Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 1 -
Article for use in a non-combustible aerosol provision system
Technical field
The present invention relates to an article for use in a non-combustible
aerosol
provision system, to a system comprising the article and a non-combustible
aerosol
provision device.
Background
Certain tobacco industry products produce an aerosol during use, which is
inhaled by a
user. For example, tobacco heating devices heat an aerosol generating
substrate such
as tobacco to form an aerosol by heating, but not burning, the substrate. Such
tobacco
industry products commonly include mouthpieces through which the. aerosol
passes to
reach the user's mouth.
Summary
In accordance with some embodiments described herein, there is provided an
article
for use in an aerosol provision system, comprising sections of aerosol-
generating
material coaxially aligned along a longitudinal axis of the article, wherein a
cross
sectional area of each section transverse to the longitudinal axis is
different.
In embodiments, the article may comprise a distal end for insertion into an
aerosol-
generating device, and said sections may comprise first and second sections.
The first
section can then be at the distal end and have a cross-sectional area smaller
than the
cross-sectional area of the second section remote from said distal end.
The first and/or second section may have a uniform cross-sectional area in a
direction
extending along the. longitudinal axis.
The first section may extend along the longitudinal axis for a distance
greater than the
distance that the second section extends along the longitudinal axis.
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 2 -
The first and second sections of aerosol-generating material may each be
formed from a
different type of aerosol-generating material. Alternatively, the first and
second
sections may be formed from the same aerosol-generating material.
The second section of aerosol generating material may comprise a cavity or
opening
and the first section of aerosol-generating material may be received within,
and extend
from, said cavity or opening.
The article may comprise a wrapping material wrapping said first and/or second
ro sections of aerosol generating material.
The wrapping material wrapping the first section may be different to the
wrapping
material wrapping the second section.
The wrapping material may comprise a ferrous and/or heat-conductive material.
The wrapping material may be configured to be conductively, or inductively,
heated to
heat the aerosol-generating material.
At least a part of the wrapping material may be permeable to air.
The wrapping material may be a mesh, may be perforated or may have openings.
Each of the first and second sections of aerosol generating material may have
a circular
cross section.
The article may comprise a mouth end remote from said aerosol-generating
material,
the mouth end being configured to be placed between the lips of a user when
the
aerosol-generating material inserted into a non-combustible aerosol provision
device.
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 3 -
A cooling segment may be located between the aerosol-generating material and
the
mouth end.
A filtration segment may be located between the cooling segment and the mouth
end.
In accordance with some other embodiments described herein, there is provided
a
system comprising a non-combustible aerosol provision device, and an article
comprising sections of aerosol-generating material coaxially aligned along a
longitudinal axis of the article, wherein the cross sectional area of each
section
io transverse to the longitudinal axis is different, and wherein
the device comprises a
article receiving cavity and a heater surrounding said cavity such that, when
the article
is received the cavity, the heater is adjacent at least one of said sections.
The sections of aerosol-generating material may comprise first and second
sections and
15 the article receiving cavity may have a first portion to receive
the first section and a
second portion to receive the second section, said second portion being larger
than the
first portion.
The article may comprise a wrapper and the heater can be configured to heat
the
20 aerosol-generating material by heating the wrapper.
The heating element may comprise a ferrous and/or heat-conductive material to
conduct heat from the heater to the aerosol-generating material.
25 The wrapper may be a susceptor, and the heater may comprise a
varying magnetic field
generator to inductively heat the wrapper.
The sections of aerosol generating material may be cylindrical.
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 4 -
The heater may comprise a tubular body such that the article receiving cavity
is formed
in said tubular body.
The heater may comprise a first part that is positioned alongside the first
section of the
,5 aerosol-generating material when the article is received in the aerosol-
generating
device.
The second section may have a distal end face and the first part of the heater
may be
adjacent to said distal end face.
The heater may comprise a second part positioned alongside the second section
of the
aerosol-generating material when the article is received in the device.
The first and second parts may be configured to heat the first and second
sections,
respectively, to different temperatures.
The first and second parts may be configured to heat the first and second
sections
consecutively.
The first and second parts may be configured such that there is a delay
between the
heating of one section relative to the heating of the other section.
Brief Description of the Drawings
Embodiments of the invention will now be described, by way of example only,
with
reference to accompanying drawings, in which:
Figures 1 shows a longitudinal cross-section through an article for use with a
non-
combustible aerosol provision device according to an embodiment of the
invention,
Figure 2 is a cross sectional view of a non-combustible aerosol provision
device into
which the article of Figure 1 may be inserted;
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 5 -
Figure 3 is a simplified schematic of the components within the housing of the
aerosol
provision device shown in Figure 2; and
Figure 4 is a cross sectional view of an aerosol-provision system comprising
the non-
combustible aerosol provision device of Figure 2 and the article of Figure 1
inserted into
it.
Detailed description
As used herein, the term "delivery system" is intended to encompass systems
that
deliver at least one substance to a user, and includes:
combustible aerosol provision systems, such as cigarettes, cigarillos, cigars,
and
tobacco for pipes or for roll-your-own or for make-your-own cigarettes
(whether based
on tobacco, tobacco derivatives, expanded tobacco, reconstituted tobacco,
tobacco
substitutes or other smokable material);
non-combustible aerosol provision systems that release compounds from an
aerosol-generating material without combusting the aerosol-generating
material, such
as electronic cigarettes, tobacco heating products, and hybrid systems to
generate
aerosol using a combination of aerosol-generating materials; and
aerosol-free delivery systems that deliver the at least one substance to a
user
orally, nasally, transdermally or in another way without forming an aerosol,
including
but not limited to, lozenges, gums, patches, articles comprising inhalable
powders, and
oral products such as oral tobacco which includes snus or moist snuff, wherein
the at
least one substance may or may not comprise nicotine.
