Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
1
Compositions and Methods
The present invention relates to concentrate compositions useful in the
preparation of
formulated products. In particularly the invention relates to concentrate
compositions for the
preparation of pearlescent formulated products.
Liquid compositions used in personal care and cleaning applications often
desirably have an
opaque iridescent appearance and may be referred to as "pearlised" or having a
pearlescent
finish. These formulations have high consumer appeal, and it is therefore
common to add
pearlising agents to a wide variety of different liquid chemical formulations.
Pearlising agents
are often added to personal cleansing formulations such as shampoos, body
washes and
liquid hand soaps; laundry detergents, dishwashing detergent compositions and
other hard
service cleaning compositions.
Common pearlising agents include ethylene glycol nionostearate (EGMS) and
ethylene glycol
distearate (EGDS). To achieve optimum pearl quality using these agents a
formulated product
must typically be heated to a temperature in excess of 70 C in order to melt
the ethylene glycol
monostearate or distearate esters within the formulation. As the formulations
cool the
pearlising agents slowly crystallise to form insoluble particles that provide
the pearl/opaque
appearance. The rate of cooling and the rate of shear mixing as well as the
size and shape of
the mixing blade affect the crystal structure of the ester particles. Thus
these factors have a
significant impact on the quality and consistency of the pearl effect
achieved. It is therefore
essential to follow heating, cooling and shearing instructions strictly in
order to achieve a
uniform pearl effect for each batch of formulated product prepared. The often
slow rates of
cooling used means that pearlising is a very time consuming step. The process
is also very
energy intensive and costly due to the high temperature at which the
formulation must be
heated in order to melt the esters; the energy needed to obtain the desired
cooling rate; and
the energy needed for mixing and/or shearing.
Additionally the variability between batches of starting materials means that
it can be difficult to
obtain a consistently formulated product.
The present inventors have advantageously developed a concentrate pearlising
composition
which can be directly added to formulated compositions in order to provide a
high quality pearl.
The concentrate composition of the invention can be mixed with the formulated
composition at
ambient temperature, avoiding the need to heat to 70 C. This advantageously
saves
formulators time and energy and provides improved product consistency.
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
2
According to a first aspect of the present invention there is provided a
concentrate composition
comprising:
(a) at least 10 wt% of a glycol ester of a fatty acid;
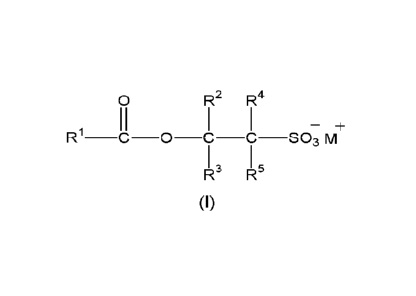
(b) at least one acyl alkyl isethionate surfactant of formula (I):
0 R2 R4
II ¨+
R1 ______________________________________ C __ 0C ___ C ______ SO3M+
R- R-
(I)
wherein R1 represents an optionally substituted C4-C36 hydrocarbyl group;
each of R2, R3, R4 and R5 independently represents hydrogen or a Ci-C4 alkyl
group and
wherein at least one of R2, R3, R4 and R5 is not hydrogen; and M. represents a
cation; and
(c) at least one zwitterionic or amphoteric surfactant.
Component (a) comprises a glycol ester of a fatty acid i.e. an ester of a
fatty acid and a
compound including at least two alcohol functional groups. Preferably
component (a)
comprises an ester of one or more glycols selected from ethylene glycol,
propylene glycol and
butylene glycol. Most preferably component (a) comprises ethylene glycol. The
ester may be a
monoester, a diester or a mixture thereof.
The fatty acid may be a saturated fatty acid, an unsaturated fatty acid or a
mixture thereof.
Preferably the fatty acid is a saturated fatty acid including a single
carboxylic acid group.
Preferably the fatty acid is a saturated monocarboxylic acid having 10 to 24
carbon atoms,
preferably 12 to 20 carbon atoms, more preferably 16 to 18 carbon atoms.
Most preferably component (a) comprises a glycol ester of stearic acid
(octadecanoic acid).
Component (a) may comprise a monoester of stearic acid and/or a diester of
stearic acid.
Preferably component (a) comprises ethylene glycol monostearate (EGMS) and/or
ethylene
glycol distearate (EGDS).
The skilled person will appreciate that commercially available sources of
stearic acid often
comprise a mixture of stearic acid and one or more other acids, for example
C16 acids. In one
embodiment component (a) comprises a glycol ester, preferably an ethylene
glycol ester of a
mixture of fatty acids comprising from 50 to 60 wt% C16 fatty acids, from 40
to 50 wt% C18
fatty acids and 0 to 5 wt% C14 fatty acids.
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/05253.5
3
This type of product is known to the person skilled in the art as a triple
pressed stearic acid.
Component (a) is present in the concentrate composition of the present
invention in an amount
of at least 10 wt%. Preferably component (a) is present in an amount of at
least 12 wt%, for
example for at least 15 wt%. Component (a) may be present in the concentrate
composition of
the present invention in an amount of up to 50 wt%, preferably up to 40 wt%,
for example up to
35 wt%.
Preferably component (a) is present in the concentrate composition of the
present invention in
an amount of from 10 to 35 wt%, preferably from 15 to 30 wt%, more preferably
from 20 to 30
wt%.
When component (a) comprises a mixture of glycol esters, the above amounts
refer to the total
amount of all such compounds present in the composition.
In this specification, unless otherwise indicated any amounts referred to
relate to the amount of
active component present in the composition. The skilled person will
appreciate that
commercial sources of some of the components referred to herein may include
impurities,
side-products and/or residual starting material, as well as solvents or
diluents. However, the
amounts specified refer only to the active material and do not include any
impurity, side-
product, starting material, solvent or diluent that may be present.
Component (b) of the concentrate composition of the present invention
comprises at least one
acyl alkyl isethionate of formula (I).
Component (b) is present in the concentrate composition of the present
invention in an amount
of at least 0.01 wt%. Preferably component (b) is present in an amount of at
least 0.1 wt%, for
example for at least 0.5 wt%. Component (b) may be present in the concentrate
composition of
the present invention in an amount of up to 40 wt%, preferably up to 30 wt%,
for example up to
20 wtcYo.
Preferably component (b) is present in the composition in an amount of from
0.1 to 18 wt%,
preferably 0.5 to 15 wt%, more preferably from 1 to 12 wt%, for example about
1 to 10 wt%.
When component (a) comprises a mixture of compounds of formula (I), the above
amounts
refer to the total amount of all such compounds present in the composition.
In the formula (I), R1 represents an optionally substituted C4-C36 hydrocarbyl
group, R2, R3, R4
and R5 each independently represents hydrogen or a substituted or
unsubstituted Ci-C4 alkyl
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/05253.5
4
group, provided that at least one of R2, R3, R4 and R5 is not hydrogen, and M*
represents a
cation.
