issuer application server 608 may be
provided by the issuer
associated with the issuer application 614. The issuer application server 608
may be configured
to establish communication between the issuer application 614 and the gateway
606 or between
the issuer application and the issuing host platform 622. The issuer
application server 608 may
include, or be associated with, computer-readable instructions that may be
executed by a
processor associated with the issuer application server.
100931 The gateway 606 may be similar to the gateway 110. The gateway 606 may
be
configured to communicate with the software development kit 616 and the issuer
application 614
via the issuer application server 608. For example, the gateway 614 may
receive a request for
information from the issuer application 614 via the issuer application server
608. The gateway
-31-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
606 may need to communicate with the token service provider 604 to fulfill the
request for
information. In some embodiments, and as discussed above, different token
service providers
may employ different communication protocols. The gateway 606 may be
configured to
determine the type (e.g., MDES, VTS, etc.) of the token service provider 604,
determine the
communication protocol associated with the type of the token service provider,
and format
messages to the token service provider in accordance with the determined
format. The gateway
606 is also configured to hide the complexity of the push provisioning
operation from the user.
Further, by virtue of the gateway 606, additional types of token service
providers may be added
without needing to alter the operations or functionality of the issuer
application 614, the pay
wallet application 610, the merchant application 612, the software development
kit 616, or the
issuer application server 608.
100941 In some embodiments, the gateway 606 may include, or be associated with
computer-
readable instructions that may be executed by a processor associated with the
gateway. In some
embodiments, the software development kit 616 and the gateway 606 may be
implemented by
the same processor (even though the software development kit and the gateway
may be located
remote from one another). In other embodiments, the software development kit
616 and the
gateway 606 may be implemented by separate processors.
10095] Notwithstanding the elements shown in FIG. 6, it is to be understood
that the push
provisioning system 600 may include other or additional elements. Generally
speaking, the push
provisioning system 600 may include any element or component that may be
considered
desirable to have or may be needed in performing the functions described
herein. Thus, the push
provisioning system 600 enables a user (e.g., cardholder) to provide a
tokenized payment card
number to merchants and pay wallets for easy and secure transactions (e.g.,
purchases). The
push provisioning system 600 allows a digital first experience to the user by
permitting new
account usage without needing to wait for a physical card activation. The push
provisioning
system 600 allows the user to complete transactions using any device (e.g.,
any web-enabled
device) and provides a frictionless enablement of the payment source as the
payment option in
the merchant checkout flow. The push provisioning system 600 is configured to
work with a
-32-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
variety of token requesting merchants and pay wallets through a variety of
token service
providers. The push provisioning system 600 provides a simple, normalized
integration through
the software development kit 616 and the gateway 606, as well as provides a
one time
provisioning of the payment source regardless of changes in the account
status, account numbers,
etc.
100961 The push provisioning system 600 also provides technical improvements.
Specifically,
the push provisioning system 600 provides technical improvements in the area
of computer
networks. The push provisioning system 600 also improves the operations of the
client device
602. For example, the push provisioning system 600 enables the user to push
provision to both
pay wallets and merchants using the same issuer application (e.g., the issuer
application 614) via
the software development kit 616. The push provisioning system 600 also allows
the user to
push provision to both the pay wallets and merchants using either mobile
application or web
application, thereby avoiding the need for the user to download specialized
software and
consuming additional memory and storage space on the client device. Thus, the
push
provisioning system 600 improves the storage capabilities of the client device
602. The push
provisioning system 600 also allows the client device 602 to hide the
complexity of the push
provisioning process by providing simple interfaces regardless of which token
service provider is
used, which merchant or pay wallet is being provisioned to, and what
communication protocols
they follow. The push provisioning system 600 simplifies communications over
the network by
using simple Application Program Interface ("API") messages and calls, and
automatically
formatting the messages in accordance with the preferred communication
protocol of the
recipient (e.g., the token service provider). The problems being addressed by
the push
provisioning system 600 are specific to transactions occurring over the web
using the client
device 602.
100971 Turning to FIG. 7, an example swimlane diagram outlining operations of
a process 700 is
shown, in accordance with some embodiments of the present disclosure. The
process 700 may
be used for push provisioning a payment source to a merchant using the issuer
application 614.
Specifically, the process 700 may be used to push provision the payment source
to the merchant
-33-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
such that the merchant may obtain a token from a token service provider, and
particularly, an
MDES token service provider. To push provision a payment source to a merchant,
a user (e.g.,
cardholder 702) logs into an issuer application 704 at operation 706. The
issuer application 704
is analogous to the issuer application 614 and may be a mobile application or
a web application.
The issuer application 704 may be accessed on a client device (e.g., the
client device 602) of the
cardholder 702. In some embodiments, the cardholder 702 may log into the
issuer application
704 by entering authentication information such as a username, password,
account number,
biometrics, and/or in any other suitable way. The issuer application 704 sends
the authentication
information (e.g., via a network) to an issuer application server 708 at
operation 710.
[00981 The issuer application server 708, which may be considered analogous to
the issuer
application server 608, may authenticate the cardholder by verifying the
authentication
information. In some embodiments, the issuer application server 708 may obtain
data from an
issuing host platform 712 to authenticate the cardholder 702. The issuing host
platform 712 is
analogous to the issuing host platform 622. Upon authenticating the cardholder
702, the issuer
application server 708 requests, from the issuing host platform 712, a list of
payment sources
(e.g., list of cards, list of accounts, etc.) issued by the issuer to the
cardholder at operation 714.
In some embodiments, the payment sources may include credit cards. In other
embodiments, the
payment sources may include debit cards or any other form of payment mechanism
that the
cardholder may use to make payments. In some embodiments, the issuer
application server 708
may also send the authentication information and/or other cardholder details
to the issuing host
platform 712 to enable the issuing host platform to retrieve the list of
payment sources. The
issuing host platform 712 may retrieve the list of payment sources and send
the list back to the
issuer application server 708 at operation 716. The issuer application server
708 sends the list of
payment sources to the issuer application 704 at operation 718, for display
(e.g., on the client
device) to the cardholder 702 in the issuer application.
100991 To push provision a payment source to a merchant, the cardholder 702
selects a payment
source from the list of payment sources displayed within the issuer
application 704 at operation
720. The issuer application 704 receives the cardholder's selection of the
payment source
-34-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
(referred to herein as the "selected payment source") at the operation 720.
The issuer application
704 sends a request to the issuer application server 708 for a list of
merchants at operation 722.
The list of merchants may include those merchants that are eligible for
receiving the selected
payment source via push provisioning. Upon receiving the request from the
issuer application
704, the issuer application server 708 transmits the request to a gateway 724
at operation 726.
The gateway 724 may be considered analogous to the gateway 606 and may be
configured to
communicate with a token service provider 728. The token service provider 728
may be
considered analogous to the token service provider 604.