According to the present disclosure, a "non-combustible" aerosol provision
system is
one where a constituent aerosol-generating material of the aerosol provision
system (or
component thereof) is not combusted or burned in order to facilitate delivery
of at least
one substance to a user.
In some embodiments, the delivery system is a non-combustible aerosol
provision
system, such as a powered non-combustible aerosol provision system.
In some embodiments, the non-combustible aerosol provision system is an
electronic
cigarette, also known as a vaping device or electronic nicotine delivery
system (END),
although it is noted that the presence of nicotine in the aerosol-generating
material is
not a requirement.
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 6 -
In some embodiments, the non-combustible aerosol provision system is an
aerosol-
generating material heating system, also known as a heat-not-burn system. An
example of such a system is a tobacco heating system.
In some embodiments, the non-combustible aerosol provision system is a hybrid
system to generate aerosol using a combination of aerosol-generating
materials, one or
a plurality of which may be heated. Each of the aerosol-generating materials
may be,
for example, in the form of a solid, liquid or gel and may or may not contain
nicotine.
In some embodiments, the hybrid system comprises a liquid or gel aerosol-
generating
io material and a solid aerosol-generating material. The solid aerosol-
generating material
may comprise, for example, tobacco or a non-tobacco product.
Typically, the non-combustible aerosol provision system may comprise a non-
combustible aerosol provision device, and a consumable for use with the non-
combustible aerosol provision device.
The disclosure relates to consumables comprising aerosol-generating material
and
configured to be used with non-combustible aerosol provision devices. These
consumables are sometimes referred to as articles throughout the disclosure.
The terms 'upstream' and 'downstream' used herein are relative terms defined
in
relation to the direction of mainstream aerosol drawn through an article or
device in
use. Reference to the 'distal end' refers to an upstream end of the device,
whereas
'proximal end' refers to the downstream end of the device.
In some embodiments, the non-combustible aerosol provision system, such as a
non-
combustible aerosol provision device thereof, may comprise a power source and
a
controller. The power source may, for example, be an electric power source or
an
exothermic power source. In some embodiments, the exothermic power source
comprises a carbon substrate which may be energised so as to distribute power
in the
form of heat to an aerosol-generating material or to a heat transfer material
in
proximity to the exothermic power source.
In some embodiments, the non-combustible aerosol provision system comprises an
area for receiving the consumable, an aerosol generator, an aerosol generation
area, a
housing, a mouthpiece, a filter and/or an aerosol-modifying agent.
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 7 -
In some embodiments, the consumable for use with the non-combustible aerosol
provision device may comprise aerosol-generating material or and aerosol-
generating
substrate, an aerosol-generating material storage area, an aerosol-generating
material
transfer component, an aerosol generator, an aerosol generation area, a
housing, a
wrapper, a filter, a mouthpiece, and/or an aerosol-modifying agent.
The consumable comprises a substance to be delivered. The substance to be
delivered
is an aerosol-generating material. As appropriate, the material may comprise
one or
io more active constituents, one or more flavours, one or more aerosol-
former materials,
and/or one or more other functional materials.
In some embodiments, the substance to be delivered comprises an active
substance.
The active substance as used herein may be a physiologically active material,
which is a
material intended to achieve or enhance a physiological response. The active
substance
may for example be selected from nutraceuticals, nootropics, psychoactives.
The active
substance may be naturally occurring or synthetically obtained. The active
substance
may comprise for example nicotine, caffeine, taurine, theine, vitamins such as
B6 or
B12 or C, melatonin, cannabinoids, or constituents, derivatives, or
combinations
thereof. The active substance may comprise one or more constituents,
derivatives or
extracts of tobacco, cannabis or another botanical.In some embodiments, the
active
substance comprises nicotine. In some embodiments, the active substance
comprises
caffeine, melatonin or vitamin B12.
As noted herein, the active substance may comprise or be derived from one or
more
botanicals or constituents, derivatives or extracts thereof. As used herein,
the term
"botanical" includes any material derived from plants including, but not
limited to,
extracts, leaves, bark, fibres, stems, roots, seeds, flowers, fruits, pollen,
husk, shells or
the like. Alternatively, the material may comprise an active compound
naturally
existing in a botanical, obtained synthetically. The material may be in the
form of
liquid, gas, solid, powder, dust, crushed particles, granules, pellets,
shreds, strips,
sheets, or the like. Example botanicals are tobacco, eucalyptus, star anise,
hemp, cocoa,
cannabis, fennel, lemongrass, peppermint, spearmint, rooibos, chamomile, flax,
ginger,
ginkgo biloba, hazel, hibiscus, laurel, licorice (liquorice), matcha, mate,
orange skin,
papaya, rose, sage, tea such as green tea or black tea, thyme, clove,
cinnamon, coffee,
aniseed (anise), basil, bay leaves, cardamom, coriander, cumin, nutmeg,
oregano,
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 8 -
paprika, rosemary, saffron, lavender, lemon peel, mint, juniper, elderflower,
vanilla,
wintergreen, beefsteak plant, curcuma, turmeric, sandalwood, cilantro,
bergamot,
orange blossom, myrtle, cassis, valerian, pimento, mace, damien, marjoram,
olive,
lemon balm, lemon basil, chive, carvi, verbena, tarragon, geranium, mulberry,
ginseng,
theanine, theacrine, maca, ashwagandha, damiana, guarana, chlorophyll, baobab
or
any combination thereof. The mint may be chosen from the following mint
varieties:
Mentha Arventis, Mentha c.v.,Mentha niliaca, Mentha piperita, Mentha piperita
citrata
c.v.,Mentha piperita c.v, Mentha spicata crispa, Mentha cardifolia, Memtha
longifolia,
Mentha suaveolens variegata, Mentha pulegium, Mentha spicata c.v. and Mentha
suaveolens.