Suitably, R1 represents an optionally substituted C4-C36 alkyl, C4-C36
alkenyl, C6-C12 aryl or C8-
C22 alkyl-Cs-Cu aryl group. More suitably, R1 represents an optionally
substituted C4-C36 alkyl
or C4-C36 alkenyl group, especially an optionally substituted C4-C36 alkyl
group. Most suitably,
R1 represents a C4-C36 alkyl or C4-C36 alkenyl group, especially a C4-C36
alkyl group.
Suitably, R1 represents an optionally substituted 04-C36 alkyl or C4-C36
alkenyl group, such as
an optionally substituted C8-C18 alkyl or C8-C18 alkenyl group.
Suitably, R1 represents a C4_C36 alkyl or C4_C36 alkenyl group, such as a
Cs_Cm alkyl or C8-Cm
alkenyl group.
Suitably, R1 represents an optionally substituted C5_C30 alkyl group, such as
an optionally
substituted C7_C24 alkyl group, for example an optionally substituted C7_C21
alkyl group,
preferably an optionally substituted C7_C17 alkyl group.
Suitably, R1 represents a Cs_C30 alkyl group, such as a C7_C24 alkyl group,
for example a C7_C21
alkyl group, preferably a C7_Ci7 alkyl group.
R1 is suitably the residue of a fatty acid. Fatty acids obtained from natural
oils often include
mixtures of fatty acids. For example, the fatty acid obtained from coconut oil
contains a
mixture of fatty acids including C12 lauric acid, C14 myristic acid, Cm
palmitic acid, CB caprylic
acid, C10 capric acid and C18 stearic and oleic acid.
R1 may include the residue of one or more naturally occurring fatty acids
and/or of one or more
synthetic fatty acids. For example, R1 may consist essentially of the residue
of a single fatty
acid.
Examples of carboxylic acids from which R1 may be derived include coco acid,
hexanoic acid,
caproic acid, caprylic acid, capric acid, lauric acid, myristic acid, palmitic
acid, palmitoleic acid,
stearic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, arachidic acid, gadoleic acid,
arachidonic acid,
eicosapentanoic acid, behinic acid, erucic acid, docosahexanoic lignoceric
acid, naturally
occurring fatty acids such as those obtained from coconut oil, tallow, palm
kernel oil, butterfat,
palm oil, olive oil, corn oil, linseed oil, peanut oil, fish oil and rapeseed
oil; synthetic fatty acids
made as chains of a single length or a selected distribution of chain lengths;
and mixtures
thereof. Suitably R1 comprises the residue of coco acid, the residue of mixed
fatty acids
derived from coconut oil or the residue of mixed fatty acids derived from palm
kernel oil. More
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/05253.5
suitably, R1 predominantly comprises the residue of a saturated fatty acid
having 12 carbon
atoms.
The acyl alkyl isethionate surfactant of the formula (I) may be prepared by
any of the methods
5 disclosed in the prior art, for example see the methods described in
W094/09763 and
W02005/075623.
In some embodiments only a single acyl alkyl isethionate surfactant of the
formula (I) may be
present in the concentrate composition of the first aspect. In some
embodiments a mixture of
two or more acyl alkyl isethionate surfactants of the formula (I) may be
present. In such
embodiments the above amounts refer to the total amounts of all acyl alkyl
isethionate
surfactants of the formula (I) present in the composition.
When any of R2, R3, R4 and R5 represents an optionally substituted Ci-C4 alkyl
group, the alkyl
group is suitably n-propyl, ethyl or methyl, such as ethyl or methyl, most
preferably methyl.
Preferably one of the groups R2, R3, R4 and R5 represents an optionally
substituted C1-C4 alkyl
group and the remaining groups represent hydrogen. For example, R2 may
represent an
optionally substituted C1-C4 alkyl group and R3, R4 and R5 may all represent
hydrogen. For
example, R4 may represent an optionally substituted C1-C4 alkyl group and R2,
R3 and R5 may
all represent hydrogen.
Preferably, R2 represents a Ci-C4 alkyl group and R3, R4 and R5 all represent
hydrogen.
Preferably, R4 represents a Ci-C4 alkyl group and R2, R3 and R5 all represent
hydrogen.
Most preferably, R2 represents a methyl group and R3, R4 and R5 all represent
hydrogen. Most
preferably, R4 represents a methyl group and R2, R3 and R5 all represent
hydrogen.
Preferably component (b) comprises an acyl alkyl isethionate surfactant of
formula (I) selected
from one or more of sodium lauroyl methyl isethionate, sodium cocoyl methyl
isethionate and
sodium oleoyl methyl isethionate. Sodium lauroyl methyl isethionate (SLMI) is
especially
preferred.
Suitably, WI represents a metal cation or an optionally substituted ammonium
cation,
preferably a metal cation. By "optionally substituted ammonium cation", we
mean to refer to an
ammonium cation wherein the nitrogen atom may be substituted with from 1 to 4
optionally
substituted hydrocarbyl groups. Suitable ammonium cations include those
derived from alkyl
amines and alkanolamines. Preferred ammonium cations include isopropanolamine,
isopropylamine, ethanolamine, diethanolamine, triethanolamine and 2-amino-2-
methyl-1,3-
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
6
propanediol (AMPD). Preferred ammonium cations include NH4* and the ammonium
cation of
triethanolamine.
Suitable metal cations include alkali metal cations, for example sodium,
lithium and potassium
cations, and alkaline earth metal cations, for example calcium and magnesium
cations.
Suitably, FM' represents an alkali metal cation or an optionally substituted
ammonium cation.
Preferably, NA represents a zinc, potassium or sodium cation. Most preferably,
MI- represents
a sodium cation.
The skilled person will appreciate that when M' is a divalent metal cation two
moles of anion
will be present for each mole of cation.
The acyl alkyl isethionate surfactant of formula (I) may comprise the reaction
product of
sodium methyl isethionate and a fatty acid, that is a compound of formula
R1COOCHR2CHR4S03-M* in which one of R2 and R4 is methyl and the other is
hydrogen.
Mixtures of these isomers may be present
The solid cleansing composition of the present invention may include a mixture
of more than
one acyl alkyl isethionate surfactant of formula (I). For example, an isomeric
mixture of acyl
alkyl isethionate surfactants of formula (I) may be present. Such a mixture
may include, for
example an acyl alkyl isethionate surfactant in which R2 represents a Ci-C4
alkyl group
(suitably methyl) and R3, R4 and R5 are all hydrogen and an acyl alkyl
isethionate surfactant in
which R4 represents a Ci-C4 alkyl group (suitably methyl) and R2, R3 and R5
are all hydrogen.