101001 In some embodiments, the gateway 724 may be configured to communicate
with a
variety of different token service providers, as discussed above. Different
token service
providers may adopt different communication protocols. For example, the MDES
token service
provider may adopt a different communication protocol than the VTS token
service provider,
which in turn may adopt a yet another communication protocol compared to
another token
service provider. A communication protocol may dictate a type and/or format of
messages or
calls (the terms "message" and "call" are used interchangeably herein) that a
particular token
service provider may communicate in. The communication protocol may include
other
communication details or operations that are specific to a particular token
service provider and
that the gateway 724 needs to follow to communicate with (e.g., request
information from, send
information to, etc.) the particular token service provider. For example, in
some embodiments,
to provide the list of merchants, an MDES token service provider (e.g., the
token service
provider 728) may require a specific type of message (e.g., a specific type of
API call) from the
gateway 724 while a VTS token service provider may require a different type of
message (e.g., a
different API call) for providing the same list of merchants.
101011 Thus, before establishing communication with a token service provider,
the gateway 724
may first determine the type of the token service provider (e.g., MDES, VTS,
etc.). In some
embodiments, the gateway 724 may determine the type of the token service
provider based upon
the issuer. In some embodiments, the gateway 724 may determine the issuer from
the
information included in the request of the operation 722. For example, in some
embodiments,
-35-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
the request may include at least some information of the selected payment
source that may
enable the gateway 724 to identify the issuer. In other embodiments, the
gateway 724 may
identify the issuer in other ways. Further, in some embodiments, the gateway
724 may maintain
an issuer registration table for each issuer that the gateway is configured to
interact with. The
issuer registration table may indicate the type of the token service provider
that the issuer is
associated with. In some embodiments, the issuer registration table may also
indicate the
communication protocol associated with that type of the token service
provider. In other
embodiments, the gateway 724 may maintain another look up table to determine
the
communication protocol of the type of the token service provider identified
from the issuer
registration table. In some embodiments, the gateway 724 may, additionally or
alternatively, use
the cardholder's account information (e.g., PAN), issuer registration data,
and/or other
information to identify the type of the token service provider and/or the
communication protocol
associated with the identified type of the token service provider.
101021 Therefore, the gateway 724 is configured to communicate with a variety
of token service
providers. To add a new token service provider, only the functionality of the
gateway 724 needs
to be modified to establish communication with the new token service provider.
There is no
need to modify the issuer application 704, the issuer application server 708,
or the issuing host
platform 712. There is also no need to modify the new token service provider
in any way. Thus,
a single gateway (e.g., the gateway 724) is configured to communicate with a
variety token
service providers, while hiding the complexity of communications occurring
between the
gateway and the token service provider 728 from the issuer application 704,
the issuer
application server 708, the issuing host platform 712, and the token service
provider 728.
10103] Upon determining the type of the token service provider (e.g., MDES in
FIG. 7) and the
communication protocol associated with the MDES token service provider, the
gateway 724
sends a request for the list of merchants to the token service provider 728.
In some
embodiments, the gateway 724 may make an API call to the token service
provider 728 to
request the list of merchants. For example, in some embodiments, the gateway
724 may make a
"getEligibleTokenRequestors" API call to the token service provider 728 to
request the list of
-36-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
merchants. In other embodiments, the gateway 724 may make another type of API
call to
request the list of merchants. In some embodiments, the gateway 724 may use
messaging
protocols other than or in addition to API calls to communicate with the token
service provider
728, as well as to request the list of merchants. By making the
"getEligibleTokenRequestors"
API call, the gateway 724 requests the list of merchants that are eligible for
receiving the
selected payment source via push provisioning. Upon receiving the
"getEligibleTokenRequestors" API call from the gateway 724, the token service
provider 728
provides the gateway with the list of merchants at operation 732.
101041 The gateway 724, in some embodiments, may send a follow-up request to
identify those
merchants from the list of merchants to which the selected payment source has
already been
provisioned. In other words, the gateway 724 may identify those merchants that
already have a
token (e.g., a payment token) from the token service provider 728 for the
selected payment
source. In some embodiments, the gateway 724 may send a "search" API call, at
operation 734,
to the token service provider 728 to request the merchants that already have a
token. In other
embodiments, the gateway 724 may use other API calls or other messaging
protocols to make the
request. In some embodiments, the gateway 724 may combine the
"getEligibleTokenRequestors" and the "search" API calls into a single API
call.
10105] At operation 736, the token service provider 728 sends the list of
merchants back to the
gateway 724 that already have a token for the selected payment source from the
token service
provider. The gateway 724 thus receives a first list of merchants (e.g., via
the
"getEligibleTokenRequestors" API call) at the operation 732 including all
merchants that are
eligible for push provisioning the selected payment source and a second list
of merchants (e.g.,
via the "search" API call) at the operation 736 including those merchants that
already have a
token for the selected payment source. The gateway 724 may then combine the
first list of
merchants and the second list of merchants to generate a third list of
merchants. For example, in
some embodiments, the gateway 724 may create the third list of merchants that
includes all of
those merchants that are included in the first list of merchants. Further, for
the merchants that
are included in the second list of merchants, the gateway 724 may include a
notification or
-37-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
indication in the third list of merchants indicating that the selected payment
source has already
been provisioned for those merchants. For example, if the first list of
merchants includes
merchants A, B, and C, and the second list of merchants includes merchant B,
the third list of
merchants may include merchants A, B, and C, with an indication against
merchant B indicating
that merchant B already has a token. This way, the cardholder 702 may easily
identify which
merchants currently do not have a token for the selected payment source.
[0106] The gateway 724 sends the third list of merchants to the issuer
application server 708 at
operation 738. In some embodiments, the gateway 724 may also send the first
list of merchants
and/or the second list of merchants to the issuer application server 708. In
some embodiments,
the gateway 724 and/or the token service provider 728 may associate an asset
identifier with
each merchant in the third list of merchants. In some embodiments, the "asset
identifier" may be
a unique identifier associated with a particular merchant to identify that
merchant. In some
embodiments, if the token service provider 728 returns a merchant that does
not have an asset
identifier associated therewith, the gateway 724 and/or the token service
provider 728 may
assign a new asset identifier to the new merchant. In other embodiments, the
gateway 724 may
include other or additional types of information for one or more merchants in
the third list of
merchants. For each merchant in the third list of merchants, the issuer
application server 708
may determine a logo, button image, or other identifying indicia (e.g., web
address, etc.) and
update the third list of merchants to include the logo, button image, or the
other identifying
indicia. In some embodiments, the issuer application server 708 may determine
that the third list
of merchants includes a new merchant that the issuer application server has
not seen before (and
thus does not have a logo, button image, or other identifying indicia cached
therefor). For
example, in some embodiments, the issuer application server 708 may identify a
new asset
identifier in the third list of merchants.