In some embodiments, the active substance comprises or is derived from one or
more
botanicals or constituents, derivatives or extracts thereof and the botanical
is tobacco.
In some embodiments, the active substance comprises or derived from one or
more
botanicals or constituents, derivatives or extracts thereof and the botanical
is selected
from eucalyptus, star anise, cocoa and hemp.
In some embodiments, the active substance comprises or derived from one or
more
botanicals or constituents, derivatives or extracts thereof and the botanical
is selected
from rooibos and fennel.
In some embodiments, the substance to be delivered comprises a flavour.
As used herein, the terms "flavour" and "flavourant" refer to materials which,
where
local regulations permit, may be used to create a desired taste, aroma or
other
somatosensorial sensation in a product for adult consumers. They may include
naturally occurring flavour materials, botanicals, extracts of botanicals,
synthetically
obtained materials, or combinations thereof (e.g., tobacco, cannabis, licorice
(liquorice), hydrangea, eugenol, Japanese white bark magnolia leaf, chamomile,
fenugreek, clove, maple, matcha, menthol, Japanese mint, aniseed (anise),
cinnamon,
turmeric, Indian spices, Asian spices, herb, wintergreen, cherry, berry, red
berry,
cranberry, peach, apple, orange, mango, clementine, lemon, lime, tropical
fruit, papaya,
rhubarb, grape, durian, dragon fruit, cucumber, blueberry, mulberry, citrus
fruits,
Drambuie, bourbon, scotch, whiskey, gin, tequila, rum, spearmint, peppermint,
lavender, aloe vera, cardamom, celery, cascarilla, nutmeg, sandalwood,
bergamot,
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 9 -
geranium, khat, naswar, betel, shisha, pine, honey essence, rose oil, vanilla,
lemon oil,
orange oil, orange blossom, cherry blossom, cassia, caraway, cognac, jasmine,
ylang-
ylang, sage, fennel, wasabi, piment, ginger, coriander, coffee, hemp, a mint
oil from any
species of the genus Mentha, eucalyptus, star anise, cocoa, lemongrass,
rooibos, flax,
ginkgo biloba, hazel, hibiscus, laurel, mate, orange skin, rose, tea such as
green tea or
black tea, thyme, juniper, elderflower, basil, bay leaves, cumin, oregano,
paprika,
rosemary, saffron, lemon peel, mint, beefsteak plant, curcuma, cilantro,
myrtle, cassis,
valerian, pimento, mace, damien, marjoram, olive, lemon balm, lemon basil,
chive,
carvi, verbena, tarragon, limonene, thymol, camphene), flavour enhancers,
bitterness
io receptor site blockers, sensorial receptor site activators or
stimulators, sugars and/or
sugar substitutes (e.g., sucralose, acesulfame potassium, aspartame,
saccharine,
cyclamates, lactose, sucrose, glucose, fructose, sorbitol, or mannitol), and
other
additives such as charcoal, chlorophyll, minerals, botanicals, or breath
freshening
agents. They may be imitation, synthetic or natural ingredients or blends
thereof. They
may be in any suitable form, for example, liquid such as an oil, solid such as
a powder,
or gas.
In some embodiments, the flavour comprises menthol, spearmint and/or
peppermint.
In some embodiments, the flavour comprises flavour components of cucumber,
blueberry, citrus fruits and/or redberry. In some embodiments, the flavour
comprises
eugenol. In some embodiments, the flavour comprises flavour components
extracted
from tobacco. In some embodiments, the flavour comprises flavour components
extracted from cannabis.
In some embodiments, the flavour may comprise a sensate, which is intended to
achieve a somatosensorial sensation which are usually chemically induced and
perceived by the stimulation of the fifth cranial nerve (trigeminal nerve), in
addition to
or in place of aroma or taste nerves, and these may include agents providing
heating,
cooling, tingling, numbing effect. A suitable heat effect agent may be, but is
not limited
to, vanillyl ethyl ether and a suitable cooling agent may be, but not limited
to
eucolyptol, WS-3.
An aerosol-generating material or substrate is a material that is capable of
generating
aerosol, for example when heated, irradiated or energized in any other way. An
aerosol-generating material may be in the form of a solid, liquid or gel which
may or
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 10 -
may not contain an active substance and/or flavourants. The aerosol-generating
material is incorporated into an article for use in the aerosol-generating
system.
As used herein, the term "tobacco material" refers to any material comprising
tobacco
or derivatives or substitutes thereof. The tobacco material may be in any
suitable form.
The term "tobacco material" may include one or more of tobacco, tobacco
derivatives,
expanded tobacco, reconstituted tobacco or tobacco substitutes. The tobacco
material
may comprise one or more of ground tobacco, tobacco fibre, cut tobacco,
extruded
tobacco, tobacco stem, tobacco lamina, reconstituted tobacco and/or tobacco
extract.
A consumable is an article comprising or consisting of aerosol-generating
material, part
or all of which is intended to be consumed during use by a user. A consumable
may
comprise one or more other components, such as an aerosol-generating material
storage area, an aerosol-generating material transfer component, an aerosol
generation
area, a housing, a wrapper, a mouthpiece, a filter and/or an aerosol-modifying
agent. A
consumable may also comprise a wrapper heatable by electrical conduction, or
the
wrapper may be a susceptor to enable the aerosol-generating material to be
heated
inductively.