In particular, the concentrate composition of the present invention may
comprise a mixture of
isomers, that is a compound of formula R1COOCH2CHR4S03-M+ in which R4
represents a Cl-
C4 alkyl group (preferably methyl) and a compound of formula R1COOCHR2CH2S03-
M+ in
which R2 represents a Cl-C4 alkyl group (preferably methyl).
Suitably such mixtures comprise approximately 90% of compounds in which R2 is
methyl and
R4 is hydrogen and approximately 10% of compounds in which R2 is hydrogen and
R4 is
methyl.
Component (c) comprises an amphoteric or zwitterionic surfactant.
Component (c) is present in the concentrate composition of the present
invention in an amount
of at least 0.01 wt%. Preferably component (c) is present in an amount of at
least 0.1 wt%, for
example for at least 0.5 wt%. Component (c) may be present in the concentrate
composition of
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/05253.5
7
the present invention in an amount of up to 40 wt%, preferably up to 30 wt%,
for example up to
20 wt%.
Component (c) is preferably present in the composition of the present
invention in an amount
of from 0.1 to 30 wt%, preferably from 0.5 to 25 wt%, more preferably from 1
to 20 wt%, more
preferably from 3 to 18 wt%, for example 5 to 15 wt%.
In some embodiments component (c) comprises a mixture two or more amphoteric
and/or
zwitterionic surfactants. In such embodiments, the above amounts refer to the
total amount of
all zwitterionic and/or amphoteric surfactants present in the composition.
Suitable amphoteric surfactants for use in compositions of the first aspect of
the invention
include those based on fatty nitrogen derivates and those based on betaines.
Suitable amphoteric or zwitterionic surfactants may be selected from betaines,
for example
alkyl betaines, alkylamidopropyl betaines, for example cocamidopropyl betaine,
alkylamidopropyl hydroxy sultaines, alkylamphoacetates, alkylamphodiacetates,
alkyl
propionates, alkylamphodipropionates, alkylamphopropionates,
alkyliminodipropionates and
alkyliminodiacetate.
Amphoteric or zwitterionic surfactants for use in compositions of the first
aspect may include
those which have an alkyl or alkenyl group of 7 to 22 carbon atoms and comply
with an overall
structural formula:
0 R8
I I I
R7I-C¨NH(CH2),, +j¨N¨X¨Y
n
R9
where R7 is alkyl or alkenyl of 7 to 22 carbon atoms; R8 and R9 are each
independently alkyl,
hydroxyalkyl or carboxyalkyl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms; m is 2 to 4; n is 0 or 1;
X is alkylene of 1
to 6 carbon atoms optionally substituted with hydroxyl; and Y is -0O2 or -S03.
Amphoteric or zwitterionic surfactants may include simple betaines of formula:
R8
I +
R7-1\I¨CH2CO2-
i
R9
and amido betaines of formula:
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
8
0 R8
I I I+
R7¨C¨NH(CH2)m¨N¨CH2CO2¨
R9
where m is 2 or 3.
In both formulae R7, R8 and R9 are as defined previously. R7 may, in
particular, be a mixture of
012 and 014 alkyl groups derived from coconut so that at least half,
preferably at least three
quarters, of the groups R7 has 10 to 14 carbon atoms. R8 and R9 are preferably
methyl.
Amphoteric or zwitterionic surfactants may include sulfobetaines of formula:
RB
I
R7-N¨+
(CH2)3S03-
R9
0 RB
I I 1+
R7¨C¨NH(CH2)m¨N¨(CH2)3S03¨
R9
where m is 2 or 3, or variants of these in which
-(CH2)3803- is replaced by
OH
CH2 CH CH2S03
where R7, R8 and R in these formulae are as defined previously.
Amphoteric or zwitterionic surfactants may include amphoacetates and
diamphoacetates.
Amphoacetates generally conform to the following formula:
R1000NHCH2CH2¨N¨CH2CH2OH
CH2C00¨ M2
Diamphoacetates generally conform to the following formula:
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/05253.1
9
¨ +
0H20H200 M2
W
¨CH2CH2¨N¨CH2CH2OH
1
CH2C00¨ M2+
where R1 is an aliphatic group of 8 to 22 carbon atoms and M2+ is a cation
such as sodium,
potassium, ammonium, or substituted ammonium.
Suitable acetate-based surfactants include lauroamphoacetate; alkyl
amphoacetate; sodium
alkyl amphoacetate; cocoampho(di)acetate;
cocoamphoacetate; disodium
cocoamphodiacetate; sodium cocoamphoacetate; disodium cocoamphodiacetate;
disodium
capryloamphodiacete; disodium lauroamphoacetate; sodium lauroamphoacetate and
disodium
wheatgermamphodiacetate.
Suitable betaine surfactants include alkylamido betaine; alkyl betaine, 012/14
alkyldimethyl
betaine; cocoamidopropylbetaine; tallow bis(hydroxyethyl) betaine;
hexadecyldimethylbetaine;
cocodimethylbetaine; alkyl amido propyl sulfo betaine; alkyl dimethyl amine
betaine; coco
amido propyl dimethyl betaine; alkyl amido propyl dimethyl amine betaine;
cocamidopropyl
betaine; lauryl betaine; laurylamidopropl betaine, coco amido betaine, lauryl
amido betaine,
alkyl amino betaine; alkyl amido betaine; coco betaine; lauryl betaine;
diemethicone propyl
PG-betaine; ley! betaine; N-alkyldimethyl betaine; coco biguamide derivative,
C8 amido
betaine; 012 amido betaine; lauryl dimethyl betaine; alkylamide propyl
betaine; amido betaine;
alkyl betaine; cetyl betaine; oleamidopropyl betaine; isosteara midopropyl
betaine;
lauramidopropyl betaine; 2-alkyl-N-carboxymethyl-N-hydroxyethyl imidazolinium
betaine; 2-
alkyl-N-carboxyethyl-N-hydroxyethyl imidazolinium betaine; 2-alkyl-N-sodium
carboxymethyl-
N-carboxymethyl oxyethyl imidazolinium betaine; N-alkyl acid amidopropyl-N,N-
dimethyl-N-(3-
sulfopropy1)-ammonium-betaine;
N-alkyl-N,N-dimethyl-N-(3-sulfopropy1)-ammonium-betaine;
cocodimethyl betaine; apricotamidopropyl betaine; isostearamidopropyl betaine;
myristamidopropyl betaine; palmitamidopropyl betaine; alkamidopropyl hydroxyl
sultaine;
cocamidopropyl hydroxyl sultaine; undecylenamidopropyl betaine;
cocoamidosulfobetaine;
alkyl amido betaine; C12118 alkyl amido propyl dimethyl amine betaine;
lauryldimethyl betaine;
ricinol amidobetaine; tallow aminobetaine.