101071 The issuer application server 708 may send a request back to the
gateway 724 at
operation 740 to obtain the logo, button image, or other identifying indicia
for the merchant(s)
associated with the new asset identifier. In some embodiments, the issuer
application server 708
may make a "Get Asset" API call to the gateway 724 to request the logo, button
image, or other
-38-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
identifying indicia of the merchant associated with the new asset
identifier(s). In some
embodiments, the gateway 724 transmits the request to the token service
provider 728 at
operation 742. In some embodiments, if the gateway 724 has the logo, button
image, or other
identifying indicia information available, the gateway 724 may send that
information to the
issuer application server 708 without asking the token service provider 728.
Upon getting the
request from the gateway 724, the token service provider 728 sends the logo,
button image, or
other identifying indicia information for the merchant(s) associated with new
asset identifier(s)
to the gateway 724 at operation 744, which then forwards that information to
the issuer
application server 708 at operation 746. Thus, the issuer application server
708 communicates
with the token service provider 728 through the gateway 724.
101081 Upon receiving the logo, button image, or other identifying indicia
information from the
gateway 724, the issuer application server 708 may add that information to the
third list of
merchants. The issuer application server 708 then sends the third list of
merchants with the logo,
button image, or other identifying indicia added, to the issuer application
704 at operation 748,
for display to the cardholder 702 (e.g., via the cardholder's client device).
Additionally, the
issuer application 704 sends initializing inputs, at operation 752, to a
software development kit
750 for initiating the push provisioning operation of the selected payment
source. The software
development kit 750 may be considered analogous to the software development
kit 616. In some
embodiments, the initializing inputs may include cardholder data associated
with the cardholder
702 such as the first name, last name, any nickname that the cardholder may
have set in the
issuer application 704, the language (e.g., English, French, etc.) associated
with the cardholder,
country where the cardholder resides, billing address, and any other
information that may be
considered useful or desirable to have. The software development kit 750
acknowledges the
receipt of initializing inputs by sending a reply to the issuer application
704 at operation 754. In
some embodiments, the reply 754 may be a "success" output indicating that the
software
development kit 750 has received the initializing inputs successfully or a
"failure" output
indicating that the software development kit has not received some or all of
the initializing inputs
successfully. If the software development kit 750 sends a "failure" reply, the
issuer mobile
-39-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
application 704 may send the initializing inputs again to the software
development kit. In some
embodiments, the software development kit 750 may perform setback checking,
syntax
checking, and/or other types of authentication to ensure the validity of the
initializing inputs.
101091 The issuer application 704 also receives a selection of a merchant
(referred to herein as a
selected merchant) from the cardholder 702 from the third list of merchants
presented to the
cardholder at operation 756. Although the operation 756 is shown as occurring
after the
operations 752 and 754, in some embodiments, the operations 756 may occur
before or along
with the operations 752/754. In some embodiments, the issuer application 704
may also receive,
along with the selected merchant, the asset identifier associated with the
selected merchant
and/or any other information associated with the selected merchant at the
operation 756. In some
embodiments, the merchants that have the selected payment source already
provisioned may be
disabled in the third list of merchants displayed to the cardholder 702 to
prevent the cardholder
from selecting those merchants. In other embodiments, those merchants may not
be disabled,
but the issuer mobile application 704 may display a notification indicating
that the selected
payment source is already provisioned with those merchants if the cardholder
selects one of
those merchants.
[0110] Upon receiving the selected merchant, the issuer application 704 passes
the selected
merchant, the asset identifier, and any other information associated with the
selected merchant to
the software development kit 750 at operation 758. The software development
kit 750 may
prepare a data package, referred to herein as pass-through data, to send to
the issuer application
704. The pass-through data may also include the cardholder information
received at the
operation 752 as part of the initializing inputs, the device information
(e.g., mobile number) of
the mobile device of the cardholder 702 on which the issuer application 704 is
accessed, the
selected payment source, the selected merchant (and the associated asset
identifier), any other
merchant information (e.g., link to merchant's application ¨ whether mobile or
web), the PAN
associated with the selected payment source, the expiration month and/or year
of the selected
payment source, the as well as any other information that may be needed or
considered desirable
in push provisioning the payment source to the selected merchant.
-40-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
101 1 11 The software development kit 750 transmits the pass-through data to
the issuer
application 704 at operation 760. The issuer mobile application 704 transmits
that pass-through
data to the issuer application server 708 at operation 762. The issuer
application server 708
makes a push provisioning request at operation 764 with the gateway 724. The
push
provisioning request may include the pass-through data. The gateway 724
forwards the push
provisioning request, including the pass-through data, to the token service
provider 728 at
operation 766 via a "pushAccount" API call. In some embodiments, the gateway
724 may
compile (e.g., sort, filter, arrange, etc.) the pass-through data to obtain
push-account data. The
push-account data may include data that the token service provider 728 needs
to push provision
the selected payment source with the selected merchant (e.g., to create a
token for the merchant).
The push-account data and the "pushAccount" API call may be in a format that
the token service
provider 728 understands. Upon receiving the "pushAccount" API call, the token
service
provider 728 may generate a receipt identifier. The receipt identifier may
assume any
configuration and size. In some embodiments, the receipt identifier may
include numbers,
letters, special characters, or a combination thereof The receipt identifier
may serve as an
acknowledgment that the token service provider 728 has received the
"pushAccount" API call
(and the associated push-account data).
101.121 The receipt identifier is sent from the token service provider 728 to
the gateway 724 at
operation 768, from the gateway to the issuer server application 708 at
operation 770, and from
the issuer application server to the issuer application 704 at operation 772.
The issuer
application 704 forwards the receipt identifier to the software development
kit 750 at operation
774. The software development kit 750 sends the receipt identifier to a
merchant server 776 at
operation 778. The merchant server 776 may be considered analogous to the
merchant server
618. To send the receipt identifier to the merchant server 776, in some
embodiments, the
software development kit 750 may redirect the cardholder 702 from the issuer
application 704 to
a merchant application (whether mobile application or web application) on the
client device of
the cardholder through which the process 700 is being performed. The merchant
application
may be considered analogous to the merchant application 612. The merchant
application may be
-41-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
associated with the merchant server 776. In some embodiments, to redirect the
cardholder 702 to
the merchant application (and therefore to the merchant server 776), the
software development
kit 750 may use a uniform resource identifier (URI) such as a Uniform Resource
Locator, etc. In
some embodiments, the software development kit 750 may also include a call
back URI along
with the receipt identifier at the operation 778. The call back URI may be a
URI (e.g., the
Uniform Resource Locator) associated with the issuer application 704 to allow
the merchant
server 776 to send a response back to the issuer application (e.g., redirect
back to the issuer
application from the merchant application).
101.131 Thus, at the operation 778, the merchant server 776 receives the
receipt identifier and the
call back URI from the software development kit 750. In other embodiments, the
software
development kit 750 may send other or additional information to the merchant
server 776. The
merchant server 776 does not receive the cardholder data (e.g., the
initializing inputs), the pass-
through data, the push-account data, etc., thereby maintaining the security
and integrity of that
data. In some embodiments, the cardholder 702 may be required to sign in or
log into the
cardholder account on the merchant application to which the redirecting has
occurred. In some
embodiments, the cardholder 702 may be required to download the merchant
application if the
mobile device does not already have the merchant application installed thereon
or the redirecting
may occur to the web application of the selected merchant.