A susceptor is a material that is heatable by penetration with a varying
magnetic field,
such as an alternating magnetic field. The susceptor may be an electrically-
conductive
material, so that penetration thereof with a varying magnetic field causes
induction
heating of the heating material. The heating material may be magnetic
material, so that
penetration thereof with a varying magnetic field causes magnetic hysteresis
heating of
the heating material. The susceptor may be both electrically-conductive and
magnetic,
so that the susceptor is heatable by both heating mechanisms. The device that
is
configured to generate the varying magnetic field is referred to as a magnetic
field
generator, herein.
An aerosol-modifying agent is a substance, typically located downstream of the
aerosol
generation area, that is configured to modify the aerosol generated, for
example by
changing the taste, flavour, acidity or another characteristic of the aerosol.
The aerosol-
modifying agent may be provided in an aerosol-modifying agent release
component
that is operable to selectively release the aerosol-modifying agent.
The aerosol-modifying agent may, for example, be an additive or a sorbent. The
aerosol-modifying agent may, for example, comprise one or more of a
flavourant, a
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 11 -
colourant, water, and a carbon adsorbent. The aerosol-modifying agent may, for
example, be a solid, a liquid, or a gel. The aerosol-modifying agent may be in
powder,
thread or granule form. The aerosol-modifying agent may be free from
filtration
material.
An aerosol-generating device is an apparatus configured to cause aerosol to be
generated from the aerosol-generating material. The aerosol generating device
comprises a heater configured to subject the aerosol-generating material to
heat
energy, so as to release one or more volatiles from the aerosol-generating
material to
_//) form an aerosol.
The filamentary tow material described herein can comprise cellulose acetate
fibre tow.
The filamentary tow can also be formed using other materials used to form
fibres, such
as polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH), polylactic acid (PLA), polycaprolactone (PCL),
poly(1-4
butanediol succinate) (PBS), poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)(PBAT),
starch
based materials, cotton, aliphatic polyester materials and polysaccharide
polymers or a
combination thereof. The filamentary tow may be plasticised with a suitable
plasticiser
for the tow, such as triacetin where the material is cellulose acetate tow, or
the tow may
be non-plasticised. The tow can have any suitable specification, such as
fibres having a
'Y' shaped or other cross section such as 'X' shaped, filamentary denier
values between
2.5 and 15 denier per filament, for example between 8.o and 11.o denier per
filament
and total denier values of 5,000 to 50,000, for example between 10,000 and
40,000.
In the figures described herein, like reference numerals are used to
illustrate equivalent
features, articles or components.
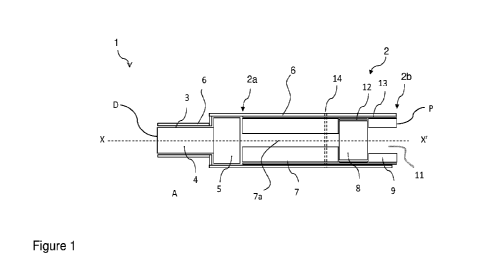
Figure 1 is a longitudinal cross-sectional side view of a non-combustible
aerosol-
generating article 1 for use in an aerosol delivery system 200 that includes
an aerosol
delivery device too (see Figures 2 to 4).
The article 1 has an upstream or distal end 'D' and a downstream or proximal
end '13'.
The proximal end P comprises a mouthpiece 2, and the distal end D comprises an
aerosol-generating substrate or material 3, connected to the mouthpiece 2. In
the
present example, the aerosol generating substrate comprises a source of
aerosol-
generating material 3 in the form of a two rod-like sections coaxially aligned
along the
longitudinal axis X-X of the article 1. The sections of aerosol-generating
material 3
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 12 -
comprises a first section 4 at the distal end D and a second section 5
downstream of the
first section 4. The first section 4 has a cross-sectional area, measured in a
direction
perpendicular to the longitudinal axis, which is less than a corresponding
cross-
sectional area of the second section 5.
Each section 4, 5 of the aerosol-generating material 3 may be cylindrical, in
which case
the diameter of the first section 4 is less than the diameter of the second
section 5. The
sections 4, 5 may also be of other shapes, and each section 4, 5 may have a
shape that
differs from the shape of the other section 4, 5. The two sections 4, 5 may
also be of
io different lengths, with the first section 4 being longer than
the second section 5 as
illustrated, although the sections 4, 5 may also be of the same length.
The first and second sections 4, 5 are adjacent to each other and may be in
abutting
relationship. However, the second section 5 may be provided with a recess or
hole (not
shown) extending partially or fully through it coaxial with the longitudinal
axis X-X'. In
this case, the first section 4 may extend fully or partly into the recess or
hole in the
second section 5 to connect the first and second sections 4, 5 together. The
first section
4 may be a snug or interference fit in the second section 5 such that once the
first
section 4 has been inserted into the second section 5, the sections 4, 5 are
held together
unless pulled apart.
Each section 4, 5 may be formed from the same or a different aerosol-
generating
material 3.
The aerosol-generating material 3 of one or both sections 4, 5 may comprise a
plurality
of strands or strips of aerosol-generating material 3. For example, the
aerosol-
generating material 3 may comprise a plurality of strands or strips of an
aerosolisable
material and/or a plurality of strands or strips of an amorphous solid.