Suitable glycinate surfactants include acyl glycinates such as
cocoamphocarboxyglycinate;
tallowamphocarboxygycinate; capryloamphocarboxyg lycinate,
oleoamphocarboxyglycinate,
bis-2-hydroxyethyl tallow glycinate; lauryl amphoglycinate; tallow
polyamphoglycinate; coco
amphoglycinate; oleic polyamphoglycinate; N-C10n2 fatty acid amidoethyl-N-(2-
hydroxyethyl)-
glycinate; N-012/18-fatty acid amidoethyl-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-glycinate;
dihydroxyethyl tallow
gycinate.
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
Preferred acetate-based amphoteric surfactants for use as component (c)
include sodium
lauroamphoacetate, disodium lauroamphoacetate and mixtures thereof
5 Preferred betaine surfactants for use as component (c) include
cocoamidopropyl betaine.
Preferred sultaine surfactants for use as component (c) include
cocoamidopropylhydroxy
sultaine.
10 Preferably component (c) comprises cocoamidopropyl betaine and/or
cocoamidopropylhydroxy
sultaine.
In preferred embodiments the weight ratio of component (a) to component (b)
present in the
composition of the present invention is from 50:1 to 1:2, preferably from 40:1
to 1:1.5, more
preferably from 30:1 to 1:1.
Preferably the weight ratio of component (a) to component (c) present in the
composition of
the present invention is from 20:1 to 1:5, preferably from 10:1 to 1:2, more
preferably from 6:1
to 1:1.
Preferably the weight ratio of component (b) to component (c) present in the
composition of
the present invention is from 10:1 to 1:10, more preferably from 4:1 to 1:4.
The concentrate composition of the first aspect may comprise one or more
further
components. Preferably the one or more further components are selected from
chelating
agents, preservatives, pH modifiers, hydrotropes and further surfactants.
The concentrate composition of the first aspect may comprise a chelating
agent. Suitable
chelating agents include ethylenediamine¨N,N'-disuccinic acid,
methylglycinediacetic acid,
glutamic acid N,N-diacetic acid, imino disuccinic acid, diethylene triamine
pentaacetic acid,
ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, diethylenetriamine penta methylene
phosphonic acid,
etidronic acid and anions, salts and mixtures thereof.
Preferred chelating agents are biodegradable chelating agents for example
ethylenediamine-
N,N'-disuccinic acid, methylglycinediacetic acid, glutamic acid N,N-diacetic
acid, imino
disuccinic acid and anions and mixtures thereof. Ethylenediamine¨N,N'-
disuccinic acid (EDDS)
is especially preferred. The skilled person will appreciate that
polycarboxylic acid chelating
agents may be present as the free acid or a salt thereof.
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
11
The concentrate composition of the invention may comprise a preservative.
Suitable
preservatives will be known to the person skilled in the art and include
sodium benzoate,
potassium sorbate, sorbic acid, phenoxyethanol, benzyl alcohol, DMDM
hydantoin,
imidazolidinyl urea, methylchloroisothiazolinone, methylisothiazolinone,
salicylic acid, benzyl
salicylate, methylparaben, propylparaben and caprylyl glycol. A preferred
preservative for use
herein is sodium benzoate.
The concentrate composition of the invention may comprise a hydrotrope.
Suitable
hydrotropes will be known to the person skilled in the art and include
propylene glycol,
hexylene glycol, glycerine, sorbitol, xylene sulfonates, cumene sulfonates,
ethanol, urea,
dipropylene glycol. A preferred hydrotrope for use herein is sorbitol.
The concentrate composition of the invention may comprise a pH modifier.
Suitable pH
modifiers will be known to the person skilled in the art and include lactic
acid, potassium
hydroxide sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, triethanolamine and sodium
gluconate. A
preferred pH modifier is citric acid.
Preferably the composition of the present invention has a pH of from 3 to 9,
preferably 4 to 8,
for example 4.5 to 7.5.
In some embodiments the composition has a pH of 4.5 to 5.5.
In some embodiments the composition has a pH of 6.5 to 7.5.
The concentrate composition of the invention may comprise one or more further
surfactants.
Such surfactants may be selected from anionic surfactants, cationic
surfactants, non-ionic
surfactants and mixtures thereof. The selection of suitable further
surfactants for use in the
composition of the present invention is within the competence of the person
skilled in the art.
Suitable anionic surfactants for use in compositions of the first aspect of
the invention include
salts of C12-C18 carboxylic acids, ethoxylated carboxylic acids, ester
carboxylates and
ethoxylated ester carboxylates and sarcosinates. Other suitable anionic
surfactants include
sulfates and sulfonates, for example alkyl sulfates, alkyl ether sulfates,
alcohol sulfates,
alcohol ether sulfates, a-olefin sulfonates, linear alkyl sulfonates; and
phosphate esters.
Suitable anionic surfactants may be selected from salts of fatty acids; alkali
metal salts of
mono- or dialkyl sulfates; mono- or dialkyl ether sulfates; lauryl ether
sulfates; alkyl sulfonates;
alkyl aryl sulfonates; primary alkane disulfonates; alkene sulfonates;
hydroxyalkane sulfonates;
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/05253.5
12
alkyl glyceryl ether sulfonates; alpha-olefinsulfonates; alkyl phosphates;
sulfonates of
alkylphenolpolyglycol ethers; salts of alkyl sulfopolycarboxylic acid esters;
alkyl sulfosuccinates
and salts thereof, alkyl ether sulfosuccinates and salts thereof, acyl
isethionates, non-acylated
alkyl isethionates; fatty acid taurates; acyl taurates; amino acid surfactants
such as glutamates
and glycinates; products of condensation of fatty acids with oxy- and
aminoalkanesulfonic
acids; sulfated derivatives of fatty acids and polyglycols; alkyl and acyl
sarcosinates;
sulfoacetates; alkyl phosphates; alkyl phosphate esters; acyl lactates;
alkanolamides of
sulfated fatty acids and salts of lipoamino acids. Particularly exemplary
salts of the above,
where applicable, are the sodium, potassium, ammonium, magnesium and
triethanolamine
salts. Suitable ammonium cations include those derived from alkyl amines and
alkanolamines.
Preferred ammonium cations include isopropanolamine, isopropylamine,
ethanolamine,
diethanolamine, triethanolamine and 2-amino-2-methyl-1,3-propanediol (AMPD).
Preferred
ammonium cations include NH4+ and the ammonium cation of triethanolamine.
Preferred anionic surfactants are selected from salts of fatty acids; alkyl
sulfonates; alkyl aryl
sulfonates; primary alkane disulfonates; alkene sulfonates; hydroxyalkane
sulfonates; alkyl
glyceryl ether sulfonates; alpha-olefinsulfonates; alkyl phosphates;
sulfonates of
alkylphenolpolyglycol ethers; salts of alkyl sulfopolycarboxylic acid esters;
alkyl sulfosuccinates
and salts thereof, alkyl ether sulfosuccinates and salts thereof, acyl
isethionates, non-acylated
alkyl isethionates; fatty acid taurates; acyl taurates; amino acid surfactants
such as glutamates
and glycinates; products of condensation of fatty acids with oxy- and
aminoalkanesulfonic
acids; alkyl and acyl sarcosinates; sulfoacetates; alkyl phosphates; alkyl
phosphate esters;
acyl lactates; and salts of lipoamino acids. Particularly exemplary salts of
the above, where
applicable, are the sodium, potassium, ammonium, magnesium and triethanolamine
salts.