101141 The merchant server 776 then sends the receipt identifier to the token
service provider
728 along with a tokenize provision request at operation 780. By way of the
tokenize provision
request, the merchant server 776 requests a token from the token service
provider 728 for the
selected payment source associated with the receipt identifier. The token
service provider 728
receives the receipt identifier from the merchant server 776 and compares the
receipt identifier
with the receipt identifier generated at the operations 766 and 768 for
verification. If there is a
match, the token service provider 728 generates a token for the selected
payment source. The
token service provider 712 also notifies the issuing host platform 712 of the
generation of the
token at operation 782. In some embodiments, the token service provider 728
may also include
the token to the issuing host platform 712. The issuing host platform 712 may
make a record of
-42-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
the token and associate the token with the selected payment source and the
selected merchant.
At operation 784, the issuing host platform 712 sends an acknowledgment to the
token service
provider 728. Upon receiving the acknowledgment, the token service provider
728 sends the
token to the merchant server 776 at operation 786, which then redirects back
to the issuer
application 704 at operation 788. The merchant server 776 may also store the
received token and
make the token available to the cardholder 702 in the merchant application for
making payments
for transactions using the merchant application.
10115] The redirection of the operation 788 may be to the call back URI that
was included along
with the receipt identifier at the operation 778. The redirection may include
a reply message
indicating a success or failure of the push provisioning process. In some
embodiments, the
merchant server 776 may send a success message if the merchant server 776
receives the token
from the token service provider 728 successfully. In some embodiments, the
merchant server
776 may send a failure message if the merchant server 776 does not receive the
token from the
token service provider 728 for some reason. In some embodiments, the merchant
server 776
may send other or additional messages to the issuer application 704. The
issuer application 704
transmits the reply message to the software development kit 750 at operation
790 for
interpretation. The software development kit 750 may interpret the reply
message from the
merchant server 776 to determine whether the merchant server 776 successfully
received the
token or not. For example, the software development kit 750 may associate a
"success" message
from the merchant server 776 as meaning that the merchant server has
successfully received the
token. In such cases, the software development kit 750 sends a "success"
message to the issuer
application 704 at operation 792, which then displays the message on the
cardholder's client
device at operation 794. On the other hand, if at the operation 790, the
software development kit
750 receives a "failure" reply message from the issuer application 704, the
software development
kit may associate that message as meaning that the merchant server has not
successfully received
the token from the token service provider 728. In such a case, the software
development kit 750
sends a "failure" message to the issuer mobile application 704 at the
operation 792, which then
displays the message on the cardholder's mobile device at the operation 794.
-43-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
101161 Thus, the process 700 provides an easy, reliable, and convenient
mechanism to a
cardholder to receive a token for a selected merchant via a mobile or web
issuer application for
an MDES token service provider.
10I171 Turning now to FIG. 8, an example swimlane diagram outlining operations
of a process
800 is shown, in accordance with some embodiments of the present disclosure.
The process 800
may be used for push provisioning a payment source to a merchant.
Specifically, the process
800 may be used to push provision the payment source to the merchant such that
the merchant
may obtain a token from a token service provider, and particularly, a VTS
token service
provider. To push provision a payment source to a merchant, a user (e.g.,
cardholder 802) logs
into an issuer application 804 at operation 806. The issuer application 804
may be considered
analogous to the issuer application 614 and may be either a mobile application
or a web
application. The issuer application 804 sends the authentication information
to an issuer
application server 808 at operation 810. The issuer application server 808 may
be considered
analogous to the issuer application server 608. The operations 806 and 810 are
equivalent to the
operations 706 and 710, and therefore, are not described again. The issuer
application server 808
requests a list of payment sources associated with the issuer from an issuing
host platform 812 at
operation 814. The issuing host platform 812 may be considered analogous to
the issuing host
platform 622. The issuing host platform provides the list of payment sources,
which are sent to
the issuer application 804 via the issuer application server 808 at operations
816 and 818 for
display on a client device associated with the cardholder 802. The operations
814-818 are
similar to the operations 714-718, respectively.
101181 At operation 820, the cardholder 802 selects a payment source (e.g.,
selected payment
source) from the list of payment sources similar to the operation 720 and the
selection is sent to
the issuer application 804. The issuer application 804 then makes a request,
at operation 822, for
a list of merchants from the issuer application server 808. The issuer
application server 808
sends the request to a gateway 824 at operation 826. The operations 820, 822,
and 826 are
equivalent to the operations 720, 722, and 726, respectively. The gateway 824
may be
considered analogous to the gateway 606. The gateway 824 sends a request to a
token service
-44-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
provider 828 for the list of merchants at operation 830. In some embodiments,
the token service
provider 828 may be a VTS token service provider. The token service provider
828 may be
considered analogous to the token service provider 604.
10I191 As discussed above, the gateway 824 adopts the communication protocol
for
communication with the token service provider 828 based upon the type of the
token service
provider. Thus, to request the list of merchants (e.g., the first list of
merchants, as discussed
above) from a VTS token service provider (e.g., the token service provider
828), the gateway
824 may format messages in a form accepted by the VTS token service provider.
For example,
the gateway 824 may send a "retrieveNHPProfiles" API call to the token service
provider 828 to
request the list of merchants at the operation 830. The token service provider
828 provides the
list of merchants to the gateway 824 at operation 832. In some embodiments,
the token service
provider 828 may include logo, button image, or other identifying information
with the list of
merchants. The gateway 824 then requests the list of merchants that already
have a token issued
for the selected payment source from the token service provider 828 at
operation 834 (e.g., the
second list of merchants, as discussed above). For example, the gateway 824
may send a
"retreieveTokenInfo" API call to the token service provider 828 at the
operation 834. At
operation 836, the token service provider 828 transmits the second list of
merchants to the
gateway 824, which creates the third list of merchants and sends the third
list of merchants to the
issuer application server 808 at operation 838.
101201 The issuer application server 808 associates each merchant on the third
list of merchants
with the logo, button image, or other identifying information and sends a
request to the gateway
at operation 840 for logo or identifier information for any new asset
identifier identified in the
third list of merchants, as discussed above at the operation 740. The gateway
824 may maintain
a cache of logo, button image, or other identifying information of each
merchant that the
gateway receives from the token service provider 828 at the operation 832. In
some
embodiments, the gateway 824 may receive the logo, button image, or other
identifying
information directly from the respective merchant and store that information
within the cache. In
some embodiments, upon receiving the request from the issuer application
server 808 at the
-45-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
operation 840, the gateway 824 provides the requested logo, button image, or
other identifying
information at operation 842 to the issuer application server. In some
embodiments, the gateway
824 may provide the logo, button image, or other identifying information to
the issuer
application server 808 at the operation 838 when providing the third list of
merchants.