The plurality of strands or strips of aerosol-generating material 3 may be
aligned within
the aerosol-generating section such that their longitudinal dimension is in
parallel
alignment with the longitudinal axis, X-X' of the article 1. Alternatively,
the strands or
strips may generally be arranged such that their longitudinal dimension
aligned is
transverse to the longitudinal axis of the article 1.
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 13 -
In the present example, the second section 5 of the rod of aerosol-generating
material 3
has a circumference of about 22.7 mm. In alternative embodiments, the rod of
aerosol-
generating material 3 may have any suitable circumference, for example between
about
20 mm and about 26 mm. The first section 4 has a circumference which is less
than the
circumference of the second section 5.
One or both sections 4, 5 may be wrapped by a wrapper 6. In the present
example, the
wrapper 6 is a moisture impermeable wrapper.
io As shown in Figure 1, the article 1 also comprises a mouthpiece 2
including a cooling
section 7, also referred to as a cooling element 7, positioned immediately
downstream
of and adjacent to the second section 5 of the aerosol-generating material 3.
In the
present example, the cooling section 7 is in an abutting relationship with the
second
section 5 of the aerosol-generating material 3, and the second section 5 has
the same
overall diameter as the cooling section 7. The mouthpiece 2 also includes, in
the present
example, a body of material 8 downstream of the cooling section 7, and a
hollow
tubular element 9 downstream of the body of material 8, at the mouth end 2 of
the
article 1.
The cooling section 7 comprises a hollow channel 7a, having an internal
diameter of
between about 1 mm and about 4 mm, for example between about 2 mm and about 4
mm. In the present example, the hollow channel 7a has an internal diameter of
about 3
mm. The hollow channel 7a extends along the full length of the cooling section
7. In the
present example, the cooling section 7 comprises a single hollow channel 7a.
In
alternative embodiments, the cooling section 7 can comprise multiple channels,
for
example, 2, 3 or 4 channels. In the present example, the single hollow channel
7a is
substantially cylindrical, although in alternative embodiments, other channel
geometries/cross-sections may be used. The hollow channel 7a can provide a
space into
which aerosol drawn into the cooling section 7 can expand and cool down. In
all
embodiments, the cooling section 7 is configured to limit the cross-sectional
area of the
hollow channel/s 7a, to limit tobacco displacement into the cooling section 7,
in use.
The cooling section 7 can have a wall thickness in a radial direction. The
wall thickness
of the cooling section 7, for a given outer diameter of cooling section 7,
defines the
internal diameter for the channel 7a surrounded by the walls of the cooling
section 7.
The cooling section 7 can have a wall thickness of at least about 1.5 mm and
up to about
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 14-
2 mm. In the present example, the cooling section 7 has a wall thickness of
about 2
mm.
The cooling section 7 is formed from filamentary tow. Other constructions can
be used,
such as a plurality of layers of paper which are parallel wound, with butted
seams, to
form the cooling section 7; or spirally wound layers of paper, cardboard
tubes, tubes
formed using a papier-mâché type process, moulded or extruded plastic tubes or
similar. The cooling section 7 is manufactured to have a rigidity that is
sufficient to
withstand the axial compressive forces and bending moments that might arise
during
manufacture and whilst the article 1 is in use.
The wall material of the cooling section 7 can be relatively non-porous, such
that at
least 90% of the aerosol generated by the aerosol generating material 3 passes
longitudinally through the one or more hollow channels 7a rather than through
the wall
material of the cooling section 7. For instance, at least 92% or at least 95%
of the
aerosol generated by the aerosol generating material 3 can pass longitudinally
through
the one or more hollow channels 7a.
In some examples, the mouthpiece 2 comprises a cavity 11 having an internal
volume
greater than no mm3. Providing a cavity 11 of at least this volume has been
found to
enable the formation of an improved aerosol. In examples, the mouthpiece 2
comprises
a cavity 11, for instance formed within the cooling section 7, having an
internal volume
greater than no mm3, or greater than 130 mm3, allowing further improvement of
the
aerosol. In some examples, the internal cavity n comprises a volume of between
about
130 mm3 and about 230 mm3, for instance about 134 mm3 or 227 mm3.
The cooling section 7 can be configured to provide a temperature differential
of at least
40 degrees Celsius between a heated volatilised component entering a first,
upstream
end of the cooling section 7 and a heated volatilised component exiting a
second,
downstream end of the cooling section 7. The cooling section 7 can be
configured to
provide a temperature differential of at least 60 degrees Celsius, or at least
80 degrees
Celsius, or at least wo degrees Celsius between a heated volatilised component
entering a first, upstream end of the cooling section 7 and a heated
volatilised
component exiting a second, downstream end of the cooling section 7. This
temperature differential across the length of the cooling section 7 protects
the
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 15 -
temperature sensitive body of material 8 from the high temperatures of the
aerosol-
generating material 3 when it is heated.
When in use, the aerosol-generating section may exhibit a pressure drop of
from about
15 to about 40 mm F120. In some embodiments, the aerosol-generating section
exhibits
a pressure drop across the aerosol-generating section of from about 15 to
about 30
mm FLO.