Suitable ammonium cations include those derived from alkyl amines and
alkanolamines.
Preferred ammonium cations include isopropanolamine, isopropylamine,
ethanolamine,
diethanolamine, triethanolamine and 2-amino-2-methyl-1,3-propanediol (AMPD).
Preferred
ammonium cations include NH4 and the ammonium cation of triethanolamine.
Suitable sulfoacetates include acyl sulfoacetates, particularly sodium acyl
sulfoacetates.
Suitable glutamate surfactants include acyl glutamates.
Acyl isethionates for use in compositions of the first aspect of the invention
may be of the
formula (II):
0
H2 H2
R6¨C¨O¨C ¨C ¨S03-M1+
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
13
(II)
wherein R6 represents an optionally substituted C4-C36 hydrocarbyl group; and
M1+ represents
a cation.
Suitably, R6 represents an optionally substituted C4-C36 alkyl, C4-C36
alkenyl, C6-C12 aryl or C3-
C22 alkyl-C6-C12 aryl group. More suitably, R6 represents an optionally
substituted C4-C36 alkyl
or C4-C36 alkenyl group. Most suitably, R6 represents a C4-C36 alkyl group or
C4-C36 alkenyl
group, especially a C4-C36 alkyl group.
Suitably, R6 represents an optionally substituted C6-C30 alkyl group, such as
an optionally
substituted C7_C24 alkyl group, for example an optionally substituted C7_C21
alkyl group,
preferably an optionally substituted C7_C17 alkyl group.
Suitably, R6 represents a C5_C30 alkyl group, such as a C7C24 alkyl group, for
example a C7_C21
alkyl group, preferably a C7_C17 alkyl group.
R6 is suitably the residue of a fatty acid. Fatty acids obtained from natural
oils often include
mixtures of fatty acids. For example, the fatty acid obtained from coconut oil
contains a
mixture of fatty acids including C12 lauric acid, C14 myristic acid, Cm
palmitic acid, Cs caprylic
acid, and C18 stearic and oleic acid.
R6 may include the residue of one or more naturally occurring fatty acids
and/or of one or more
synthetic fatty acids. For example, R6 consists essentially of the residue of
a single fatty acid.
Examples of carboxylic acids from which Rs may be derived include coco acid,
hexanoic acid,
caproic acid, caprylic acid, capric acid, lauric acid, myristic acid, palmitic
acid, palmitoleic acid,
stearic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, arachidic acid, gadoleic acid,
arachidonic acid,
eicosapentanoic acid, behinic acid, erucic acid, docosahexanoic lignoceric
acid, naturally
occurring fatty acids such as those obtained from coconut oil, tallow, palm
kernel oil, butterfat,
palm oil, olive oil, corn oil, linseed oil, peanut oil, fish oil and rapeseed
oil; synthetic fatty acids
made as chains of a single length or a selected distribution of chain lengths;
and mixtures
thereof. Suitably R6 comprises the residue of coco acid, the residue of mixed
fatty acids
derived from coconut oil or the residue of mixed fatty acids derived from palm
kernel oil.
Suitably, M1' represents a metal cation or an optionally substituted ammonium
cation,
preferably a metal cation. Suitable ammonium cations include NH4' and the
ammonium cation
of triethanolamine. Suitable ammonium cations include those derived from alkyl
amines and
alkanolamines. Preferred ammonium cations include isopropanolamine,
isopropylamine,
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
14
ethanolamine, diethanolamine, triethanolamine and 2-amino-2-methyl-1,3-
propanediol
(AMPD). Preferred ammonium cations include NH4+ and the ammonium cation of
triethanolamine.
Suitable metal cations include alkali metal cations, for example sodium,
lithium and potassium
cations, and alkaline earth metal cations, for example calcium and magnesium
cations.
Preferably Mi+ represents a zinc, potassium or sodium cation. Most preferably
Mi+ represents
a sodium cation.
The skilled person will appreciate that when M1+ is a divalent metal cation
two moles of anion
will be present for each mole of cation.
In some embodiments only a single acyl isethionate of the formula (II) may be
present in the
solid cleansing composition of the first aspect. In some embodiments a mixture
of two or more
acyl isethionates of the formula (II) may be present.
For example, the acyl isethionates of the formula (II) may be selected from
one or more of
sodium lauroyl isethionate, sodium cocoyl isethionate and sodium myristoyl
isethionate.
Sodium cocoyl isethionate is especially preferred.
Preferred additional anionic detersive surfactants for use in compositions of
the first aspect of
the invention include alkyl glyceryl ether sulfonate, ammonium lauryl sulfate,
ammonium
laureth sulfate, triethylamine lauryl sulfate, triethylamine laureth sulfate,
triethanolamine lauryl
sulfate, triethanolamine laureth sulfate, monoethanolamine lauryl sulfate,
monoethanolamine
laureth sulfate, diethanolamine lauryl sulfate, diethanolamine laureth
sulfate, lauric
monoglyceride sodium sulfate, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium laureth sulfate,
potassium lauryl
sulfate, potassium laureth sulfate, sodium !amyl sarcosinate, sodium lauroyl
sarcosinate, lauryl
sarcosine, cocoyl sarcosine, ammonium cocoyl sulfate, ammonium lauroyl
sulfate, sodium
cocoyl sulfate, sodium lauroyl sulfate, potassium cocoyl sulfate, potassium
lauryl sulfate,
triethanolamine !amyl sulfate, triethanolamine !amyl sulfate, monoethanolamine
cocoyl sulfate,
monoethanolamine lauryl sulfate, sodium tridecyl benzene sulfonate, sodium
dodecyl benzene
sulfonate, and combinations thereof.
Suitable non-ionic surfactants for use in compositions of the first aspect of
the invention
include alcohol alkoxylates such as alcohol ethoxylates, alcohol propoxylates,
and ethylene
oxide/propylene oxide copolymer derived surfactants, aliphatic esters,
aromatic esters, sugar
esters, especially sorbitan esters, alkyl polyglucosides, fatty acid
alkoxylates such as fatty acid
ethoxylates and fatty acid propoxylates or polyethylene glycol esters and
partial esters,
glycerol esters including glycerol partial esters and glycerol triesters,
fatty alcohols (such as
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/05253.5
cetearyl alcohol, lauryl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, behenyl alcohol),
alkanolamides and
amineoxides.