[01211 The issuer application server 808 transmits the third list of merchants
having the logo,
button image, or other identifying information therein to the issuer
application 804 at operation
844, similar to the operation 748. The issuer application 804 displays the
third list of merchants
on the client device of the cardholder 802. The issuer application 804 also
sends the initializing
inputs to a software development kit 846 at operation 848. The software
development kit 846 is
analogous to the software development kit 616. The software development kit
846
acknowledges the receipt of the initializing inputs at operation 850. The
operations 848 and 850
are equivalent to the operations 752 and 754, respectively. The issuer
application 804 also
receives the selected merchant from the cardholder 802 at operation 852,
similar to the operation
756. The issuer application 804 then passes the selected merchant to the
software development
kit 846 at operation 854 similar to the operation 758. The software
development kit 846 prepares
the pass-through data and sends that pass-through data to the issuer
application 808 at operation
856 similar to the operation 760. The issuer application 808 sends the pass-
through data to the
issuer application server 808 at operation 858 and the issuer application
server makes a push
provision request at operation 860 to the gateway 824. The operations 858 and
860 are similar to
the operations 762 and 764, respectively.
[0122) The gateway 824 receives the pass-through data and prepares an
encrypted payload by
encrypting the pass-through data. The gateway 824 encrypts the pass-through
data as discussed
above. The gateway 824 sends the encrypted payload back to the issuer
application server 808 at
operation 862, which then sends the encrypted payload to the issuer
application 804 at operation
864. Thus, instead of sending the receipt identifier as in FIG. 7 with the
MDES token service
provider, the gateway 824 sends the encrypted payload to the issuer
application 804. The issuer
application 804 then passes the encrypted payload to the software development
kit 846 at
operation 866. Since the issuer application 804 is simply transferring the
encrypted payload (as
-46-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
in FIG. 8) or the receipt identifier (as in FIG. 7) to the software
development kit 846, the
complexity of different communication protocols associated with different
token service
providers may be hidden from the issuer application. Further, any time a new
token service
provider is associated with the issuer, the issuer application 804 does not
need to be updated. At
operation 868, the software development kit 846 redirects the cardholder 802
from the issuer
application 804 to a merchant server 870. The merchant server 870 may be
considered
analogous to the merchant server 618. The software development kit 846 may
also send the
encrypted payload to the merchant server 870 as part of the redirection.
101231 The merchant server 870 transfers the encrypted payload to the token
service provider
828 at operation 872 and request validation of the encrypted payload. The
token service provider
828 may decrypt the encrypted payload, as discussed above, using a key to
verify the
authenticity of the encrypted payload. If the token service provider 828 is
able to decrypt the
encrypted payload, the token service provider 828 confirms validation of the
encrypted payload
at operation 874. Upon receiving the confirmation, the merchant server 870
makes a
"provisionedToken" API call to the token service provider 828 to request a
token for the selected
payment source included in the encrypted payload at operation 876. The token
service provider
828 generates a token for the selected payment source and sends the token to
the merchant server
870 and the issuing host platform 812 at operations 878, 880, 882 similar to
the operations 782,
784, and 786, respectively. The merchant server 870 then redirects back to the
issuer application
804 at the callback URI and sends a reply message to the issuer application at
operation 884.
The reply message may be similar to the message described above at the
operation 788. The
issuer application 804 sends the reply message to the software development kit
846 at operation
886, which then interprets the reply message and sends the interpretation
result back to the issuer
application 804 at operation 888 for display to the cardholder on the client
device at operation
890. The operations 886-890 are similar to the operations 790-794,
respectively.
101241 Referring now to FIGS. 9A-9E, example interfaces of push provisioning a
payment
source to a merchant is shown, in accordance with some embodiments of the
present disclosure.
It is to be understood that the shape, size, configuration, orientation,
information, etc. of the
-47-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
various features shown in FIGS. 9A-9E are only examples and not intended to be
limiting in any
way. Similarly, the names, logos, and other information of merchants shown in
the list of
merchants in FIGS. 9A-9E are only an illustrative example and not intended to
be limiting (e.g.,
not intended to be the actual or only list of merchants who can receive a
payment source via push
provisioning). The number of merchants shown in the list are also only an
example. Referring
to FIG. 9A, to push provision a payment source 900 to a merchant, the
cardholder associated
with the payment source may log into an issuer application 902 associated with
the payment
source. For example, if the payment source 900 is issued by First Bank, the
cardholder may log
into the First Bank application on a client device 904. The issuer application
902 may be
analogous to the issuer application 614 and the client device 904 may be
analogous to the client
device 602. The issuer application 902 may be either a mobile application or a
web application.
User interface 906 of the client device 904 shown in FIG. 9A may correspond to
the operation
720 or 820. To push provision the payment source 900 to a merchant, the
cardholder may select
an "add to merchants" option 908. The user may also select to push provision
the payment
source 900 to a pay wallet, as discussed above and further discussed below, by
selecting an "add
to pay wallet" option 910.
101251 Upon selecting the "add to merchants" option 908, a user interface 912
of FIG. 9B may
be presented in the issuer application 902. The user interface 912 may present
a list of merchants
914, as obtained in the operations 722-748 or the operations 822-844. The
cardholder may select
a merchant 916 for push provisioning the payment source 900 to. Upon selecting
the merchant
916, a user interface 918 of FIG. 9C on the client device 904 may be
presented. The user
interface 918 may correspond to the redirecting to the merchant server 776 in
the operation 778
or to the merchant server 870 in the operation 868. Thus, the user interface
918 opens a
merchant application 920 associated with the merchant 916 that the cardholder
selected in FIG.
9B. In some embodiments, the merchant application 920 may require the
cardholder to log in.
In other embodiments, the merchant application 920 may automatically log the
cardholder into
the merchant application.
-48-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
101261 The merchant application 920 may display the payment source 900 that
the cardholder is
attempting to push provision to the merchant 916. The cardholder may confirm
the push
provisioning operation by clicking on an add button 922. When the cardholder
clicks the add
button 922, the operations 780-786 or the operations 872-882 may be performed
in the
background. Upon clicking the add button 922, the cardholder may be directed
to a user
interface 924 of FIG. 9D. The user interface 924 may indicate whether the push
provisioning
operation is successful. For example, the user interface 924 may indicate a
message 926 in the
merchant application 920. The cardholder may confirm completion of the push
provisioning
operation by clicking on a done button 928. Upon clicking on the done button
928, the
operations 788-794 or the operations 884-890 may be performed. Specifically,
the cardholder
may be redirected back to the issuer application 902, as shown in user
interface 930 of FIG. 9E.
101271 The user interface 930 may show the list of merchants 914, including
the merchant 916
that the user just push provisioned the payment source 900 too. The merchant
916 may be
associated with a notification 932 indicating that the payment source 900 has
been push
provisioned to the merchant 916. Thus, the cardholder may easily and
conveniently push
provision a payment source to a merchant without needing to wait for a
physical copy of the
payment source while hiding all the background complexity associated with
varying
communication protocols of various token service providers by virtue of using
the software
development kit 750/the gateway 724 and the software development kit 846/the
gateway 824.