In the present embodiment, the moisture impermeable wrapper 6 which
circumscribes
io one or both sections of the aerosol-generating material 3 comprises
aluminium foil. In
other embodiments, the wrapper 6 comprises a paper wrapper, optionally
comprising a
barrier coating to make the material of the wrapper 6 substantially moisture
impermeable. Aluminium foil has been found to be particularly effective at
enhancing
the formation of aerosol within the aerosol-generating material 3. In the
present
example, the aluminium foil has a metal layer having a thickness of about 6
um. In the
present example, the aluminium foil has a paper backing. However, in
alternative
arrangements, the aluminium foil can be other thicknesses, for instance
between 4 um
and 16 um in thickness. The aluminium foil also need not have a paper backing,
but
could have a backing formed from other materials, for instance to help provide
an
appropriate tensile strength to the foil, or it could have no backing
material. Metallic
layers or foils other than aluminium can also be used. The total thickness of
the
wrapper 6 may be between 20 um and 6o um, or between 30 um and 50 um, which
can
provide a wrapper 6 having appropriate structural integrity and heat transfer
characteristics. The tensile force which can be applied to the wrapper 6
before it breaks
can be greater than 3,000 grams force, for instance between 3,000 and 10,000
grams
force or between 3,000 and 4,500 grams force. Where the wrapper 6 comprises
paper
or a paper backing, i.e. a cellulose based material, the wrapper 6 can have a
basis
weight greater than about 30 gsm. For example, the wrapper 6 can have a basis
weight
in the range from about 40 gsm to about 70 gs, which can provide an improved
rigidity
to the rod of aerosol-generating material 3.
In the present example, the moisture impermeable wrapper 6 is also
substantially
impermeable to air. In alternative embodiments, the wrapper 6 can have a
permeability of less than ioo Coresta Units, or less than 6o Coresta Units. It
has been
found that low permeability wrappers, for instance having a permeability of
less than
loo Coresta Units, or less than 6o Coresta Units, result in an improvement in
the
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 16 -
aerosol formation in the aerosol-generating material 3. Without wishing to be
bound
by theory, it is hypothesised that this is due to reduced loss of aerosol
compounds
through the wrapper 6. The permeability of the wrapper 6 can be measured in
accordance with ISO 2965:2009 concerning the determination of air permeability
for
materials used as cigarette papers, filter plug wrap and filter joining paper.
The body of material 8 defines a substantially cylindrical overall outer shape
and is
wrapped in a first plug wrap 12. The first plug wrap 12 can havea basis weight
of less
than 50 gsm, orbetween about 20 gsm and 40 gsm. The first plug wrap 12 canhave
a
_ro thickness of between 30 !_trn and 6o p.m, or between 35 pm and 45 pm.
The first plug
wrap 12 is a non-porous plug wrap, for instance having a permeability of less
than wo
Coresta units, for instance less than 50 Coresta units. However, in other
embodiments,
the first plug wrap 12 can be a porous plug wrap, for instance having a
permeability of
greater than 200 Coresta Units.
As shown in Figure 1, the mouthpiece 2 of the article 1 comprises an upstream
end 2a
adjacent to the second section 5 of the rod of aerosol-generating material 3.
At the
proximal end, the mouthpiece 2 has a hollow tubular element 9 formed from
filamentary tow. This has advantageously been found to significantly reduce
the
temperature of the outer surface of the mouthpiece 2 at the downstream end 2b
of the
mouthpiece 2 which comes into contact with a consumer's mouth when the article
1 is
in use. In addition, the use of the tubular element 9 has also been found to
significantly
reduce the temperature of the outer surface of the mouthpiece 2 even upstream
of the
tubular element 9. Without wishing to be bound by theory, it is hypothesised
that this
is due to the tubular element 9 channelling aerosol closer to the centre of
the
mouthpiece 2, and therefore reducing the transfer of heat from the aerosol to
the outer
surface of the mouthpiece 2.
The "wall thickness" of the hollow tubular element 9 corresponds to the
thickness of the
wall of the tube 9 in a radial direction. This may be measured, for example,
using a
calliper. The wall thickness is advantageously greater than 0.9 mm, or i.omm
or
greater. The wall thickness may be substantially constant around the entire
wall of the
hollow tubular element 9. However, where the wall thickness is not
substantially
constant, the wall thickness can be greater than 0.9 mm at any point around
the hollow
tubular element 9, or tomm or greater. In the present example, the wall
thickness of
the hollow tubular element 9 is about 1.3 mm.
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 17 -
A plug wrap 13 is wrapped around the full length of the mouthpiece 2. The
mouthpiece
2 and the sections 4, 5 of aerosol-generating material 3 are also wrapped in
wrapper 6.
The article 1 has a ventilation level of about 10% of the aerosol drawn
through the
article 1. In alternative embodiments, the article 1 can have a ventilation
level of
between 1% and 20% of aerosol drawn through the article 1, for instance
between 1%
and 12%. Ventilation at these levels helps to increase the consistency of the
aerosol
inhaled by the user at the mouth end 2h, while assisting the aerosol cooling
process.
io The ventilation is provided directly into the mouthpiece 2 of the
article 1. In the
present example, the ventilation is provided into the cooling section 7, which
has been
found to be particularly beneficial in assisting with the aerosol generation
process. The
ventilation is provided via perforations 14, in the present case formed as a
single row of
laser perforations, positioned 13 mm from the downstream, mouth-end 2h of the
mouthpiece 2. In alternative embodiments, two or more rows of ventilation
perforations 14 may be provided. These perforations 14 pass though the wrapper
6 and
the plug wrap 13, and cooling section 7. In alternative embodiments, the
ventilation
can be provided into the mouthpiece 2 at other locations, for instance into
the body of
material 8 or first tubular element 9. The article 1 may be configured such
that the
perforations 14 are provided about 28mm or less from the upstream end of the
article
1, or between 20MM and 28mm from the upstream end of the article 1. In the
present
example, the apertures are provided about 25mm from the upstream end of the
article
1.
The aerosol-generating material 3 of each section 4, 5 may comprise tobacco
material.
The aerosol-generating material 3 may be a sheet or shredded sheet of
aerosolisable
material comprising a plant-based material, such as a tobacco material.