Suitable non-ionic surfactants may be selected from the following: reaction
products of
5 compounds having a hydrophobic group and a reactive hydrogen atom, for
example aliphatic
alcohols, acids, amides or alkyl phenols with alkylene oxides, especially
ethylene oxide either
alone or with propylene oxide (for example alkyl (C6-C22) phenol-ethylene
oxide condensates,
the condensation products of aliphatic (Ca-Ci8) primary or secondary linear or
branched
alcohols with ethylene oxide, and products made by condensation of ethylene
oxide with the
10 reaction products of propylene oxide and ethylenediamine); long chain
tertiary amine oxides,
long chain tertiary phosphine oxides and dialkyl sulfoxides; alkyl amine
oxides, alkyl amido
amine oxides; alkyl tertiary phosphine oxides; alkoxyl alkyl amines; sorbitan;
sorbitan esters;
sorbitan ester alkoxylates; glycerol ester alkoxylates; sucrose esters; sugar
amides, such as a
polysaccharide amide; lactobionamides; and alkyl polysaccharide nonionic
surfactants, for
15 example alkylpolyglycosides.
Suitable cationic surfactants for use in compositions of the first aspect of
the invention are
typically based on fatty amine derivates or phosphonium quaternary ions, and
quaternary
ammonium compounds. Polymeric cationic surfactancts may also be used.
Suitable cationic surfactants for use in compositions of the first aspect of
the invention include
tertiary amine salts, mono alkyl trimethyl ammonium chloride, mono alkyl
trimethyl ammonium
methyl sulfate, dialkyl dimethyl ammonium chloride, dialkyl dimethyl ammonium
methyl sulfate,
trialkyl methyl ammonium chloride and trialkyl methyl ammonium methyl sulfate.
Examples of suitable cationic surfactants include quaternary ammonium
compounds,
particularly trimethyl quaternary compounds.
Preferred quaternary ammonium compounds include cetyltrimethylammonium
chloride,
behenyltrimethylammonium chloride (BTAC), cetylpyridinium chloride,
tetramethylammoniurn
chloride, tetraethylammonium chloride,
octyltrimethylammonium chloride,
dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride,
hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride,
octyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride,
decyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride,
stearyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride,
didodecyldimethylammonium chloride,
dioctadecyldimethylammonium chloride, tallowtrimethylammonium chloride,
cocotrimethylammonium chloride, PEG-2 oleylammonium chloride and salts of
these where
the chloride is replaced by halogen (e.g. bromide), acetate, citrate, lactate,
glycolate,
phosphate nitrate, sulfate, or alkylsulfate.
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
16
Further suitable cationic surfactants include those materials having the CTFA
designations
Quatemium-5, Quatemium-31 and Quatemium-18. Mixtures of any of the foregoing
materials
may also be suitable. A particularly useful cationic surfactant for use as a
hair conditioning
agent is cetyltrimethylammonium chloride, available commercially, for example
as GENAMIN
CTAC, ex Hoechst Celanese.
Salts of primary, secondary, and tertiary fatty amines are also suitable
cationic surfactants.
The alkyl groups of such amines preferably have from 12 to 22 carbon atoms,
and can be
optionally substituted.
Useful cationic surfactants include amido substituted tertiary fatty amines,
in particular tertiary
amines having one C12 to C22 alkyl or alkenyl chain. Such amines include
stearamidopropyldimethylamine, stearamidopropyldiethylamine,
stearamidoethyldiethylamine,
stearamidoethyldimethylamine,
palmitamidopropyldimethylamine,
palmitamidopropyldiethylamine, pal
mitamidoethyldiethylamine,
palmitamidoethyldimethylamine,
behenamidopropyldimethylamine,
behenamidopropyldiethylamine,
behenamidoethyldiethylamine,
behenamidoethyldimethylamine, arachidamidopropyldimethylamine,
arach id
amidopropyldiethylamine, arachidamidoethyldiethylamine,
arachidamidoethyldimethylamine,
diethylaminoethylstearamide.
Also useful are dimethylstearamine, dimethylsoyamine, soyamine, myristylamine,
tridecylamine, ethylstearylamine, Ntallowpropane diamine, ethoxylated (with 5
moles of
ethylene oxide) stearylamine, dihydroxyethylstearylamine, and arachidyl
behenylamine.
These amines are typically used in combination with an acid to provide the
cationic species.
Suitable acids include L-glutamic acid, lactic acid, hydrochloric acid, malic
acid, succinic acid,
acetic acid, fumaric acid, tartaric acid, citric acid, L-glutamic
hydrochloride, and mixtures
thereof; more preferably L-glutamic acid, lactic acid, citric acid.
Other useful cationic amine surfactants include those disclosed in US4275055.
Suitable polymeric cationic surfactancts include polyquaternium-7,
polyquaternium-10,
polyquaterniu m-11, guar hydroxypropyltrimonium chloride, and hydroxypropyl
guar
hydroxypropyltrimonium chloride.
In some preferred embodiments the concentrate composition of the first aspect
comprises less
than 2.5 wt% sulfate containing surfactants, preferably less than 2 wt%, more
preferably less
than 1.5 wt%, preferably less than 1 wt%, suitably less than 0.75 wt%, more
preferably less
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
17
than 0.5 wt%, preferably less than 0.25 wt%, preferably less than 0.1 wt%,
suitably less than
0.05 wt%, for example less than 0.01 wt%, preferably less than 0.005 wt% and
most preferably
less than 0.001 wt%.
In some embodiments the concentrate composition of the first aspect of the
present invention
is preferably free of sulfate containing surfactants.
In some preferred embodiments components (b) and (c) together comprise at
least 70 wt% of
all surfactants present in the concentrate composition of the first aspect,
preferably at least 75
wt%, more preferably at least 80 wt%, suitably at least 85 wt%, more
preferably at least 90
wt%.
The concentrate composition of the present invention is preferably an aqueous
composition.
In some embodiments the composition may comprise one or more further solvents
in addition
to water. Such suitable co-solvents will be known to the person skilled in the
art.
However in preferred embodiments water is the major solvent present in the
concentrate
composition of the present invention and suitably comprises at least 80 wt% of
all solvents
present, preferably at least 90 wt%, more preferably at least 95 wt%.
In some preferred embodiments the concentrate composition of the first aspect
of the present
invention is an aqueous composition comprising:
- from 10 to 40 wt% component (a);
- from 0.1 to 20 wt% component (b);
- from 1 to 25 wt% component (c); and
- optionally one or more further components are selected from chelating
agents,
preservatives, pH modifiers, hydrotropes and further surfactants.
In some preferred embodiments the concentrate composition of the first aspect
of the present
invention is an aqueous composition comprising:
- from 15 to 30 wt% component (a);
- from 1 to 12 wt% component (b);
- from 5 to 15 wt% component (c); and
- optionally one or more further components are selected from chelating
agents,
preservatives, pH modifiers, hydrotropes and further surfactants.