101281 Referring to FIG. 10, an example swimlane diagram outlining operations
of a process
1000 is shown, in accordance with some embodiments of the present disclosure.
The process
1000 may be used for push provisioning a payment source to a pay wallet, and
particularly to an
Apple Pay wallet, using a web application of the issuer application 614. The
process 1000
starts with a cardholder 1002 selecting a payment source at operations 1004-
1014 similar to the
operations 706-720, respectively. Upon receiving the selected payment source
at the operation
1014, an issuer web application 1016 requests a list of pay wallets, at
operation 1018, from an
issuer application server 1020. The issuer web application 1016 may be
considered analogous to
the issuer application 614 and the issuer application server 1020 may be
considered analogous to
-49-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
the issuer application server 608. The issuer application server 1020 forwards
the request to a
gateway 1022 at operation 1024 similar to the operation 726. The gateway 1022
may be
considered analogous to the gateway 606.
10I291 In some embodiments, the gateway 1022 may prepare the list of pay
wallets. In some
embodiments, since there are a limited number of pay wallets, the gateway 1022
may maintain
all the data needed to prepare the list of pay wallets without needing to
request that data from a
token service provider. In other embodiments, the gateway 1022 may request the
list of pay
wallets from a token service provider 1026 similar to the operations 730-736
for an MDES token
service provider or the operations 830-836 for a VTS token service provider.
The token service
provider 1026 may be considered analogous to the token service provider 604.
The gateway
1022 returns the list of pay wallets to the issuer application server 1020 at
operation 1028. In
response, the gateway 1022 receives a request from the issuer application
server 1020 at
operation 1030 for the logo, button image, or other identifying information
for each pay wallet
that the issuer application server 1020 does not have the logo, button image,
or other identifying
information for. The operation 1030 is similar to the operation 840. In some
embodiments, the
gateway 1022 may maintain the logo, button image, or other identifying
information for each pay
wallet. In such cases, the gateway may retrieve the logo, button image, or
other identifying
information and send it back to the issuer application server 1020 at
operation 1032 similar to the
operation 842. In other embodiments, the gateway 1022 may request the logo,
button image, or
other identifying information from the token service provider 1026 similar to
the operations 734
and 736.
101301 In some embodiments, the gateway 1022 may also indicate which pay
wallets already
have tokens for the selected payment source. The issuer application server
1020 may generate a
list of pay wallets (e.g., similar to the third list of merchants but with pay
wallets instead of
merchants) and send that list to the issuer web application 1016 at operation
1034. The issuer
web application 1016, upon receiving the list of pay wallets, sends
initializing inputs to a
software development kit 1036 at operation 1038. The software development kit
1036 may be
considered analogous to the software development kit 616. The operation 1038
is similar to the
-50-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
operation 752. The initializing inputs may include any inputs that may be
needed to provision
the selected payment source to Apple Pay wallet. The initializing inputs may
be provided (e.g.,
via an "initiAddToAppleWallet" call) to the browser of the issuer web
application 1016 to
facilitate pushing the initializing inputs to a software development kit
associated with a wallet
server 1040 associated with Apple Pay wallet at operation 1042. Thus, in some
embodiments,
the initializing inputs may sit in a holding state in the browser of the
issuer web application 1016
before sending to the wallet server 1040. At operations 1044 and 1046, the
issuer web
application 1016 receives a response, via the software development kit 1036,
from the browser of
issuer web application that the initializing inputs have been received.
[01311 At operation 1048, the cardholder 1002 selects a pay wallet, and
particularly Apple Pay
wallet, for provisioning the selected payment source to. The selected pay
wallet (e.g., Apple
Pay wallet) is sent to the issuer web application 1016 at the operation 1048
along with an asset
identifier associated with the selected pay wallet. The issuer web application
1016 sends the
selected pay wallet and the associated asset identifier to the software
development kit 1036 at
operation 1050. At operation 1052, the software development kit 1036 receives
a Java web
token (or another type of identifier) from the wallet server 1040. The Java
web token may be
associated with a current push provisioning session. Although the operations
1038, 1042, and
1048-1052 have been described as occurring in a specific order, in other
embodiments, those
operations may occur in a different order.
101321 The software development kit 1036 passes the Java web token to the
issuer web
application 1016 at operation 1054, which then transmits the Java web token
along with pass-
through data (as discussed above) to the issuer application server 1020 at
operation 1056 to make
a push provisioning request. The issuer application server 1020 forwards the
push provisioning
request along with the Java web token and the pass-through data to the gateway
1022 at
operation 1058. The gateway 1022 may temporarily store all the pass-through
data, including
the Java web token temporarily and acknowledge receipt at operations 1060 and
1062. The
issuer web application 1016 then calls the software development kit 1036 at
operation 1064
similar to the operation 774. The software development kit 1036, at operation
1066, redirects the
-51-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
cardholder 1002 to the web application associated with the wallet server 1040
(e.g., the Apple
pay web page). The redirection may be similar to the operation 778 but to the
wallet server 1040
instead of the merchant server 776. The wallet server 1040 may be similar to
the pay wallet
server 620. Upon being redirected to the pay wallet application associated
with the wallet server
1040, the cardholder 1002 logs into the cardholder's pay wallet account at
operation 1068 using,
for example, their Apple identifier. Upon logging into the wallet server
account, in some
embodiments, the cardholder 1002 may be presented a list of Apple devices
(e.g., mobile devices
(e.g., iPhone), iPad, Apple TV, etc.) on which the selected payment source may
be provisioned
to. In some embodiments, only those Apple devices may be presented that are
suitable for
receiving the selected payment source.
101331 Upon selecting an Apple device for provisioning the selected payment
source to, at
operation 1070, the wallet server 1040 sends the Java web token to the gateway
1022 to request a
target identifier. The gateway 1022 receives the Java web token, matches the
Java web token
with the Java web token receives at the operation 1058, and issues a receipt
identifier upon
finding a match. If there is no match, the gateway 1022 may issue an error
message. The
gateway 1022 sends the receipt identifier back to the wallet server 1040 at
operation 1072. Upon
receiving the receipt identifier, in some embodiments, the wallet server 1040
may send a status
message to the gateway 1022 at operation 1074 to ensure that the current push
provisioning
session is still active. Upon receiving a response from the gateway 1022 at
operation 1076
indicating that the current push provisioning session is still active, the
wallet server 1040
requests the pass-through data from the gateway at operation 1078. In some
embodiments, the
wallet server 1040 may also send the receipt identifier to the gateway 1022.
10134] The gateway 1022 may retrieve the pass-through data that was stored at
the operation
1058 and sends that data to the wallet server 1040 at operation 1080. The
wallet server 1040
sends the pass-through data to the token service provider 1026 at operation
1082 to request a
token (e.g., a payment token) for the selected payment source. The token
service provider 1026
generates a token and sends the token to the wallet server at operations 1084,
1086, and 1088 via
an issuing host platform 1090. The issuing host platform 1090 may be
considered analogous to
-52-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
the issuing host platform 622. The operations 1084-1088 are similar to the
operations 782-786.