The a plant-based material material may be a particulate or granular material.
In some
embodiments, the a plant-based material material is a powder. Alternatively,
or in
addition, the tobacco a plant-based material material may comprise may
comprise
strips, strands or fibres of tobacco. For example, the tobacco material may
comprise
particles, granules, fibres, strips and/or strands of tobacco. In some
embodiments, the
tobacco material consists of particles or granules of tobacco material.
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 18 -
The density of the tobacco material has an impact on the speed at which heat
conducts
through the material, with lower densities, for instance those below 900
mg/cc,
conducting heat more slowly through the material, and therefore enabling a
more
sustained release of aerosol.
The tobacco material can comprise reconstituted tobacco material having a
density of
less than about 900 mg/cc, for instance paper reconstituted tobacco material.
For
instance, the aerosol-generating material comprises reconstituted tobacco
material
having a density of less than about 800 mg/cc. Alternatively, or in addition,
the
io aerosol-generating material can comprise reconstituted tobacco
material having a
density of at least 350 mg/cc.
The tobacco material may comprise tobacco obtained from any part of the
tobacco
plant. In some embodiments, the tobacco material comprises tobacco leaf.
The sheet or shredded sheet can comprise from 5% to about 90% by weight
tobacco
leaf.
The aerosol-generating material 3 may comprise an aerosol-former material. The
aerosol-former material comprises one or more constituents capable of forming
an
aerosol. The aerosol-former material comprises one or more of glycerine,
glycerol,
propylene glycol, diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, tetraethylene glycol,
1,3-butylene
glycol, erythritol, meso-Erythritol, ethyl vanillate, ethyl laurate, a diethyl
suberate,
triethyl citrate, triacetin, a diacetin mixture, benzyl benzoate, benzyl
phenyl acetate,
tributyrin, lauryl acetate, lauric acid, myristic acid, and propylene
carbonate. The
aerosol-former material can be glycerol or propylene glycol.
The sheet or shredded sheet of aerosolisable material comprises an aerosol-
former
material in one or both sections 4, 5. The aerosol-former material is provided
in an
amount of up to about 50% on a dry weight base by weight of the sheet or
shredded
sheet. In some embodiments, the aerosol former material is provided in an
amount of
from about 5% to about 40% on a dry weight base by weight of the sheet or
shredded
sheet, from about 10% to about 30% on a dry weight base by weight of the sheet
or
shredded sheet or from about io% to about 20% on a dry weight base by weight
of the
sheet or shredded sheet.
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 19 -
The aerosol-generating material 3 may comprise a filler in one or both
sections 4, 5. In
some embodiments, the sheet or shredded sheet comprises the filler. The filler
is
generally a non-tobacco component, that is, a component that does not include
ingredients originating from tobacco. The filler may comprise one or more
inorganic
filler materials, such as calcium carbonate, perlite, vermiculite,
diatomaceous earth,
colloidal silica, magnesium oxide, magnesium sulphate, magnesium carbonate,
and
suitable inorganic sorbents, such as molecular sieves. The filler may be a non-
tobacco
fibre such as wood fibre or pulp or wheat fibre. The filler can be a material
comprising
cellulose or a material comprises a derivate of cellulose. The filler
component may also
ro be a non-tobacco cast material or a non-tobacco extruded material.
The aerosol-generating material 3 herein can comprise an aerosol modifying
agent in
one or both sections 4, 5, such as any of the flavours described herein. In
one
embodiment, the aerosol-generating material 3 comprises menthol. When the
aerosol-
generating material 3 is incorporated into an article 1 for use in an aerosol-
provision
system, the article may be referred to as a mentholated article 1. The aerosol-
generating material 3 can comprise from 0.5mg to 20mg of menthol, from 0.7 mg
to 20
mg of menthol, between ring and 18mg or between 8mg and 16mg of menthol.
In some embodiments, the composition comprises an aerosol-forming "amorphous
solid", which may alternatively be referred to as a "monolithic solid" (i.e.
non-fibrous).
In some embodiments, the amorphous solid may comprise a dried gel. The
amorphous
solid is a solid material that may retain some fluid, such as liquid, within
it.
In some examples, the amorphous solid comprises:
- 1-60 wt% of a gelling agent;
- 0.1-50 wt% of an aerosol-former material; and
- 0.1-80 wt% of a flavour;
wherein these weights are calculated on a dry weight basis.
In some further embodiments, the amorphous solid comprises:
- 1-50 wt% of a gelling agent;
- 0.1-50 wt% of an aerosol-former material; and
- 30-60 wt% of a flavour;
wherein these weights are calculated on a dry weight basis.
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 20 -
The amorphous solid material may be provided in sheet or in shredded sheet
form in
one or both sections 4, 5. The amorphous solid material may take the same form
as the
sheet or shredded sheet of aerosolisable material.
The aerosol-generating material 3 of either or both sections 4, 5 can comprise
a impel
reconstituted tobacco material. The composition can alternatively or
additionally
comprise any of the forms of tobacco described herein. The aerosol generating
material
3 can comprise a sheet or shredded sheet comprising tobacco material
comprising
between 10% and go% by weight tobacco leaf, wherein an aerosol-former material
is
_ro provided in an amount of up to about 20% by weight of the sheet or
shredded sheet,
and the remainder of the tobacco material comprises paper reconstituted
tobacco.
Where the aerosol-generating material 3 comprises an amorphous solid material,
the
amorphous solid material may be a dried gel comprising menthol.