The concentrate composition of the first aspect of the present invention may
be an opaque
composition.
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
18
The concentrate composition of the first aspect of the present invention is
preferably a
pearlescent composition.
The concentrate composition of the first aspect is preferably a liquid
composition or semi-liquid
composition. It may be a thick viscous liquid in the form of a thick paste or
it may be a runny
liquid. Preferably the concentrate composition is flowable and pumpable.
Preferably the concentrate composition of the first aspect has a Brookfield
Viscosity at 25 C
measured using a No 5 spindle g 2.5 RPM of from 1000 to 100000 cps, preferably
from 1000
to 50000 cps.
The concentrate composition of the first aspect of the present invention is
highly advantageous
because it can be added to a composition which is almost fully formulated to
provide a pearl
effect without the need for complex heating, cooling or shearing steps.
The concentrate composition of the invention can be added in a small about to
a formulation
with simple mixing under ambient conditions.
The concentrate composition of the present invention is suitably made by
heating the
components and slowing cooling with agitation. Heating a concentrated mixture
is much more
energy efficient than heating a final formulated product. Furthermore addition
of a concentrate
composition at ambient temperature means that a formulator does not need to
use a long,
complex heating and cooling process.
According to a second aspect of the present invention, there is provided a
method of preparing
a concentrate composition, the method comprising the steps of:
(i) admixing the following components:
(a) at least 10 wt% of a glycol ester of a fatty acid;
(b) at least one acyl alkyl isethionate surfactant of formula (I):
0 R2 R4
I I ¨+
R1¨C ¨ ¨C ¨C¨S03 M
R- R-
(I)
wherein R1 represents an optionally substituted C4-C36 hydrocarbyl group;
each of R2, R3, R4 and R5 independently represents hydrogen or a Ci-C4 alkyl
group and
wherein at least one of R2, R3, R4 and R5 is not hydrogen; and FM' represents
a cation; and
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
19
(c) at least one zwitterionic or amphoteric surfactant;
(ii) heating the mixture obtained in step (i) to a temperature of at least
60 C; and
(iii) slowly cooling the composition.
Step (i) may involve adding one or more further components. Preferably the one
or more
further components are selected from chelating agents, preservatives, pH
modifiers,
hydrotropes and further surfactants. These are suitably as defined in relation
to the first
aspect.
Preferably water is added in step (i) to provide an aqueous composition.
Optionally one ore
more further solvents may be added, for example one or more water miscible
solvents. In
preferred embodiments water is the only solvent used.
Preferred features of the second aspect are as defined in relation to the
first aspect.
The mixture is heated in step (ii) to a temperature of at least 60 C.
Preferably the mixture is
heated to a temperature of at least 70 C, for example at least 75 C.
Preferably the composition is agitated as it is cooled during step (iii),
preferably by the
application of shear forces.
The selection of suitable shear rates and cooling profiles will be within the
competence of the
person skilled in the art. Guidance is provided for example in W0200125378,
W02003066796,
W02004028676A1 and W02011023803.
For example the skilled person would understand that cooling and/or shearing
rates help
control crystallisation; preferably the ester crystallizes into platelet
structures. Larger platelet
structures are preferred for pearlescent formulations.
According to a third aspect of the present invention there is provided a
method of providing a
pearlescent finish to a formulation, the method comprising admixing into the
formulation a
pearlising composition comprising:
(a) at least 10 wt% of a glycol ester of a fatty acid;
(b) at least one acyl alkyl isethionate surfactant of formula (I):
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/05253.5
0 R2 R4
¨+
R1¨C-0¨C¨C¨S03 M
IR- IR-
,
(I)
wherein R1 represents an optionally substituted C4-C36 hydrocarbyl group;
5 each of R2, R3, R4 and R5 independently represents hydrogen or a Ci-C4
alkyl group and
wherein at least one of R2, R3, R4 and R5 is not hydrogen; and M+ represents a
cation; and
(c) at least one zwitterionic or amphoteric surfactant.
Preferred features of the third aspect are as defined in relation to the first
and second aspects.
By "formulation" we mean to refer to a chemical composition which contains
multiple
components which have been mixed together. The formulation is suitably
prepared to contain
specific ingredients and has a particular purpose. For example the formulation
may be a
cleaning composition or a personal care composition. The types of components
that are
typically present in such compositions will be known to the person skilled in
the art.
For example laundry and dishwashing compositions typically comprise
ingredients such as
surfactants, builders, bleaches, bleach activators, redeposition additives,
dye transfer
inhibitors, enzymes, colorants and fragrances.
Personal care compositions typically comprise ingredients such as surfactants
(including
anionic, amphoteric, nonionic and cationic surfactants); conditioning
agents (including
quaternary ammonium compounds, cationic polymers, cationic conditioning
polymers,
silicones, synthetic or natural oils or resins etc), fatty alcohols,
electrolytes or other rheology
modifiers, opacifying/pearlising agents, scalp benefit agents, fragrances,
dyes, UV filters,
penetration enhancers (eg, propylene carbonate, benzyl alcohol etc),
preservatives,
antioxidants, emulsifiers, pH adjusting agents and buffers and styling
polymers (eg,
polyvinylpyrrolidone etc).
The formulation is preferably a liquid composition or semi-liquid composition.
It may be a thick
viscous liquid in the form of a thick paste or it may be a runny liquid.
Preferably the
concentrate composition is flowable and pumpable.
Preferably the formulation provided by the method of the third aspect
comprises 0.1 to 3 wt%,
suitably 0.5 to 2 wt%, preferably 0.5 to 1.5 wt% of component (a).
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
21
Preferably the method of the third aspect is carried out at a temperature of
less than 60 C,
preferably less than 50 C, more preferably less than 40 C, preferably less
than 30 C.
Preferably the formulation is not heated in the method of the third aspect of
the present
invention.
In some embodiments, preferably the formulation is not initially opaque or
pearlescent.
The product obtained by the method of the third aspect is a
pearlised/pearlescent formulated
product.
The method of the third aspect preferably increased the opacity of the
formulated product.
According to a fourth aspect of the present invention there is provided a
method of preparing a
pearlescent formulation, the method comprising:
(x) preparing a formulation which is not pearlescent; and
(y) adding a concentrate composition of the first aspect to the formulation
prepared in step
(x).
Preferably the concentrate composition of the first aspect used in step (y) is
prepared by the
method of the second aspect.
According to a fifth aspect of the present invention there is provided the use
of a composition
comprising:
(a) at least 10 wt% of a glycol ester of a fatty acid;
(b) at least one acyl alkyl isethionate surfactant of formula (I):
0 R2 R4
¨+
R1¨C-0¨C¨C¨S03 m
IR- R5
(I)
wherein R1 represents an optionally substituted Ca-Cm hydrocarbyl group;
each of R2, R3, R4 and R5 independently represents hydrogen or a Ci-C4 alkyl
group and
wherein at least one of R2, R3, R4 and R5 is not hydrogen; and M+ represents a
cation; and
(c) at least one zwitterionic or amphoteric surfactant;
as a pearlising agent.