Upon receiving the token, the wallet server 1040 redirects back to the issuer
web application
1016 and sends a reply message (e.g., success, failure, etc.) to the software
development kit 1036
at operation 1092, which then interprets the message and sends a result back
to the issuer web
application 1016 at operation 1094 for display to the cardholder 1002 at
operation 1096. The
operations 1094 and 1096 are similar to the operations 792 and 794,
respectively.
[0135] Referring to FIG. 11, an example swimlane diagram outlining operations
of a process
1100 is shown, in accordance with some embodiments of the present disclosure.
The process
1100 may be used for push provisioning a payment source to a pay wallet, and
particularly to a
Google PayTM wallet using a web application of the issuer application 614. The
process 1100
starts with a cardholder 1102 selecting a payment source at operations 1104-
1114 similar to the
operations 1004-1014, respectively. Upon selecting the payment source, the
cardholder 1102
requests a list of pay wallets to select a pay wallet (e.g., Google PayTM
wallet) from at operations
1116-1126 similar to the operations 1018-1034, respectively. An issuer web
application 1128
sends initializing inputs to a software development kit 1130 at operations
1132 and 1134 similar
to the operations 758 and 760. The issuer web application 1128 may be
considered analogous to
the issuer application 614 and the software development kit may be considered
analogous to the
software development kit 616. At operation 1136, the cardholder 1102 selects a
pay wallet (e.g.,
Google PayTM wallet) from the list of pay wallets via the issuer web
application 1128. The
selected pay wallet along with the associated asset identifier is sent to the
software development
kit 1130 at operation 1138, which then redirects the cardholder 1102 to a web
page associated
with a wallet server 1140 of Google PayTM wallet. The wallet server 1140 may
be considered
analogous to the pay wallet server 620.
101361 The cardholder 1102 logs into their Google account using their Google
credentials and
selects a suitable Google device at operation 1142 for provisioning the
selected payment source
to similar to the operation 1068. Upon logging in and selecting a device, the
wallet server 1140
sends a session identifier (or token) to the software development kit 1130 at
operation 1144. The
software development kit 1130 passes on the session identifier along with pass
through data to
-53-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
the issuer web application 1128 at operation 1146. The issuer web application
1128 sends the
pass through data along with the session identifier, at operations 1148 and
1150, to a gateway
1152 via an issuer application server 1154. The gateway 1152 may be considered
analogous to
the gateway 606 and the issuer application server 1154 may be considered
analogous to the
issuer application server 608.
101371 The gateway 1152 encrypts the pass-through data to generate an
encrypted payload
similar to the operation 860 and sends the encrypted payload to the wallet
server 1140 at
operation 1152, which acknowledges receipt at operation 1154. In some
embodiments, upon the
wallet server 1140 acknowledging receipt of the encrypted payload, the gateway
1152 sends a
message (without the encrypted payload) to the software development kit 1130
via the issuer
application server 1154 and the issuer web application 1128 at operations 1156-
1160. The wallet
server 1140 sends the encrypted payload to a token service provider 1162 for
requesting a token
for the selected payment source at operation 1164. The token service provider
1162 may be an
MDES token service provider, a VTS token service provider, or any other token
service provider
similar to the token service provider 604. The token service provider 1162
generates a token and
sends that token to the wallet server 1140 via an issuing host platform 1166
at operations 1168-
1172, as discussed above. The wallet server 1140 generates a reply message
(e.g., success,
failure, etc.) indicating whether the wallet server successfully received the
token or not, and
sends the message to the software development kit 1130 at operation 1174. The
software
development kit 1130 interprets the reply message and sends an interpretation
back to the issuer
web application 1128 at operation 1176 (similar to the operation 1094) for
display to the
cardholder 1102 at operation 1178.
10138] Referring to FIG. 12, an example swimlane diagram outlining operations
of a process
1200 is shown, in accordance with some embodiments of the present disclosure.
The process
1200 may be used for push provisioning a payment source to a pay wallet, and
particularly to a
Samsung Pay wallet, using a web application of the issuer application 614.
The process 1200
starts with a cardholder 1202 selecting a payment source at operations 1204-
1214 similar to the
operations 1004-1014, respectively. Upon selecting the payment source, the
cardholder 1202
-54-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
requests a list of pay wallets to select a pay wallet (e.g., Samsung Pay
wallet) from at
operations 1216-1226 similar to the operations 1018-1034, respectively. An
issuer web
application 1228 sends initializing inputs to a software development kit 1230
at operations 1232
and 1234 similar to the operations 1132 and 1134, respectively. The issuer web
application 1228
may be considered analogous to the issuer application 614 and the software
development kit
1230 may be considered analogous to the software development kit 616. At
operation 1236
similar to the operation 1136, the cardholder 1102 selects a pay wallet (e.g.,
Samsung Pay
wallet) from the list of pay wallets via the issuer web application 1228. The
selected pay wallet
along with the associated asset identifier is sent to the software development
kit 1230 at
operation 1238 (similar to the operation 1138).
101391 The software development kit 1230 prepares pass-through data and sends
that pass-
through data to the issuer web application 1228 at operation 1240, which then
makes a push
provisioning request to a gateway 1242 via an issuer application server 1244
at operations 1246
and 1248. The issuer application server 1244 may be considered analogous to
the issuer
application server 608 and the gateway 1242 may be considered analogous to the
gateway 606.
The gateway 1242 may hold on to the pass-through data temporarily and send a
receipt identifier
to a wallet server (e.g., Samsung wallet server) 1250 at operation 1252. The
wallet server 1250,
may be considered analogous to the pay wallet server 620, may send an
acknowledgment
message to the gateway at operation 1254. The gateway 1242 also sends a
message to the
software development kit 1230 via the issuer application server 1244 and the
issuer web
application 1230 at operations 1256, 1258, and 1260 indicating the start of
the push provisioning
process. The software development kit 1230 redirects the cardholder 1202 to a
pay wallet
application associated with the wallet server 1250 and sends the receipt
identifier to the wallet
server.
101401 At operation 1264, upon being redirected to the pay wallet application
of the wallet
server 1250, the cardholder 1202 logs into their Samsung account and selects a
suitable device
for push provisioning the selected payment source to, similar to the operation
1068. Upon
selecting a device, the wallet server 1250 sends the receipt identifier to the
gateway 1242 at
-55-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
operation 1266. The gateway 1242 compares the receipt identifier received from
the wallet
server 1250 at the operation 1266 with the receipt identifier sent at the
operation 1252 to
determine a match. If the gateway 1242 determines that the receipt identifier
received from the
wallet server 1250 at the operation 1266 matches with the receipt identifier
sent at the operation
1252, and that the current session is still active, the gateway retrieves the
pass-through data and
sends the pass-through data to the wallet server at operation 1268. In some
embodiments, the
gateway 1242 may encrypt the pass-through data before sending to the wallet
server 1250.