In Figure 2, the components of an embodiment of a non-combustible aerosol
provision
device wo, according to an embodiment of the invention, are shown in a
simplified
manner. Particularly, the elements of the non-combustible aerosol provision
device
wo are not drawn to scale in Figure 4. Elements that are not relevant for the
understanding of this embodiment have been omitted to simplify Figure 4.
As shown in Figure 4, the non-combustible aerosol provision device wo
comprises a
housing 101 comprising an area 102 for receiving an article 1.
The area 102 is arranged to receive the article 1. When the article 1 is
received into the
area 102, at least a portion of the aerosol-generating material 3 comes into
thermal
proximity with a heater 103. When the article 1 is fully received in the area
102, at least
a portion of the aerosol-generating material 3 may be in direct, or indirect,
contact with
the heater 103. The aerosol-forming material 3 will release a range of
volatile
compounds at different temperatures. By controlling the maximum operation
temperature of the electrically heated aerosol generating system 200, the
selective
release of undesirable compounds may be controlled by preventing the release
of select
volatile compounds.
As shown in Figure 3, within the housing 101 there is an electrical energy
supply 104,
for example a rechargeable lithium-ion battery. A controller 105 is connected
to the
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 21 -
heater 103, the electrical energy supply 104, and a user interface 106, for
example a
button or display. The controller 105 controls the power supplied to the
heater 103 in
order to regulate its temperature. Typically, the aerosol-forming substrate is
heated to
a temperature of between 250 and 450 degrees centigrade.
Figure 4 is a schematic cross-section of a non-combustible aerosol-provision
system
200 that includes the non-combustible aerosol-provision device roo of the type
shown
in Figure 2, and the article 1 in engagement with the aerosol-generating
device roo for
consumption of the aerosol-generating article 1 by a user.
The housing ror of non-combustible aerosol provision device roo defines an
area 102 in
the form of a cavity, open at the proximal end (or mouth end), for receiving
an aerosol-
generating article 1.
The heater 103 may conductively heat the wrapper 6 surrounding the aerosol-
generating material 3, particularly if the wrapper 6 is made from a heat-
conductive
material such as aluminium, which in turn heats the sections of aerosol
generating
substrate 3. Alternatively, the heater 103 may conduct heat directly to the
aerosol-
generating substrate 3.
With reference to Figure 4, it can be seen that the heater 103 primarily
extends
alongside the first section 4 of the aerosol-generating material 3. In this
arrangement,
heat is primarily transferred or conducted from the heater 103 into the first
section 3.
Due to the proximity of the heater 103 to the distal most surface 14 of the
second
section 5, at least some heat may also be transferred into the second section
5. The first
and second sections 4, 5 may be heated at different rates. In other
embodiments, the
heater 103 may extend alongside both sections 4, 5. The heater 103 itself may
also be
formed from parts each of which are heated to a different temperature. Each
part of the
heater may be independently controlled by a controller to heat each section 4,
5 at a
different time or to a different temperature.
For example, one part of the heater 103 may be placed alongside the first
section 4 to
heat the first section 4 to a first temperature, and another part of the
heater may be
placed alongside the second section 5 to heat the second section 5 to another
temperature, which may be higher or lower than the first temperature.
Alternatively,
the first and second sections 4, 5 may be heated consecutively, or the heating
of one
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 22 -
section 4, 5 may be started before heating of the other section 4, 5 such
there is a delay
between heating sections 4, 5. It may be more desirable to heat one section 4,
5 after
the other, or to different temperatures, if the aerosol-forming material 3 of
the first
section 4 is different to the aerosol-forming material 3 of the second section
5.
In another embodiment, the heater 103 is a varying magnetic field generator
surrounding the area 102 into which the article 1 of Figure 2 is inserted.
This
embodiment of device 100 is for use with an article 1 that incorporates a
wrapper 6
io formed from a magnetic, electrically conductive material, so
that it acts as a susceptor
that is inductively heated in response to activation of the varying magnetic
field, and so
heats the aerosol-generating material 3 which is wrapped by wrapper 6. The
control of
the device 100 may be otherwise similar to the control described above in
relation to
Figure 3. It will also be appreciated that the varying magnetic field
generator may have
parts that generate magnetic fields at different strengths so that the
sections 4, 5 of
aerosol-generating material 3 are heated at different rates or to different
temperatures,
as previously explained above.
In any embodiment, the wrapper 6, or at least a part of the wrapper 6 that
surrounds
the aerosol-generating material 3, may be permeable. For example, it may be
perforated, formed from a mesh or have openings in it to allow for the passage
of air
and aerosol through it. In other embodiments it may be formed from a sheet of
impermeable material. The wrapper 6 may be formed from a single component or a
plurality of components. For example, it could be formed from a plurality of
discrete
sections separated from each other in a longitudinal direction.
The various embodiments described herein are presented only to assist in
understanding and teaching the claimed features. These embodiments are
provided as
a representative sample of embodiments only, and are not exhaustive and/or
exclusive.
It is to be understood that advantages, embodiments, examples, functions,
features,
structures, and/or other aspects described herein are not to be considered
limitations
on the scope of the invention as defined by the claims or limitations on
equivalents to
the claims, and that other embodiments may be utilised and modifications may
be
made without departing from the scope of the claimed invention. Various
embodiments
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13
WO 2022/263836
PCT/GB2022/051529
- 23 -
of the invention may suitably comprise, consist of, or consist essentially of,
appropriate
combinations of the disclosed elements, components, features, parts, steps,
means, etc,
other than those specifically described herein. In addition, this disclosure
may include
other inventions not presently claimed, but which may be claimed in future.
CA 03222656 2023- 12- 13