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
22
Preferred features of the fourth and fifth aspects are as defined in relation
to the first, second
and third aspects.
The present invention relates to providing a composition with a pearlescent
finish. Preferably
the pearlescent effect provided by the invention is consistent and can be
readily reproduced
under the same conditions. Such a pearlescent effect can be assessed visually
by the skilled
person.
In some embodiments the present invention may be used to increase the
pearlescence of a
composition.
The invention will now be further defined with the reference to the following
non-limiting
examples.
Examples
The compositions of table 1 were prepared comprising the listed ingredients,
according to the
method below:
Table 1
Composition 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
8
Component (wt% (wt% (wt% (wt% (wt% (wt% (wt% (wt%
active) active) active) active) active) active) active) active)
A Sodium
0.491 0.5 0.49 0.5 0.5 0.5
0.5 0.5
Benzoate
A EDDS 0.207 0.209 0.205 0.205 0.198 0.19 0.19 0.19
A CAPB 7.5 7.2 7.2 7.05
7.2
A CAPHS 11.64 10 9.8
A Sorbitol 3.15 3.5 3.43 3.5 3.36
Citric Acid 0.25 QS QS QS 0.2 0.15 0.1
0.25
SLM I 6.188 5.95 5.831 5.95 5.695
5.695 5.61 5.525
EGDS 18.2 20 24.52 25 24 24 23.5 30
Deionised To To To To To To To To
water 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
100
Sodium benzoate was provided as a 100% active ingredient.
EDDS was provided as a 38 wt% aqueous solution of the trisodium salt of
ethylenediamine-
N,N'-disuccinic acid.
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/05253.5
23
CAPB was provided as a 30 wt% aqueous solution of cocamidopropyl betaine.
CAPHS was provided as a 30 wt% aqueous solution of cocamidopropyl
hydroxysultaine.
Sorbitol was provided as a 70 wt% aqueous solution.
Citric Acid was provided as a 50 wt% aqueous solution.
SLMI was provided as a solid ingredient comprising 85 wt% active sodium
lauroyl methyl
isethionate.
EGDS was provided as a commercially available product comprising predominately
ethylene
glycol distearate and minor amounts of the monostearate product.
Method
1. Combine "A" ingredients. With smooth, mechanical agitation, mix until
completely uniform.
As detailed above several of the component A ingredients were provided in as
aqueous
solutions. The amounts of the component A ingredients referred to in table 1
are the amounts
of active component present, ignoring any solvent or diluent present. However
in step 1 such
water is included and further water may also be added at this stage.
2. With smooth mechanical agitation adjust pH of system to 4.8-5.2 with 50%
aqueous citric
acid as needed. With smooth agitation warm system to 50 C.
3. With Smooth agitation slowly blend in flakes of sodium lauroyl methyl
isethionate. Mix until
completely clear and uniform. With smooth agitation, continue heating the
system to 70-80 C.
4. With rapid but smooth agitation blend EGDS/EGMS flakes into the heated
system.
Continue heating to 80-85 C. Maintain 80-85 C temperature with mixing for 20
minutes and
then remove heat source. Continue cooling to 45-50 C with rapid but smooth
agitation.
5. With rapid but smooth agitation, slowly blend in 20-25 C water. Further
water is added at
this stage to provide a 100% of the components listed in table 1 for each
composition.
However some water will have already been added as part of the component A
ingredients
and optionally additionally in step 1. Mix until completely uniform. Continue
to cool system to
25-30 C with rapid but smooth agitation. Package at 20-25 C.
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
24
Pearlising effect
The pearlising effect of the compositions of examples 3 to 8 was assessing by
adding
6 g of each concentrated composition to 194 g deionised water and 1 drop of
food colouring.
The ingredients were combined at room temperature and with mechanical
agitation mixed until
the cold pearl concentrate is completely dispersed. The resulting system was
visually
observed and assessed for pearl quality. The following rating system was used:
Rating Scale
Poor = Opaque Liquid with no Pearl Appearance
Moderate = Opaque Liquid with slight pearl appearance
Good = Opaque liquid with moderate pearl appearance
Excellent = Opaque liquid with high sheen, pearl appearance
The results are shown in table 2:
Table 2
Composition Pearl rating
4 Excellent
5 Excellent
6 Excellent
7 Excellent
8 Excellent
Example 2
Further compositions were prepared according to the method described below
having the
ingredients detailed in table 3. Composition 9 is of the invention.
Composition 10 is
comparative.
Table 3
Composition
Component (wt% active) 9 10
(comparative)
A Dl Water 46.11 46.11
A Sodium Benzoate 0.5 0.5
A EDDS 0.19 0.19
A CAPB 7.2 7.2
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
50% Citric Acid 0.15 0.15
SLMI 6.7
SCI 6.7
EGDS 24.0 24.0
DI Water 15.0 15.0
SCI is was provided as a solid ingredient comprising 85% active Sodium Cocoyl
Isethionate.
The remaining ingredients are as described in example 1.
5 Method:
1. Component "A" ingredients were mixed until a clear and homogeneous
composition was
obtained. The deionized water component of ingredients A includes the water
that forms part
of the ingredient added as solutions and additional water added separately.
2. The pH of the system was adjusted to to 4.8-5.2 with citric acid solution
and then heated
with mixing to 45-50 C.
3. Component "C" ingredients were added and heating was continued to 70-80 C
with rapid
but smooth mechanical mixing.
4. Component "C" ingredients were added with rapid but smooth mechanical
agitation.
Heating was continued to 85 C with rapid but smooth agitation. The temperature
was
maintained for 20+ minutes and then the heat source was removed. Cooling was
carried out
with rapid but smooth agitation until the system reaches a temperature of 45-
50 C (system
starts to settle into a lotion/paste).
5. With rapid but smooth agitation, 20-25 C water was slowly blended in and
cooling continued
to 25 C with rapid but smooth agitation.
The compositions obtained had the properties listed in table 4.
Table 4
Composition 9 Composition 10
Appearance @ 25 C Thin, White Liquid/Lotion Thick,
gooey paste
Brookfield Viscosity @ 25 C:
No 5 Sp. @ 2.5 RPM 4100 cps 120600 cps
No 5 Sp. @ 5 RPM 3040 cps 69800 cps
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2
WO 2023/057767
PCT/GB2022/052535
26
Composition 9 rapidly dispersed and provided a composition having an excellent
pearl quality
and composition 10 was very slow to disperse.
Unlike composition 10, composition 9 is readily pourable meaning that it is
easier to handle
and has an improved environmental profile since heating is not required to
manipulate the
composition.
CA 03233671 2024- 4- 2