101411 The wallet server 1250 sends the pass-through data to a token service
provider 1270 at
operation 1272. The token service provider 1270 may be an MDES token service
provider, a
VTS token service provider, or any other token service provider similar to the
token service
provider 604. The token service provider 1270 generates a token and sends that
token to the
wallet server 1250 via an issuing host platform 1274 at operations 1276-1280,
as discussed
above. The issuing host platform 1274 may be considered analogous to the
issuing host platform
622. The wallet server 1250 generates a message (e.g., success, failure, etc.)
indicating whether
the wallet server successfully received the token or not, and sends the
message to the software
development kit 1230 at operation 1282. The software development kit 1230
interprets the
message and sends an interpretation back to the issuer web application 1228 at
operation 1284
(similar to the operation 1094) for display to the cardholder 1202 at
operation 1286. In some
embodiments, the wallet server 1250 may also send a status message to the
gateway 1242 at
operation 1288 to indicate whether the wallet server successfully received the
token or not. The
gateway 1242 may send a response back at operation 1290.
101421 Turning now to FIGS. 13A-13E, example interfaces of push provisioning a
payment
source to a pay wallet using an issuer's web application is shown, in
accordance with some
embodiments of the present disclosure. It is to be understood that the shape,
size, configuration,
orientation, information, etc. of the various features shown in FIGS. 13A-13E
are only examples
and not intended to be limiting in any way. Similarly, the names, logos, and
other information
shown in FIGS. 13A-13E are only an example and not intended to be limiting.
Although FIGS.
-56-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
13A-13E are directed to push provisioning to Apply Pay , similar operations
may be performed
for Google PayTM and Samsung Pay .
10143] To push provision a payment source issued by an issuer to a pay wallet,
the cardholder
logs into an issuer web application 1300 associated with the issuer on a
client device 1302. The
cardholder may access the issuer web application 1300 by opening a web browser
on the client
device 1302 and entering URI information (e.g., the Uniform Resource Locator
(URL)) of the
issuer into the web browser. For example, if the issuer is First Bank, the
cardholder may enter
the web address of First Bank into a web browser to be taken to First Bank's
website. It is to be
understood that First bank is only an example and not intended to be limiting
in any way. In
other embodiments, the description applies to other issuers as well. On the
issuer's website, the
cardholder may log into their cardholder account similar to the operation
1004. Upon
successfully logging into the cardholder account on the issuer web
application, the cardholder
may be presented with a list of accounts 1304 of the operation 1012 in a user
interface 1306 of
FIG. 13A.
101441 The cardholder may select one account from the list of accounts 1304
for push
provisioning by clicking on an "add to Apple wallet" button. For example, in
some
embodiments, to select debit card associated with account 1308 for push
provisioning, the
cardholder may select button 1310. In the user face 1306, the selection of the
payment source
and the selection of the pay wallet occurs by way of the select button 1310.
In other
embodiments, the cardholder may first select a payment source (e.g., account)
and then click on
another button to start the push provisioning process. Upon clicking on the
select button 1310 to
start the push provisioning process, the cardholder may be directed to a user
interface 1312 of
FIG. 13B. The user interface 1312 may redirect the cardholder to a web
application 1314
associated with Apple server as in the operation 1066. The cardholder may be
required to log in
to their Apple account and select an Apple device. Upon selecting an Apple
device, the
cardholder may click on a next button 1316 to open a user interface 1318 of
FIG. 13C. The user
interface 1318 may present terms and conditions to the cardholder to accept.
The cardholder
-57-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
may accept the terms and conditions by clicking on an agree button 1320. In
other embodiments,
the cardholder may be presented other or additional user interfaces.
[01451 Upon clicking on the agree button 1320, the cardholder may be directed
to a user
interface 1322 of FIG. 13D where the cardholder may get a message 1324
indicating whether the
push provisioning process is successful. The message 1324 may correspond to
the operation
1096. When the cardholder clicks on the agree button 1320, the operations 1070-
1094 may be
performed in the background. Upon clicking on a done button 1326, the
cardholder may be
directed to a user interface 1328 of FIG. 13E. The user interface 1328 takes
the cardholder back
to the issuer web application 1300 and shows a message 1330 indicating that
the selected
payment source has been push provisioned to the pay wallet.
101461 The methods, systems, and devices discussed above are examples. Various
configurations may omit, substitute, or add various procedures or components
as appropriate.
For instance, in alternative configurations, the methods may be performed in
an order different
from that described, and/or various stages may be added, omitted, and/or
combined. Also,
features described with respect to certain configurations may be combined in
various other
configurations. Different aspects and elements of the configurations may be
combined in a
similar manner. Also, technology evolves and, thus, many of the elements are
examples and do
not limit the scope of the disclosure or claims.
[0147] Specific details are given in the description to provide a thorough
understanding of
exemplary configurations including implementations. However, configurations
may be practiced
without these specific details. For example, well-known circuits, processes,
algorithms,
structures, and techniques have been shown without unnecessary detail in order
to avoid
obscuring the configurations. This description provides example configurations
only, and does
not limit the scope, applicability, or configurations of the claims. Rather,
the preceding
description of the configurations will provide those skilled in the art with
an enabling description
for implementing described techniques. Various changes may be made in the
function and
arrangement of elements without departing from the spirit or scope of the
disclosure.
-58-
CA 03220470 2023-11-16
WO 2022/245343 PCT/US2021/033110
101481 Also, configurations may be described as a process which is depicted as
a flow diagram
or block diagram. Although each may describe the operations as a sequential
process, many of
the operations can be performed in parallel or concurrently. In addition, the
order of the
operations may be rearranged. A process may have additional steps not included
in the figure.
Furthermore, examples of the methods may be implemented by hardware, software,
firmware,
middleware, microcode, hardware description languages, or any combination
thereof. When
implemented in software, firmware, middleware, or microcode, the program code
or code
segments to perform the necessary tasks may be stored in a non-transitory
computer-readable
medium such as a storage medium. Processors may perform the described tasks.
[01491 Having described several example configurations, various modifications,
alternative
constructions, and equivalents may be used without departing from the spirit
of the disclosure.
For example, the above elements may be components of a larger system, wherein
other rules
may take precedence over or otherwise modify the application of the
technology. Also, a
number of steps may be undertaken before, during, or after the above elements
are considered.
Accordingly, the above description does not bind the scope of the claims.
[01501 As used herein and in the appended claims, the singular forms "a",
"an", and "the"
include plural references unless the context clearly dictates otherwise. Thus,
for example,
reference to "a user" includes a plurality of such users, and reference to
"the processor" includes
reference to one or more processors and equivalents thereof known to those
skilled in the art, and
so forth.
10151] Also, the words "comprise", "comprising", "contains", "containing",
"include",
"including", and "includes", when used in this specification and in the
following claims, are
intended to specify the presence of stated features, integers, components, or
steps, but they do
not preclude the presence or addition of one or more other features, integers,
components, steps,
acts, or groups.
-59-